kaitlyn PHR 936 Block 1 - Neuroanatomy and Neurobiology
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
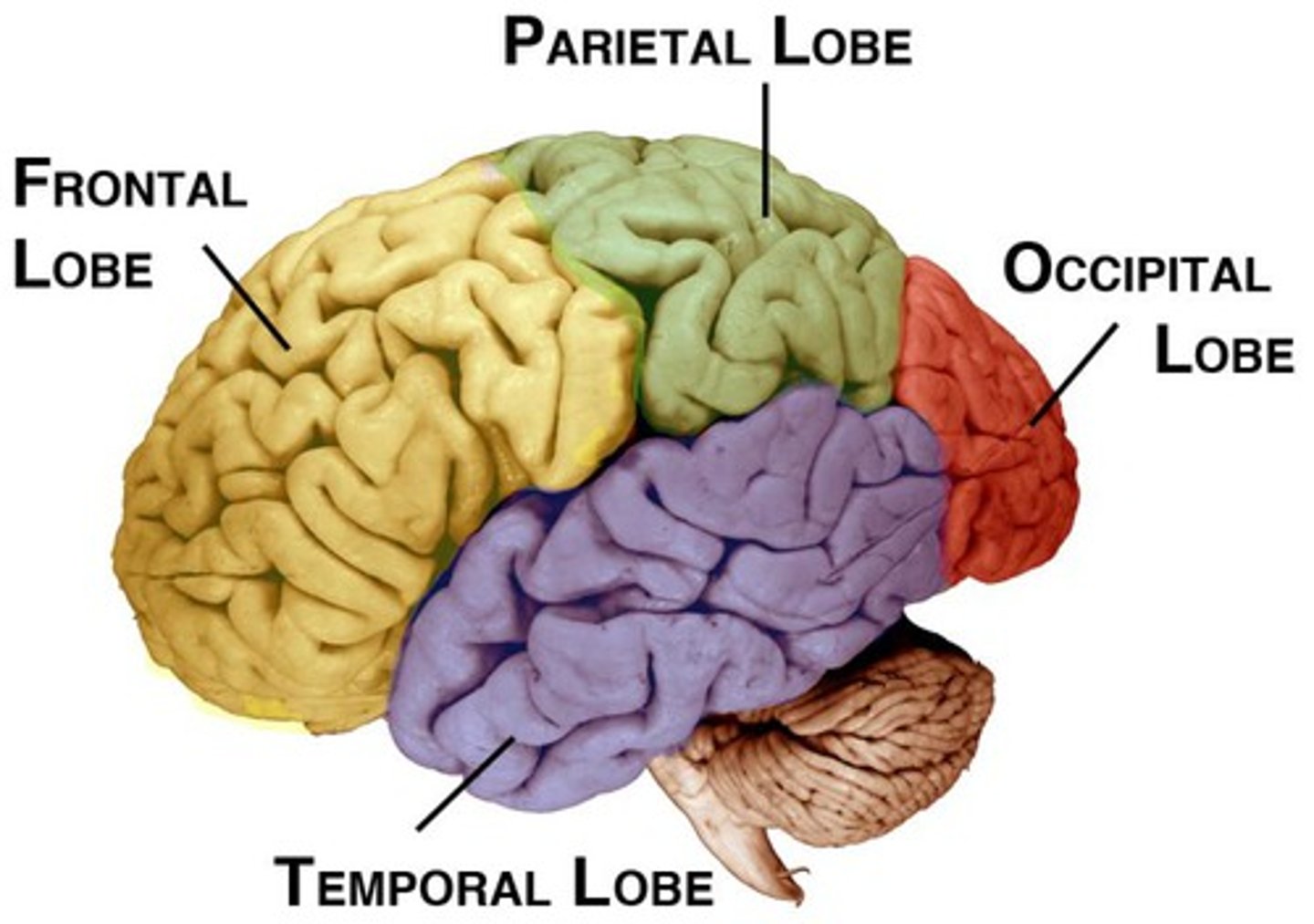
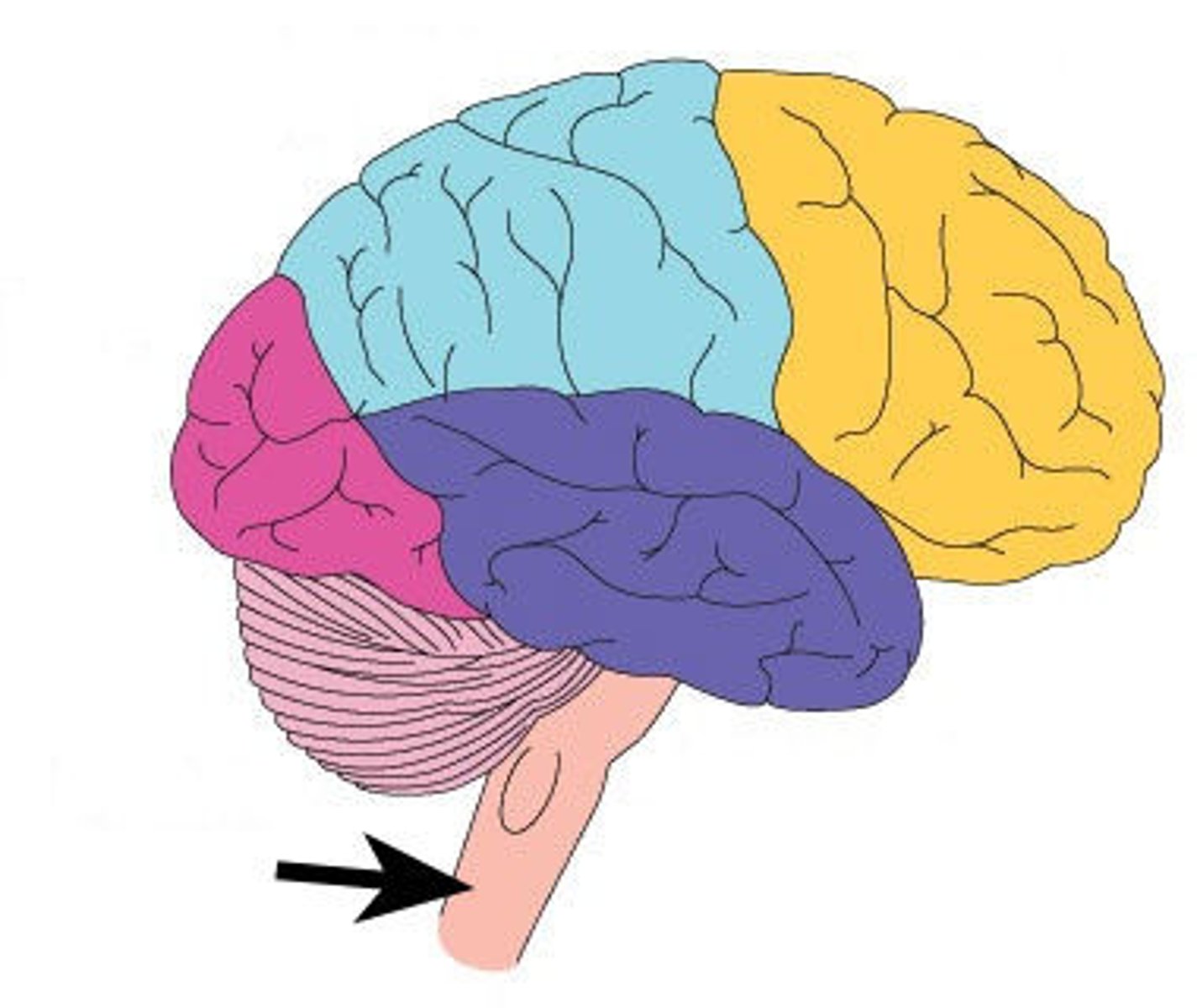
lobes of the brain
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
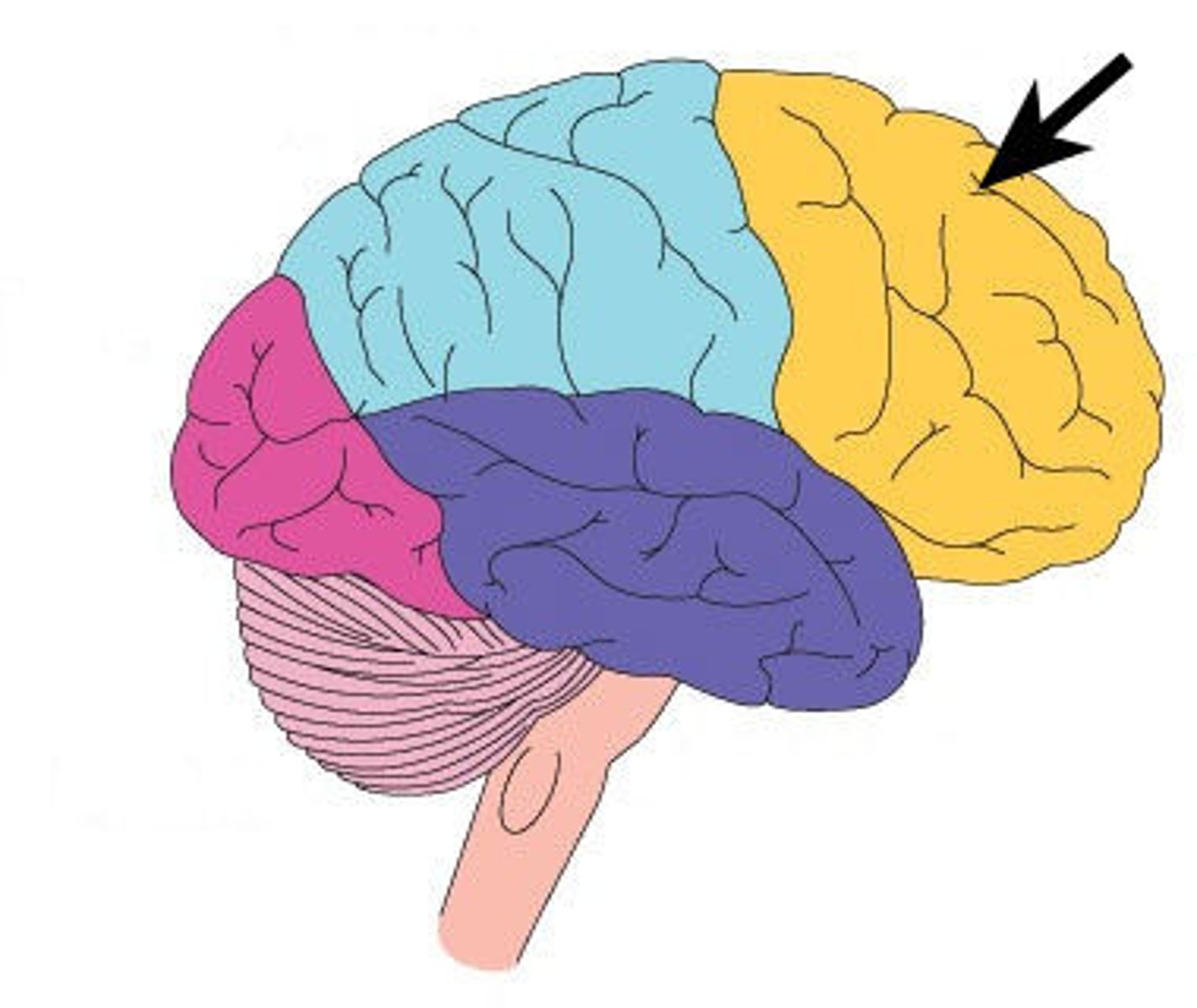
frontal lobe
thinking
memory
behavior
movement
