Anatomy Lab Practical 3
1/350
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
351 Terms
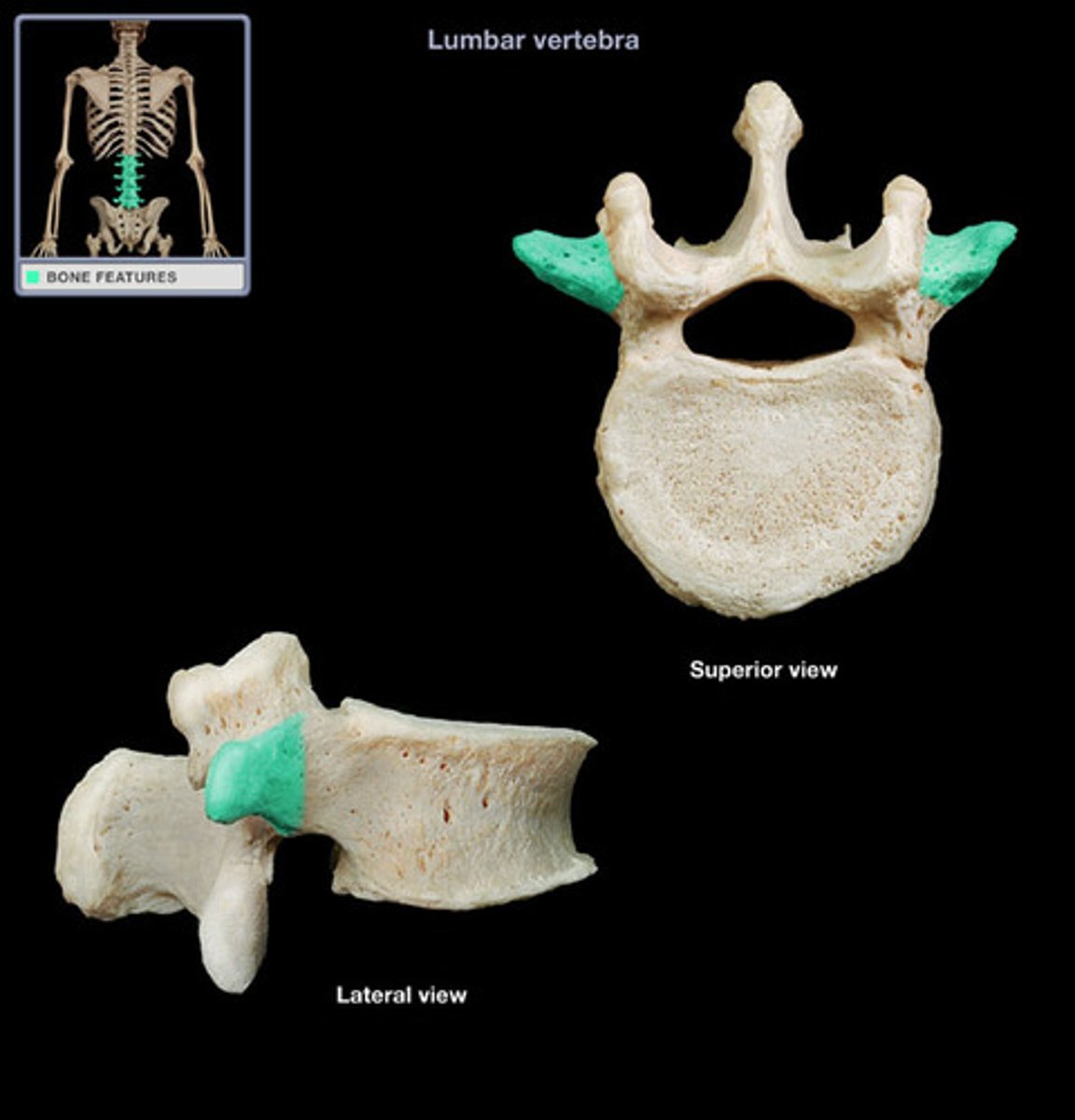
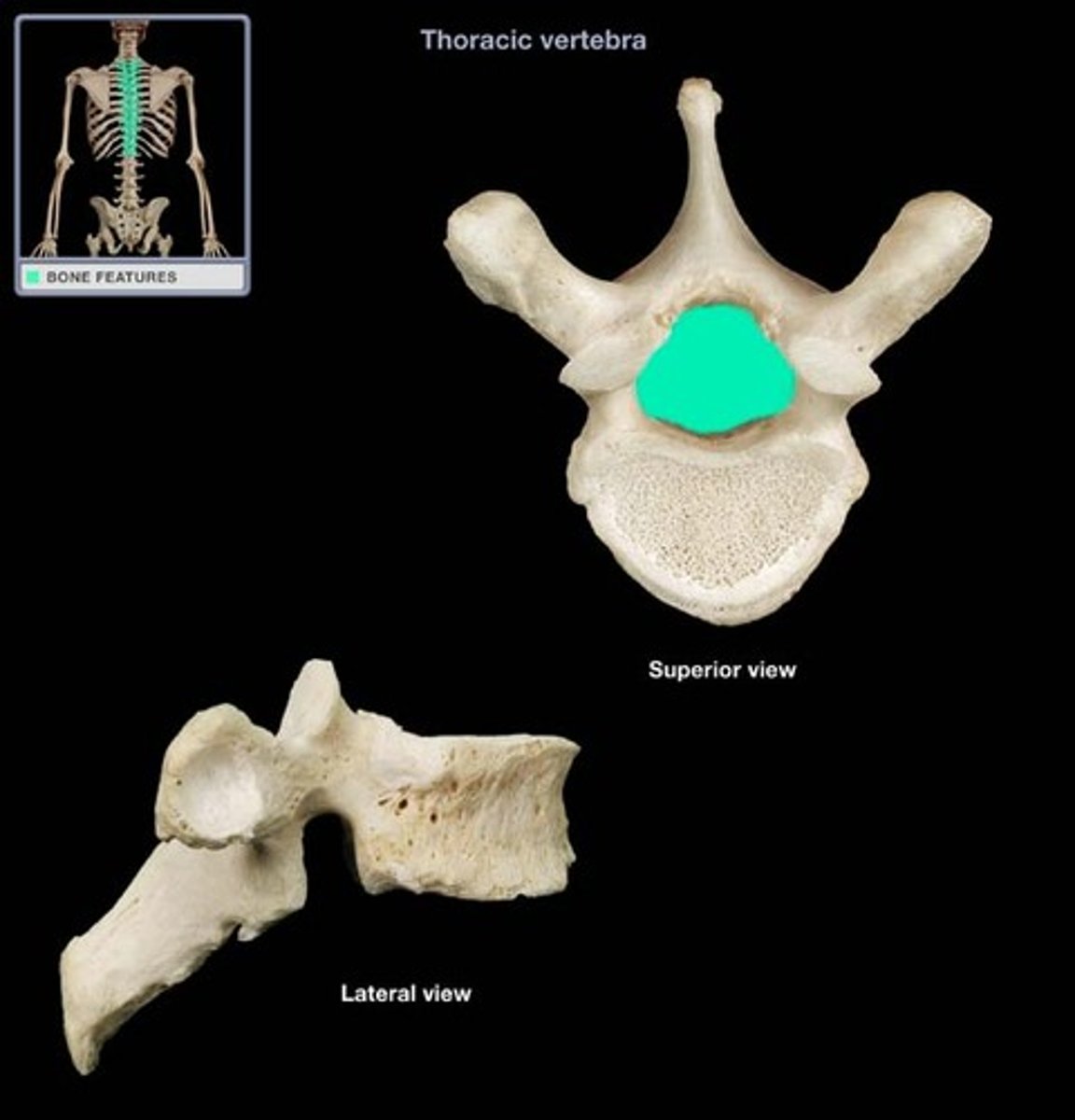
vertebra body
solid anterior portion of a vertebra
vertebra pedicle
a stub of bone that connects the lamina to the vertebral body to form the vertebral arch
vertebra lamina
posterior arch of vertebral bone lying between spinous process
vertebral arch
structure that encloses the nerve cord
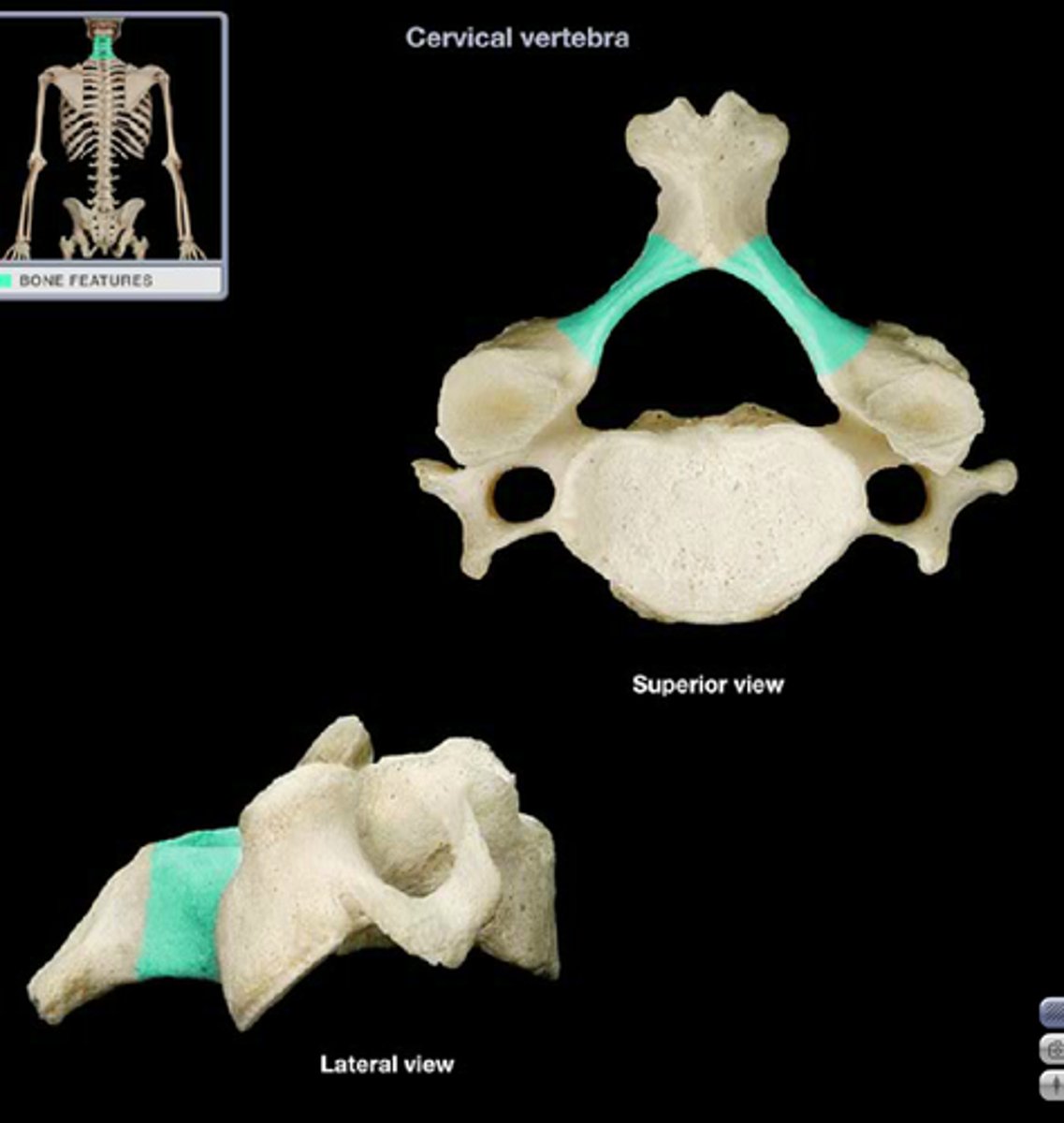
transverse process
two lateral projections from the vertebral arch
vertebral foramen
canal through which spinal cord passes
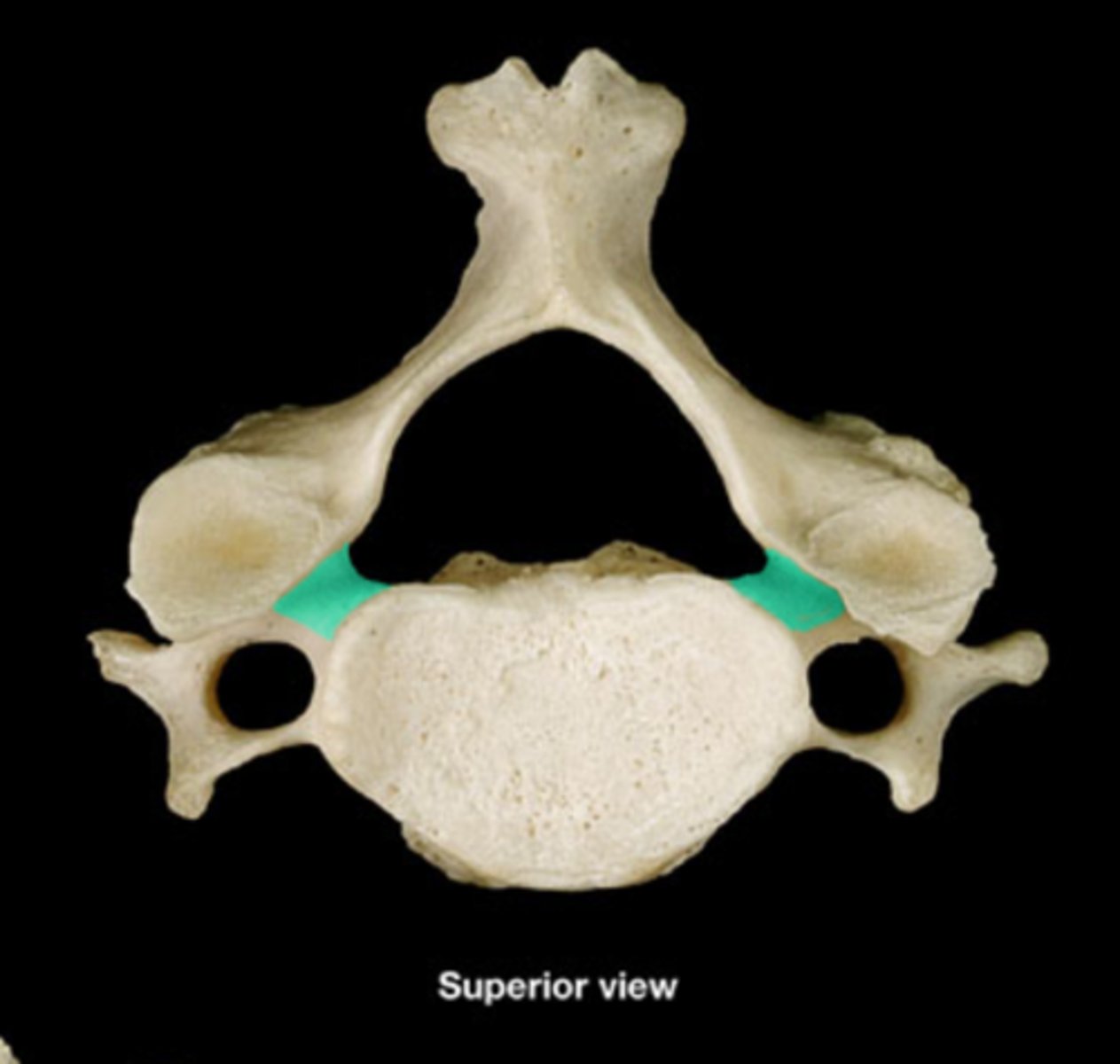
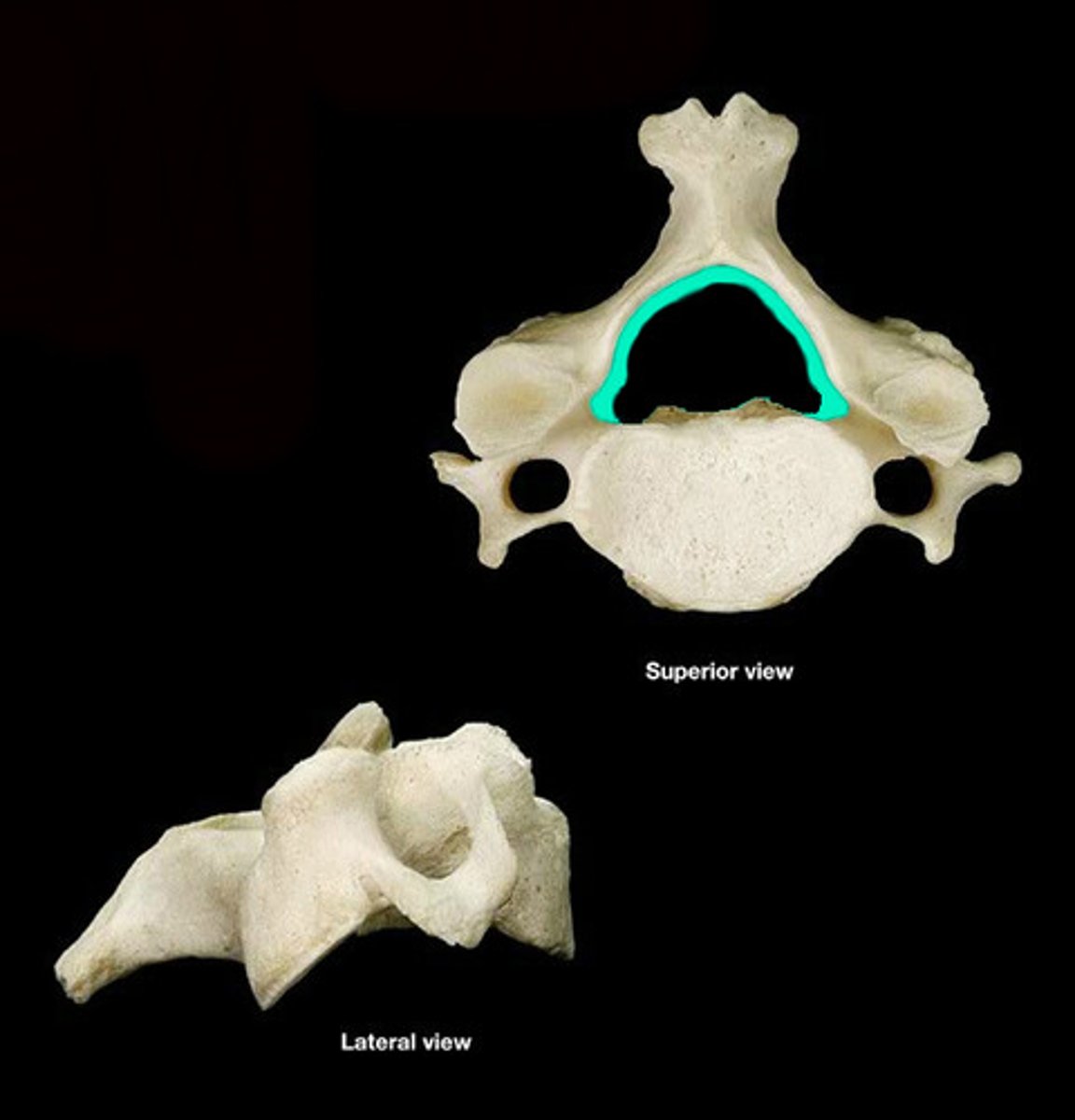
superior vertebral notch
indentation of the superior edge of pedicle
inferior vertebral notch
indentation of the inferior edge pedicle
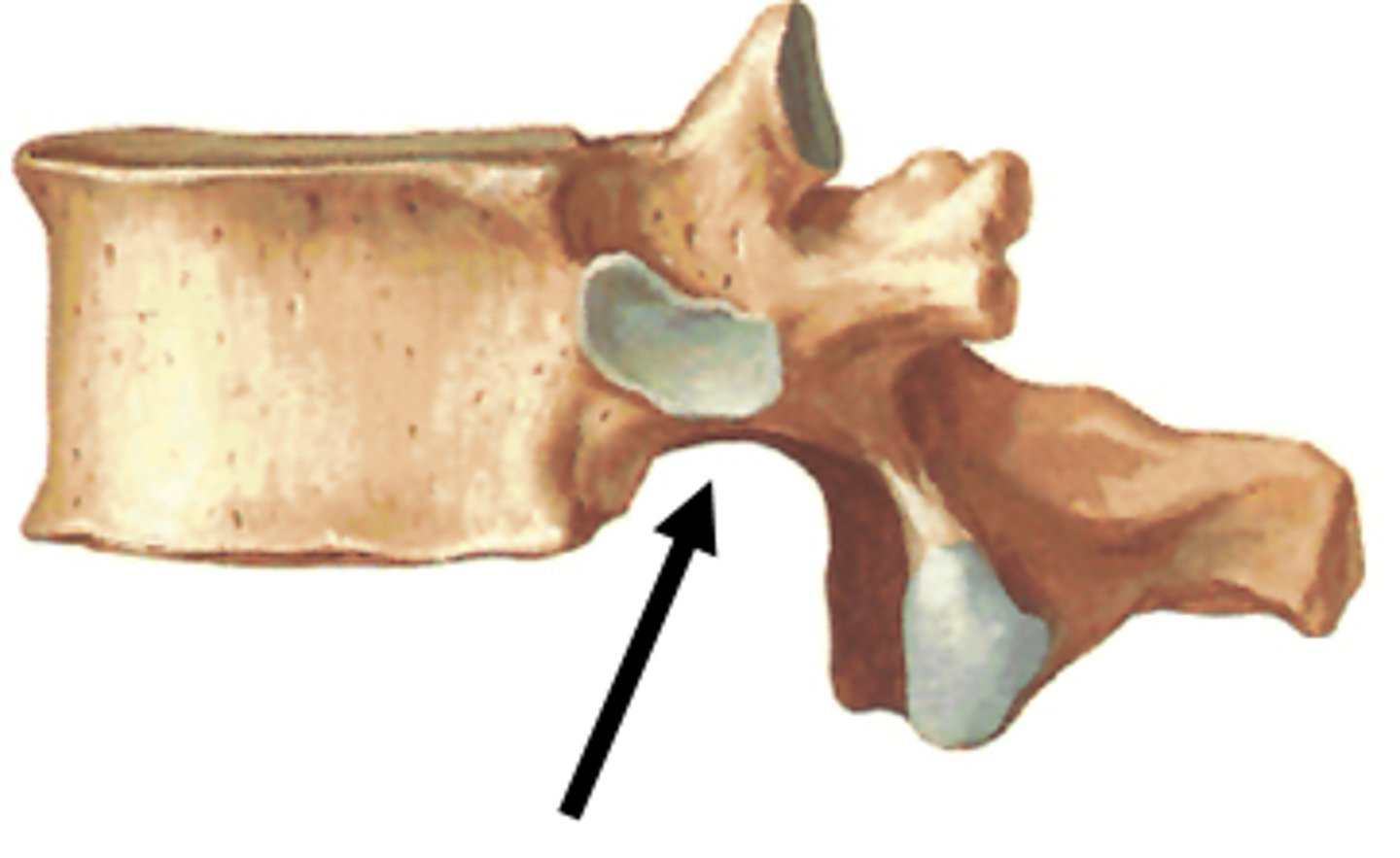
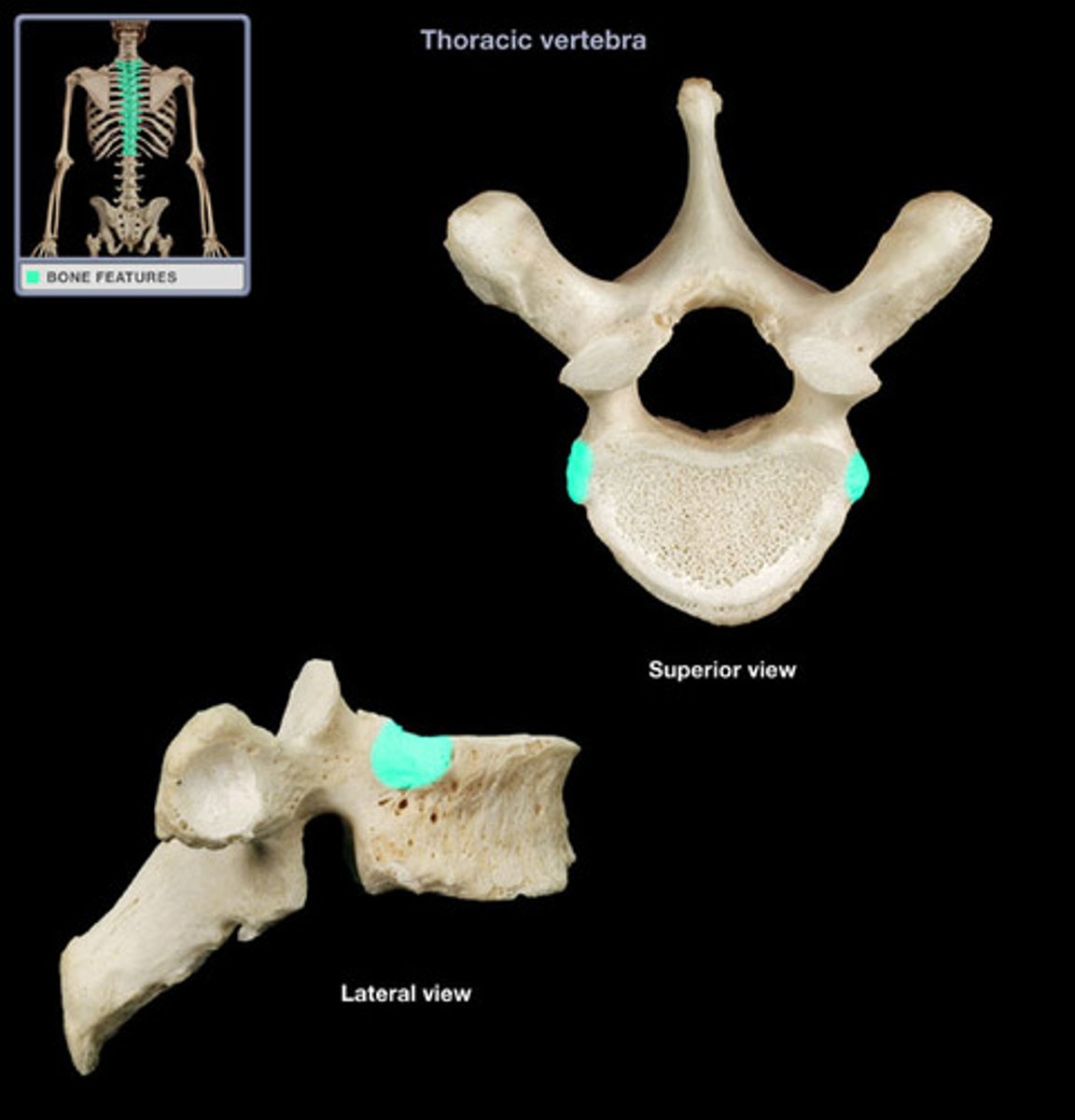
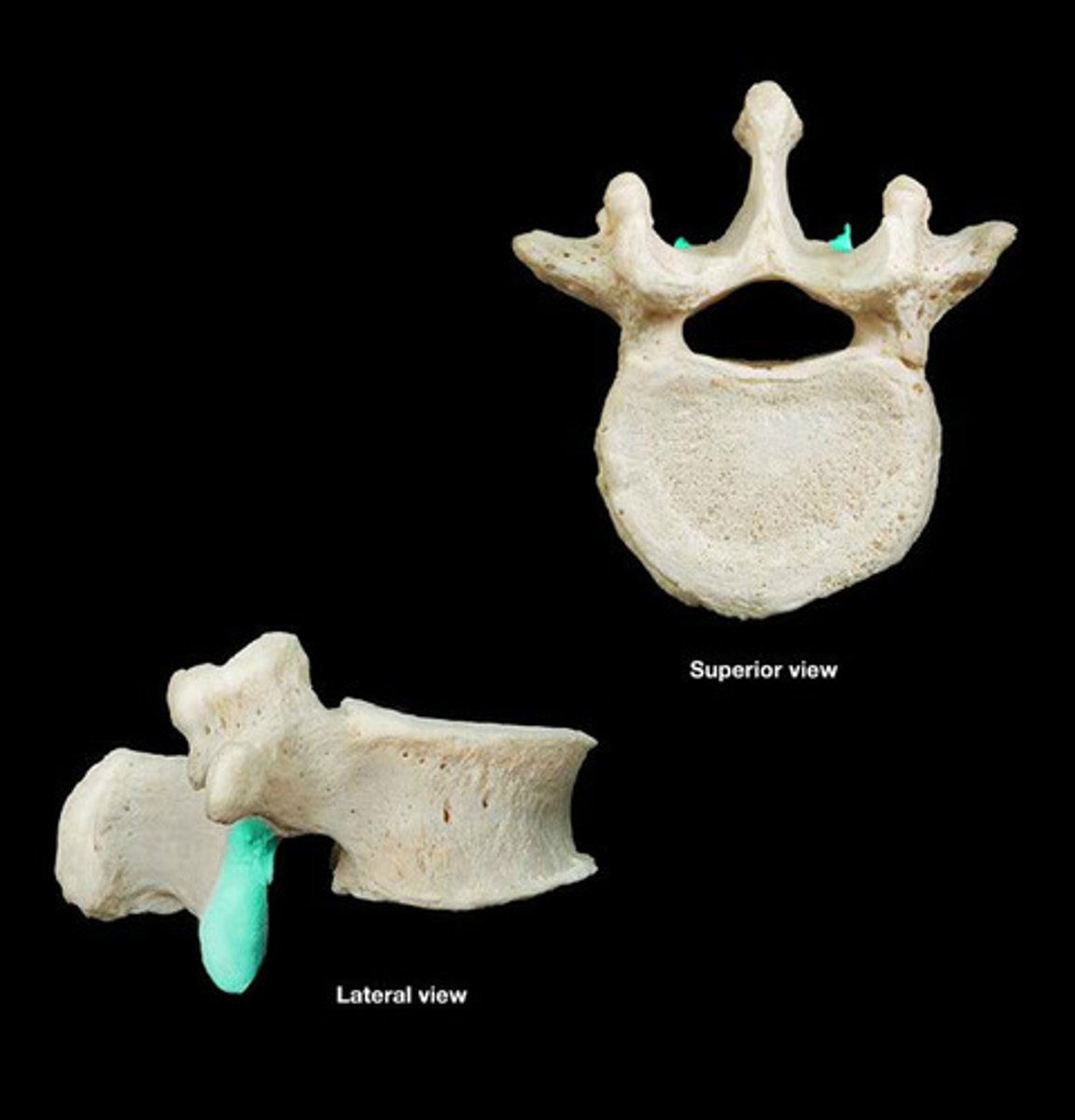
superior costal facet
receive the head of the ribs on the superior side; only in thoracic vertebrae
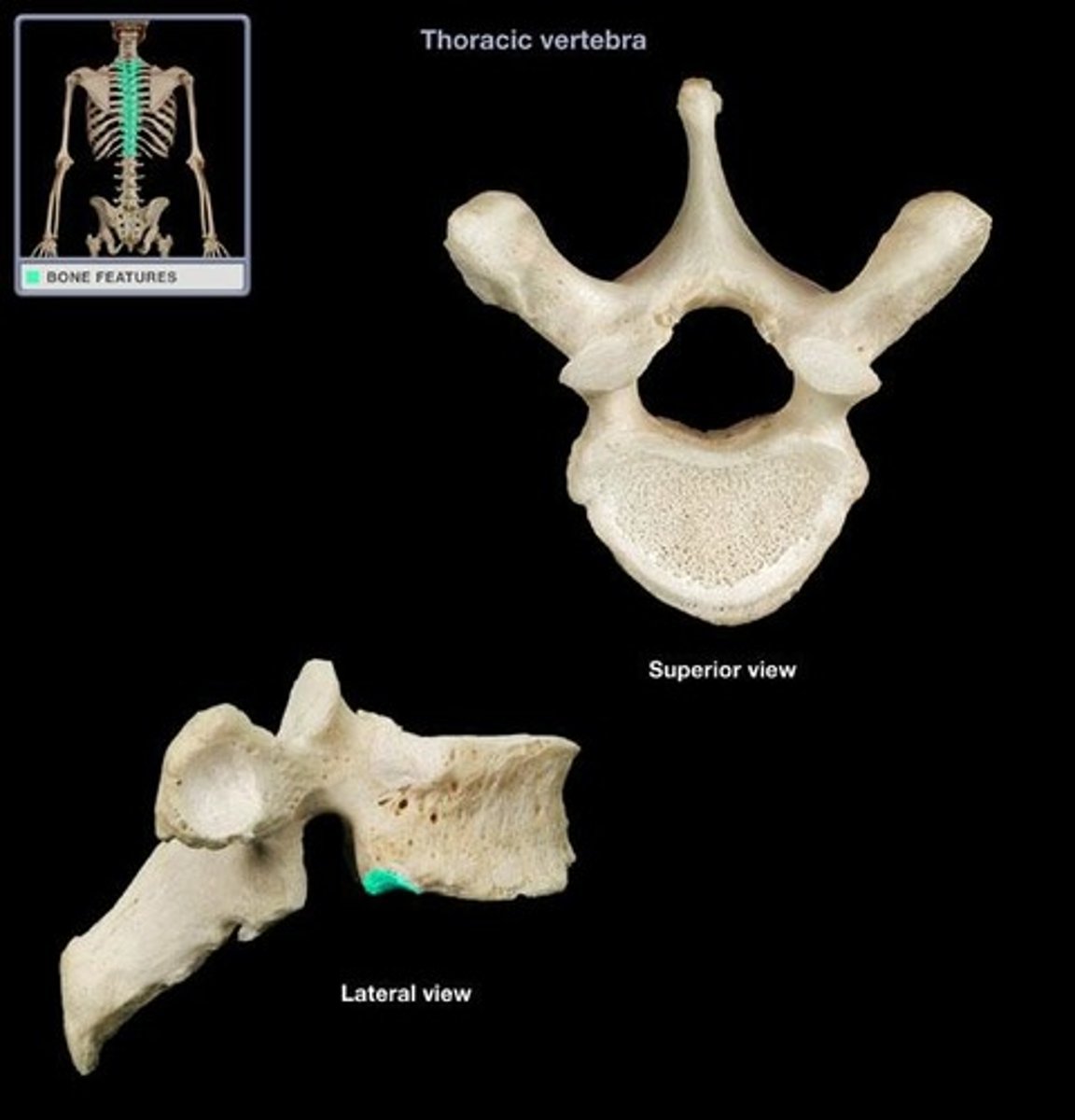
inferior costal facet
receive the head of the ribs on the inferior side; only in thoracic vertebrae
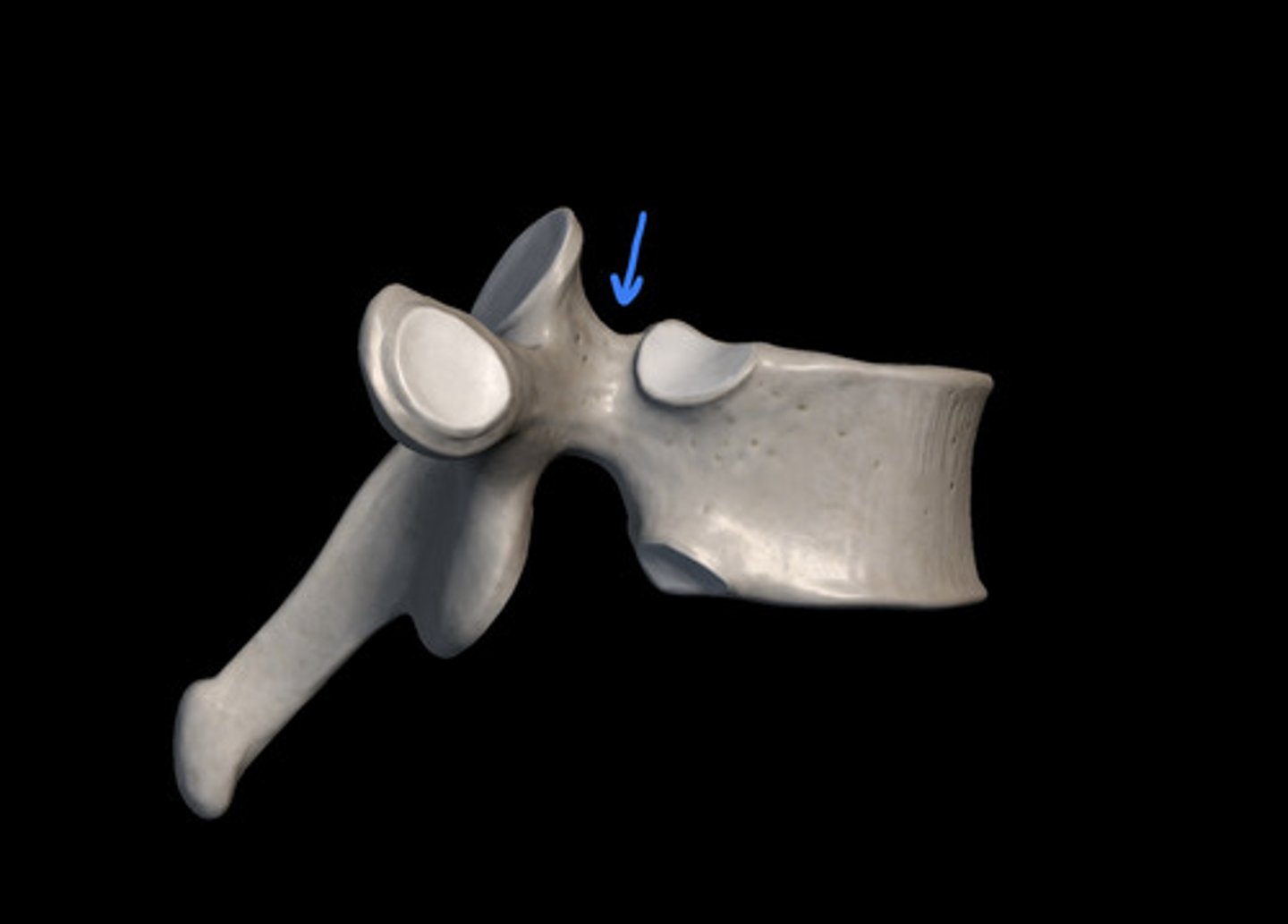
superior articular process
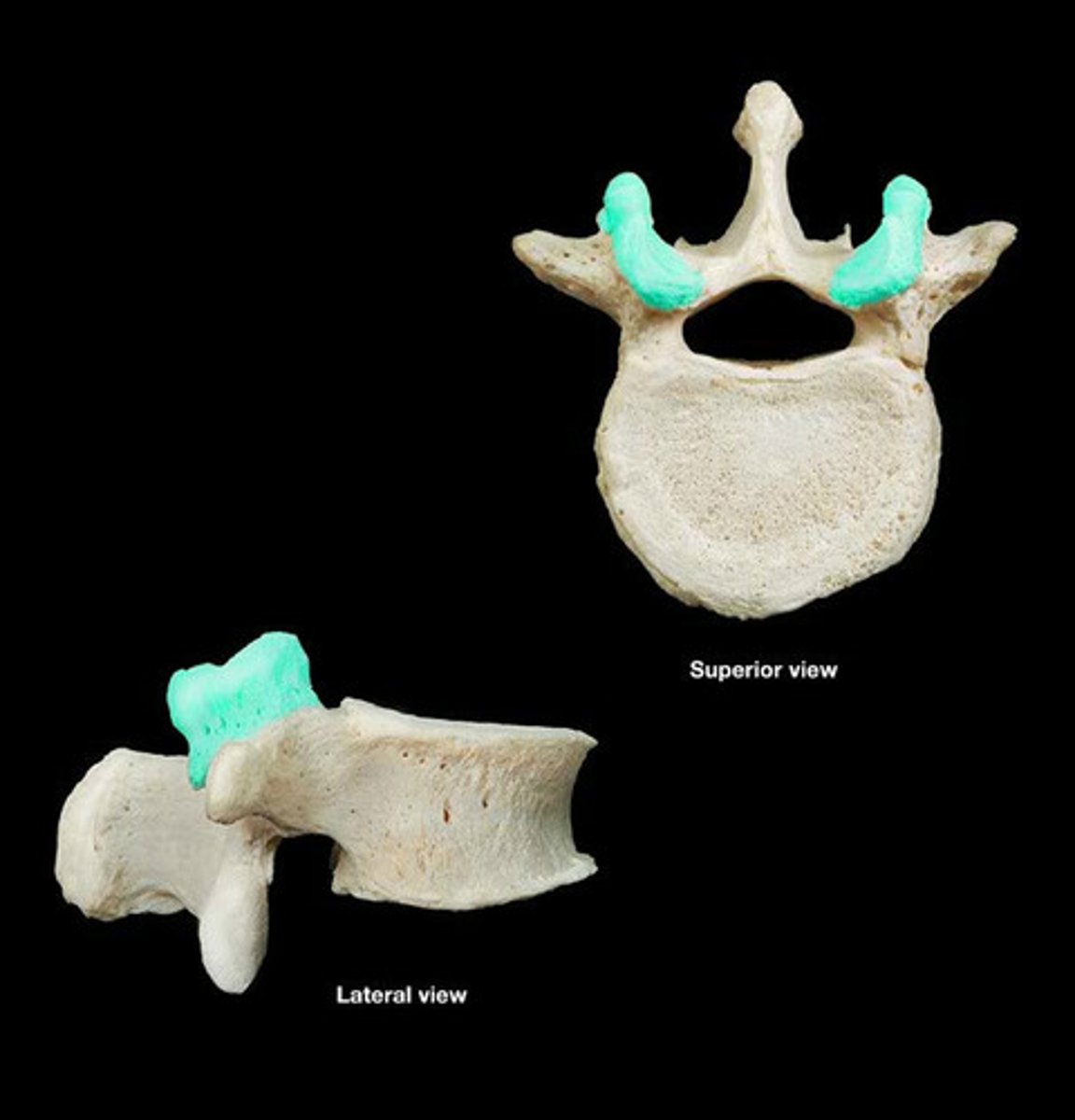
inferior articular process
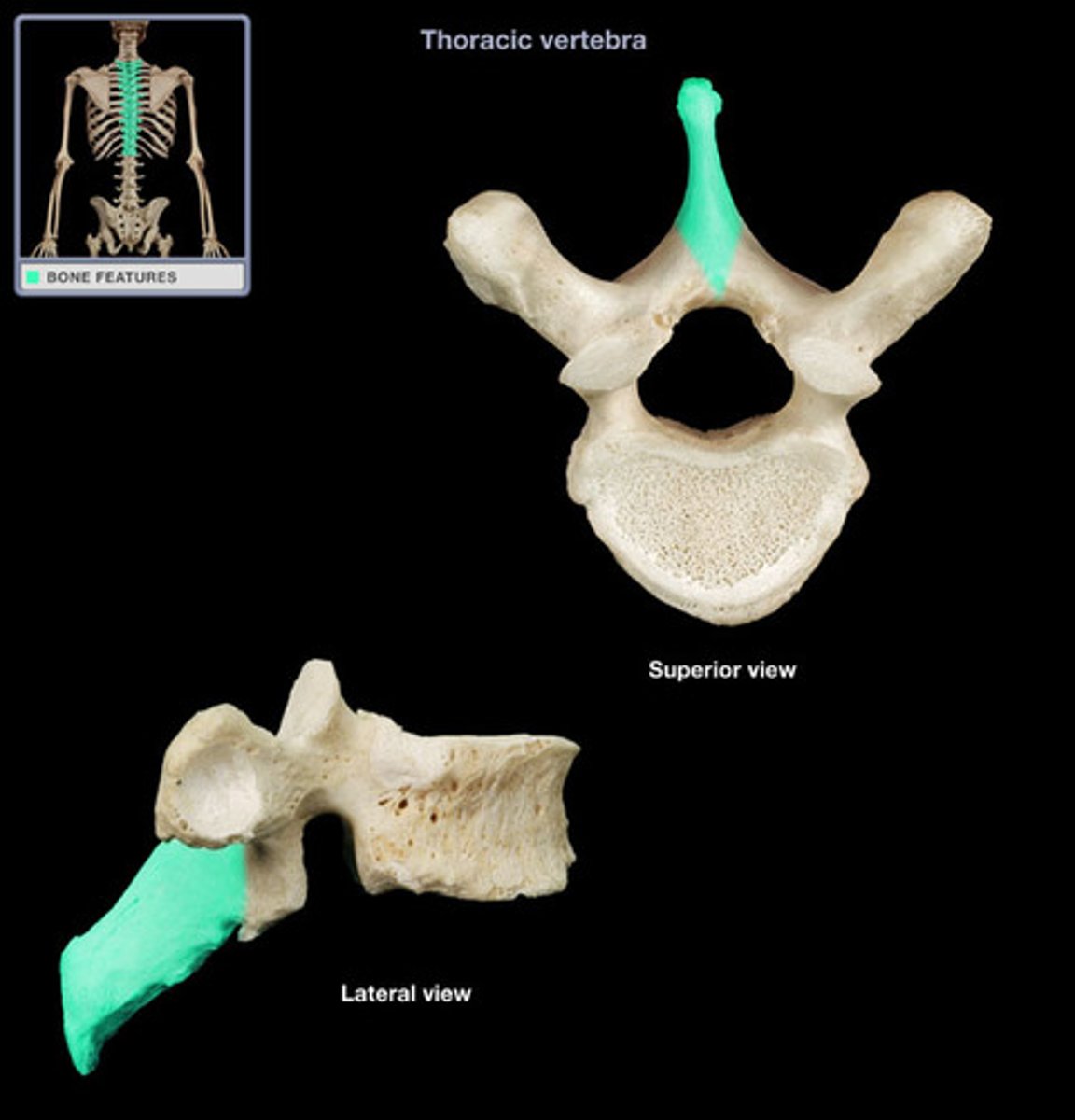
spinous process
sharp, slender projection
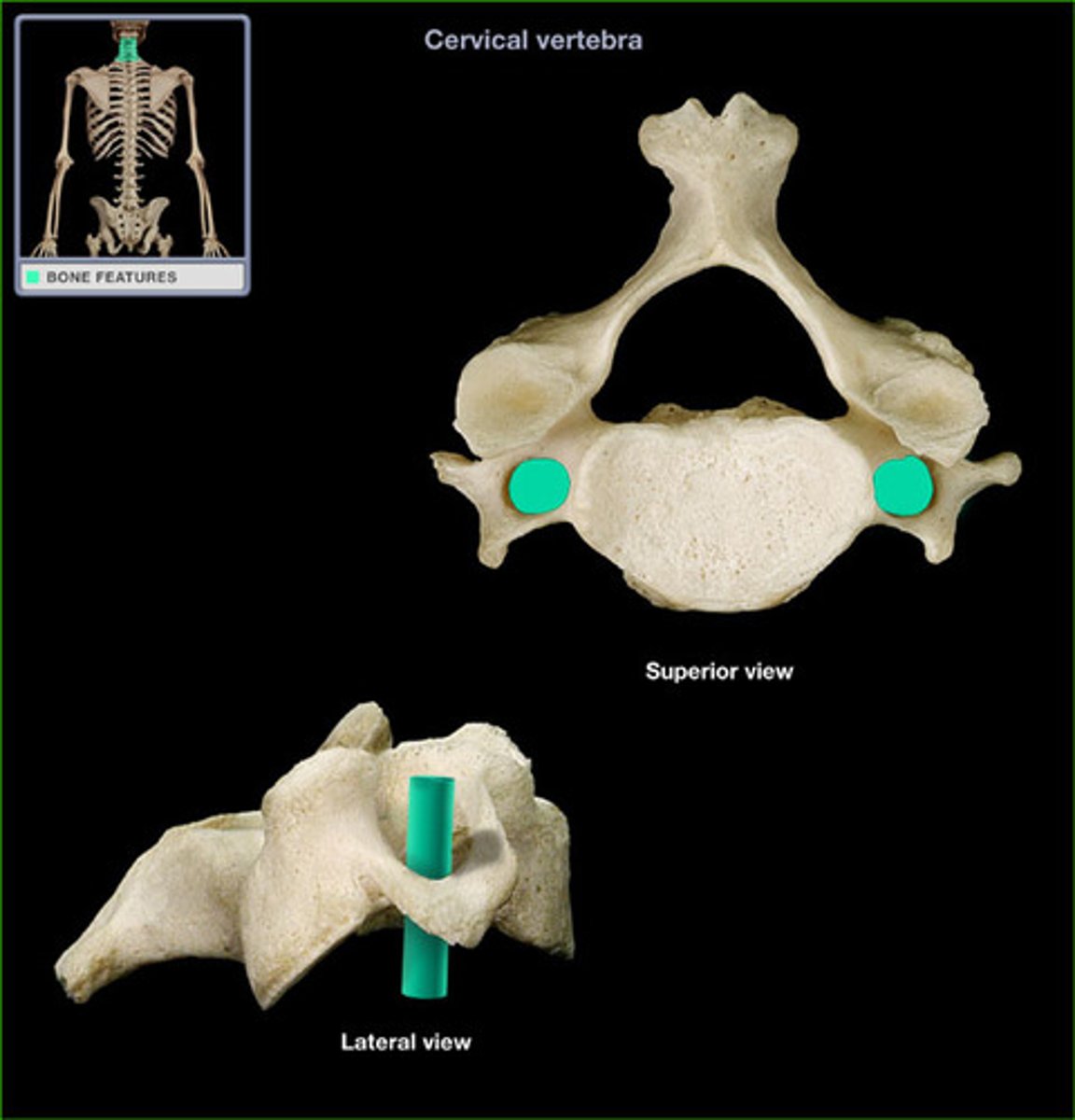
transverse foramen
only found in the cervical vertebrae and allow passage of the vertabral artery, vein, and nerve
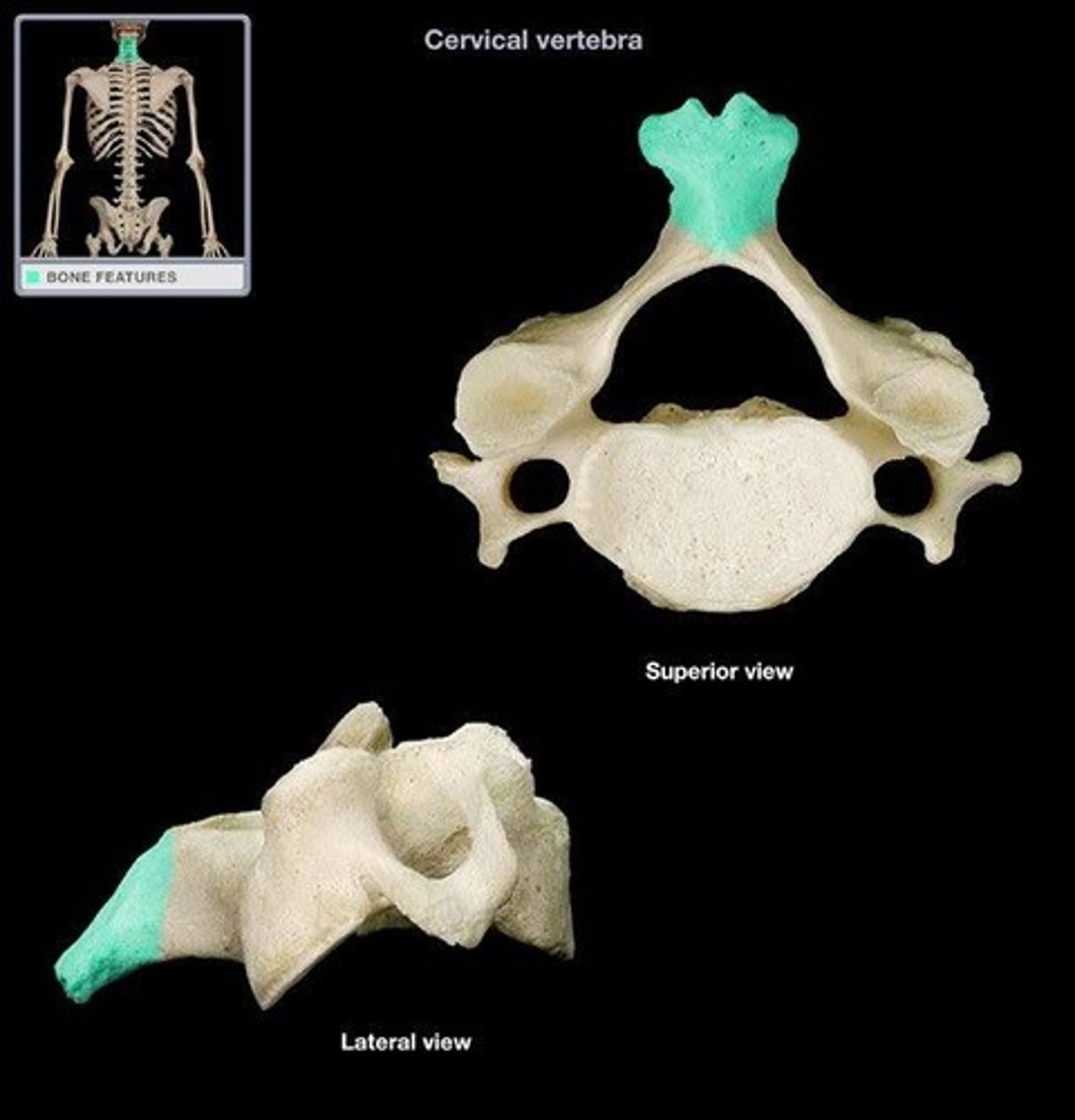
bifid spinous process
on cervical vertebrae C3-C5. Forked.
