Gene Expression and Regulation: (30-31)
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
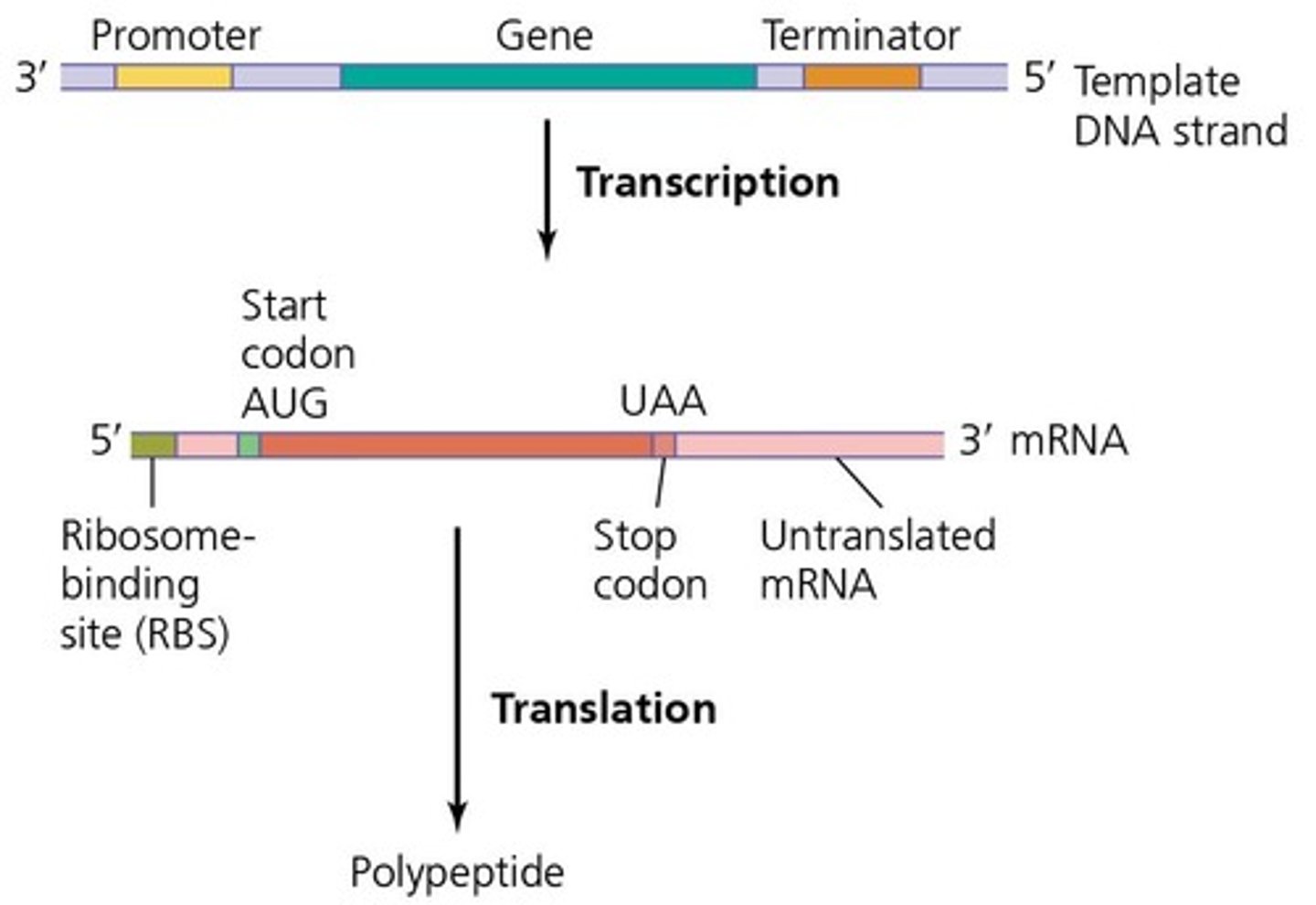
Promoter
A DNA sequence that initiates transcription of a gene.
Transcriptional start site
The location on the DNA where transcription begins.
5' UTR
The untranslated region at the 5' end of an mRNA molecule.
Start codon
The codon that signals the start of translation, typically AUG.
