Unit 7: Natural Selection
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
LaMarck theory
If an organism changes during life in order to adapt to its environment, those changes are passed on to its offspring.
Evolution through use and disuse. Inheritance of acquired characteristics.
Fitness
Ability to contribute genes to the next generation (reproduction)
Mutation
A change in a DNA sequence. Happens spontaneously and unavoidably
Alleles
Different versions of the genes for a trait (dominant or recessive)
Grant and Grant
Studied the finch population on an isolated island in the Galapagos.
Measured the beak dimensions of all birds on the island every year for decades.
changes in population can happen very quickly in response to bottleneck
Artificial selection
When reproductive success is determined by human requirements
Biogeography
Fossils distributed in patterns that reflect the continents at one point in time being connected
Molecular Biology
- Molecular evidence comes from comparing DNA, RNA, and proteins across different organisms.
Genetic Similarities: All living organisms share a universal genetic code, and closely related species often have very similar DNA sequences.
Protein Homology: Many proteins (such as cytochrome c) are remarkably similar across different species, which supports the idea of common descent.
Molecular Clocks: By measuring the rate of genetic mutations, scientists can estimate the time since two species diverged, providing a timeline for evolutionary events.
Fossil Record
preserved remains or traces of organisms from the past that establishes history of life on Earth
Temporal Sequence
Fossils found in different rock layers show gradual changes in species over millions of years.
Transitional Fossils
Show evolutionary progression between groups
Vestigial structures
structures that have lost their primary adaptive purpose
Homologous Structures
Structures present in a common ancestor, which have diverged during evolution. (Divergent evolution)
Analogous Structures
Structures that have evolved multiple times in different lineages to fill similar adaptive needs. (Convergent evolution)
Population
localized group of interbreeding individuals
Gene pool
collection of alleles in the population
Allele frequency
how common that allele is in the population
Evolution
change of allele frequencies in a population
Genetic Drift
Random, non-selective, changes in allele frequency due to chance. Can lead to loss of genetic diversity.
Has a larger effect on smaller populations, since each individual is more of the total alleles.
Founder Effect
The descendants of a small, founding population have different allele percentages than the population the founders came from.
Bottleneck Effect
The survivors of a catastrophic decrease in a population may have a different allele frequency than the pre-______ population.
Ex: Earthquake, fire, or flood
Gene Flow
Movement of alleles due to immigration and emigration.
Sexual Selection
Persistence of traits that signify fitness and aid in reproduction.
Directional Selection
Shifts the overall makeup of the population by favoring variants that are at one extreme of the distribution.
Darker mice favored living among dark rocks—their darker fur conceals them from predators.
Disruptive Selection
Favors variants at both ends of the distribution.
In a patchy habit made up of light and dark rocks, mice of intermediate color are at a disadvantage.
Stabilizing Selection
Removes extreme variants from the population and preserves intermediate types.
If the environment consists of rocks of an intermediate color, both light and dark mice will be selected against.
Non-evolving population
Large size (no genetic drift)
Random mating (no sexual selection)
Stable environment (no natural selection)
No immigration/emigration (no gene flow)
No mutations.
No real population is in H.W. equilibrium.
Biological species
A group of organisms that are capable of successfully producing fertile, viable offspring.
Gradualism
species are the product of slowly accumulating, small evolutionary changes
Punctuated equilibrium
species undergo long periods of very little change, followed by rapid, large evolutionary changes
Adaptive Radiation
One species evolves into many species that occupy open niches
Reproductive Isolation
Speciation occurs when a population can no longer interbreed with any other population.
Allopatric Reproductive Isolation
ex) emergence of mountain range, formation of land bridge, evaporation of large lake producing several small lakes
reproductive isolation due to physical separation
Sympatric Reproductive Isolation
Examples: part of population switching to new habitat/food source, or polyploidy plants.
reproductive isolation occurring while occupying the same area.
Pre-zygotic Species Barriers
EX: (physical) - geographical
(temporal) - time of day/season
(behavioral) - mating rituals
(mechanical) - incompatibility of reproductive structures
(chemical) - incompatibility of proteins on gametes
Prevent gametes from combining into a fertilized zygote
Post-zygotic Species Barriers
EX: Reduced viability - Hybrid is frail
Reduced fertility - Hybrid is sterile
Hybrid breakdown - Fertile, viable hybrids mate, but their offspring are weak or sterile.
