3.1 revision organic general
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
saturated
containing single C-C bonds only
unsaturated
contains a C=C double bond
alkane
suffix: -ane
alkenes
suffix: -ene
alcohols
suffix: -ol
prefix: hydroxy-
halogenoalkanes
prefix: chloro-, bromo-, iodo-
aldehydes
suffix: -al
prefix: formyl-
ketones
suffix: -one
prefix: oxo-
carboxylic acids
suffix: -oic acid
esters
suffix: -yl, -oate
highest group takes the
suffix
order of functional group priority
carboxylic acids>aldehydes>alcohols>alkenes>halogenoalkanes
when there are two or more of the same groups
use di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, etc. s
separate words and numbers
with dashes se
separate numbers
with commas
if there is more than one functional group/side chain
list in alphabetical order
alkenes
double bond between 2 carbons, use lower number to show position
E or Z alkenes //stereoisomer
suffix -en goes in front of other suffixes
alcohols
has higher priority than halogenoalkane => higher number
aldehydes
C=O bond on the first carbon => doesn’t need a number (use -al)
ketones
when ketones have 5 or more carbons in chain => need number to show position of the double bond (-one)
carboxylic acids
no number needed, carboxylic acid is highest prioirty
if carboxylic acid groups on both ends => -dioic acid
homolytic fission
each atom gets one electron from the covalent bond
broken bond forms two free radicals
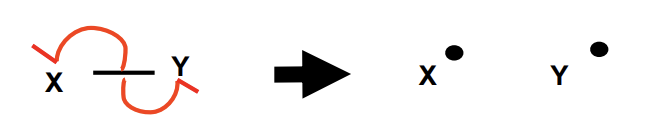
free radical
reactive species that possesses an unpaired electron
do not have charge, represented by dot
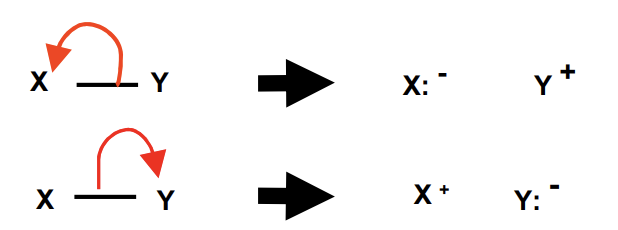
heterolytic fission
