The Brainstem, Cranial nerves and their nuclei
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANHB2217
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what are the 3 major divisions of the brain and what are some of their roles
Midbrain- ex. vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, alertness, temperature regulation
Pons- ex. respiration, control of involuntary actions, sensory roles (hearing, equilibrium, taste), motor roles (eye movement, facial expressions, chewing, swallowing, secretion of saliva and tears)
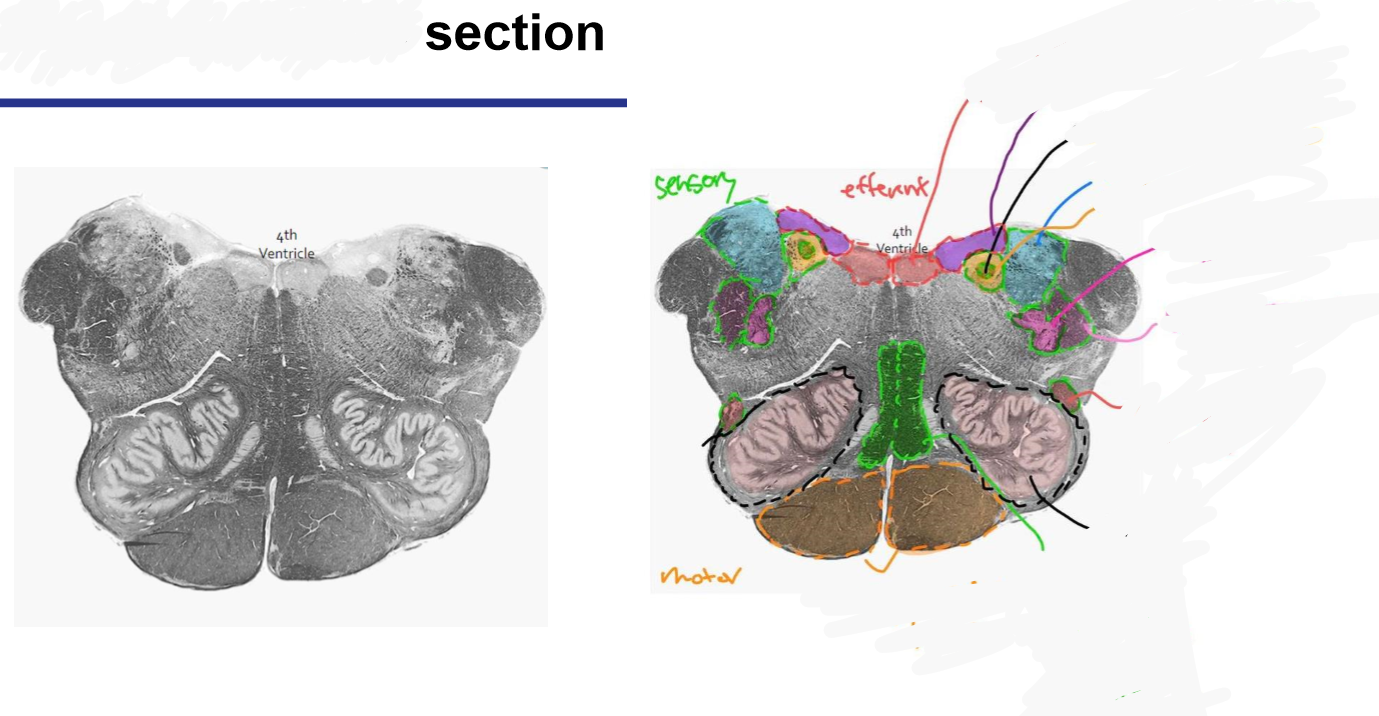
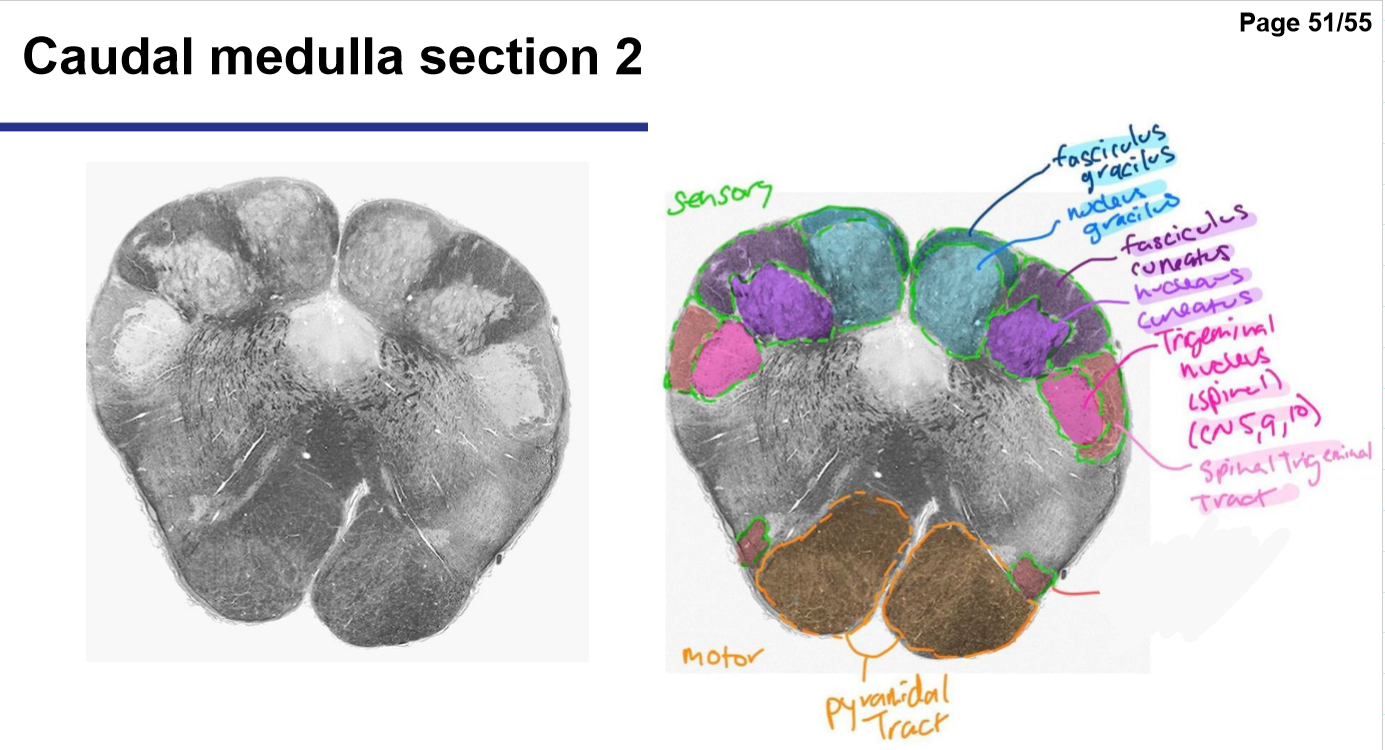
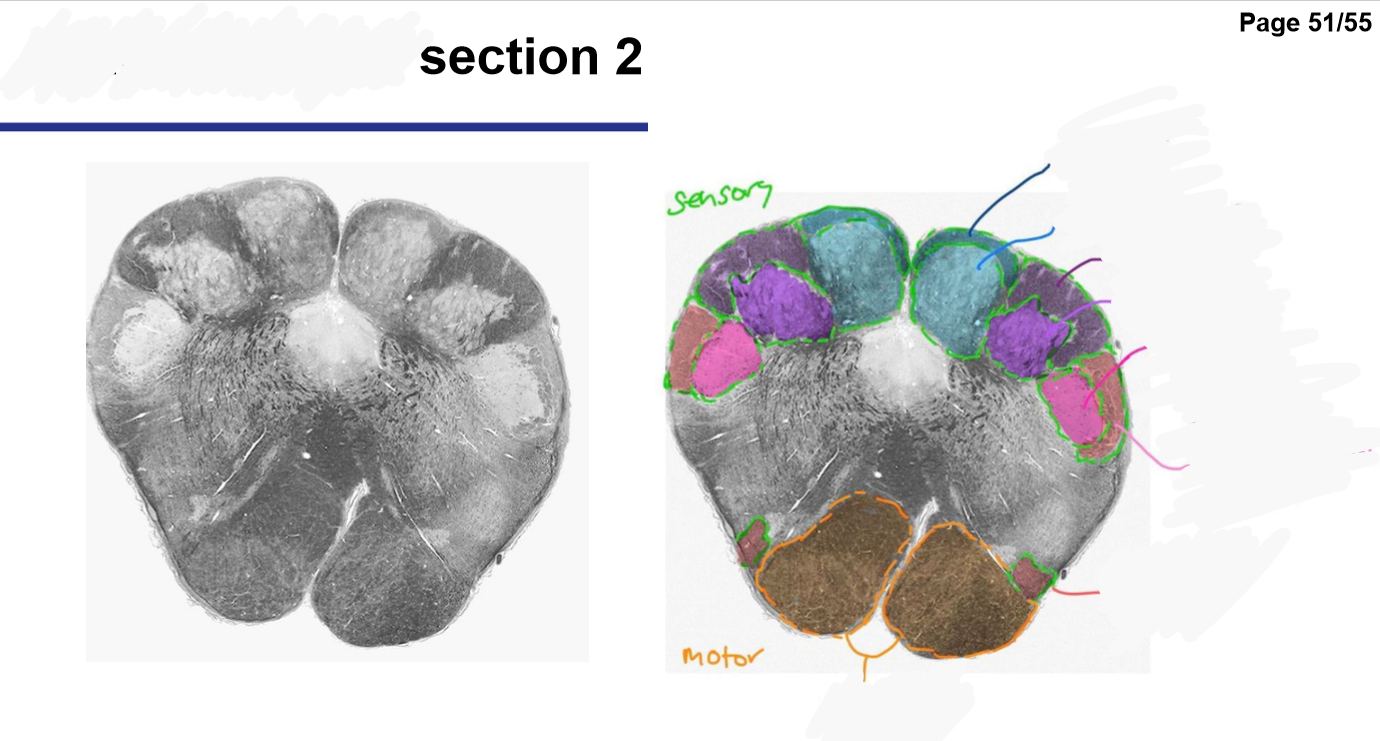
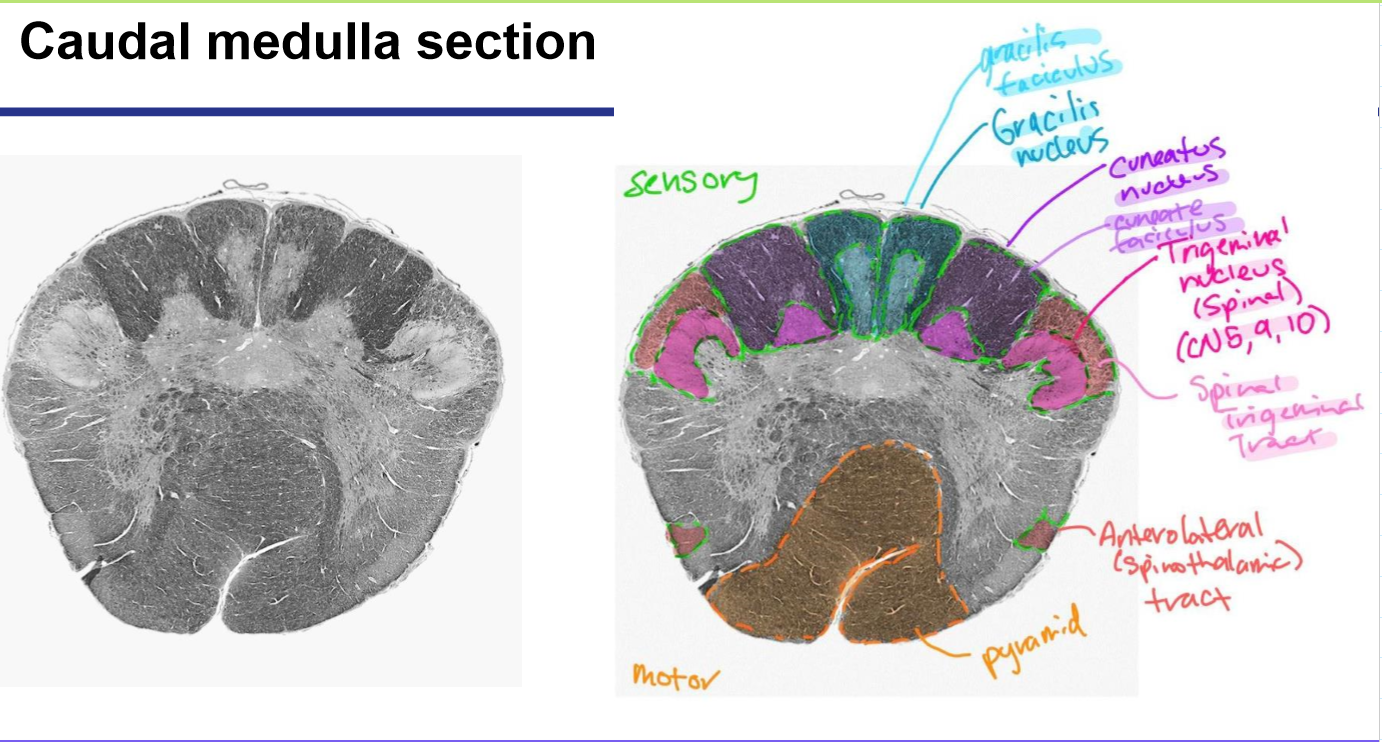
Medulla oblongata- ex. control of ventilation, cardiovascular and vasomotor control, Reflex centers of vomiting, coughing, sneezing and swallowing
