MHR 322 Exam 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Entrepreneurship is
An economic phenomena
A possible career choice
A mindset that can be used in any organizational context
Management mindsets: Given and Challenges
Given:
Resources available based on current state
Goal to achieve based on incremental steps
Challenge:
Find the most effective/ efficient path linking the resources to the goa
Entrepreneurial Mindsets: Given and Challenges
Given:
Opportunities arise from uncertainty
Resources can be acquired/ assembled
Challenge:
Utilize a flexible, adaptive process to simultaneously explore possible goals and path to those goals
In an uncertain world…
An entrepreneurial mindset will be valuable
new , complex challenges
Unequal access to resources
Changing time frames
Globalization
Increased competition, access to resources and customers
Technology- facilitated scaled up
Bocks Definition of Entrepreneurship
recognizing an opportunity and taking action to create change
Being vs. Succeeding
The traits that lead people to become entrepreneurs may not be the same traits that helps entrepreneurs succeed.
Traits of people more likely to become entrepreneurs
Greater self-esteem
Need for achievement and independence
Good on learning aptitude test (GPA not so much)
Comfortable with calculated risk-taking
Innovativeness creativity
Optimistic
Non-trait drivers of entrepreneurship
Socio-economic factors
Educational attainment
national/immigrant status
Nature v. nurture
Prior experience
Traits of Entrepreneurs: Seeking Balance
High self-esteem and optimism can lead to trouble
Need to validate your idea with customer/market feedback
The nest entrepreneurs are both determined and willing to be wrong
Failure in real learning
Learn valuable information
Build new skills
Be vulnerable
Stay on a path that can be found by trial and error
To be successful soon
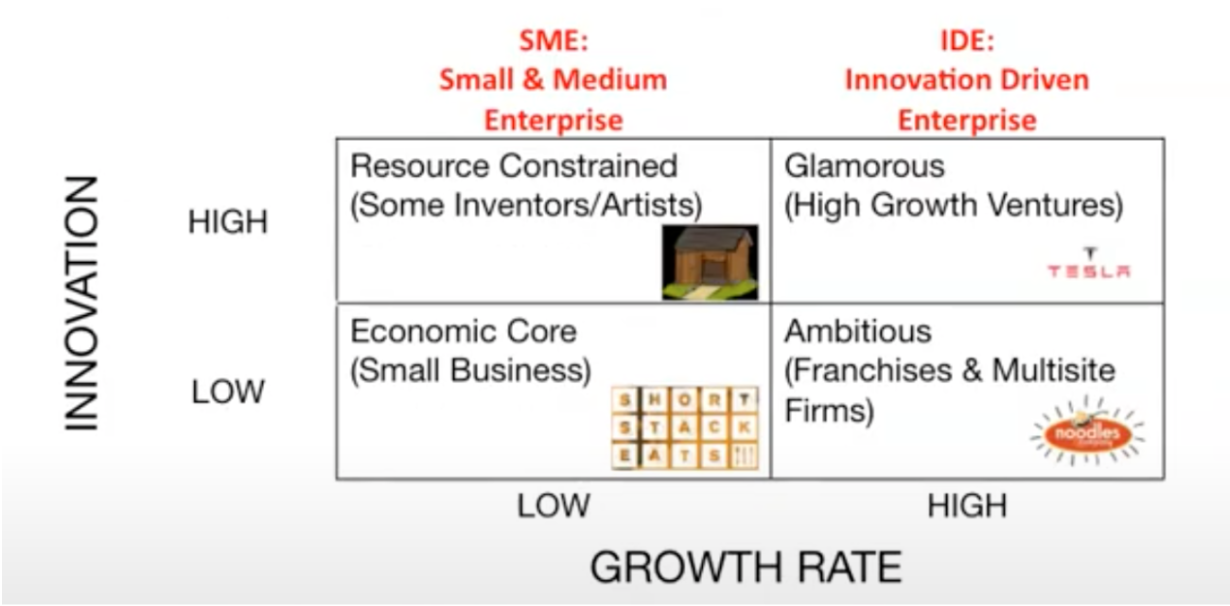
Dynamic Capitalism Typology
Separating out entrepreneurship types
Economic core: restaurants
Resource Constrained: lot of innovation but low growth rate
Ambitious: noodles and company, set of meals were created it can be replicated everywhere, low innovation
Glamorous Ventures: Tesla, significant technological change
Entrepreneurship is also:
Social entrepreneurship
Corporate entrepreneurship
Family business
Social Entrepreneurship
Innovations in non-profit management
Solving societal problems via new for-profit firms (ex. Whole Foods, TOMs Shoes)
Including non-profit maximizing metrics as goals for the firm, such as…
Reduce IT items in landfills
Donate 10% of profits to charity
Corporate and Family
Corporate entrepreneurship (Intrapreneurship)
Innovation and entrepreneurial culture in large firms
Better support structure/lower idk
Limited rewards
Family Business
Significant component of firms of all sizes
Large firms: Johnson Wax, Menards
Family issues can be very real, for good and bad
3 Motivations to start a venture (from DE reading)
Passion: I like doing X and want to build a company around it
Technology: Robot that can do X
Idea: Came up with an idea that can change the world (by solving a problem)
Passion in Entrepreneurship
Passion is great
Passion is probably required… but alone it isn't enough
Technology/Push risks lack of market demand
Great solution for a problem I don't have
Need to either pivot to new market or create demand
Key Questions-Technology
The technology is?
Why do you have a significant advantage over anyone else with regard to this technology/invention?