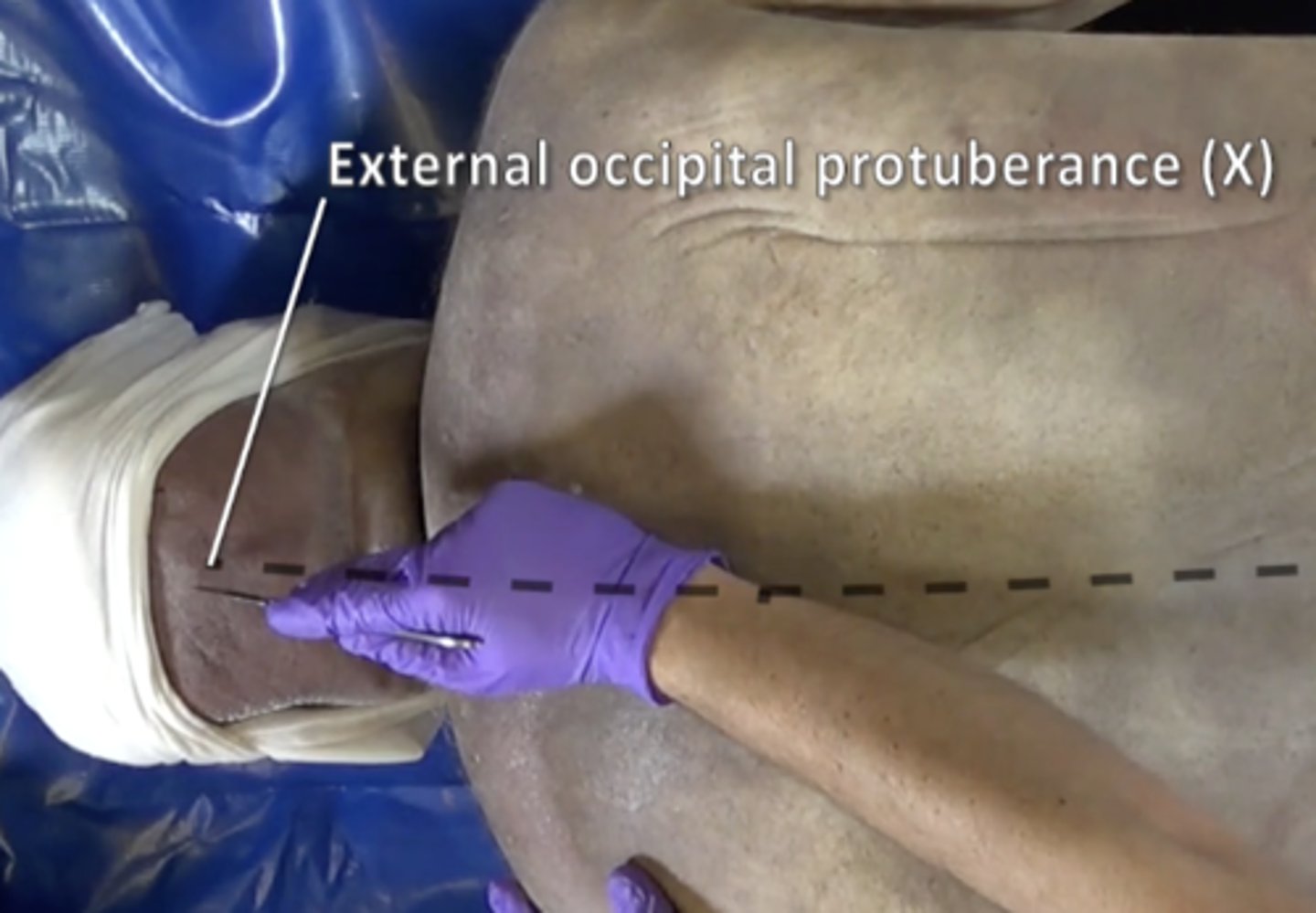
external occipital protuberance
bump on back of head
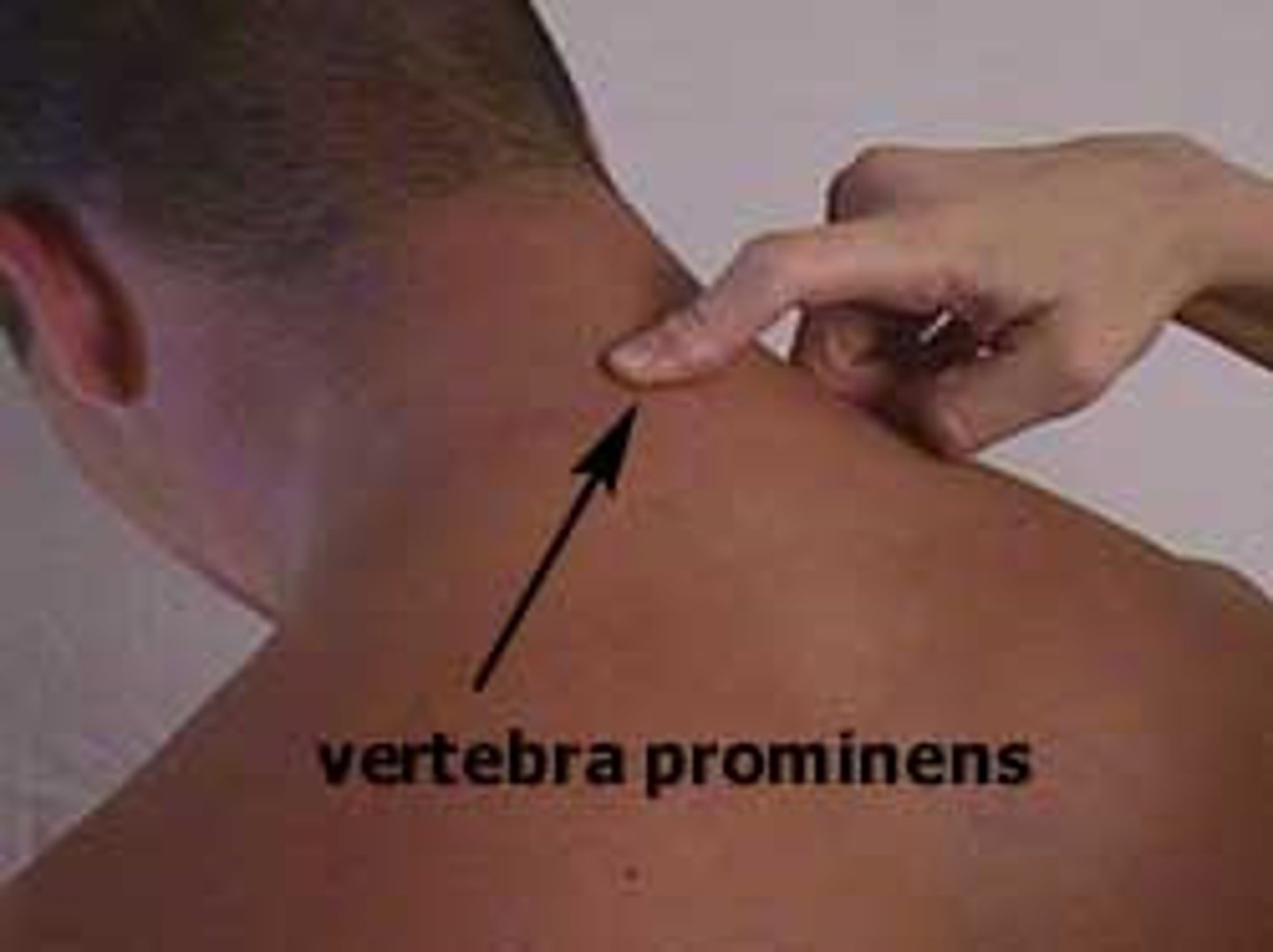
vertebra prominens (C7)
Transitions to thoracic vertebrae
Has a long spinous process with a broad tubercle
Has large transverse processes
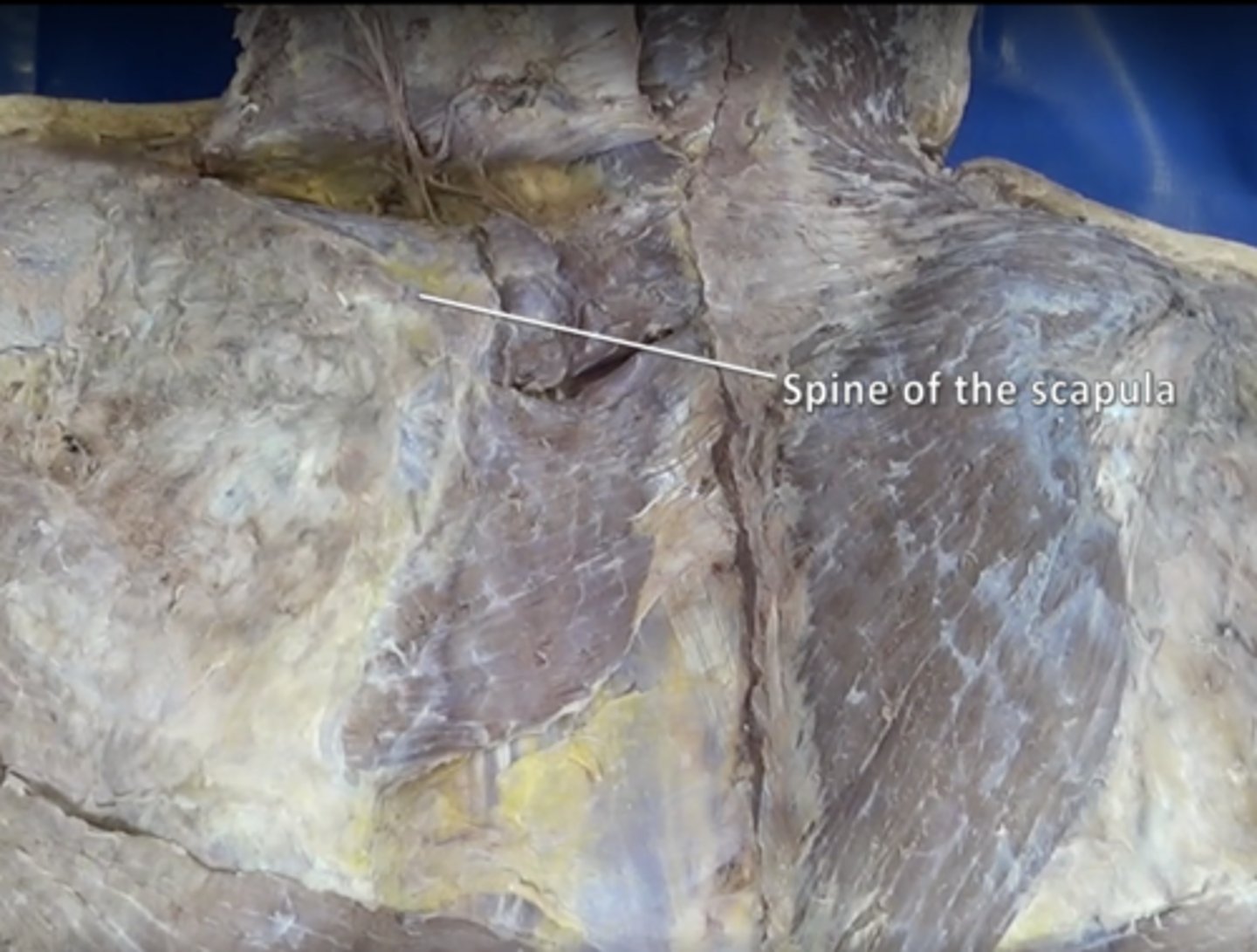
subscapular spine
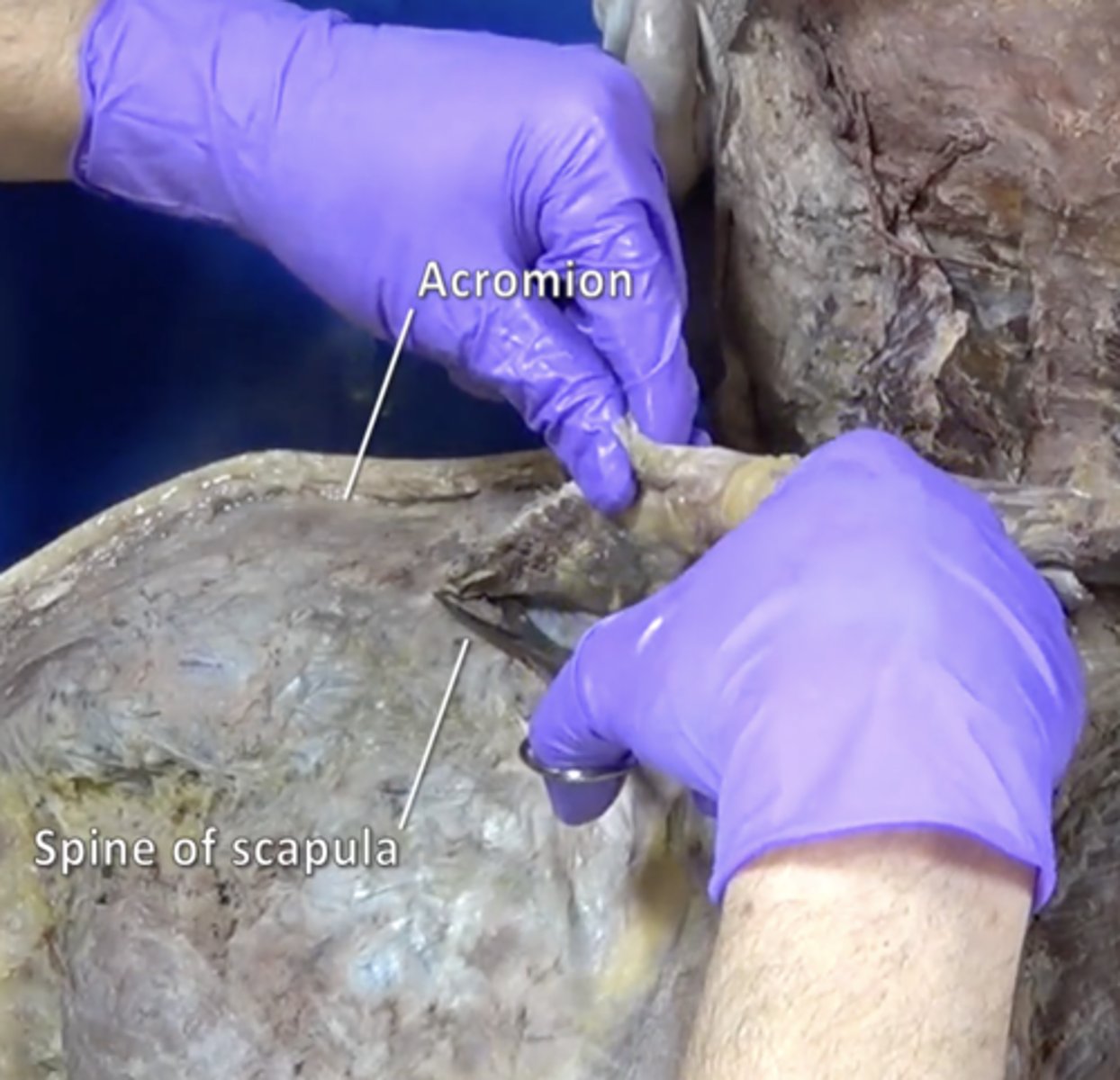
acromion
Outward extension of the shoulder blade forming the point of the shoulder.
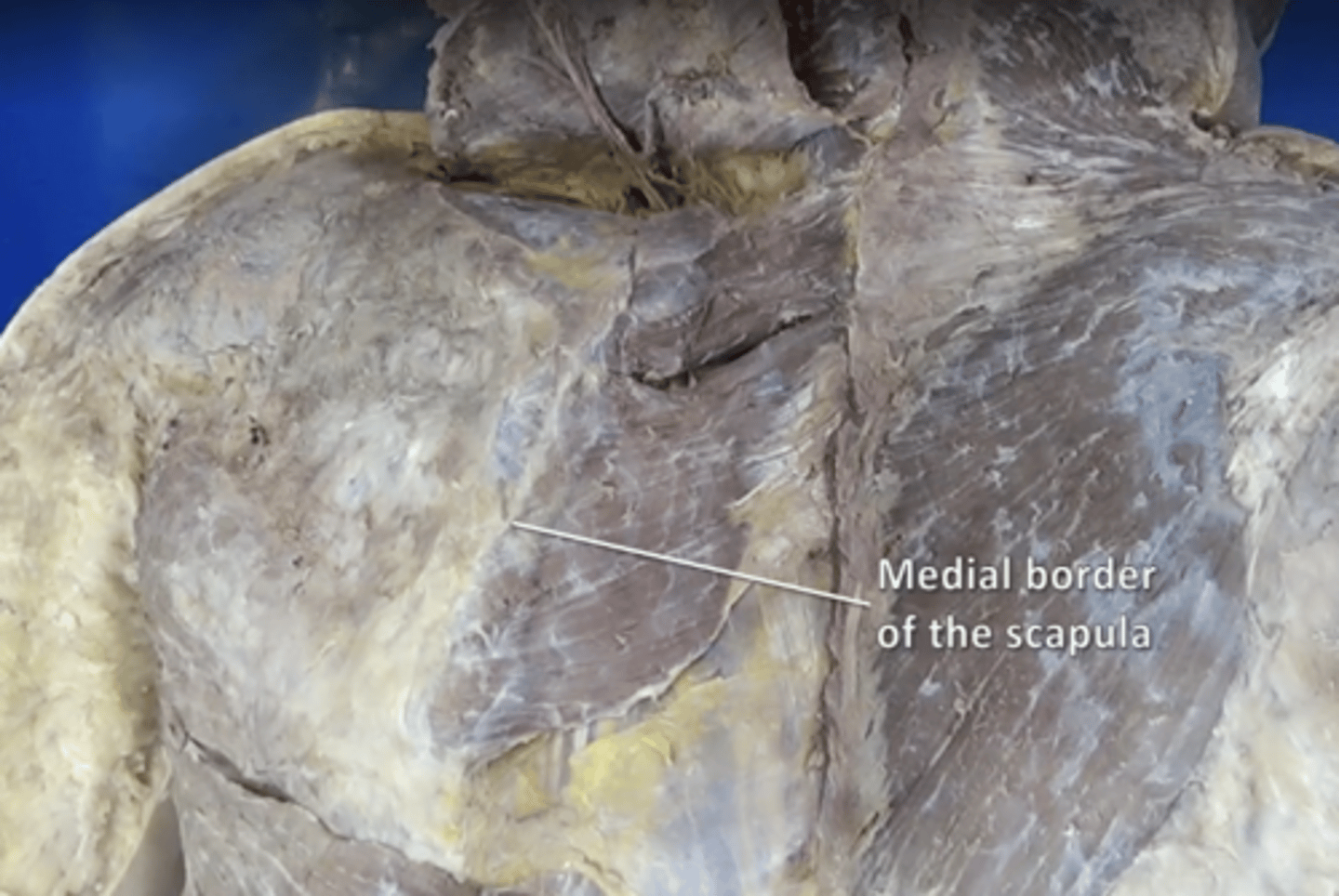
medial border of scapula
serratus anterior insertion
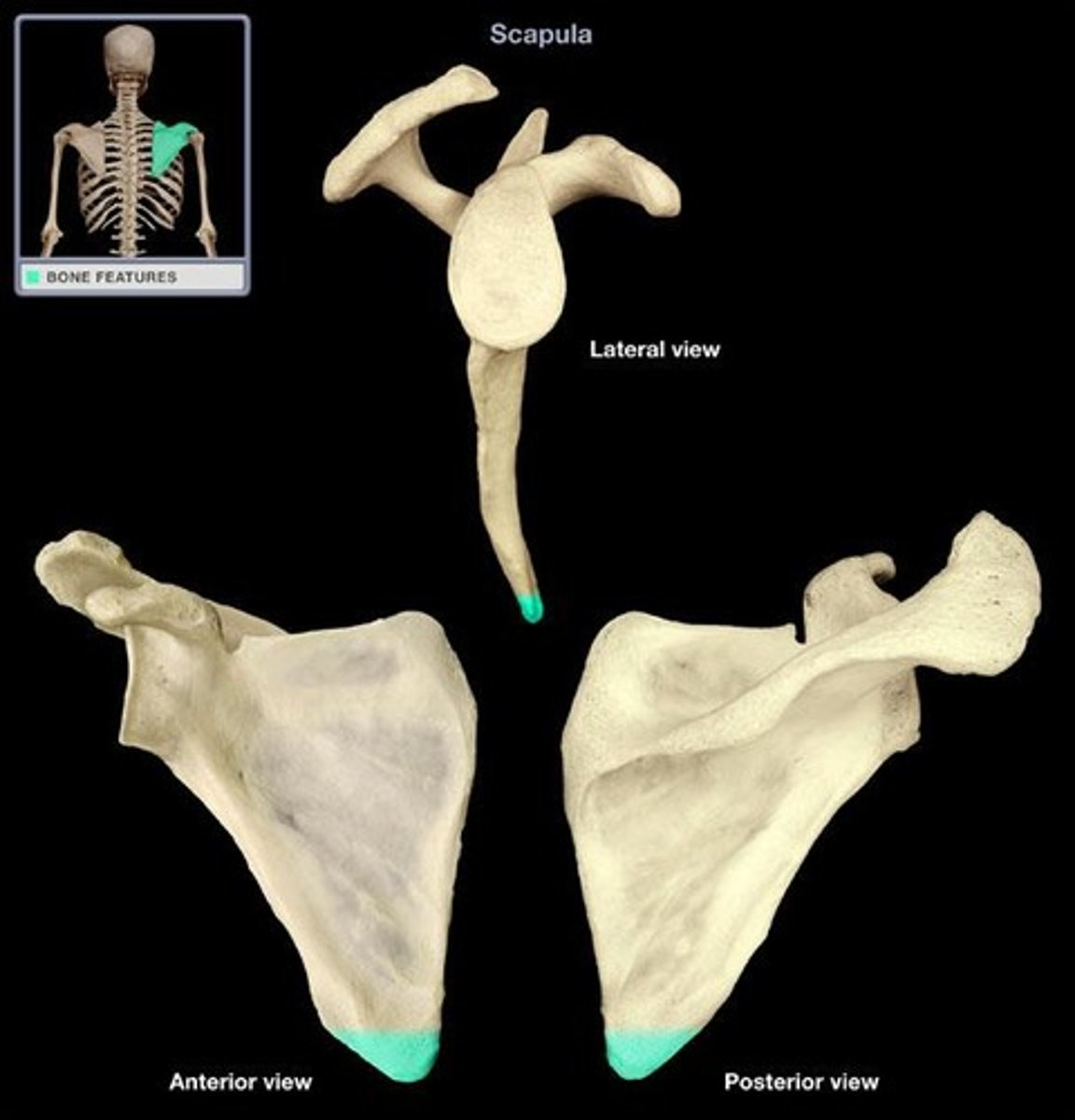
inferior angle of scapula
bottom point of scapula
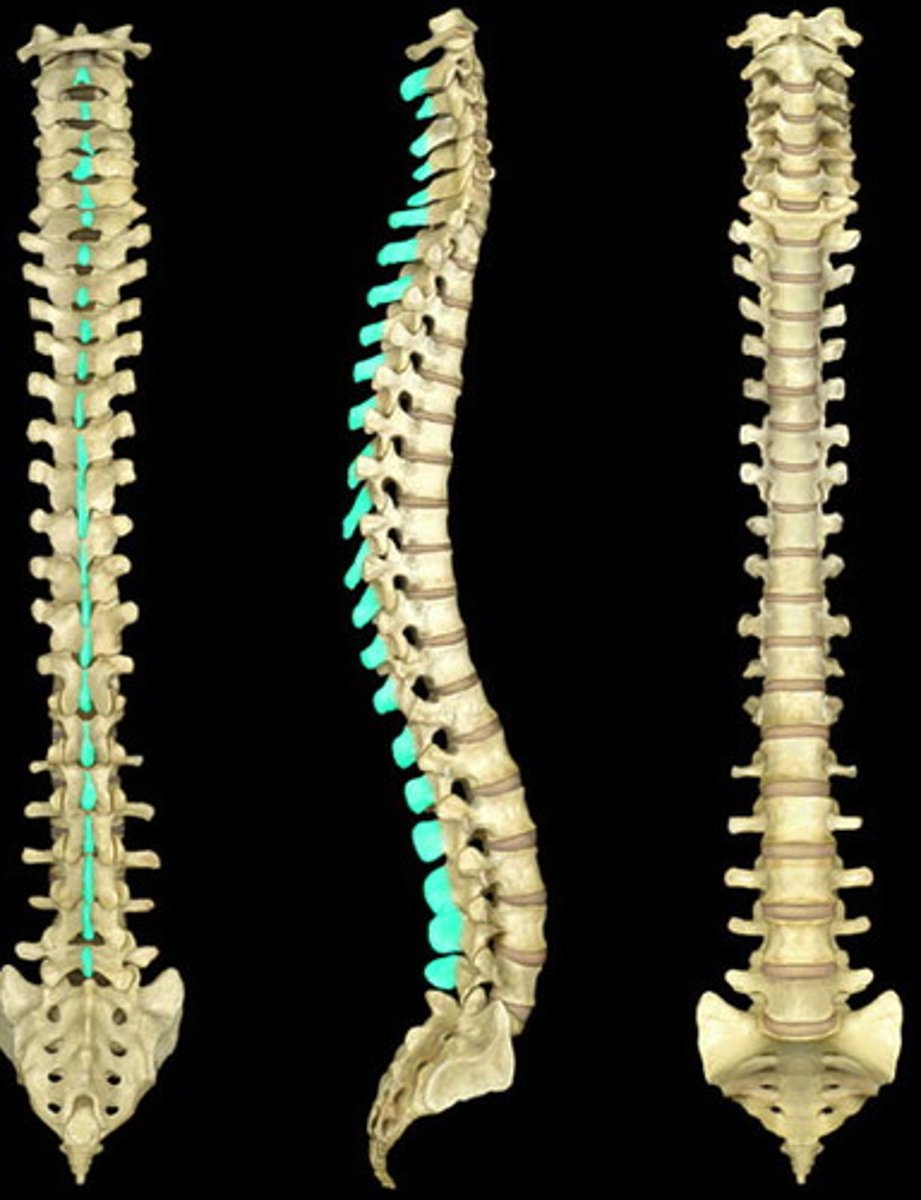
spinous process of vertebrae
The portion of the vertebrae that sticks out posteriorly.