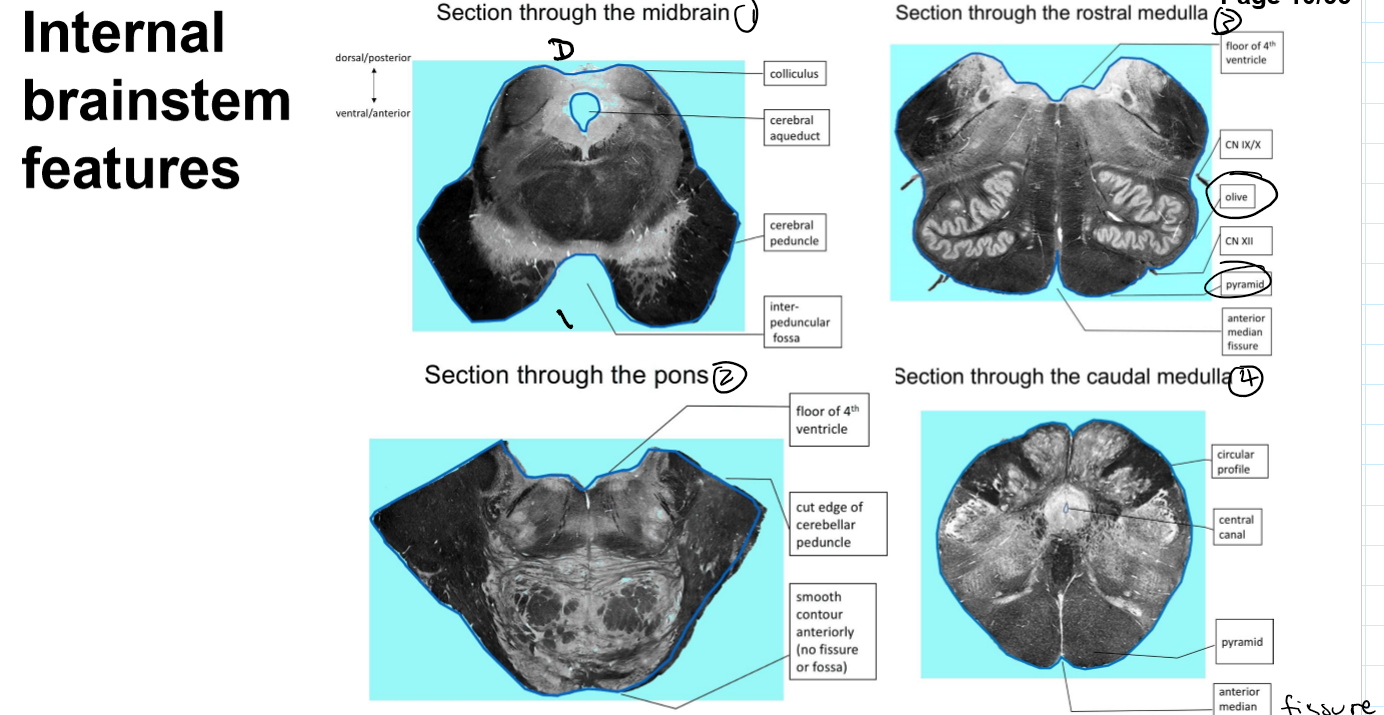
dorsal
ventral
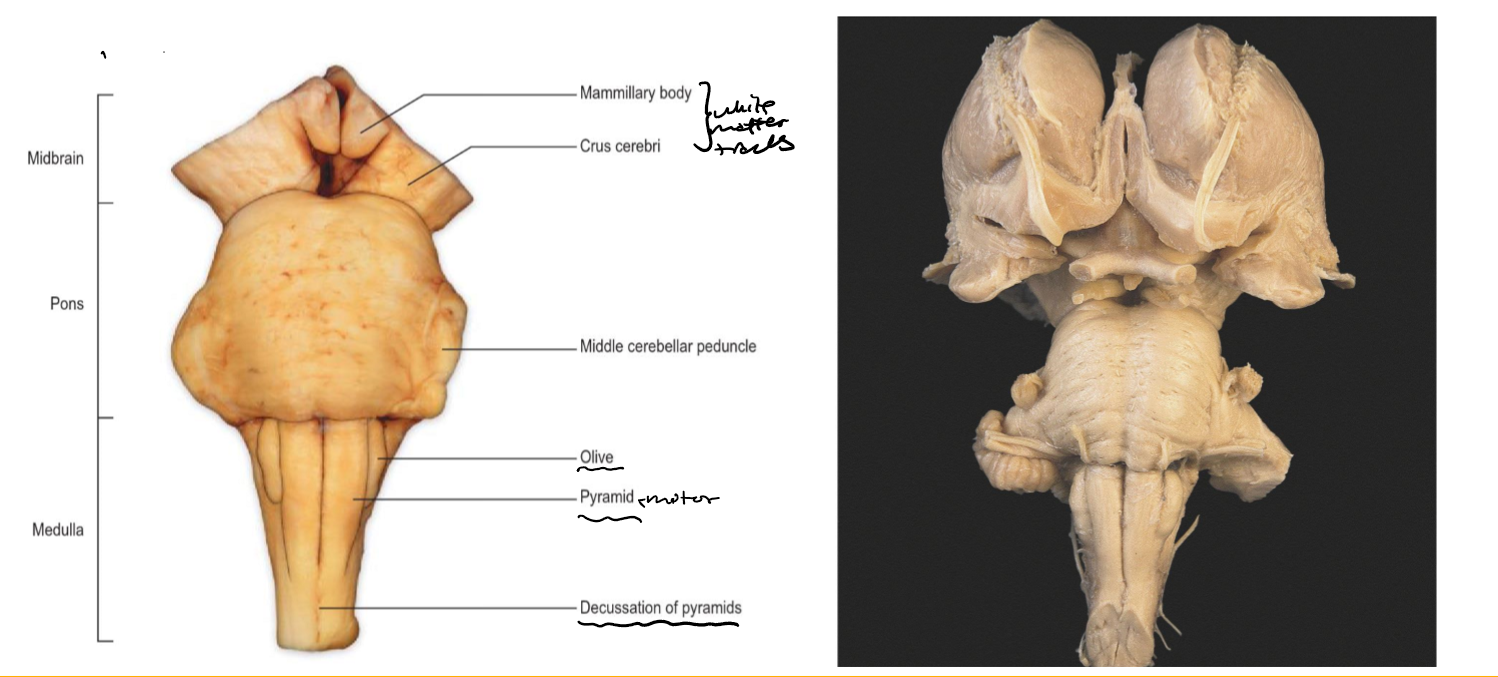
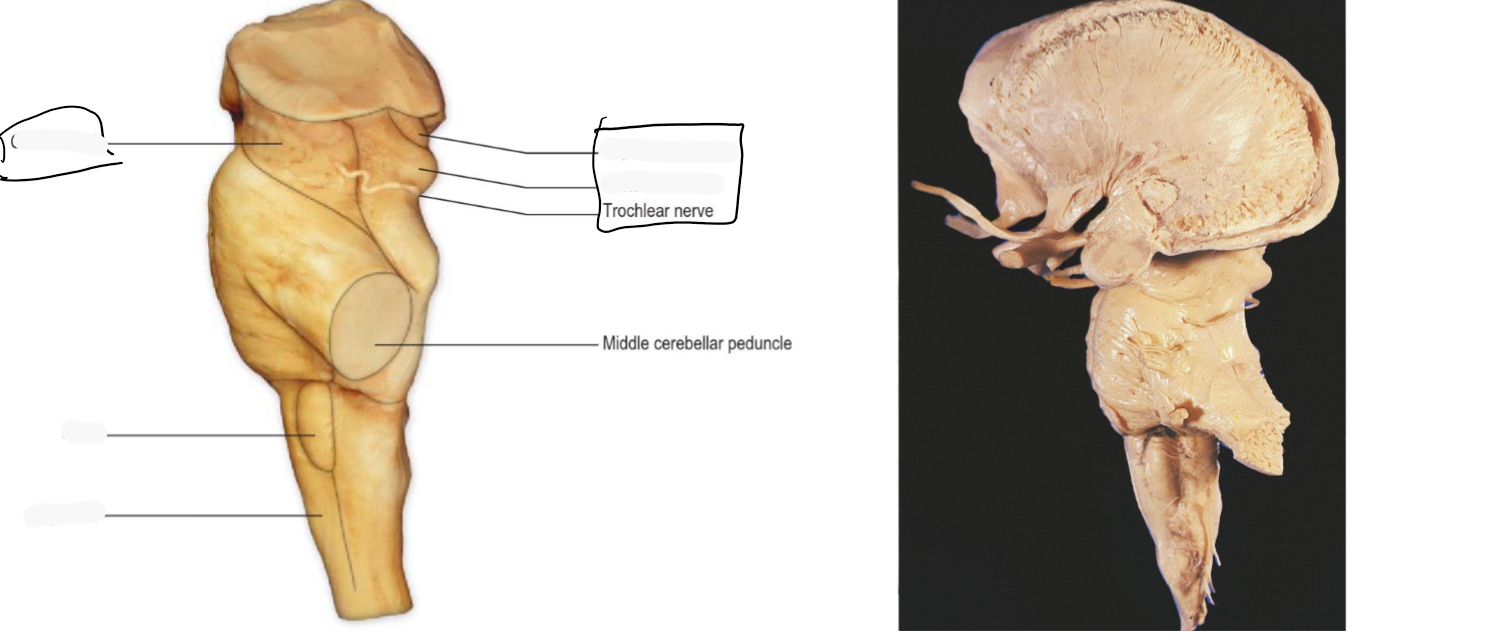
lateral
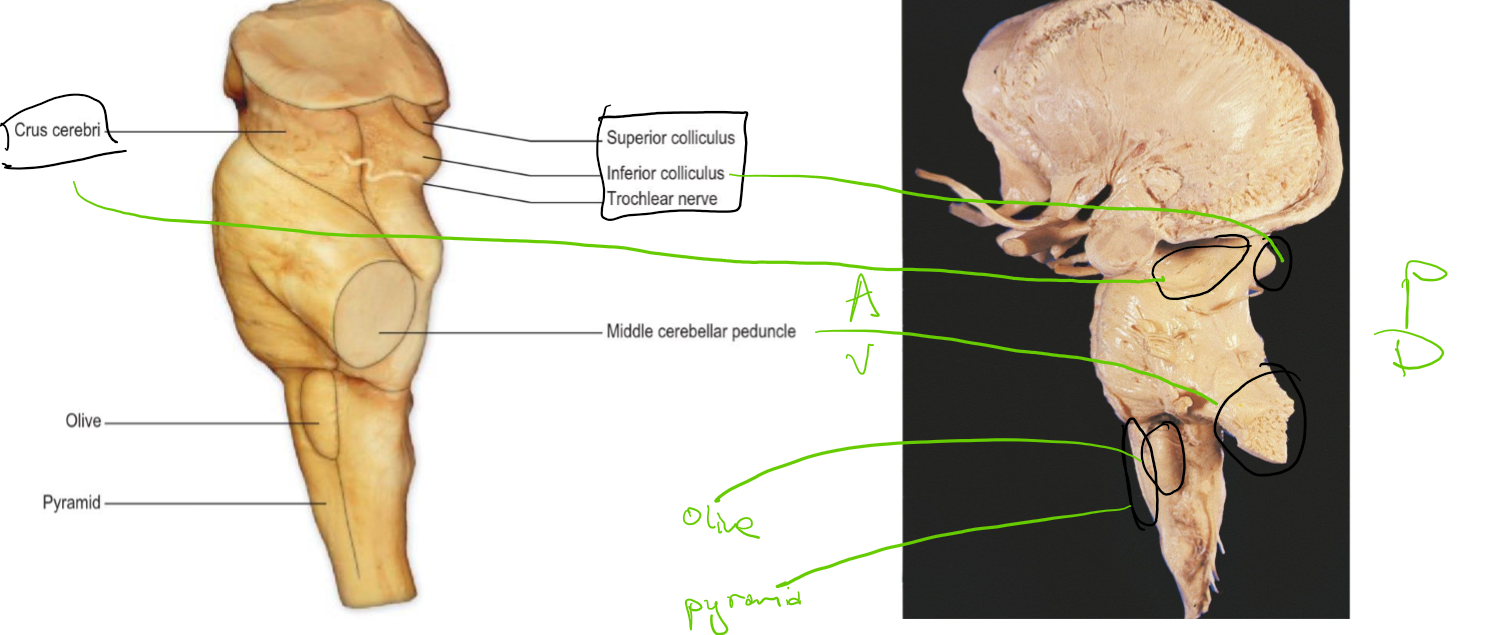
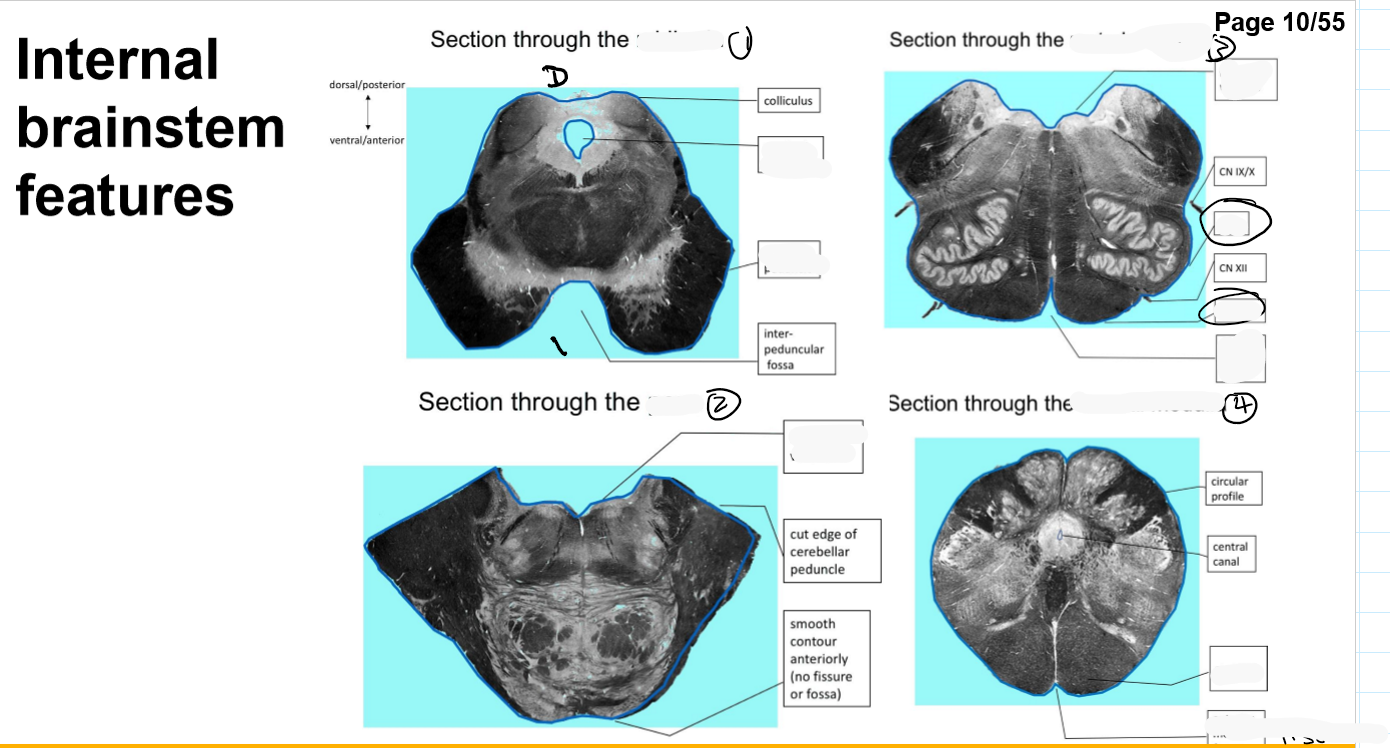
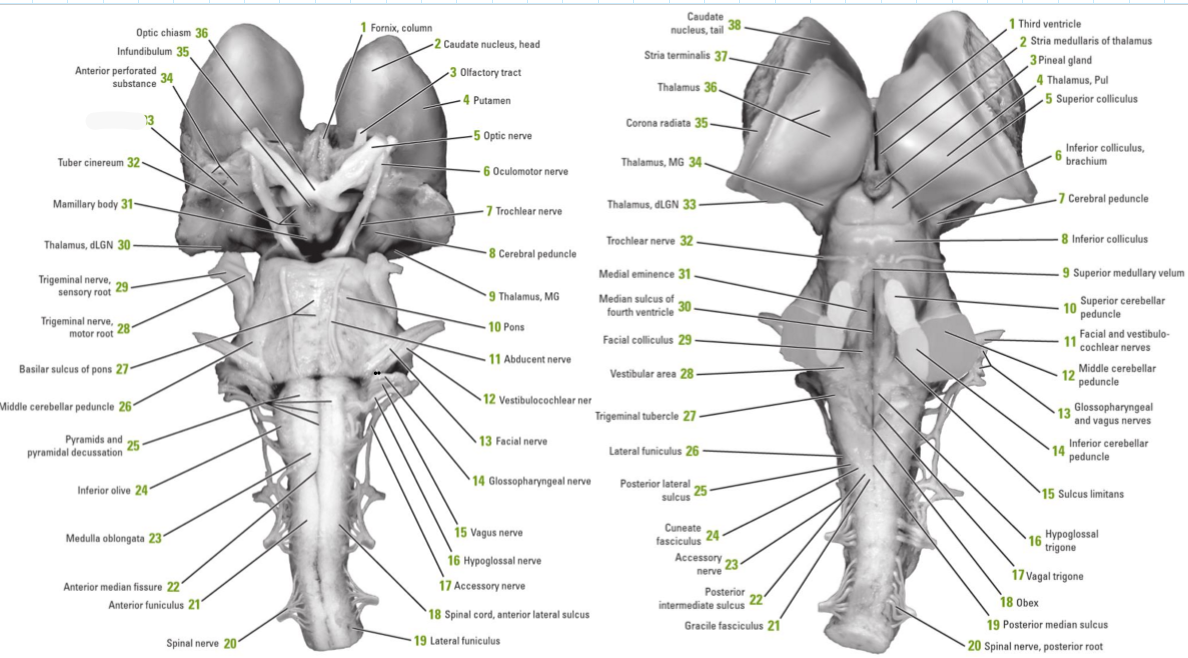
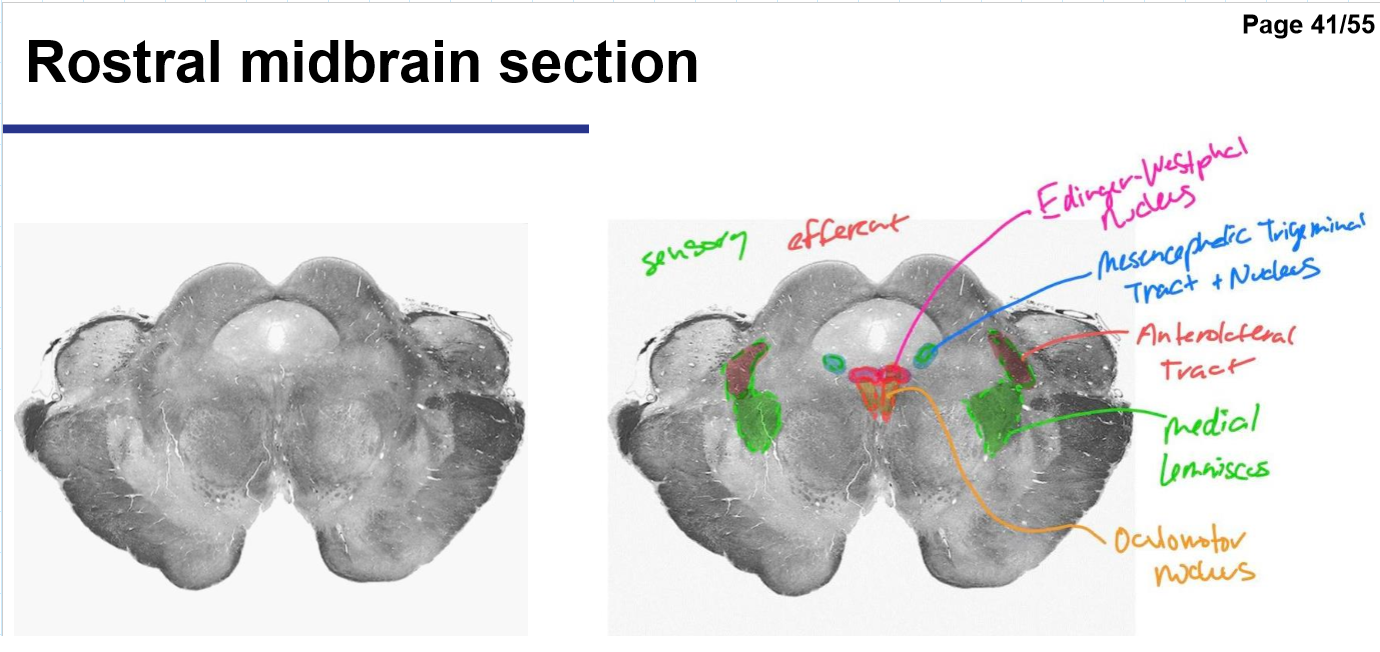
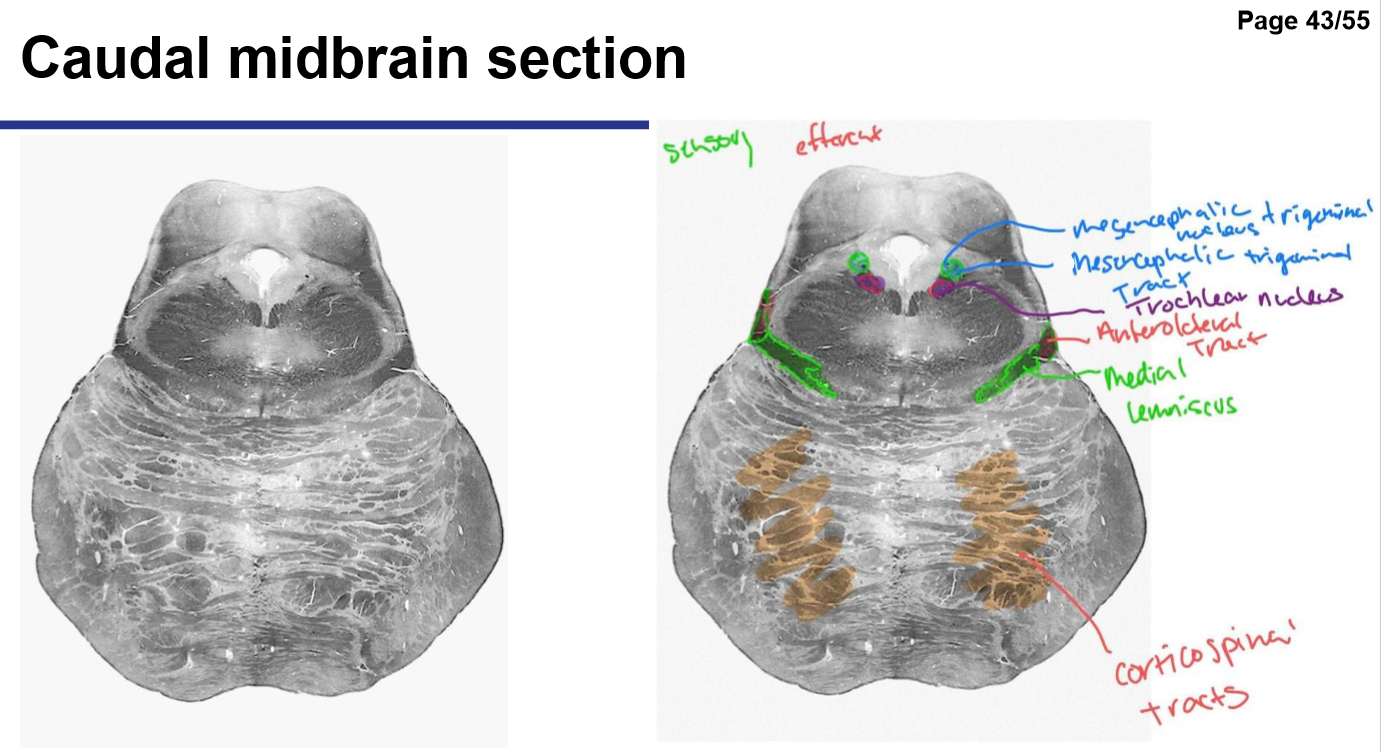
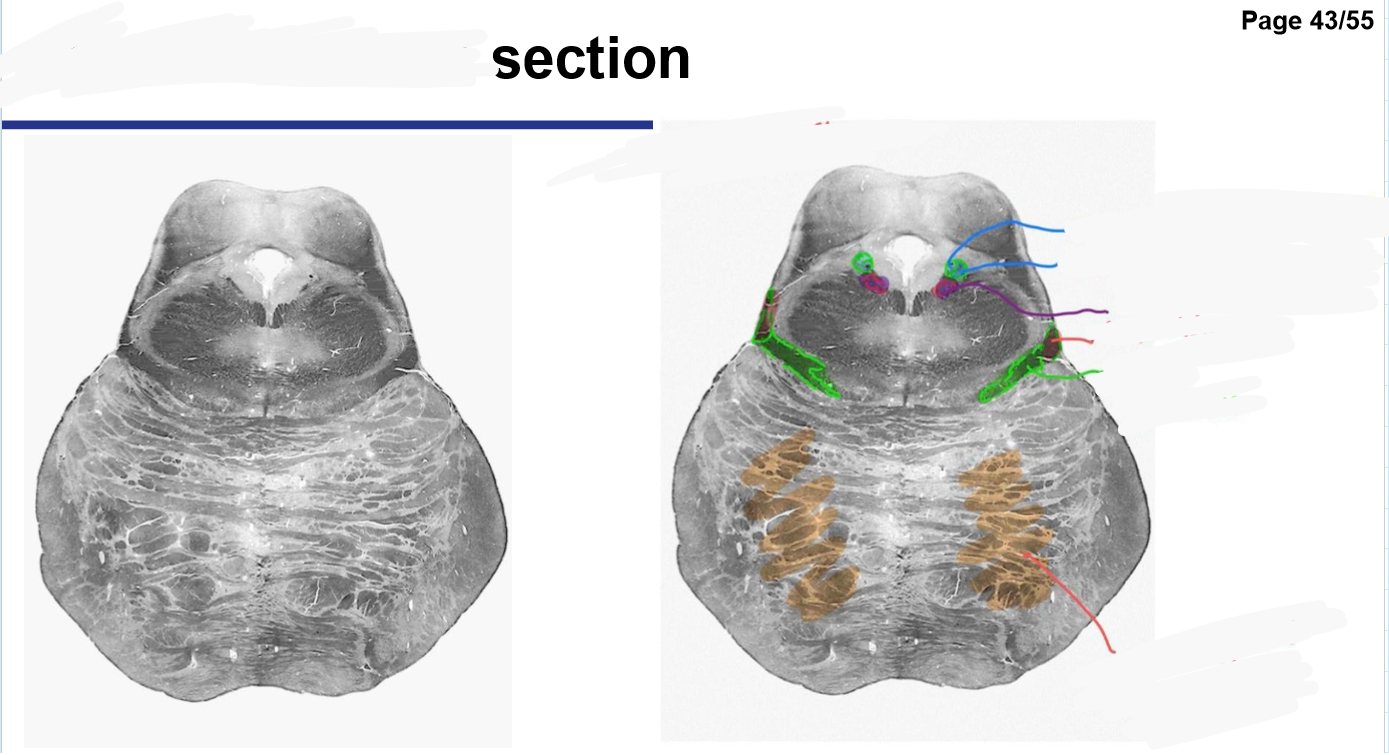
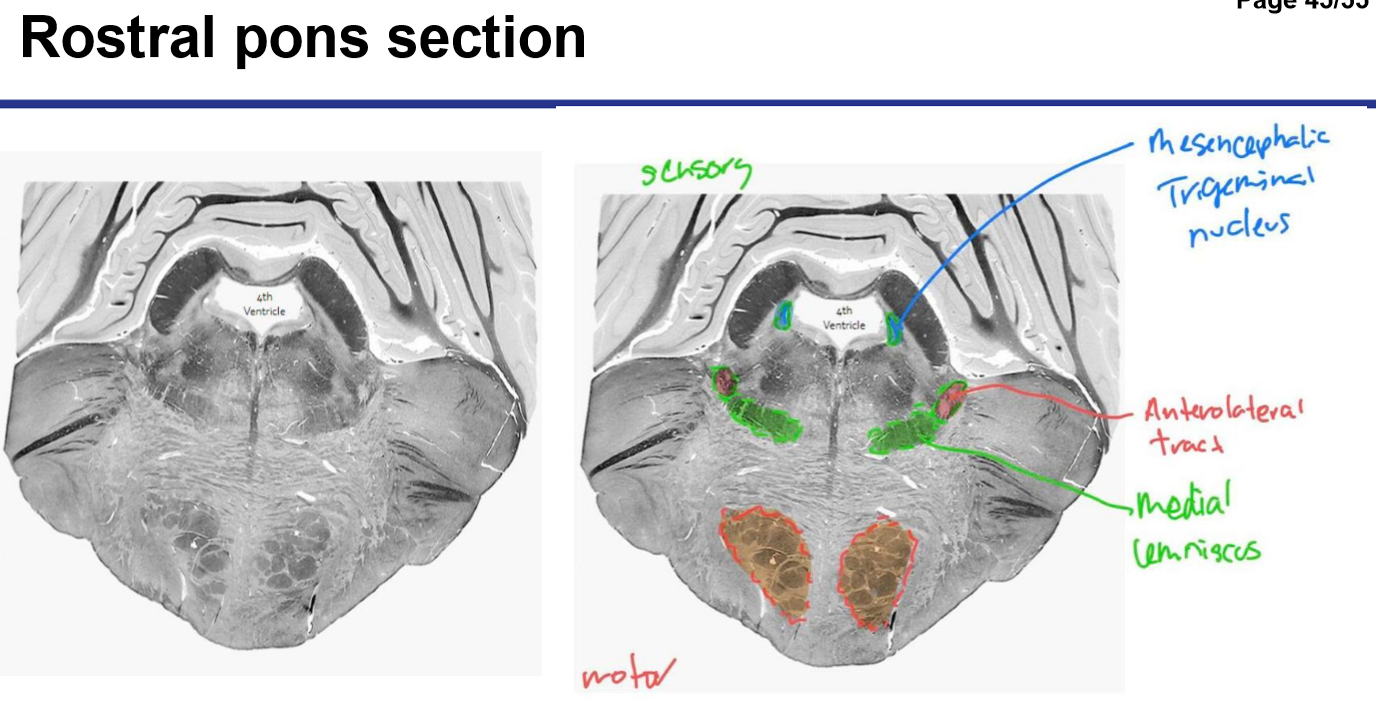
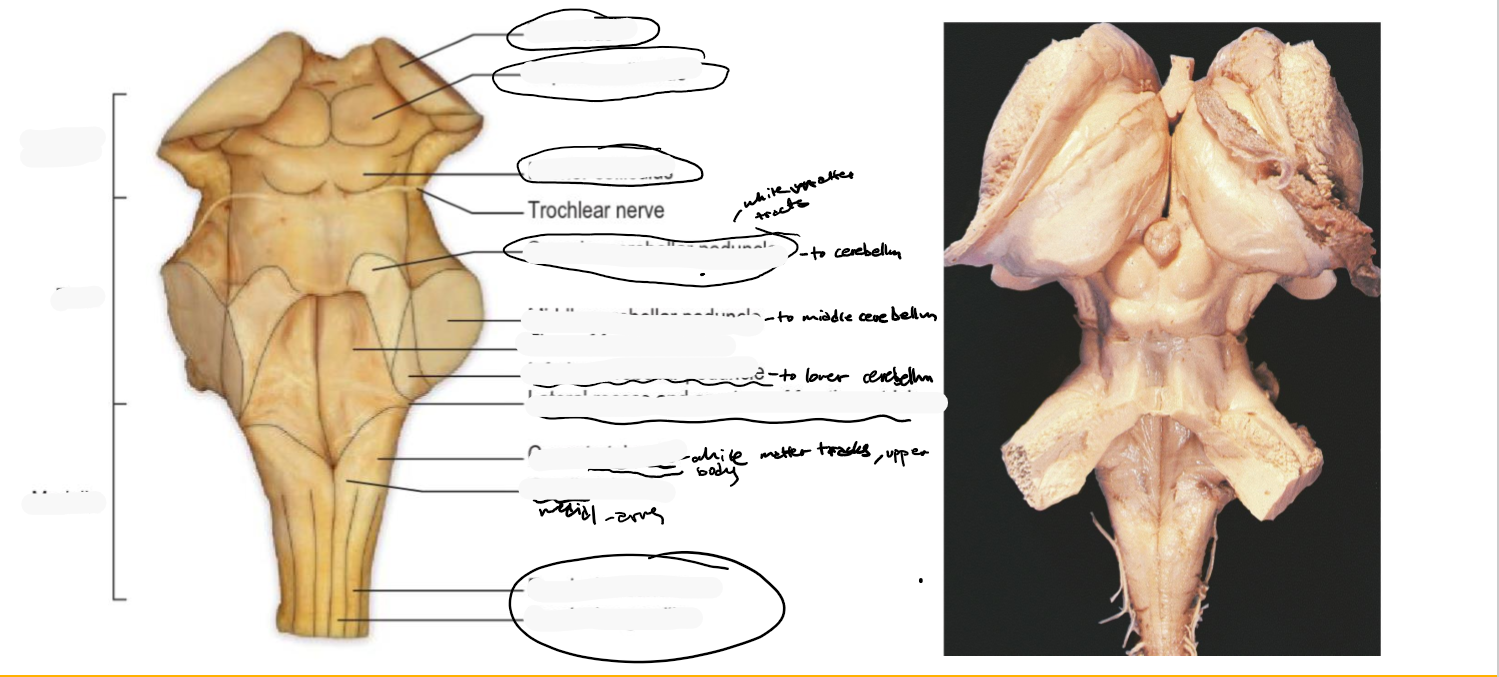
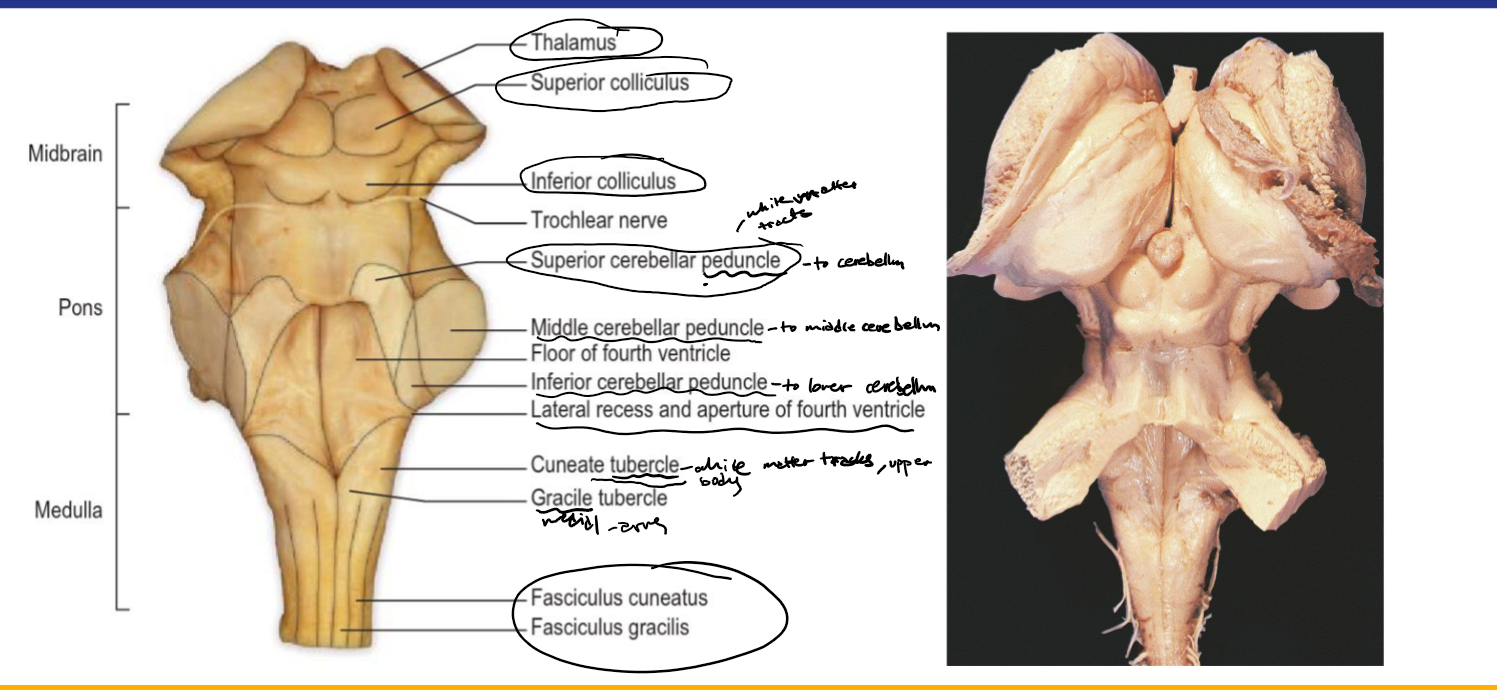
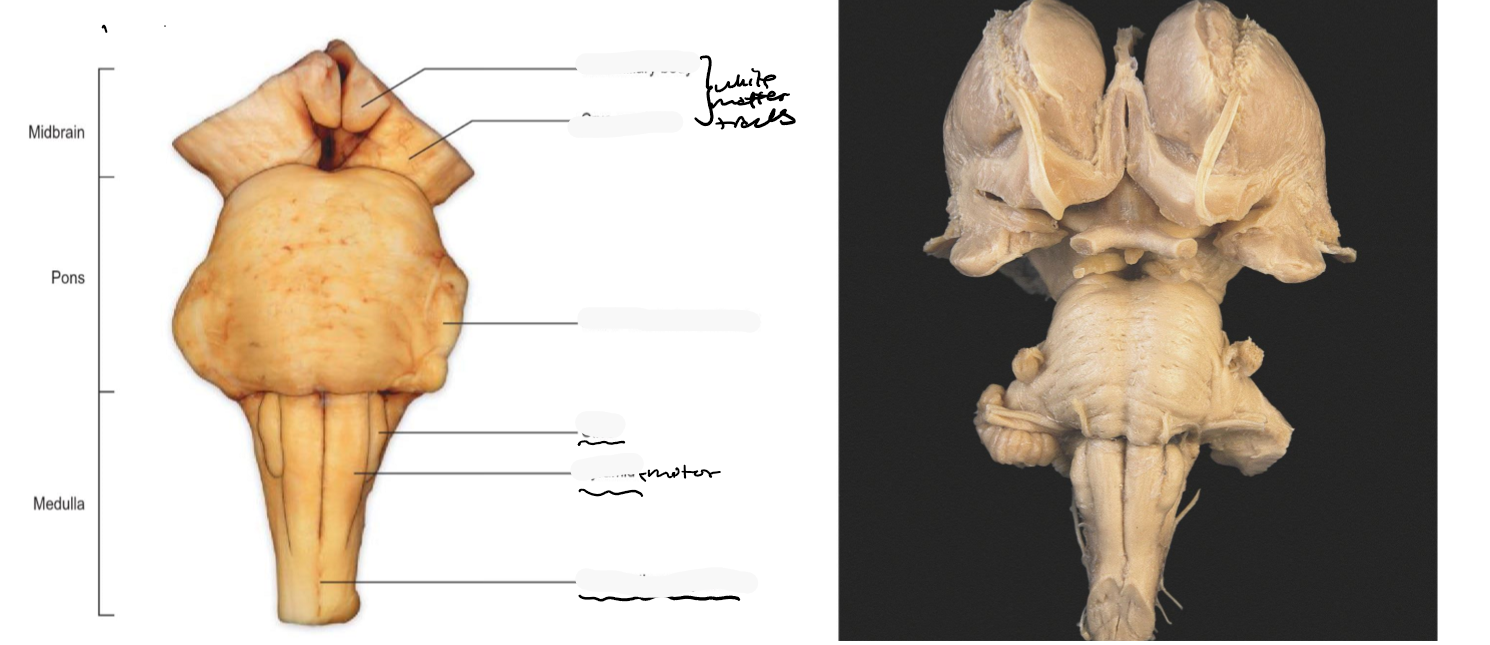
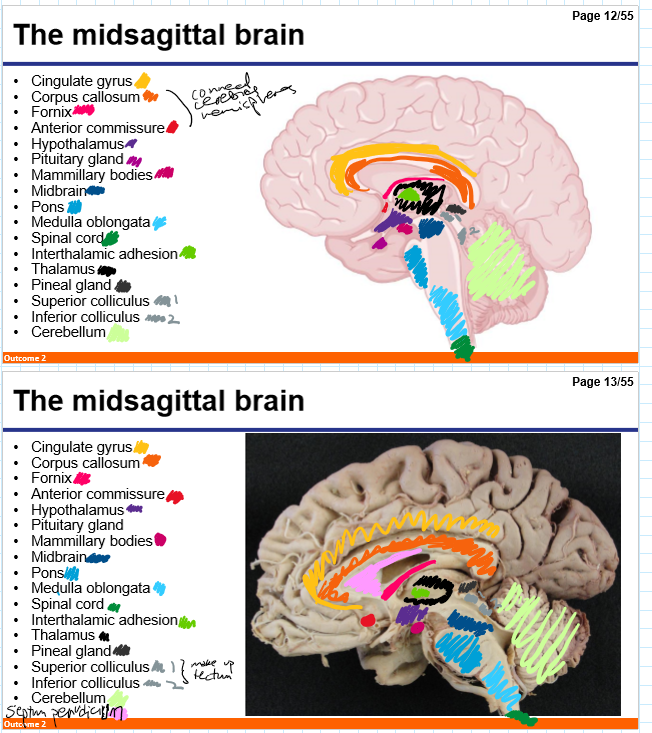
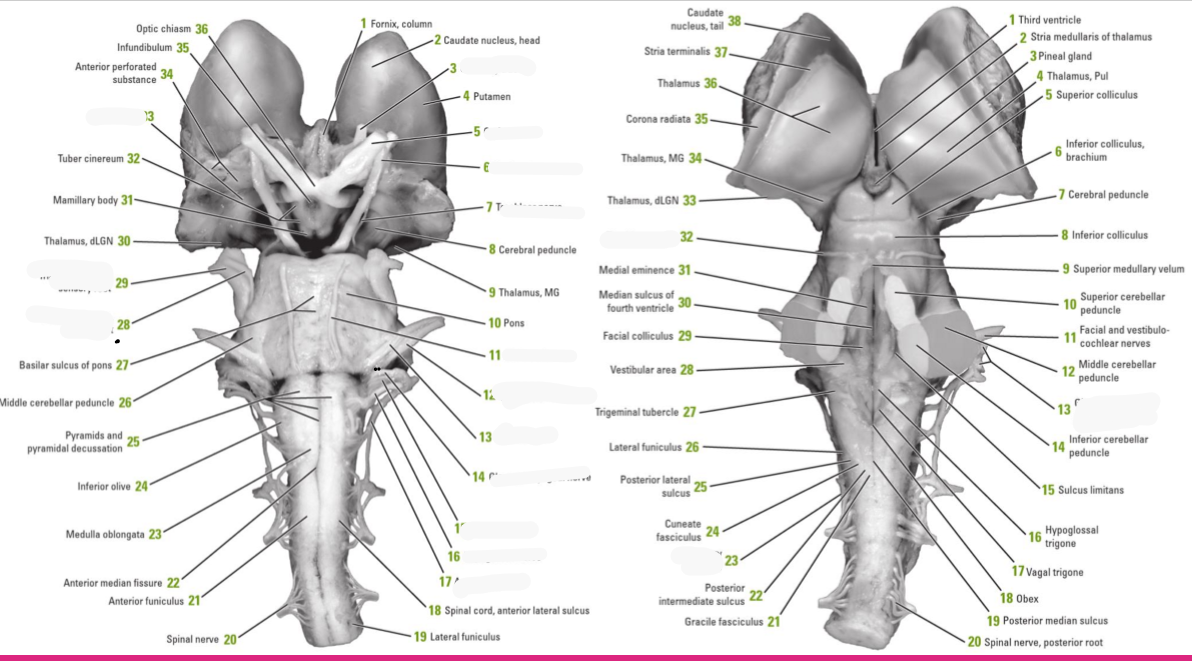
Identify the 18 features of the mid sagittal brain
Cingulate gyrus
Corpus callosum
Fornix
Anterior commissure
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Mamillary bodies
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Spinal cord
