Cellular communication - Lecture 10: Generation and propagation of action potentials
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What triggers action potential?
change in membrane voltage in response to a stimulus
change in membrane voltage activates voltage-gated sodium channels
increases membrane voltage to positive values
Na+ channels close
voltage gated K+ channels will get activated to return the membrane to resting value
What is the difference between the K+ and Na+ channels?
Na+ channels open faster and stop working within 1 msec
K+ channels open slower and stop working in ~2.5 msec
What causes the plateau phase and slow repolarisation?
rapid Ca2+ release from the ER
What causes cardiac muscle contraction?
cytoplasmic Ca2+
What is the term used for the part of the action potential that lies above 0 mV?
overshoot
What is the term used for the area under the resting potential?
hyperpolarizing phase
What are the refractory periods of the action potential
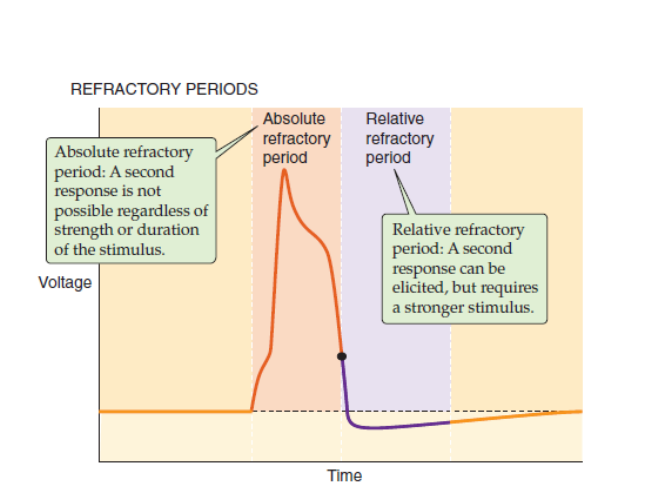
What causes the refractory period?
sodium channel inactivation
What are the distinct structures in a neuron?
cell soma
dendrites
axon hillock
axon
What effect does excitatory inputs have on the neuron cell membrane?
depolarise the membrane potential (more positive membrane potential)
What effect does inhibitory inputs have on the neuron cell membrane?
hyperpolarise the membrane potential (more negative membrane potential)
What is the function of neurons?
receive, combine, transform, store, and send information
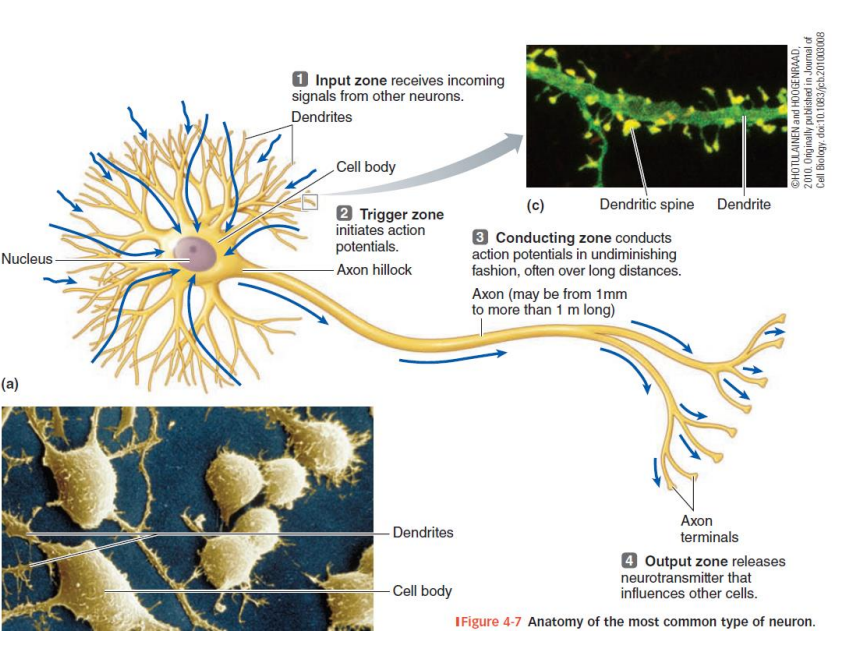
What does the excitation of a nerve or muscle depend on?
product (strength x duration) of the stimulus and on the refractory period
What disease can cause axon demyelination?
multiple sclerosis