Gait Assessment + Intervention in Neurological Disorders
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
what are 6 TEMPORAL DESCRIPTORS of GAIT
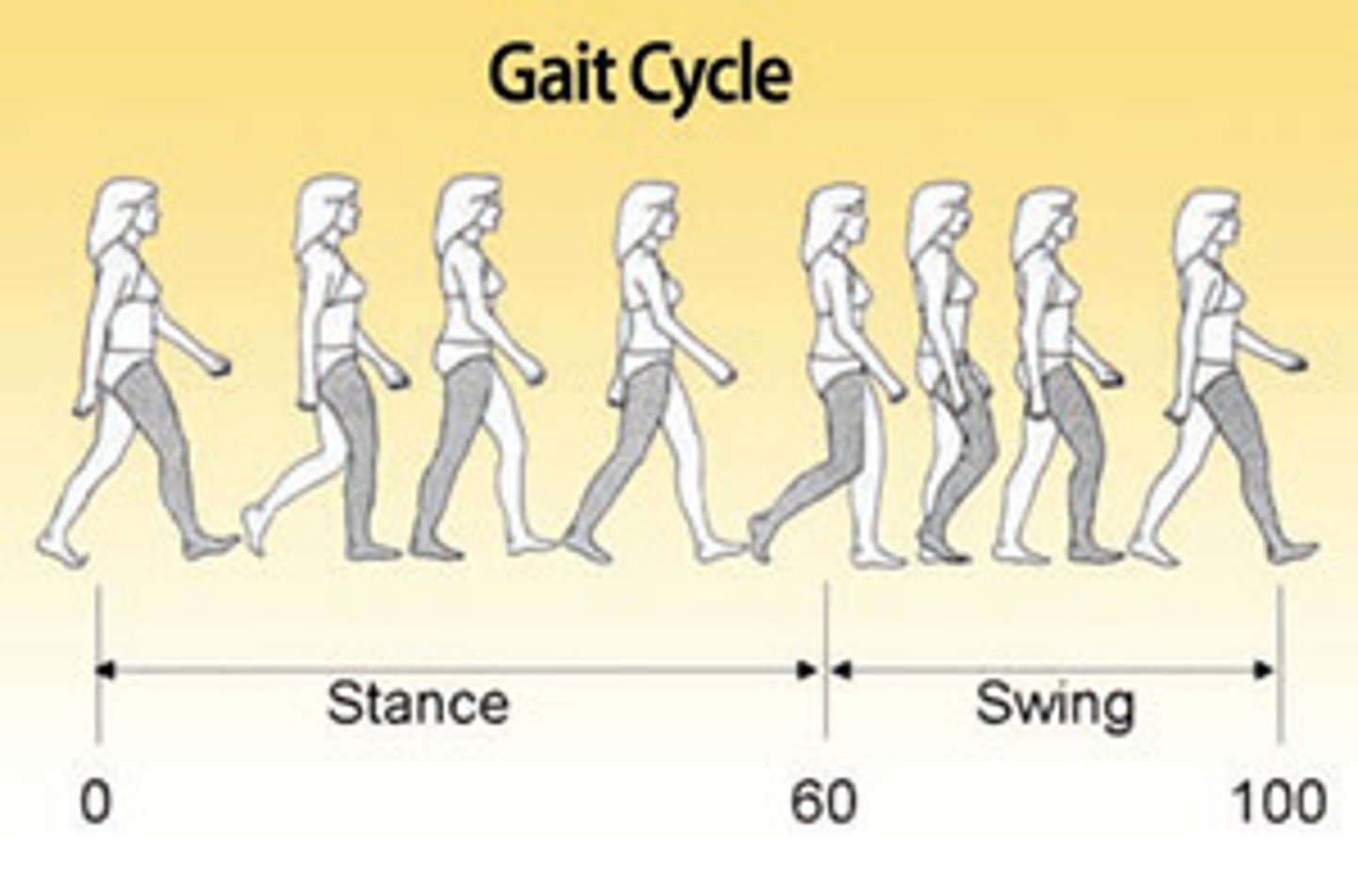
1. stance time (60% gait cycle)
2. single support time (time on one leg)
3. double support time (time on both legs)
4. swing time (40% gait cycle)
5. cadence (steps/min)
6. speed (m/s)
what PERCENTAGE of the gait cycle is the foot in the STANCE PHASE
60%
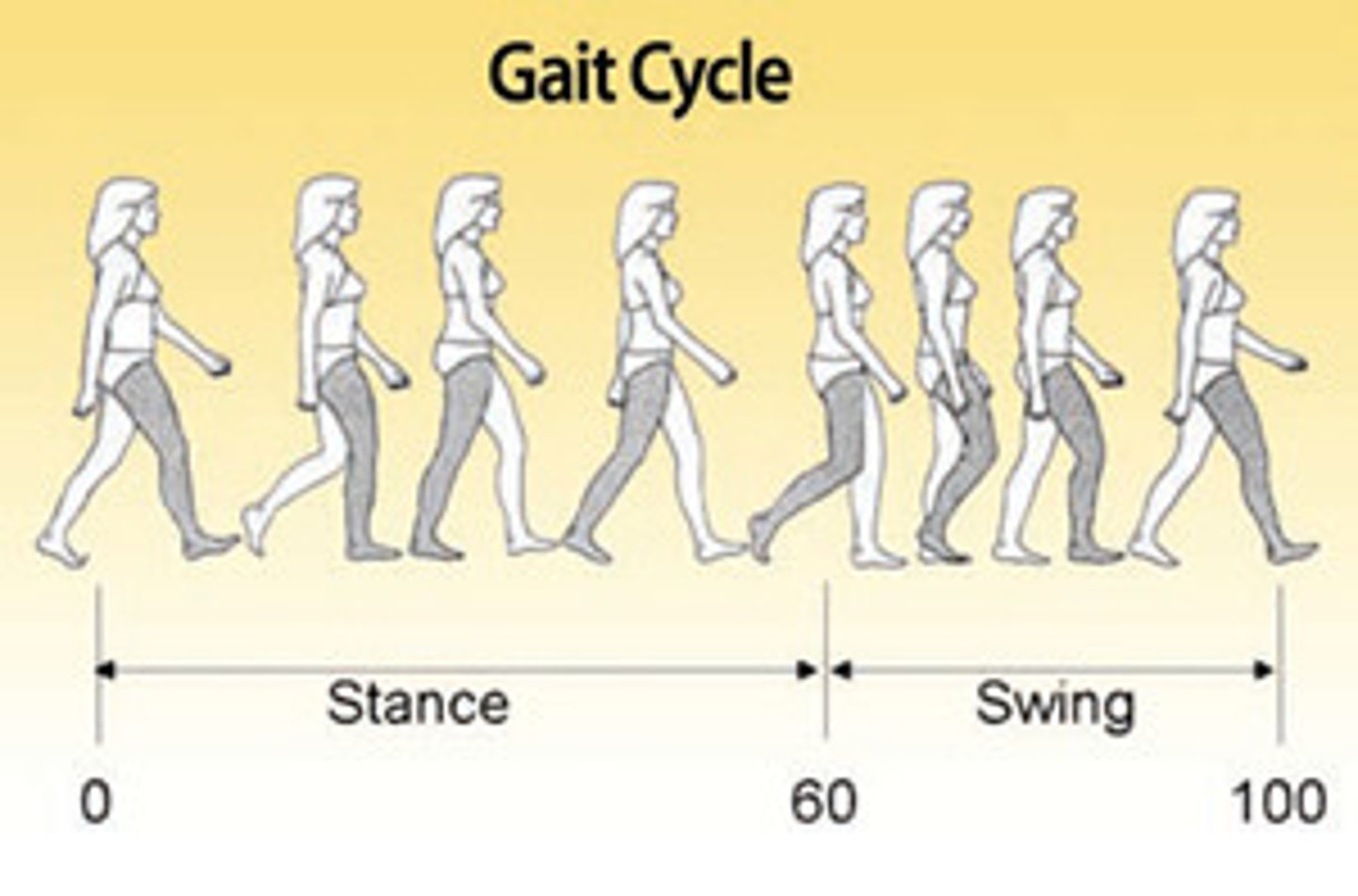
what PERCENTAGE of the gait cycle is the foot in the SWING PHASE
40%
what does SINGLE SUPPORT TIME refer to
time on one leg
what does DOUBLE SUPPORT TIME refer to
time on both legs
what is the CADENCE for MEN + WOMEN
Men: 110 steps/min
Women: 116 steps/min
regarding the GAIT CYCLE, what is the SPEED for MEN
1.37 m/s
regarding the GAIT CYCLE, what is the SPEED for WOMEN
1.24 m/s
what are 5 SPATIAL DESCRIPTIONS of GAIT
1. stride length
2. step length
3. width of BOS
4. angle of toe out
5. endurance
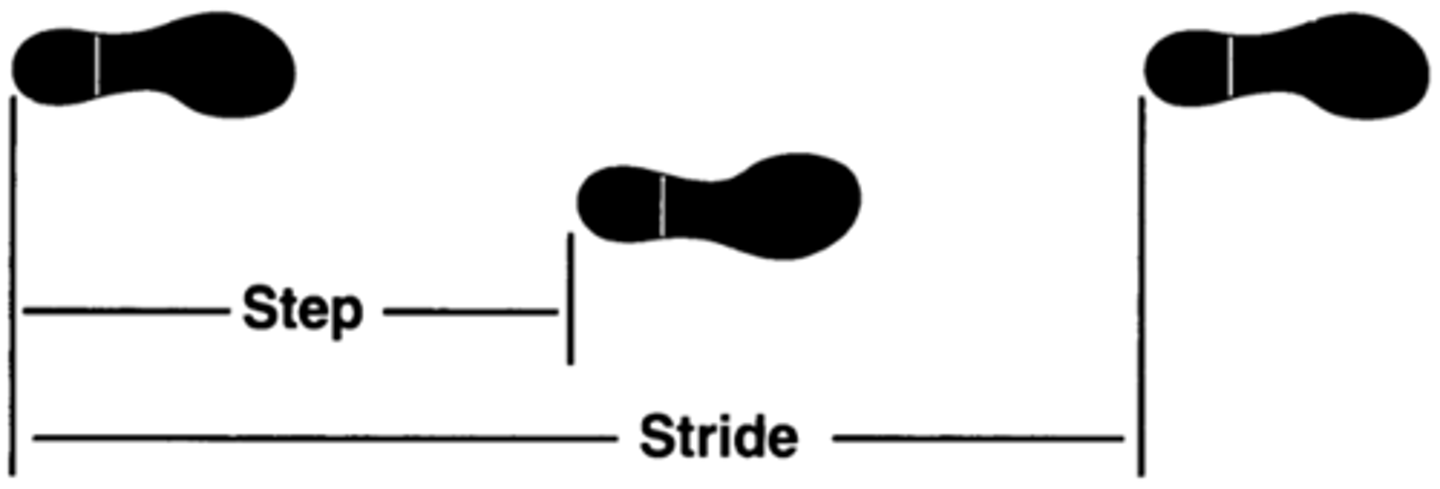
what is STRIDE LENGTH
distance covered from initial contact of one foot to the initial contact by the same foot
- initial contact to initial contact of one leg
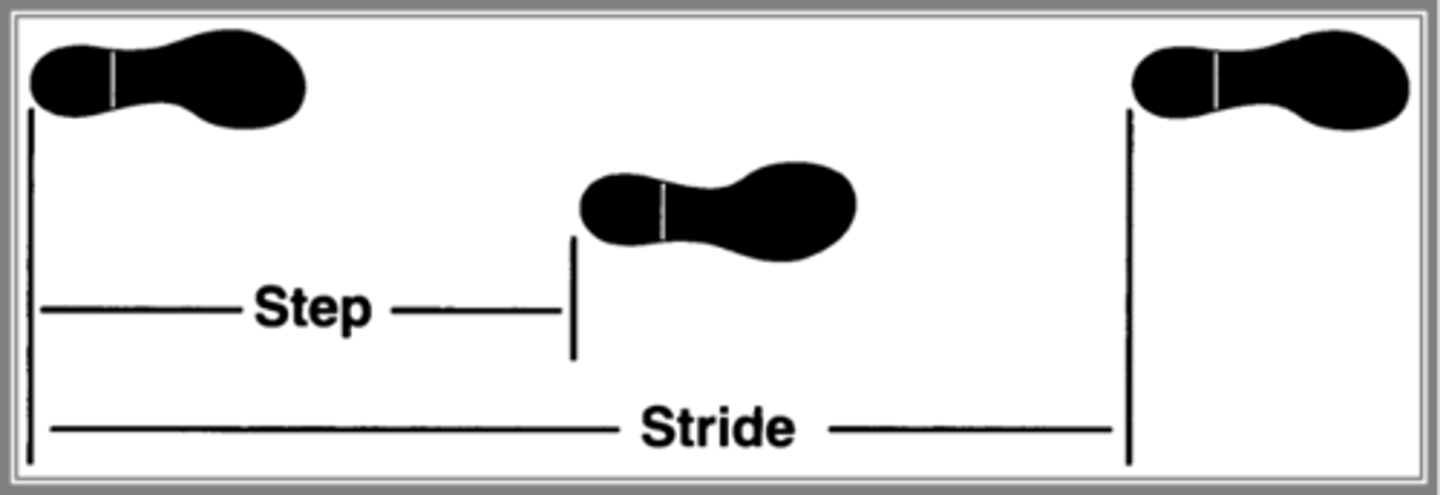
what is the STRIDE LENGTH for MEN + WOMEN
Men: 4.8 ft
Women: 4.2 ft
what is STEP LENGTH
distance between heel strike of one foot + heel strike of the other foot
- initial contact of one leg to initial contact of other leg
what is the STEP LENGTH for MEN + WOMEN
Men: 2.4 ft
Women: 2.1 ft
regarding SPATIAL DESCRIPTORS of GAIT, what is the NORMAL WIDTH of BOS
2-4 inches