Interthalamic adhesion
Thalamus
Pineal gland
Superior colliculus
Inferior colliculus
Cerebellum
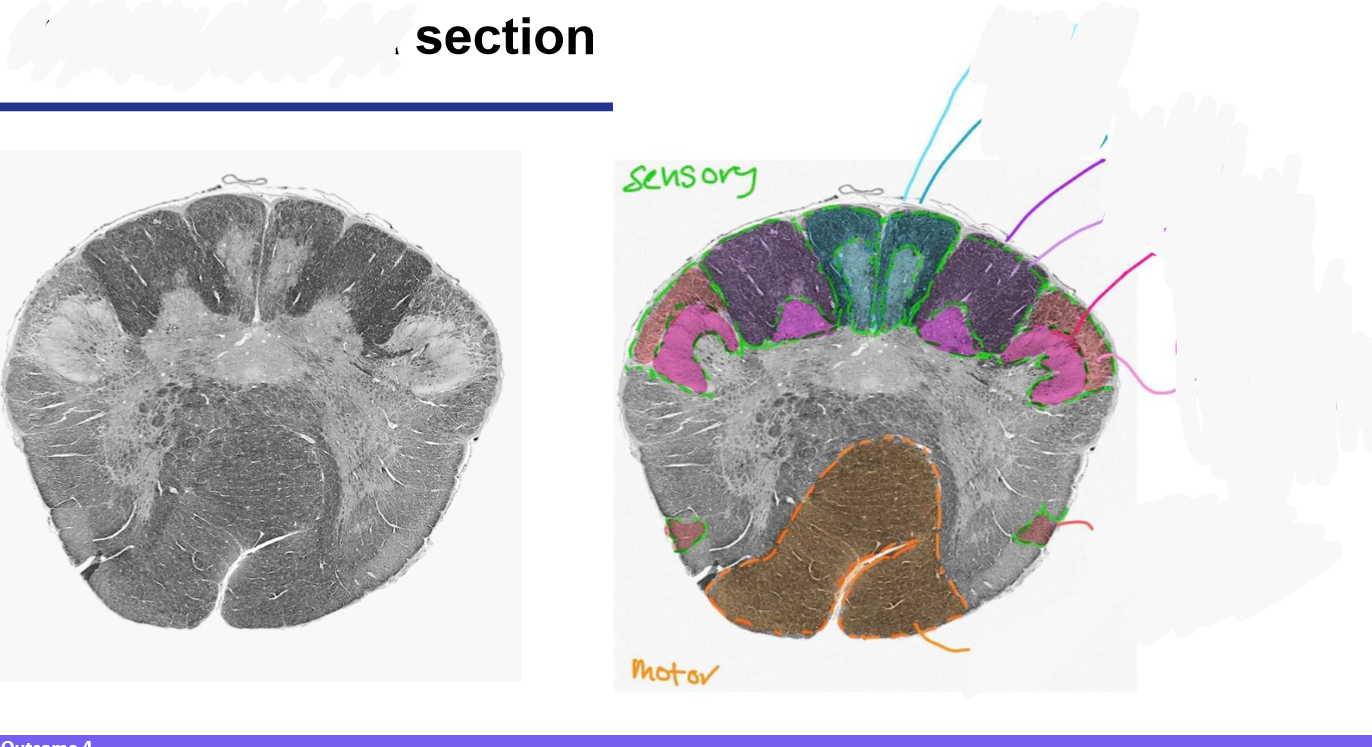
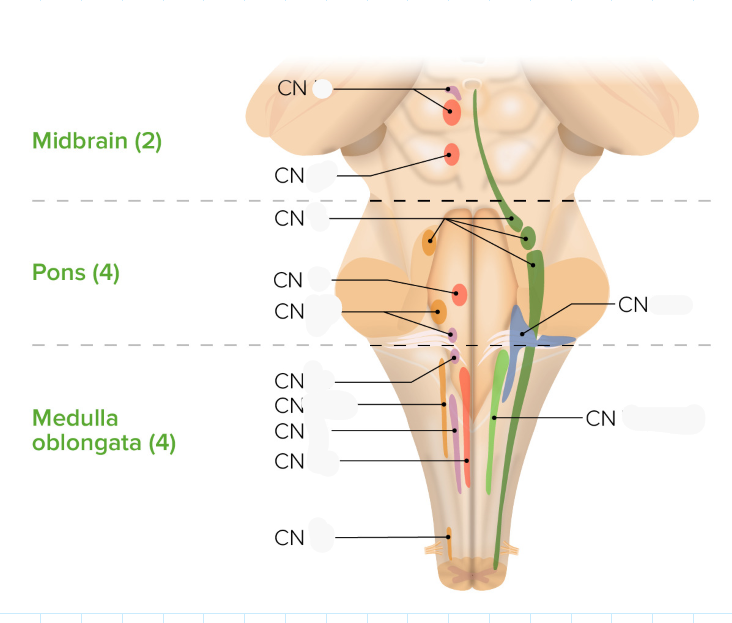
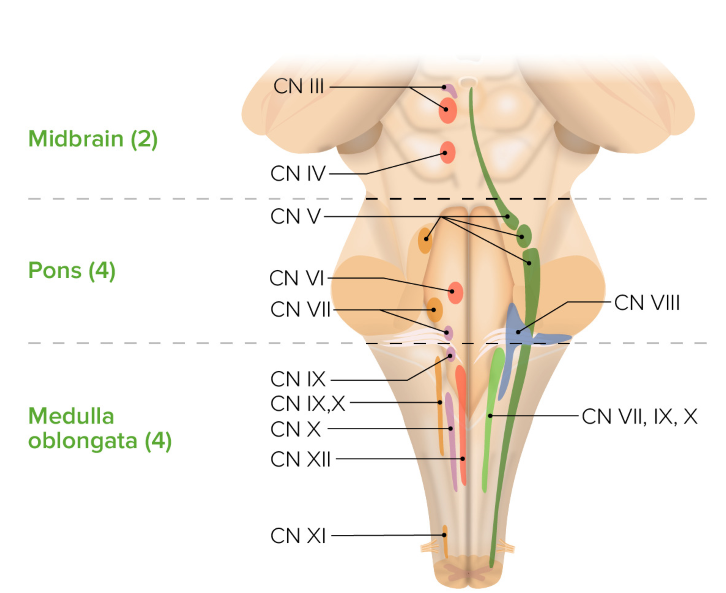
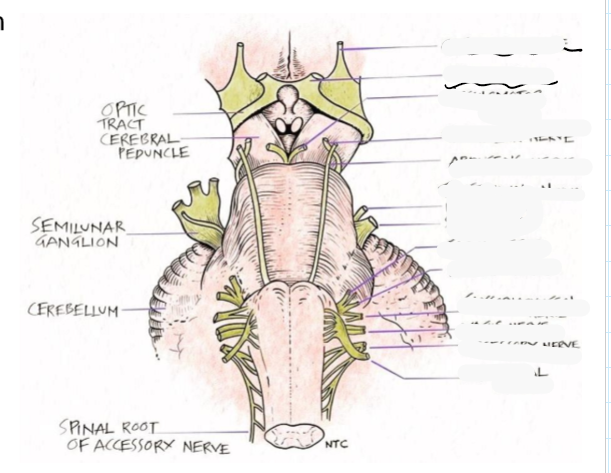
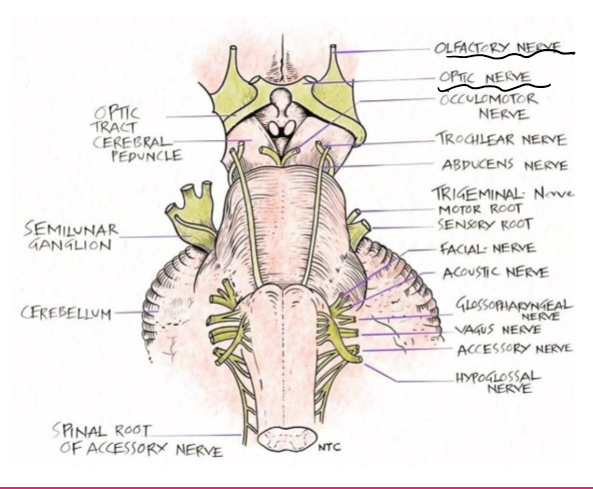
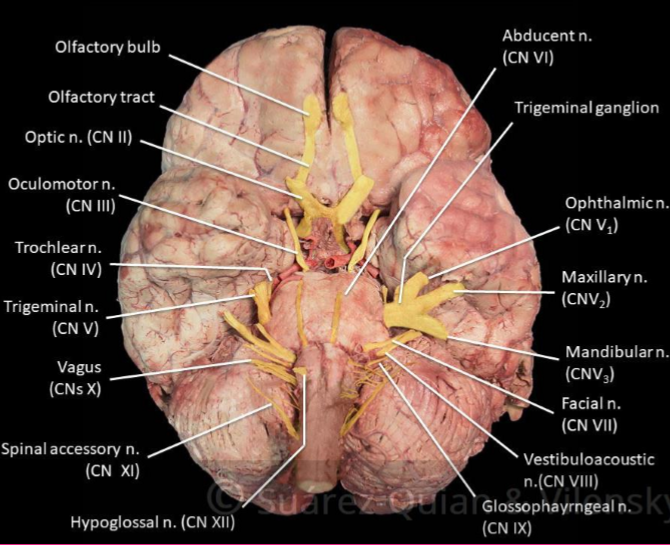
Name the 10 +2cranial nerves
Olfactory (1) and optic (2) nerve attach directly to the forebrain while rest attach to brainstem
Oculomotor (3)
Trochlear (4)
Trigeminal (5)
Abducens (6)
Facial (7)
Vestibulocochlear (8)
Glossopharyngeal (9)
Vagus (10)
Accessory (11)
Hypoglossal (12)
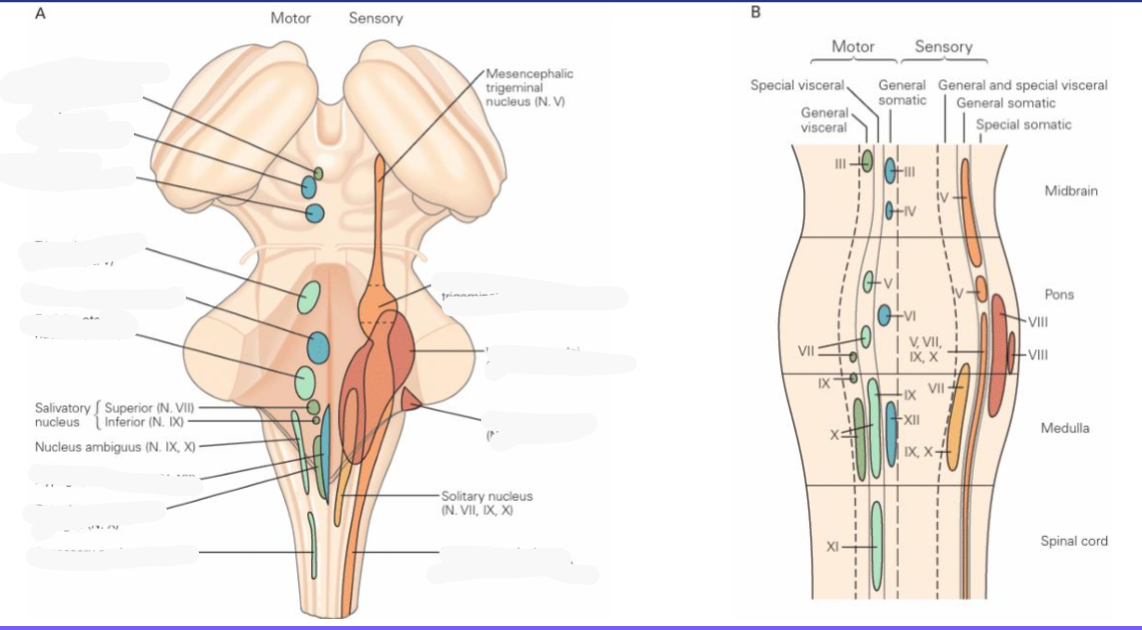
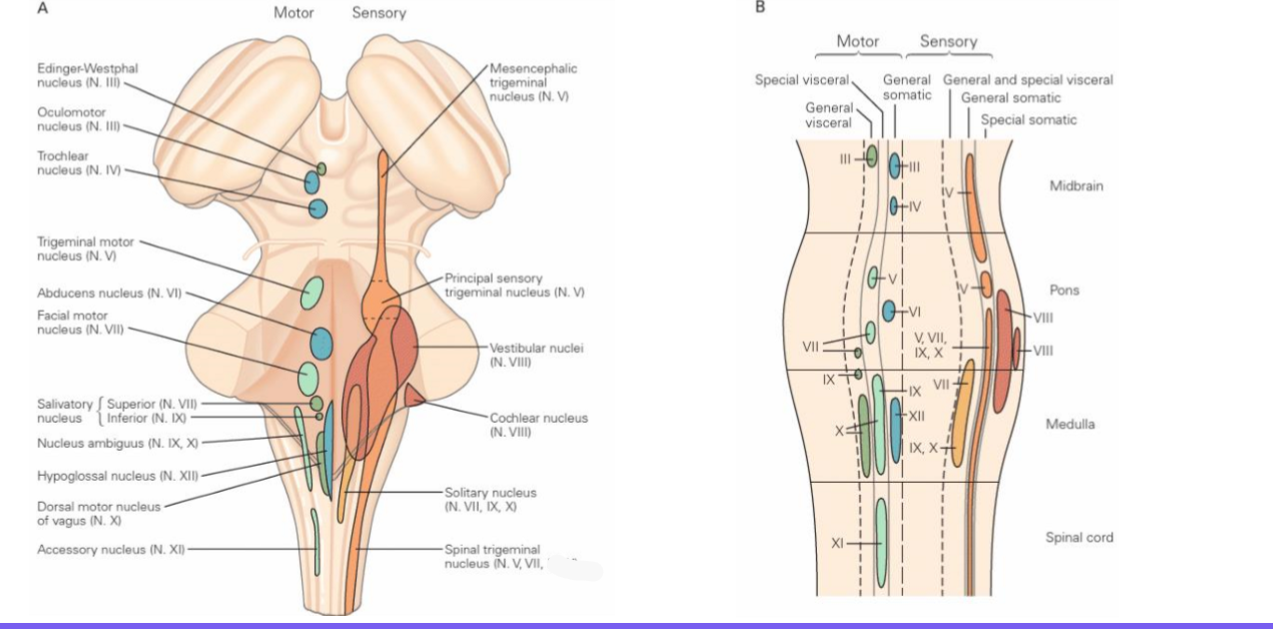
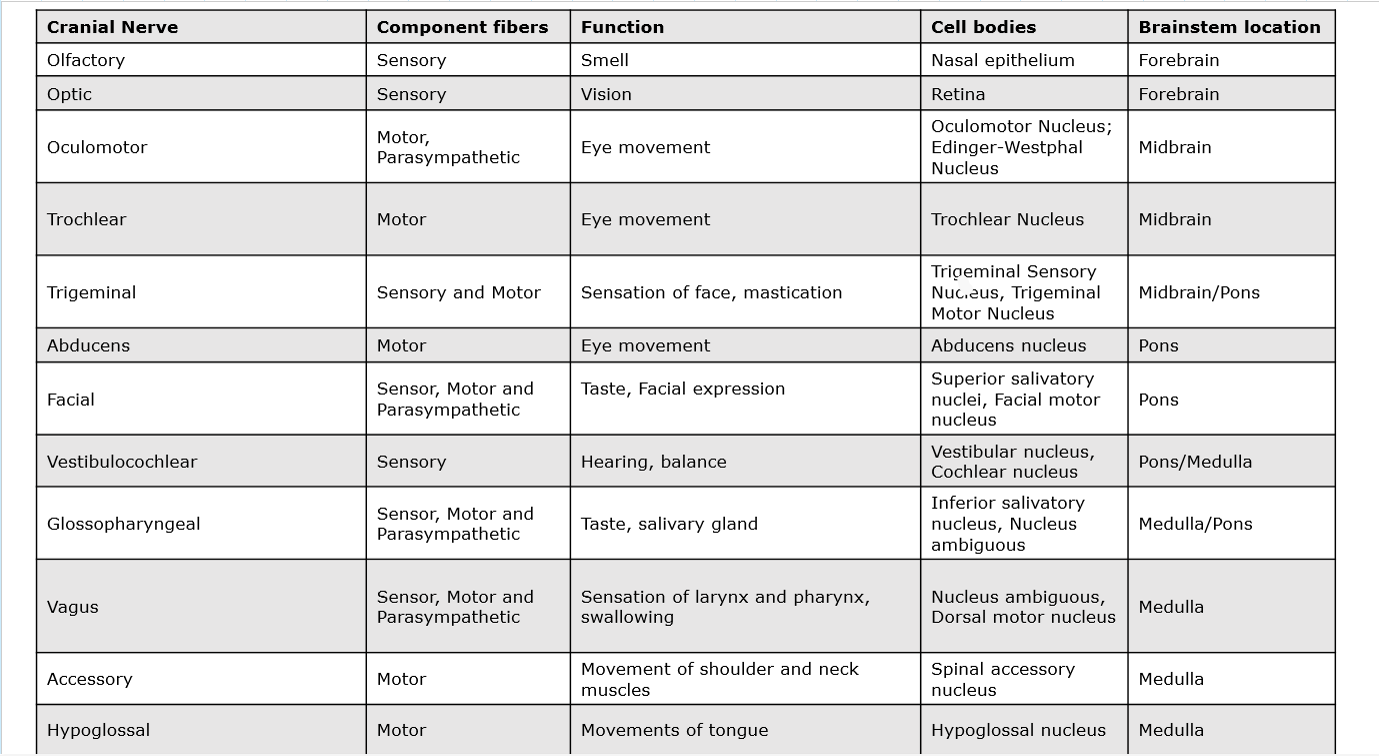
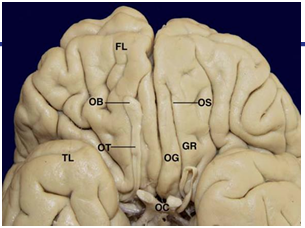
CN1: olfactory
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Sensory
Smell