attention
impulse control
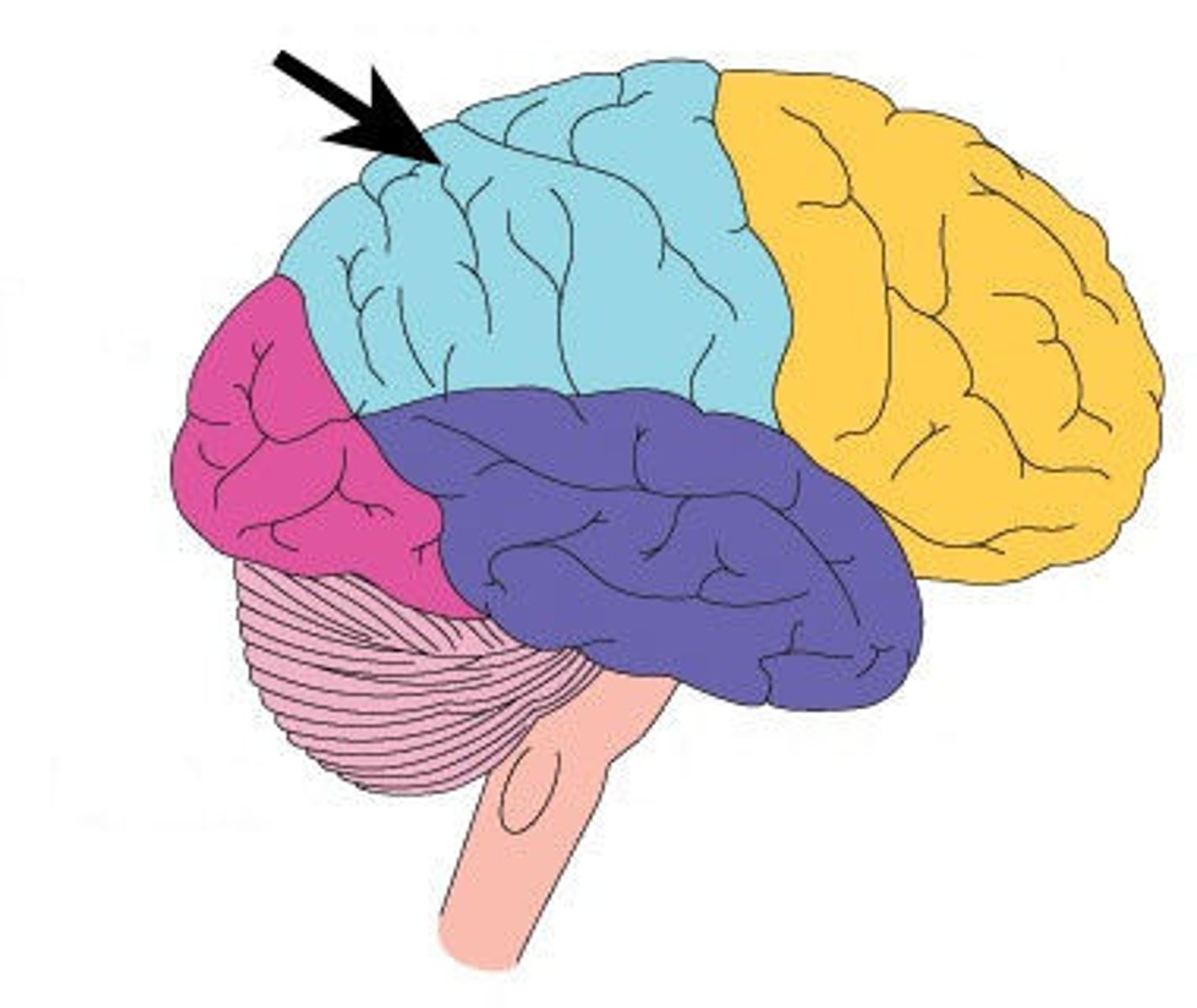
parietal lobe
somatosensation (touch)
language
occipital lobe
vision
reading
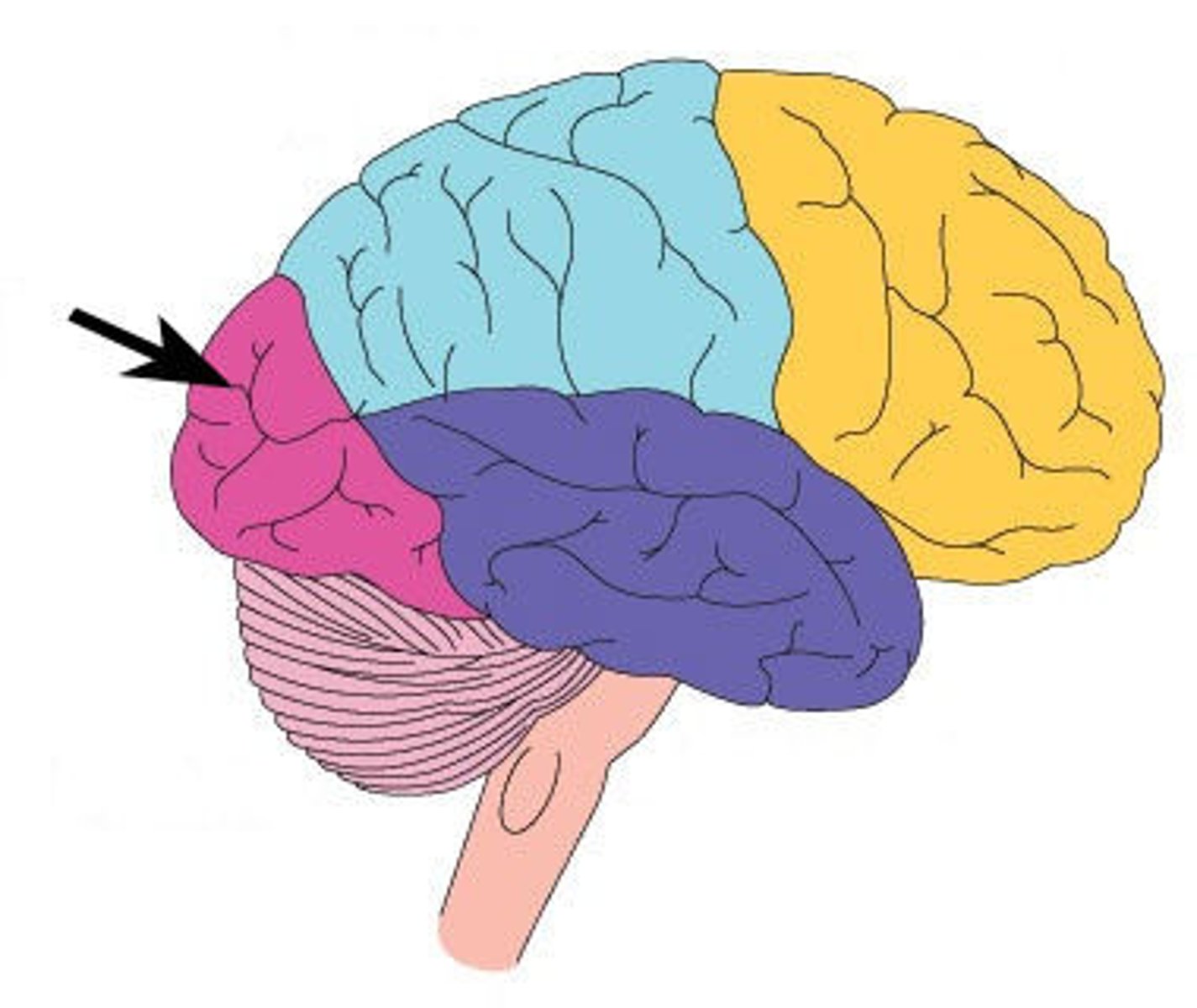
temporal lobe
hearing
learning
emotions
memory
visual processing
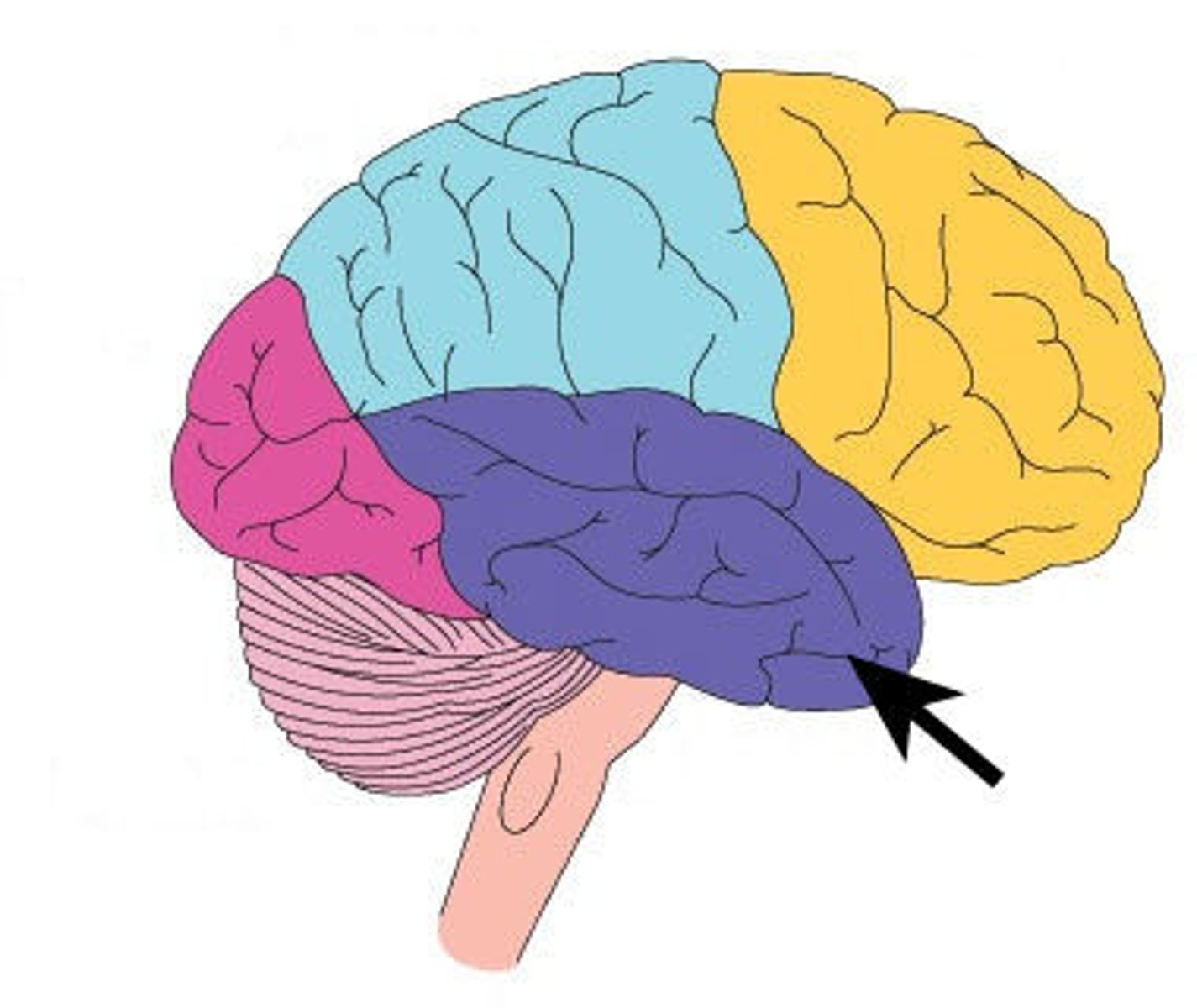
insula
5th cortical lobe deep within the brain
subconscious