regarding SPATIAL DESCRIPTORS of GAIT, what is the NORMAL ANGLE of TOE OUT
7 degrees
what are 3 ESSENTIAL REQUIREMENTS of GAIT
1. upright postural control
2. progression
3. adaptation
what are 4 CHARACTERISTICS of what PROGRESSION should look like with GAIT
1. rhythmic
2. reciprocal
3. smooth
4. maintaining momentum
what are 3 CONTROL MECHANISMS of GAIT
1. pattern generators
2. descending influences
3. sensory feedback
what 2 STRUCTURES are classified as PATTERN GENERATORS for GAIT
1. brainstem
2. spinal cord
what 4 STRUCTURES are classified as DESCENDING INFLUENCES for GAIT
1. cerebrum
2. basal ganglia
3. cerebellum
4. brainstem
what are 4 COMPONENTS classified as SENSORY FEEDBACK for GAIT
1. somatosensation
2. proprioception
3. vision
4. vestibular
what is the RESULT if any of the CONTROL MECHANISMS of GAIT are DAMAGED
degradation of gait
what does COGNITIVE DEMANDS of GAIT + POSTURE increase with
increasing complexity of:
- environment
- speed of movement
- difficulty of task
what causes COGNITIVE DEMANDS of GAIT + POSTURE to increase
dual-task conditions/training
what are 3 MAJOR TASKS ASSOCIATED with GAIT CYCLE
1. weight acceptance
2. single limb support
3. swing limb advancement
weight acceptance
2 Phases Involved:
1. initial contact
2. loading response
What Occurs:
1. shock absorbed
2. momentum preserved
3. foot flat position achieved
Peak Demand On: quads, glutes + anterior tibialis
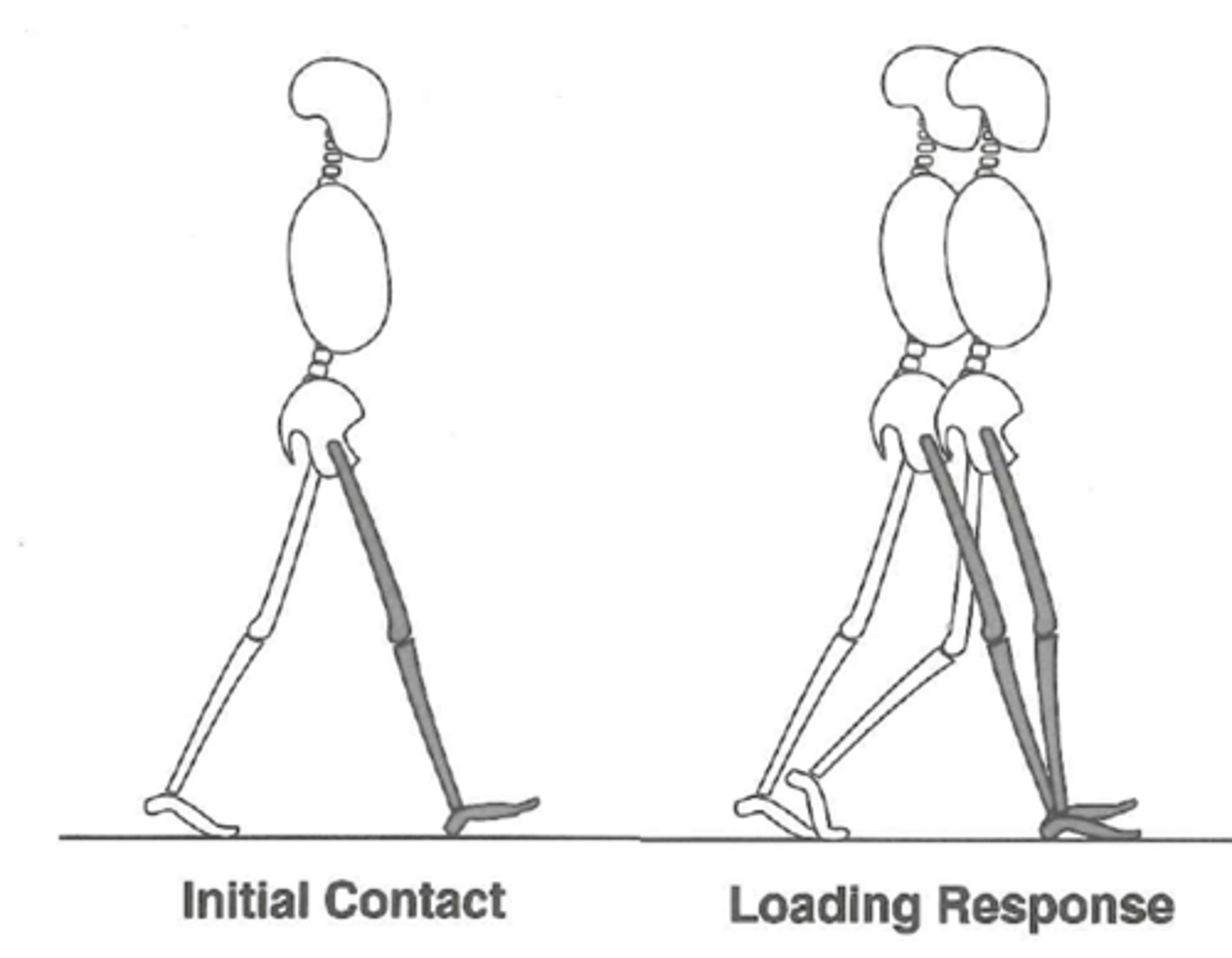
what 2 PHASES of the GAIT CYCLE make up WEIGHT ACCEPTANCE
1. initial contact (heel strike)
2. loading response (foot flat)
what does INITIAL CONTACT (heel strike) refer to
moment when heel contacts/strikes the ground
