RCIS
1/466
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
467 Terms
negative
what charge is AVR
atrial depolarization
p wave
ventricle depolarization
QRS
ventricles repolarize
T wave
sa, av, bundle of his, r and l bundle branches, purkinje fibers
order of conduction system
deep s wave v1 larger r wave v5
signs in EKG for left ventricle hypertrophy, 2
R wave in v1 positive to v6 negative
signs in EKG for right ventricle hypertrophy, 1
peak T waves
Ekg sign for early MI
inverted T waves
EKG sign for ischemia
low q wave
EKG sign for infarction
mitral regurgitation
complication post MI in inferior wall
inferior wall
Leads 11, 111, avf part of the heart
RCA
Leads 11, 111, avf coronary
inferior wall
RCA is affected by what side of the heart
anterior wall
Leads v1,v2,v3,v4 is what part of the heart
LAD
anterior wall of the heart affects what vessel
v1,v2,v3,v4
what leads are affected for LAD
lateral wall
Leads 1, avl, v5, v6 affect what part of the heart
circumflex
The lateral wall affects what vessel
2nd degree type 2 or infranodel 3rd heart block
what arrythma do you need to worry about with an anterior wall MI
I negative avf negative
what does the EKG look like for extreme right axis deviation; I and avf
right axis deviation
lead I is negative and lead avf is positive; ekg
I postive avf positive
whats a normal ekg leads I and avf look like
I positive avf negative
what does the ekg look like for left axis deviation
60-100
rate of sinus rhythm
40-60
rate of AV rhythm
20-40
rate of ventricle rhythm
atria and ventricles
sympathetic nervous system effects what parts of the heart
increase hr, increase conduction, increase irritability
sympathetic nervous system causes what
only atria
parasympathetic nervous system effects what parts of the heart
decrease hr, decrease conduction, decrease irritability
parasympathetic nervous system causes what
0.04
each box in ekg is how many seconds
interventricular groove
where does the LCA lay
sinus of valsalva
what protects coronary arteries during systole
diastole
most coronary blood flow is during
central venous pressure
another term for RA pressure
aortic diastole
what is the driving pressure
ao diastole - ra pressure
how do you figure the amount of pressure to the coronaries