Innervates olfactory epithelium via olfactory bulb—>olfactory tract which sit within olfactory sulcus
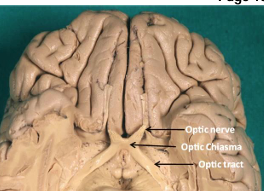
CN2: optic
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Sensory
Function: Vision
How: Innervates retina to transmit visual info from the retina to the brain
Optic nerve→ optic chiasma→ optic tract
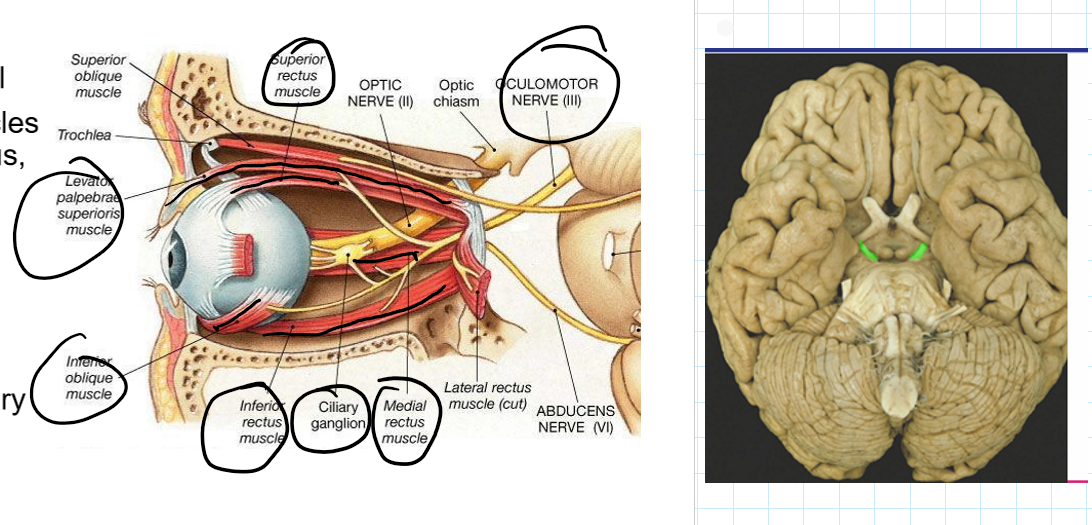
CN3: Oculomotor
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Examples of issues that could arise from damage to this CN
Motor
Function: Movement of the eyeball
How: Innervates extraocular muscles (superior, inferior and medial rectus, inferior oblique, levator palpebrae muscles)
Parasympathetic
Function: Pupillary constriction
How: pupillary constrictor and ciliary muscle of the eyeball via ciliary ganglion
Issue with this CN can cause dilated pupil and drooping eyelid, constricted pupil and upper lid elevation, dilation and drooping eyelid