what does LOADING RESPONSE (foot flat) refer to
entire foot contacts the ground
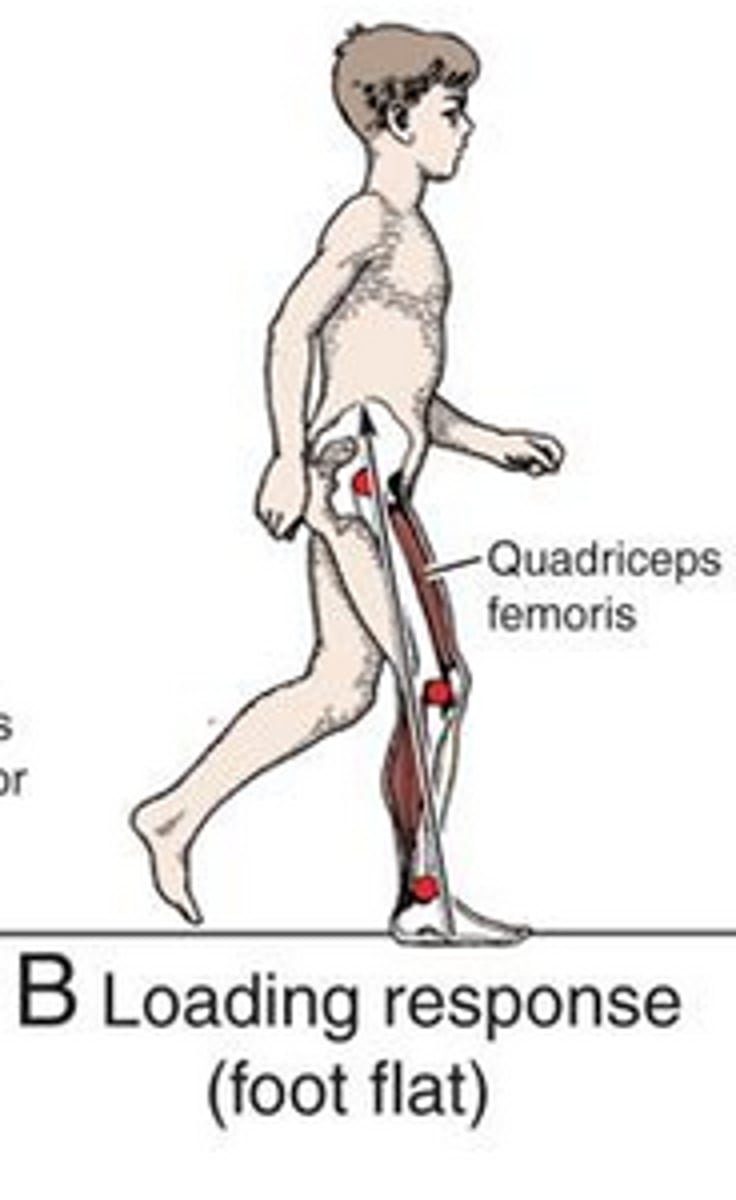
what occurs during the LOADING RESPONSE (4)
1. knee flexes to accept weight
2. anterior tibialis eccentrically lowers foot as it contacts the ground; prevents foot drop/slap
3. glutes maximums helps stabilize hip + control forward motion
4. quads eccentrically contract to help control knee flexion
what is ABSORBED during WEIGHT ACCEPTANCE of the gait cycle
shock absorbed
what is PRESERVED during WEIGHT ACCEPTANCE of the gait cycle
momentum preserved
what is ACHIEVED during WEIGHT ACCEPTANCE of the gait cycle
foot flat position
what is there PEAK DEMAND ON during WEIGHT ACCEPTANCE (initial contact + loading response) of the gait cycle (3)
1. quads
2. glutes
3. anterior tibialis
single limb support
2 Phases Involved:
1. mid stance (early + late)
2. terminal stance
Controlled: tibial advancement
Peak Demand On:
1. hip abductors (early/late mid stance)
2. gastrocnemius (terminal stance)
what 2 PHASES of the GAIT CYCLE make up SINGLE LIMB SUPPORT
1. mid stance (early + late)
2. terminal stance
what does MID-STANCE refer to
entire body progresses directly over the stance limb (single stable limb)
what occurs during MID-STANCE (4)
1. in early mid-stance: opposite knee bends + crosses stance leg
2. in late mid-stance: tibia moves forward
3. gluteus medius turns on when on single stable limb
4. gastroc working eccentrically
what does TERMINAL STANCE refer to
heel of stance limb rises off the ground + heel of other foot makes contact with the ground
