Chem 1150 Midterm 2 Study Guide
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fuck this game
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
How does the nuclear charge of an element change across the periodic table? (Z_Eff)
It increases as you go across the period (more protons) and decreases as you go down the group (more shells, bigger n to shield)
How does the number of Atomic Radii change across the periodic table? (Atomic size/radius)
Decreases as you go across the period (bigger Z_eff) and increases down the group because there is a greater number of shells (n)
How does Ionization Energy (IE) change across the periodic table?
Increases across the period because there is a bigger Z_eff and decreases down the group since the valence electro is lost in a higher shell.
How does Electron Affinity changes across the periodic table?
Elements become more negative across the period and less negative down the group due to larger n.
How does Electronegativity change across the periodic table? (EN)
Elements become more electronegative as you go across the period (greater Z_eff) and become less electronegative as you go down the group (Z_eff is smaller).
Ion Size
Cations < Neutral Element < Anions
Anions have a greater size because there are more electron-electron repulsions and Cations are smaller because there is larger Z_eff and because the valence electron is in the n-1 shell.
Ionization Energy
Successive ionization energies always increase (E1 < E2 < E3)
Relative Bond Lengths (Which bonds are bigger)
Singe bonds > Double bonds > Triple bonds
Relative bond strengths
Single bond (weakest) < double bond < triple bond (strongest)
Bond Dissociation Energy (which releases the most energy when broken)
Triple bonds > double bonds > single bonds

Electronic: Linear
Molecular: Linear
Bond Angle: 180
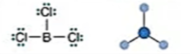
Electronic: Trigonal Planar
Molecular: Trigonal Planar
Bond Angle: 120

Electronic: Trigonal Planar
Molecular: Bent
Bond Angle: <120
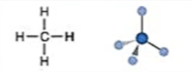
Electronic: Tetrahedral
Molecular: Tetrahedral
Bond Angle: 109.5

Electronic: Tetrahedral
Molecular: Trigonal Pyramidal
Bond Angle: <109.5

Electronic: Tetrahedral
Molecular: Bent
Bond Angle «109.5
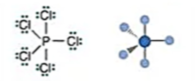
Electronic: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Molecular: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Bond Angle: 120 (equatorial) & 90 (axial)
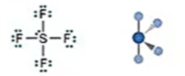
Electronic: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Molecular: Seesaw
Bond Angle: <120 (equatorial) & <90 (axial)

Electronic: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Molecular: T-Shaped
Bond Angle: <90

Electronic: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Molecular: Linear
Bond Angle: 180
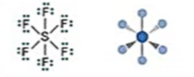
Electronic: Octahedral
Molecular: Octahedral
Bond Angle: 90
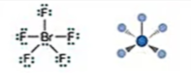
Electronic: Octahedral
Molecular: Square Pyramidal
Bond Angle: <90
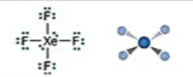
Electronic: Octahedral
Molecular: Square Planar
Bond Angle: 90