Biopsychology 151
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/129
Earn XP
Last updated 1:11 AM on 3/31/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
1
New cards
Mind-Body Problem
Dualism, Monism, Materialism, Idealism, Identity Position
2
New cards
Monoism
the idea that the universe consists of only one type of being
3
New cards
Dualism
the idea that minds are one type of substance and matter is another
4
New cards
Materialism
mental ideas and events are matter and only matter
5
New cards
Idealism
the perception of the world in the mind cannot be separated by the understanding of the outside world, ideas are connected to the outside world
6
New cards
Identity Position
states and processes of the mind are identical to states and processes of the brain
7
New cards
Broca
person knows what they want to say but is unable to produce the words or sentence
8
New cards
Wernicke
discovered that damage in part of the left temporal cortex characterized by poor language comprehension and impaired ability to remember the names of objects
9
New cards
Fritsch and Hitzig
electrical stimulation of the cerebral cortex of a dog produced movements
10
New cards
Sir Charles Sherrington
showed how muscular contractions are followed by relaxation
the spinal cord and brain process nerve impulses and turn them into new impulses to muscles and organs
the spinal cord and brain process nerve impulses and turn them into new impulses to muscles and organs
11
New cards
Phineas Gage
famous man to suffer a rod lunging itself into his brain and through his eye, his personality changed afterwards. Gage's accident helped teach us that different parts of the brain play a role in different functions.
12
New cards
Otto Loewi
provided the first proof that chemicals were involved in the transmission of impulses from one nerve cell to another and from neuron to the responsive organ
13
New cards
karl lashley
pioneered experimental work conducted on rats with surgically induced brain lesions
14
New cards
Descartes
raised the question of consciousness (“I think, therefore I am”) and argued that you cannot deny the existence of your mind while using your mind to deny it
15
New cards
Hydraulic Theory
the nerves are filled with water that carry motor and sensory information to the ventricles of the brain much in the same way that hydraulic fluid travels through machines
16
New cards
Mind/Body Dualism - Pineal Gland
considered the body and the soul to be ontologically separate but interacting entities, each with its own particular attributes
17
New cards
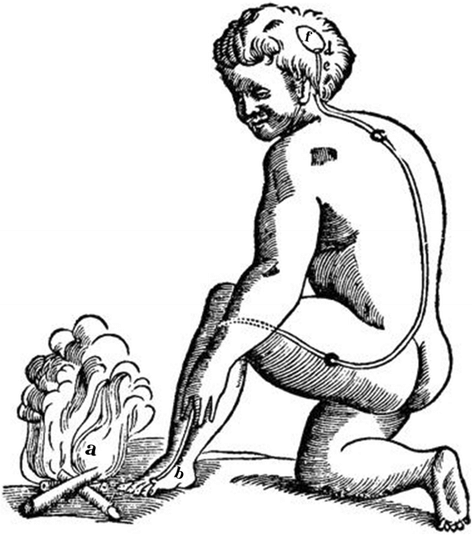
Reflexes
The reflex arc of pain according to Descartes. The fire (a) is a stimulus afflicting the skin (b) and moving the fine thread (c), which goes to valves (d, e). The valves open the cavity (f), from which an animal spirit is released, which in turn makes the head turn and move the hand and the foot
18
New cards
Law of Bell and Magendie
the finding that the anterior spinal nerve roots contain only motor fibers and posterior roots only sensory fibers and that nerve impulses are conducted in only one direction in each case
19
New cards
types of bio psychologist
Physiological Psychology, Psychophysiology, Neuropsychology, Psychopharmacology, Cognitive Neuroscience, Comparative Psychology, ethology
20
New cards
Physiological Psychology
changes physiology of a person to see how the psyche if effected (what changed)
21
New cards
Psychophysiology
changes the psyche to see if the physiology is affected
22
New cards
Neuropsychology
clinical (in hospital) deals with injury to the brain and study how certain injuries affect behavior
23
New cards
Psychopharmacology
how drugs (psychotropic) affect the mind
24
New cards
Cognitive Neuroscience
study of how the brain effect thought and brain process
25
New cards
Comparative Psychology
study of how non-human animals, compares different species
26
New cards
Ethology
study of non-humans without the use of a lab
27
New cards
methods for studying the brain
Ablation/Lesioning, Computerized Axial Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Electroencephalogram, Positron Emission Topography, Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Magnetoencephalography (MEG), Autoradiography, Micro dialysis, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS), Direct Stimulation of the Brain
28
New cards
Ablation/Lesioning
damage to part of brain
29
New cards
Computerized Axial Tomography
brain scan, up the brain
30