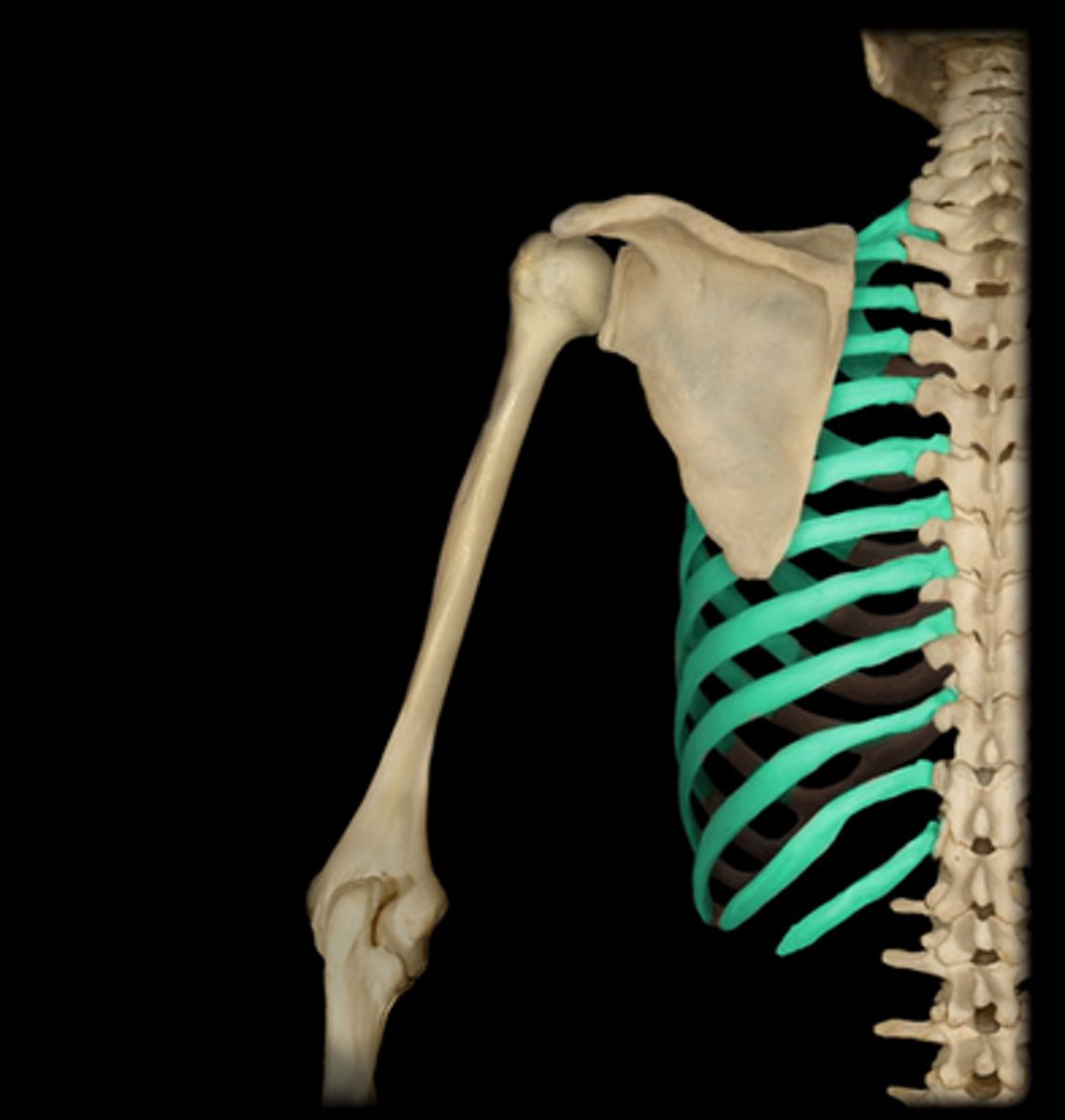
ribs
12 pairs
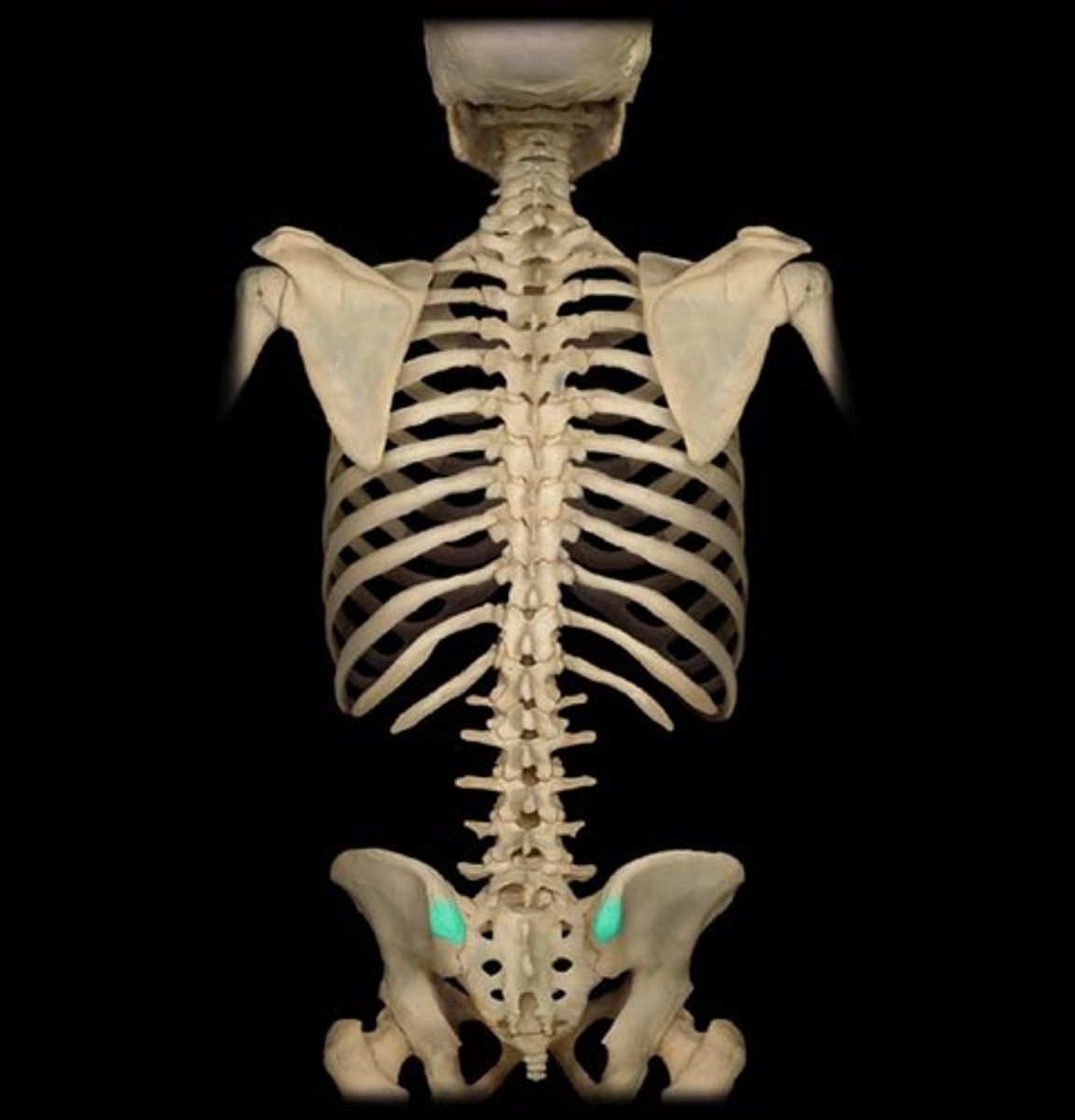
iliac crest
upper margin of iliac bones
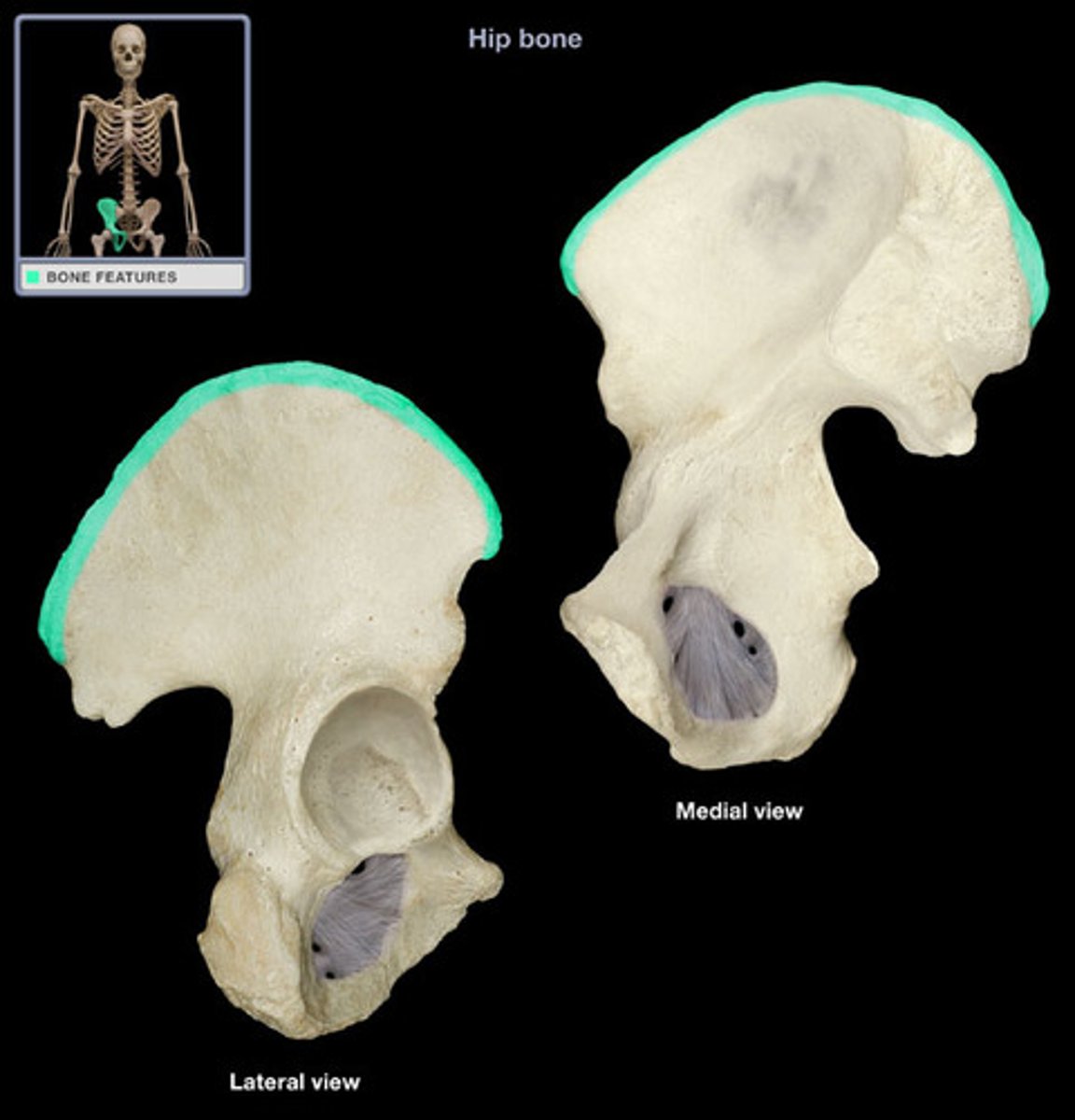
posterior superior iliac spine
the sharp posterior end of the iliac crest
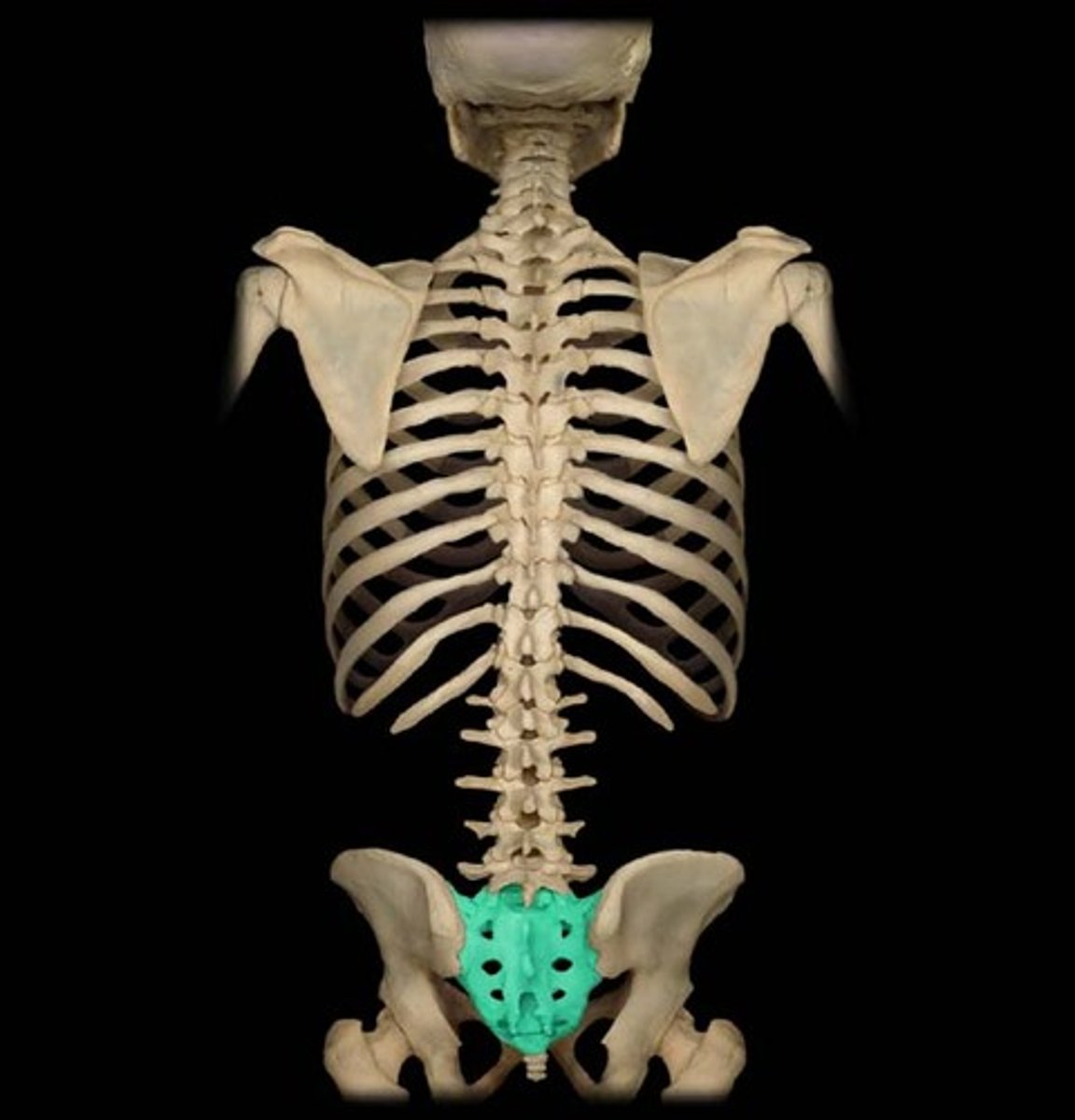
sacrum
5 fused vertebrae
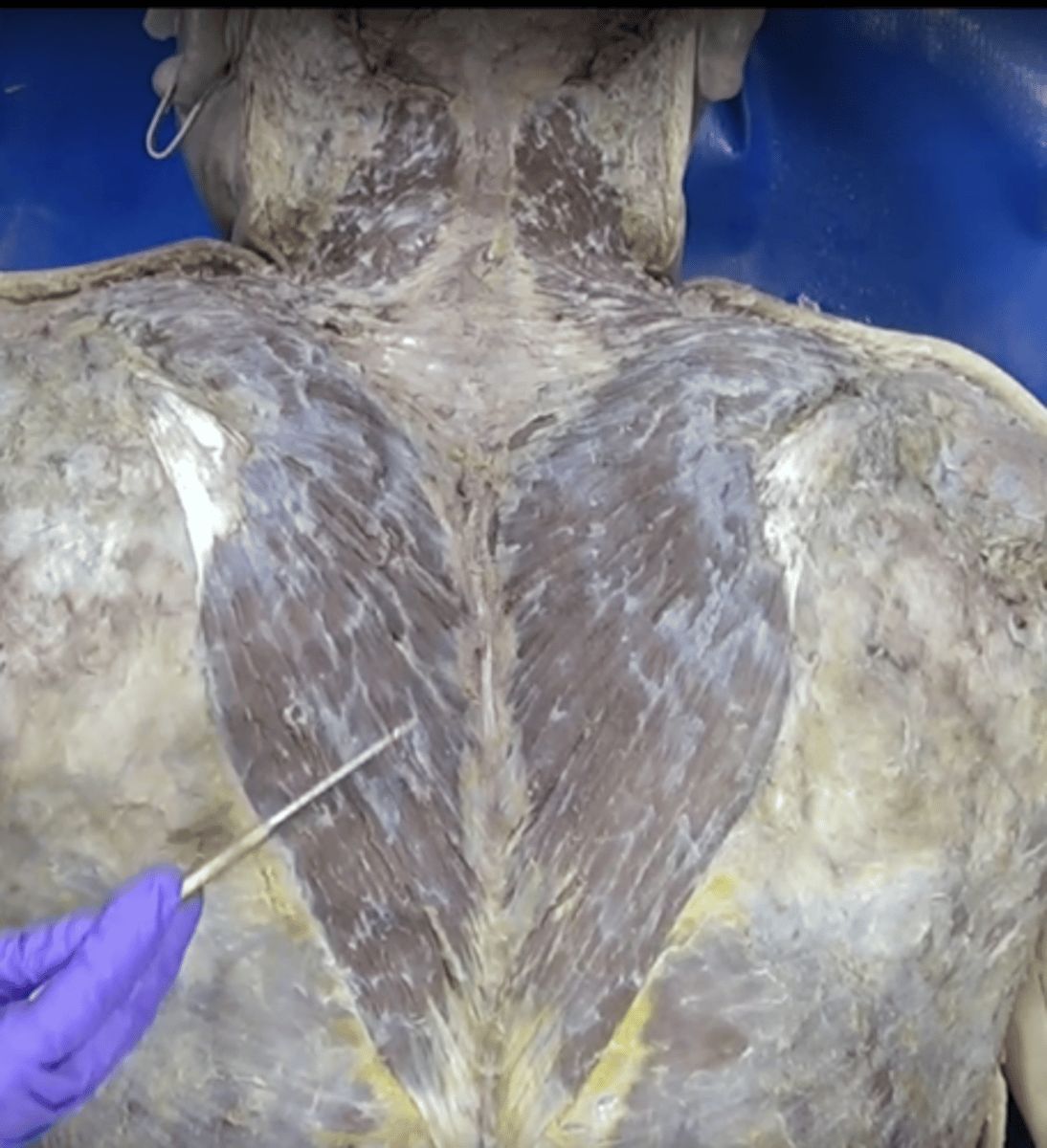
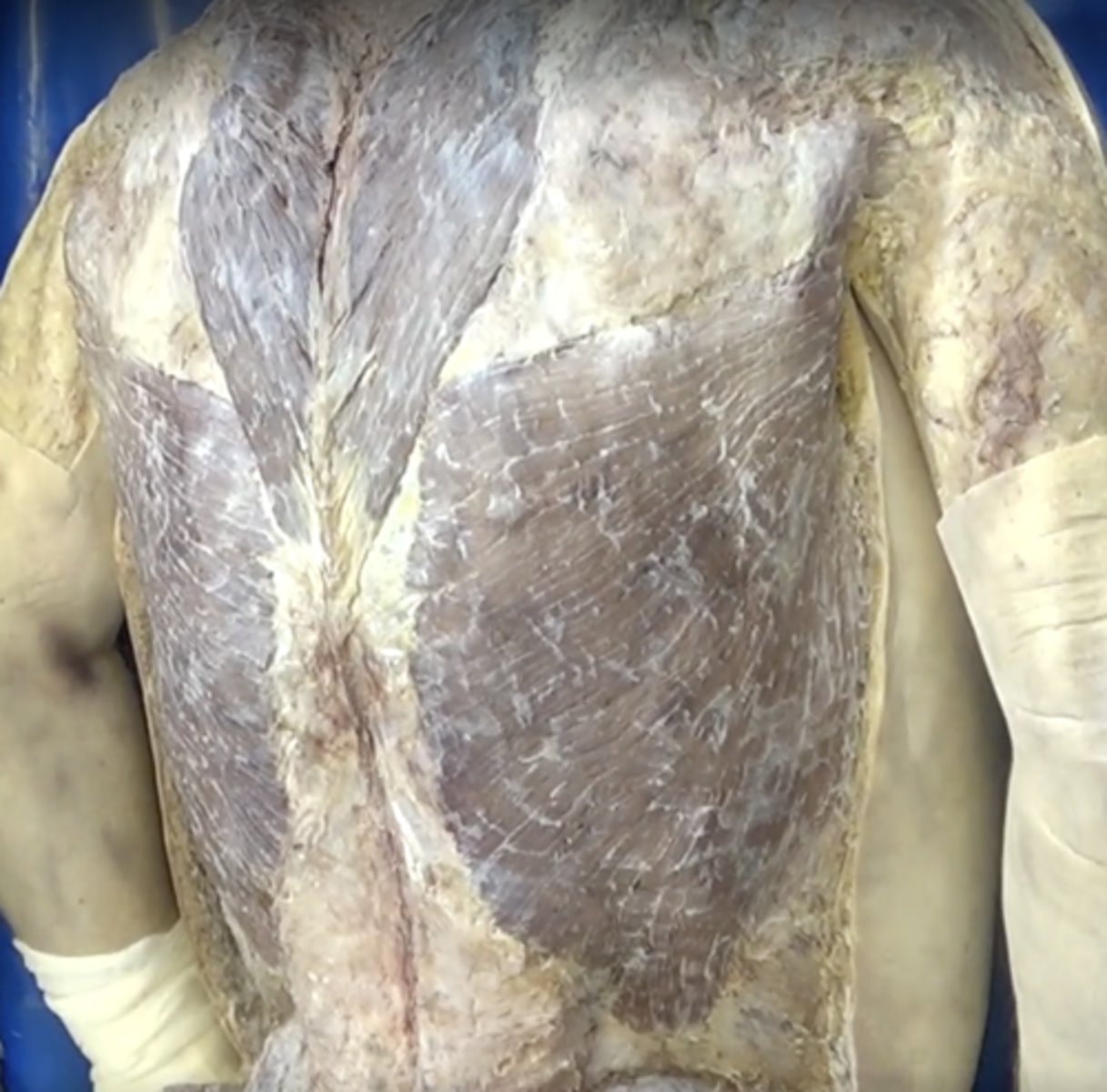
trapezius muscle
Function: Extends head and neck, Insertion: Scapula, Origin: Skull and upper vertebrae
accessory nerve (XI)
swallowing, head, neck, and shoulder movements
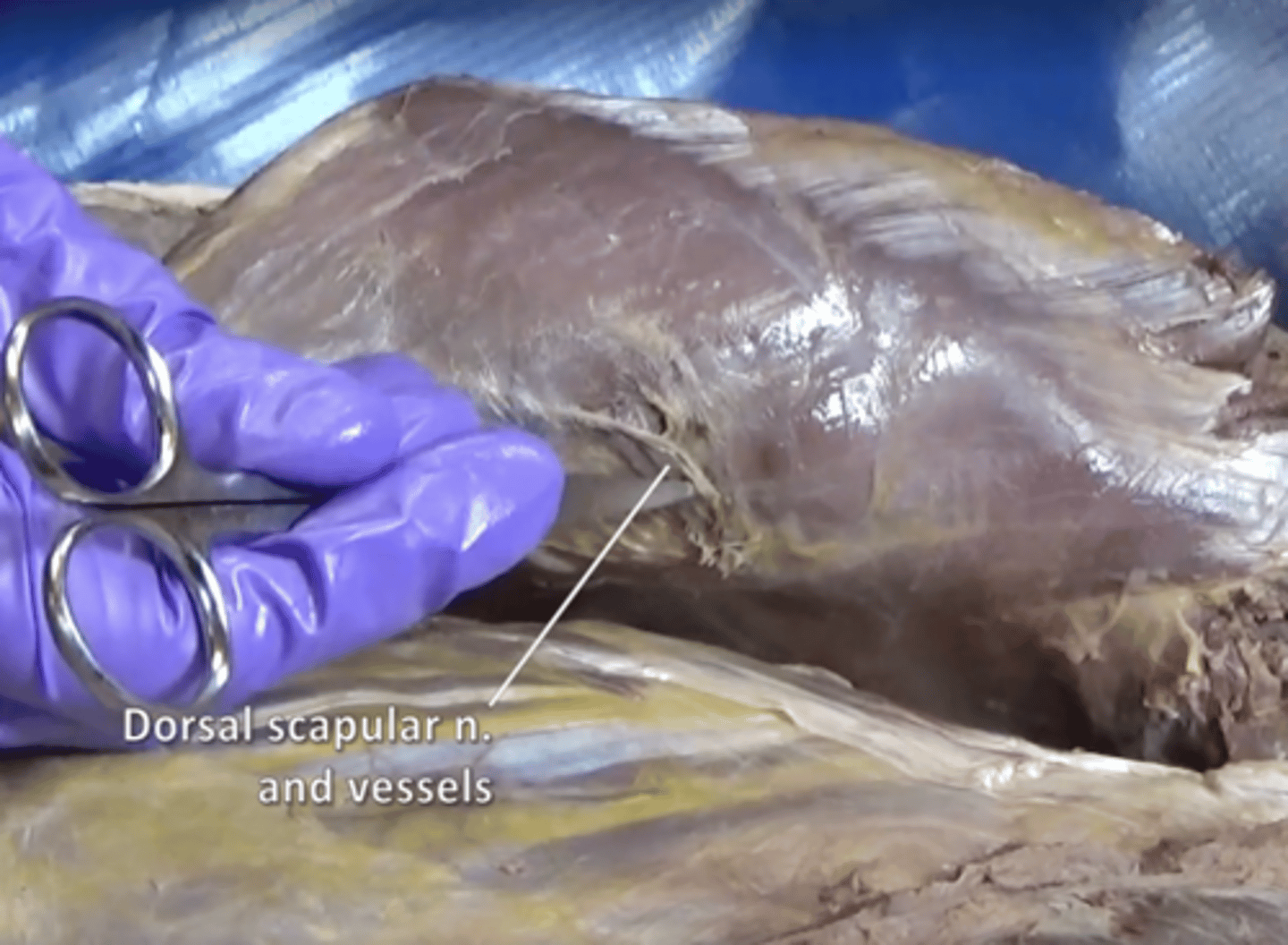
dorsal scapular nerve
Innervates rhomboids and levator scapulae.
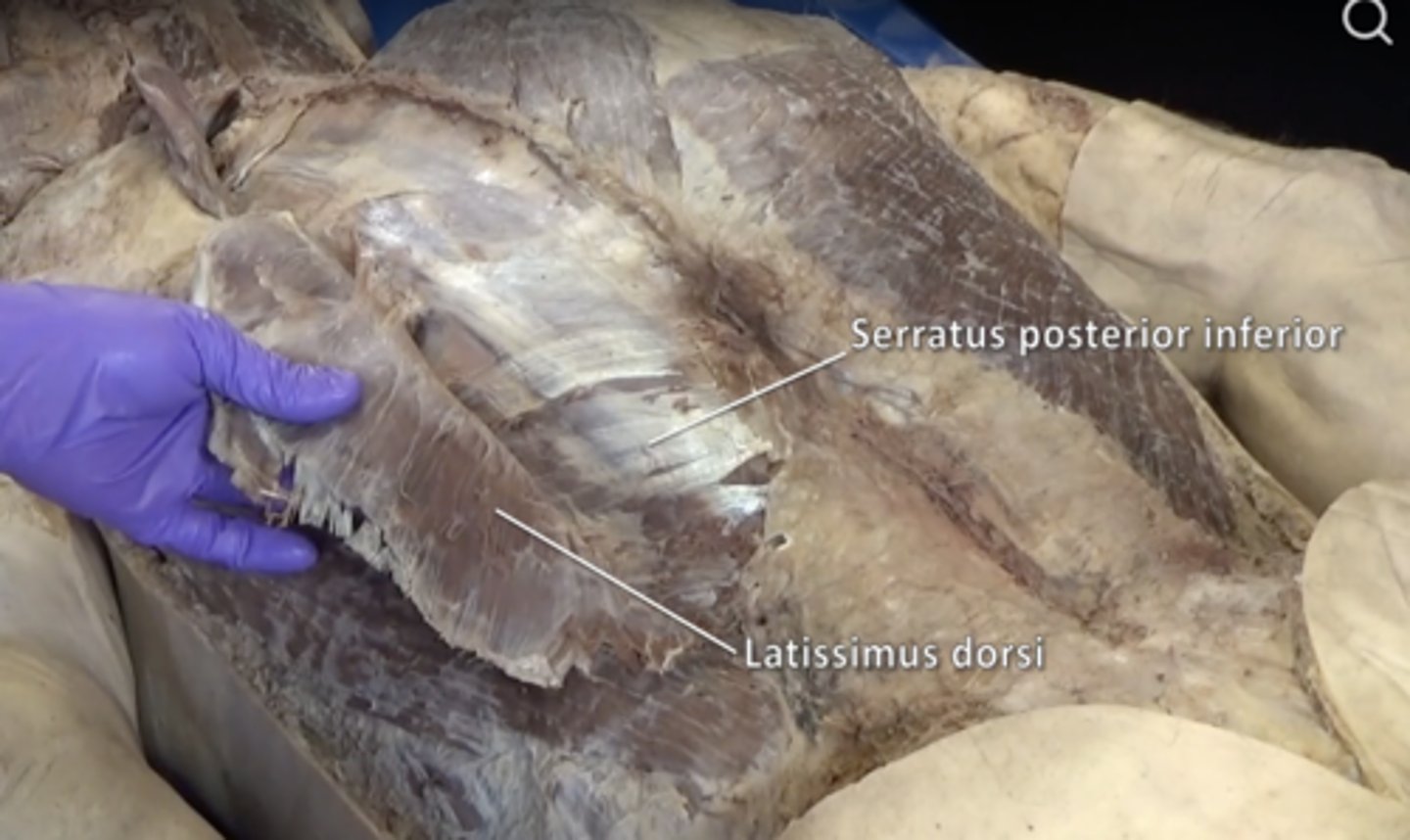
latissimus dorsi muscle
Function: Extends and helps adduct upper arm, Insertion: Humerus, Origin: Vertebrae and illium
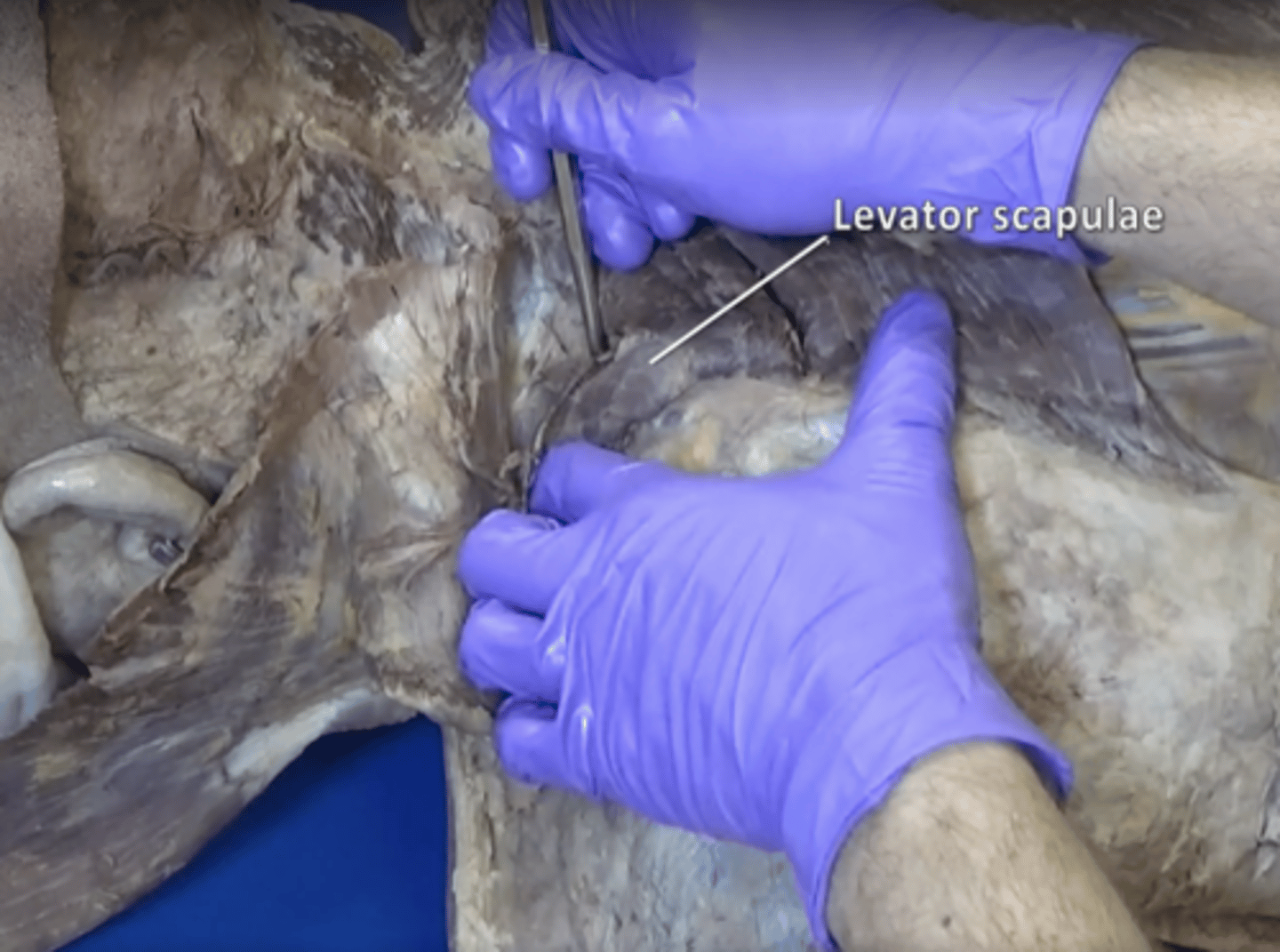
levator scapulae muscle
elevates the medial margin of the scapula
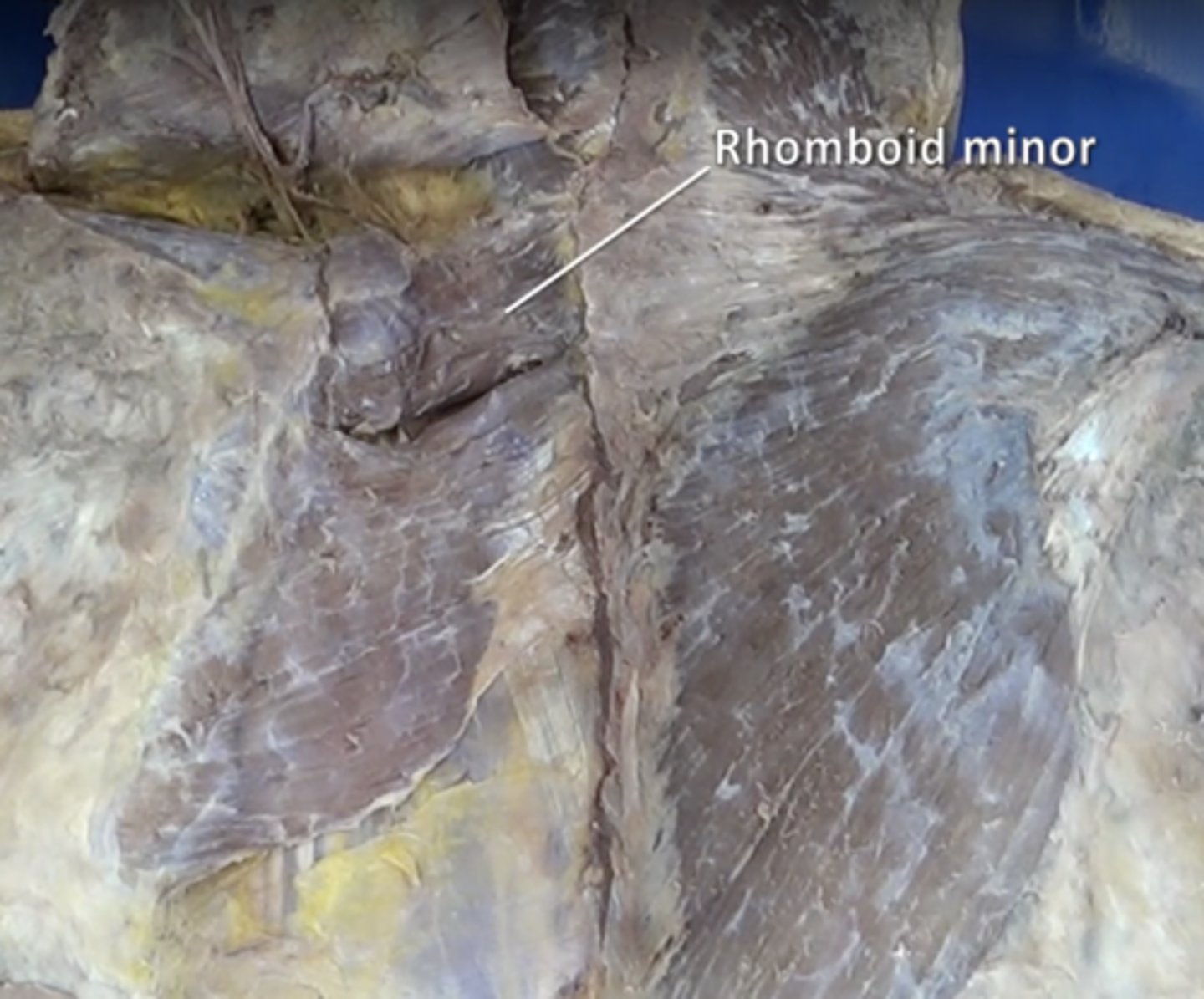
rhomboid minor muscle
elevation and retraction of scapula

rhomboid major muscle
elevation and retraction of scapula
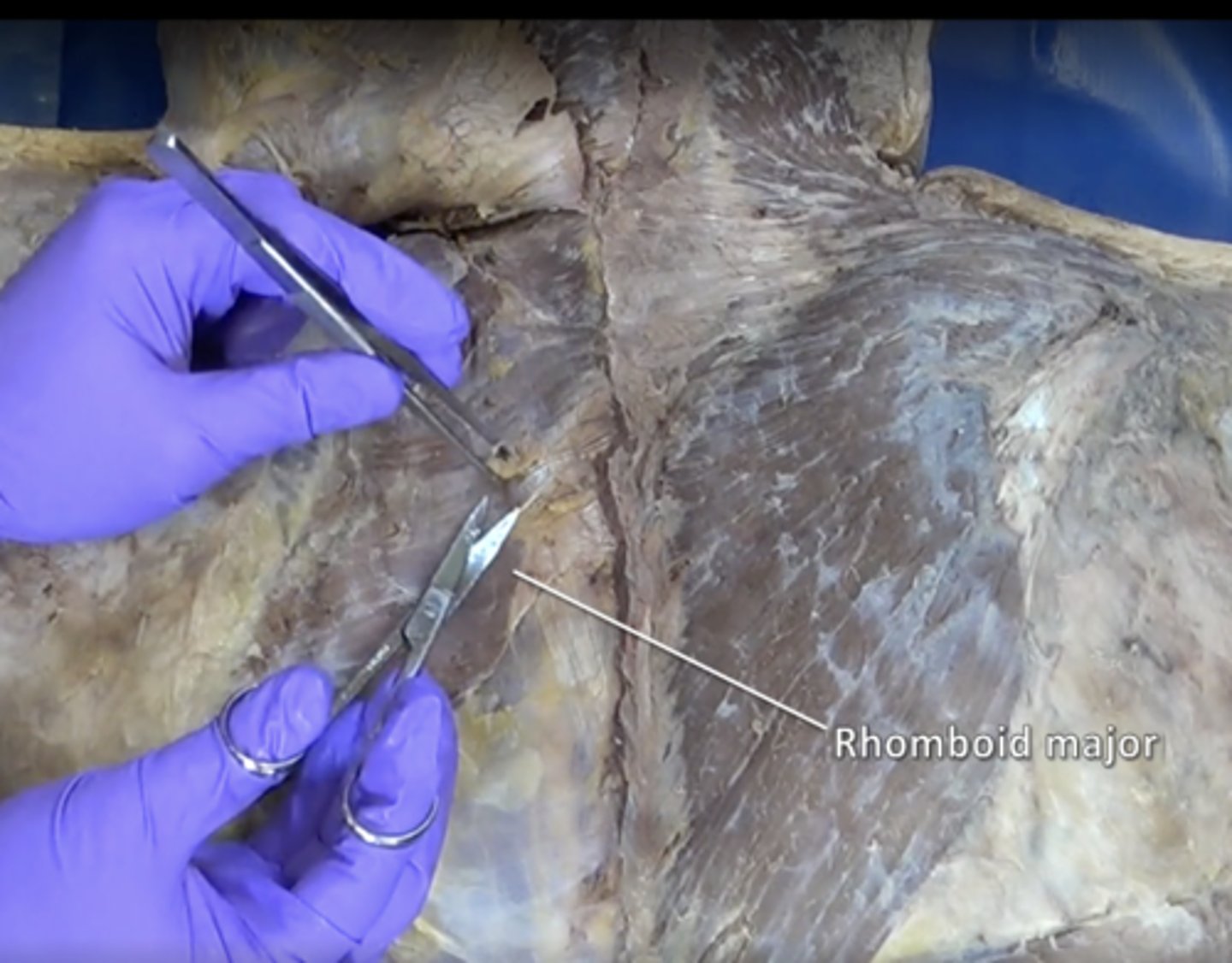
Triangle of Auscultation
trapezius, latissimus dorsi, medial border of scapula
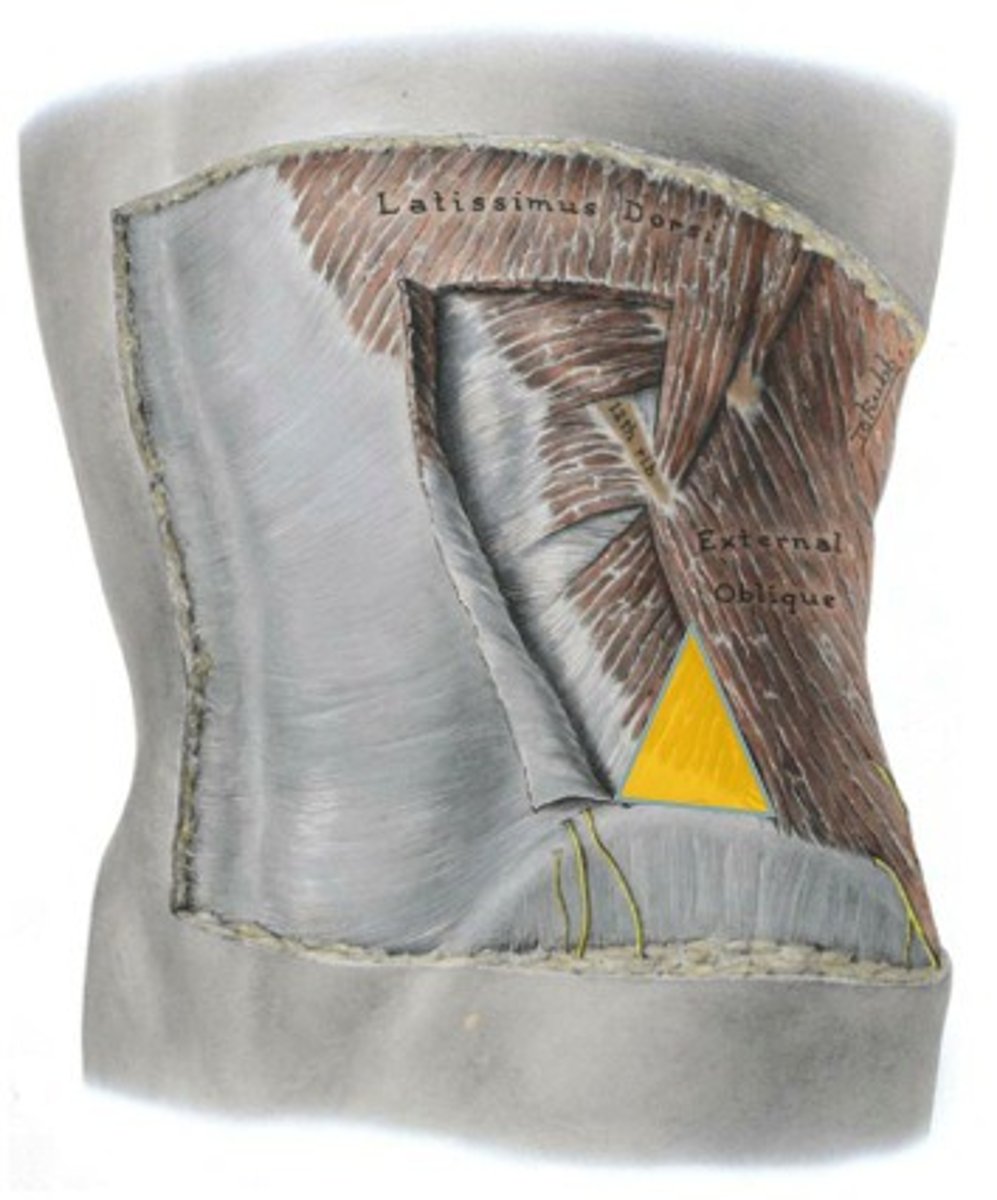
lumbar triangle
latissimus dorsi, external oblique, iliac crest
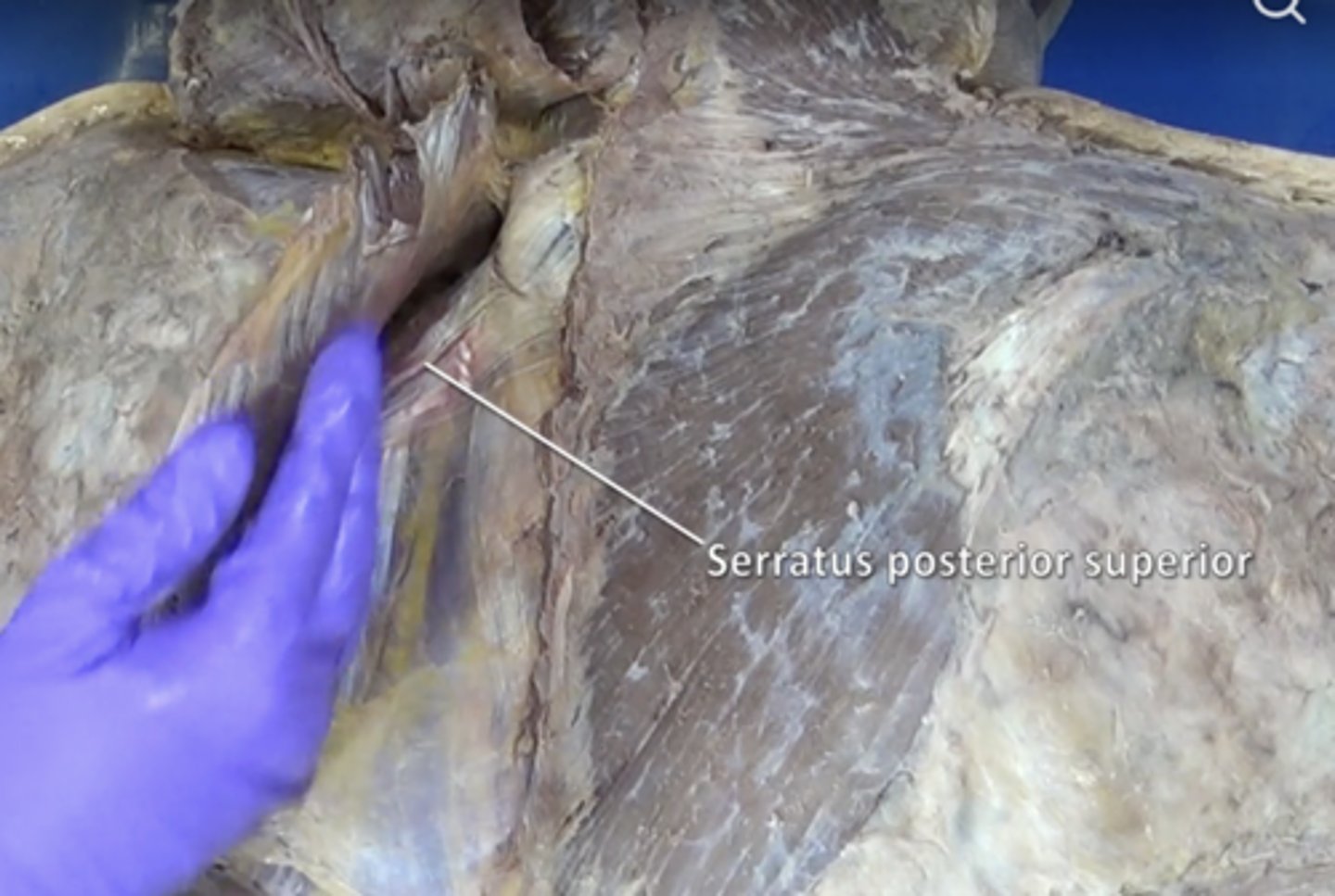
serratus posterior superior muscle
muscle at the top of the back that elevates ribs 2-5
serratus posterior inferior muscle
posterior thoracic muscle that supports exhalation by pulling the rib cage down when contracted
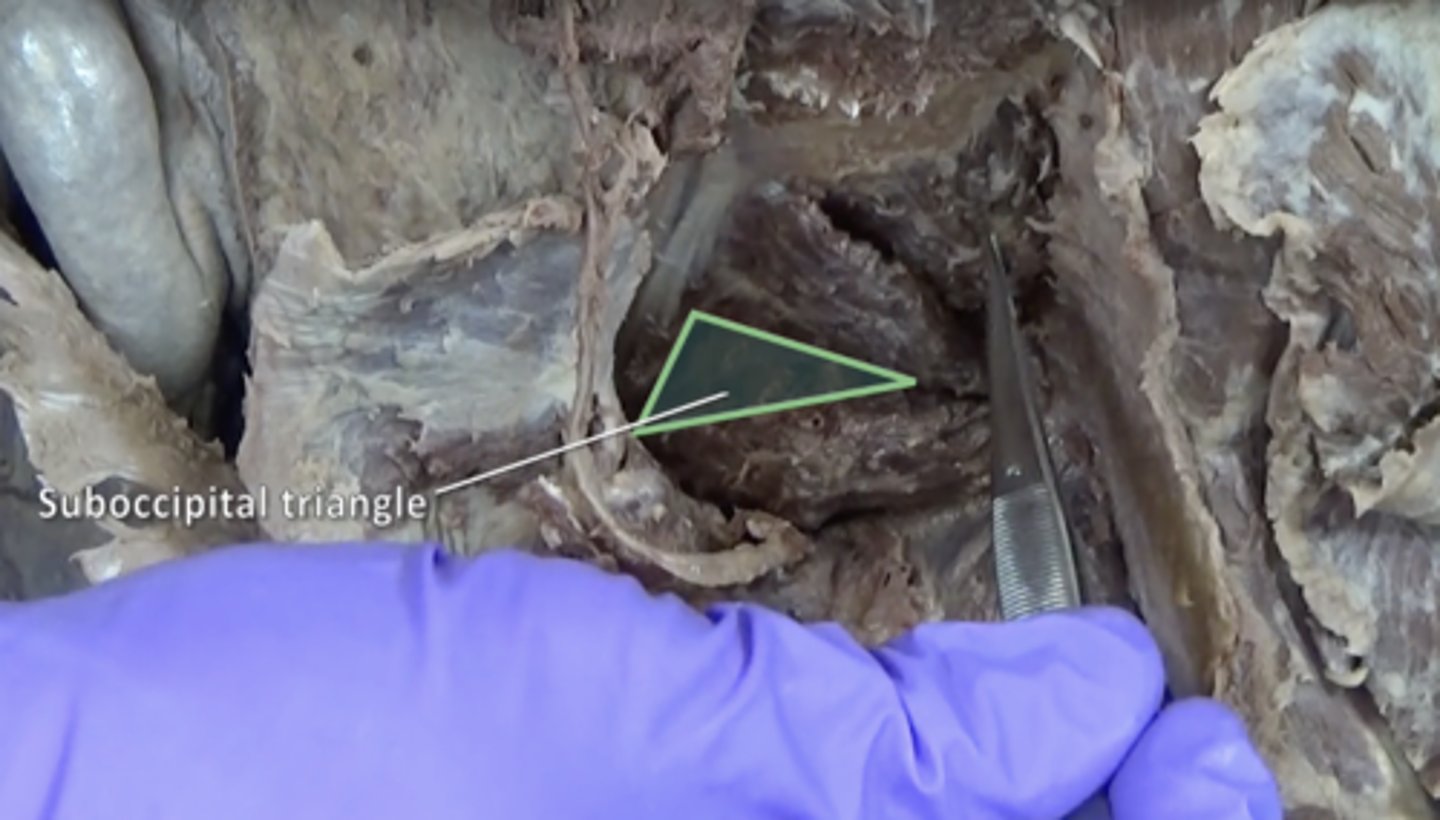
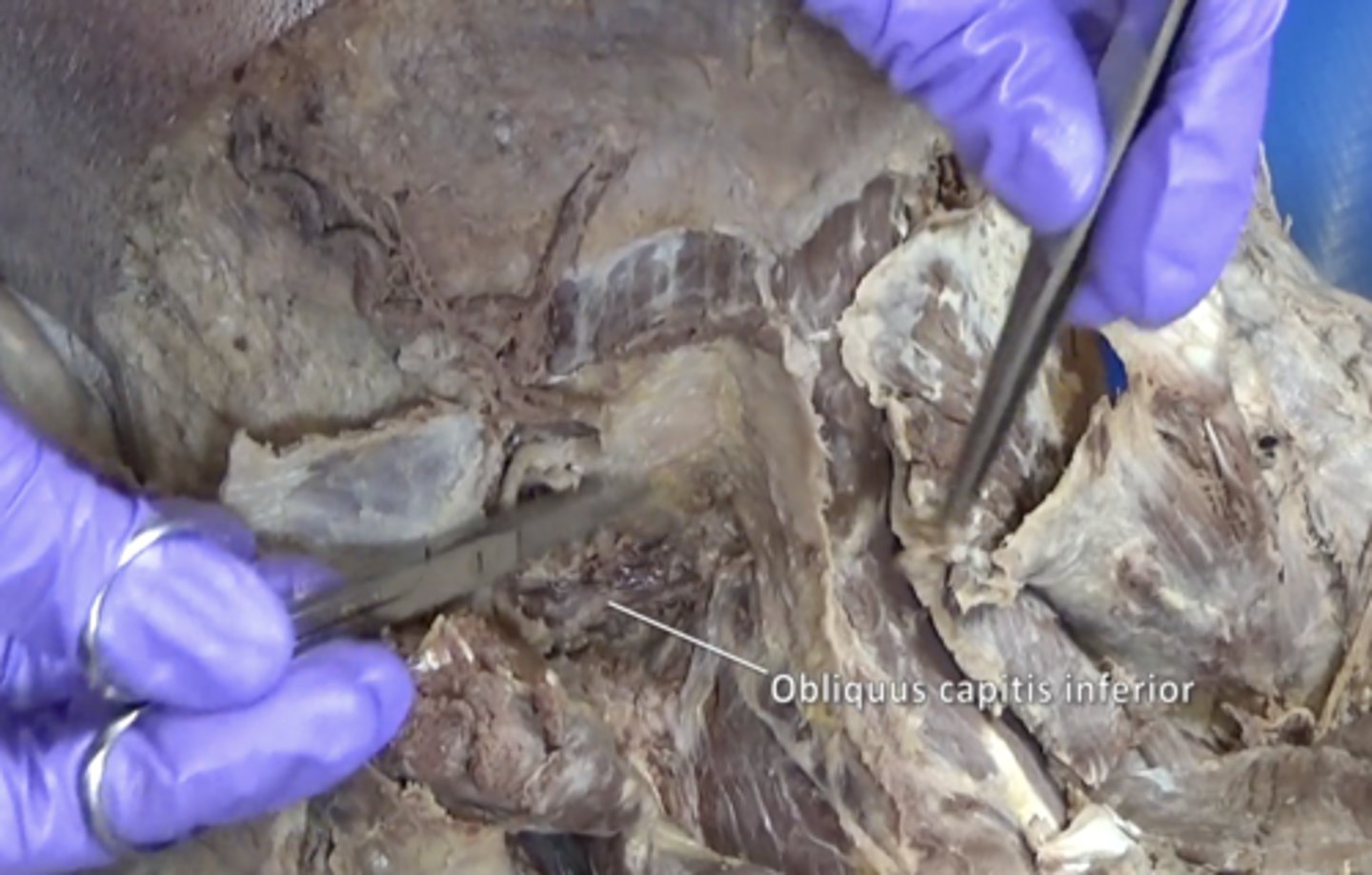