Stop codon
A codon that signals the end of translation.
Intron
A non-coding segment of a gene that is removed during RNA splicing.
Exon
A coding segment of a gene that is retained in the final mRNA.
3' UTR
The untranslated region at the 3' end of an mRNA molecule.
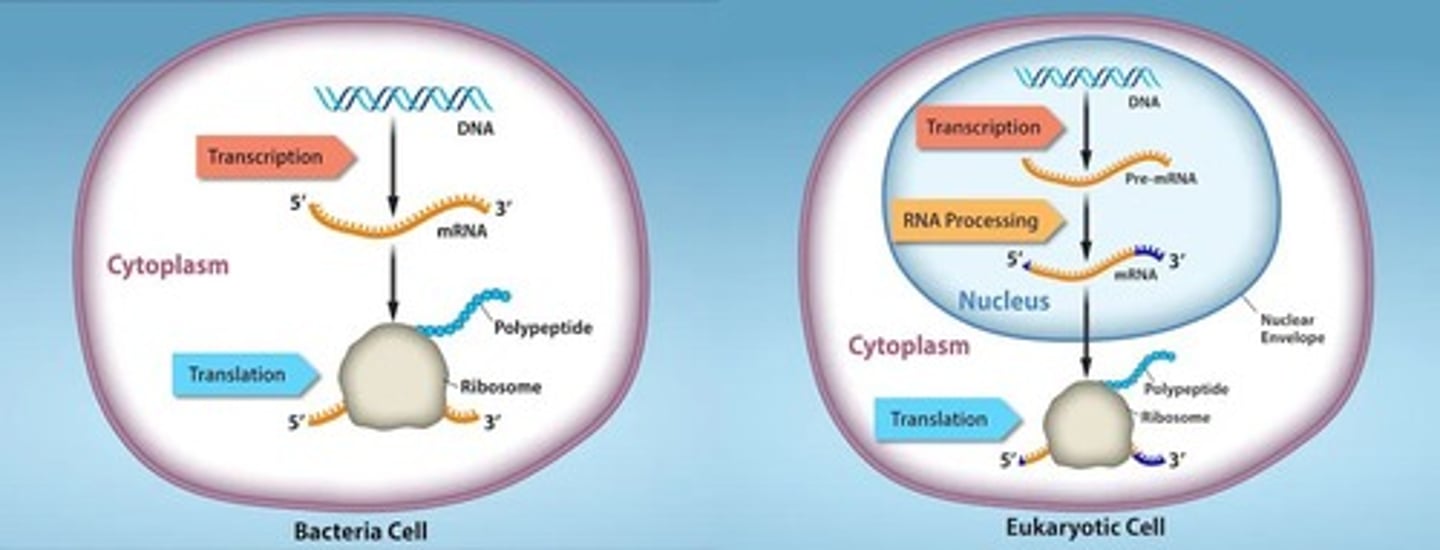
Prokaryotic translation
Occurs in the cytosol where transcription and translation can occur simultaneously.
Eukaryotic translation
Occurs in the cytosol, separated from transcription.
Post-translational processing
Modifications that occur to a protein after it has been synthesized from the DNA code.
Chemical Modification
The covalent attachment of various chemical groups to specific amino acid residues in a protein.
Protein Folding
The proper folding of the polypeptide chain into its functional conformation.
Chaperone proteins
Proteins that assist in the proper folding of other proteins.
