Vocabulary Terms for Chapter 9
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Chromatic Color
Color with hue, such as blue, yellow, red, or green occur when some wavelengths are reflected more than others.
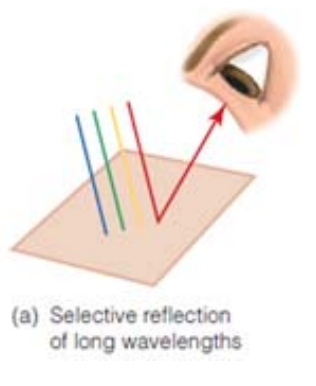
Selective Reflection
When an object reflects some wavelengths of the spectrum more than others.
Achromatic Colors
Color without hue such as white, black, & all the grays between these 2 extremes occur when light is reflected equally across the spectrum.
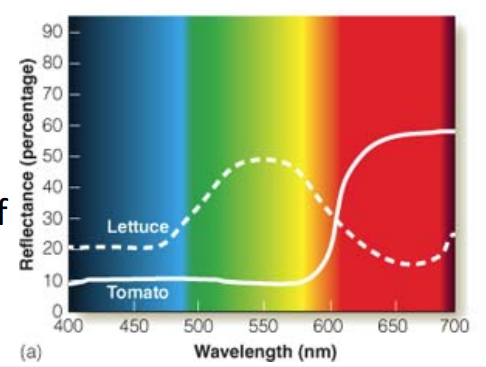
Reflectance Curves
A plot showing the percentage of light reflected from an object versus wavelength.
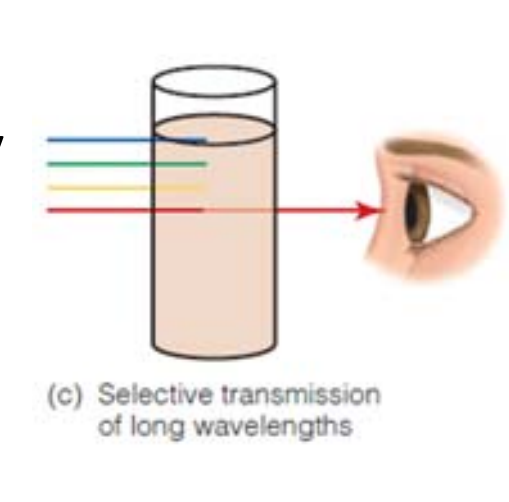
Selective Transmission
When some wavelengths pass through visually transparent objects or substances & others do not.
Transmission Curves
For transparent materials, plots of the percentage of light transmitted at each wavelength. Similar to the reflectance curves, but with percent transmission plotted on the vertical axis.
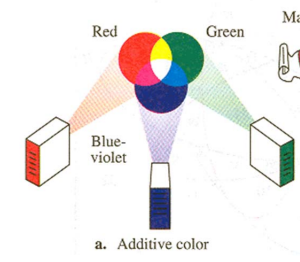
Additive Color Mixture
Mixing lights of different wavelengths.
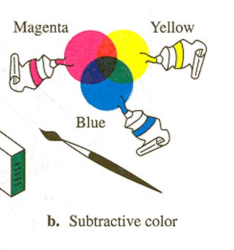
Subtractive Color Mixture
Mixing paints with different pigments.

Spectral Color
Colors that appear in the visible spectrum.
Nonspectral Colors
Colors that don’t appear in the spectrum because they are mixtures of other colors. (EX: Magenta)
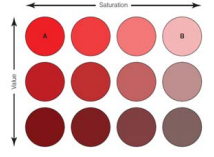
Hues
The experience of a chromatic color, such as red, green, yellow, or blue, or combinations of these colors (EX: The 12 color patches in the picture have the same hue, red).
Saturation
Determined by the amount of white that has been added to a particular hue. The less whiteness a color contains, the more saturated it is.
Value
Refers to light-to-dark dimension of color.
Color Solid
A three dimensional color space where dimensions can be arranged systematically.
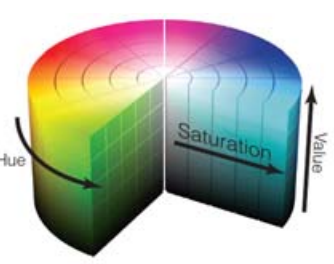
HSV Color Solid
A solid in which colors are arranged in an orderly way based on their hue, saturation, & value.
Trichromatic Theory (became known as the Young-Helmholtz Theory)
Color vision is based on 3 principle colors.
It depends on the activity of 3 different receptor mechanisms.
Behavioral Evidence
Color matching experiments.
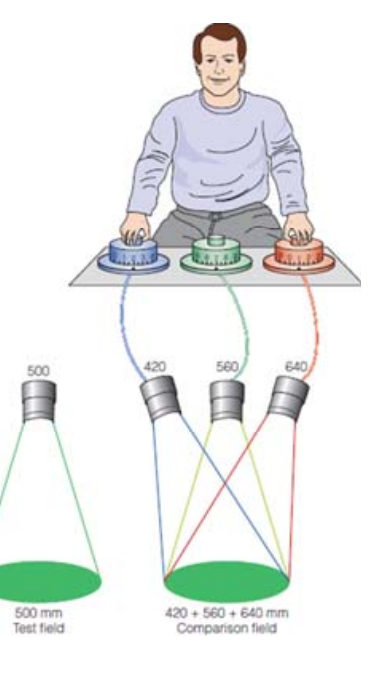
Color Matching
A procedure in which observers are asked to match the color in 1 field by mixing 2 or more lights in another field.
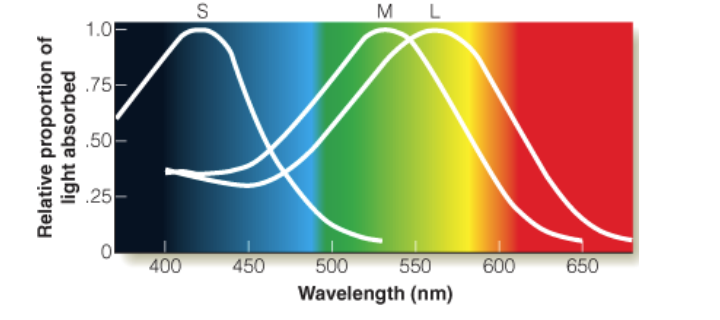
Physiological Evidence
In the 1960s researchers were able to determine that there were 3 different cone pigments:
The short wavelength (S), with maximum absorption at 419 nm
The middle wavelength (M), with maximum absorption at 531 nm
The long wavelength pigment (L) with maximum absorption at 558 nm
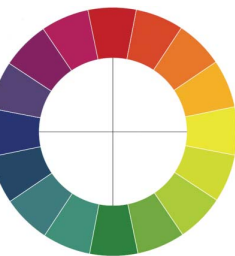
Color Circle
It arranges perceptually similar colors located next to each other & arranged in a circle. It is like a color solid, but it leaves out variations in a hue’s saturation & value.
Can be divided into:
An upper portion where the colors possess some amount of redness
A lower portion where the colors have some amount of greenness
A left portion where the colors seem to contain varying degrees of blueness
A right portion where the colors have more or less yellowness