is there UNCONTROLLED/CONTROLLED TIBIAL ADVANCEMENT during single limb support
controlled tibial advancement
regarding SINGLE LIMB SUPPORT, what is there PEAK DEMAND ON during EARLY/LATE MID-STANCE
hip abductors
regarding SINGLE LIMB SUPPORT, what is there PEAK DEMAND ON during TERMINAL STANCE
gastrocnemius
swing limb advancement
Phase Involved: initial swing
What Occurs:
1. rapid hip/knee flexion
2. toe clearance
Peak Demand Of: hip flexors
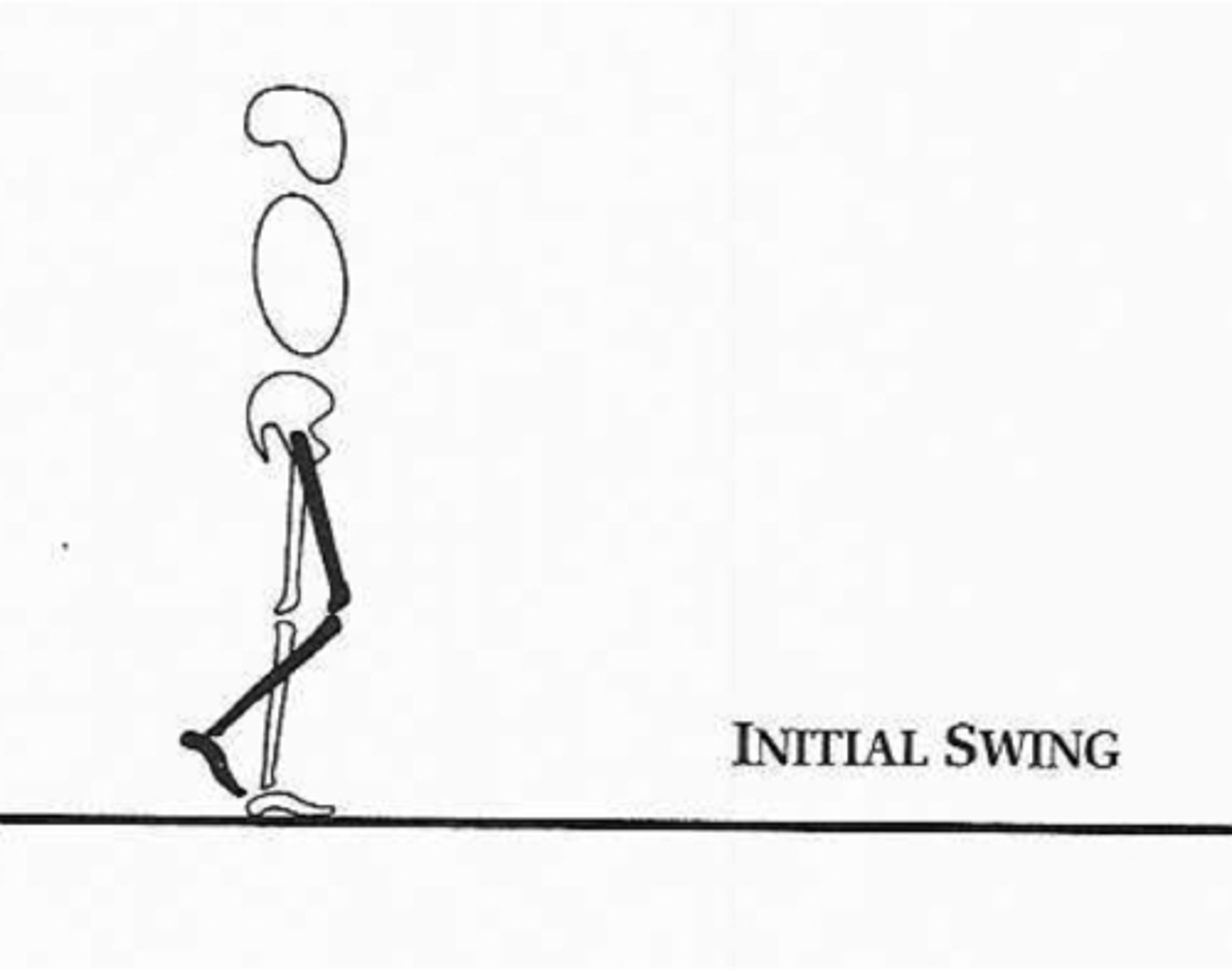
what PHASE of the GAIT CYCLE make up SWING LIMB ADVANCEMENT
initial swing
what PHASE is the INITIAL SWING PHASE classified under
swing phase
what does INITIAL SWING refer to
leg is lifted off the ground + moves forward
- hip + knee flexing
- ankle dorsiflexing to clear foot
what occurs during SWING LIMB ADVANCEMENT (2)
1. rapid hip/knee flexion
2. toe clearance
what is there PEAK DEMAND OF during SWING LIMB ADVANCEMENT (initial swing) of the gait cycle
hip flexors
what are 7 GAIT TEST + MEASURES
1. gait speed
2. 2/6/12 MWT
3. TUG (Timed Up + Go)
4. gait portion of Tinetti
5. dynamic gait index
6. functional ambulation category (FAC)
7. step/stride length test (w/ dry erase marker)
what are 4 GUIDELINES for GAIT SPEED
1. 15-30ft (5-10 meter) walkway
2. allow several feet/meters for acceleration/deceleration
3. one practice trial + two timed trials
4. test self-selected pace + fastest pace
what are 2 GUIDELINES for the 2/6/12 MWT
1. measure distance covered
2. measure HR + BP before + after test
what is a 0 on the FUNCTIONAL AMBULATION CATEGORY (FAC) classified as
nonfunctional (unable)
what does NON-FUNCTIONAL (UNABLE) indicate on the FAC