thebesian veins
what empties deoxygenated blood to left ventircle
vasodilates
what does intracoronary adenosine do
double
what should adenosine do to pressure
Fractional flow reserve
the ratio of maximal flow in stenotic artery to maximal flow in same artery
less than 0.80
at what value do you intervene an FFR lesion
0.5-1 mm/sec
how many seconds should an IVUS pullback take
1mm
dot to dot in IVUS is what measurement
IVUS
what is good to access stent deployment
increases aortic end diastole, increases coronary perfusion
what does the balloon pump do
intima, basal lamina, media, adventitia
layers of a cell
media
what part of a cell contains smooth muscle cells
adventitia
what part of the cell contains connective tissue
vasovasorum
blood vessels own supply feeds the wall of coronaries itself
posterior and inferior
what does the PDA feed wall
85
what percent of people are right dominant
7
what percent of people are co dominant
8
what percent are left dominant
RAO
Cx is in front, what view
LAO
LAD is in front, what view
RAO
spine is on left, what view
LAO
spine is on right, what view
RAO
apex points to the right, what view
LAO
apex points to the left, what view
RAO
RCA looks like an L, what view
LAO
RCA looks like an C, what view
cranial
diaphragm seen on the bottom of screen, what view
caudal
spine is seen on bottom left or right, what view
rao cranial
view
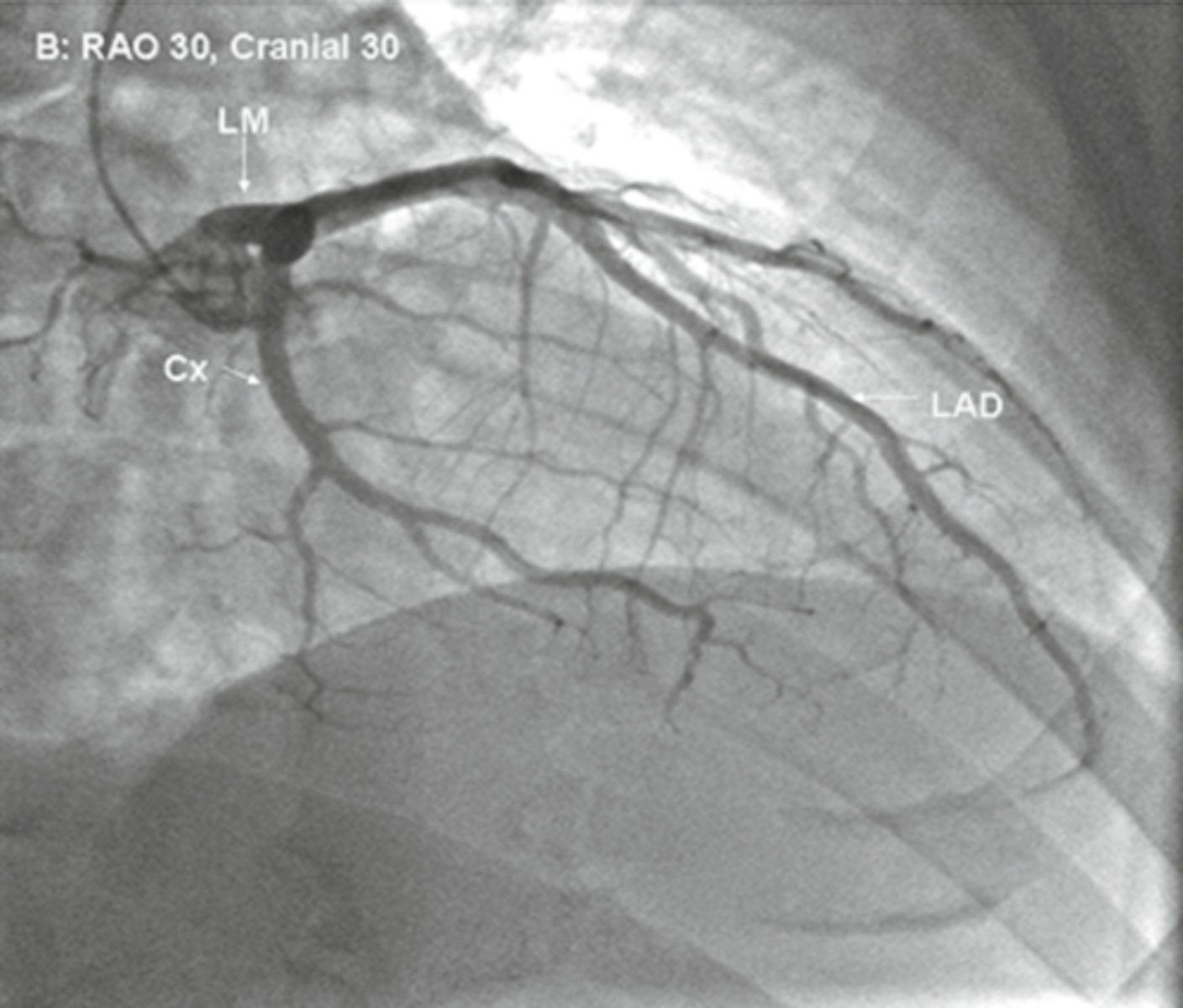
rao caudal
view
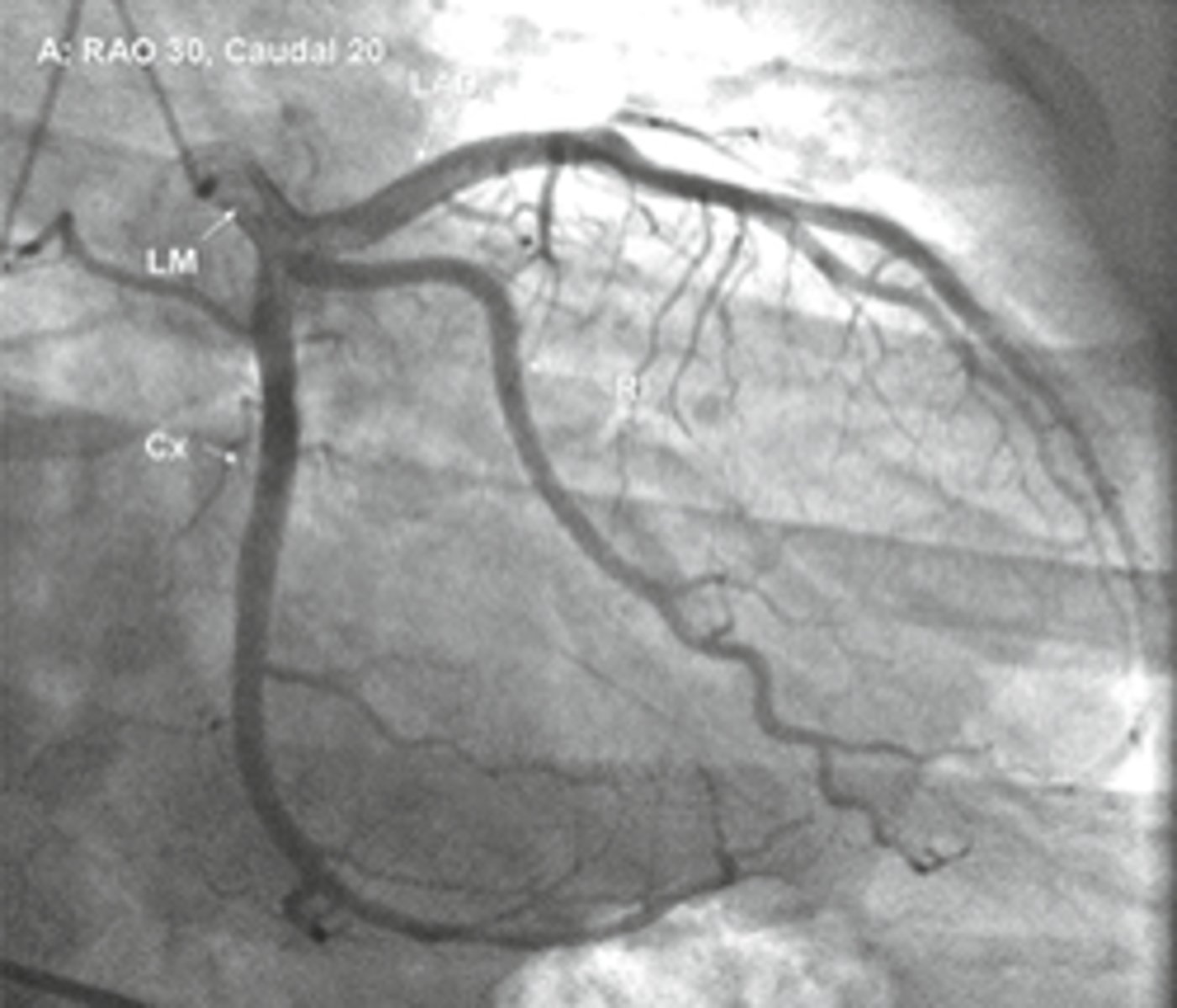
lao cranial
View
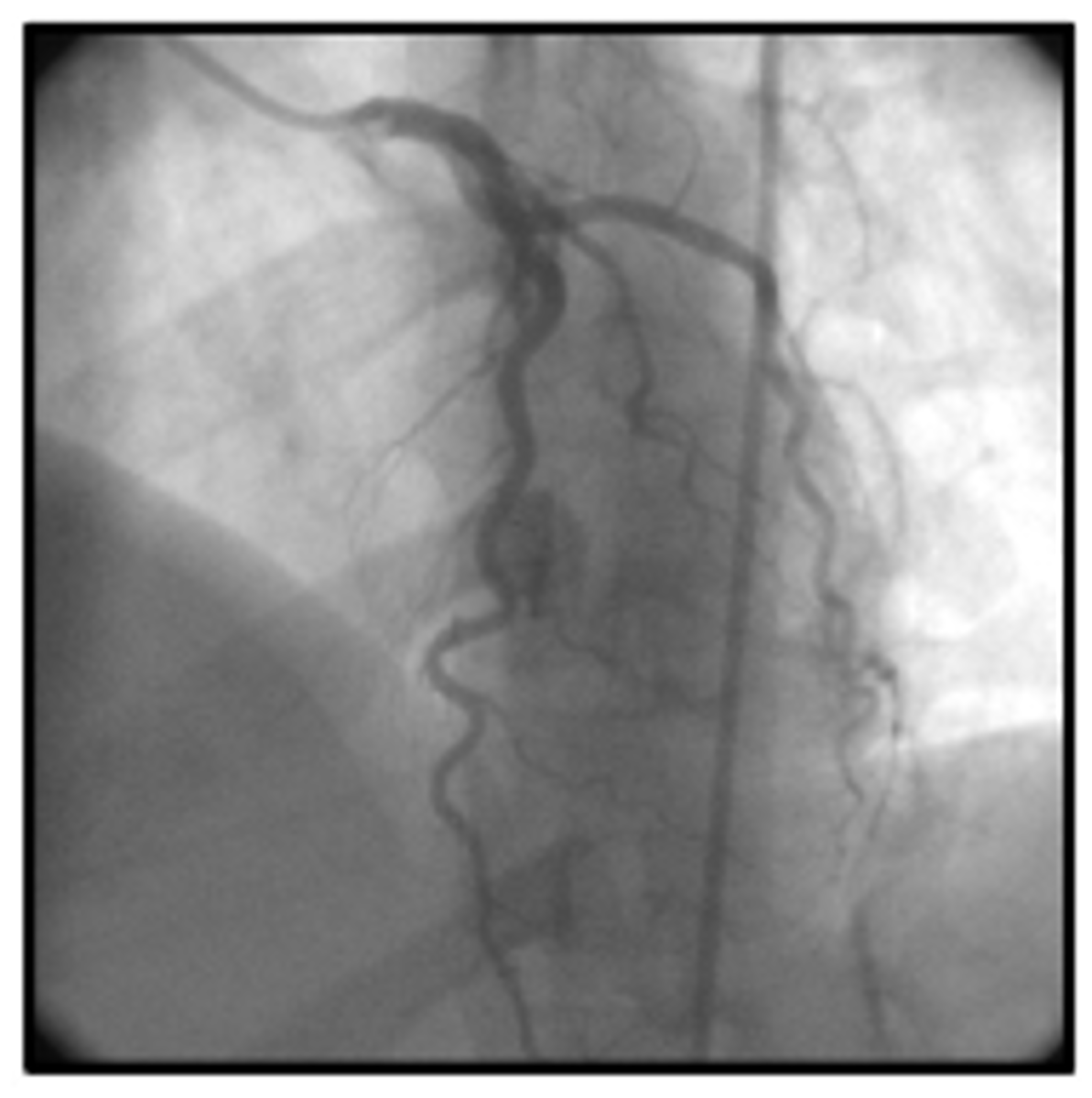
lao caudal
view
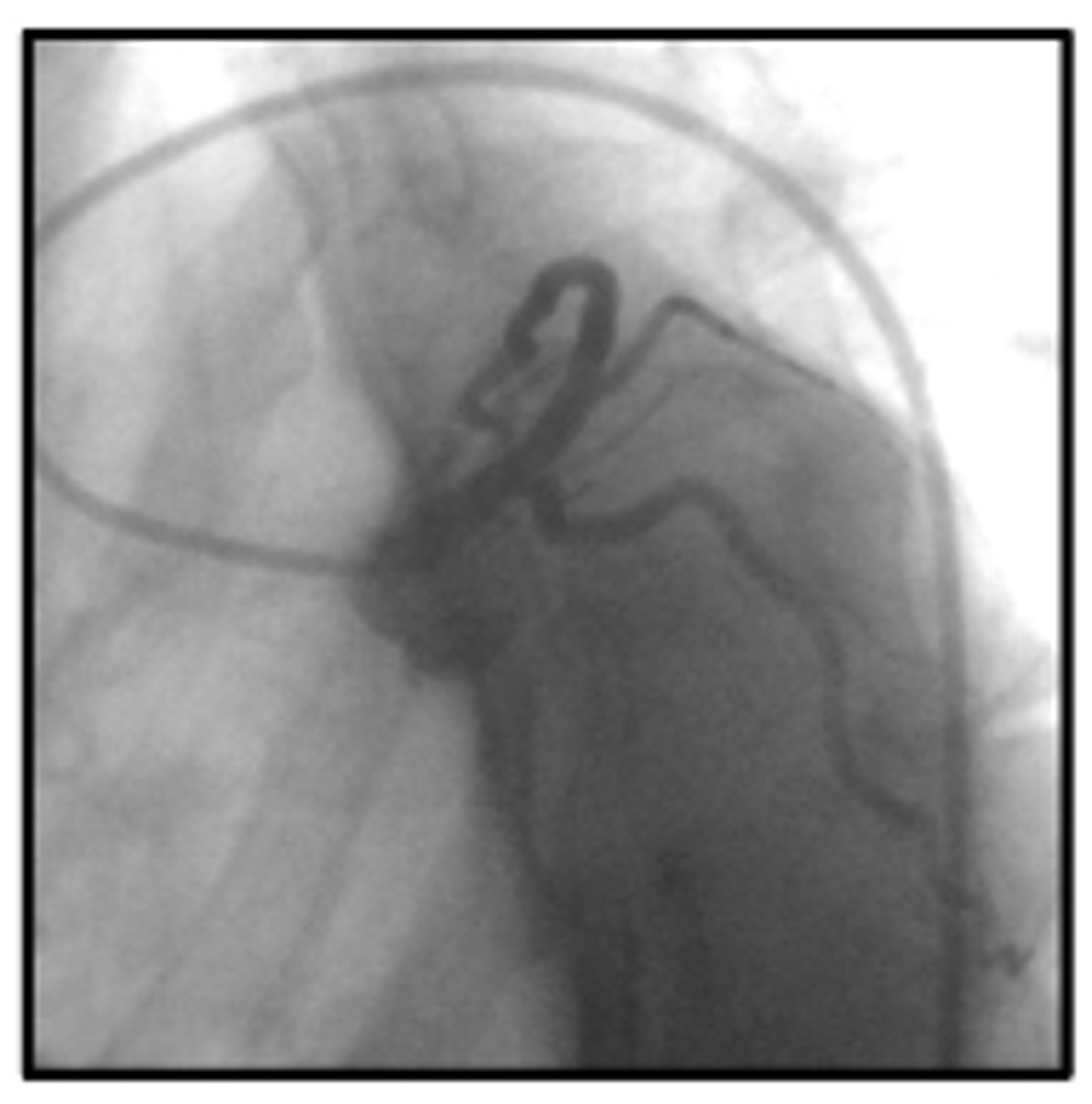
lao caudal
whats the spider shot
LAD
in LAO caudal what vessel is on top
diagonals and septals
LAD has what branches
left atrial branch, obtuse marginals, possibly PDA
CX has what branches
conus, sa nodal, rv bronchus, acute marginals, av nodal, possibly PDA
RCA has what branches
intermediate ramus
branch between LAD and CX
hypokinesis
little contraction of LV wall
asyneresis
diminished contraction of part of LV wall
akinesis
no contraction of part of the LV wall
dyskinesis
bulging, opposite of contraction of part of the LV wall
asynchrony
contractions but at different times throughout the LV walls
mitral regurgitation
RAO Lv gram is used to show
septal defect and aortic regurgitation
LAO Lv gram is used to show
deep breath
what can the patient do to help prior to coronary injection to move diaphragm out of xray view
cx
in most oblique x- ray views what is closest to the backbone
myocardial bridge
a segment of the LAD that occludes during systole and opens during diastole
LAD
what vessel is anterior
cx and obtuse marginal
what vessels are lateral/ posterior
same
which cardiac output is larger LV or RV
PA
mixed venous blood should be taken from
68 76 73 75 75 95, 95, 95
normal o2 sats SVC, IVC, RA, RV, PA, PCW, LV, AO
40
normal o2 sat for coronary sinus
lower
the lower the CO what happens to the o2 sats
4-8 l/min
normal CO
2.5-4 l/mim/m2
normal CI
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
heart rate is controlled by what
increases
decreasing blood pressure does what to the heart rate
stretch and baroreceptors
what is stimulated to decrease bp and increase heart rate
chemoreceptors
what reads o2 levels and ph levels
aortic arch and carotid sinuses
where are baroreceptors located
aortic arch
arterial chemoreceptors are located where