sulcus
grooves between the gyri
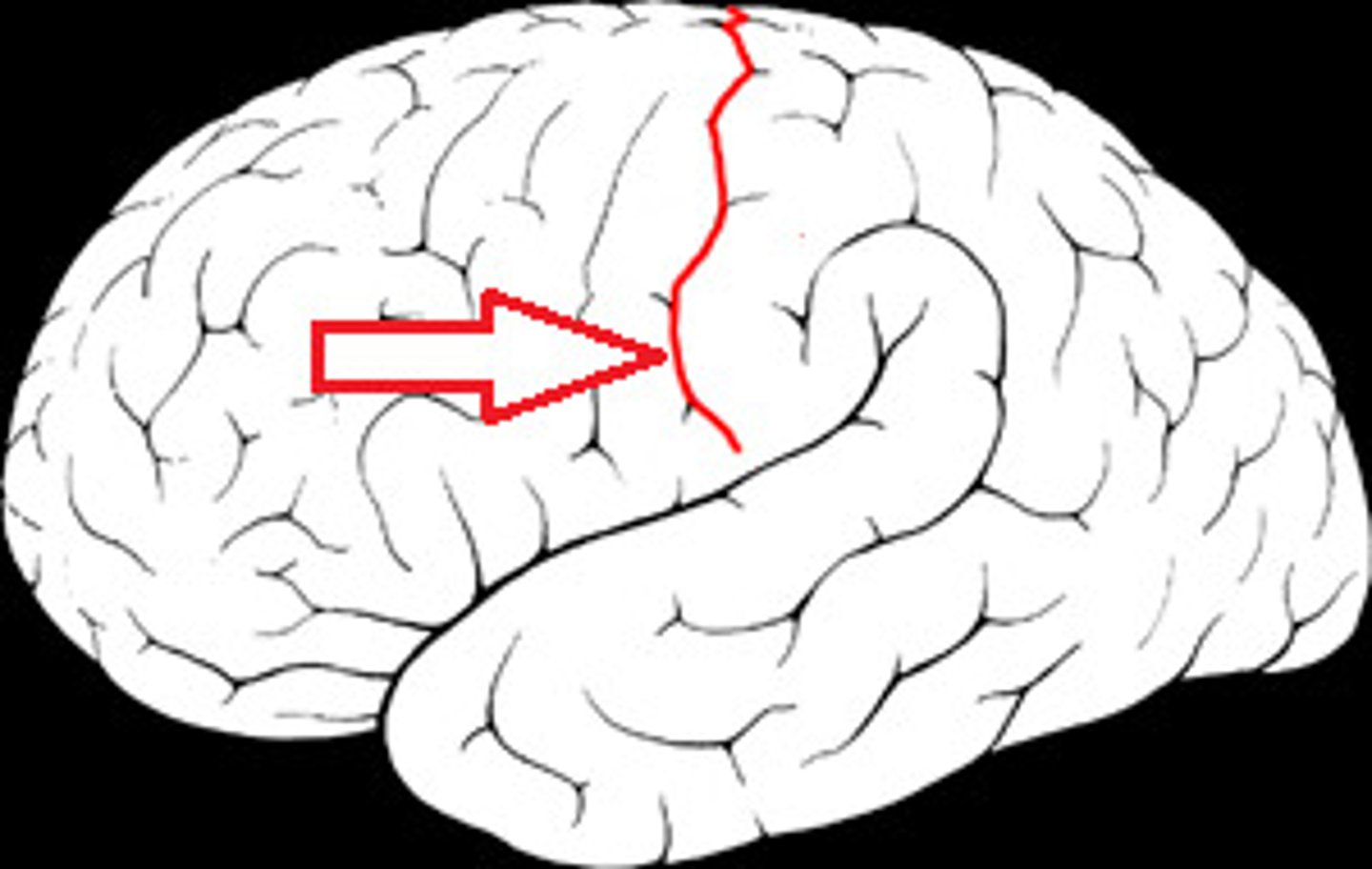
gyrus
outwardly rounded ridges of the cortex
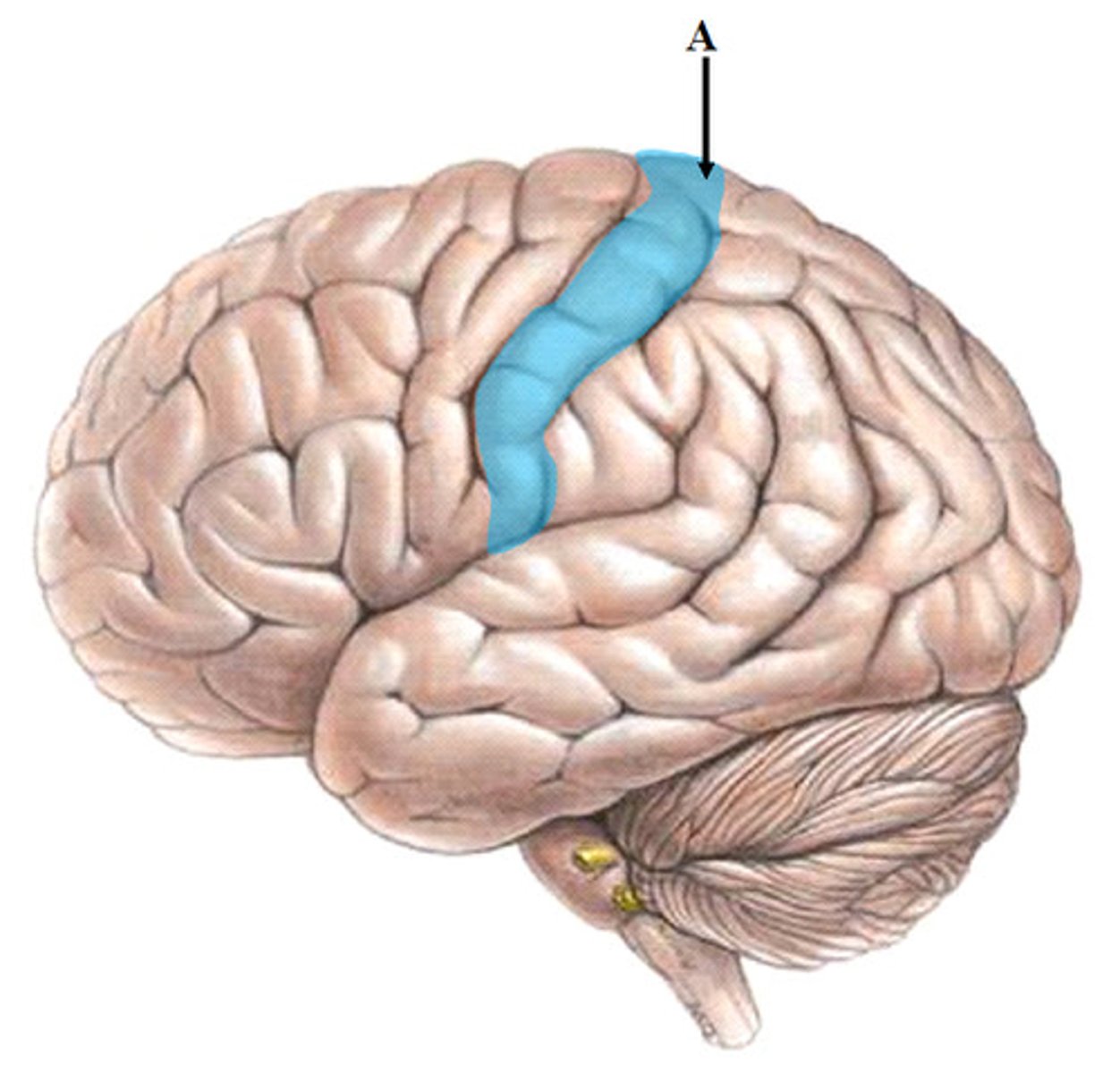
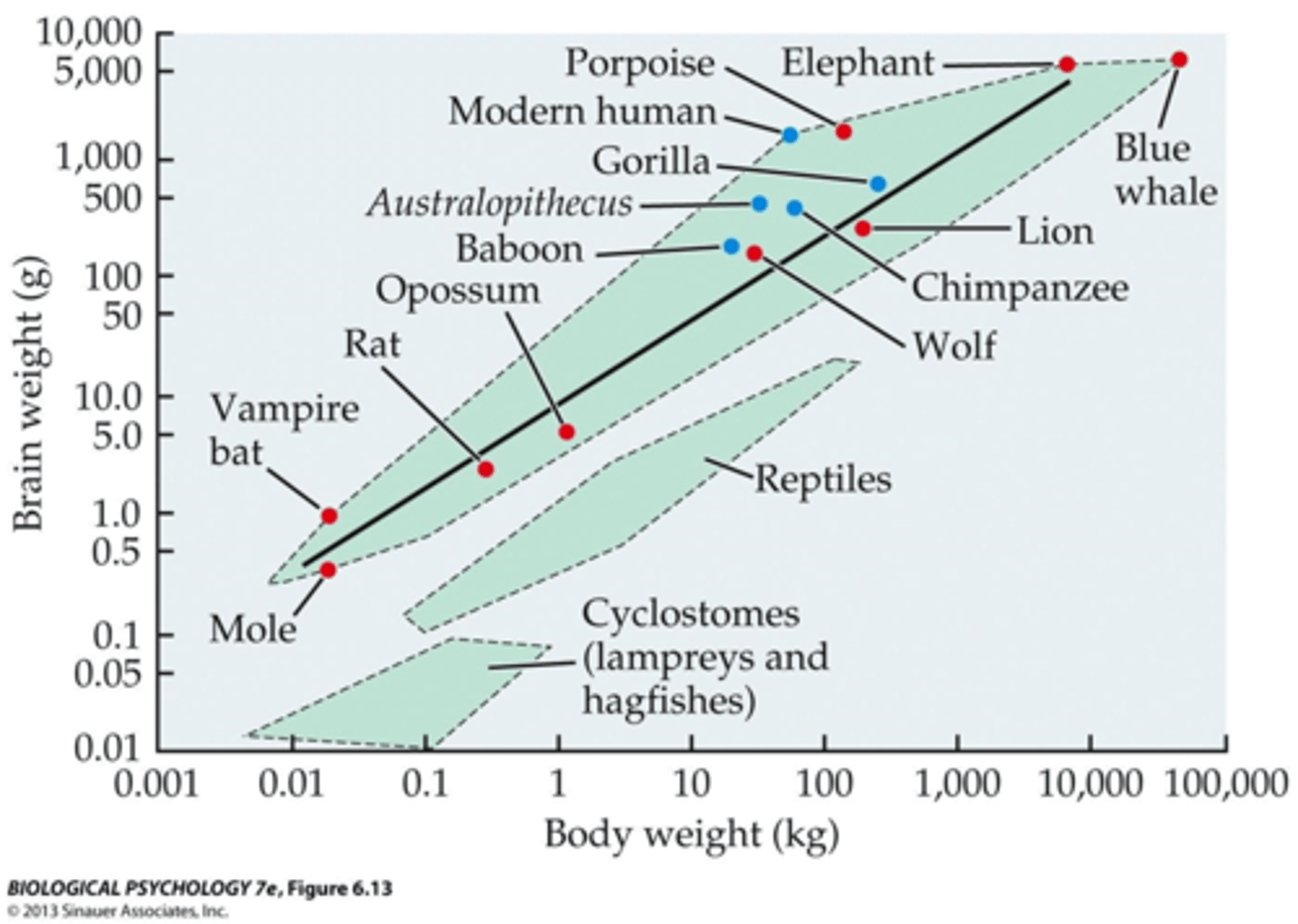
encephalization
the evolutionary process which results in increased brain mass, without corresponding changes in body size
- folds and grooves increase brain surface area