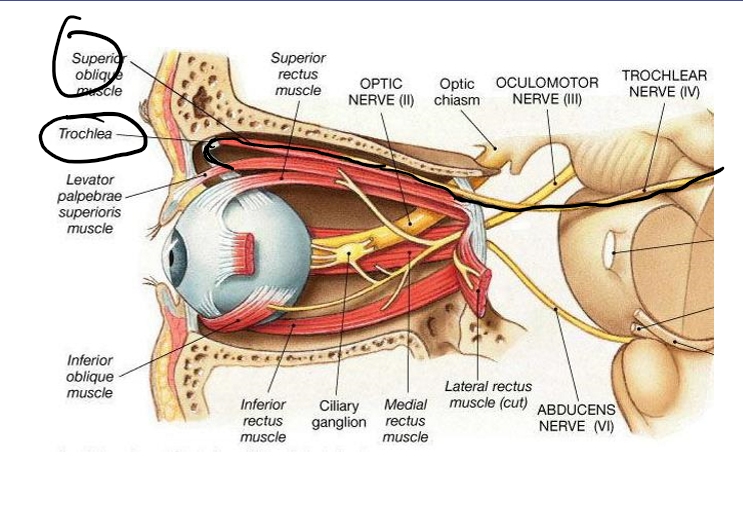
CN4: Trochlear
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Examples of issue that could arise from damage to this CN
Motor
Function: Movement of the eyeball down and medially
How: Only innervates the superior oblique muscle
Trochlear (4) Nerve Palsy: One iris that is higher than the other, double vision, head tilt
CN5: trigeminal
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Sensory
Function: General sensation
How: Innervates face, scalp, cornea, nasal and oral cavities, cranial dural mater
Motor
Function: 1. Opening and closing of the mouth, 2. Tension on tympanic membrane
How: 1. Innervation of the muscles of mastication, 2. Innervation of tensor tympani muscle
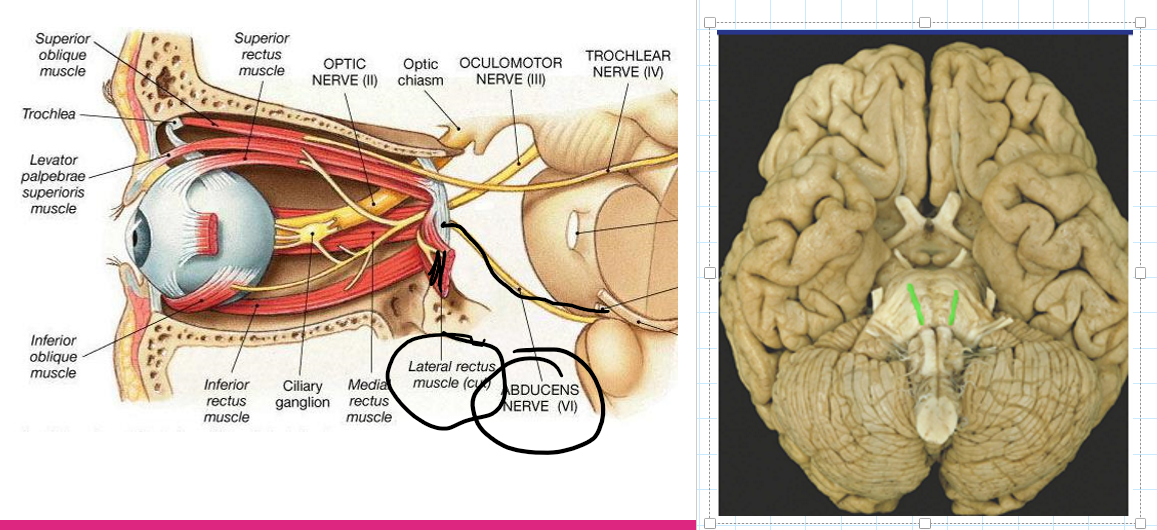
Abducens