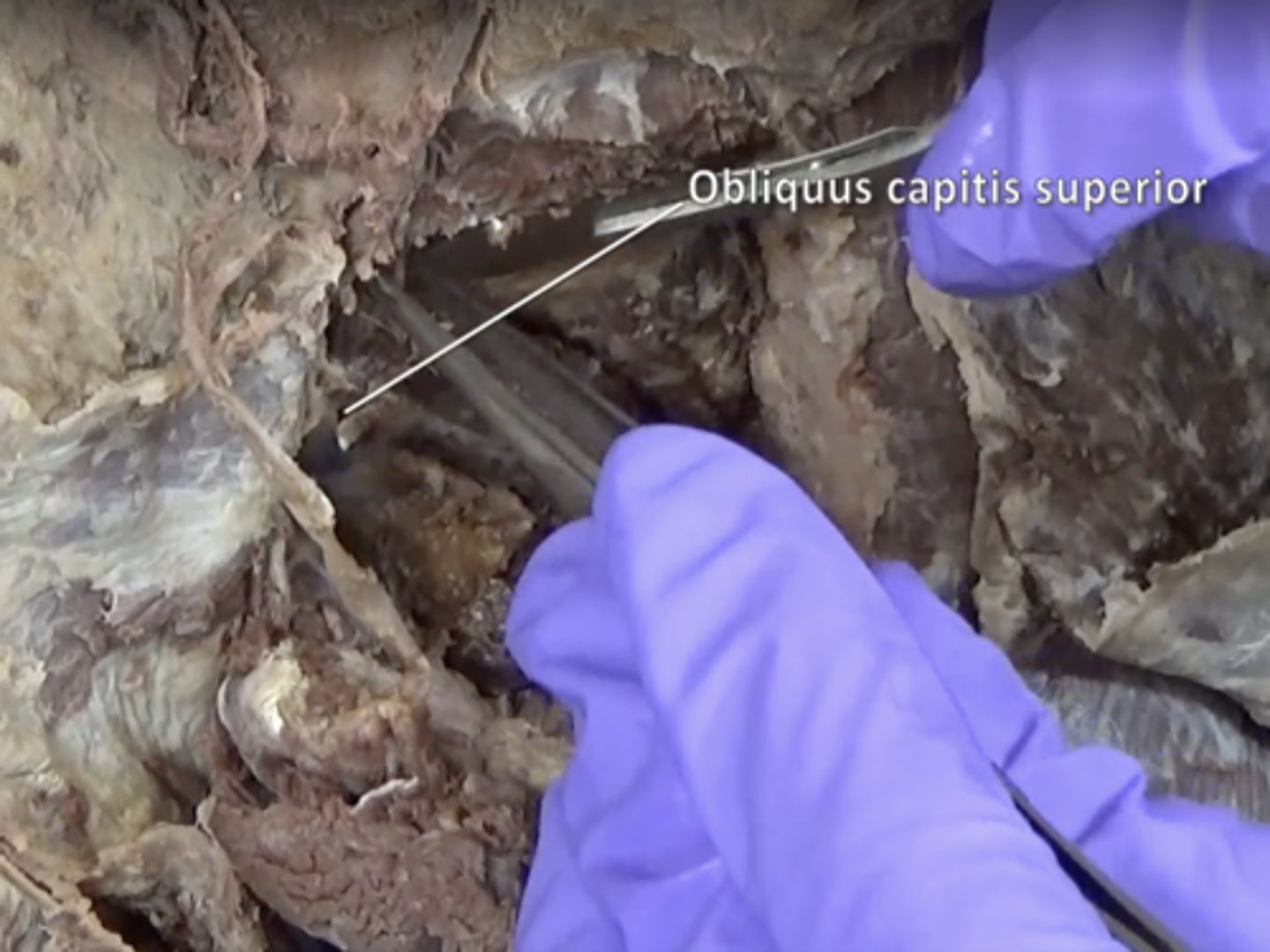
suboccipital triangle
Rectus capitis posterior major, Obliquus capitis superior, Obliquus capitis inferior
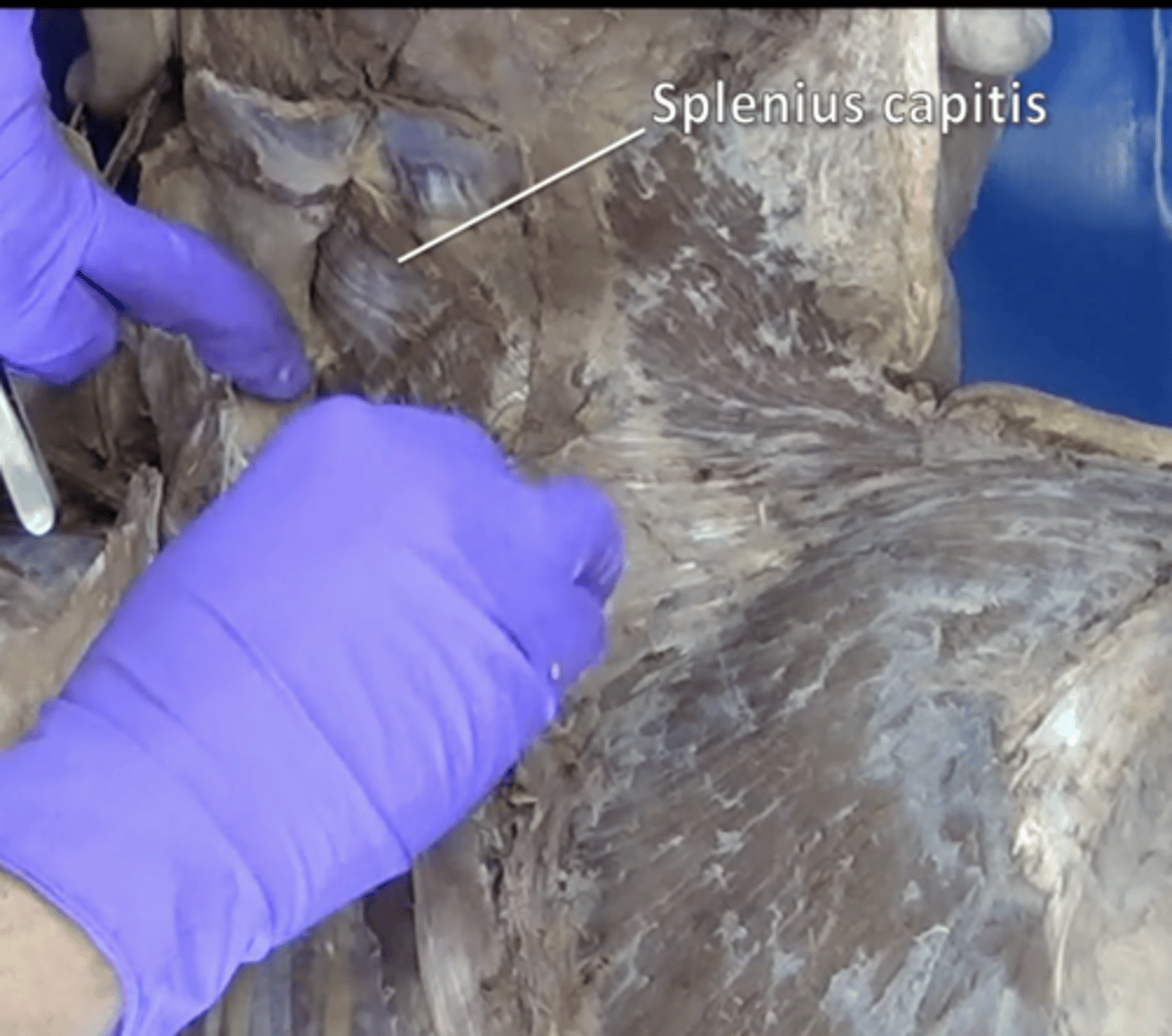
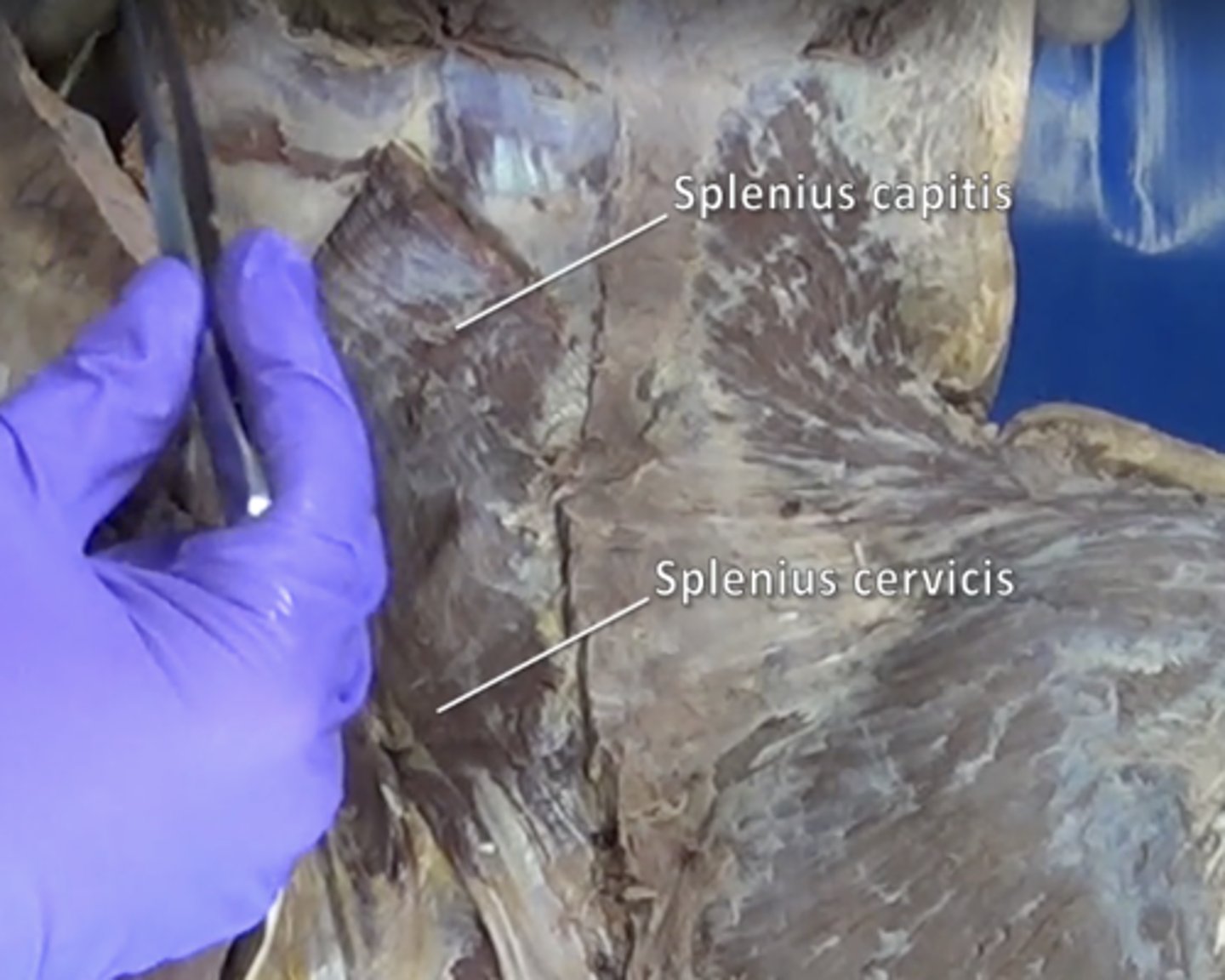
splenius capitis muscle
Extend, rotate, and laterally flex the head
splenius cervicis muscle
extend and hyperextend head and neck
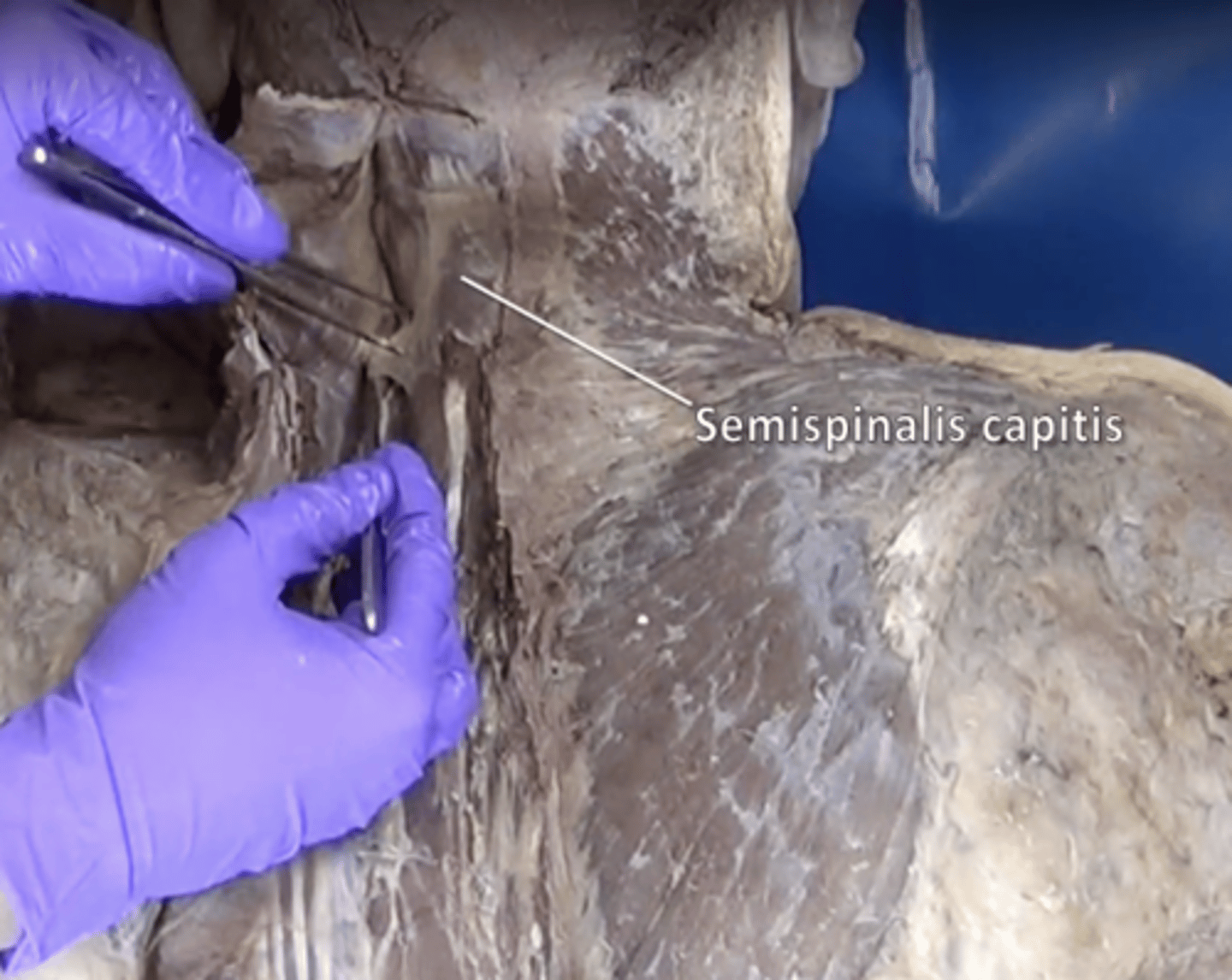
Semispinalis capitis muscle
extends and rotates head and vertebral column. Lies deep to splenius capitis muscle with vertical fibers
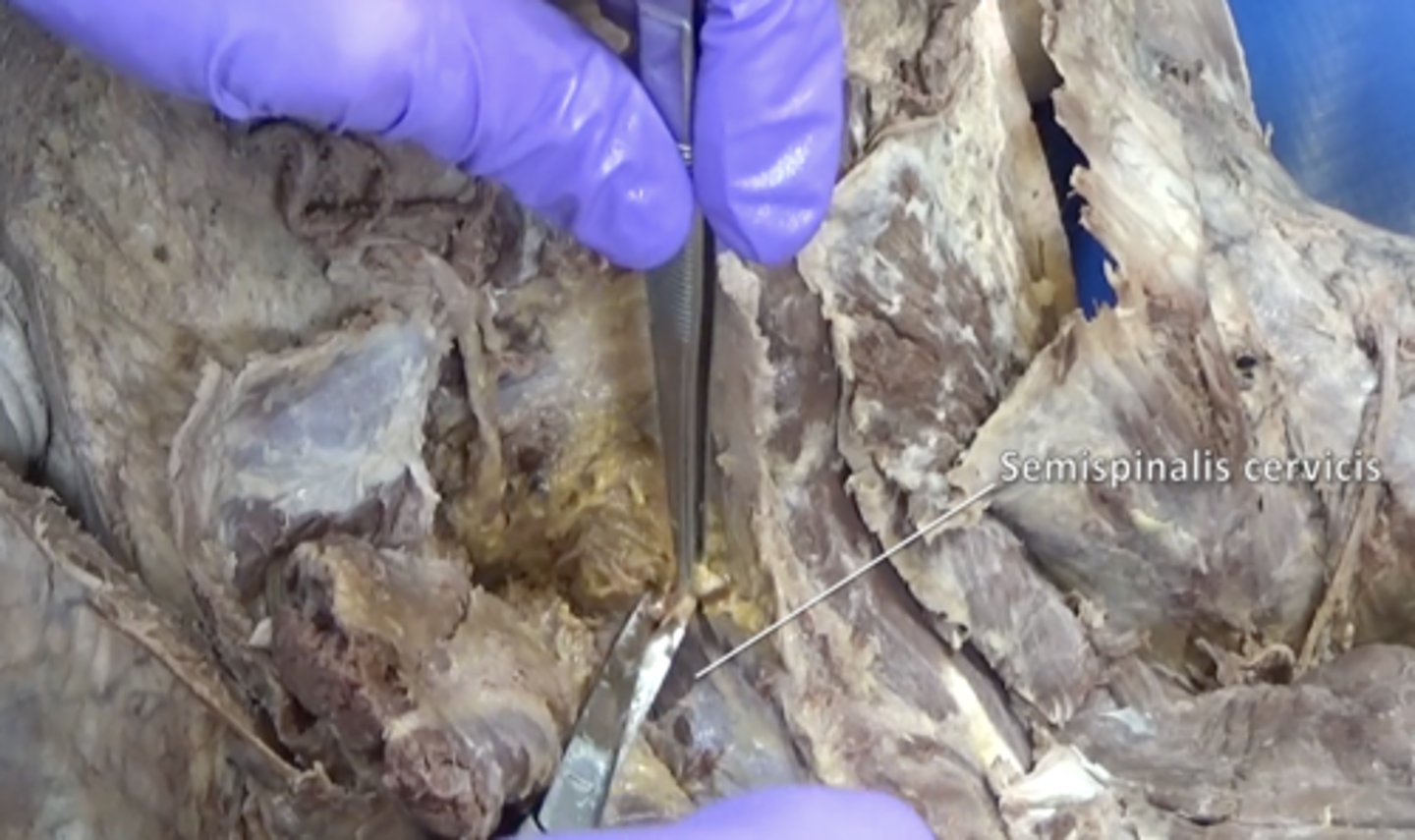
Semispinalis cervicis muscle
deep to the Semispinalis capitis muscle and superiorly attaches to the spinous process of the axis (C2)
Obliquus capitis inferior muscle
Obliquus capitis superior muscle
Rectus capitis posterior major muscle
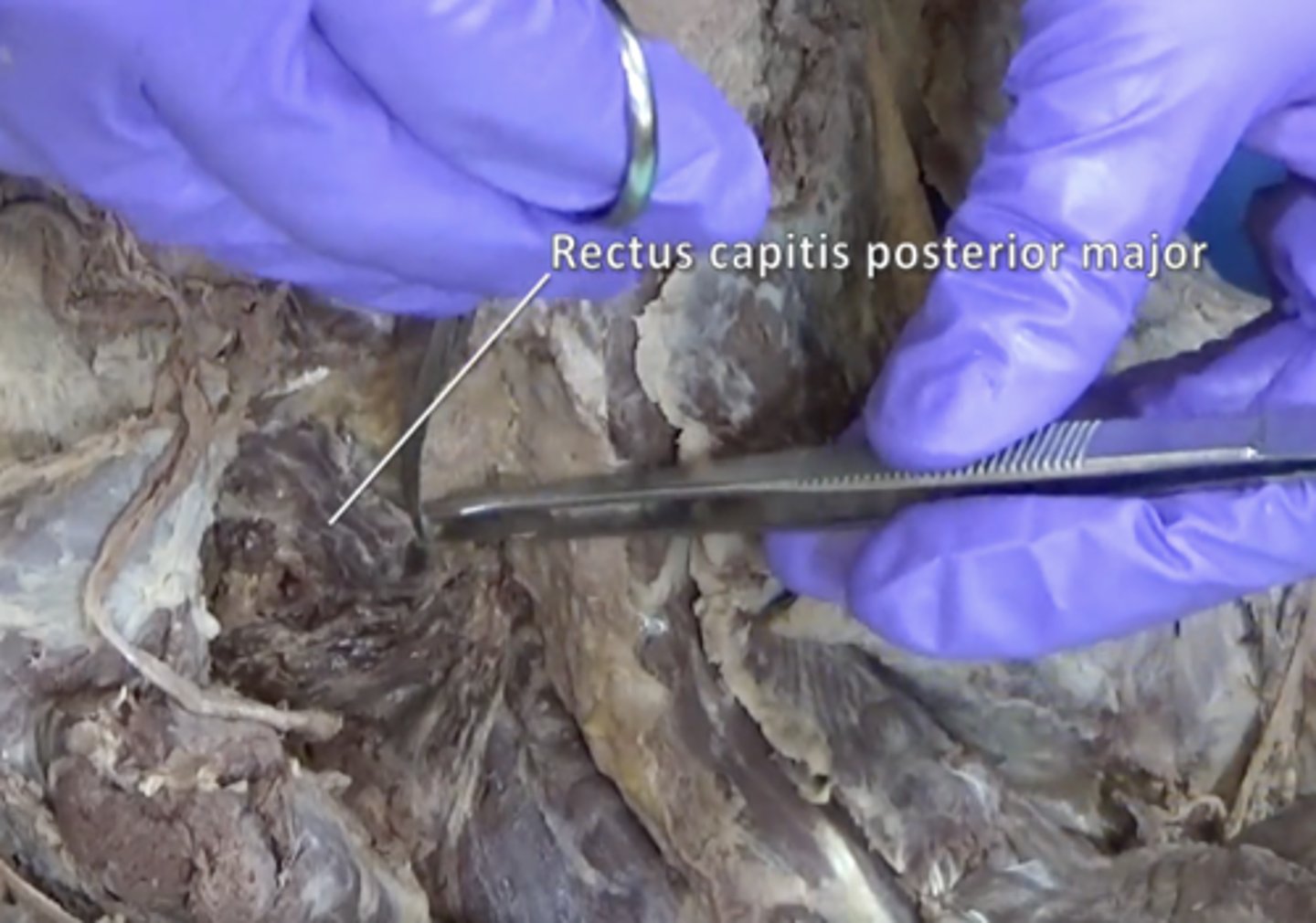
Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
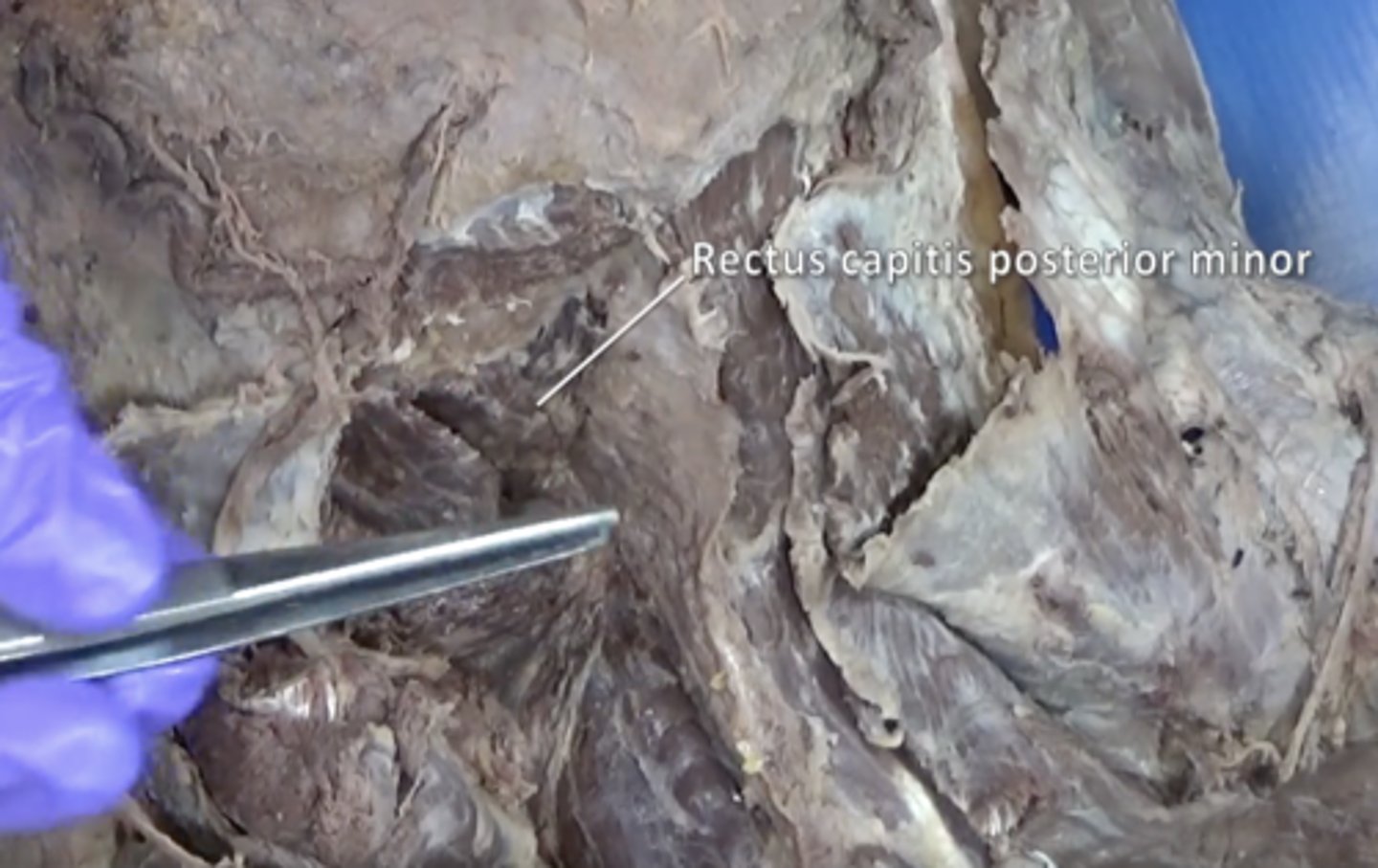
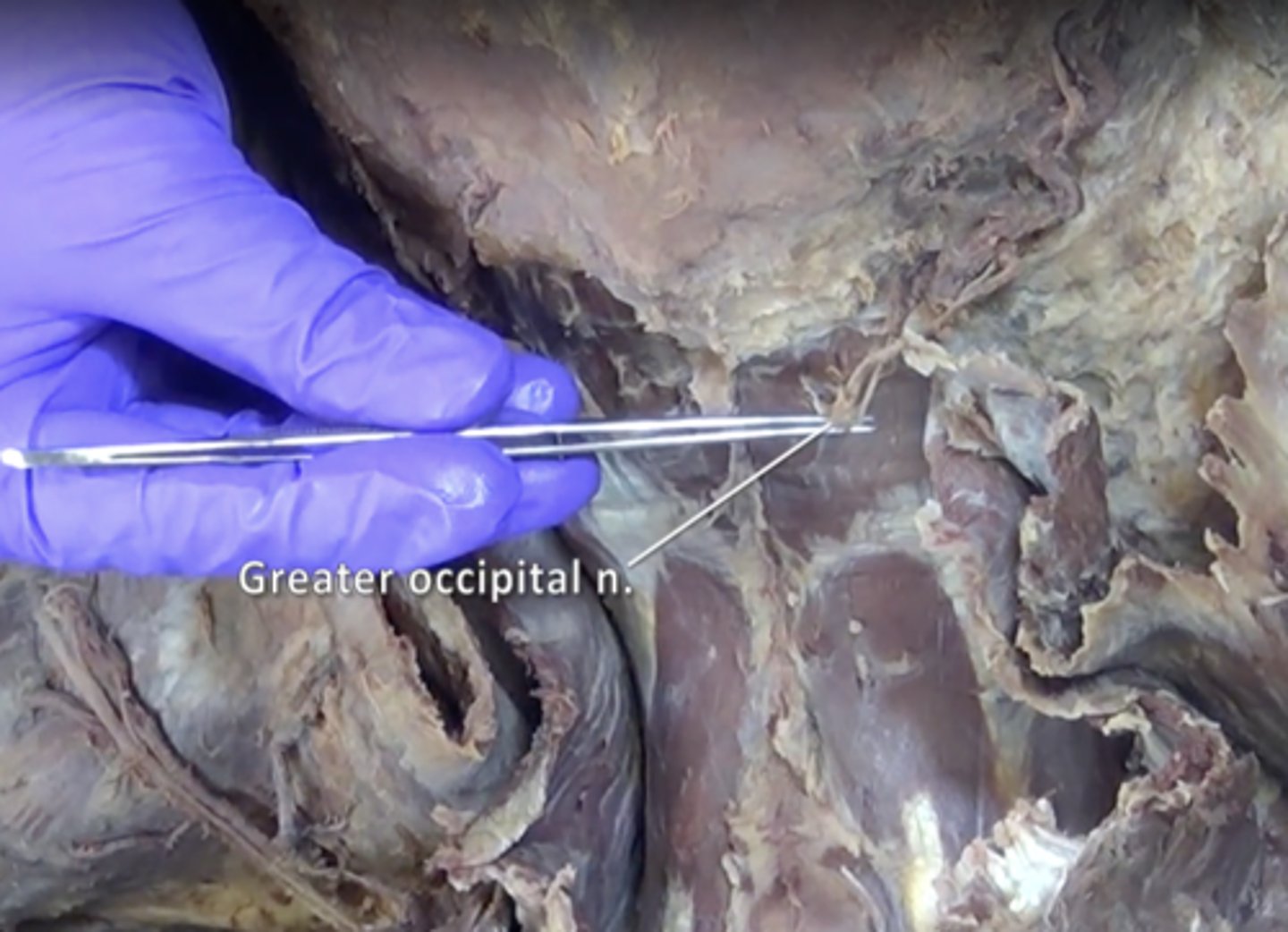
greater occipital nerve
Nerve located in the back of the head and pierces the superior border of the trapezius muscle
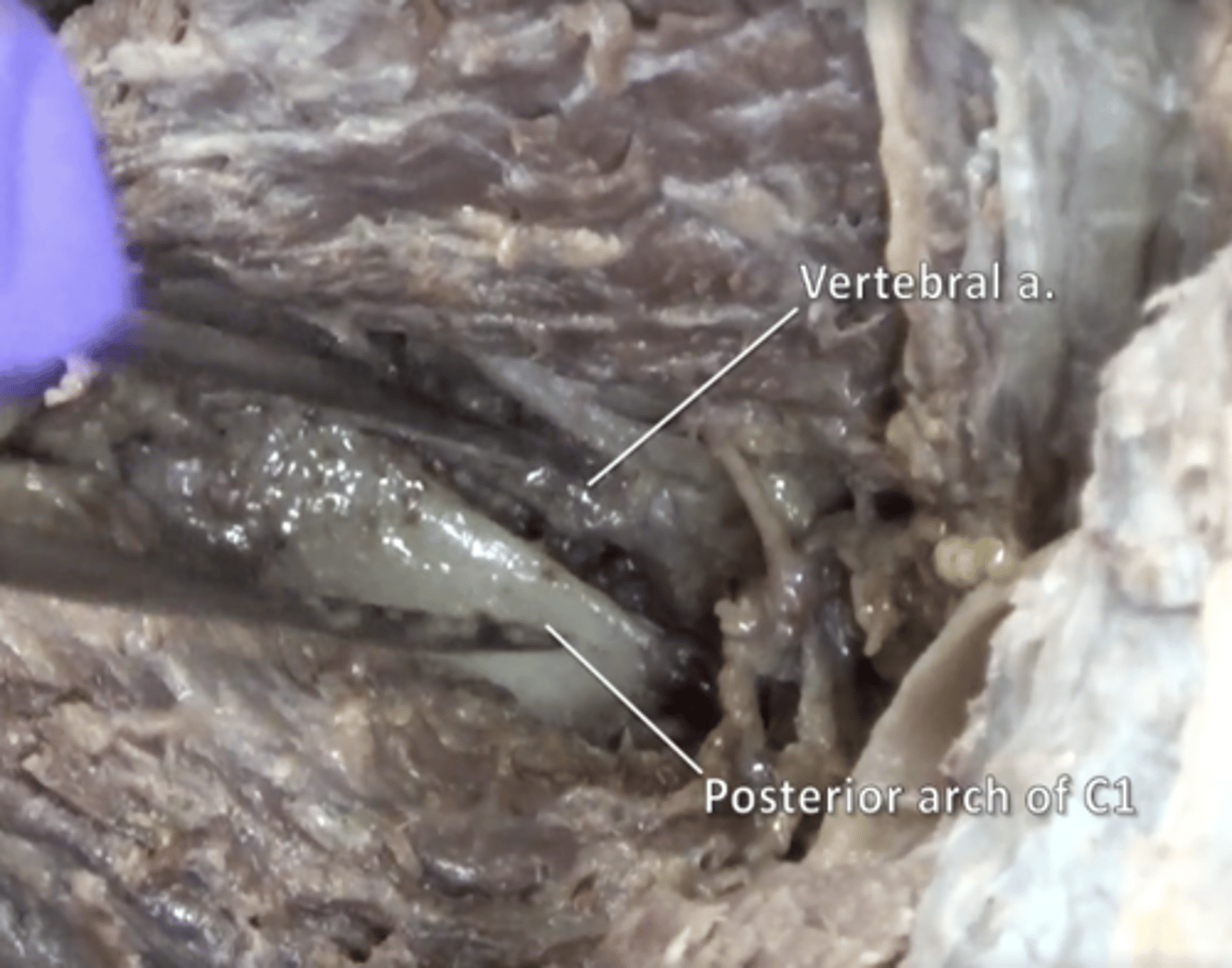
vertebral artery
Supplies blood to the spinal column and brain. Located between rectus capitis posterior major and obliquus capitis inferior
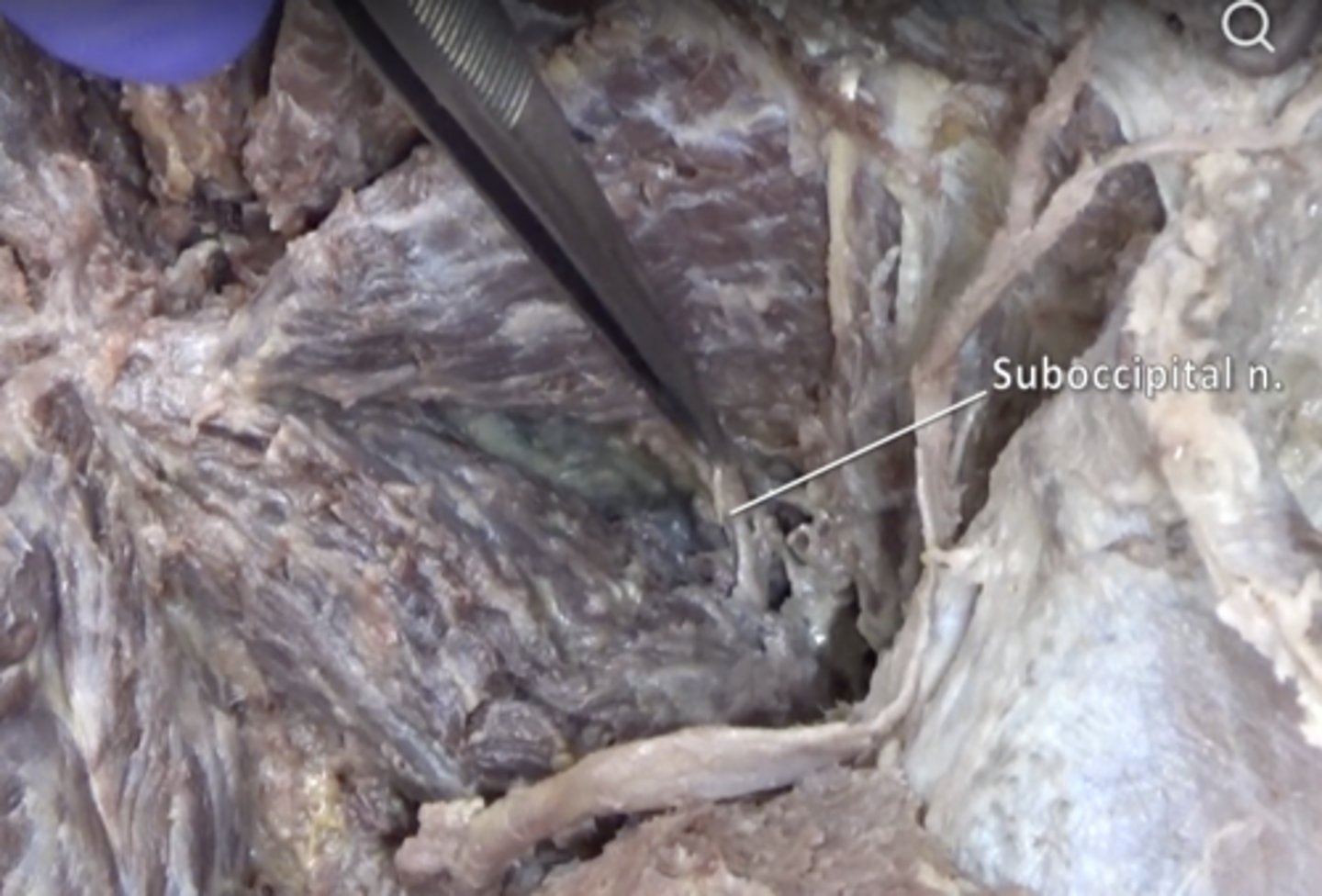
suboccipital nerve
Innervation of suboccipital muscles. Located between rectus capitis posterior major and obliquus capitis inferior
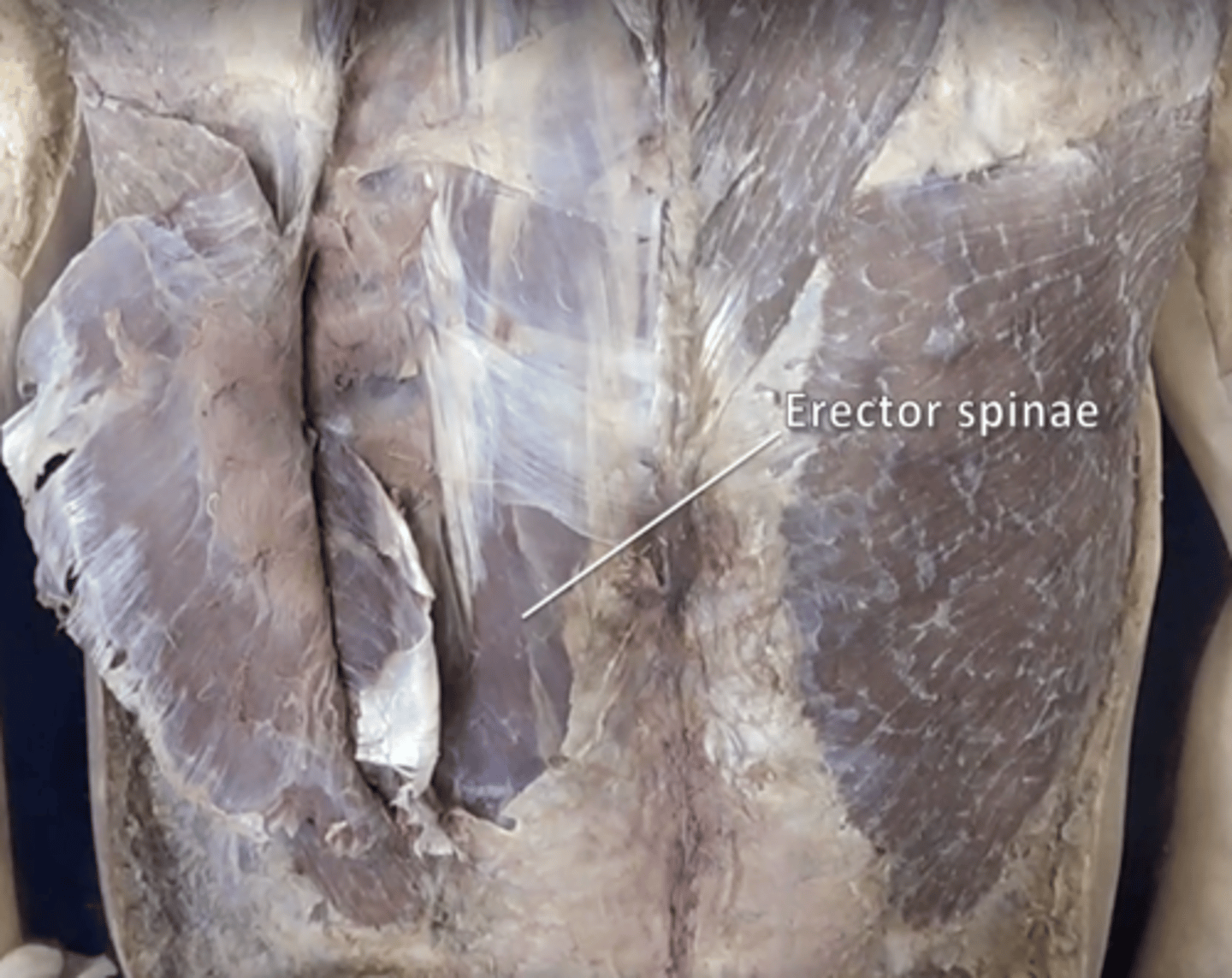
erector spinae muscle
contains iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis muscle
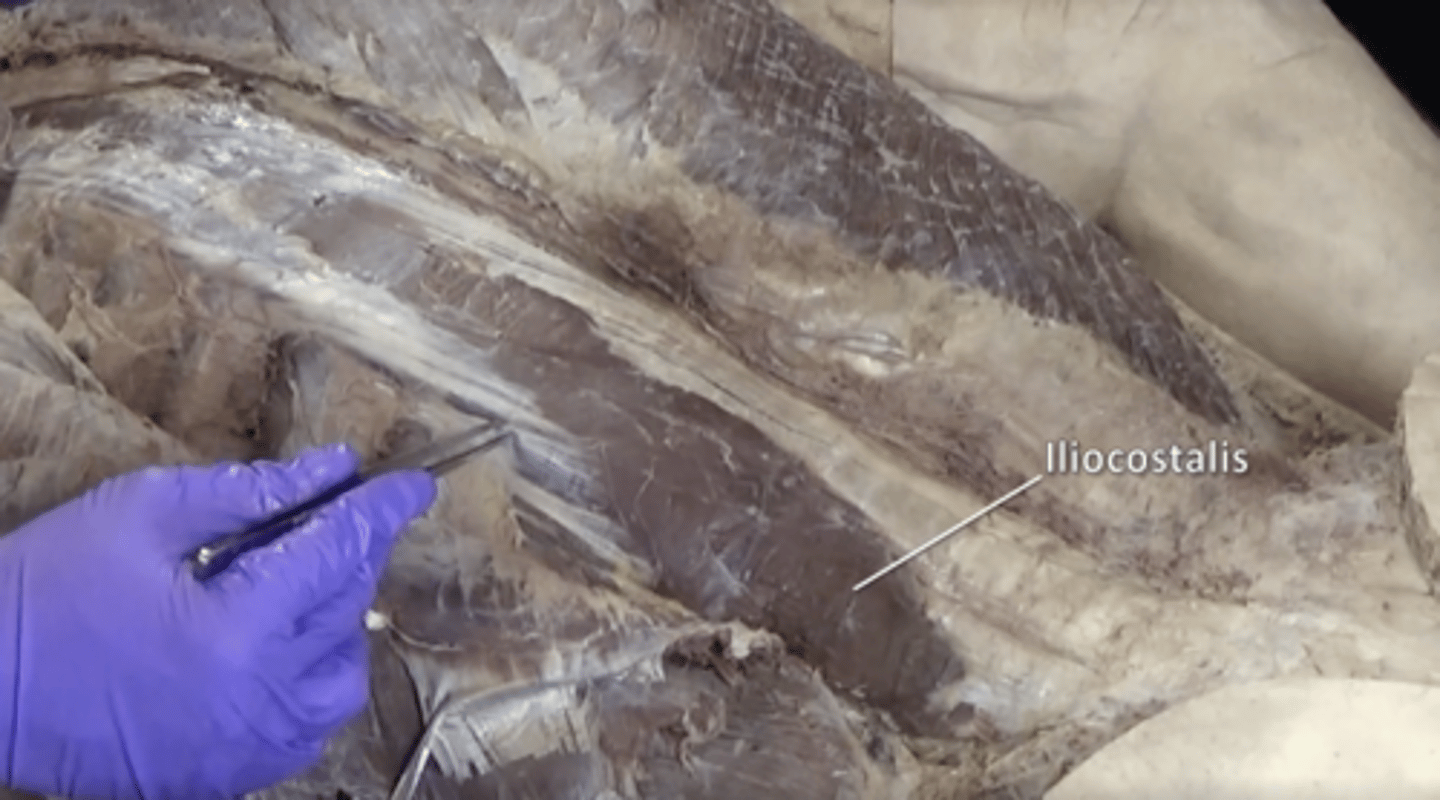
iliocostalis muscle
Lateral muscle of the erector spinae group.

