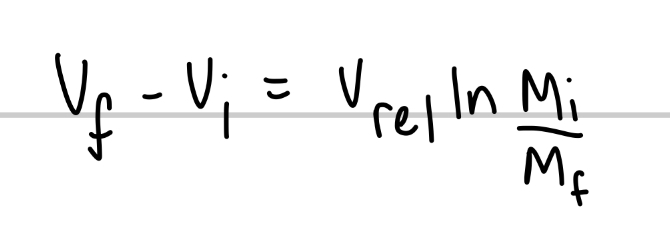AP Physics Chapter 9
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is the center of mass?
The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though
All of the system’s mass were concentrated there
All external forces were applied there
What are the formulas for calculating center of mass when particles are distributed in three dimensions?
M is total mass of the system
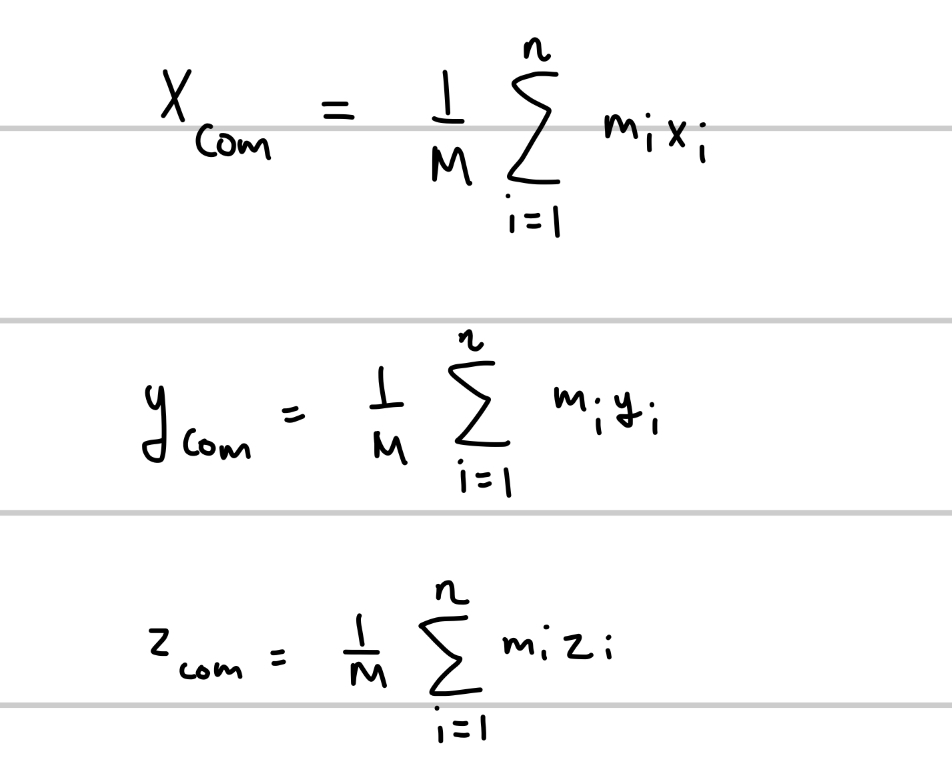
What are the formulas for calculating center of mass for the position vector as a whole?
M is total mass of system
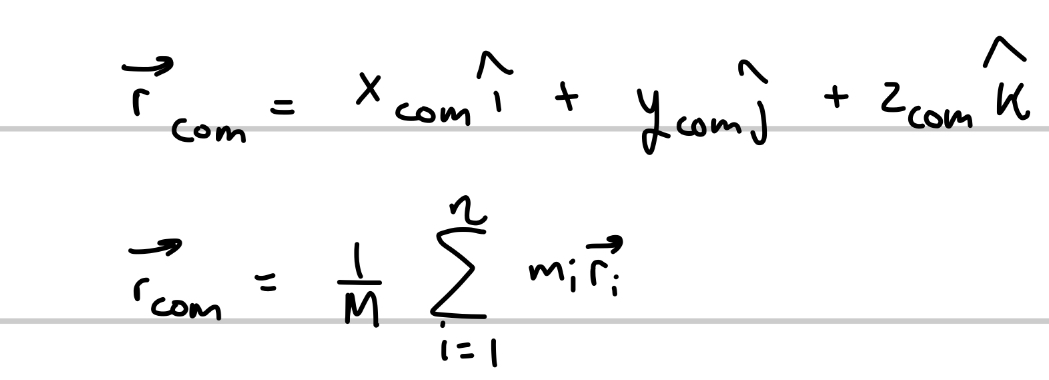
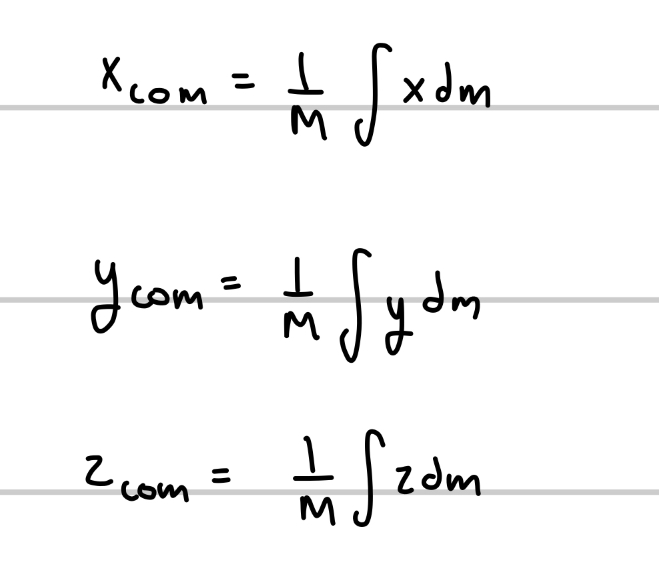
What do we do to the formulas when there are MANYYYYYY particles?