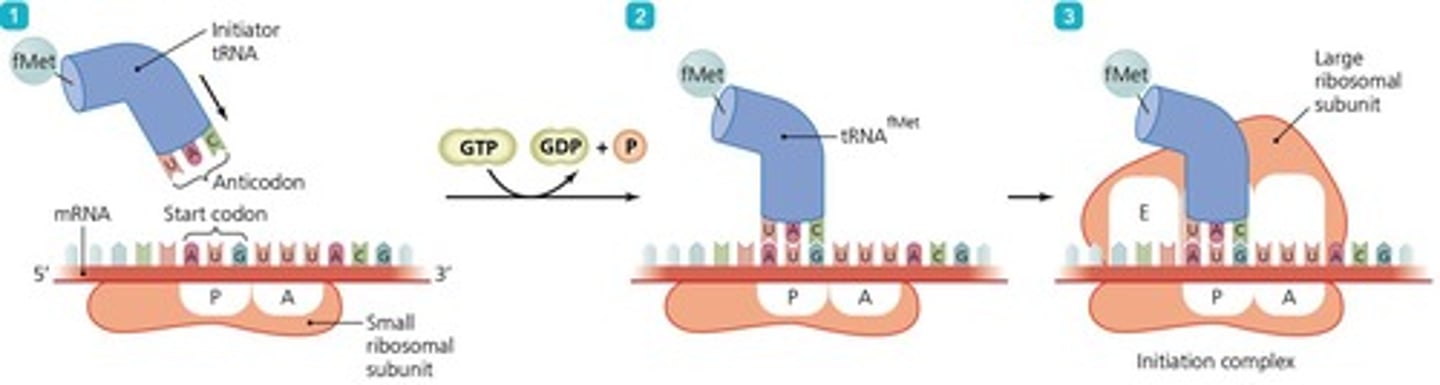
Initiation
The step where the small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA and the initiator tRNA binds to AUG.
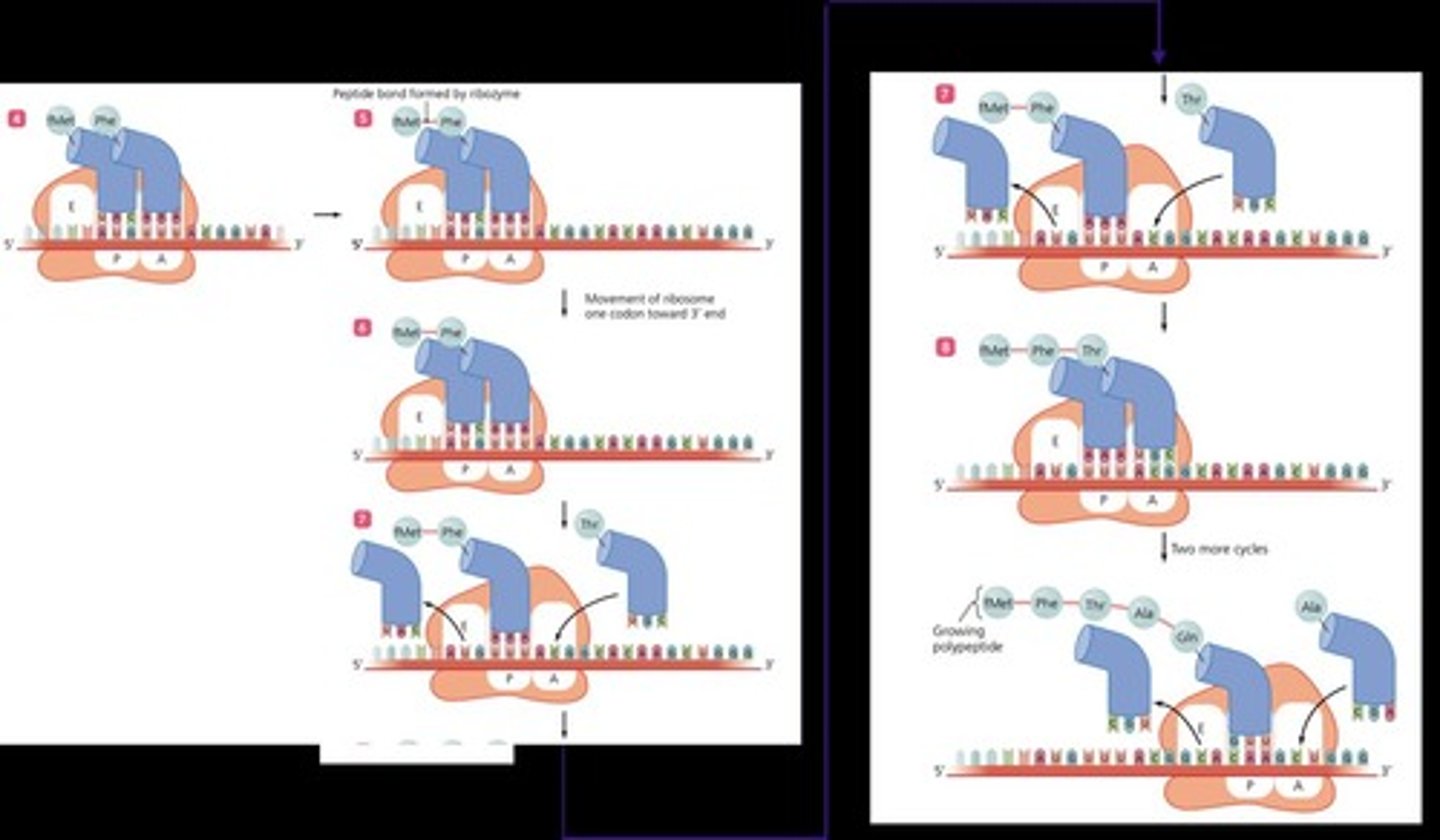
Elongation
The step where amino acids are added one by one to the growing protein chain.
