respiratory exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/184
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:51 AM on 1/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
1
New cards
what is the upper respiratory tract responsible?
warms and filters inspired air
2
New cards
what test is used to determine is a pt can undergo anesthesia?
pulmonary function test
3
New cards
what does a PFT do?
measures volume and capacity of air to
4
New cards
what does a PFT DETERMINE?
lung function and breathing difficulties
5
New cards
who commonly gets PFTs done?
clients who have dyspnea
6
New cards
How long before a PFT does a pt need to stop smoking?
6-8 hrs prior
7
New cards
How long before a PFT does a pt need to stop taking bronchodilators?
4-6 hours prior
8
New cards
Why is it important to stop bronchodilators before a PFT test?
they alter the test results by showing inaccurate pulmonary function
9
New cards
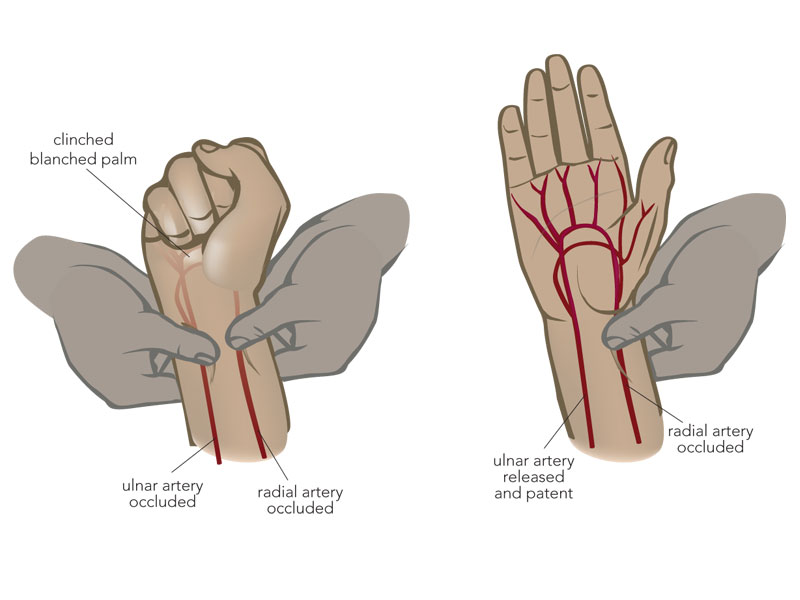
What test must be performed prior to getting an ABG?
ulnar test
10
New cards
What is the most effective means of assessing effectiveness of an oxygen therapy?
ABG
11
New cards
An ABG is an invasive procedure. What interventions can a RN do before doing an ABG?
make sure O2 pulse reader is working correctly, no nail polish on fingernail, if it’s on the finger, etc.
12
New cards
What artery is an ABG usually drawn from?
radial or arterial line
13
New cards
what does an ABG report?
oxygen and acid-base balance of the blood
14
New cards
what do the results of an ABG indicate if a pt is on oxygen therapy?
it will tell you if the oxygen therapy if working for the pt
15
New cards
before a bronchoscopy, the nurse must verify:
allergies, informed consent, use of meds like anticoagulants
16
New cards
A pt must be NPO how many hours prior to bronchoscopy?
4-8 hours prior
17
New cards
What is a pt given during a bronchoscopy to reduce aspiration?
sedative & local anesthesia to numb gag reflex
18
New cards
what is the purpose of a bronchoscopy?
permits visualization of the larynx, trachea, bronchi
19
New cards
who can a bronchoscopy be performed on?
pts receiving mechanical ventilation by inserting scope thru endotracheal tube
20
New cards
what kind of problems is a bronchoscopy performed?
tumors, inflammation, strictures, biopsies, aspiration of deep sputum or lung abscesses for culture and sensitivity (pneu.)
21
New cards
what is a normal or expected finding of a pt who underwent a bronchoscopy?
absent gag reflex
22
New cards
what has to be assessed in order for a pt to resume oral intake?
gag reflex & ability to swallow (due to aspiration pneu.)
