Chapter 39 (PART 2) : Pancreatic hormones and antidiabetic drugs
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What type of diabetes are oral antidiabetic drugs used for?
type 2 diabetes (B cells work but receptors don’t)
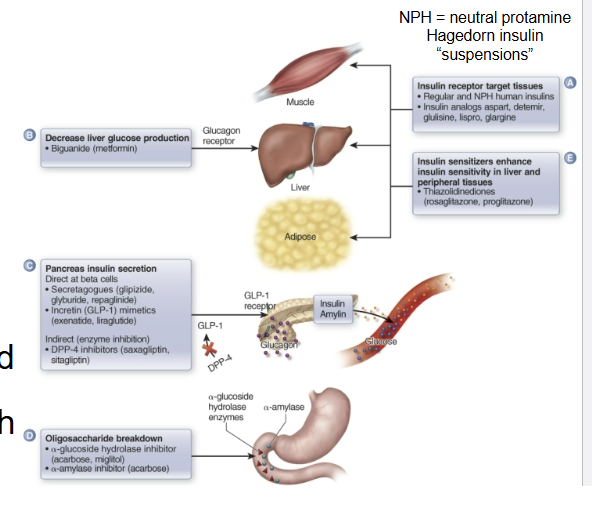
When are oral antidiabetics approved for treatment?
when diet and exercise have not achieved target glycemic control
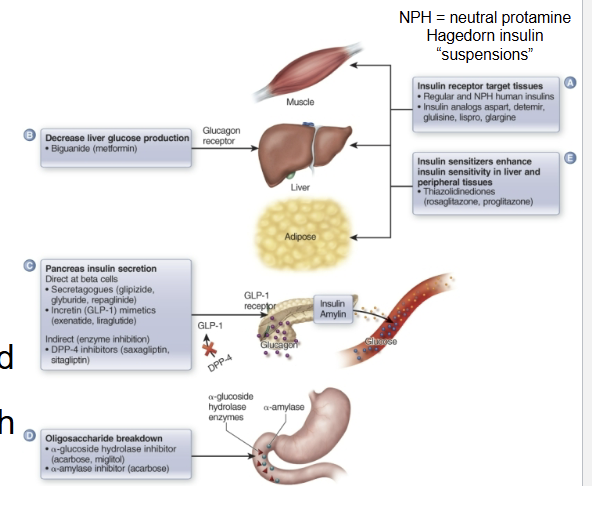
True or False:
Oral antidiabetic drugs can wither be used as a monotherapy or concurrently with other antidiabetic drugs, including insulin
True
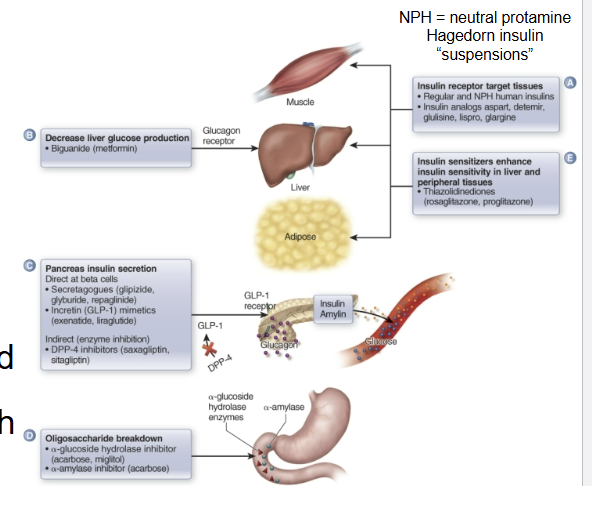
What class of oral hypoglycemic drugs is being described:
enter or act on beta cells and cause the release of insulin (increase release of insulin and amylin)
secretagogues
True or False:
Secretagogues should be used in type 1 diabetes
False, it should not
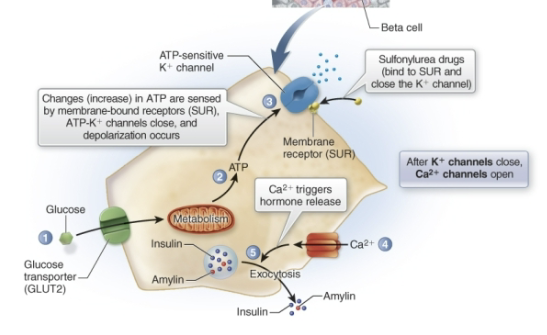
What do sulfonylureas do?