break it into integrals
(can do this bc the distance between dm is extremely small)
What is a uniform object?
An object with uniform density, or mass per unit volume
that is
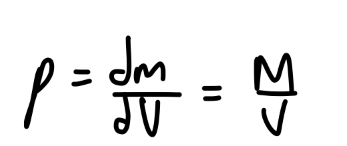
How can we solve center of mass problems given volume instead of mass?
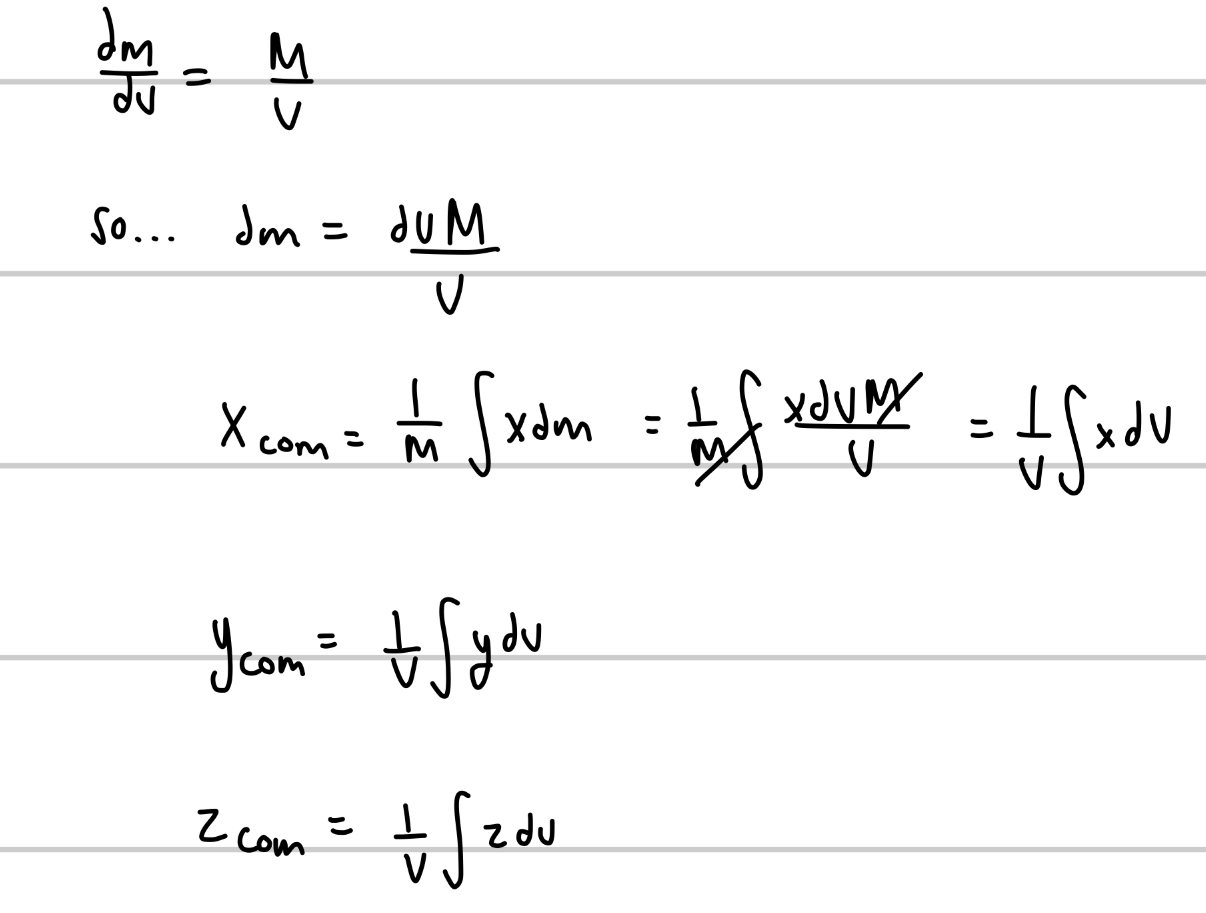
What is Newton’s 2nd Law for the center of mass of a system of particles?