person can't walk/require help of 2 or more people
what is a 1 on the FUNCTIONAL AMBULATION CATEGORY (FAC) classified as
dependent, level 2
what does DEPENDENT, LEVEL 2 indicate on the FAC
person requires firm, continuous support from 1 person to help with carrying weight + balance
what is a 2 on the FUNCTIONAL AMBULATION CATEGORY (FAC) classified as
dependent, level 1
what does DEPENDENT, LEVEL 1 indicate on the FAC
person needs continuous/intermittent support from 1 person to help with balance or coordination
what is the DICHOTOMY for SCORES 0-2 on the FAC
physical dependent gait
what is a 3 on the FUNCTIONAL AMBULATION CATEGORY (FAC) classified as
dependent on supervision
what does DEPENDENT on SUPERVISION indicate on the FAC
person requires verbal supervision/stand-by help from 1 person without physical contact
what is a 4 on the FUNCTIONAL AMBULATION CATEGORY (FAC) classified as
independent on level ground
what does INDEPENDENT on LEVEL GROUND indicate on the FAC
person can walk independently on level ground but requires help on stairs, slopes or uneven surfaces
what is a 5 on the FUNCTIONAL AMBULATION CATEGORY (FAC) classified as
independent
what does INDEPENDENT indicate on the FAC
person can walk independently anywhere
what is the DICHOTOMY for SCORES 3-5 on the FAC
physical independent gait
what are 3 NEUROLOGICAL GAIT PROBLEMS that occurs during WEIGHT ACCEPTANCE
1. excessive knee flexion/buckling
2. excessive knee extension
3. forefoot contact/foot slap
what are 5 CAUSES of EXCESSIVE KNEE FLEXION/BUCKLING during weight acceptance
1. quad weakness
2. glute weakness
3. knee flexion contracture