stimulate insulin release → reduce fasting plasma glucose
ex. Glipizide (Glucotrol)
What do non-sulfonylureas (aka. meglitinides) do?
stimulate insulin secretion
quicker onset of action than sulfonylureas
bind to SUR receptors and do the same thing but different chemical structure
ex. Repaglinide (Prandin)
True or False:
Secretagogues are contraindicated in type 1 diabetes, patients with liver or kidney disease, and pregnancy
True
True or False:
Glucose absorption inhibitors alter insulin secretion and blood glucose levels.
False, they do not alter insulin secretion or blood glucose levels.
What is the MOA of glucose absorption inhibitors?
interrupt carb digestion from diet (inhibit key enzymes → glycoside hydrolase)
glucose absorption delayed or less but not eliminated
keep blood glucose levels from peaking after meals
for type 1 or type 2
Ex. Miglitol (Glyset)
What drugs are being described:
antihyperglycemic drugs that keep blood glucose levels from rising too fast
biguanides
What is the MOA of biguanides?
decrease blood glucose levels after meals by decreasing liver glucose production and intestinal glucose absorption
also appears to enhance glucose use by other tissues in the body
mainly for type 2
When are biguanides contraindicated?
alcohol use increases the action of biguanides on lactic acid metabolism (more lactic acid made)
What is the MOA of insulin sensitizers?
enhance peripheral cell response to insulin (thus mainly for type 2)
allow glucose to be used more efficiently (can bind better)
decrease insulin resistance and increase insulin sensitivity of fat, skeletal muscle, and liver cells (activate nuclear receptors inside cells that regulate insulin activity)
leads to decreased circulating levels of glucose
Ex. Pioglitazone (Actos)
When are insulin sensitizers contraindicated?
in patients with CHF (congestive heart failure)
What does the gut hormone GLP-1 do?
stimulates the release of insulin from B cells
What enzyme metabolizes the gut hormone GLP-1?
dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4)
What is the MOA of DPP-4 inhibitors?
inhibits DPP-4 in the intestine causing:
stimulation of insulin secretion
decreased glucagon secretion
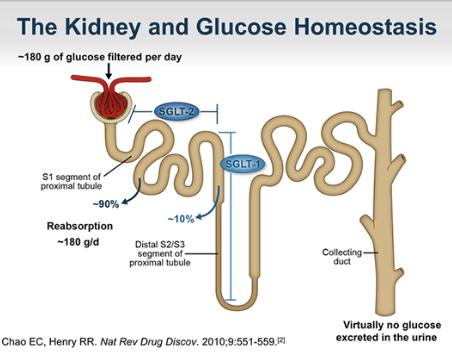
What is the MOA of SGLT-2 inhibitors?
acts at kidneys; inhibition of glucose reabsorption in the nephron, leaving excess glucose in urine to be excreted → decreasing blood glucose levels
used in type 1
Ex. Canagliflozin (Invokana)
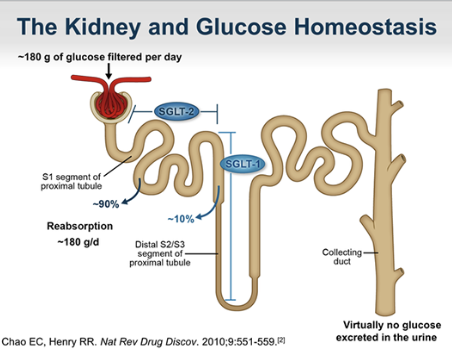
What are SGLT-1 and SGLT-2 ?
glucose transporters