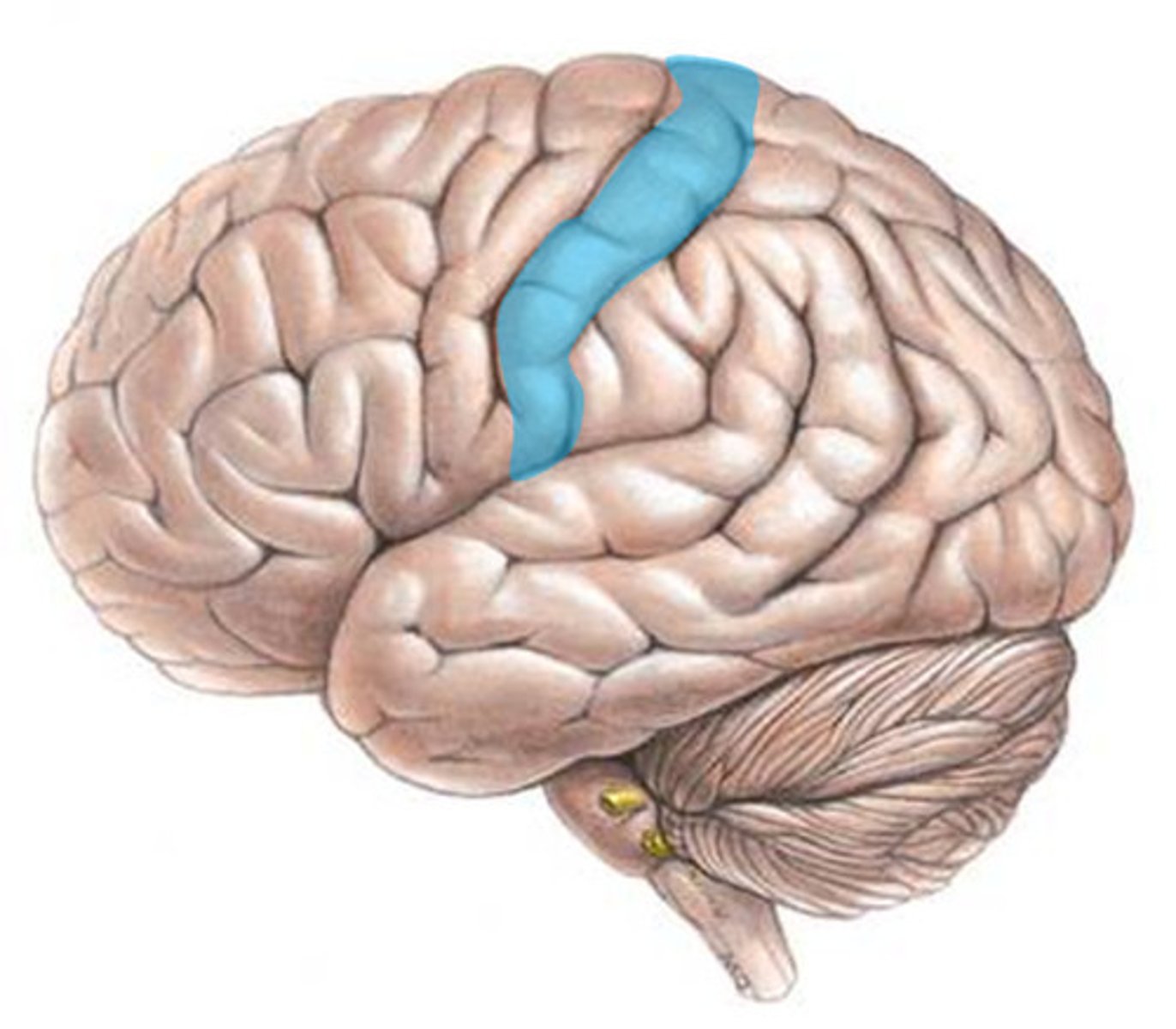
primary somatosensory cortex
the region of the anterior parietal lobe whose primary input is from the somatosensory system
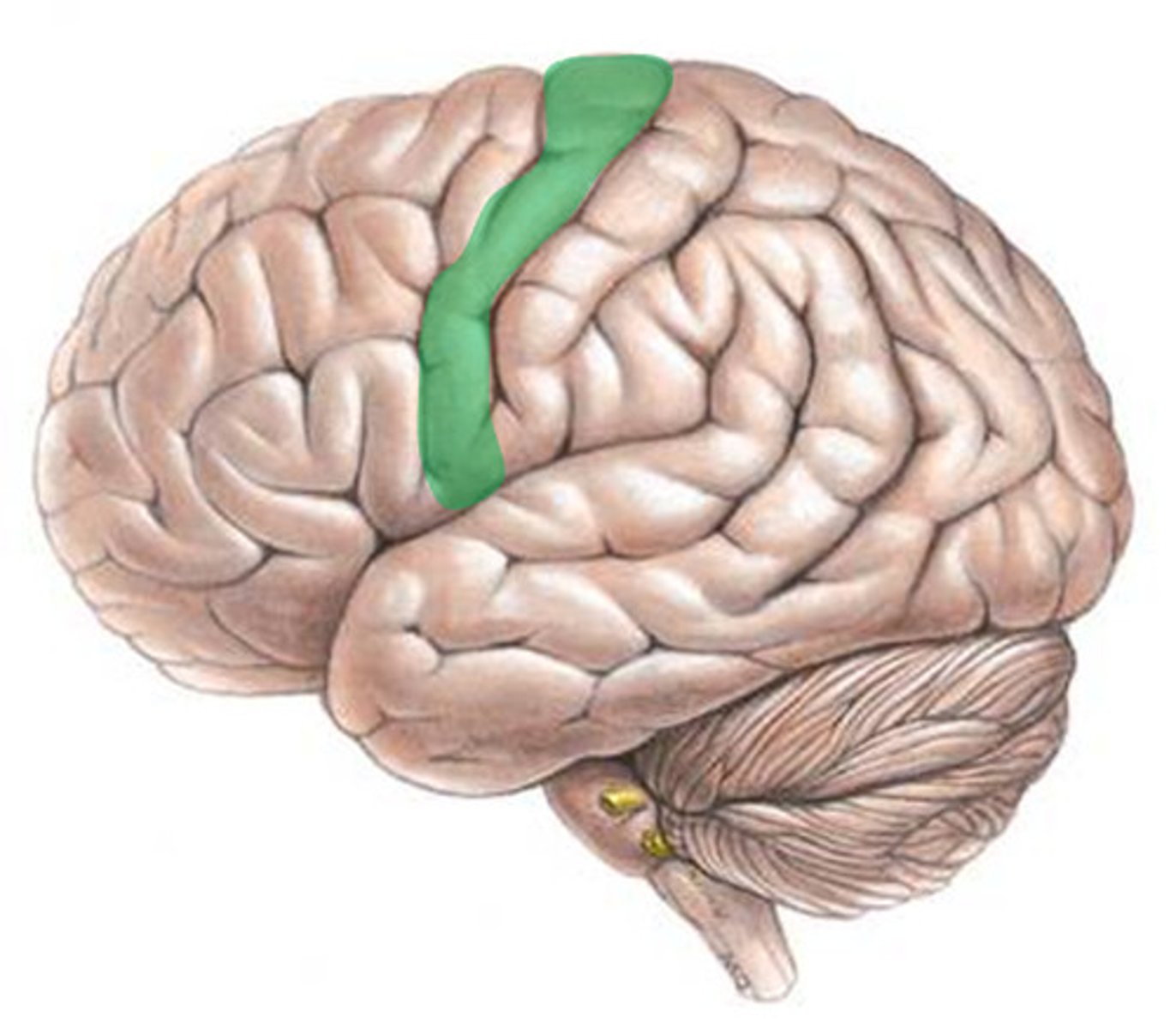
primary motor cortex
the section of the frontal lobe responsible for voluntary movement (precentral gyrus)
limbic system