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Examples of issue that could arise from damage to this CN
Motor
Function: Movement of the eyeball away from the midline
How: Innervates the lateral rectus muscle
Abducens (6) Nerve Palsy: One eye is pulled to look towards the midline, double vision, head rotate to look
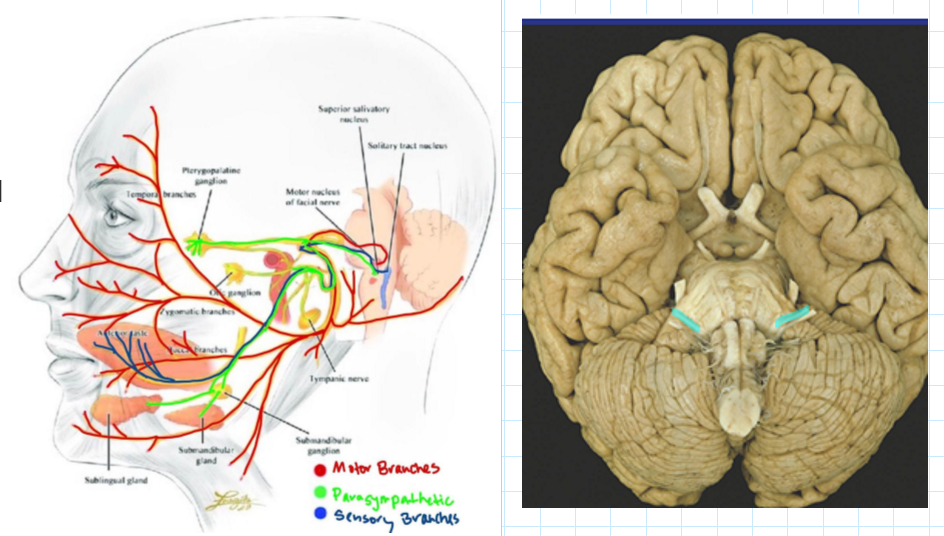
CN7: Facial
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Sensory
Function: Taste
How: Innervates anterior 2/3rd of tongue
Motor
Function: 1. Facial movement, 2. Tension on middle ear bones
How: 1. Innervates muscles of facial expression, 2. Innervates stapedius muscle
Parasympathetic
Function: Salivation and lacrimation
How: Innervates salivary and lacrimal glands
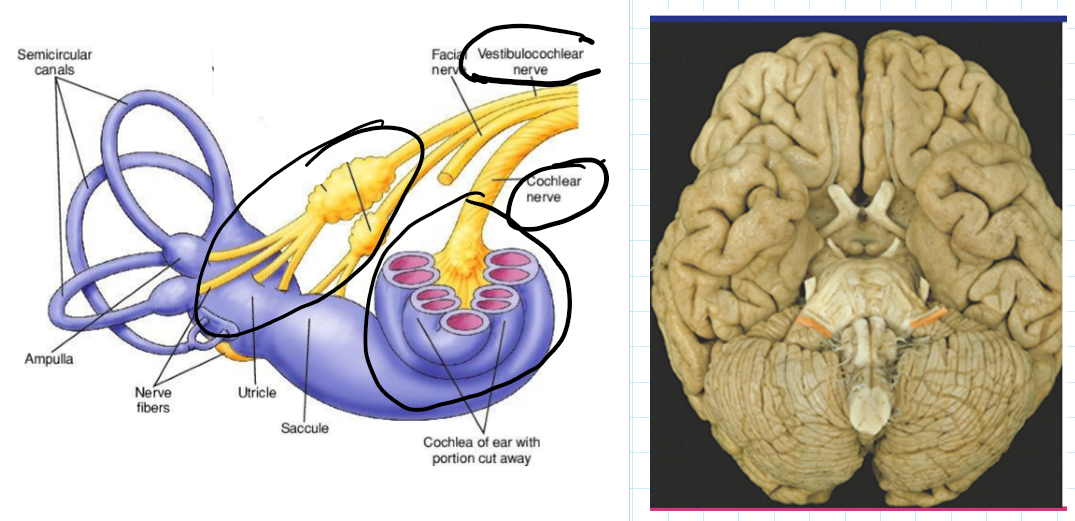
CN8: Vestibulocochlear
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Sensory
Function: 1. Vestibular sensation, 2. Hearing