New cards
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
brain scan inside the brain, uses magnet to move hydrogen molecules so we can capture picture
31
New cards
Electroencephalogram
measures electricity in brain using waves, better function, uses electrons connected to cap/head, more active the area or the brain, more activity there will be
32
New cards
Positron Emission Topography
allows brain movement to be tracked by following glucose, positron clings too
33
New cards
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
detects regional cerebral blood flow, blood on covering of brain, follows around brain
34
New cards
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
measures magnetic field in brain to see where activity lies
35
New cards
Autoradiography
traces neuron pathway, different pathways, and structure
36
New cards
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
apply a small magnetic field to brain, can turn parts of the brain off and on
37
New cards
Optogenetics
uses light to turn specific genes on and off in the brain
38
New cards
sociobiology
describe humans by evolutionary perspective
39
New cards
parts of a neuron
•Sensory/Motor Neurons; Afferent/efferent
•Unipolar, bipolar, multipolar, pseudounipolar
•Cell Body (Soma)
•Dendrites/Dendritic Spines
•Axon
•Axon Hillock
•Myelin
•Nodes of Ranvier
•Synaptic Buttons/Terminals
•Unipolar, bipolar, multipolar, pseudounipolar
•Cell Body (Soma)
•Dendrites/Dendritic Spines
•Axon
•Axon Hillock
•Myelin
•Nodes of Ranvier
•Synaptic Buttons/Terminals
40
New cards
Sensory Neurons
nerve cells that are activated by sensory input from the environment
41
New cards
Motor Neurons
a specialized type of brain cell called neurons located within the spinal cord and the brain.
42
New cards
Afferent
into the brain
43
New cards
Efferent
out of the brain
44
New cards
Unipolar
only has one nerve process extending from the cell body: an axon that extends into dendrites
45
New cards
Bipolar
a type of neuron that has two extensions (one axon and one dendrite)
46
New cards
Multipolar
a type of neuron that possesses a single axon and many dendrites (and dendritic branches)
47
New cards
Pseudounipolar
a type of neuron which has one extension from its cell body
48
New cards
Cell Body (Soma)
where the neuron's DNA is housed, and where proteins are made to be transported throughout the axon and dendrites
49
New cards
Dendrites
receive input from many other neurons and carry those signals to the cell body.
a neuron fires an action potential — an electrical impulse that then stimulates other neurons
a neuron fires an action potential — an electrical impulse that then stimulates other neurons
50
New cards
Dendric Spines
Spines serve as the major target for excitatory synaptic input onto principal neurons in the hippo- campus, the neocortex, and other brain regions
51
New cards
Axon
where electrical impulses from the neuron travel away to be received by other neurons
52
New cards
Axon Hillock
is the part of the neuron where nerve electrical activity is summated to determine the likelihood of firing an action potential
53
New cards
Myelin Sheath
is an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord
allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells
allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells
54
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
periodic gap in the insulating sheath (myelin) on the axon of certain neurons that serves to facilitate the rapid conduction of nerve impulses
55
New cards
Synaptic Buttons
are small swellings that are found at the terminal ends of axons.
sites where synapses with other neurons are found
neurotransmitters are stored there to communicate with other neurons via these synapses
sites where synapses with other neurons are found
neurotransmitters are stored there to communicate with other neurons via these synapses
56
New cards
Terminals
facilitate intercellular communication by allowing synaptic vesicles to bind to their membrane and release neurotransmitters into the synaptic rift after an action potential stimulates them
57
New cards
ion distribution at rest
\-70mV, caused by Na+, K+, Cl- and various proteins, polarized neuron
58
New cards
Sodium- Potassium Pumps
Sodium is outside the membrane while Potassium is inside
59
New cards
electrostatic gradient
the electrostatic force due to the charge separation across the membrane tends to move ions in a direction determined by its particular charge.