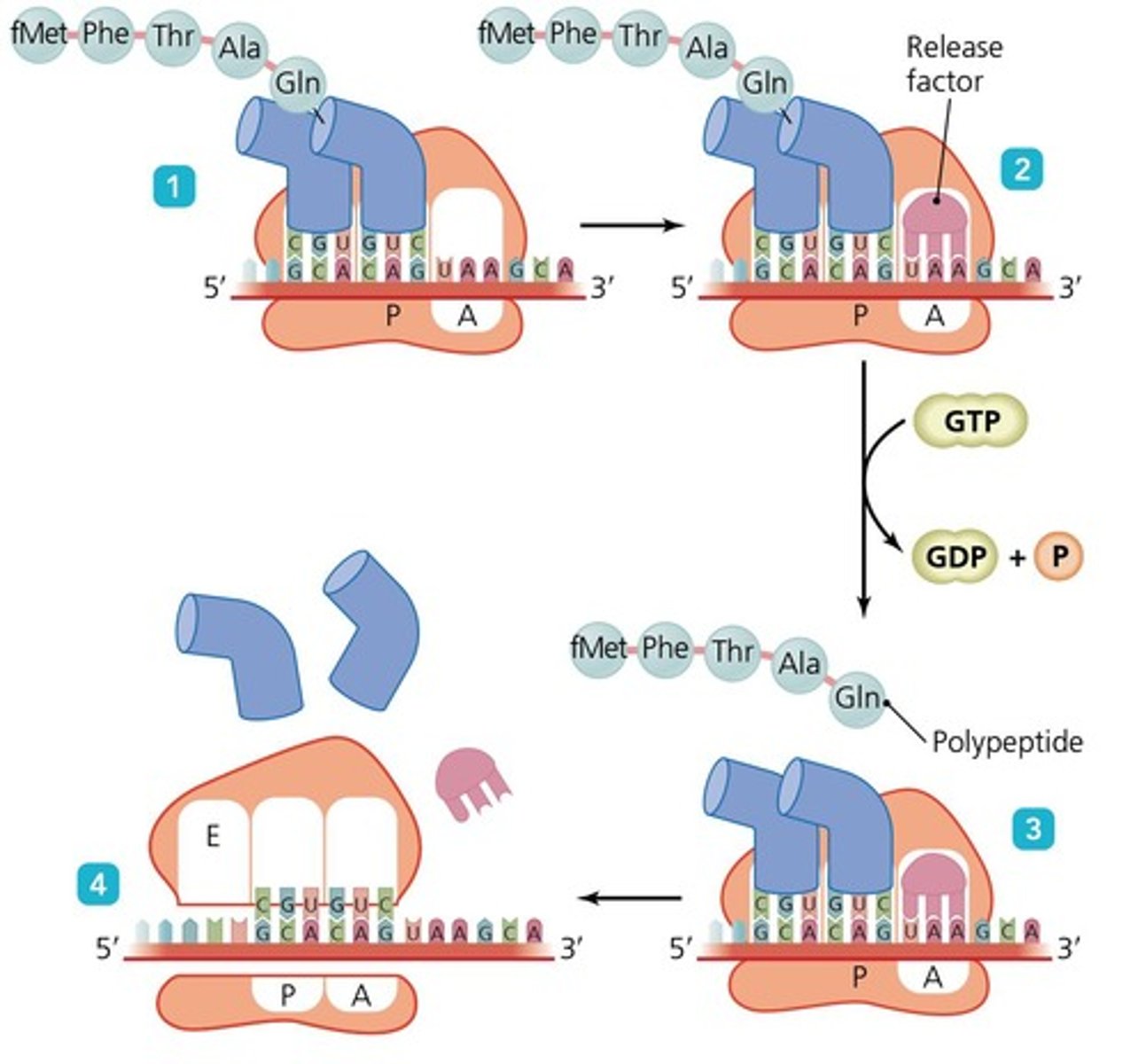
Termination
The step where the ribosome reaches a stop codon, signaling the end of the protein chain.