How: 1. Innervates vestibular apparatus, 2. Innervates cochlea
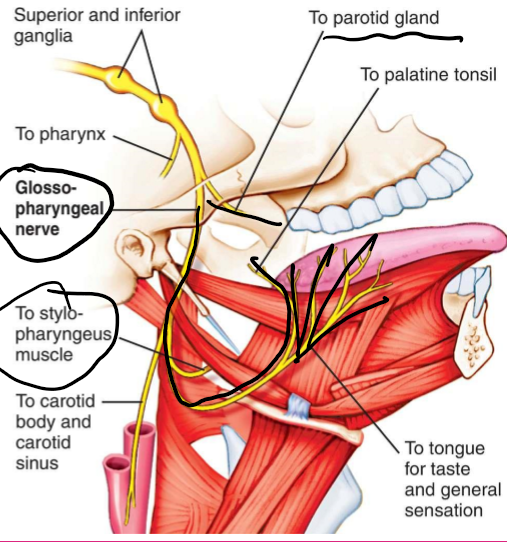
CN9: Glossopharyngeal
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Sensory
Function: 1. Generation sensation and taste, 2. General sensation of eustachian tube, 3. Chemo- and baroreception
How: 1. Innervates pharynx, posterior 1/3rd of tongue, 2. Innervates eustachian tube, middle ear, 3. Innervates carotid body and carotid sinus
Motor
Function: Swallowing
How: Innervates stylopharyngeus muscle
Parasympathetic
Function: Salivation
How: Innervates parotid salivary gland
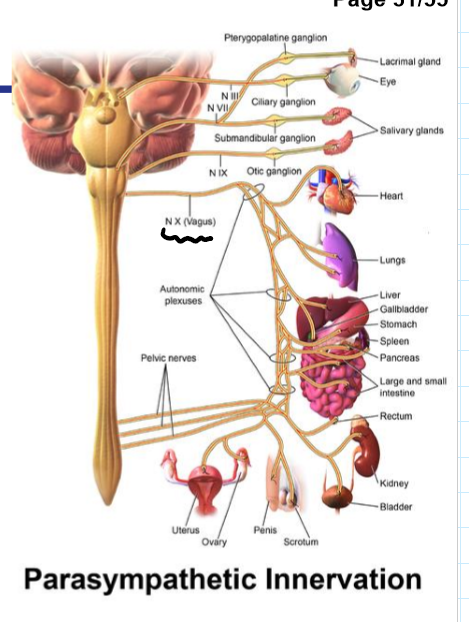
CN10: Vagus
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Sensory
Function: 1. Generation sensation and taste, 2. Chemo- and baroreception, 3. Visceral sensation
