Proteins & Amino Acids
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms by lowering the activation energy. They are typically proteins and are specific to substrates.
They speeds up the reaction
Hormones
Released by endocrine cells ( like cells of our pituitary glands)
Insulin
is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates glucose levels in the blood.
They bind to cells in liver and facilitated uptake of glucose. Helps return blood sugar to normal.
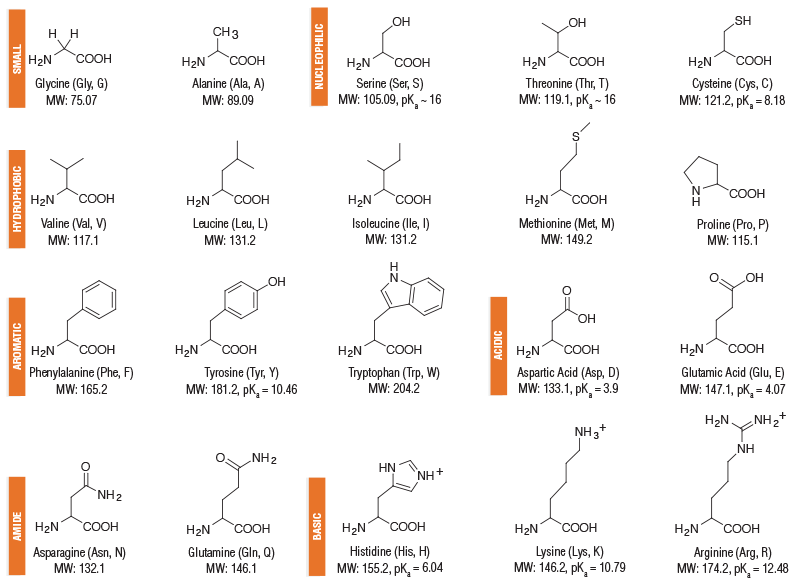
Amino Acids
Monomers that make up the proteins.
They are organic compounds that combine to form proteins and contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side chain and an alpha carbon.
How many amino acids are commonly found in proteins?
20
pH 7.2-7.4
amino acids is protonated and bears a positive charge
Carboxyl group
deprotonated and bears a negative charge
What determines the identity of the Amino ACids?
the R group which varies for each amino acid and determines their chemical properties.
Negatively charged amino acids [ acidic]
Aspartic acid & Glutamic acid
Positively charged [ BASIC]
Histidine
Lysine
Arginine
Amino acids polar charged
include Serine, Threonine, Glutamine and Asparagine, which have side chains that can form hydrogen bonds with water.
Non-polar hydrophobic
Alanine
Valine
Proline
Leucine
Isoleucine
Methionine
Tryptophan
phenylalanine
glycine
Proline
Forming a ring structure
Causes bends or kinks in amino acid chains
Cysteine
contain a thiol ( SH) group
Peptide bonds
are covalent bonds that connect amino acids in proteins.
they form through dehydration ( condensation) reaction
-C=O- NH
One end is N-terminus and other end is C-terminus
Amino acids that is not chiral
Glycine
All 20 amino acids have both their amino and carboxyl groups attached to the
alpha carbon
Aspartic acids
Asp, D
Glutamic acid
Glu, E
Lysine
Lys , K
Arginine
Arg, R
Histidine
His , H
Tryrosine
Tyr, Y ( polar, hydrophilic aromatic )
Phenalyanine
Phe, F ( non-polar, aromatic AA)
Tryptophan
Trp, W ( Hydrophic -aromatic )
Serine
Ser, S
Threonine
Thr, T
Cysteine
Cys, C
Asparagine
Asn, N
Glutamine
Gln, Q
Glycine
Gly, G
Alanine
Ala, A
Valine
Val, V
Leucine
Leu, L
Isoleucine
ILe, I
Methionine
Met, M ( thioether group)
Proline
Pro, P
Amino acids structure
Essential amino acids
Body cannot synthesize must be obtained from the diet.
Histidine
Leucine
isoleucine
lysine
methionine
phenylalanine
threonine
tryptophan
valine
Non-essential amino acdids
Can be synthesized by the body
Alanine
asparagine
aspartic acid
glutamic acid
serine
arginine
cysteine
gkutamine
glycine
proline
tyrosine
Post-translational modifications
Phosphorylation:- addition of phosphate group (serine, threonine & tyrosine)
Glycosylation:- attach carbohydrate groups, affect protein stability, folding and cell recognition
Acetylation & Methylation:- On lysine residue
Ubiquitination:- ubiquitin binds to lysine residues, taggs protein for degradation
Simplest level of protein structure
primary structure
sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
sequence of a protein is determined by the DNA of the gene that encode the protein
T or F. A change in the gene’s DNA sequenece may lead to change in the amino acid sequence of protein
TRUE
Sickle cell diseasea
Sixth amino acid change from glutamic acid to valine
local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone.
Secondary structure ( alpha helics & beta sheets )
Proline
Tertiary structures
Three dimensional folding due to side chain Interactions between the R groups of the amino acids that make up the protein.
Include hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, dipole-dipole interactions and london dispersion forces.
Hydrophobic interactions
Disulfide bonds
quaternary structure
Multiple polypeptide chains known as subunits
An example :- hemoglobin, DNA polymerase
Denatured protein
When a protein loses its higher order structure ( secondary, tertiary, quaternary) but not its primary sequence
They are non- functional
Chaperones
Heat shock proteins
ensure correct protein folding
prevent aggregation
Reversible denatration
Protein can refold into its native structure upon removing the denaturing agent
Irreversible denaturation
Results loss of protein structure and function often due to covalent modifications or aggregation of denatured proteins
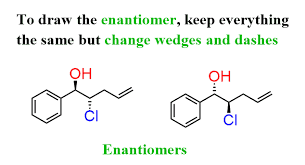
Chiral configuration that is found in the human body
L-form
L- configuration
NH2 on left side ( fischer)
D- configuration
on the R side
enantionmers
isomers