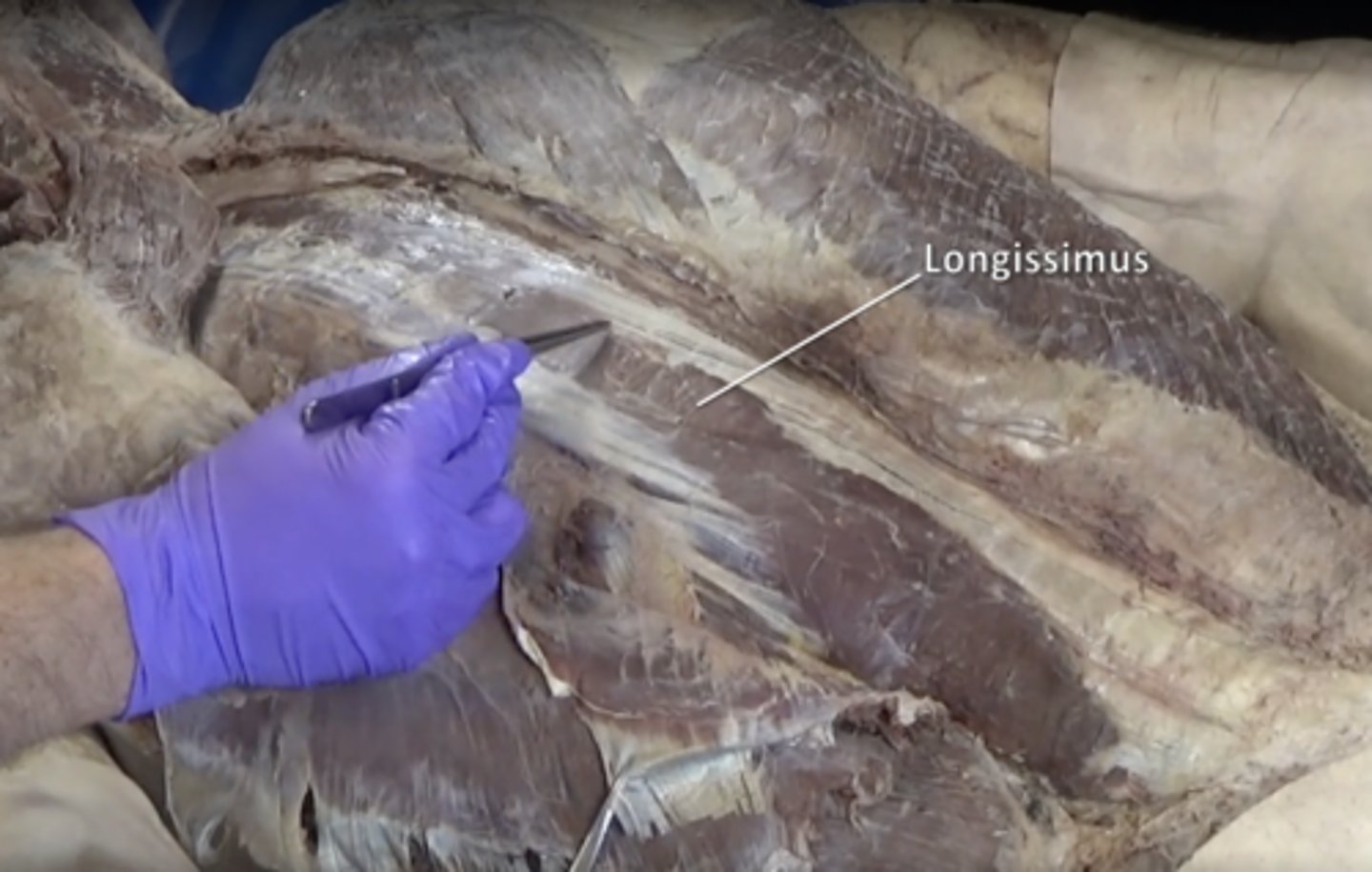
longissimus muscle
Middle muscle of the erector spinae group.
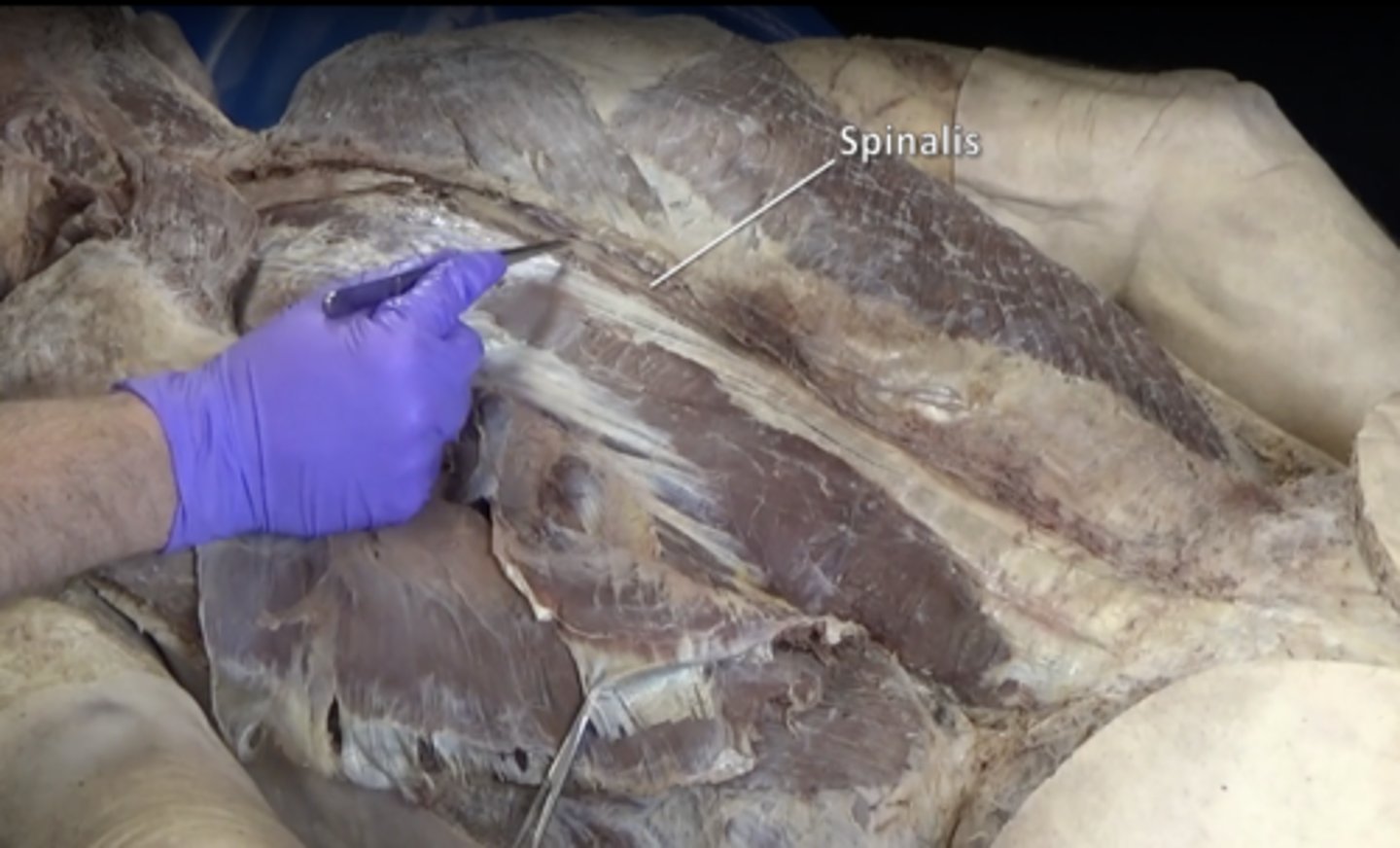
spinalis muscle
Smallest and most medial of erector spinae group
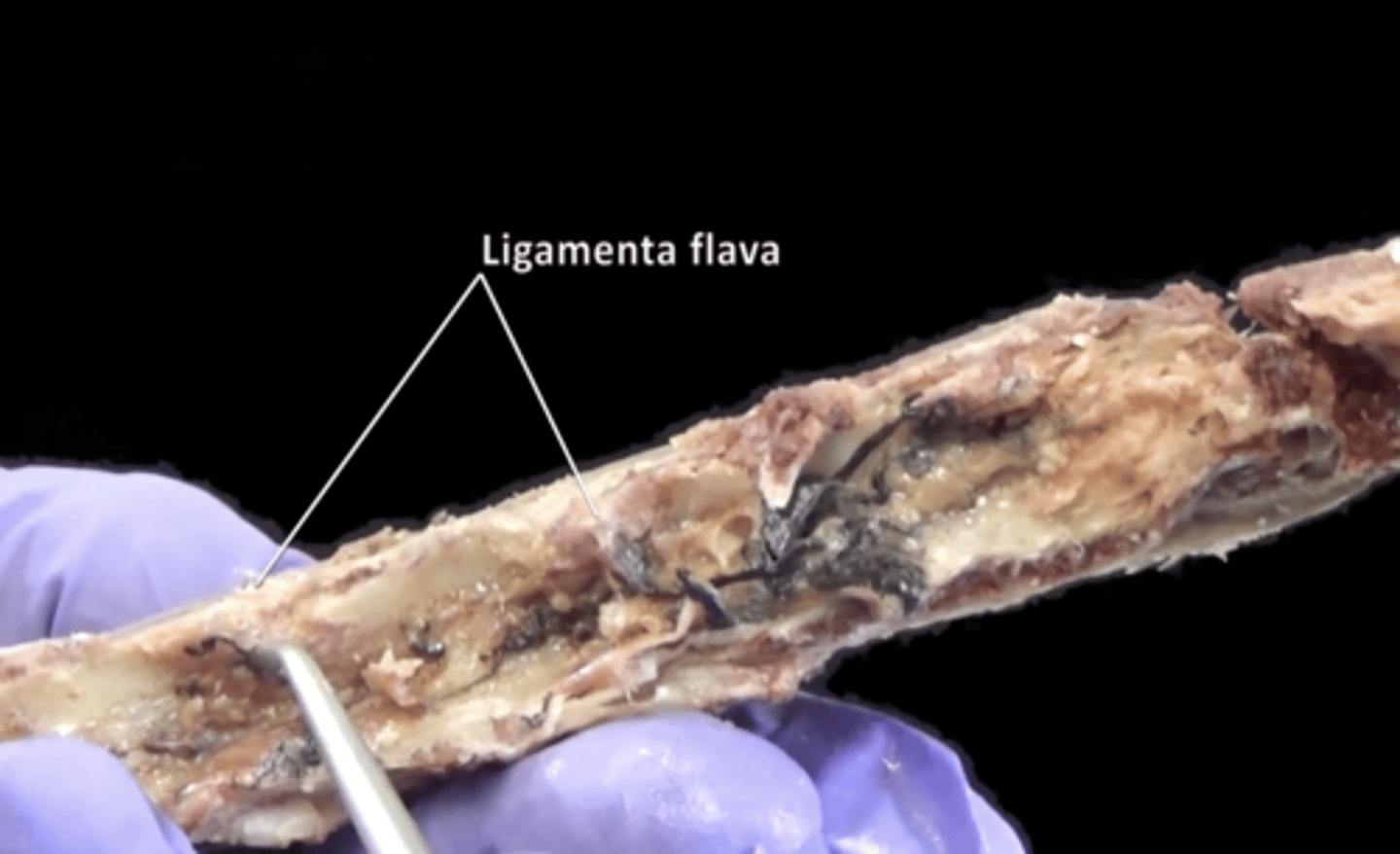
ligamentum flava
Elastic connective tissue connecting the laminae of adjacent vertebrae.
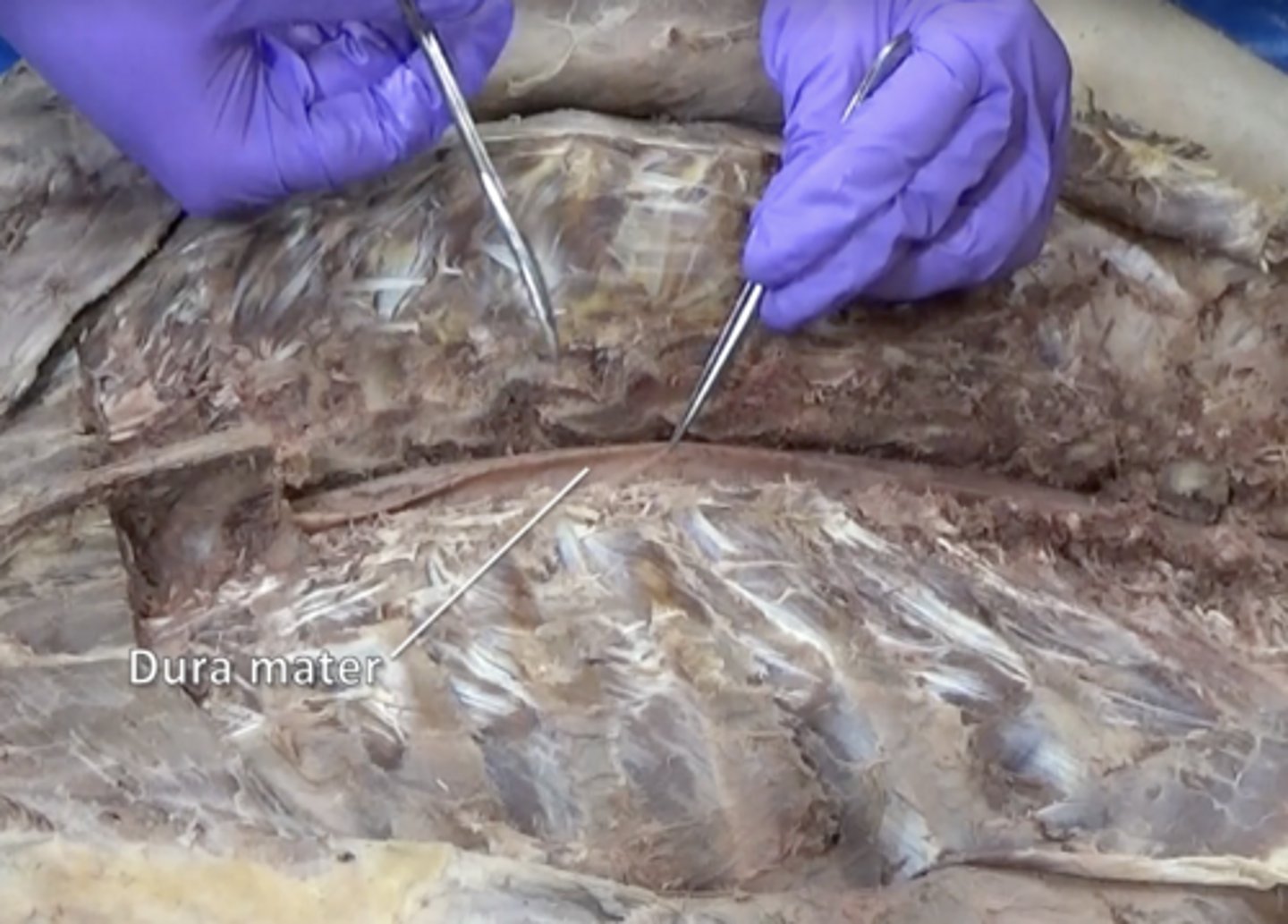
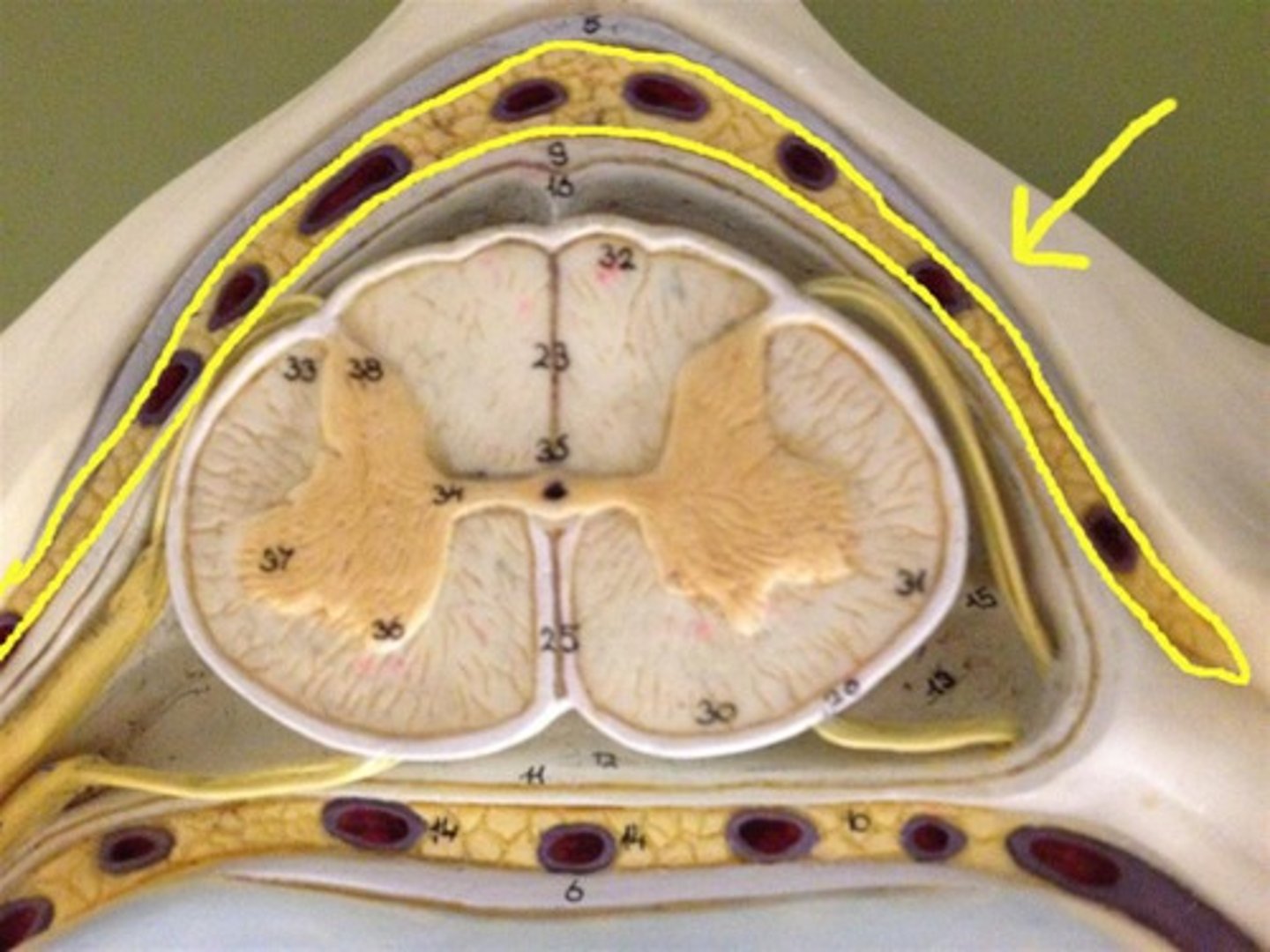
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
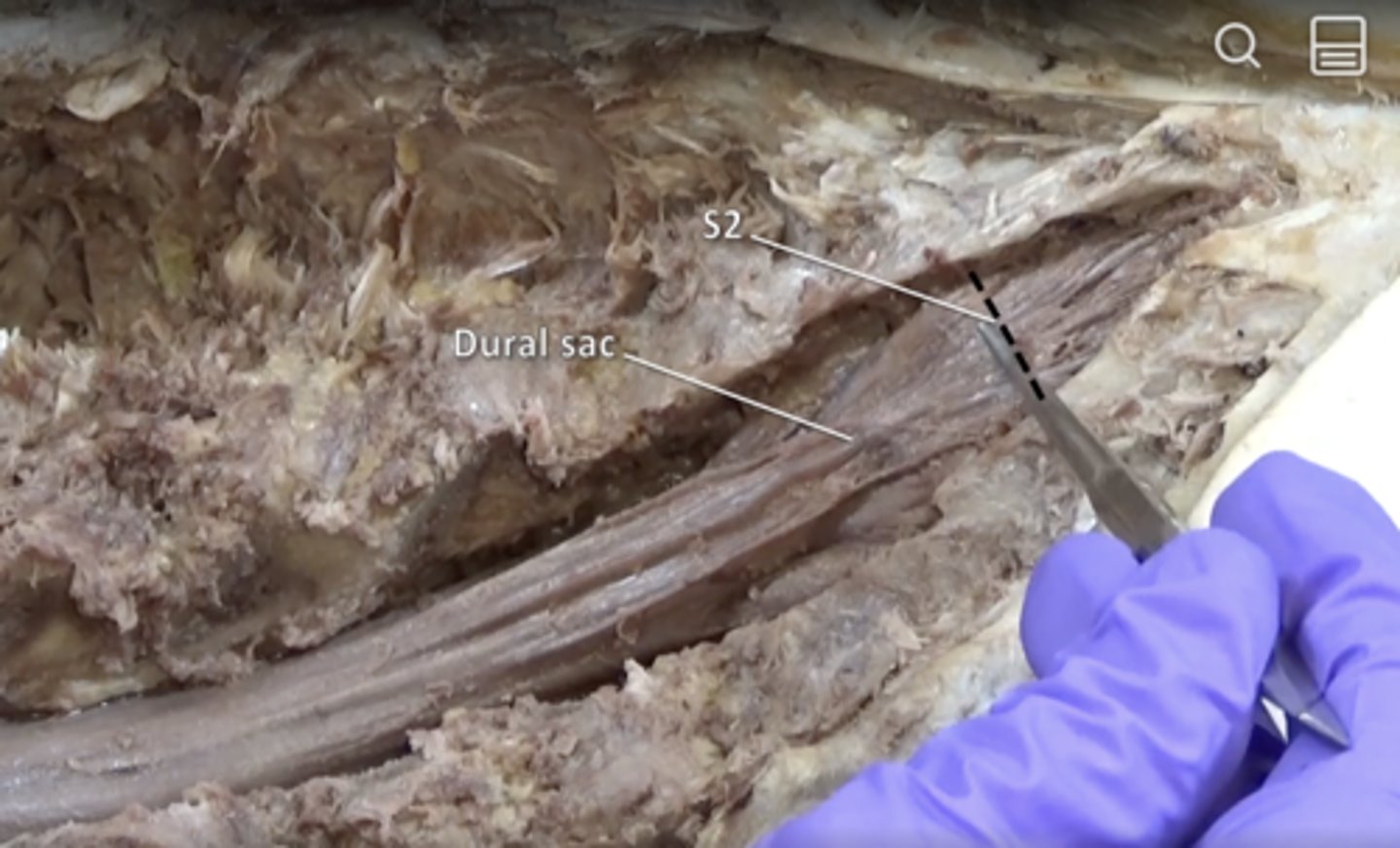
dural sac
tubular sheath containing spinal cord formed by dura mater. Ends at S2
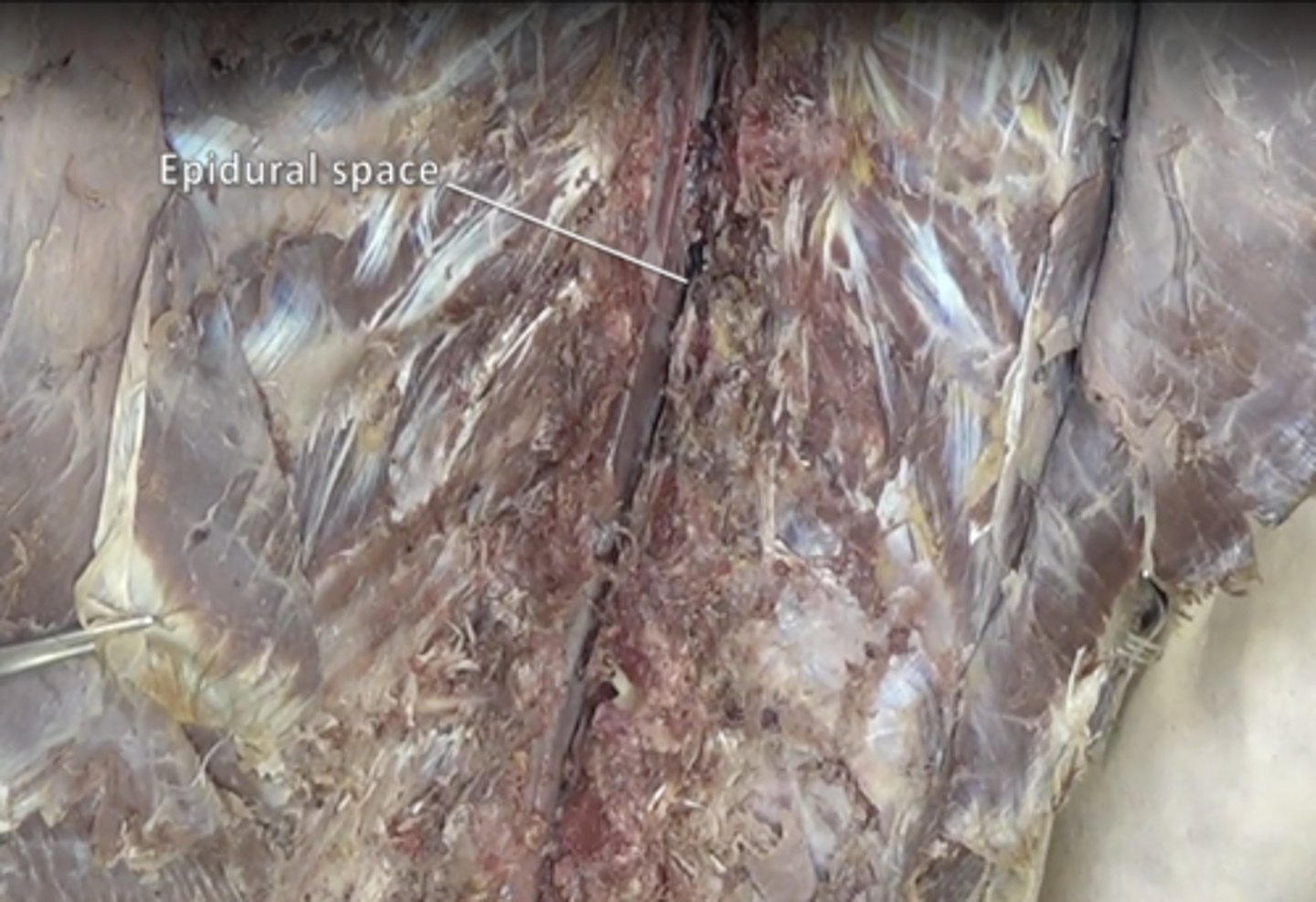
epidural space
space between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater
epidural fat
around the spinal cord (difficult to see on donor)
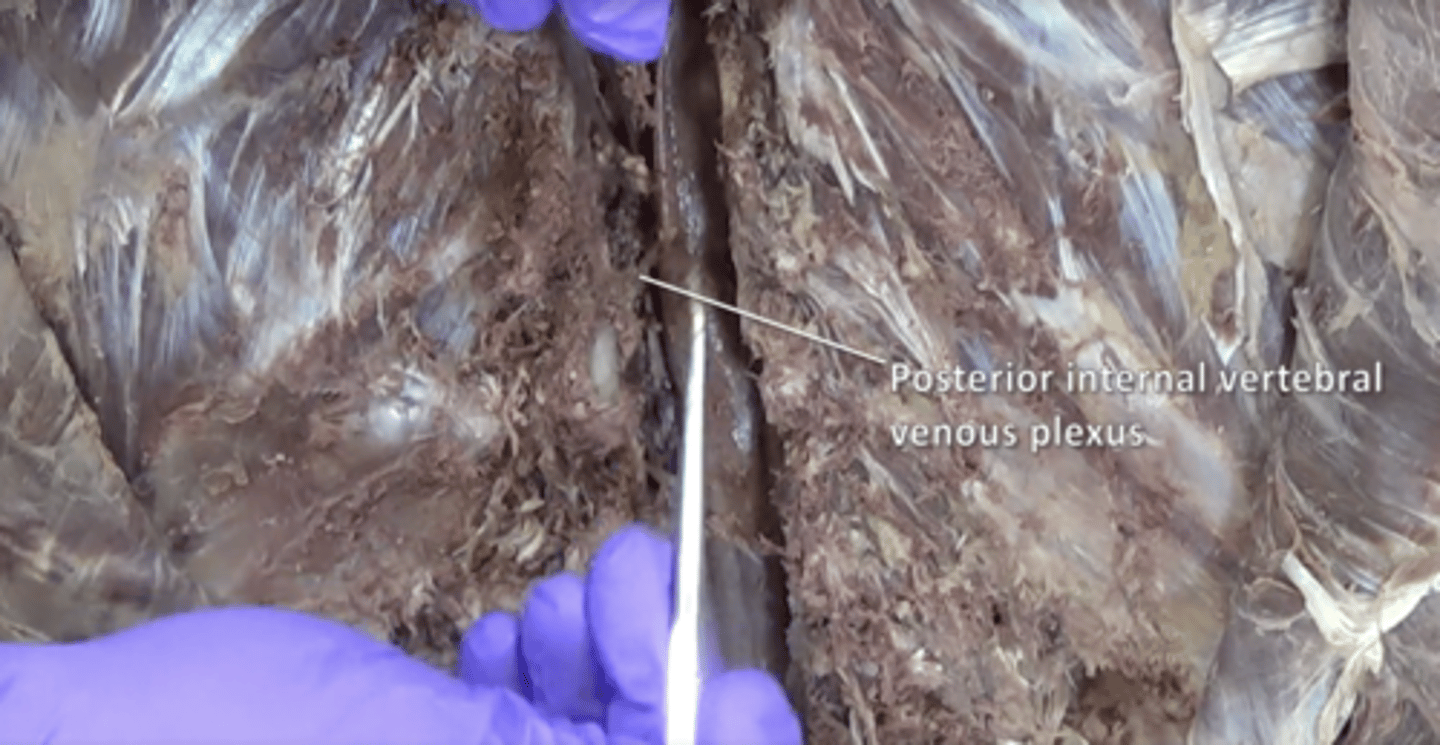
posterior internal vertebral venous plexus
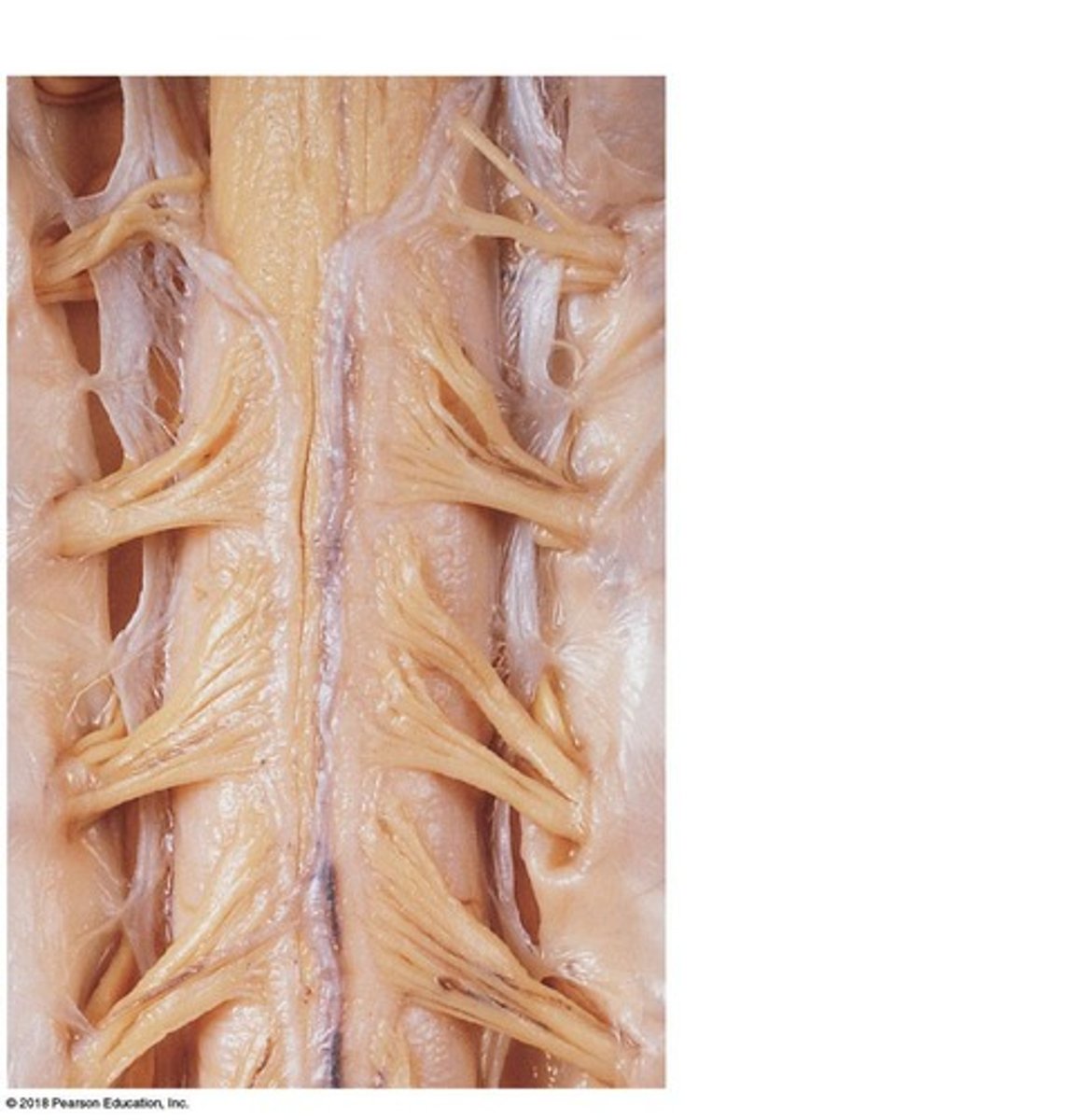
spinal ganglia
contain cell bodies of sensory neurons
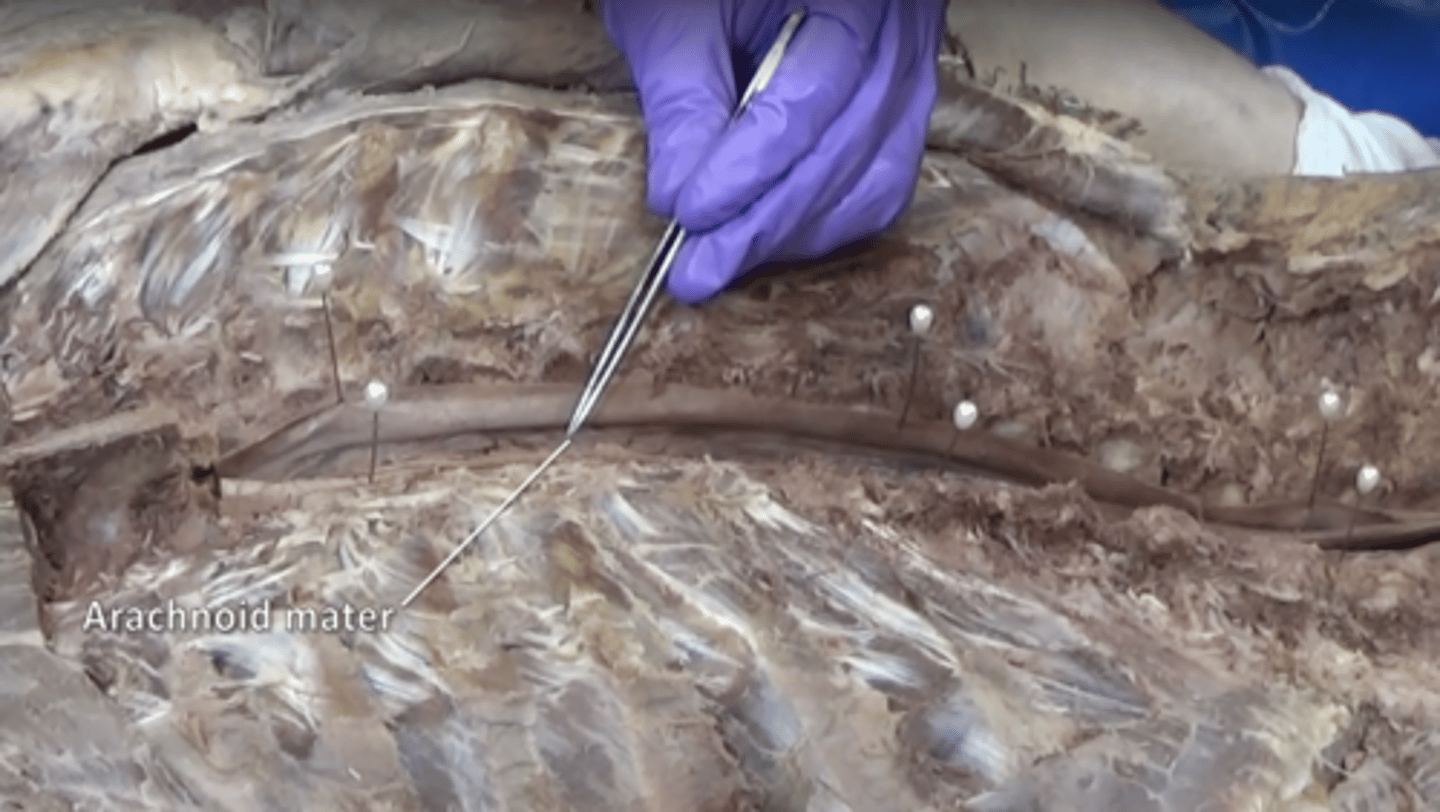
arachnoid mater
middle layer of the meninges
subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
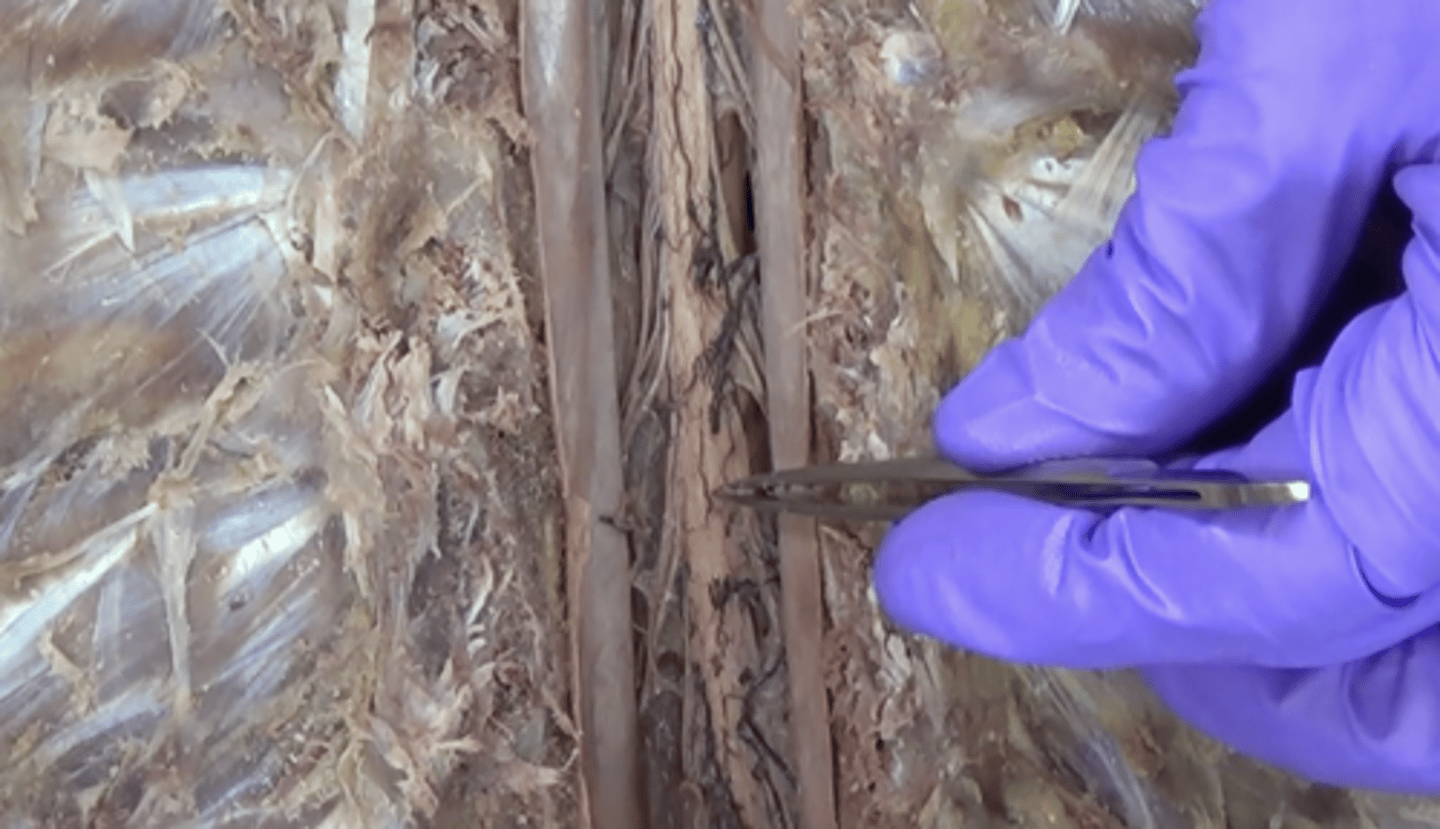
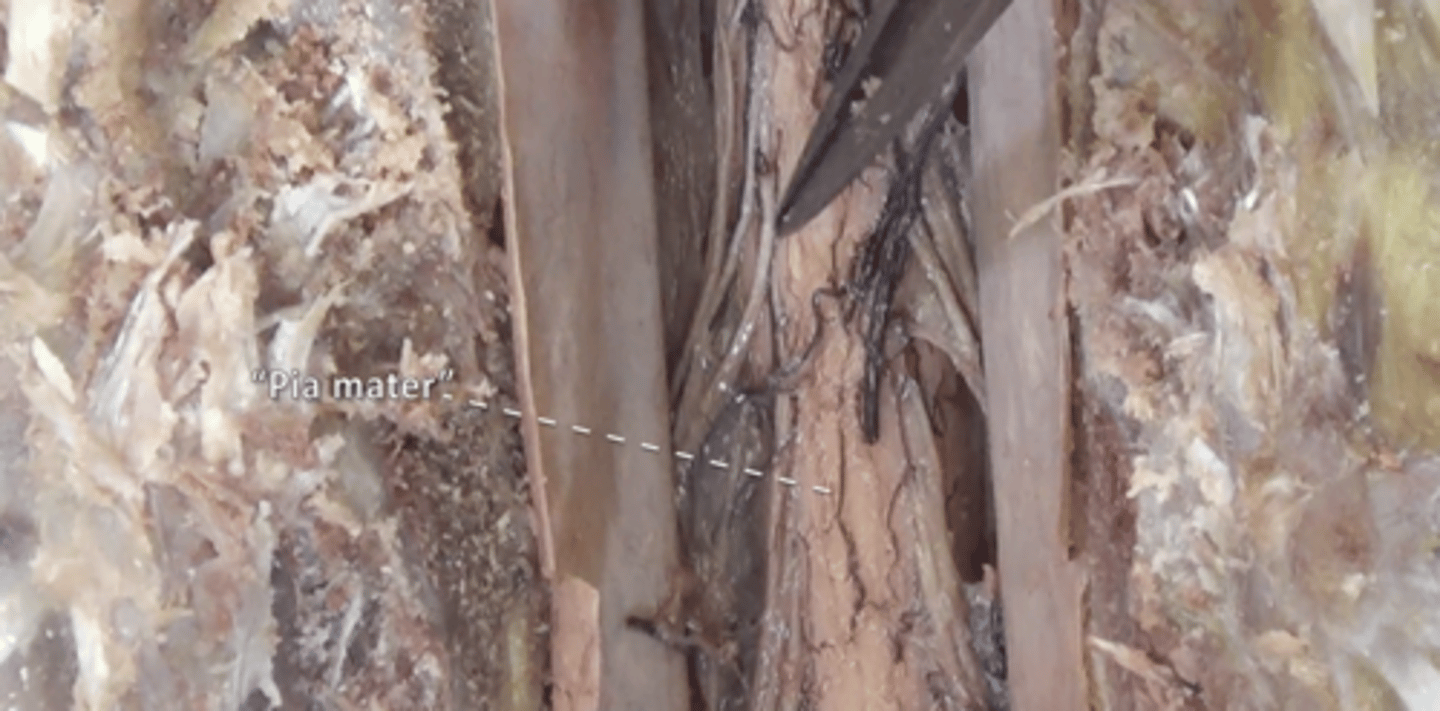
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane surrounding the spinal cord

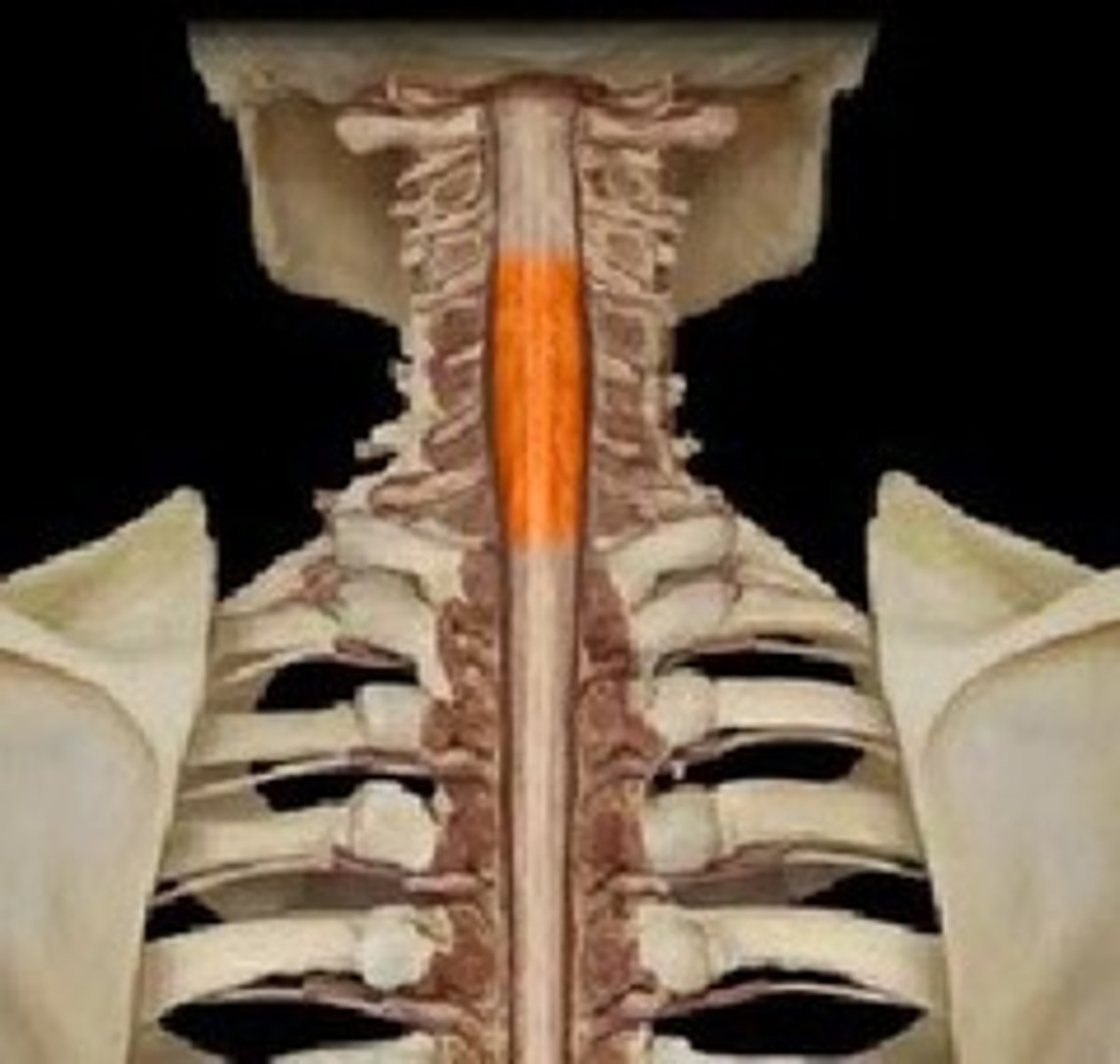
cervical enlargement
supplies nerves to the shoulder and upper limbs
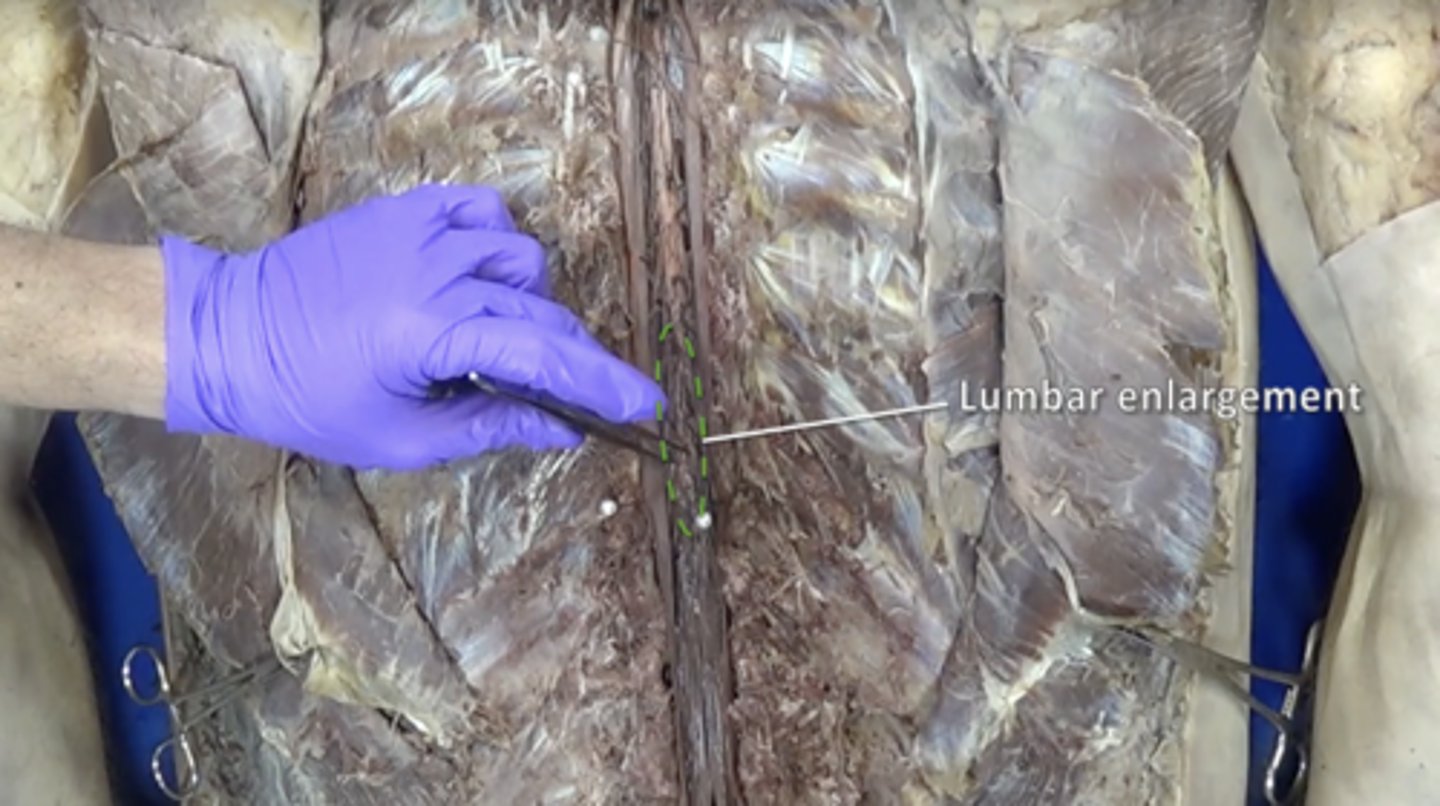