How: 1. Innervates pharynx, larynx, oesophagus, external ear, 2. Innervates aortic bodies aortic arch, 3. Innervates thoracic and abdominal viscera
Motor
Function: Speech and swallowing
How: Innervates soft palate, pharynx, larynx, upper oesophagus
Parasympathetic
Function: Control of cardiovascular, respiratory and gastrointestinal systems
How: Innervates thoracic and abdominal viscera
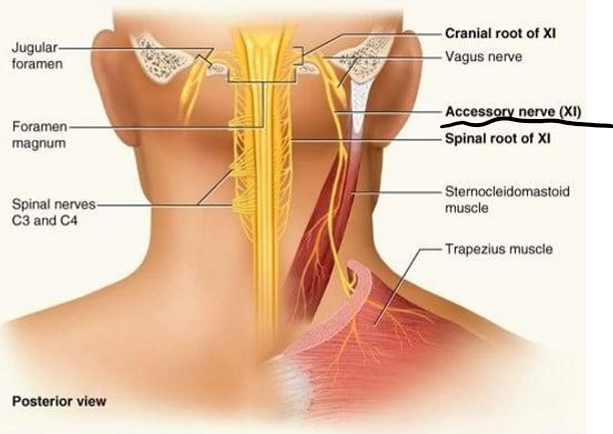
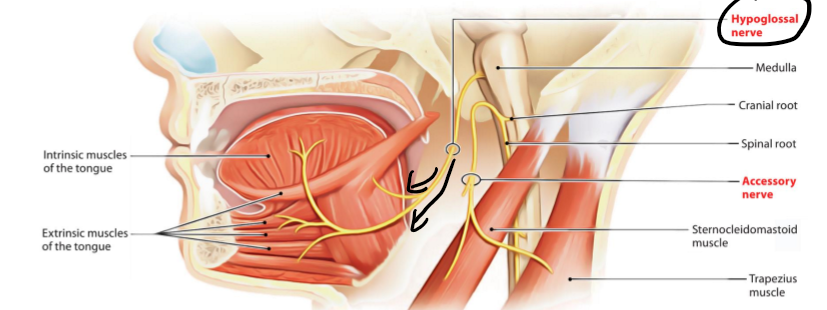
CN11: Accessory
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Motor
Function: Movement of the head and shoulder
How: Innervates the sternomastoid and trapezius muscles
CN12: Hypoglossal
Sensory, motor, parasympathetic
Function
Innervates where
Motor
Function: Movement of the tongue
How: Innervates the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue
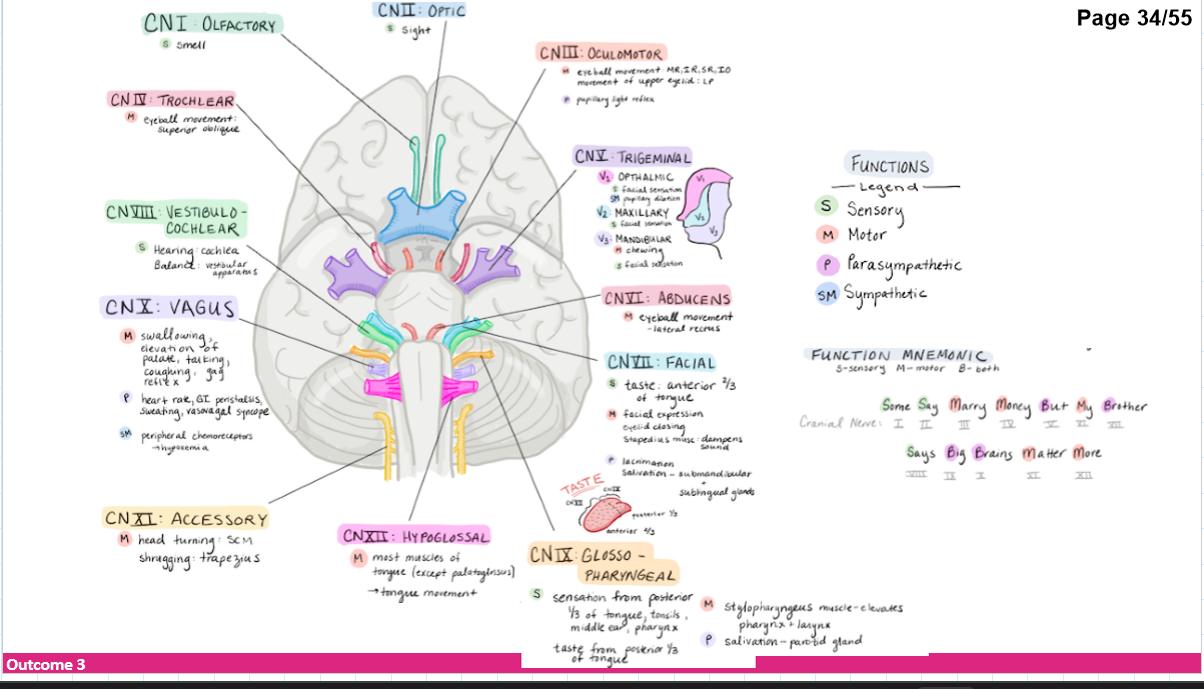
identify the cranial nerves
Identify the cranial nerves