Important things to note:
M is the constant total mass of the system
Fnet is the net force of all external forces that act on the system. Forces on one part of the system from another part of the system (internal forces) are not included
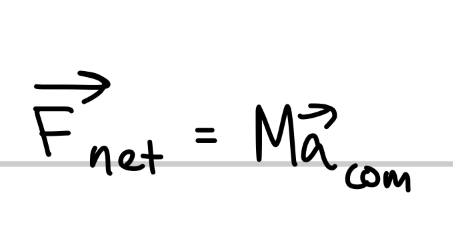
What is the linear momentum of a particle?
unit is kg m/s
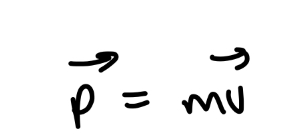
What is Newton’s second law of motion in terms of momentum?
The time rate of change of the momentum of a particle is equal to the net force acting on the particle and is in the direction of that force
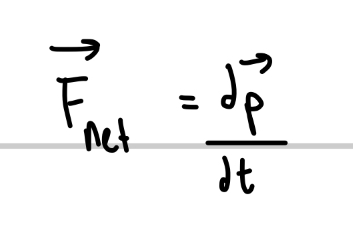
T/F Momentum can not change unless there’s a net external force
T
What is the momentum of a system of particles
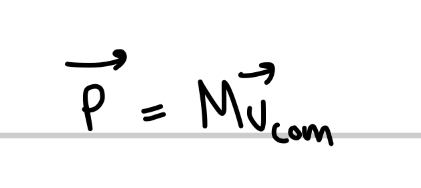
What is impulse?
change in an object’s momentum
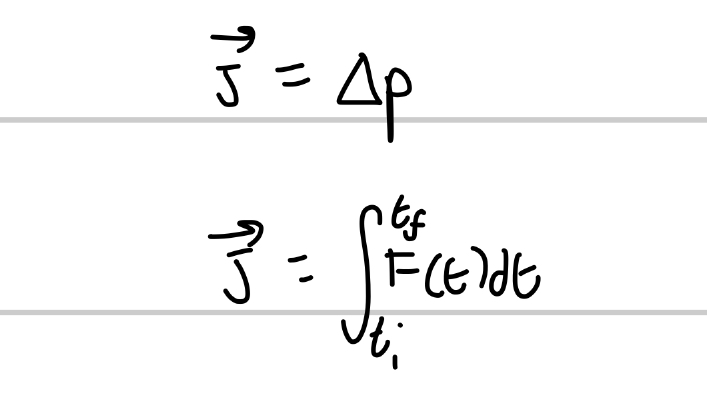
When a steady stream of bodies, each with mass m and speed v, collides with a body whose position is fixed, the average force on the fixed body is
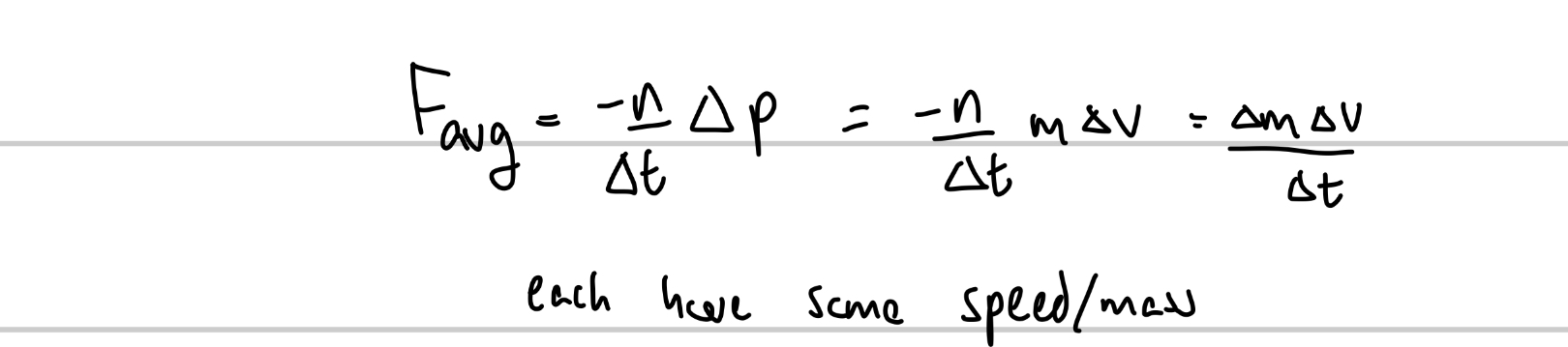
What is the law of conservation of linear momentum?