4. hamstring spasticity
5. flexion syngery
what are 2 INTERVENTIONS for treating EXCESSIVE KNEE FLEXION/BUCKLING
1. quad + glute strength emphasize eccentric loading
2. knee stretching
what TYPE of LOADING should be emphasized for QUAD + GLUTE STRENGTH when treating EXCESSIVE KNEE FLEXION/BUCKLING
eccentric loading
what are 3 CAUSES of EXCESSIVE KNEE EXTENSION during weight acceptance
1. severe quad weakness
2. extension synergy
3. plantarflexor spasticity/contracture
what are 3 INTERVENTIONS for treating EXCESSIVE KNEE EXTENSION
1. quad + glute strengthening, emphasize eccentric loading
2. ankle ROM
3. bracing
what are 3 CAUSES of FOREFOOT CONTACT/FOOT SLAP during weight acceptance
1. plantar flexor contracture
2. dorsiflexor weakness
3. spasticity
what are 4 INTERVENTIONS for treating FOREFOOT CONTACT/FOOT SLAP
1. ankle ROM
2. dorsiflexor strengthening
3. bracing
4. functional e-stim
what are 4 NEUROLOGICAL GAIT PROBLEMS that occurs during SINGLE LIMB SUPPORT
1. excessive knee flexion
2. excessive knee extension
3. trendelenburg sign
4. poor terminal stance/trailing limb position
what are 3 CAUSES of EXCESSIVE KNEE FLEXION during single limb support
1. knee flexion contracture
2. flexion synergy
3. poor knee control
what are 3 INTERVENTIONS for treating EXCESSIVE KNEE FLEXION that occurs during single limb support
1. quad strength
2. knee ROM
3. inner knee control work
what are 2 CAUSES of EXCESSIVE KNEE EXTENSION during single limb support
1. quad weakness
2. plantar flexor contracture/spasticity
what are 3 INTERVENTIONS for treating EXCESSIVE KNEE EXTENSION that occurs during single limb support
1. quad strength