Prevent the hybrid zygote from becoming an organism capable of reproducing
Panspermia
One of two major hypotheses for life on Earth.
Life from Earth came from extraterrestrial life. (arriving on meteor or similar delivery system)
Abiogenesis
One of two major hypotheses for life on Earth.
Life from Earth came from non-life. Requires 4 major milestones to occur:
Development of biological molecules that living systems are made of
Development of Proto-cells: encapsulation of those chemicals into isolated systems.
Information Molecule Evolution: development of an information storage molecule that can be inherited.
Reproduction of living systems.
RNA World
The hypothesis that RNA preceded DNA. Due to RNA’s “double function” in living systems as an information storage molecule and a catalytic molecule.
Cleaves its own RNA or another RNA molecule. Ribosomal RNAs form the two subunits of ribosome, catalyzing peptide bond formation between two amino acids.
Evolution of Metabolism
The development of the major ways that living systems process matter and energy.
“Heterotroph Hypothesis”:
Glycolysis → Photosynthesis (oxygenation of atmosphere) → Aerobic Cellular Respiration (requires oxygen).
Endosymbiosis
The origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic ancestors. Free-living ancestors of eukaryotic mitochondria and chloroplasts were engulfed by eukaryotic ancestors, and a symbiotic arrangement was established.
Miller-Urey Experiments
Simulated “Early Earth” conditions (no O2).
Starting with simple chemical building blocks and appropriate energy supply, simple organic molecules were produced.
Radiometric Dating
Used to date geological formations and fossils.
Establishes chronological history of Earth, and establishes Earth’s age at ~4.5 billion years.
*Radioactive decay occurs when the nucleus of a radioactive atom spontaneously transforms into an atomic nucleus of a different, more stable isotope.
Some isotopes are radioactively unstable and decay over a known period of time.
Half Life: the amount of time it takes for one-half of a radioactive isotope to decay.
We can use this to determine the age of a sample with radioactive isotopes, based on the ratio of how much of the parent and daughter isotopes are present.
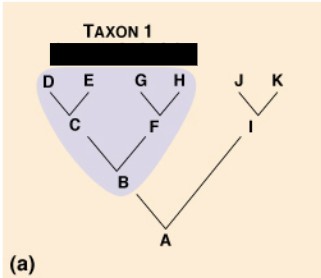
Monophyletic
A group that consists of an ancestral species and all of its descendants
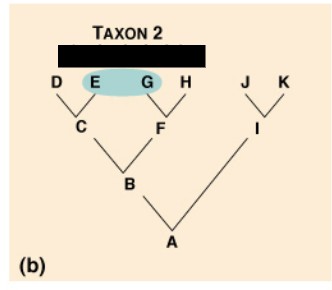
Paraphyletic
A group which consists of an ancestral species and some, but not all, of its descendants
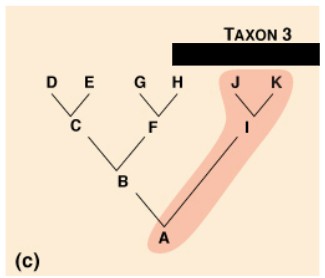
Polyphyletic
A group which includes distantly related species but does not include their most recent common ancestor
Outgroup
Diverged from the lineage leading to the ingroup (before the common ancestor of the ingroup)
Identifying the ______ helps determine the direction of evolutionary change and which traits are ancestral or derived.
Ancestral Traits
inherited from a common ancestor and shared by multiple species descended from that ancestor.
Derived Traits
traits evolved recently and unique to a specific lineage.
A population in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium:
No mutations: The allele pool is not altered by genetic changes.
Random mating: Individuals pair by chance, not based on genotype or phenotype.
No natural selection: All genotypes have equal probabilities of survival and reproduction.
Large (effectively infinite) population size: This minimizes genetic drift.
No gene flow (migration): No new alleles are introduced or lost through movement in or out of the population.
Hardy Weinberg equation
p²+2pq+q²=1
p² is the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype,
2pq is the frequency of the heterozygous genotype, and
q² is the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype.
How do you calculate frequency of an allele in a population?
For a gene with two alleles (e.g., A and a):
The frequency of allele A (p) is calculated by:
p = (frequency of AA + (1/2)) x (frequency of Aa)The frequency of allele a (q) is:
q = (frequency of aa + (1/2) x (frequency of Aa)
Note: p + q = 1