lumbar enlargement
nerves of pelvis and lower limbs
conus medullaris
tapered end of spinal cord located inferior to lumbar enlargement between L1 and L2
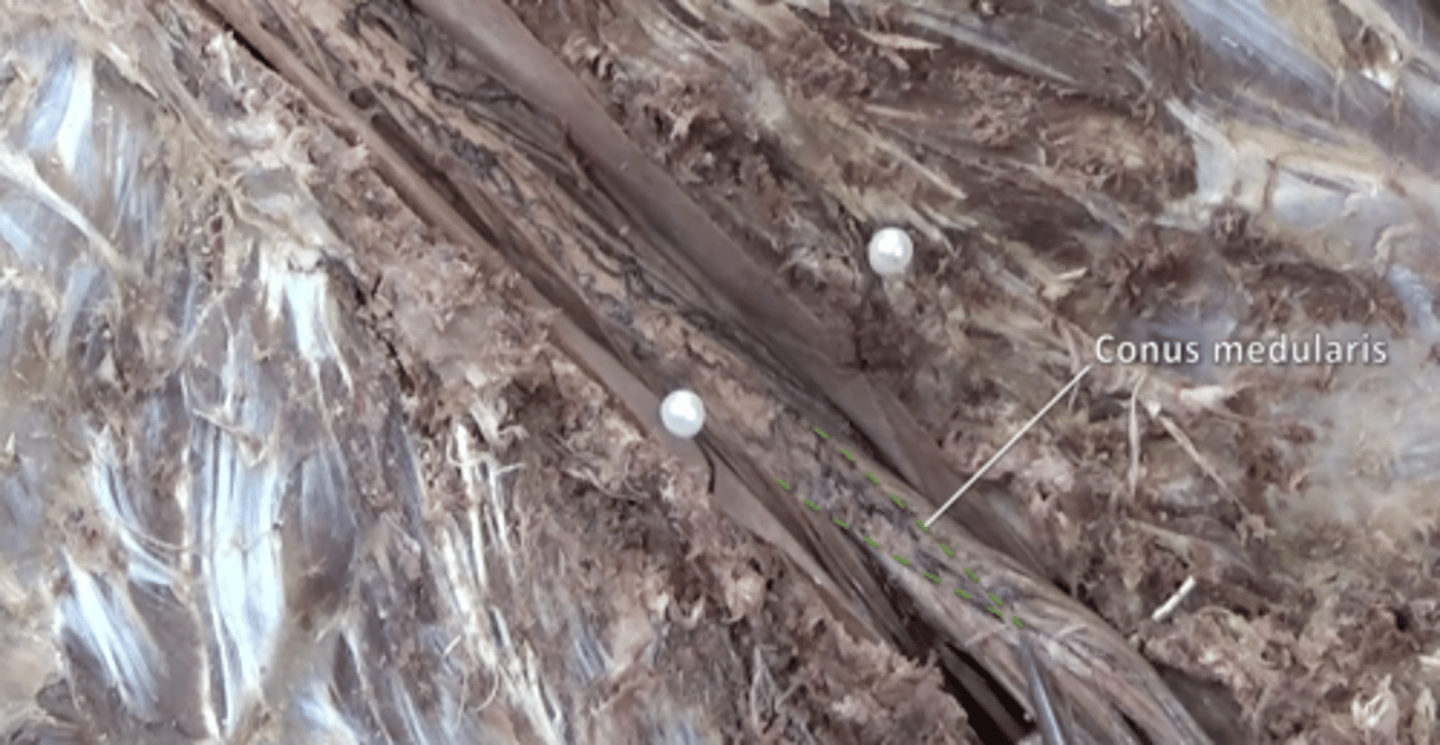

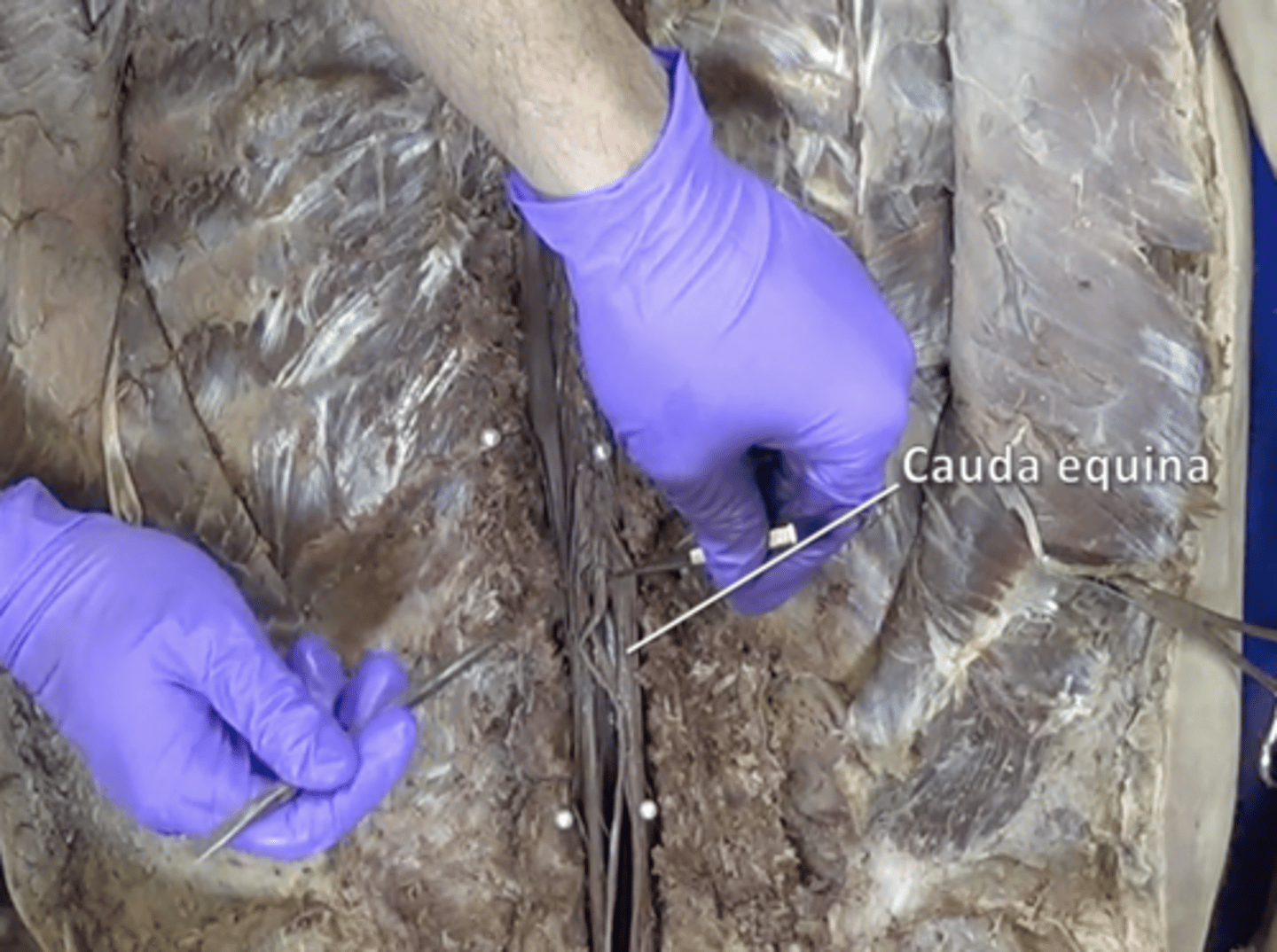
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
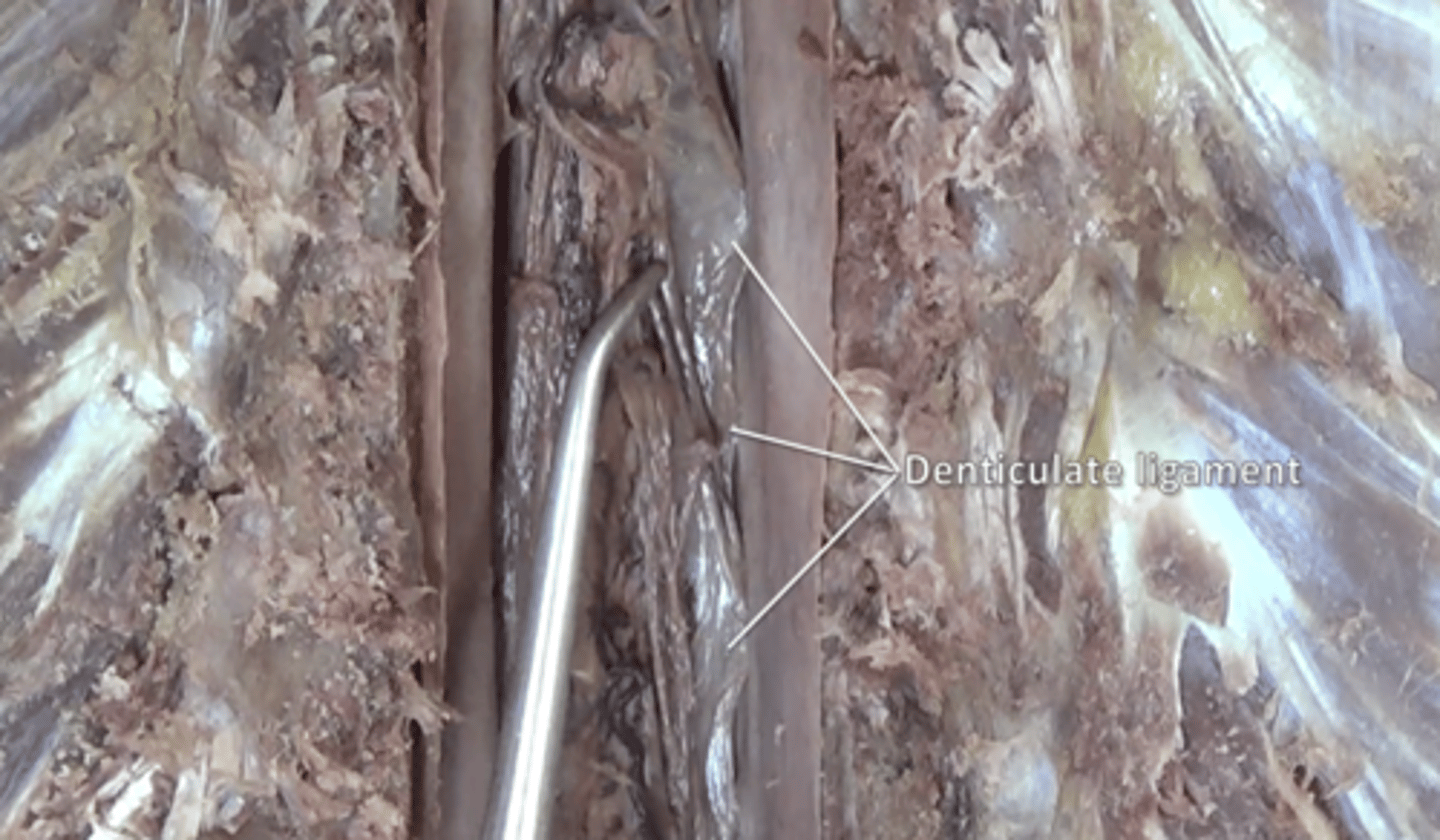
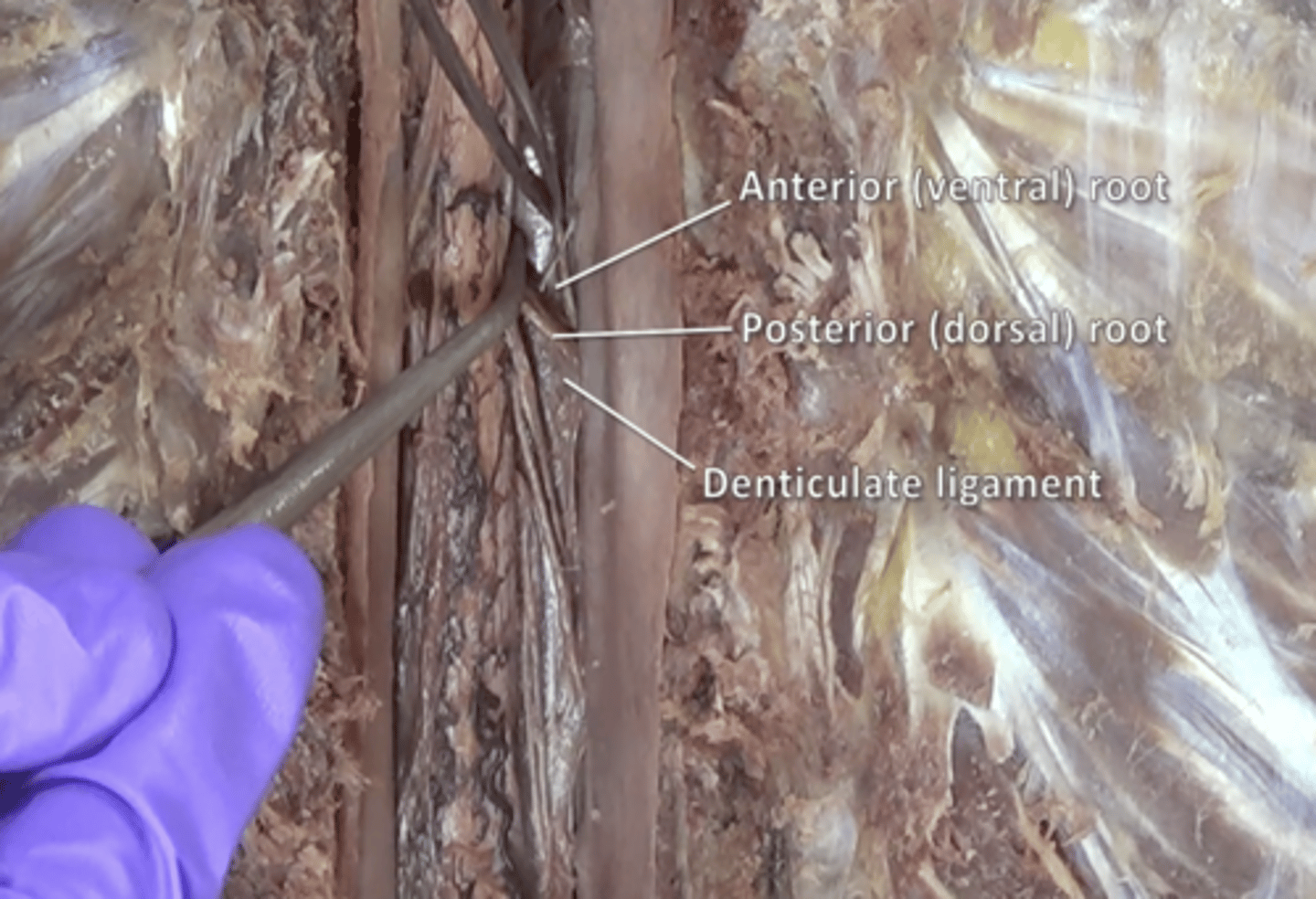
denticulate ligaments
extensions of pia mater that secure cord to dura mater

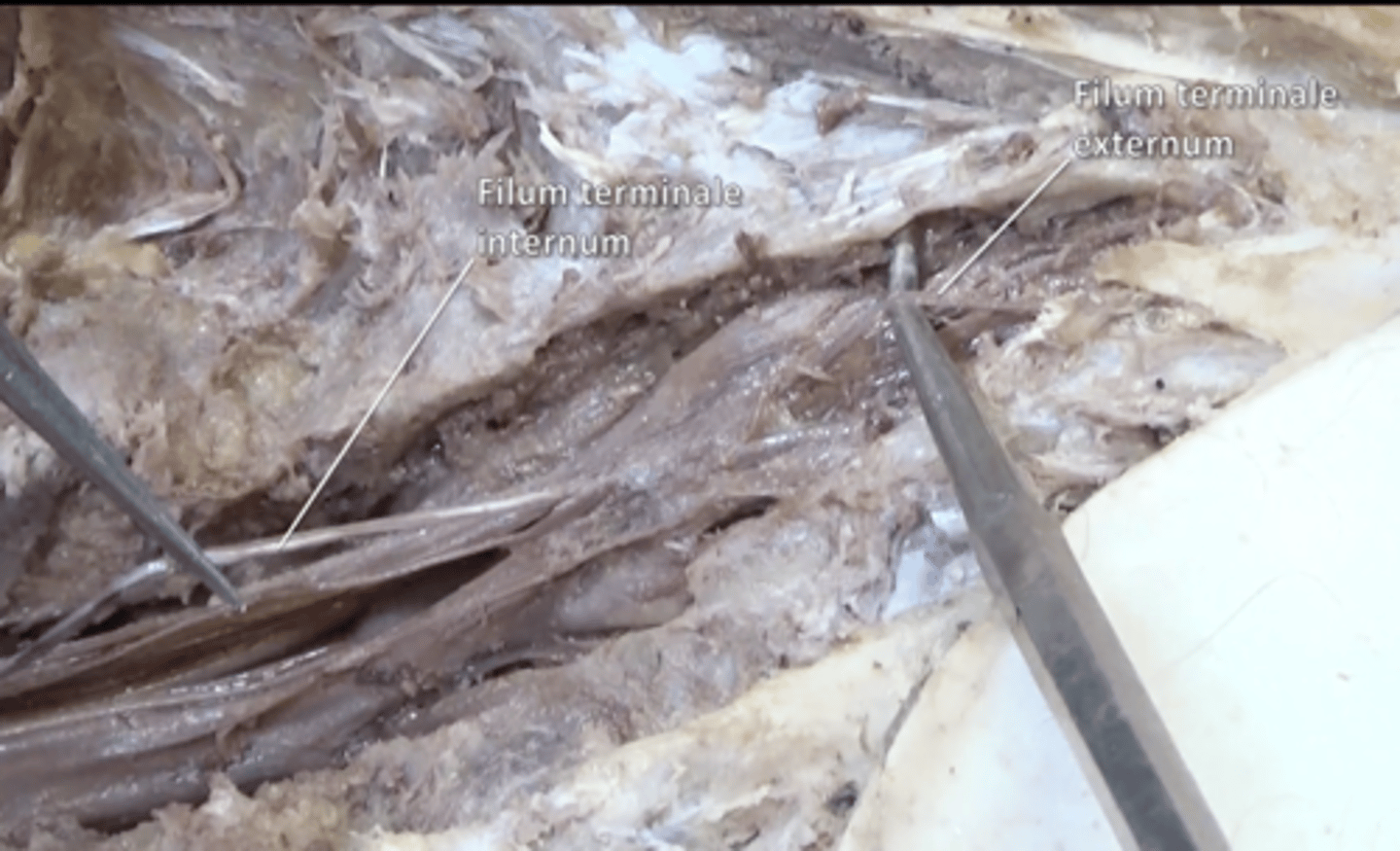
filum terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx located inside the cauda equina

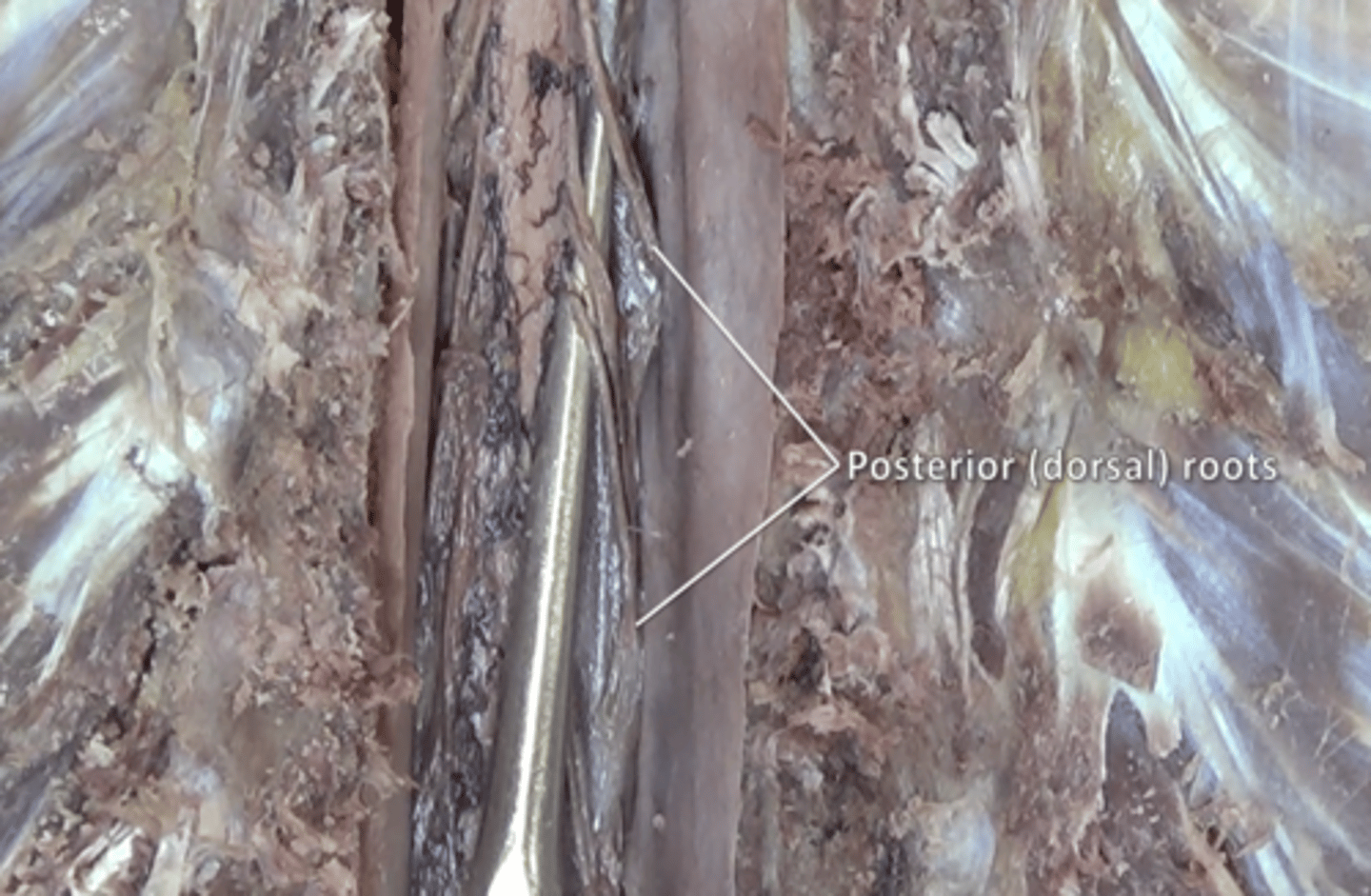
posterior roots
fibers carry sensory information located posteriorly to denticulate ligaments
anterior roots
fibers carry motor information located anteriorly to the denticulate ligaments
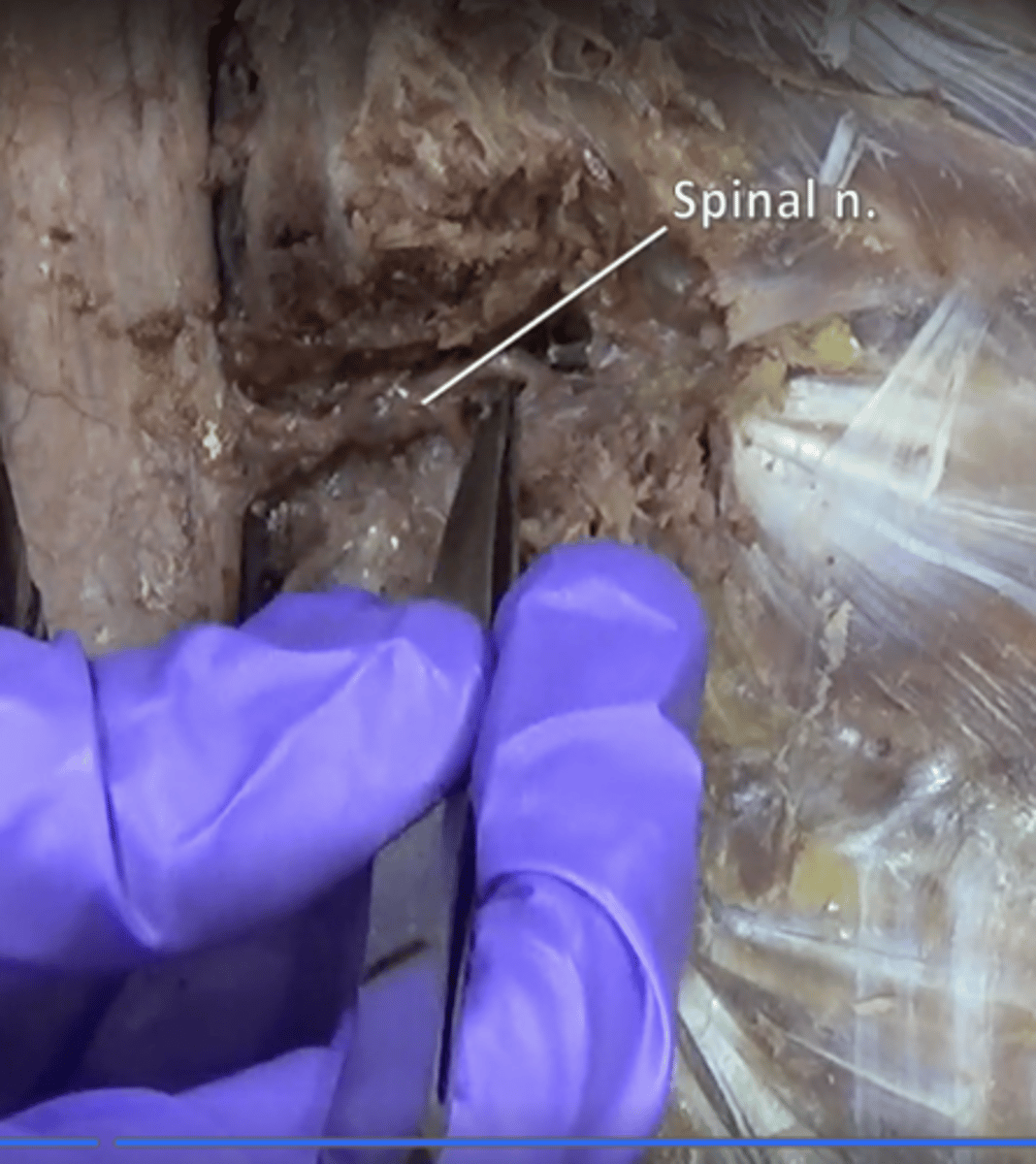
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
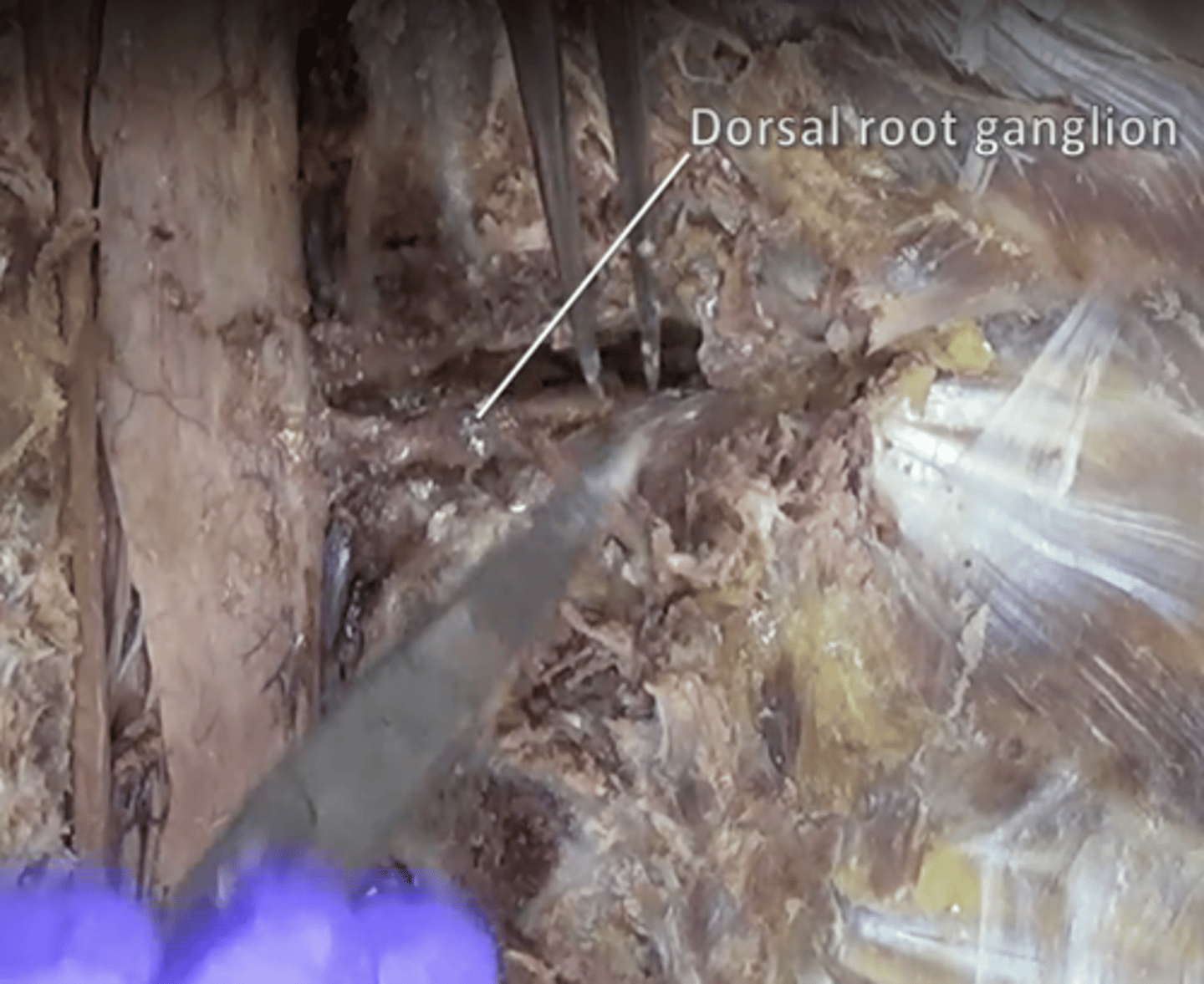
posterior (dorsal) root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons

anterior rami of spinal nerve
travel anteriorly to supply the muscles of the upper and lower limbs, the anterior thorax and abdomen, and part of the back
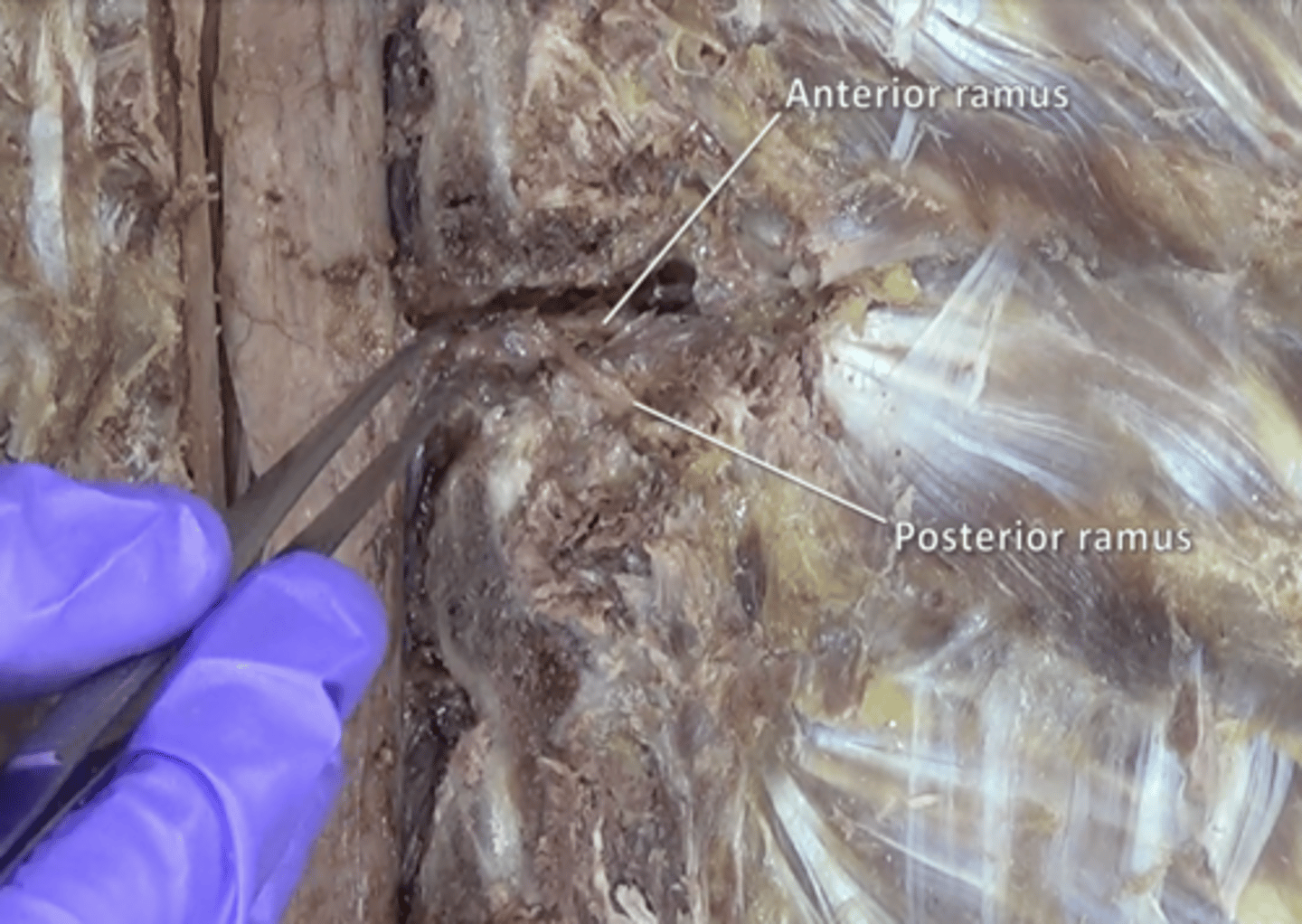
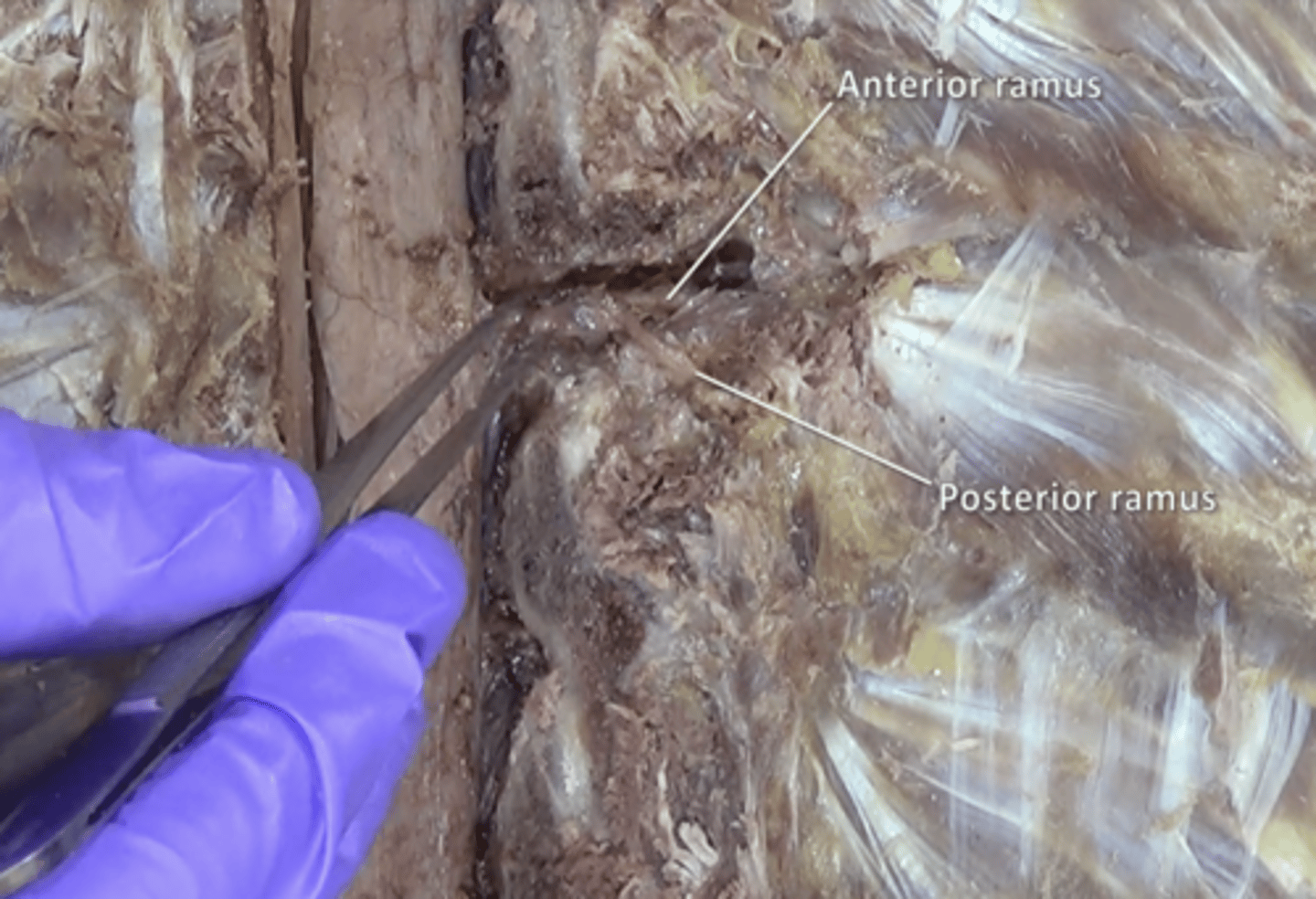
posterior rami of spinal nerve
the dorsal branch of a spinal nerve that forms from the dorsal root of the nerve after it emerges from the spinal cord