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The framework for understanding the transfer of sequence information from DNA to RNA to protein.
Protein Synthesis
The biological process by which cells generate proteins from genetic information.
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
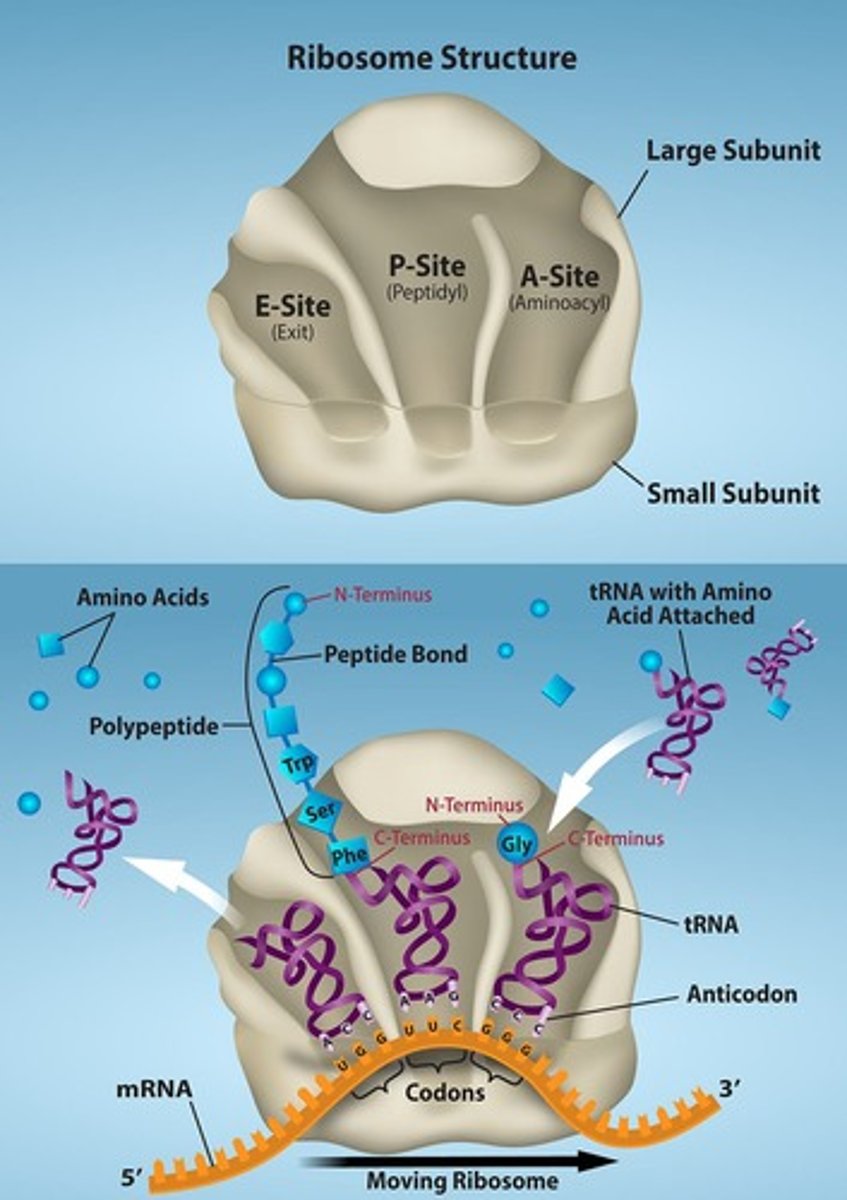
Ribosomes
Cellular structures where protein synthesis occurs.
tRNA
Transfer RNA, which transports amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis.

