AP Bio Unit 4
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
intercellular signaling
Communication between cells
intracellular signaling
communication
within a cell
signaling cell
cell that releases signal molecules that allow communication with another cell
ligand
molecule produced by a signaling cell that binds with a specific receptor, delivering a signal in the process
signaling molecule
target cell
cell that has a receptor for a signal or ligand from a signaling cell
cells that are affected by chemical signals
receptor
protein in or on a target cell that bind to ligands
3 Stages
Reception
Transduction
Response
Reception
Ligands are released and hit a receptor
Intracellular
Transduction
chain reaction between molecules to send the signal to target molecules
Phosphorylation cascade
a series of enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation reactions commonly used in signal transduction pathways to AMPLIFY a message
protein modification
proteins can change shape which changes the reception site which changes the signal it receives
second messengers
small (often nonpolar) molecules that relay signals received by transmembrane receptors to the final target
kinase
enzyme that attaches a phosphate group
phosphatase
enzyme that removes a phosphate group
Response
ex. protein synthesis, changes in metabolism, cell division and growth, nerve stimulation
Transcription Factors
protein that binds to the DNA to convert or transcribe it into RNA, which influences transcription of a gene and gene expression
apoptosis
programmed cell death
cell shrinks and ‘blebs’ to protect neighboring cells
autocrine signal
signal that is sent and received by the same or similar nearby cells
paracrine signal
signal between nearby cells that is delivered by ligands traveling in the liquid medium in the space between the cells
juxtacrine signal
signal between cells that are in direct contact through gap junctions
plasmodesma in plant cells
tight junctions, adherens, desmosome, hemidesmosome in animal cells
endocrine signal
long-distance signal that is delivered by ligands (hormones) traveling through an organism's circulatory system from the signaling cell to the target cell
internal receptor
(also, intracellular receptor) receptor protein that is located in the cytosol of a cell and binds to ligands that pass through the plasma membrane
Many intracellular receptors are transcription factors that interact with DNA in the nucleus and regulate gene expression.
cell-surface receptor
cell-surface protein that transmits a signal from the exterior of the cell to the interior, even though the ligand does not enter the cell
There are 3 types:
• G-protein-linked receptors
• Ion channel-linked receptors
• Enzyme-linked receptors
quorum sensing
method of cellular communication (using auto inducers) used by bacteria that informs them of the abundance of similar (or different) bacteria in the environment
positive feedback
uses a stimuli to start or ramp up a cellular process, usually moving farther away from homeostasis temporarily
intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition, produces a greater response
positive feedback examples
childbirth: hormones are released to increase the frequency and intensity of contractions until the baby is born
blood clotting: Platelets in the blood start to cling to the injured site and release chemicals that attract additional platelets until the clot is large enough to stop the bleeding.
negative feedback
uses a stimuli to trigger a response bringing an organism back to homeostasis
reverses a deviation, maintains body parameters within their normal range
negative feedback examples
blood sugar levels: when blood sugar increases or decreases, the pancreas releases insulin or glycogen to counteract
body temperature: When the brain’s temperature regulatory center receives data that body temperature is lower or higher than the setpoint, it sets into motion the responses to counteract
set point
the physiological optimum value, a set value around which the normal range fluctuates
amplification
an increase in the intensity of a signal through networks of intracellular interactions
homeostasis
process by which internal variables are kept within a range of values appropriate to the system
the condition in which a system such as the human body is maintained in a more-or-less steady state
feedback inhibition
inhibitor binds to enzyme and changes the active site so no reaction occurs
Mitosis
a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth
Parts of Interphase
G1
S
G2
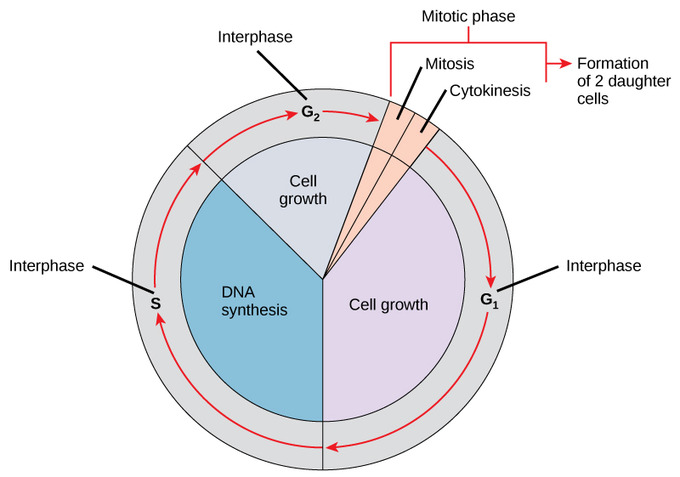
G1
a period of intense growth and activity
S
used to stand for the synthesis of DNA. The DNA is replicated so the cell now has two sets of the same DNA
G2
the cell continues to grow in order to finish cell division.
G0
a phase where a cell never divides, rests
Steps for Mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
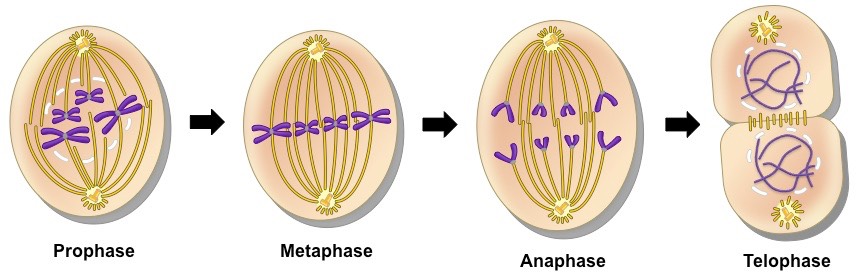
Prophase
the first phase of mitosis. In prophase, the nuclear membrane begins to disintegrate, chromosomes condense, and the spindle begins to form
metaphase
chromosomes begin to line up in the middle of the cell. Also, the centrosomes move to the ends of the cell
anaphase
when the centromeres finally separate. The spindle pulls apart the now sister chromosomes (identical copies)
telophase
begins when the chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. The chromosomes begin to uncoil and return to their threadlike shape
Cytokinesis
when the cytoplasm is divided
For plant cells, a cell plate
For animal cells, a cleavage furrow
cell plate
A plate that develops at midline of dividing plant cell during cytokinesis, eventually becoming the cell wall for each of the two daughter cells.
Cleavage furrow
The cleavage furrow is a shallow groove in the cell membrane where cytoplasmic division will occur. It's the first sign of cytokinesis during cell division in an animal cell.