Eyewitness testimonies & Cognitive Interview
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Outline 2 (opposing) explanations for how anxiety can affect recall
Tunnel theory
High anxiety → weapon focus, other details forgotten
Fight or flight response
Increases alertness and memory
Explain what Johnson & Scott’s study suggest about the influence of anxiety on eyewitness testimony
after a staged argument
fewer participants were able to identify a person carrying a knife with blood on it
than a person carrying a pen with grease on it
This study supports tunnel theory, as focus had been on the weapon
Explain what Yuille & Cutshall’s real life study suggest about the influence of anxiety on eyewitness testimony
After a real robbery in a gun shop
Participants who reported higher anxiety during the robbery had better recall than those reporting lower anxiety
This study suggests higher stress led to increased alertness / recall
Describe Yerkes-Dodson law, including how it applies to memory
Some arousal (anxiety) is good
Too much and too little is bad
Highest recall at moderate levels of arousal (anxiety)
Lowest recall at low or high levels of arousal (anxiety)

Explain what Parker’s study on the impact of a hurricane suggest about the influence of anxiety on eyewitness testimony
tested impact of anxiety on recall after hurricane
IV: anxiety - measured by amount of damage
DV: recall - measured by amount recalled
Mothers & Children recalled more at moderate levels than low levels of anxiety
Mothers recalled slightly more at moderate than high levels
Children recalled significantly more
This study broadly supports Yerkes-Dodson law
Identify 2 types of misleading information and explain how misleading information can affect eyewitness memory
Leading questions
Post-event discussion
New, misleading information from questioning or discussion retroactively interferes with original recall
When information fades / decays people reconstruct memories from a combination of original memories and other (misleading) information
Explain what Loftus & Palmer’s experiment, involving recall of events in a video, showed about the influence of leading questions
Participants watched videos, including one involving cars
They were then asked about how fast the cars were going when they …… each other
The results show leading questions can influence response
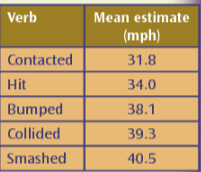
Explain what the 2nd part of Loftus & Palmer’s experiment shows
Participants returned a week later and were asked if they’d seen broken glass (non-existent)
Participants who’d heard ‘smash’ were more likely to say ‘yes’
This study shows the genuine effect on memory, (memory compliance)
Explain what Gabbert’s experiment, using videos of crimes, showed about the influence of post-event discussion
Participants watched videos of a crime from different angles and then discussed what they saw
71% of participants recalled aspects of the crime they didn’t actually see
These results show how participants incorporated aspects of what they had been told into their memories
This study shows the strong influence of post-event discussion on eyewitness recall
Identify the real-world implications of findings on the influence of misleading information on eyewitness memory
Miscarriages of justice
during police questioning (affecting recall)
Witnesses confidence will be largely unaffected
Jurors are impressed by eyewitness evidence
Identify the 4 elements of the cognitive interview
Report everything
Reinstate context
Reverse Order
Change Perspective
Explain how and why report everything and reinstate context are used in the cognitive interview
Report everything: no matter how minor the detail report it
Reinstate the context: put yourself mentally back in the situation
Based on retrieval failure, RE and RC provides context and state cues, so memory is triggered
Explain how and why reverse order and change perspective are used in the cognitive interview
Reverse order: describe what happened from the end back to the beginning
Change perspective: Put yourself in the shoes of someone else who was there
Both RE and CP disturb the effects of schemas on recall, making dishonesty harder
Explain what Kohnken’s study showed about accuracy of eyewitness testimony in the cognitive interview compared to standard interviews
Meta-analysis of 55 experiments
41% increase in accurate recall compared to standard police interviews
Some increase in inaccurate information
Explain what Milne & Bull’s study showed about the effectiveness of the different components of the cognitive interview
RE and RC are the most important techniques
Effective on own or in combination with each other
Others are less important / effective
Explain the main practical problem with using the cognitive interview during public investigations
Time Consuming - takes much longer than standard interview to conduct