emotion center + learning/ memory
- means "border"
- contains: extended amygdala, hippocampus, pituitary, olfactory gland
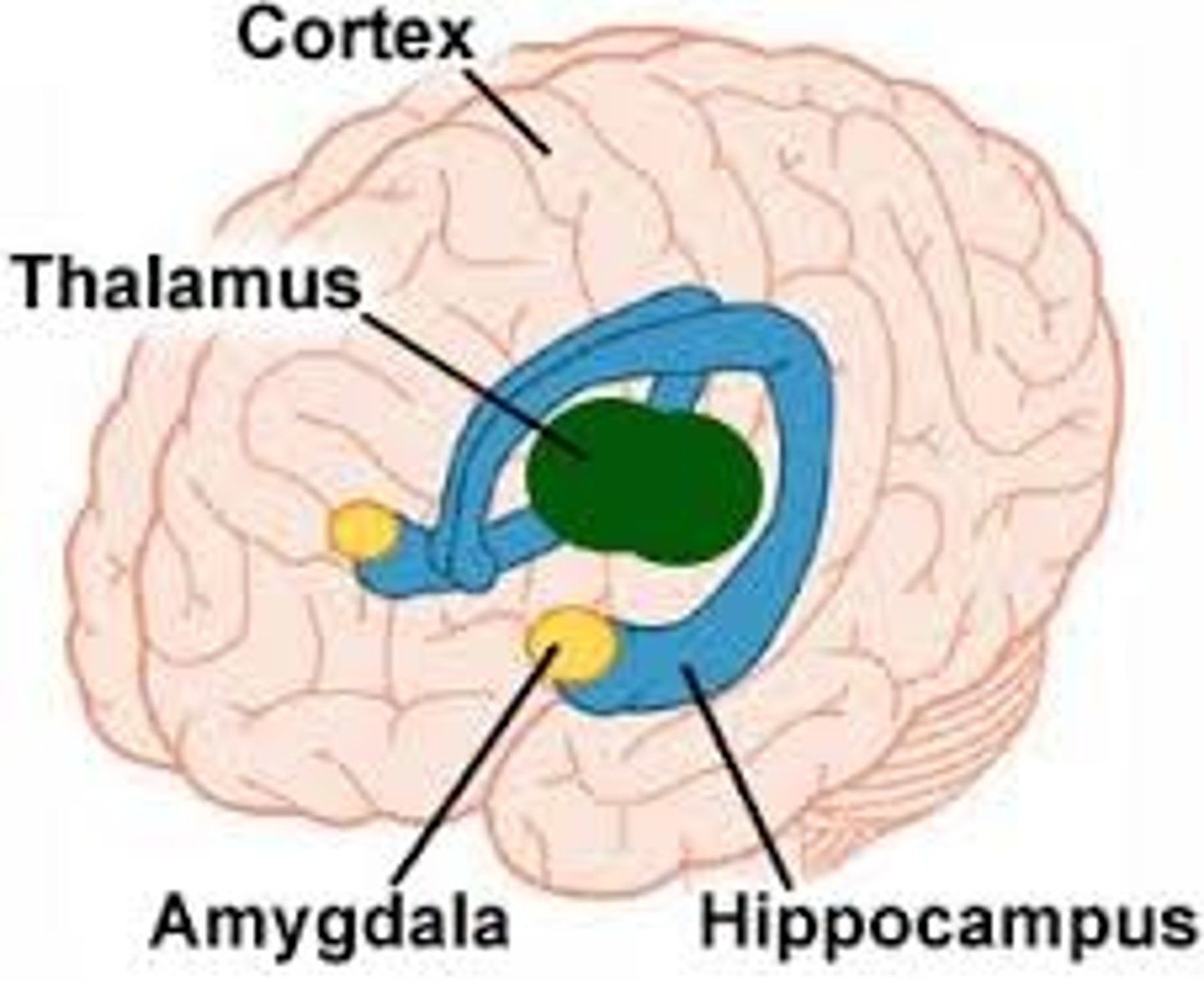
extended amygdala
response and memory of emotions, especially fear
- located at the end of the hippocampus
- means "almond"
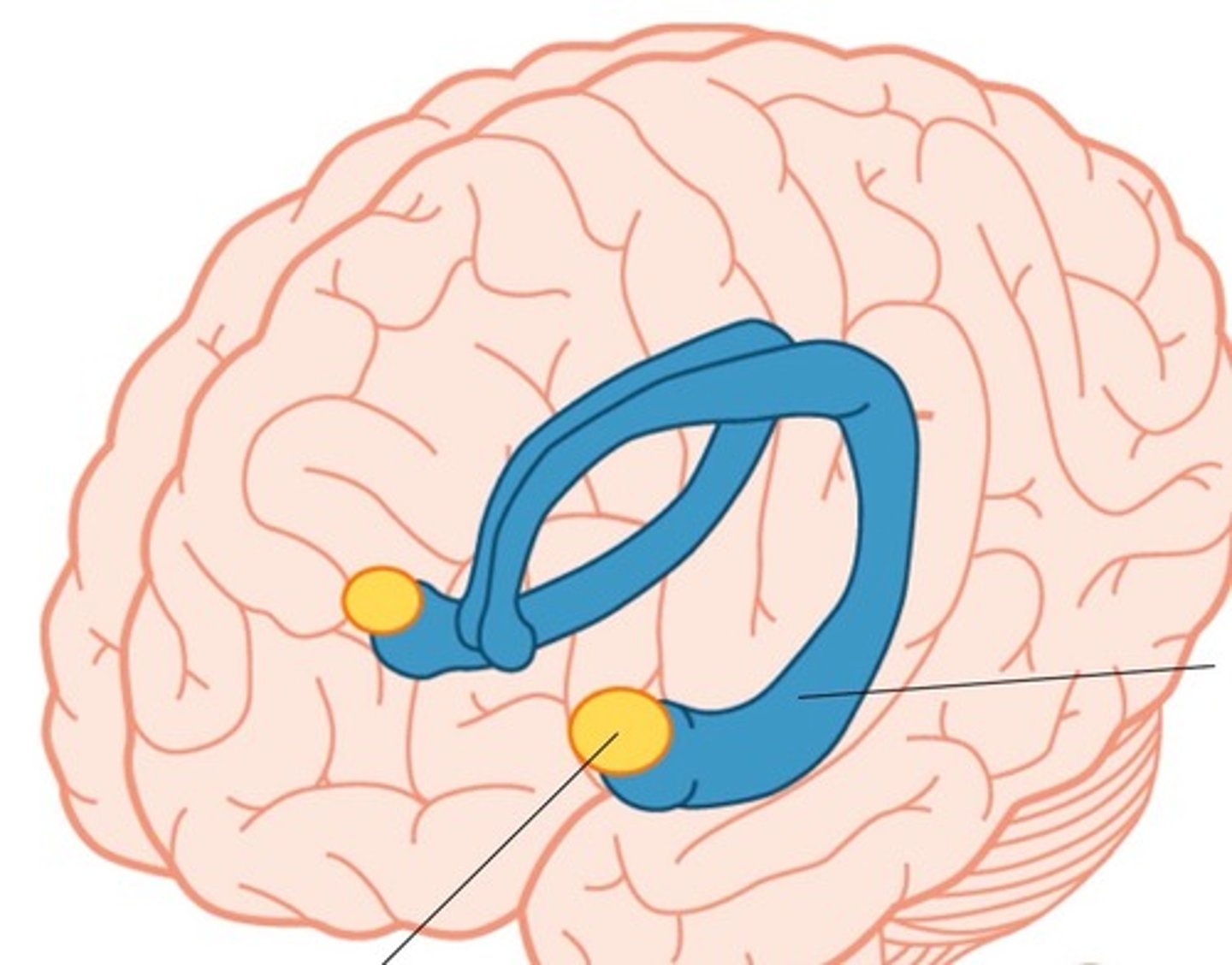
hippocampus