Compared with the most relevant current alternative, why is your technology so compelling that it will make people and industries change
Idea/Risk is that demand pull exist but no solution
Problem that has yet to be solved
Solution isn't Profitable
Real problem has been solved but not cost effectively
Key Questions-Problem/Market Pull
What is the general problem you are trying to solve or the opportunity you are looking to capitalize on?
How urgent/big of a problem is this for customers?
What makes you and your team uniquely qualified to implement your idea?
Key Questions-Hybrid
The idea is relevant to the ________ market because it will produce significant value by ____________
The enabling technology invention is? Why wasn't this solution possible 5 years ago?
What makes you and your team uniquely qualified to pursue this opportunity?
Two Key Questions for Entrepreneurship Idea
Does customer demand exist for what you are selling?
If “yes,” can I generate long-term profits in the business?
Two main Approaches in Entrepreneurship
Predictive (Forecasting)
Try to predict characteristics of ideas, or conditions, that will
Learning (Experimentation)
May Perform experiments and use results to assess future outcomes
Learning Framework
Have an idea for a product/company
Realize that your “idea” may or may not be correct
Formalize your idea into a theory
Test your theory by building an experiment
Inexpensive
As real as possible
Measure the results
change/pivot your idea in response to what you learn
Repeat
Why is failure is normal
Attractive customer segment is smaller/different than expected
Why Industry Analysis
Anticipate the most profitable industries
Enter Where profitability will increase or stay high
exit/avoid those where profit is low and will remain low.
Good manager vs. good business, who wins?
What drives profitability of a market/industry
Threat of Entry
Brand name
Patents
Network effects
High switching costs
Scale economies
Others
The Five Forces: (Reading)
determine the competitive structure of an industry, and its profitability. Industry structure together with a company’s relative position within the industry = two basic drivers of company profitability
help companies predict shifts in competition, shape how industry structures evolves, and find better strategic positions within the industry
Top-Down for calculating Total Addressable Market (TAM)
using industry research and reports
overestimates market size
Bottom-Up for calculating Total Addressable Market (TAM)
using data for early selling efforts
Value Theory for calculating Total Addressable Market (TAM)
using conjecture about buyers willingness to pay
Factors affecting adoption rate
Relative advantage
Compatibility
Trainability
Observability
Risk
Complexity
Pros and Cons of creating a Market
Pros: first-mover advantage over competitors: potential brand power, potentially high profit margins
Cons: difficult to conduct market research: cost of educating customers: high risk of getting it wrong
China Syndrome
market is huge meaning only need a small % to do well (WRONG)
“Top-down” analysis → almost always wrong
Potential Segment Characteristics
Demographics, Geographics
what drives these characteristics (loyal, sensitive)
True segments are determined by
behavior
Target Customer Segment
a group of potential customers who share many characters and who would all have similar reasons to buy a particular product.