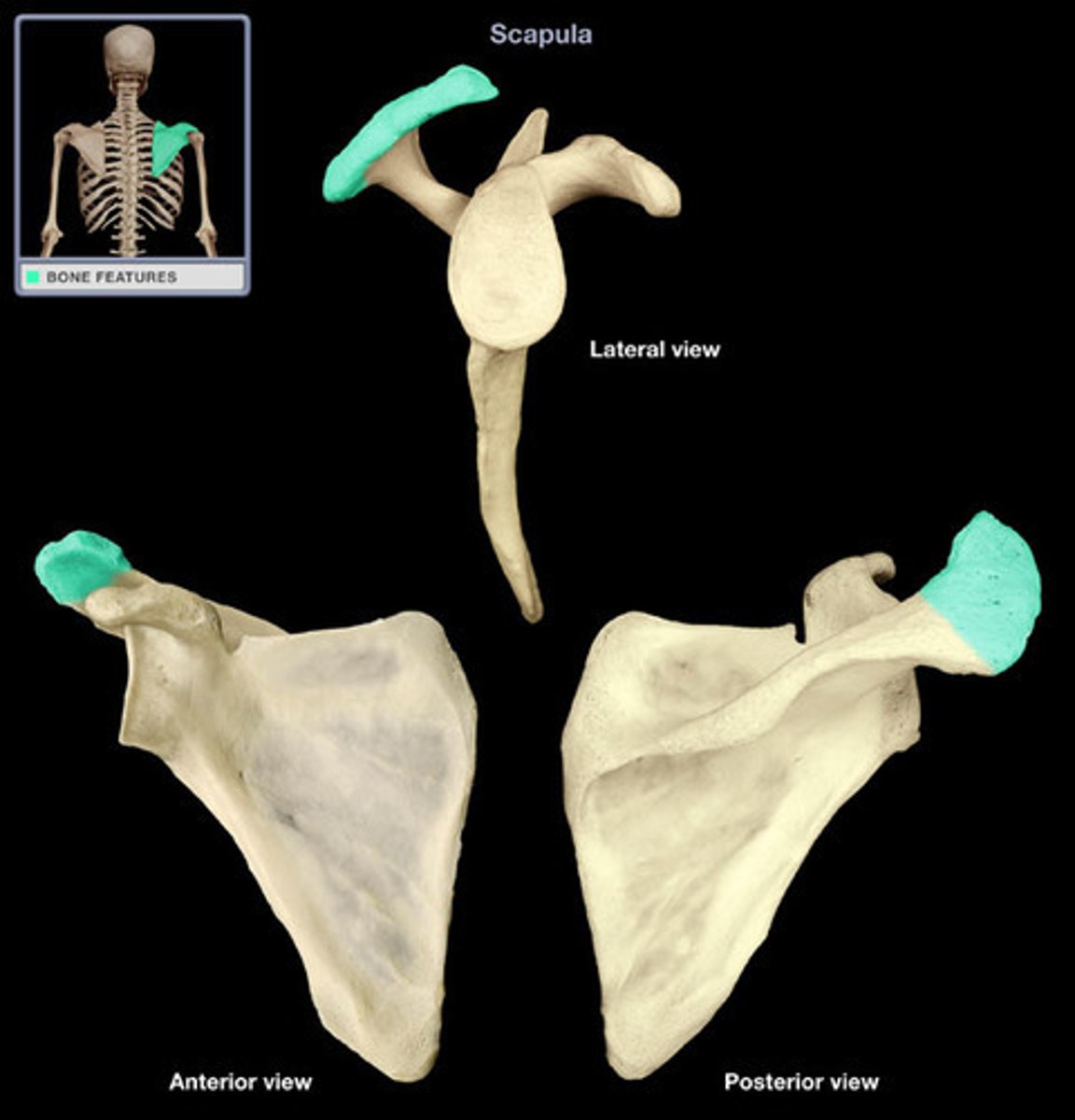
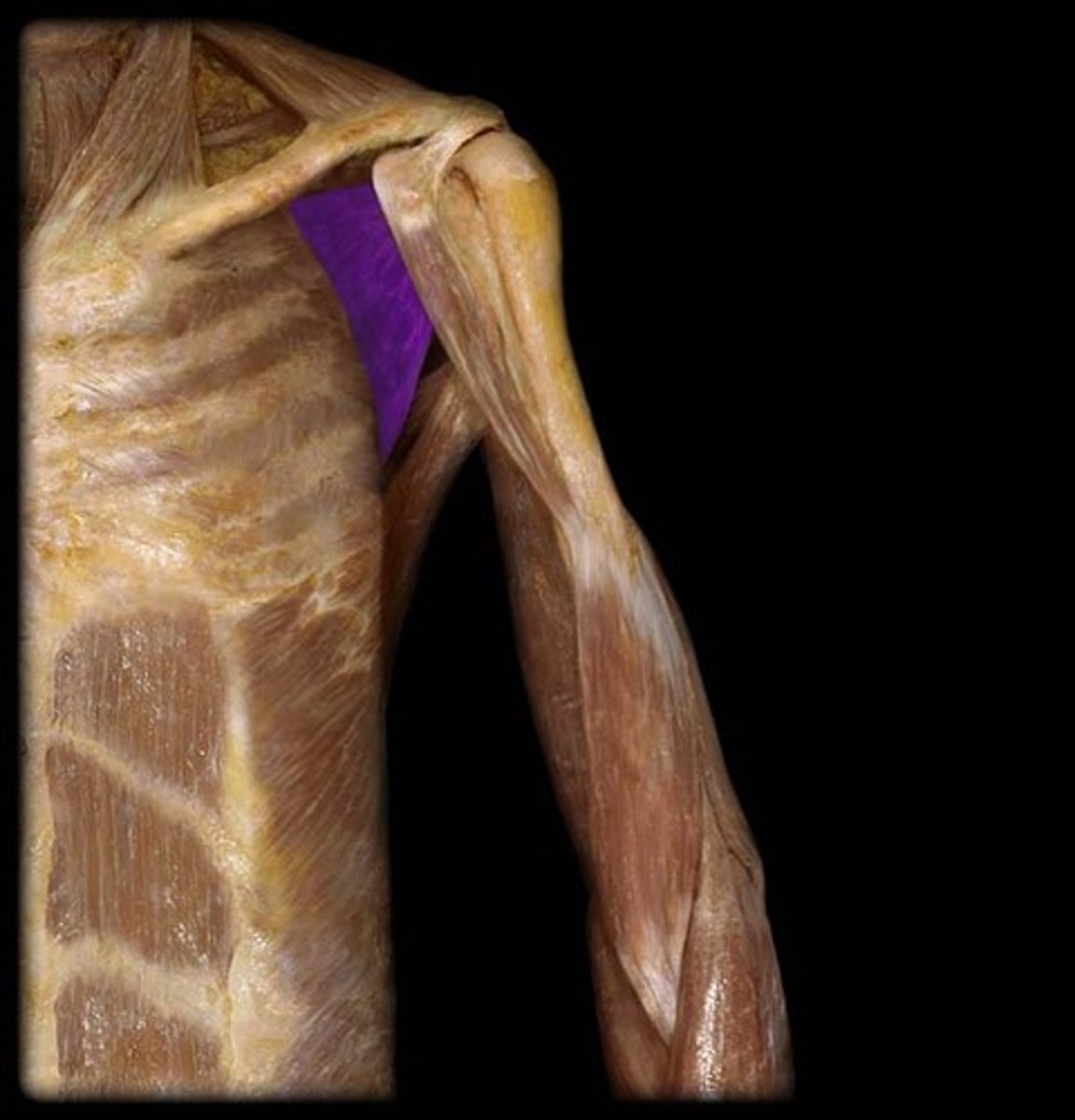
scapular spine
Divides posterior aspect of scapula into supraspinatus fossa (above) and infraspinatus fossa (below)
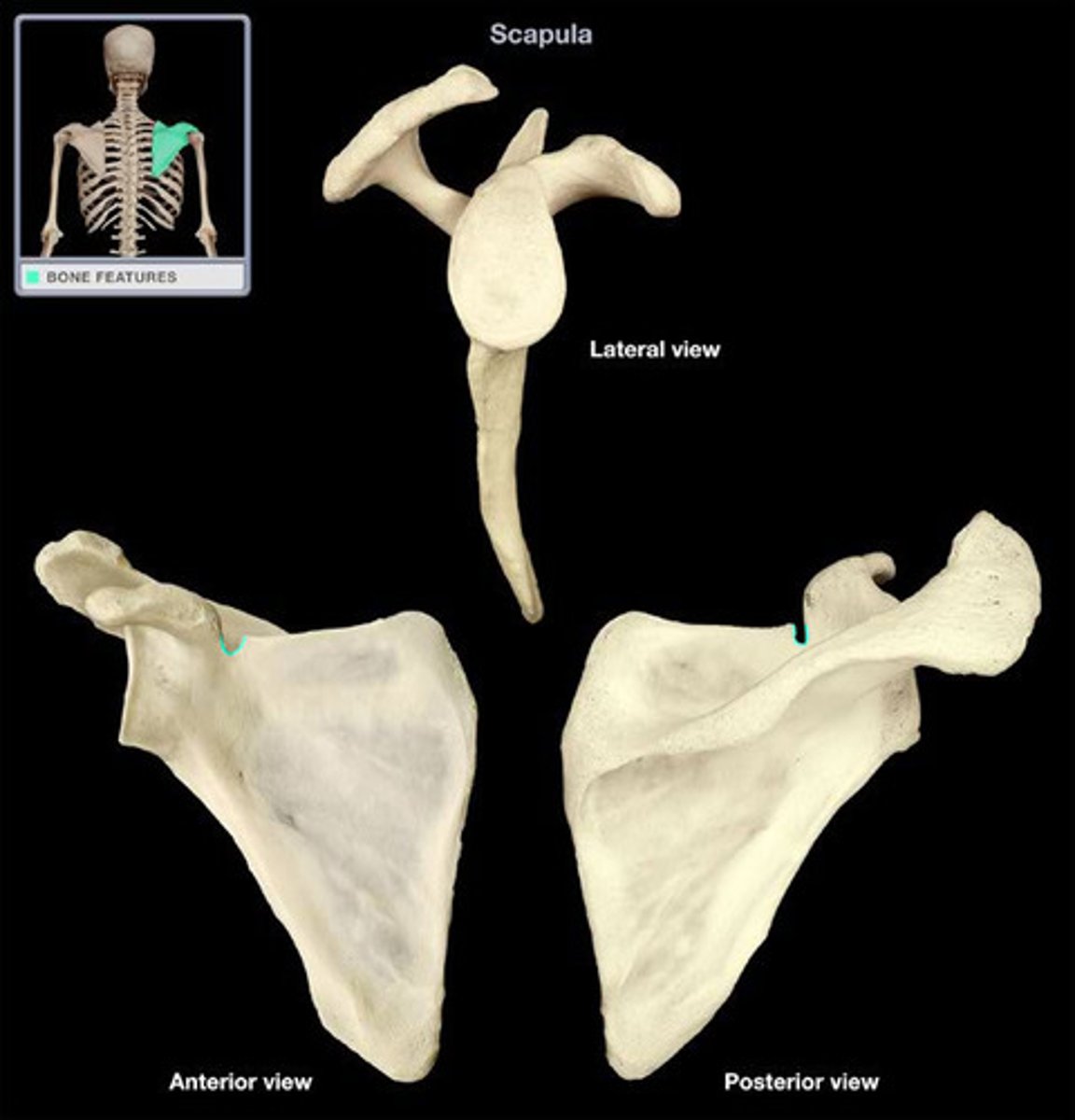
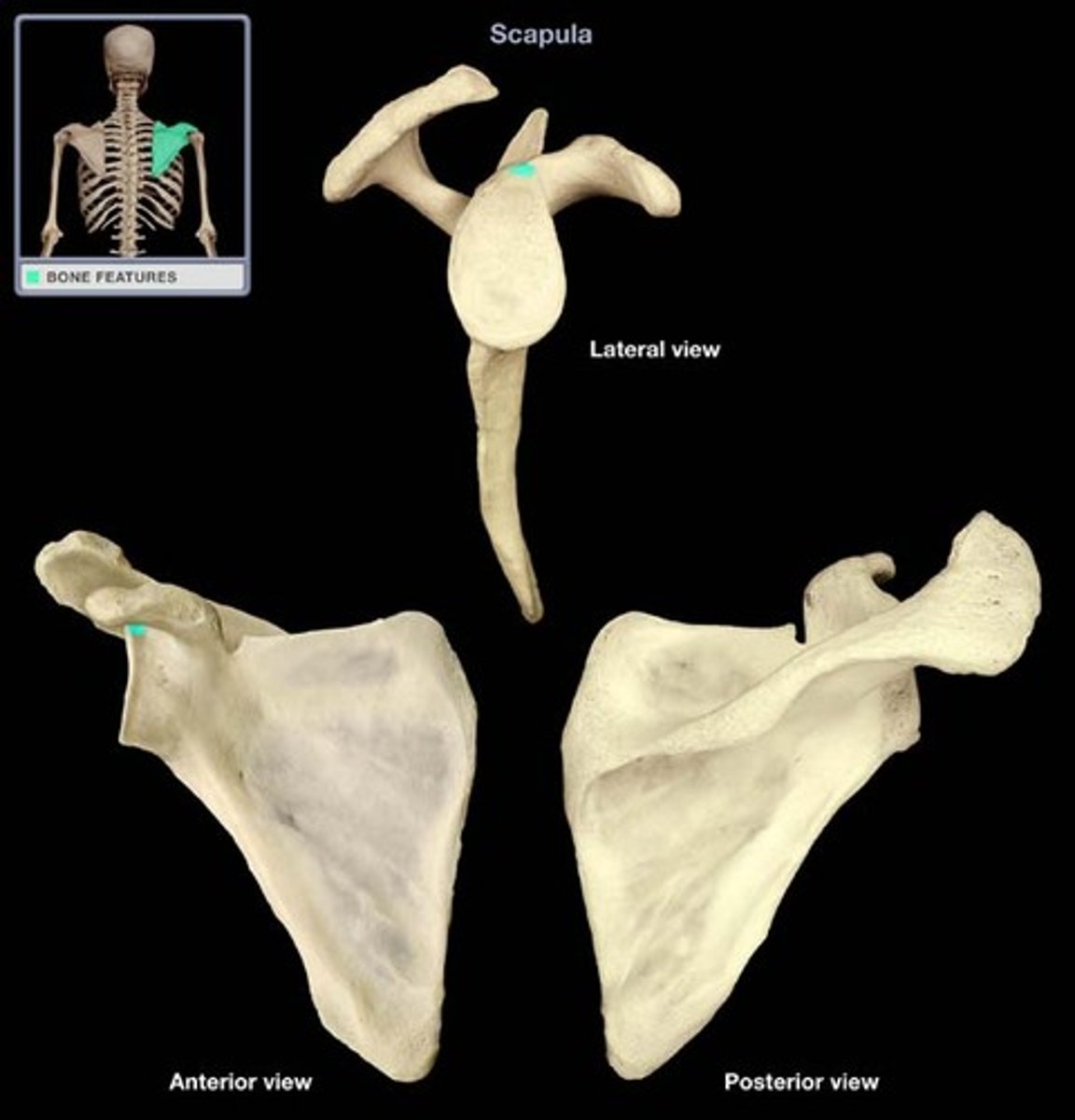
scapular notch
depression in superior border of scapula
acrominion process
the highest portion of the shoulder
coracoid process
process above the glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment
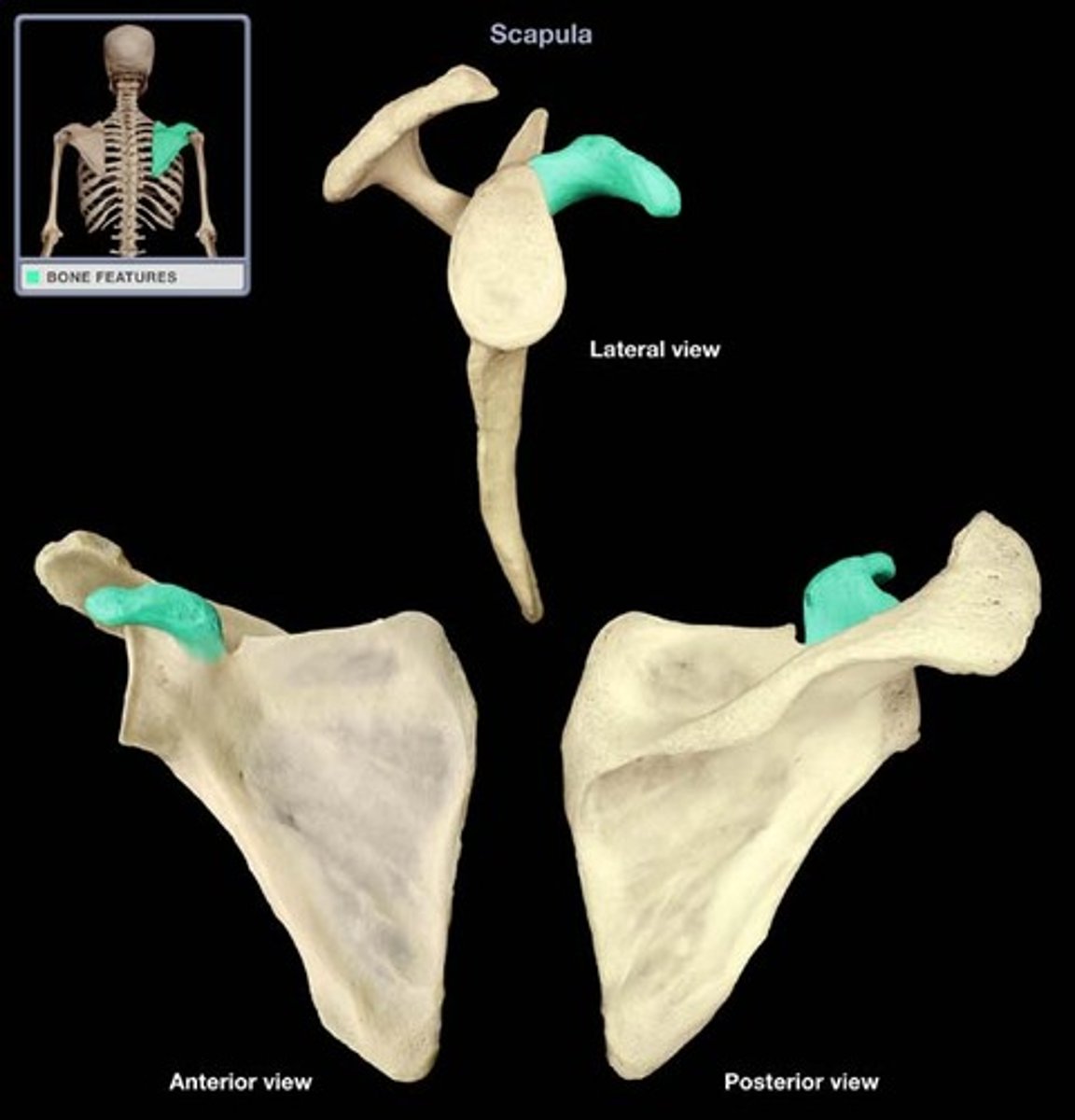
supraglenoid tubercle
prominence superior to the glenoid cavity
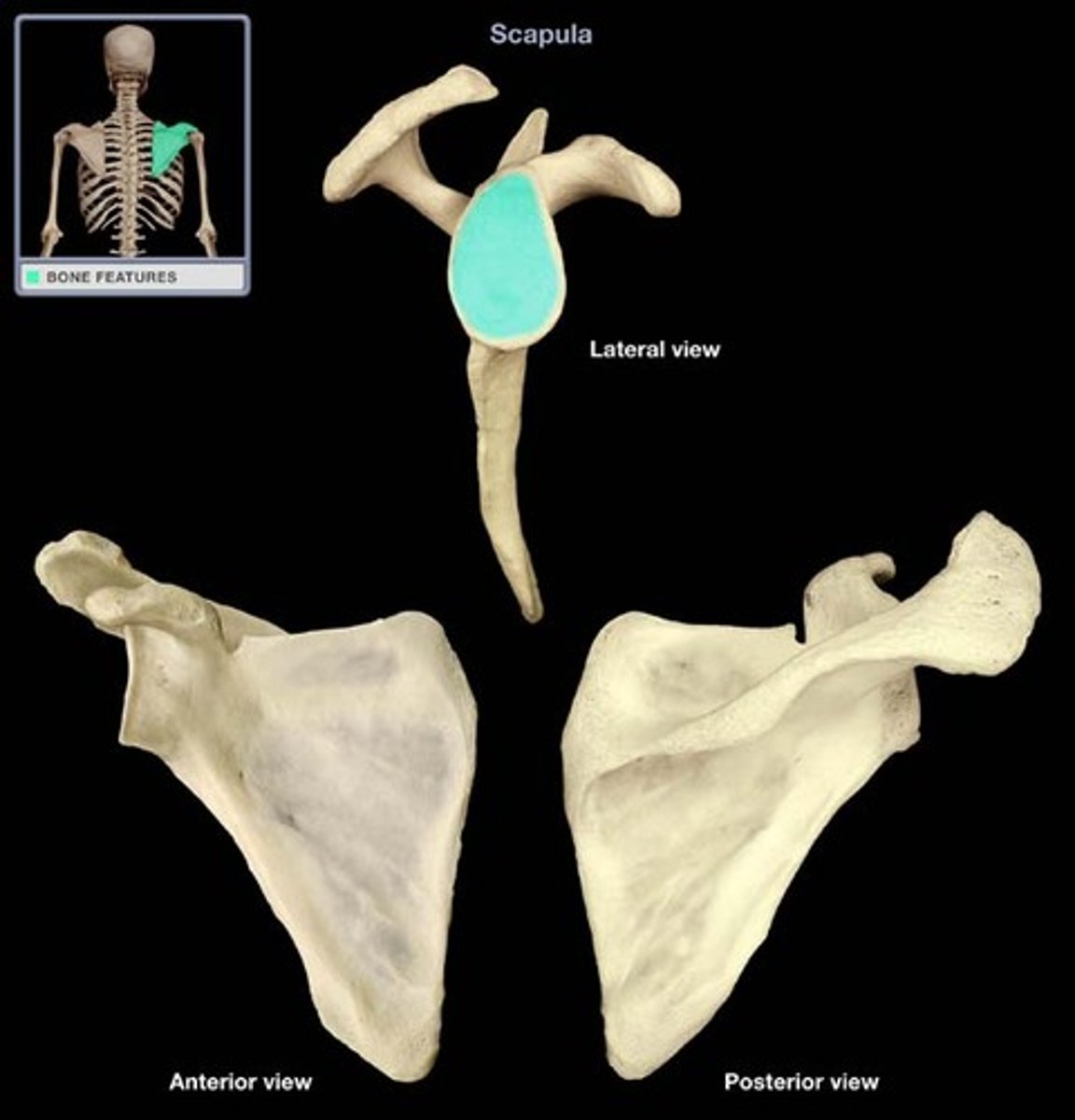
glenoid fossa
The part of the scapula that joins with the humeral head to form the glenohumeral joint.
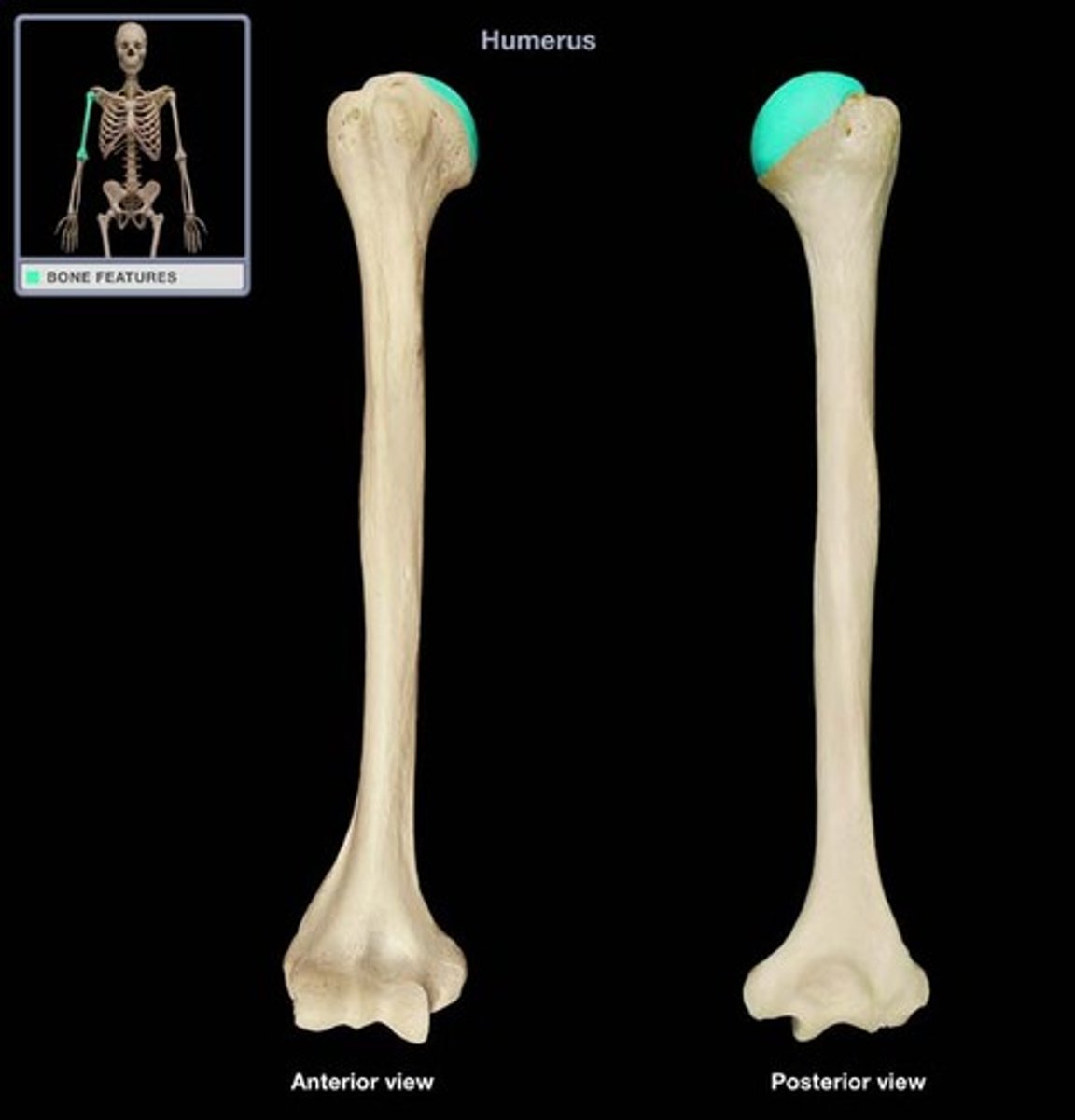
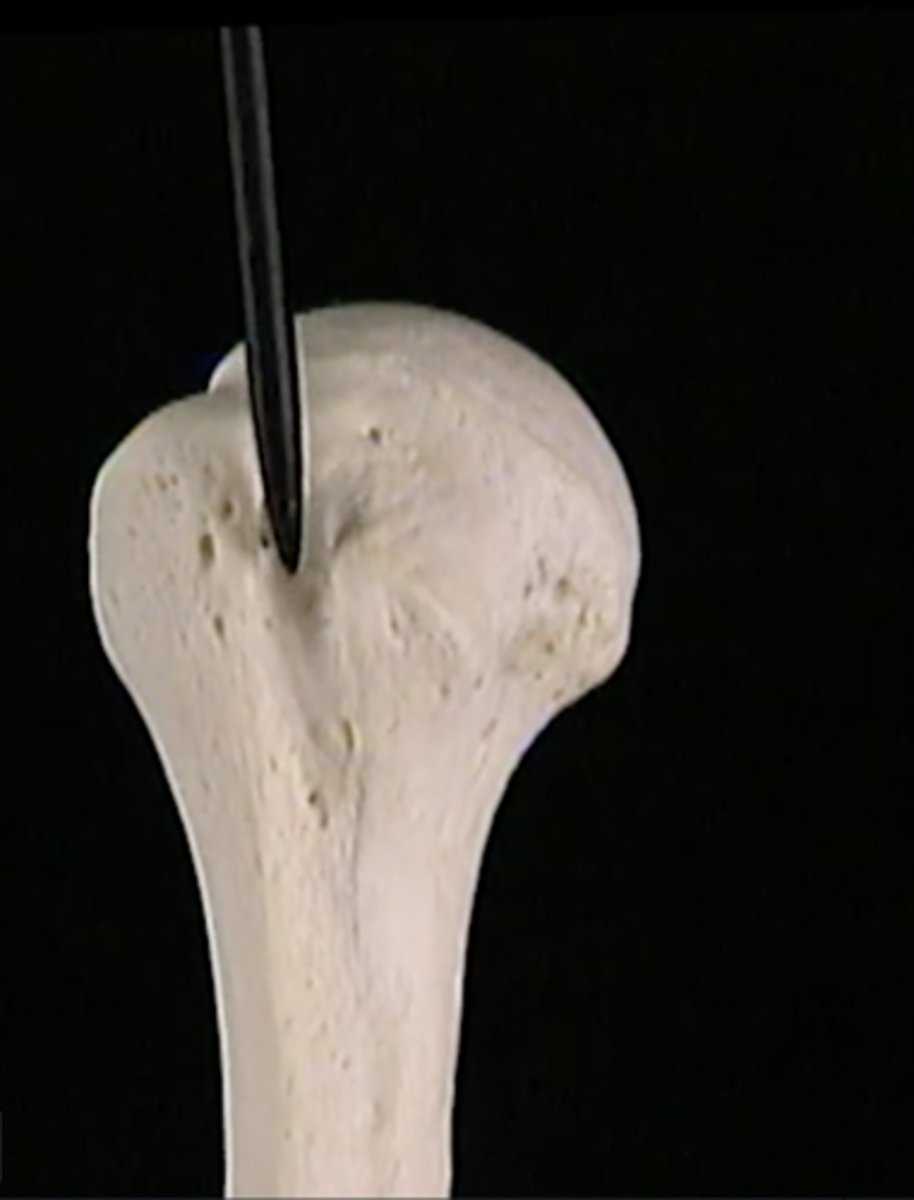
head of humerus
articulates with glenoid cavity of scapula
greater tubercle
Large lateral prominence; site of the attachment of rotator cuff muscles
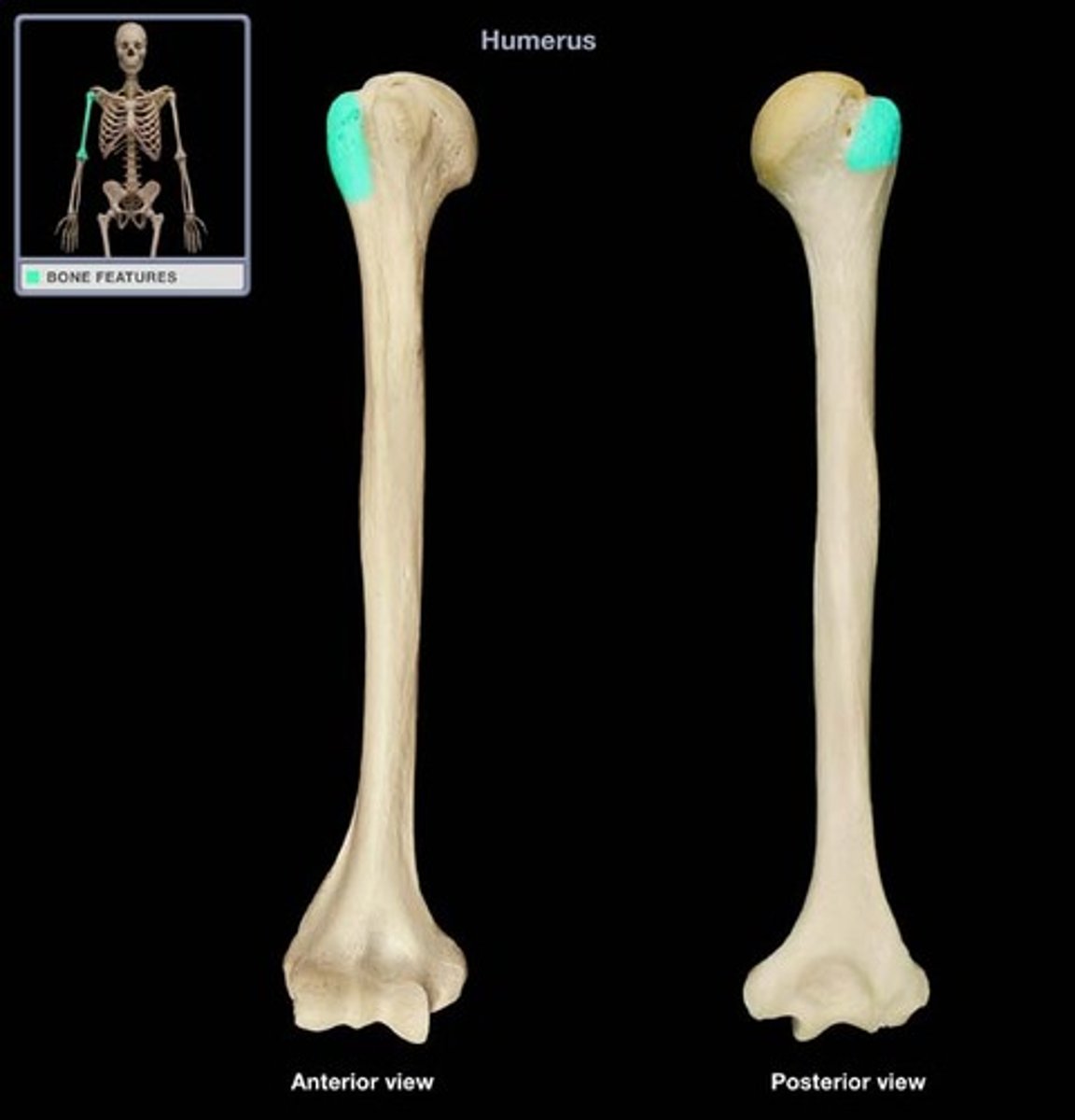
lesser tubercle
insertion of subscapularis
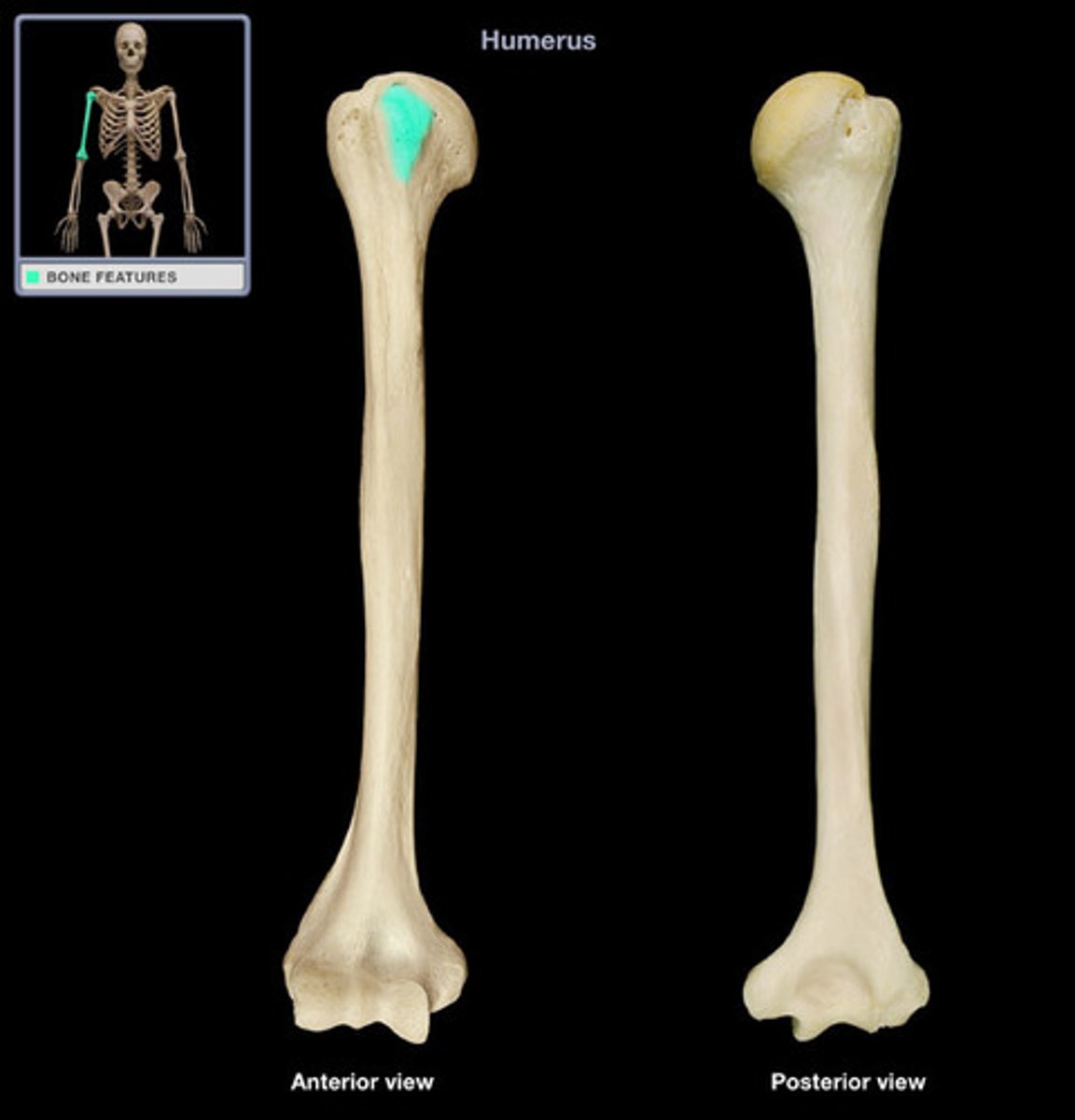
Intertubercular/Bicipital Groove (Sulcus)
a narrow channel between the two tubercles
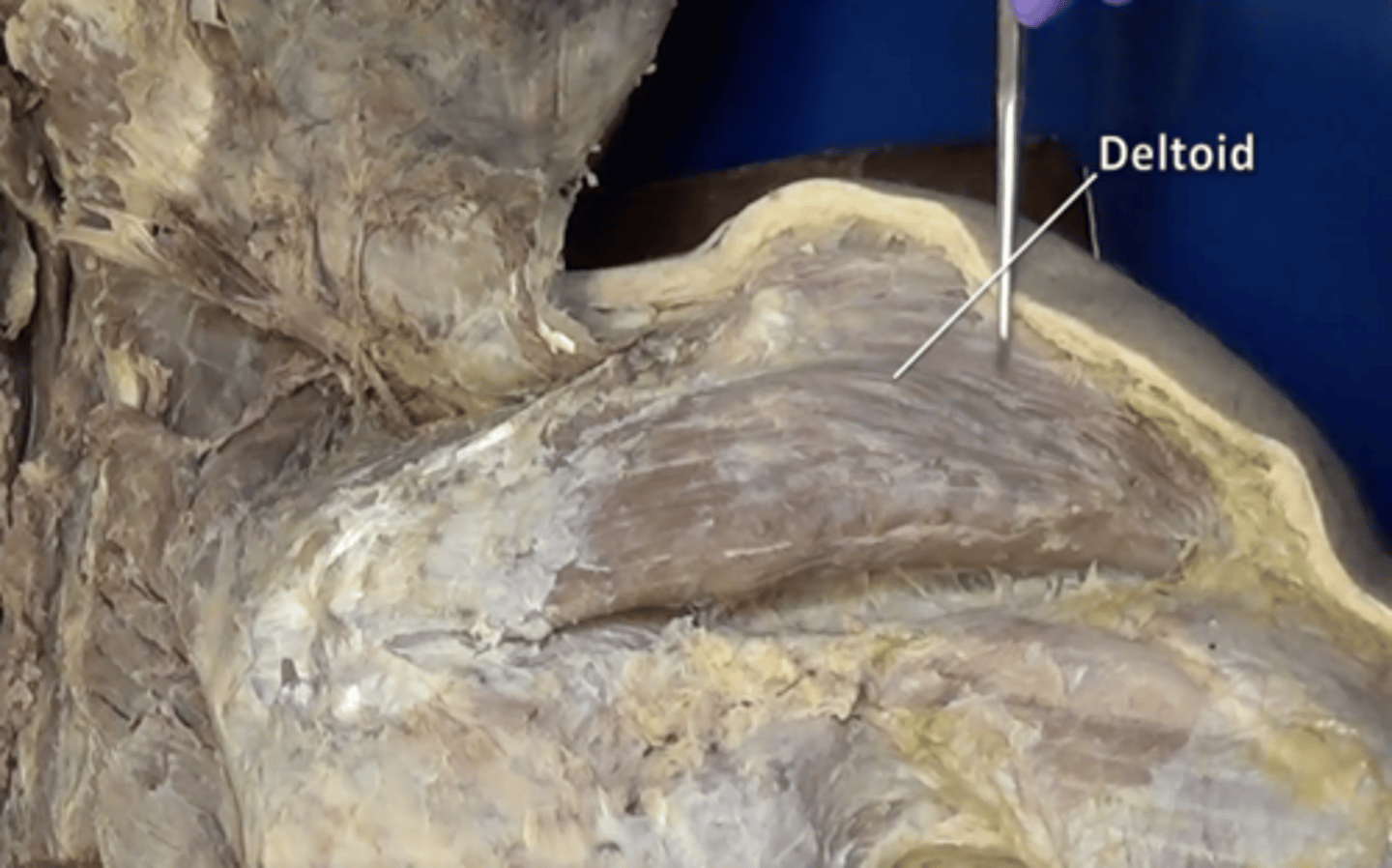
deltoid muscle
forms the muscular cap of the shoulder
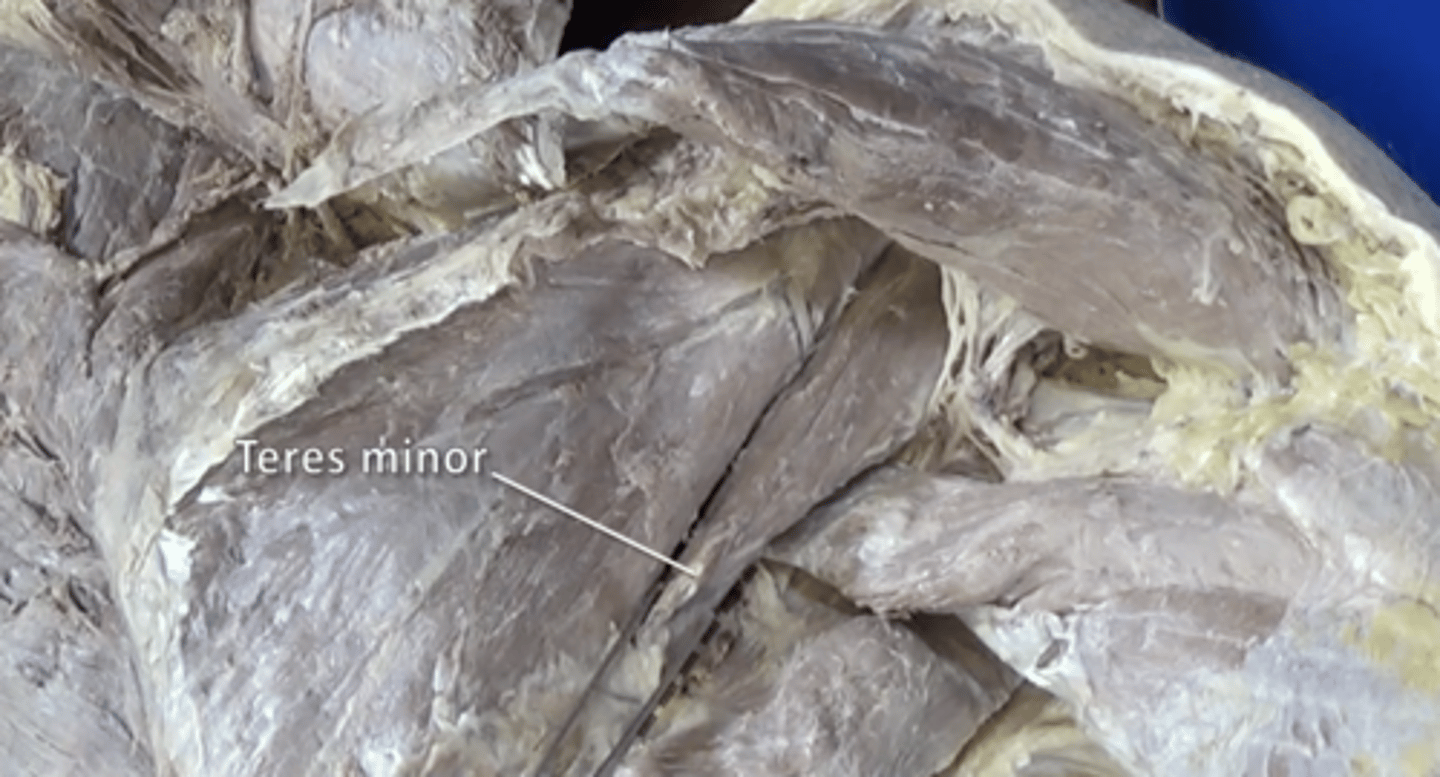
teres minor muscle
adduction and lateral rotation of arm

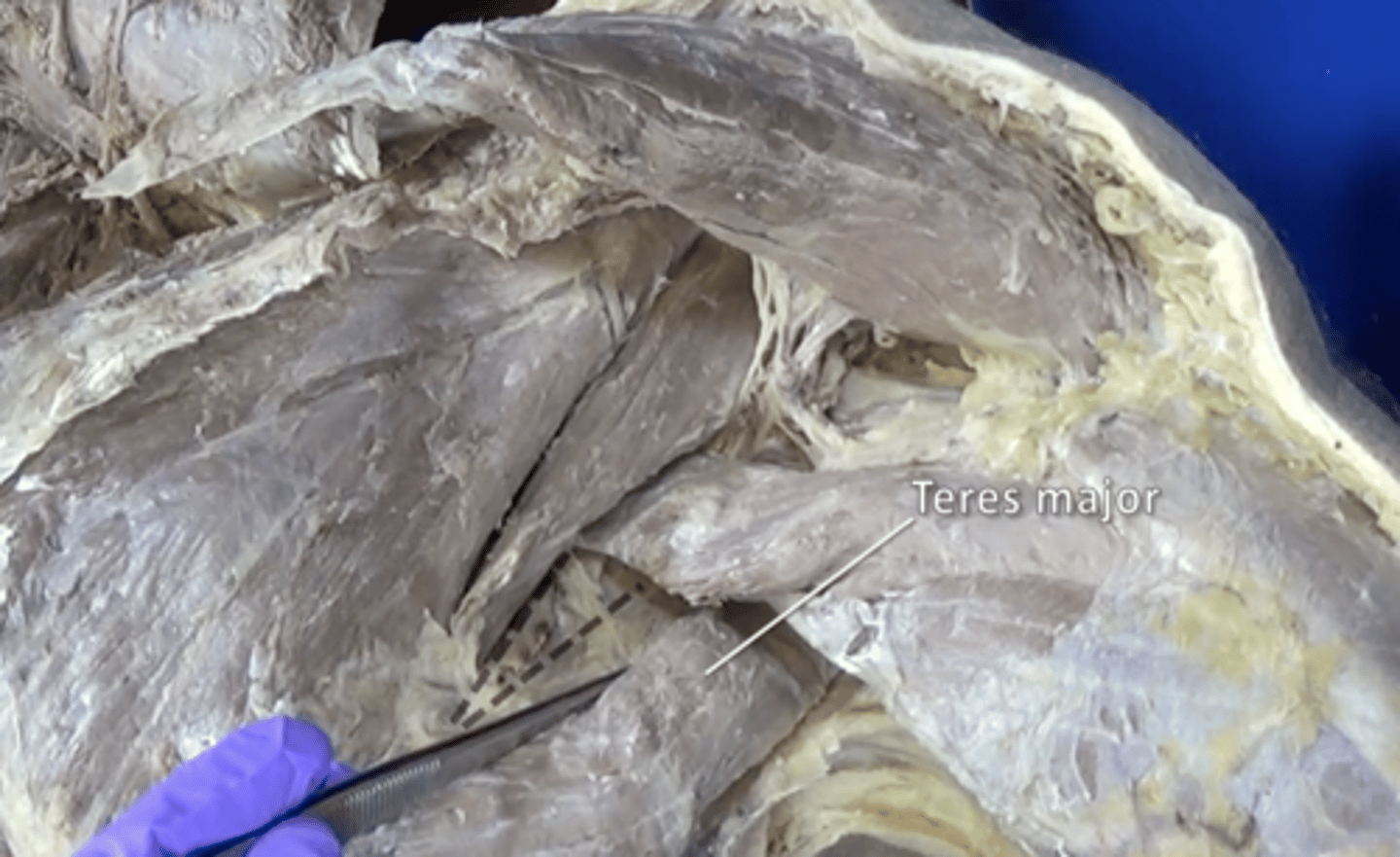
teres major muscle
extension, adduction, and medial rotation of arm