60
New cards
osmotic gradients
the difference in concentration between two solutions on either side of a semipermeable membrane
61
New cards
Action Potential
\+50mV, depolarized, Na+ In, K+ out, when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls
62
New cards
Voltage-Activated Ion Channels
integral membrane proteins that enable the passage of selected inorganic ions across cell membranes.
open and close in response to changes in transmembrane voltage, and play a key role in electrical signaling by excitable cells such as neurons
open and close in response to changes in transmembrane voltage, and play a key role in electrical signaling by excitable cells such as neurons
63
New cards
Neural Threshold
the level that a depolarization must reach for an action potential to occur. In most neurons the threshold is around -55mV to -65mV
64
New cards
All or Nothing Rule
signal transmission between neurons is not dependent on the strength of the stimuli but, rather, only that the initial threshold is met
65
New cards
Propagation
that the action potential doesn't move but rather causes a new action potential of the adjacent segment of the neuronal membrane
66
New cards
Refractory Period
the time after initiation of an action potential when it is impossible or more difficult to generate a second action potential
67
New cards
relative \n (hyperpolarization)
when the membrane potential becomes more negative at a particular spot on the neuron's membrane
68
New cards
absolute \n (repolarization)
depolarization is when the membrane potential becomes less negative (more positive)
69
New cards
Polarization
an electric field distorts the negative cloud of electrons around positive atomic nuclei in a direction opposite the field
70
New cards
depolarization
the gated sodium ion channels on the neuron's membrane suddenly open and allow sodium ions (Na+) present outside the membrane to rush into the cell. As the sodium ions quickly enter the cell, the internal charge of the nerve changes from -70 mV to -55 mV
71
New cards
parts of synapse
Presynaptic (axon) and Postsynaptic \n (dendrite) membranes
Synaptic vesicles \n Microtubules
Neurotransmitter release
Synaptic vesicles \n Microtubules
Neurotransmitter release
72
New cards
Presynaptic (axon)
the place where the electrical signal (the action potential) is converted into a chemical signal (neurotransmitter release)
\
releases neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft between nerve cells
\
releases neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft between nerve cells
73
New cards
Postsynaptic (dendrite)
receives a signal (binds neurotransmitter) from the presynaptic cell and responds via depolarisation or hyperpolarisation
74
New cards
\n Synaptic vesicles
stores neurotransmitter molecules before releasing them into the synapse in response to electrical signaling within the cell
75
New cards
Microtubules
assembly of mitotic spindle, in dividing cells, or axon extension, in neurons
76
New cards
What happens at a Synapse?
neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse
77
New cards
What are the ways to destroy a Neurotransmitter?
diffusion, degradation, and reuptake.
78
New cards
ESPS
synaptic inputs that depolarize the postsynaptic cell, bringing the membrane potential closer to threshold and closer to firing an action potential
79
New cards
ISPS
decrease action potential
80
New cards
Diffusion
the neurotransmitter drifts away, out of the synaptic cleft where it can no longer act on a receptor
81
New cards
degradation
breaks down the neurotransmitter molecule by enzyme activity
82
New cards
Reuptake
neurotransmitter molecules that have been released at a synapse are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron that released them
83
New cards
Gluamate
excitatory, learning and memory
84
New cards
GABA
inhibitory neurotransmitter for the central nervous system (CNS), reduce neuronal excitability by inhibiting nerve transmission.
85
New cards
Dopamine
allowing you to feel pleasure, satisfaction and motivation
86
New cards
epinephrine/norepinephrine
arousal, wakefulness, depression (theory of \n depression - (MAO inhibitors increase \n levels)
87
New cards
Serotonin
chemical that carries messages between nerve cells in the brain and throughout your body
88
New cards
Acetylcholine
muscle control, autonomic body functions, and in learning, memory, and attention
89
New cards
Endorphins
help relieve pain, reduce stress and improve mood
90
New cards
\n glial cells
astrocytes, microglial cells, oligodendrocytes
91
New cards
Astrocytes
regulation of blood flow, homeostasis of extracellular fluid, ions and transmitters, energy provision, and regulation of synapse function
92
New cards
oligodendrocytes
A cell that forms the myelin sheath (a layer that covers and protects nerve cells) in the brain and spinal cord
93
New cards
microglial cells
regulate brain development, maintenance of neuronal networks, and injury repair
94
New cards
2 Parts of the Nervous System
Central Nervous System
Peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
95
New cards
CNS
the body's processing centre
brain, spinal cord
brain, spinal cord
96
New cards
PNS
are responsible for relaying information between the body and the brain
somatic/skeletal
Autonomatic
somatic/skeletal
Autonomatic
97
New cards
Sympathetic
“fight-or-flight” responses
this system prepares the body for strenuous physical activity.
this system prepares the body for strenuous physical activity.
98
New cards
Parasympathetic
regulates “rest and digest” functions
99
New cards
Occipital
back of the head
visual perception
visual perception
100
New cards
Temporal
processing auditory information and with the encoding of memory