Beachhead Market
Pick one (only one!)
Small has advantages
Most compelling value proposition
Easy access for testing
End User
person using the product
Champion
closely related and encourage the product
Primary Economic Buyer
paying for the product, but not using the product
Influencers
experts, endorsements, veto power (matters a lot)
Total Addressable Market (TAM)
Annual revenue your business would earn if it had 100% market share
As if every (realistically) possible customer made the purchase
#of potential customers x average price of the product/service calculate per year
Value Proposition
The benefits that a company offers a specific customer segment that makes a purchase worthwhile
Pains removed from customer from product
Price
Performance (time/quality)
Cost reduction
Risk reduction
convenience/usability
Accessibility to new segment
Feel better/ remove guilt
Other
Benefits Gained by customer
Customization
Newness
Design
Social status/brand
Entertained
How to confirm value proposition
take complete theory to market
test theory in smaller, quicker components
Good Value Proportions (Osterwalder)
difficult to copy
outperform competition
align with how customers measure success
focus on unsatisfied jobs
Common Value Proposition Problems
Idea is just a feature extension for someone else’s product
Nice to have but not got to have
Too small of a potential market actually cares about the V.P
Prospect Theory
people would rather avoid a loss than have a chance at a gAIN
Endowment Theory
people value what they have more than what they dont
The Innovator’s Curse
Self-Selection
Results in a clash in perspective
knowledge gap (innovator knows the need but the customer doesnt)
Degrees of Change
Incremental/Tinkering: Low Behavior Change, Low Product Change
Strike Out: high behavior change, low product change
Long Haul: high behavior change, high product change
Home Run: low behavior chnge, high product change
Intellectual Property
inventions
literacy and artistic works, symbols, names and images
protected by law
Copyright
legal protection provided to authors of creative work
doesn’t protect facts or ideas, not plagiarism
Patents
not an automatic protection
inventor and who signs the rights to invention
limit of years they can protect the invention
only in US
Types of Patents
Utility Patents: new useful and nonobvious processes, machines
Plant Patent: protect asexually reproducing plants
Design Patent: protect ornamental designs
Trademark
words, phrases, logos, shapes, colors, sounds and scents
Trade Dress
Identified a brand or product with its overall look, distinctive non-functional design element of a product, packaging
Core Competitive Advantage Potential
Quality
Network effect
Customer service
Low cost
User experience
manufacturing /design expertise
Core- Competitive Advantage Cons
Better technology’ product
First mover advantage
Locking up suppliers
Low price (careful!)
Network Effect
Value of product/service depends on number of users/customers
The value to a new user/customer increases as the size of the network increases
Ex. ebay, facebook,
High switching cost – switching to something else you lose significant value
Customer Service - Competitive Advantages
Can be a powerful advantage
Often appears easy to create and maintain, but usually not!