23
New cards
what can indicate a pneumothorax is a post op bronchoscopy pt?
high fever, cough, hemoptysis, hypoxemia
24
New cards
Why should hemoptysis be reported IMMEDIATELY?
patient is coughing up blood
25
New cards
Thoracentesis is a ____ procedure.
sterile
26
New cards
what position must the pt be in while throacentesis?
upright position with arms and shoulders raised supported on pillows on overbed table with feet and legs supported
27
New cards
what is a thoracentesis?
surgical perforation of the chest wall and pleural space with a large-bore needle
28
New cards
why is a thoracentesis performed?
diagnostic evaluation, instill medications into the pleural space and remove fluid or air from the pleural space for therapeutic relief of pleural pressure
29
New cards
how is a thoracentesis performed?
under local anesthesia by a provider at the client's bedside, in a procedure room, or in a provider’s office
30
New cards
what decreases the risk of complications during a thoracentesis?
ultrasound
31
New cards
what is to be obtained to locate pleural effusion and determine/confirm insertion site?
x-ray
32
New cards
what must a nurse do of a post op thoracentesis?
•Apply a dressing over the puncture site and assess dressing for bleeding and drainage
•Obtain a post procedure x-ray to rule out possible pneumothorax
•Obtain a post procedure x-ray to rule out possible pneumothorax
33
New cards
where are chest tubes inserted?
pleural space
34
New cards
why is a chest tube needed?
drain fluid, blood or air; reestablish a negative pressure; facilitate lung expansion and restore normal intrapleural pressure
35
New cards
what kind of problems is a chest tube inserted?
pneumothorax, post-op chest drainage, pleural effusion, pulmonary empyema
36
New cards
A partial to complete collapse of the lung due to the accumulation of air in the pleural space is ____.
pneumothorax
37
New cards
**Hemothorax is** partial to complete collapse of the lung due to ___.
to accumulation of blood in pleural space
38
New cards
What are examples of post - op drains?
thoracotomy or open-heart surgery
39
New cards
What is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space?
pleural effusion
40
New cards
**Pulmonary empyema is an** accumulation of what?
pus in the pleural space due to pulmonary infection
41
New cards
What is the first chamber used for?
drainage collection
42
New cards
What do you expect to see in the second chamber?
tidaling of water (sterile)
43
New cards
what is tidaling?
movement of water caused by inhalation/exhalation
44
New cards
what is the purpose of the 2nd chamber/water seal?
allows air to exit pleural space via exhalation, stops the air form entering via inhalation
45
New cards
what is an expected finding in the third chamber?
continuous bubbling
46
New cards
the third chamber is the ___/
suction control that can be wet/dry
47
New cards
How do you create a water seal?
adding sterile fluid to 2 cm line
48
New cards
where should the chest tube be kept at all times?
below chest tube insertion site with chamber upright
49
New cards
What does cessation of tidaling signal/indicate?
lung re-expansion or an obstruction w/i the system
50
New cards
Continuous bubbling is ONLY normal in the third chamber, but in the second chamber it may indicate:
air leak
51
New cards
chest tube pt should always
deep breathe, cough, incentive spirometer
52
New cards
how much excess drainage should an RN alert the physican?
70 ml/hr
53
New cards
what should a nurse assess on a chest tube pt?
skin for any redness, pain, infection ,crepitus
54
New cards
if a pt if encourage to ambulate with a chest tube:
administer pain meds prior to movement
55
New cards
air leaks can result from?
connection is not taped securely
56
New cards
what does rn do is air leak is detcted?
monitor water seal for bubbling, check all connections,
57
New cards
Rn calls physician is she/he cannot ___
resolve air leak
58
New cards
If disconnection of tube occurs, nurse instructs pt to:
to exhale as much as possible and to cough to remove as much air as possible from the pleural space
59
New cards
where does rn place end of chest tube system if compromised?
sterile water (temporary water seal)
60
New cards
what does rn do if chest tube is accidently removed?
dress area with petroleum gauze w dry sterile gauze and tape it
61
New cards
what is an indicative of a tension pneumothorax?
tracheal deviation, absent breath sounds, distended neck veins
62
New cards
what causes a tension pneumothorax?
sucking chest wounds, prolonged clamping of the tubing, kinks or obstruction in the tubing, or mechanical ventilation with high levels of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP)
63
New cards
tension pneumothorax requires
provider or rapid response team
64
New cards
when removing chest tube, rn must tell client to
exhale and bear down (Valsalva maneuver)
65
New cards
why does pt do Valsalva maneuver with removal of tube?