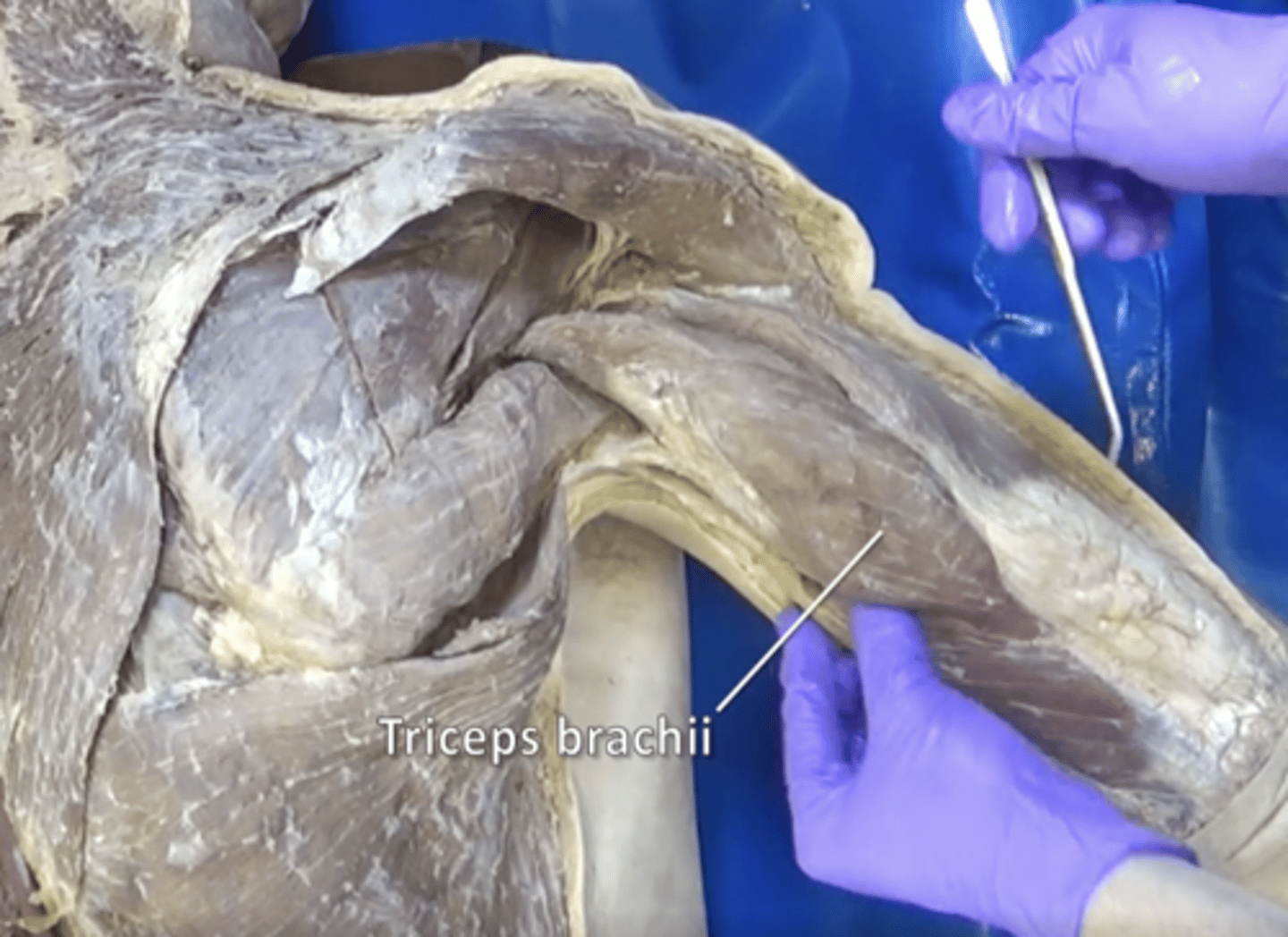
triceps muscle
Contracts to cause extension (straightening) of the arm
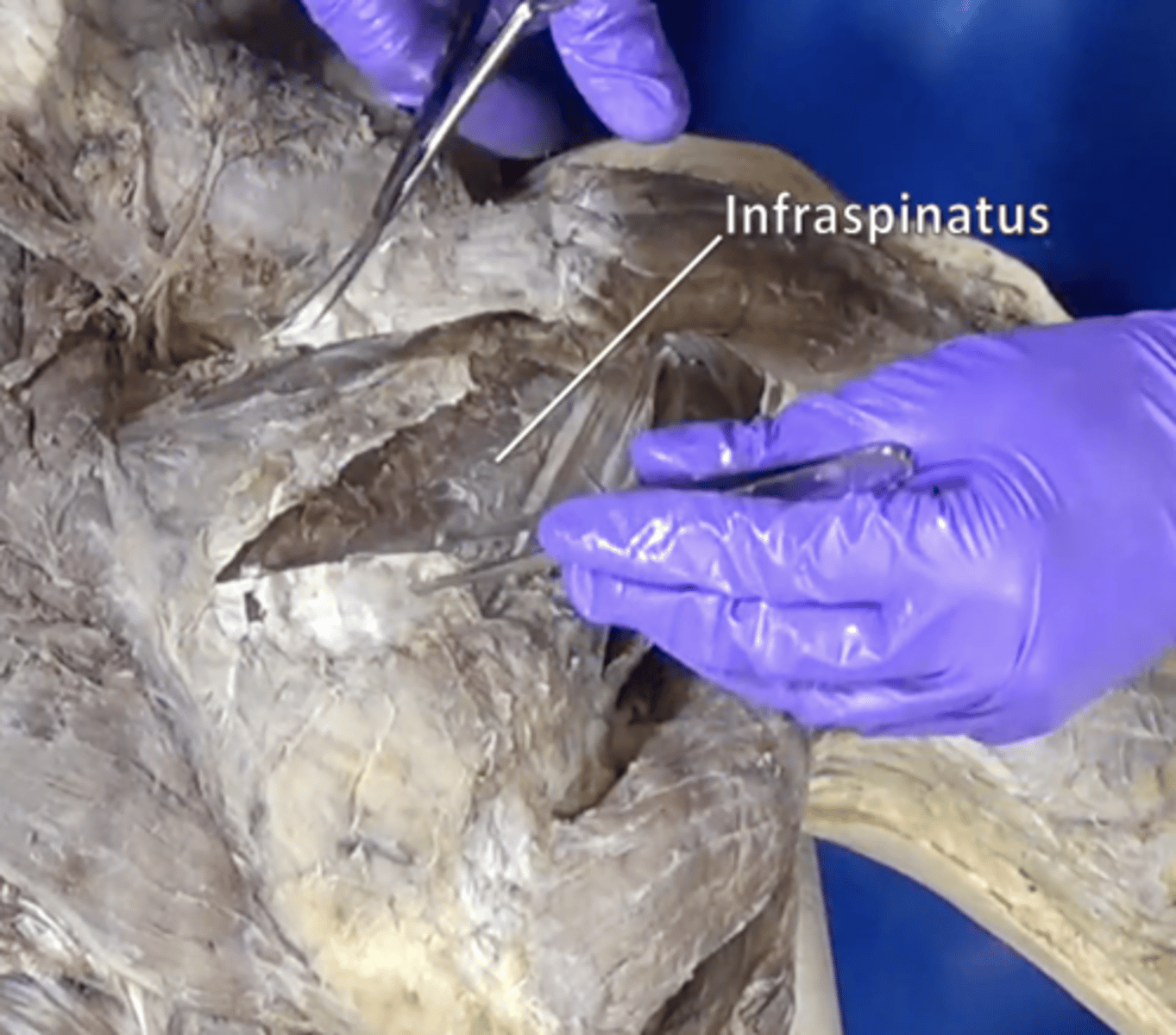
infraspinatus muscle
adduction and lateral rotation of arm
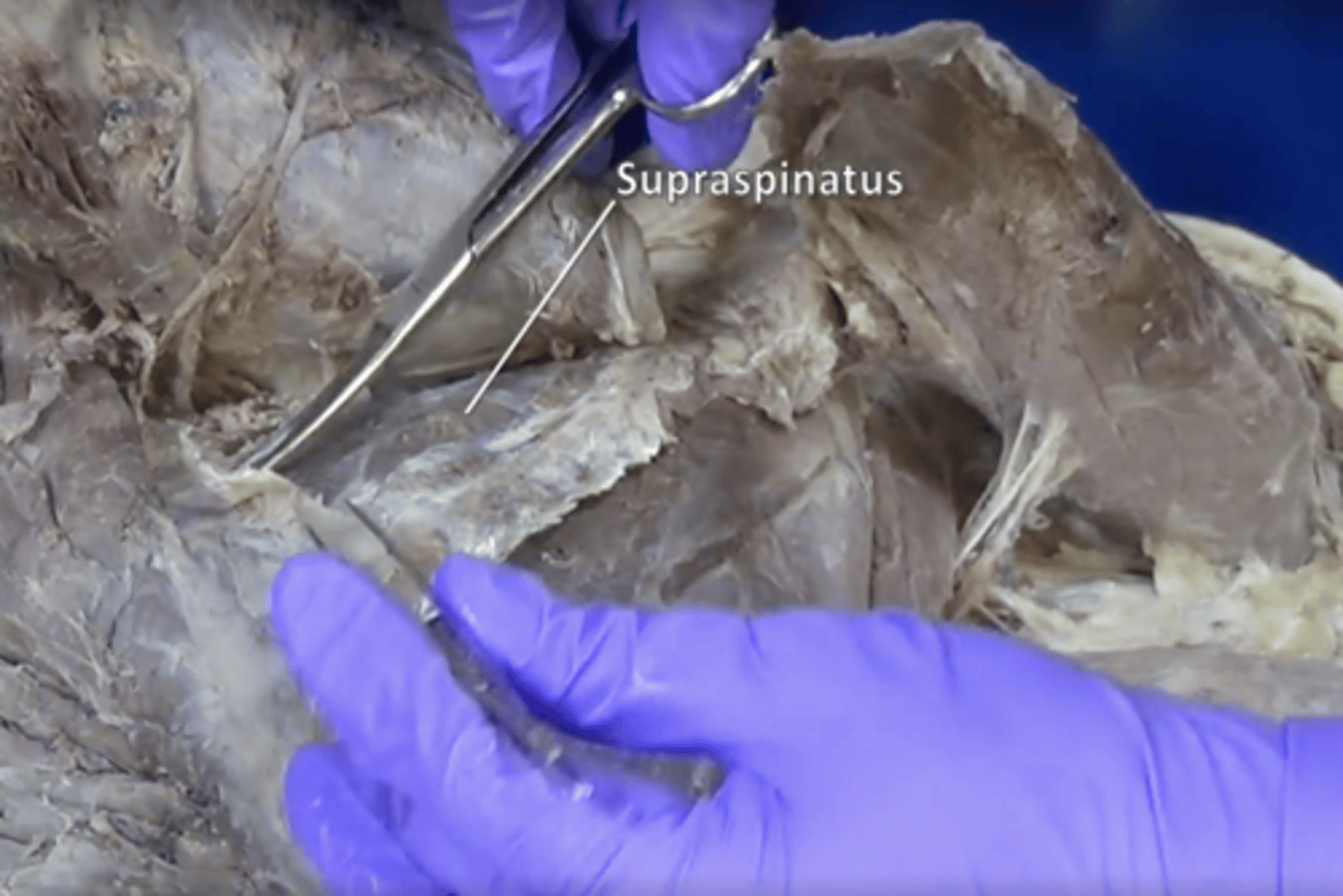
supraspinatus muscle
abduction of arm
Subscapularis muscle
Medial rotation and adduction
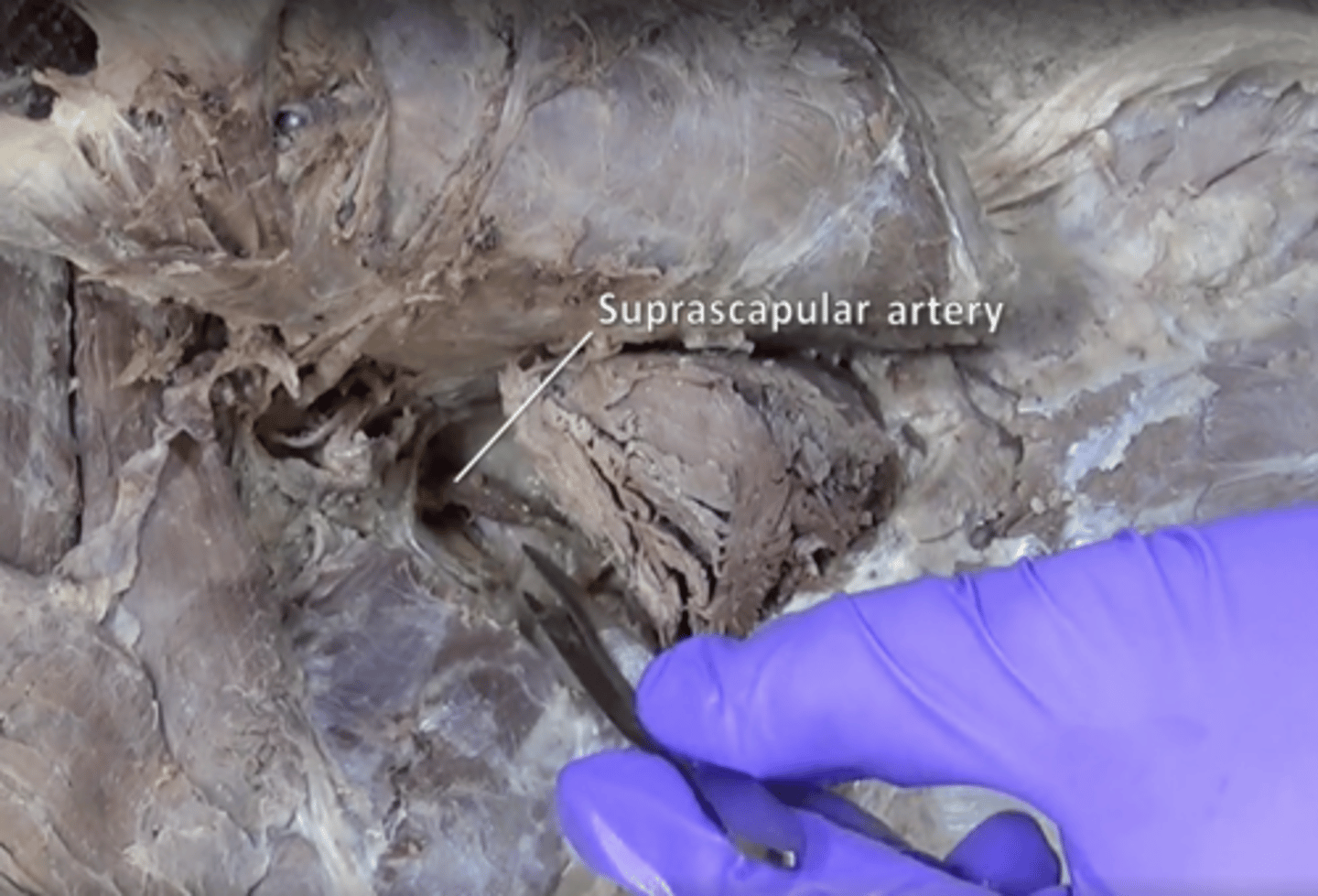
suprascapular artery
supplies supraspinatus and infraspinatus. Located above teres minor and underneath spinatus muscles
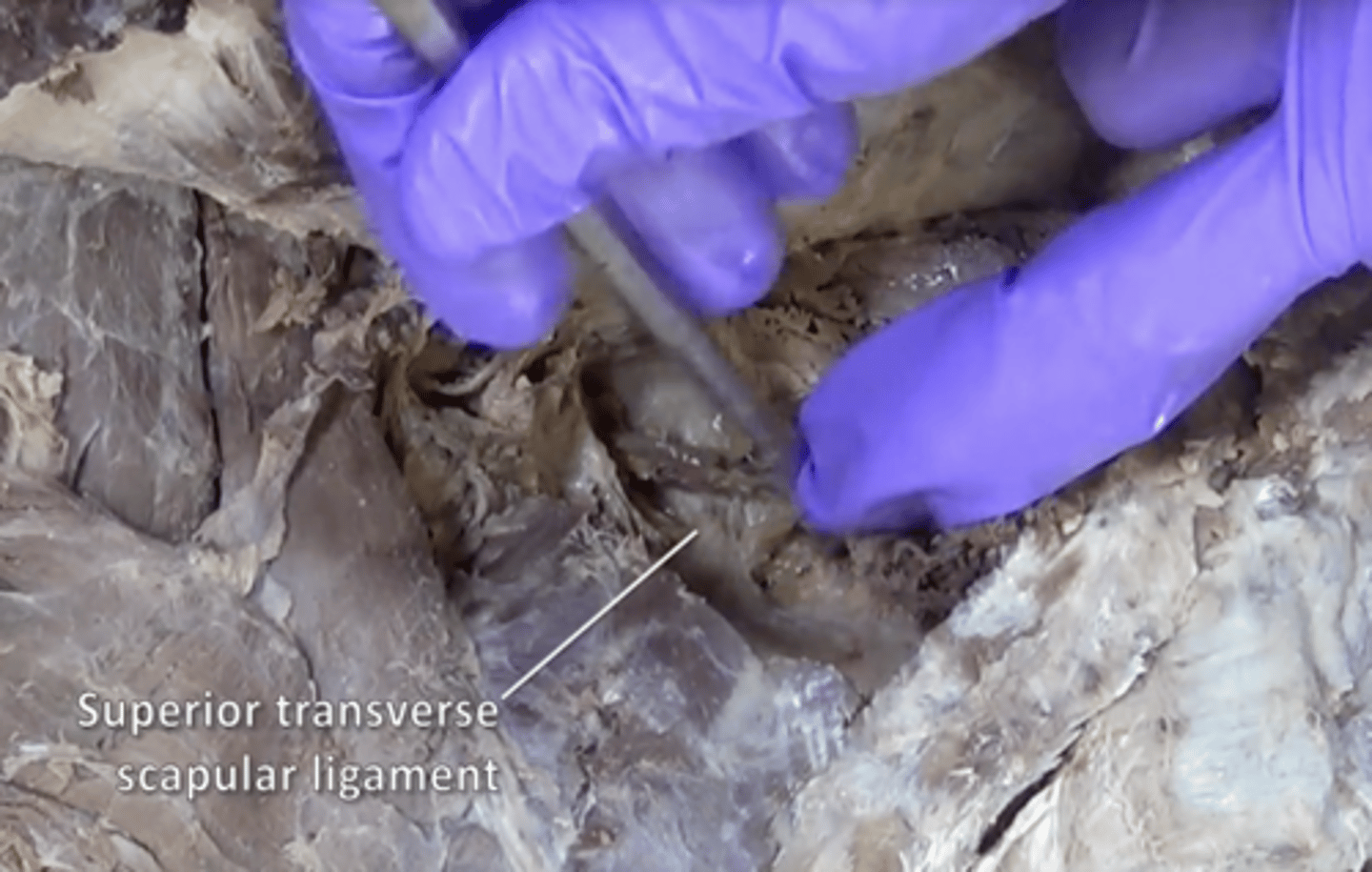
superior transverse scapular ligament
bridges the scapular notch
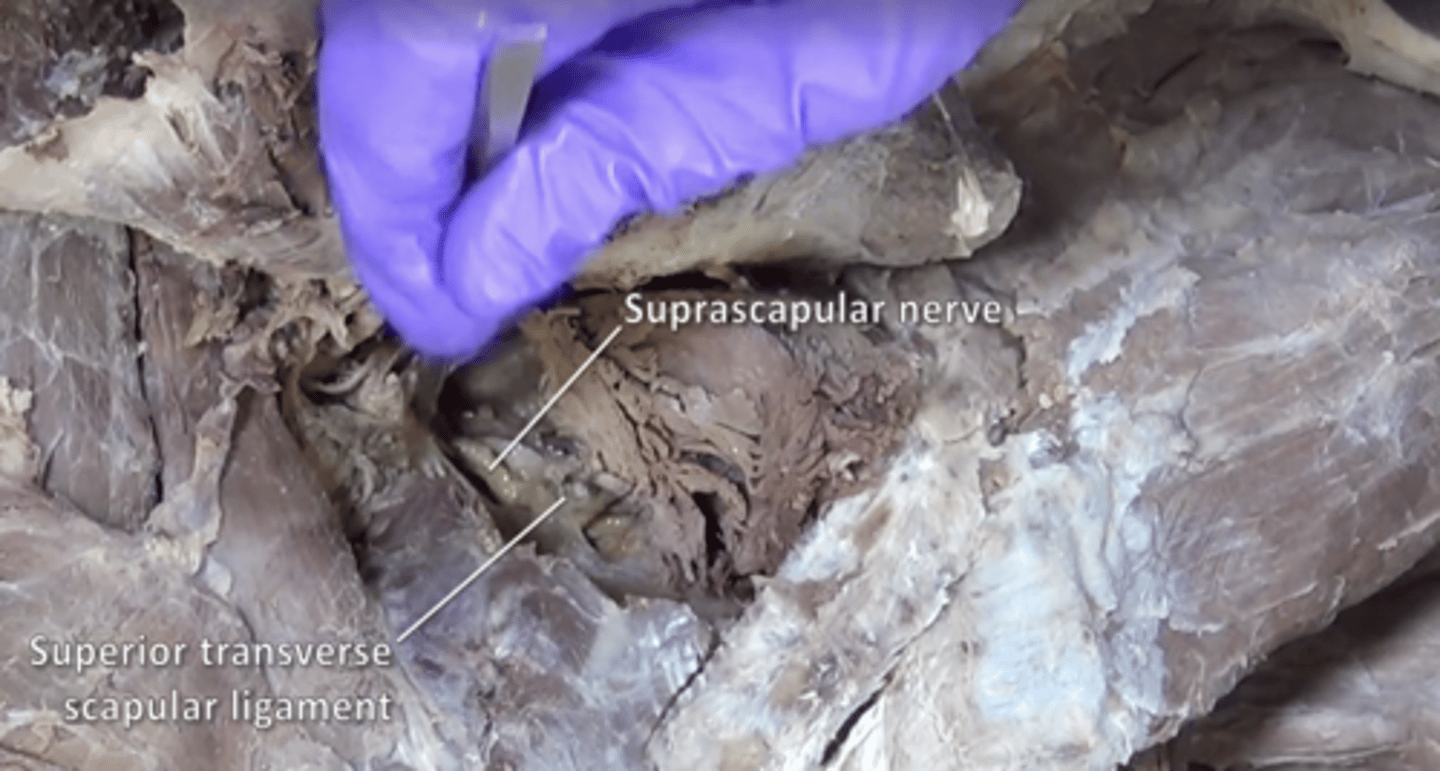
suprascapular nerve
supraspinatus and infraspinatus
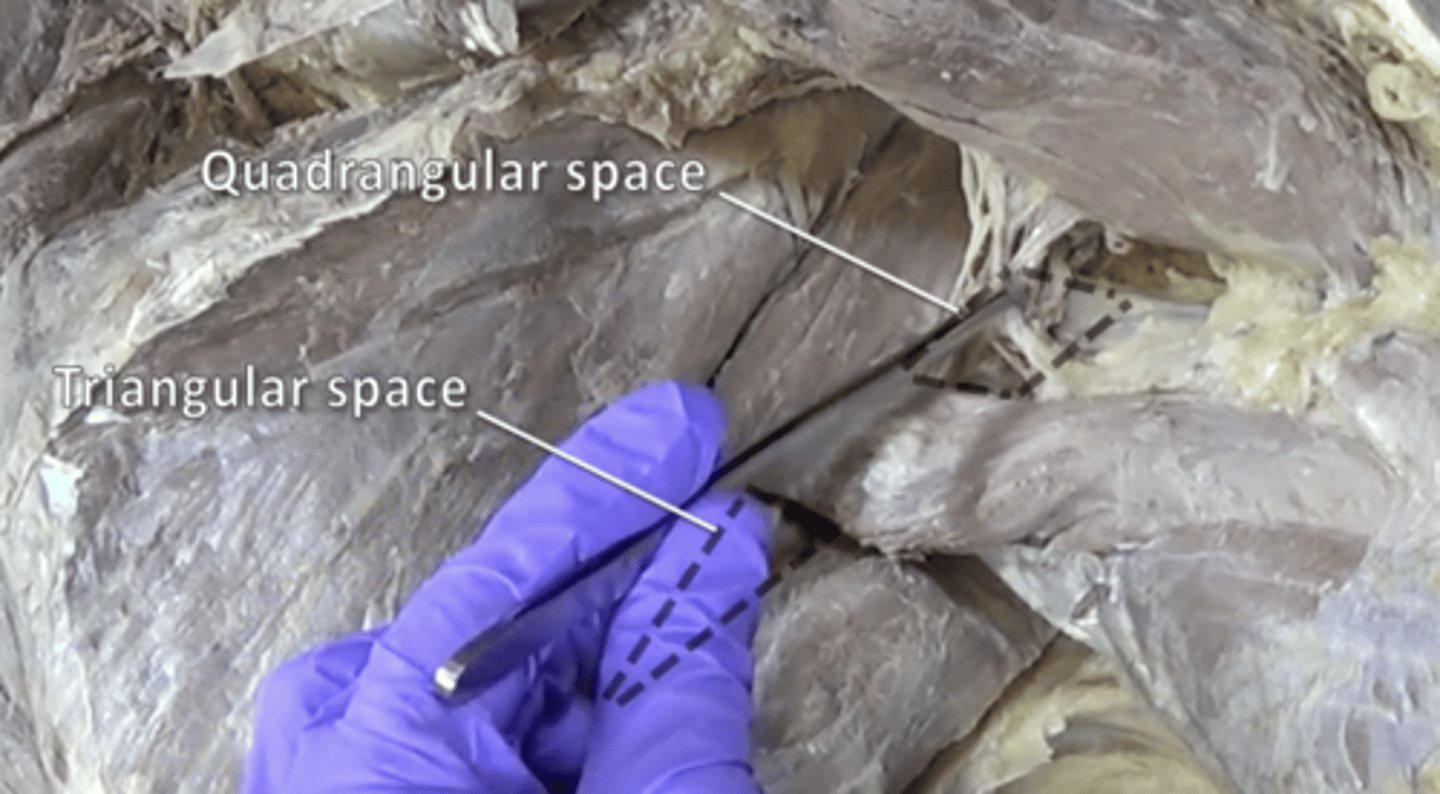
quadrangular and triangular space
quadrangular: axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery; triangular: circumflex scapular artery

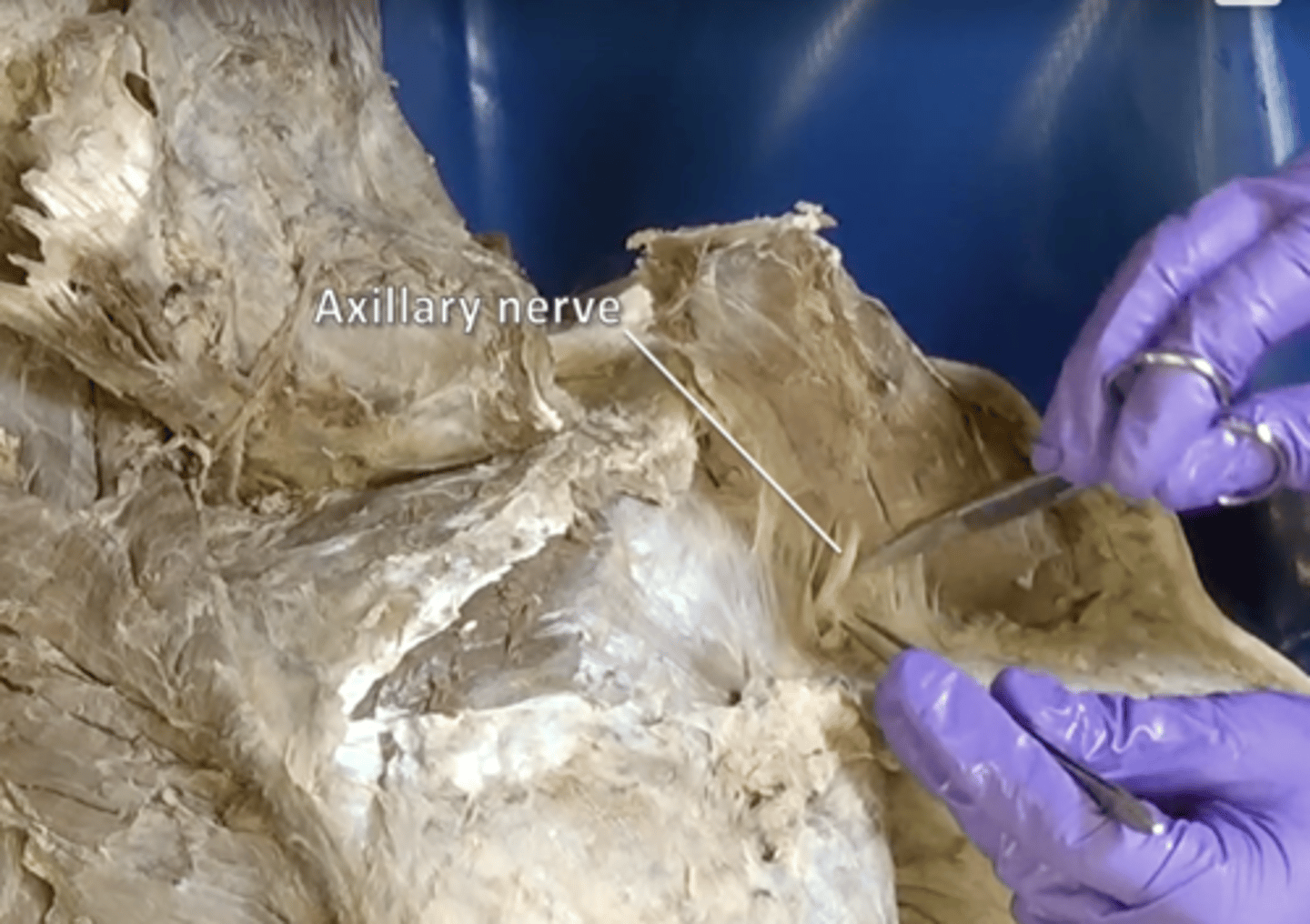
axillary nerve
deltoid and teres minor

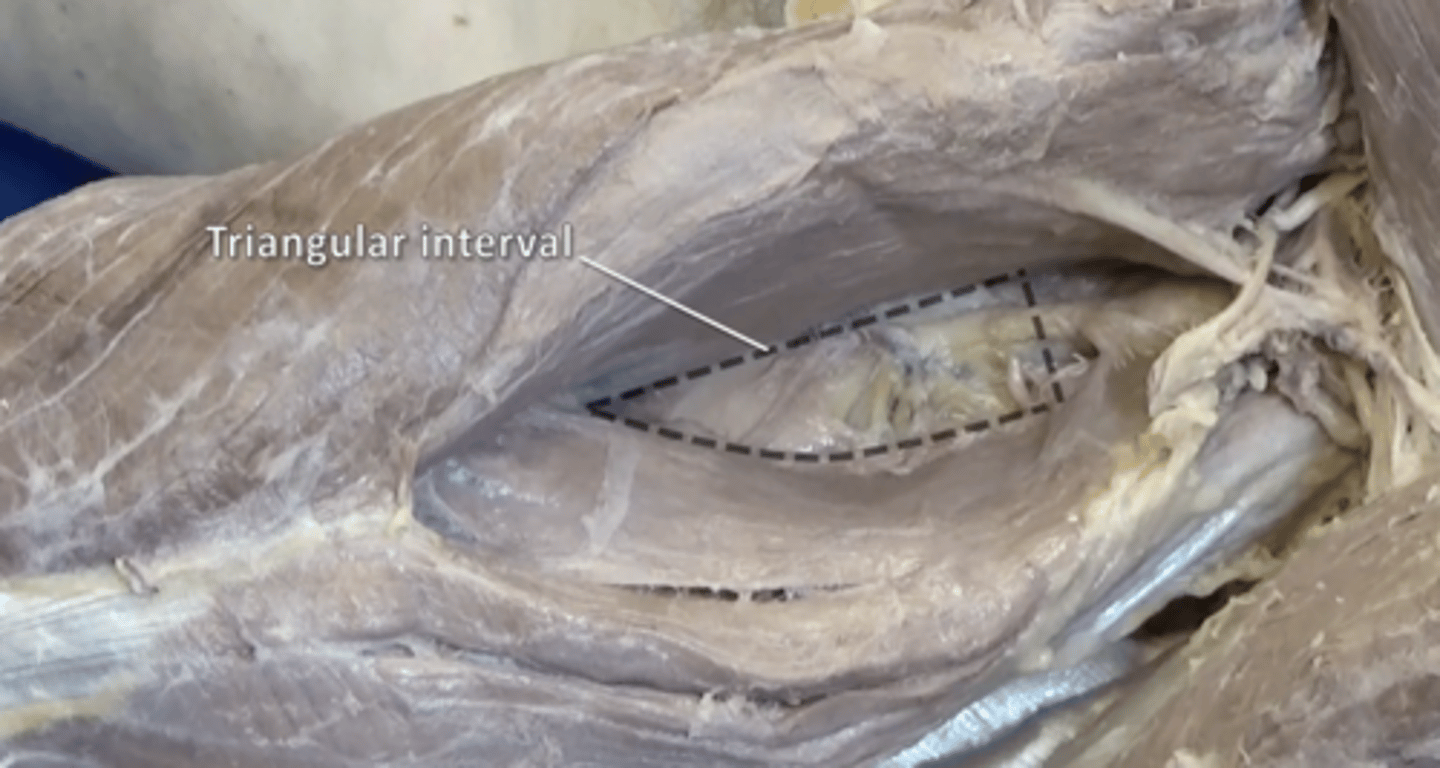
triceps hiatus
profunda brachii artery and radial nerve. Located inferior to quadrangular space

profunda brachii artery
Runs the posterior course of the humerus, is "Deep" between the triceps brachii
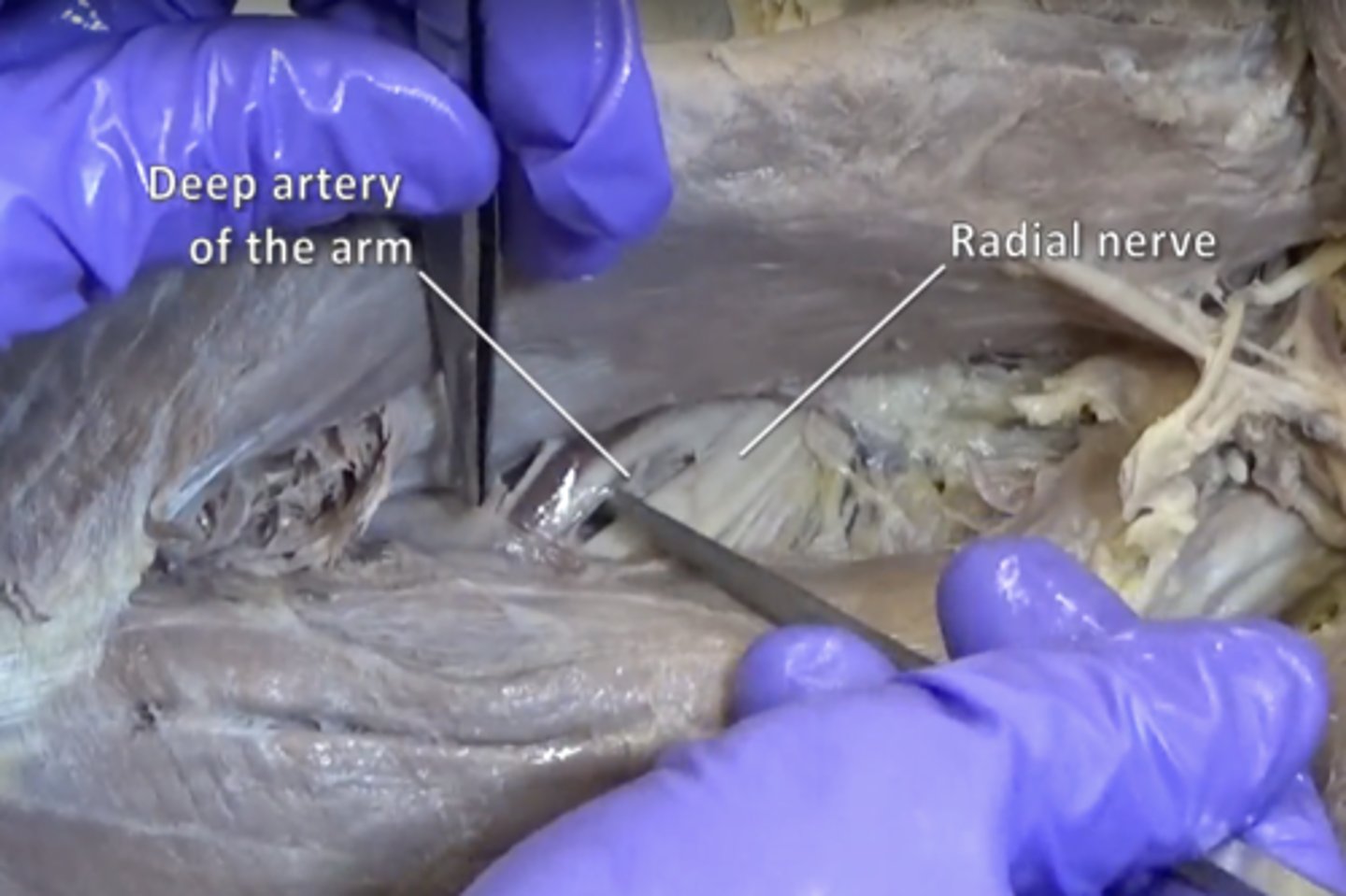
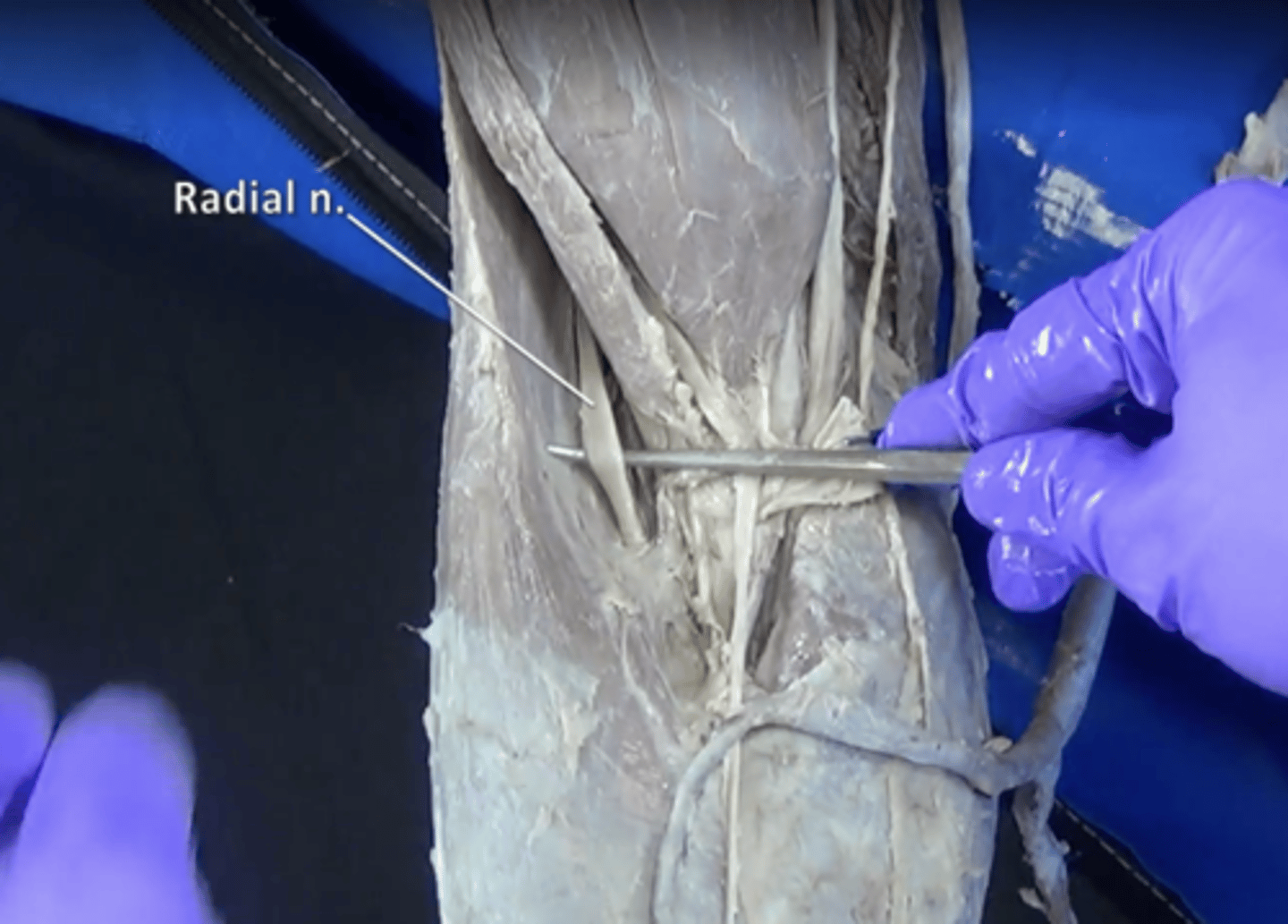
radial nerve
Sensory-motor nerve that, with its branches, supplies the thumb side of the arm and back of the hand.