Component 2 additional knowledge (beyond GCSE) (copy) (copy)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Definition of enthalpy change of reaction
is the enthalpy change when the molar quantities of reactants, as stated in the balanced equation, react under standard condition
Definition of enthalpy change of combustion
is the enthalpy change when one mole of a substance burns completely in oxygen under standard conditions.
Definition of enthalpy change of formation
is the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements, in their standard states, under standard conditions.
Define Hess' Law
that the enthalpy change converting reactants to products is the same regardless of the route taken provided the initial and final conditions are the same.
Define bond energy
is the energy required to break one mole of that particular bond in the gaseous state.
Defin enthalpy change
is the overall energy exchanged with the surroundings when a change happens at constant pressure and the final temperature is the same as the starting temperature.
Define exothermic
there is a net transfer of energy from the system to the surroundings.
Define endothermic
there is a net transfer of energy from the surroundings to the system.
Sign for exothermic is
negative
Sign for endothermic is
positive
Define calorimetry
the measurement of energy changes of a system by measuring their effect on surroundings.
Define specific heat capacity
the energy needed to raise the temperature of 1g of the material by 1K
Calorimetry equation
q= mc∆T
Standard conditions are
1 mol dm-3 100kPa 298K
Define rate of reaction
Amount of chemical change per unit time
Factors affecting rate
Concentration (pressure), surface area, temperature, catalyst
Define catalyst
a substance that speeds up a reaction by providing an alternative pathway of lower activation energy. The substance is not consumed in the process.
Define transition state
this is the point where energetically all of the energy added breaks bonds. It does not exist in isolation so cannot be extracted or detected.
Define intermediate
a temporary substance formed in a reaction that can be isolated.
Heterogeneous catalyst
reactants and catalyst are in different phases
Homogeneous catalyst
reactants and catalyst are in the same phase
Equations for oxidation of iodide ions by peroxodisulphate using iron
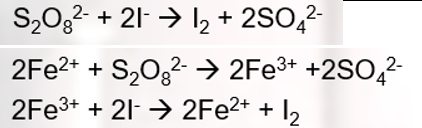
Equations for autocatalysis of ethanedioate with manganate (VII)
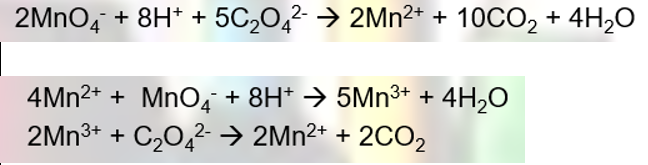
Green chemistry
An approach by chemists to reduce the environmental impact of chemical proceses. Whether that is reducing energy or using/producing chemicals that produce less waste or uses/produces less toxic materials.
Skeletal formulae
A formula that shows just the carbon backbone and any functional group.
Carboxylic acid prefix
Carboxy-
Aldehydes prefix
formyl
Ketones prefix
Oxo-
Esters prefix
alkoxycarbonyl
Amide prefix
carbamoyl
Alkene prefix
alkenyl
Alcohols prefix
Hydroxy-
Amines prefix
Amino-
Alkane (and branches) prefix
-yl e.g. Methyl
Halogeno prefix
eg Chloro-
Nitrile prefix
Cyano-
Alkyne prefix
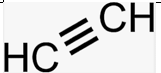
Alkynyl
Carboxylic acid suffix
-oic acid
Aldehydes suffix
-al
Ketones suffix
-one
Esters suffix
-oate
Amide suffix
-amide
Alkene suffix
-ene
Alcohols suffix
-ol
Amines suffix
-amine
Alkane (and branches) suffix
-ane
Nitrile suffix
nitrile
Alkyn suffix
yne
Addition
Two or more substances reacting to form one.
Substitution
Part of one molecule swapping place with a part of another.
Elimination
One compound releasing a small molecule and forming an unsaturated compound.
Hydrolysis
Using water to break a bond (sometimes using acids or bases as a catalyst).
Polymerisation
Where one or more monomer units join to form a long repeating chain.
Oxidation
Addition or oxygen or removal of hydrogen
Reduction
Removal of oxygen or addition of hydrogen
Electrophile
A lone-pair acceptor
Nucleophile
A lone-pair donor
Radical
A highly excited species with an unpaired electron (formed from homolytic fission)
Homolytic fission
Where a covalent bond splits equally with each species taking one electron
Heterolytic fission
Where a covalent bond splits unevenly (most common form of bond breaking in organic chemistry)
monomer
a single unit from which a polymer is built
polymer
a long chain of repeating units
repeating unit
a short-hand way of showing what repeats within the polymer
Primary classification
Where the ---------- is attached to a carbon that is attached to just one other carbon.
Secondary classification
Where the ---------- is attached to a carbon that is attached to two other carbons.
Tertiary classification
Where the ---------- is attached to a carbon that is attached to three other carbons.
Reflux
the continuous vapourisation and condensation of a substance using a vertically fitted condenser.
Hydrolysis
the splitting of part of a compound using water.
Standard answer for IR questions
the peak at pick a value is in the region …….cm-1 to …….cm-1 this suggest that this is a [type of bond] from a ……….
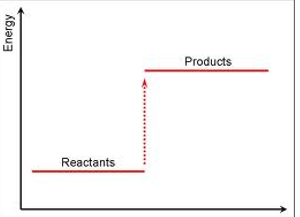
Exothermic energy level diagram
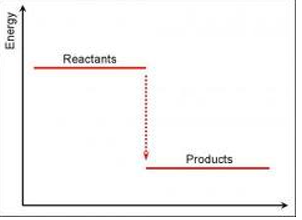
Endothermic energy level diagram
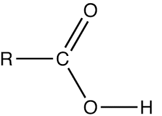
Carboxylic Acid
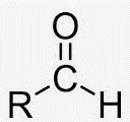
Aldehyde
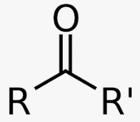
ketone
Ester
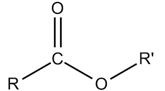
Amide
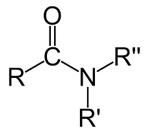
Alkene
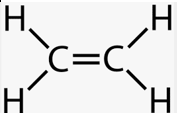
Alcohol
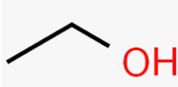
Amine
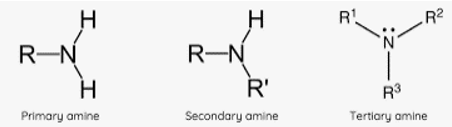
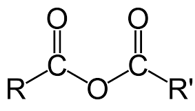
Acid anhydride
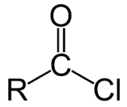
Acid chloride
Nitrile

Alkyne