consolidation of new memories, short -> long term; emotions, navigation, spatial orientation, learning
- located in each temporal lobe
- means "seahorse"
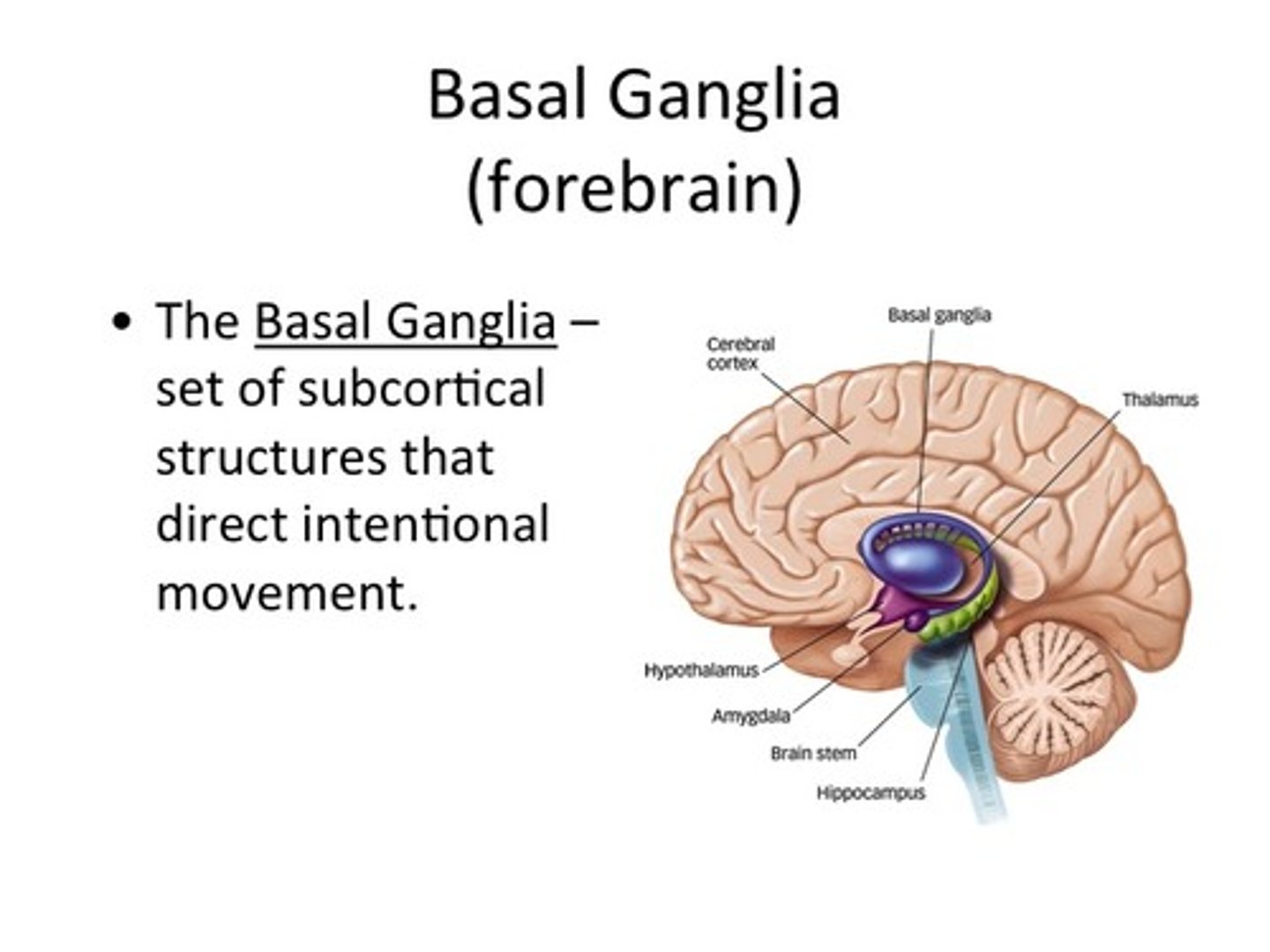
basal ganglia
voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, emotion, eye movement, cognition, addiction
- located at the base of the forebrain (middle of the brain)