mRNA
Messenger RNA, which carries the genetic code from DNA to the ribosome.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA, a component of ribosomes.
Reading frame
The way nucleotides in mRNA are divided into codons.
Release factor
A protein that recognizes the stop codon during termination of translation.
tRNA binding sites
The sites on the ribosome where tRNA molecules bind during translation (E, A, and P sites).
Transfer RNA
When tRNA is bound to an amino acid, it is called charged or an aminoacyl-tRNA.
Ribosome
The ribosome is responsible for translating the mRNA into protein.
Ribosomal Subunits
The ribosome consists of a large and small ribosomal subunit.
A-site
During translation, charged tRNAs enter the A-site, and the anticodon on the tRNA base pairs with the codon in the mRNA.
P-site
After the incoming amino acid forms a peptide bond with the growing polypeptide chain, the ribosome will move three nucleotides toward the 3' end of the mRNA, transferring the tRNA with the growing polypeptide to the P-site.
E-site
The empty tRNA exits at the E-site.
Initiation of Translation
The initiation of translation in prokaryotes involves several key steps, starting with the binding of the small ribosomal subunit to the mRNA molecule.
Initiation Complex
The next step involves the binding of an initiator tRNA molecule to the start codon, carrying the amino acid methionine.
Large Ribosomal Subunit
After the formation of the initiation complex, the large ribosomal subunit associates with the small subunit, completing the initiation complex.
Elongation Stage of Translation
The elongation phase of translation involves the sequential addition of amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain.
Binding of tRNA
The elongation phase begins when a tRNA binds to the A site of the ribosome.
Peptide Bond Formation
The ribosome catalyzes peptide bond formation between the amino acid on the tRNA in the A site and the growing polypeptide chain on the tRNA in the P site.
Termination of Translation
The ribosome reaches a stop codon, which signals the end of the protein chain.
Newly Synthesized Protein
The newly synthesized protein is then released from the ribosome and folds into its final three-dimensional structure.
Translocation
The process where the ribosome moves one codon along the mRNA in the 3' direction after peptide bond formation.
Exit of tRNA
The discharge of tRNA from the E site of the ribosome, making room for a new tRNA to enter the A site.
Recognition of the Stop Codon
When the ribosome reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) on the mRNA, there are no corresponding tRNA molecules that recognize these codons.
Release Factors (RFs)
Proteins that bind to the A site of the ribosome, recognizing the stop codon.
Peptide Release
The binding of the release factor triggers hydrolysis of the bond between the completed polypeptide chain and the tRNA at the P site.
Dissociation of Ribosomal Subunits
After peptide release, the ribosomal subunits, mRNA, and any remaining tRNA molecules dissociate from each other.
Polyribosome
Groups of ribosomes bound to a single mRNA molecule simultaneously during translation.
Advantages of Polyribosomes
They increase the efficiency of protein synthesis, enable quick responses to environmental changes, and protect mRNA from degradation.
Misfolded proteins
Proteins that can be degraded by the cell's quality control machinery or can lead to protein aggregation and disease, such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease.
Gene
A fundamental unit of heredity and a segment of DNA that encodes the information to make a specific product, typically a protein, but also various types of RNA.

Transcription Start Site (TSS)
The DNA sequence where RNA polymerase begins the synthesis of RNA.
Core Promoter
The minimal portion of the promoter region needed to start transcription, often containing essential elements such as the TATA box, Initiator element, and others.
Poly(A) Site
The DNA sequence where the pre-mRNA is cleaved and a polyadenylate tail is added during RNA processing, which is important for mRNA stability, nuclear export, and translation initiation.
TATA Box
A DNA sequence (TATAAA) found in the promoter region of many genes, helping to determine the transcription start site by binding the TATA-binding protein.
3' UTR
The portion of an mRNA molecule directly downstream of the coding sequence, often containing regulatory elements that influence mRNA stability and translation efficiency.
5' UTR
The portion of an mRNA molecule directly upstream of the coding sequence, often containing regulatory elements that influence translation.
Exons
Segments of a gene or mRNA molecule that contain the protein-coding sequence; they remain in the mature mRNA after splicing.