2. ankle ROM
3. bracing
what are 2 CAUSES of the TRENDELENBURG SIGN during single limb support
1. weak hip abductors
or
2. weak hip extensors
what are 2 MAJOR CHARACTERISTICS of the TRENDELENBURG SIGN
1. contralateral hip drop
2. hip moves backwards
what are 2 INTERVENTIONS for treating TRENDELENBURG SIGN
1. dynamic hip strengthening
2. BWS (body weight support)
what are 3 CAUSES for POOR TERMINAL STANCE/TRAILING LIMB POSITION during single limb support
1. weak, spastic + contracted plantar flexors
2. hip flexor contracture
3. poor gait speed
what is POOR TERMINAL STANCE described as
heel pulled off the ground too early
what are 3 INTERVENTIONS for treating POOR TERMINAL STANCE/TRAILING LIMB POSITION
1. plantar flexor strengthening
2. hip ROM
3. increase gait speed
what are 2 NEUROLOGICAL GAIT PROBLEMS that occurs during SWING LIMB ADVANCEMENT
1. poor hip/knee flexion, circumduction
2. poor toe clearance/toe drag
what are 4 CAUSES of POOR HIP/KNEE FLEXION + CIRCUMDUCTION during swing limb advancement
1. hip/knee flexor weakness
2. extension synergy
3. failure to achieve trailing limb posture
4. slow gait speed
what are 2 MAJOR CHARACTERISTICS of CIRCUMDUCTION
1. lateral trunk lean
2. hip hike
what are 3 INTERVENTIONS for treating POOR HIP/KNEE FEXION + CIRCUMDUCTION
1. hip/knee flexor strengthening
2. manual assistance
3. increase gait speed
what are 6 CAUSES for POOR TOE CLEARANCE/TOE DRAG during swing limb advancement
1. hip/knee flexor weakness
2. extension synergy
3. failure to achieve trailing limb posture
4. slow gait speed
5. dorsiflexor weakness
6. plantar flexor contracture/spasticity