connected to the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem
- means "pedestal knot"
- contains many parts
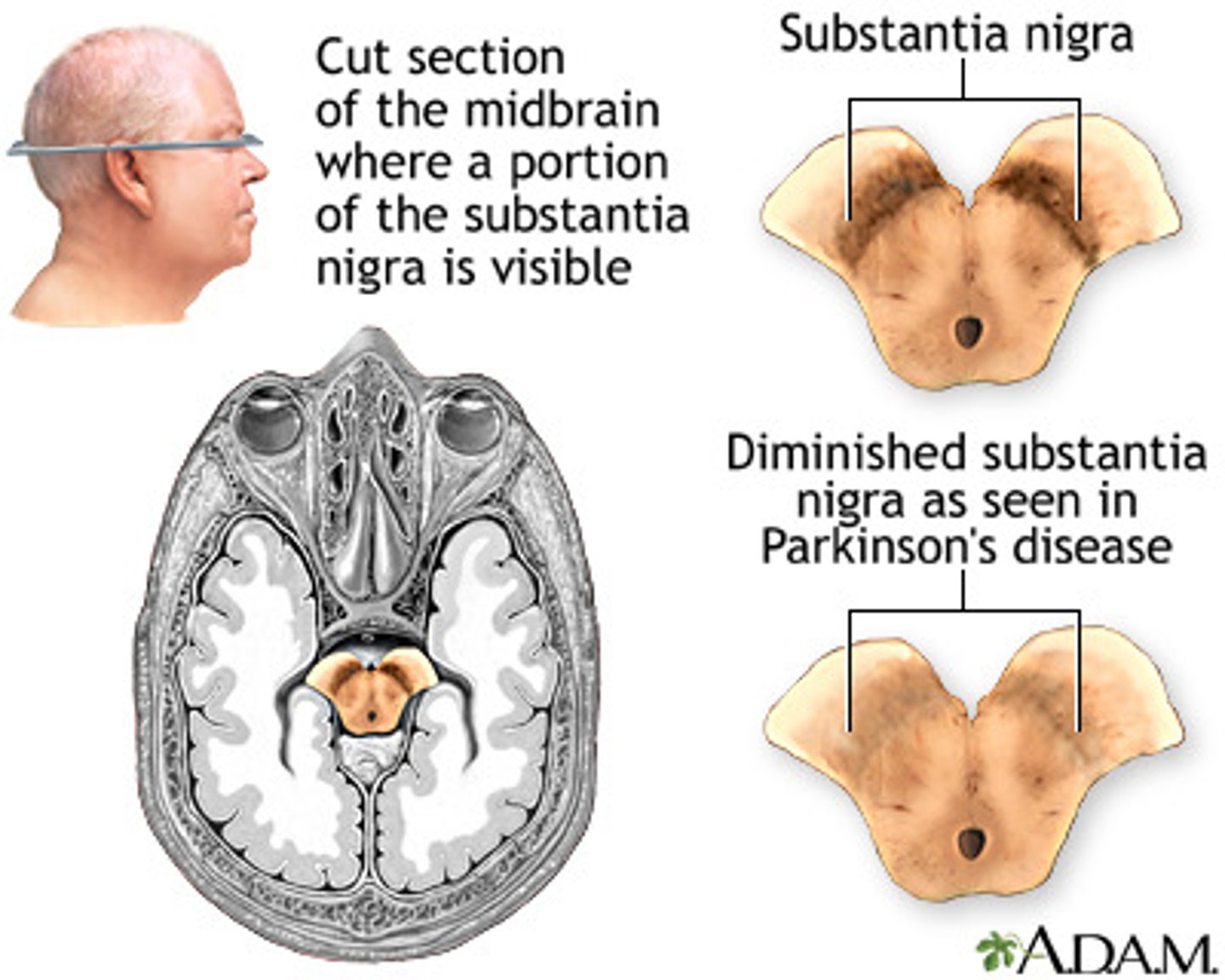
substantia nigra
eye movement, motor planning, reward-seeking, learning, addiction
- part of the basal ganglia
- means "black substance"
- nucleus consists of Pars Compacta (dopaminergic) and Pars Reticulata (GABAergic)