Introns
Non-coding segments of a gene that are transcribed into RNA but are removed by splicing during the processing of the pre-mRNA into mature mRNA.
Translation in Eukaryotes
Initiation occurs when ribosomal subunit binds to 5′ guanine cap; ribosomes synthesize polypeptides into the cavity of the rough endoplasmic reticulum and on free ribosomes; translation and transcription are decoupled.
Tetracycline
An antibiotic that blocks the A site on the bacterial ribosome, affecting tRNA binding to the ribosome, ribosome assembly, and growth of the protein chain.
Chloramphenicol
An antibiotic that blocks peptidyl transfer on the bacterial ribosome, affecting tRNA binding to the ribosome, ribosome assembly, and growth of the protein chain.
Gene Regulation
The ability of cells to control their level of gene expression.
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation
Primarily occurs at the transcriptional level.
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
Involves more complex regulatory mechanisms allowing greater control over gene expression.
Transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA.
RNA Processing
The modification of RNA before it is translated into protein.
Translation
The process of synthesizing proteins from RNA.
Post-Translational Modification
Changes made to proteins after they are synthesized.
Chromatin Structure
Influences whether genes are accessible for transcription and can be expressed.
Euchromatin
Less densely packed chromatin generally associated with gene expression.
Heterochromatin
Densely packed chromatin generally associated with gene silencing.
Methylation
The addition of methyl groups to histone proteins, which can activate or repress gene expression.
Acetylation
Neutralizes the positive charge on histones, making chromatin more open and accessible to transcription machinery.
Structural Genes
Genes that code for proteins that perform a function, such as metabolic enzymes.
Regulatory Genes
Genes that affect the transcription and translation of other genes.
Lac Repressor Protein (lacI)
A regulatory protein that prevents transcription of genes needed for lactose metabolism in the absence of lactose.
Constitutive Genes
Genes that are transcribed continually.
Non-constitutive Genes
Genes that can be switched on (induced) or off (repressed).
Gene Expression Efficiency
Regulation maintains efficiency in energy, space, and time by preventing unnecessary gene expression.
Somatic Cells
Cells that contain the full genome of an organism but do not express all genes simultaneously.
Open Chromatin
Less densely packed chromatin generally associated with gene expression.
Closed Chromatin
Densely packed chromatin generally associated with gene silencing.
Epigenetic Control
Includes histone modifications (methylation and acetylation) and DNA methylation.
Lac Repressor
Part of the lac operon, a regulatory system in E. coli and other bacteria.
Transcription Factors
Bind to DNA sequences called promoters which control the initiation of transcription in eukaryotes.
Post Transcriptional Modification
In eukaryotes, RNA transcripts must be processed into their final form before translation can begin, and this step can be regulated to control gene expression.
RNA Splicing
The process of alternatively splicing pre-mRNA to create different proteins, occurring in the nucleus.
5' Cap
A methylated guanosine triphosphate molecule (GTP) that prevents degradation of the transcript.
Poly-A Tail
Prevents degradation of the transcript and is found at the end of mRNA.
Untranslated Regions (UTRs)
The protein-coding region of mRNA is flanked by 5' and 3' UTRs.
RNA-binding Proteins (RBPs)
Influence RNA stability at UTRs, can increase or decrease the length of time mRNA is present in the cytoplasm, and regulate mRNA localization and protein translation.
Differential Gene Expression
The patterns of gene expression that arise in different cells, leading to the development of a complete organism.
Transcriptional Regulation in Prokaryotes
Occurs primarily through mechanisms like the lac operon and lac repressor.
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes
Occurs at multiple levels: transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational.
Translational Control
Occurs at the ribosomes; translocation at the ribosome cannot occur when elongation factor 2 is phosphorylated.
Chemical Modifications Affect Protein Activity
Proteins can be chemically modified through the addition or removal of various markers, tags, and functional groups, regulating protein activity or length of time the protein exists in the cell.
Effects of Chemical Modifications
Can alter epigenetic accessibility, transcription, mRNA stability, translation, and protein stability.
Ubiquitin Tags
Proteins with ubiquitin tags are marked for degradation.
Protein Phosphorylation
Can regulate gene expression by altering the activity, localization, or interaction of transcription factors and other proteins involved in the gene expression machinery.