Requires significant investment in training, HR management and culture
Cost < or > Price
Low price = low margin
Anyone can do this and fail
Low cost = competitive advantage
Few companies do this and win
Core is NOT
First mover advantage
Despite what many entrepreneurs want to believe
May facilitate network effect but isn't sustainable by itself
Locking up suppliers (careful…)
Rare that there is a single provider
Ever rarer that they will be happy with an exclusive distributor/customer
Comparing your Offering to the competition
Define market
Define attributes you think customers will care about the most
Include status-quo
Include direct competitors
Competitive Strategy
Two sources of competitive advantage:
Cost
Differentiation
Degree of Scope:
Broad
Focused (niche)
Start-Up Competition
looks different
dont look to competition for solutions
dont respond instantly to competitive shifts
focus on competing in one event at first
Competition Factors
Be careful about assumptions
Recognize small firm advantages
Look for switching costs
High Switching Cost
switching to something else means you lose significant value
Low Switching Cost
what entrepreneurs wants,
the customer isnt losing significant value in switching to something else
Small Firm Advantages
high powered incentives
idea
speed
fit with environment
no legacy costs : costs from the past of this company that customers compare
potentially closer to customers
Switching Costs
cognitive/ user level
complementary assets
search costs
network effects
costs from switching products
time, money, knowledge, opportunity cost
lead to lock in
Overcoming Switching Costs
removes/reduces switching cost
technologically better than the others
benefits outweigh the costs, risks, and uncertainty of switching
fits customers purchase logic
Establish Switching Costs
contractual provisions
extended, exclusive
stagger purchases (durable purchases)
unique interfaces (brand specific)
acquire/ neutralize other suppliers
customize solutions (search cost)
establishing loyalty programs
Success is
execution
creating demonstrable value for customers
compared to what they have
compared to what is offered by competition
Porters Generic Strategies for gaining competitive advantage
cost leadership:
lowering prices while maintaining profitability
differentiation
offering unique features
focus
niche market
Why Porters model doesnt work
the shift of mass market to customization
consumer feedback to tailor
decline of size as competitive advantage
reduced barriers to enter and zero marginal cost of reaching consumers
size is no longer sufficient for success
Distinct vs Generic good
customers buy bother
role of social media: direct engagement
customer-centric approach
adaptability and learning
reward for moving fast
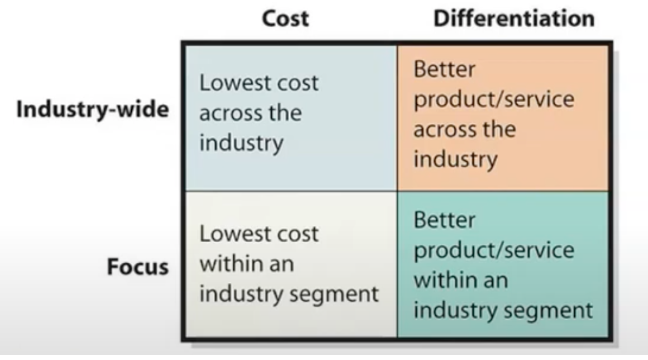
Competitive Strategy Chart
industry-wide and cost = lowest cost across country
Industry wide and differentiation = better product across country
focus and cost = lowest cost in industry
differentiation and focus = better product in industry
Why cant you do both low cost and differentiation
low cost requires, lower price and high volume for the minimum customer need while differentiation requires high price at lower volume for customers who need more than minimum
Differentiation
invest to create better products who need MORE THAN minimum
high price, low volume
reinvest profits in further improving products
Low Cost
drive down cost AND meet minimum customer need
lower price at high volume
reinvest in driving costs down further to maintain advantage
First-to-Market Challenges
High cost of _______
Building supplier network
Setting up distribution and support
Customer education
Fixing errors
Brand-building
Fast Follower Advantages
Suppliers already identified and vetted
Copy distribution and support from 1st mover
1st mover has already educated customers
Most major errors addressed by 1st mover
Brand-building compares against 1st mover
First-to-Market
not a sustainable long term competitive advantage
When can First-to-Market convert to long-term advantages?
take advantage of economies of scale
leverage network effects
build unique brand identity
create supplier/ customer lock in
use advantages to make a defensible strategic position
3 types of capital required to launch a venture
financial capital
social capital
human capital
Solo Founds
deep human and social capital
prefers to maintain control
small business or slow moving industry
Co-Founders
lacks one or more types of needed capital
needs validation
business is in a fast-moving industry
1-4 co-founders
Homophily
the tendency to form strong social connections with people who share defining characteristics
Homogenous Teams
they get work down effectively and quickly at beginning
Heterogenous Teams
outperform in long run because of diverse opinions and problem-solving processes
Phases of a New Company
jungle
dirt road
highway
“Jungle” Phase of a New Company driving forces
startups change
people change
Risk of picking a cofound similar to you
venture lacks breadth of skills needed to succeed quickly, (learning takes a long time)
Risk of picking a cofound who are students
limited business knowledge, significant potential for people to change their minds