one atom gets both electrons
*most organic reactions occur via heterolytic fission => ions
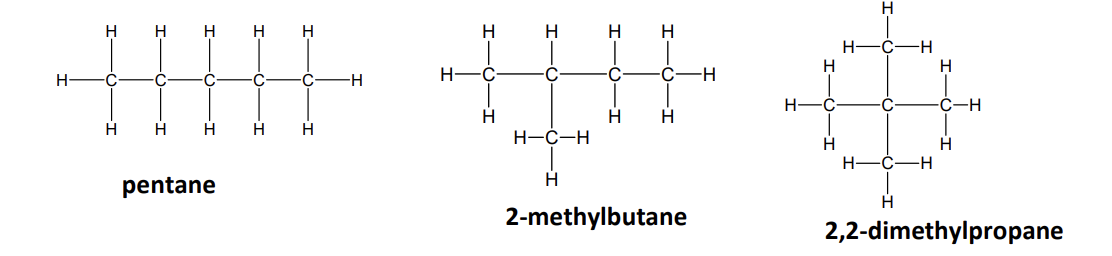
structural isomerism can arise from
chain isomerism
position isomerism
functional group isomerism
chain isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures of the carbon skeleton
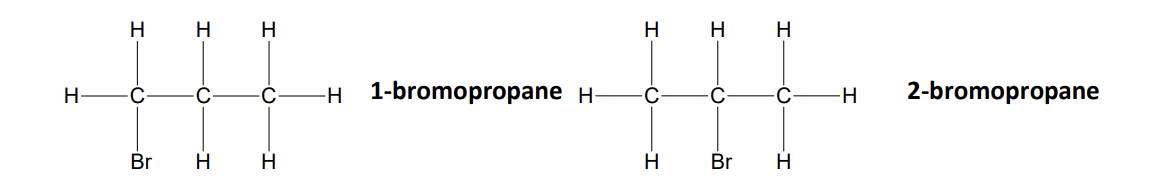
position isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures due to different positions of the same functional group on the same carbon skeleton
functional group isomers
compounds with the same molecular formula but with atoms arranged to give different functional groups
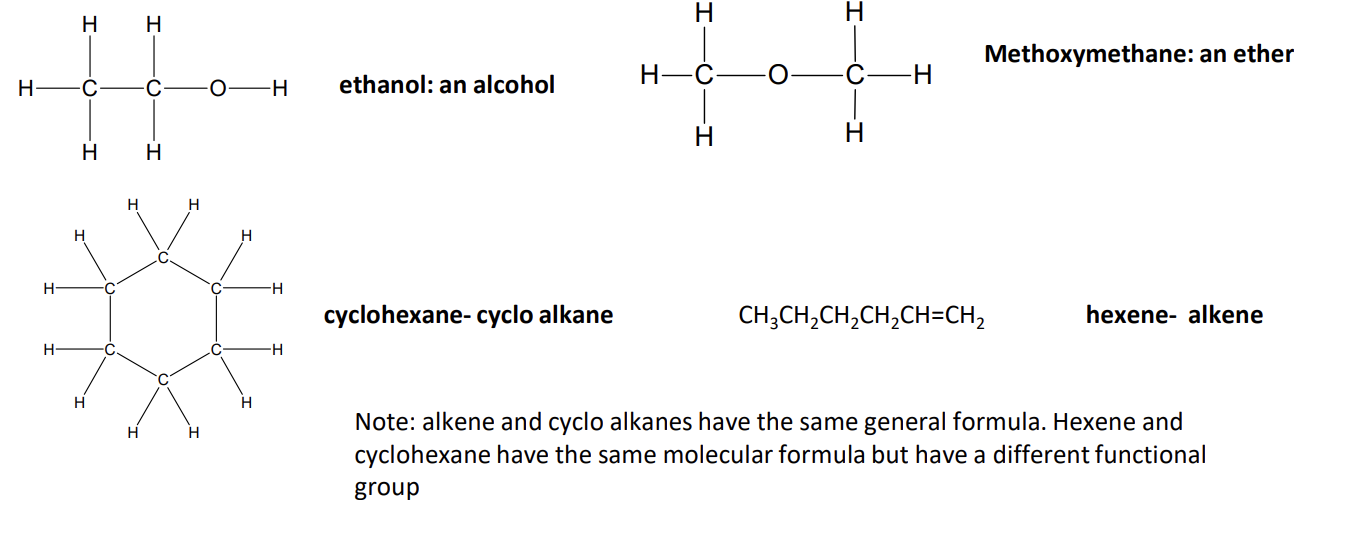
E/Z isomers arise when
there is restricted rotation around the C=C double bond
there are two different groups/atoms attatched to each C at both ends of the double bond
priority group
atom with the bigger atomic number
Z isomer
both priority 1 groups are on the same side of the double bond
E isomer
each priority 1 group is on opposite sides of the double bond
CIP priority rules
compare atomic number of each atom directly attatched to each side of the double bond, determine priority
if atoms are the same, consider atoms at distance 2 from double bond until there is a difference
effect of Z isomer on physical properties (ex: Z-1,2-dichloroethene)
molecule is polar (partial charges due to group placement); there are both van der waals and permanent dipole-dipole attractions => higher boiling point
effect of E isomer on physical properties (ex: E-1,2-dichloroethene)
molecule is nonpolar // dipoles cancel out; there are only van der waals attractions => lower boiling point