If a system is isolated so that no net external forces act on it, the linear momentum (P) of the system remains constant
that is
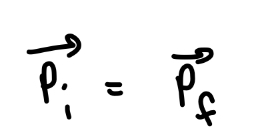
What is an inelastic collision?
In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the kinetic energy of the two-body system is not conserved
If system is closed and isolated, the total linear momentum of the system must be conserved which can be written as
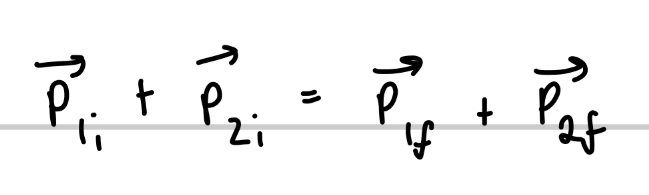
What is a totally inelastic collision?
If after the bodies collide, they stick together, this is a totally inelastic collision
have same final velocity V
t/f The center of mass of a closed, isolated system of two colliding bodies is not affected by a collision
t
t/f The Vcom of a closed, isolated system of two colliding bodies is not affected by a collision
t
What are elastic collisions?
Special type of collision in which the kinetic energy of a system of colliding bodies is conserved
If system is closed and isolated, its linear momentum is also conserved
For a one-dimensional collision in which body 2 is a target and body 1 is a incoming projectile, then immediately after the collision
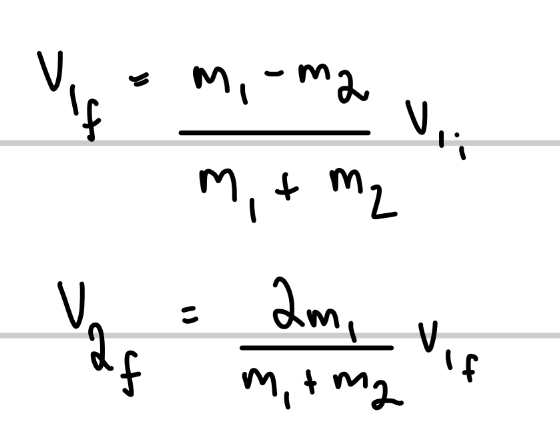
How do collisions work in two-dimensions?
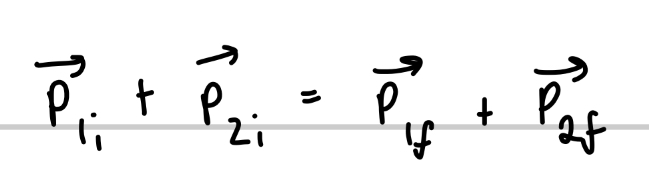
In two dimensions, if a collision is elastic how can the kinetic energy be written?
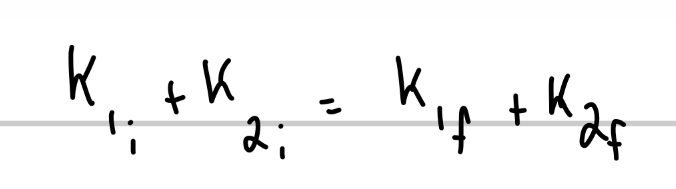
How do variable-mass systems work/rockets?
In the absence of external forces, a rocket accelerates at an instantaneous rate which is
where R is the fuel consumption rate
M is the rocket’s instantaneous mass (including unexpended fuel)
vrel is the fuel’s exhaust speed relative to the rocket
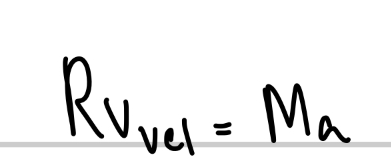
What is thrust equal to?
Rvrel
What is the change in velocity for a rocket with constant R and vrel whose speed changes from vi to vf and mass changes from Mi to Mf