what are 5 INTERVENTIONS for treating POOR TOE CLEARANCE/TOE DRAG
1. hip/knee flexor strengthening
2. manual assistance
3. increase gait speed
4. dorsiflexor strengthening
5. functional e-stim
what are 8 GENERAL GAIT PROBLEMS
1. decreased gait speed
2. poor trunk/postural control
3. decreased rhythmicity
4. decreased step/stride length
5. increased double support time
6. poor gait initiation + stopping
7. poor turning, object negotiation
8. difficulty with dual-task situations
what are 6 KEY POINTS for GAIT TRAINING
1. if want to get better at walking have to walk; specificity of training
2. work on speed (intervals)
3. use tools/devices (treadmill, BWS, knee/ankle braces) as needed to increase practice opportunities + intensity
4. use FES, auditory + manual cues as needed
5. work on walking in multiple directions
6. do obstacle courses + obstacles
what is PROPULSIVE/SENILE GAIT
a stooped, rigid posture with head + neck bent forward
what 2 CONDITIONS is PROPULSIVE/SENILE GAIT common with
1. Alzheimer's
2. senile dementia
what is PARKINSON'S GAIT
stopped, rigid posture with head + neck bent forward accompanied with less arm swing + more shuffling/festinating steps
what is PARKINSON'S GAIT common with
parkinson's disease + other disorders that affect basal ganglia
what is SCISSORS GAIT
legs flexed slightly at hips + knees, giving appearance of crouching with knees + thighs hitting/crossing in a scissors-like movement
what is SCISSORS GAIT common with
cerebral palsy
what is SCISSORS GAIT some times a component of
spastic gait
what is SPASTIC/HEMIPARETIC GAIT
a stiff (extension synergy), foot-dragging walk