Complementary Afterimages
An afterimage that’s on the opposite side of the color circle from the inducing color.
Hue Cancellation Method
Experimental technique in which a person cancels out any perception of a particular color (EX: blue) in a test light by adding the light of the complementary color (EX: yellow).
Color Deficiency
A condition that affects the perception of colors. In some cases, colors tend to drop out in pairs, so people lose the ability to perceive blue & yellow or to perceive red & green.
Monochromatism
A rare form of color blindness in which the absence of cone receptors results in the perception of only shades of lightness (white, gray, & black), with no chromatic color present.
Usually hereditary
Only rods & no functioning cones
Poor visual acuity
Eyes are very sensitive to bright light
Dichromatism
A form of color deficiency in which a person is missing 1 of the 3 cone pigments & hence experiences some colors, & not others. The 3 major forms of dichromatism are Protanopia, Deuteranopia, & Tritanopia.

Ishihara Plates
A display of colored dots used to test for the presence of color deficiency. The dots are colored so that people with normal (trichromatic) color vision can perceive numbers in the plate, but people with color deficiency cannot perceive the numbers.
Protanopia
Individuals see short wavelengths as blue.
They are missing the LONG wavelength pigment.
The neutral point occurs at 492 nm.
Above the neutral point, they see yellow.
Deuteranopia
Individuals see short wavelengths as blue.
They are missing the MEDIUM wavelength pigment.
The neutral point occurs at 498 nm.
Above the neutral point, they see yellow.
Tritanopia
Individuals see short wavelengths as blue.
They are missing the SHORT wavelength pigment.
The neutral point occurs at 570 nm.
Above the neutral point, they see red.

Color Constancy
We perceive objects' colors as relatively constant, even under changing illumination.

Chromatic Adaptation
The ability of a human visual system to discount the color of the illumination & to approximately preserve the appearance of an object.
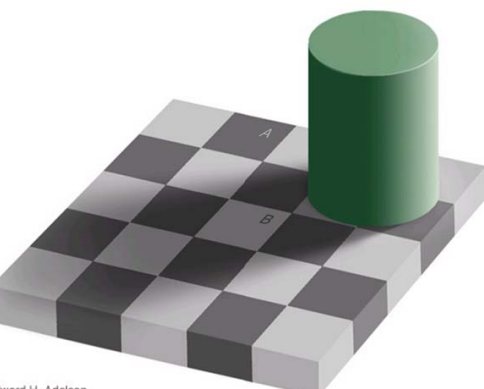
The Effect of the Surroundings
Color constancy works best when an object is surrounded by objects of many different colors, a situation that often occurs when viewing objects in the environment.

Memory & Color
Past knowledge of an object’s color can have an impact on color perception.
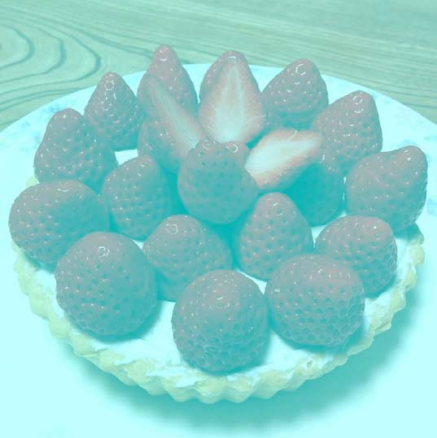

Memory Color
The idea that an object’s characteristic color influences our perception of that object’s color.