increase intrathoracic pressure and reduce risk of air emboli
66
New cards
Oxygen is considered a med, therefore
provider order is needed
67
New cards
Oxygen via nasal cannula can be used @ any time of pt stay to
improve O2 status due to standing order
68
New cards
The goal of oxygen therapy is
provide adequate transport of oxygen in the blood
69
New cards
Early findings of hypoxemia/hypoxia:
EARLY=HIGH
EARLY=HIGH
tachypnea, tachycardia, restlessness, pale skin and mucous \n membranes, ELEVATED blood pressure, findings of respiratory distress
70
New cards
Late findings of hypoxemia.hypoxia:
LATE=LOW
LATE=LOW
Confusion and stupor, cyanosis, \n bradypnea, bradycardia, hypotension and cardiac dysthymias
71
New cards
what is a big indicator that a pt has become hypoxic?
if pt states he/she is anxious
72
New cards
The longer the extension tubing for an at home pt, the longer ___.
the long O2 takes to inhale
73
New cards
What are things a pt MUST do if he/she is receiving oxygen at home?
wear cotton clothes, put “NO SMOKING” signs, refrain from smoking, no alcohol (or acetone), have fire *extinguisher*
74
New cards
PT must call provider if more liters of oxygen is needed. (T/F)
true, pt must follow prescription
75
New cards
A nasal cannula breaks down the skin in the ___.
nose and ears
76
New cards
A simple face mask is a low flow oxygen delivery method that has to be
sealed tightly around mouth
77
New cards
When a pt is not wearing delivery methods other than nasal cannula, a nasal cannula is still neded to
eat/drink
78
New cards
any type of masks are contradicted in pt who
have claustrophobia or anxiety
79
New cards
partial rebreather mask:
has reservoir bag attached with no valve, which allows the patient to rebreathe up to one third of exhaled air together with room air
80
New cards
Why must the bag always have to be INFLATED with breather masks?
CO2 can build up
81
New cards
What O2 delivery method gives the most amount of oxygen?
nonrebreather mask
82
New cards
who benefits from NONrebreather masks?
best for those that may require intubation
83
New cards
what advantages does a nonrebreather have?
inhale maximum O2 from the reservoir bag
84
New cards
The venturi mask is a high flow and precise oxygen concentration best suited for
chronic lung dx pts
85
New cards
disadvantage of venturi mask
expensive due to multiple parts
86
New cards
Aerosol mask, face tent and tracheostomy collar is a high Flow that is good for
pts. who do not tolerate masks well, useful for clients who have facial trauma, burns or thick secretions
87
New cards
disadvantages of aerosol mask
high humidification requires frequent monitoring
88
New cards
nursing actions for aerosol mask
Empty condensation from the tubing often
Ensure that there is adequate water in the humidification canister
Ensure that the aerosol mist leaves from the vents during inspiration and expiration
Make sure the tubing does not pull on the tracheostomy
Ensure that there is adequate water in the humidification canister
Ensure that the aerosol mist leaves from the vents during inspiration and expiration
Make sure the tubing does not pull on the tracheostomy
89
New cards
What position should a patient be in for chest tube placement?
supine or semi-fowler's
90
New cards
Provide pain medication ______ before removing chest tubes
30 mins
91
New cards
What are important nursing actions for nasal cannulas?
assess nostril latency, ensure prongs fit nares properly, use water-soluble gel to prevent dry nares, provide humidification
92
New cards
In case of a chest tube accidently came out, how many pieces of tape are need when re-inserting?
3 because there needs to be a side that allows air out
93
New cards
What are advantages of a T-piece?
can be used for clients who have tracheostomies, laryngectomies, or endotracheal tubes
94
New cards
Ensure that exhalation port is ___ and uncovered with t-piece.
open
95
New cards
Ensure t-piece does not pull on ___ or ET tube.
tracheotomy
96
New cards
Ensure that the __ *is evident during* __.
mist; inspiration and expiration
97
New cards
Oxygen toxicity can result from what?
High concentrations of oxygen
98
New cards
What clinal manifestations occur from oxygen toxicity?
cough, substemal pain, nasal stiffness, N/V, fatigue, HA, sore throat and hyperventilation
99
New cards
Oxygen-induced hypoventilation can develop in client who:
have COPD and hypoxemia
100
New cards
What is another teaching factor for patients on oxygen?
must also educate family members about dangers of smkoing during O2 use, ensure electric devices are grounded and working