COGSCI 1 Lecture 18 - Robotics
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
GOFAI
Good Old-Fashions Artificial Intelligence Robotics
Shakey
Early robot developed by Stanford Research Institute (c. 1970)
First robot that was able to move around, perceive, follow instructions, and implement complex instructions
Software on a separate computer system and communicated withe Shakey via radio antenna
Limitations of GOFAI
the robot is not embedded in a real-life environment and can never really come to terms with real-life problems and challenges;
Can only operate in a highly constrained environment
Cannot learn to solve problems; solutions are built in
Dynamical Systems
behaviors emerge out of complex interactions between an organism and its environment
Traditional explanation for U-shaped developmental trajectory of stepping
Infant’s initial stepping movements are purely reflexive
They disappear during the non-stepping window bc the cortex has matured enough to inhibit reflex responses
Studies by Esther Thelen and Linda Smith
research indicated that stepping movements could be artificially induced or inhibited in infants by manipulating features of the environment
Placing baby on treadmill or suspending them in warm water
→ Stepping movements vary independently of how the cortex has developed
Dynamical Models
Are used to understand how agents are embedded in their environments
Use calculus-based methods to track the evolving relationship between a small number of variables over time
Situated Cognition
Propose a dynamical systems-like approach to robotics
Believe that we should start small and focus on basic ecologically valid problems
Barbara Webb Robot Crickets
Can identify the source of a sound and move automatically toward the source without any of the systems normally assumed by GOFAI
Biorobotics
Using knowledge of living insects, as well as AI, to create agents capable of moving about and solving problems in their environment
Morphological Computation
exploiting features of body shape to simplify what might otherwise be highly complex information-processing tasks
Morphological Computation in Robotics
building as much of the computation as possible directly into the physical structure of the robot
Yokoi Hand
Constructed from elastic and deformable materials that allow the hand to adapt itself to the shape of the objects being grasped
Subsumption Architectures
Operate on a set of relatively simple stimulus-response mechanism
Bottom up intelligence
Based on the idea that intelligence does not require formal symbolic representation
Robots make reflexive responses to environmental stimuli
Obstacle Avoidance Layer
Directly connects perception to action
Rodney Brook’s Robot Allen
Basic layer = obstacle-avoidance layer
More layers were added overtime, mimicking evolution
Semi-autonomous subsystems operate independently of each other
No central “controller” comparable to PLANEX in SHAKEY
Direct perception-action links allows robot to deliver immediate motor responses
Situated Cognition
embedded in the world, and which does not deal with abstract descriptions, but through its sensors with the here and now
Embodied Cognition
has a physical body and experiences the
world directly through the influence of the world on that body
Xenobot
Small Biological Machine (<1mm) created by scientists at the University of Vermont and Tufts University
Built using skin and heart cells harvested from frog embryos
Designed and programmed by a supercomputer using an evolutionary algorithm
Able to move in a coherent fashion to explore their watery environment
and can survive for days or weeks, powered by embryonic energy stores
Imitation Learning
Roboticist puppeteers pairs of metallic robotic arms;
helps master fine motor movements of hands: one of the biggest challenges in robotics
Reinforcement learning
subdivides each demonstration into a series of sub-tasks and mines successful simulations
→ able to learn more from less data
Affective Computing
Computing that relates to, arises from, or deliberately influences emotions
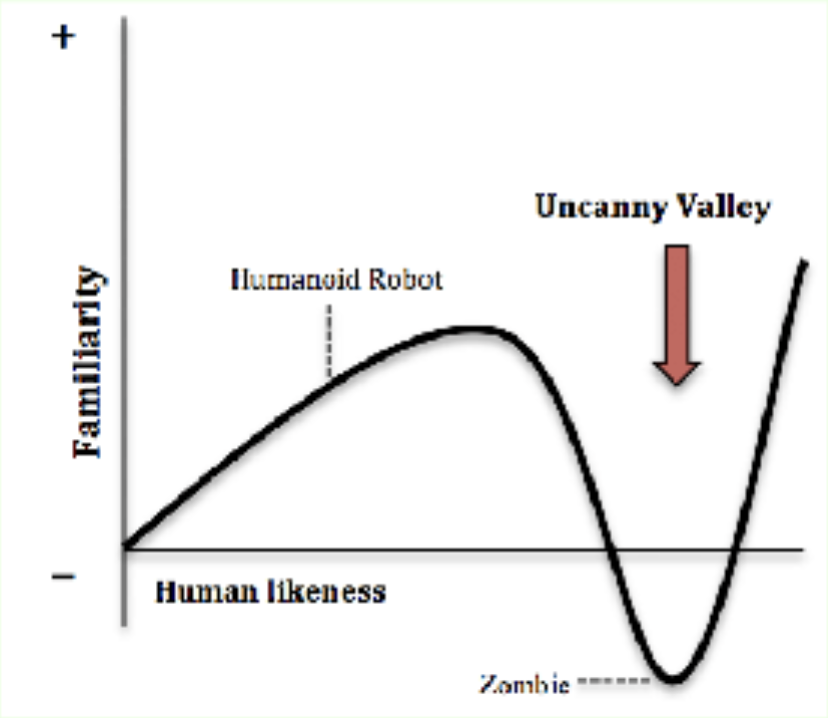
Uncanny Valley Effect
humanoid objects that imperfectly resemble actual human beings provoke uncanny feelings of uneasiness and revulsion in observers
(eg. Polar Express)
Moley Roboics
robot kitchen that cooks and cleans up after itself
Automated Restaurants
Spyce Restaurant in Boston: created by a team of MIT graduates
CaliExpress by Flippy in Pasadena is first AI-powered eatery
Qianxi Robot Catering Group has introduced fully automated restaurant where all processes from cooking to serving are handled by robotic machines
Advantages of Autonomous Restaurants
Every second added to someone waiting for their meal is lost opportunity for revenue for restaurant, so speed of automation at these restaurants is a big plus
Prices at these restaurants tend to be very competitive
Can produce 300 bowls of food an hour
Can sear proteins, steam grains, and measure toppings to create delicious food in less than 3 min
Also, the food will presumably be cooked precisely the same every time so the automation “should result in improvement in taste”
Customers tend to love robot waiters