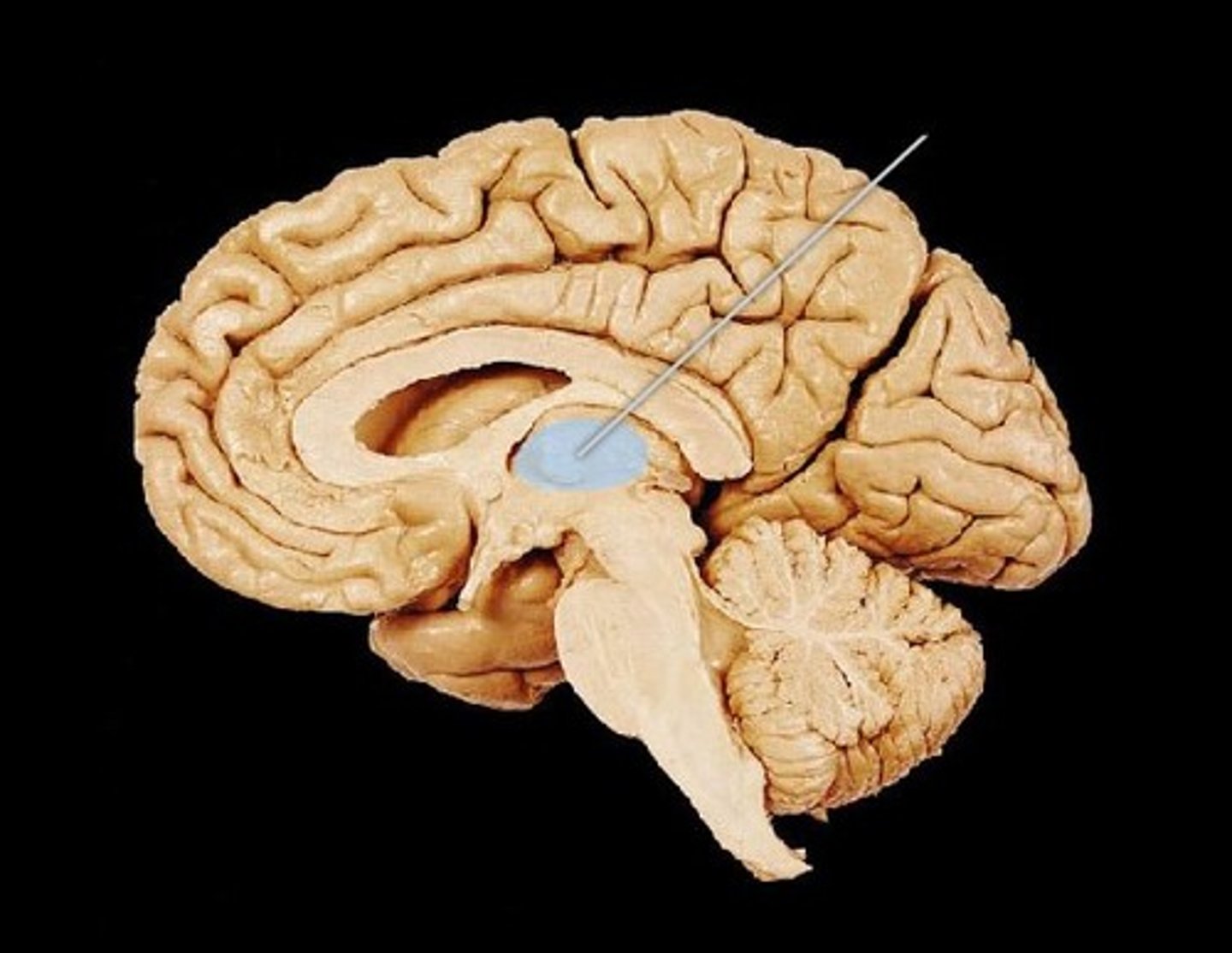
thalamus
relays information from all sensory receptors (not olfactory) to brain areas to be processed, regulation of sleep/wake
- located below the corpus callosum in the forebrain
- means "chamber"
- has 2 symmetrical halves on each side
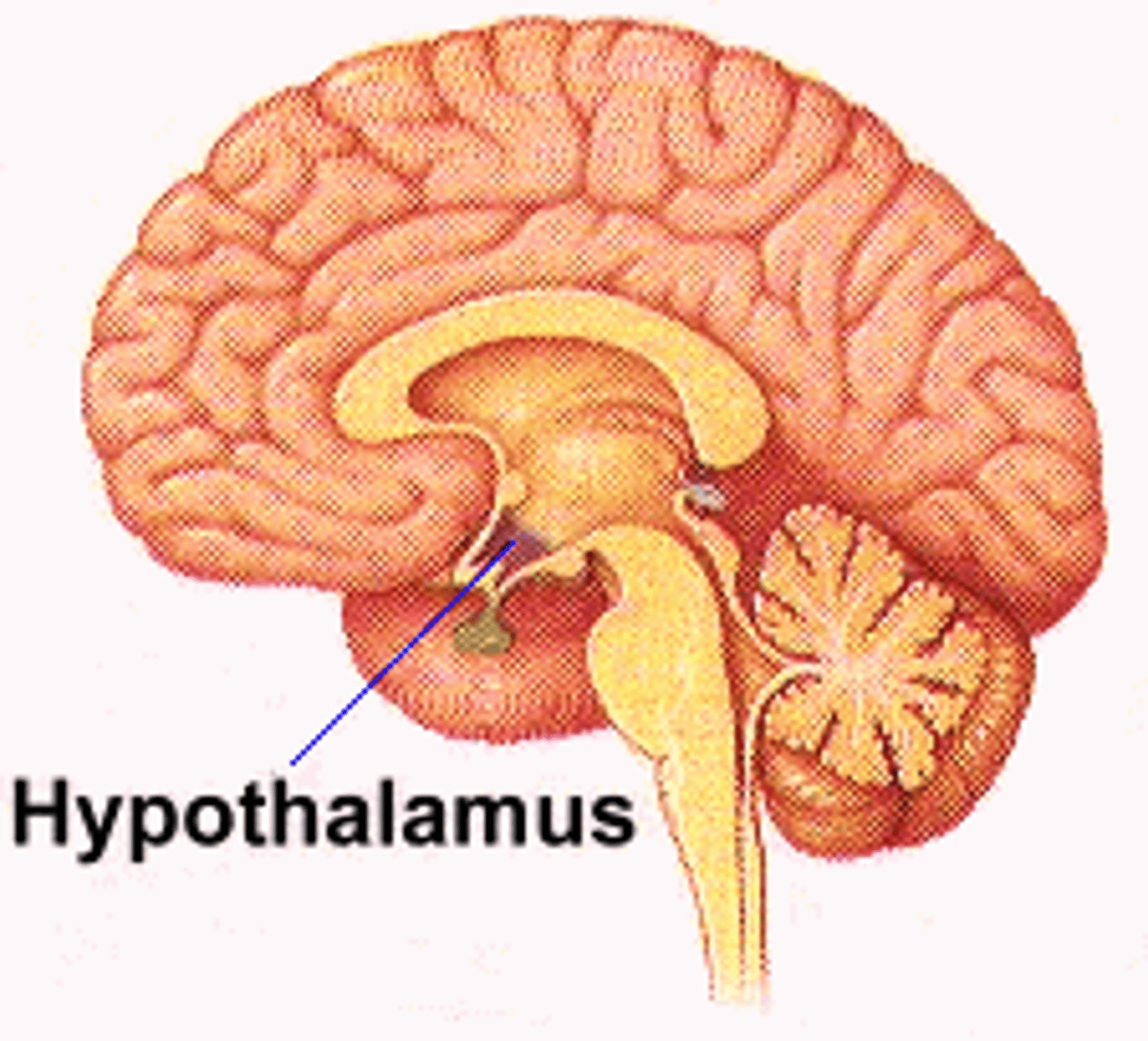
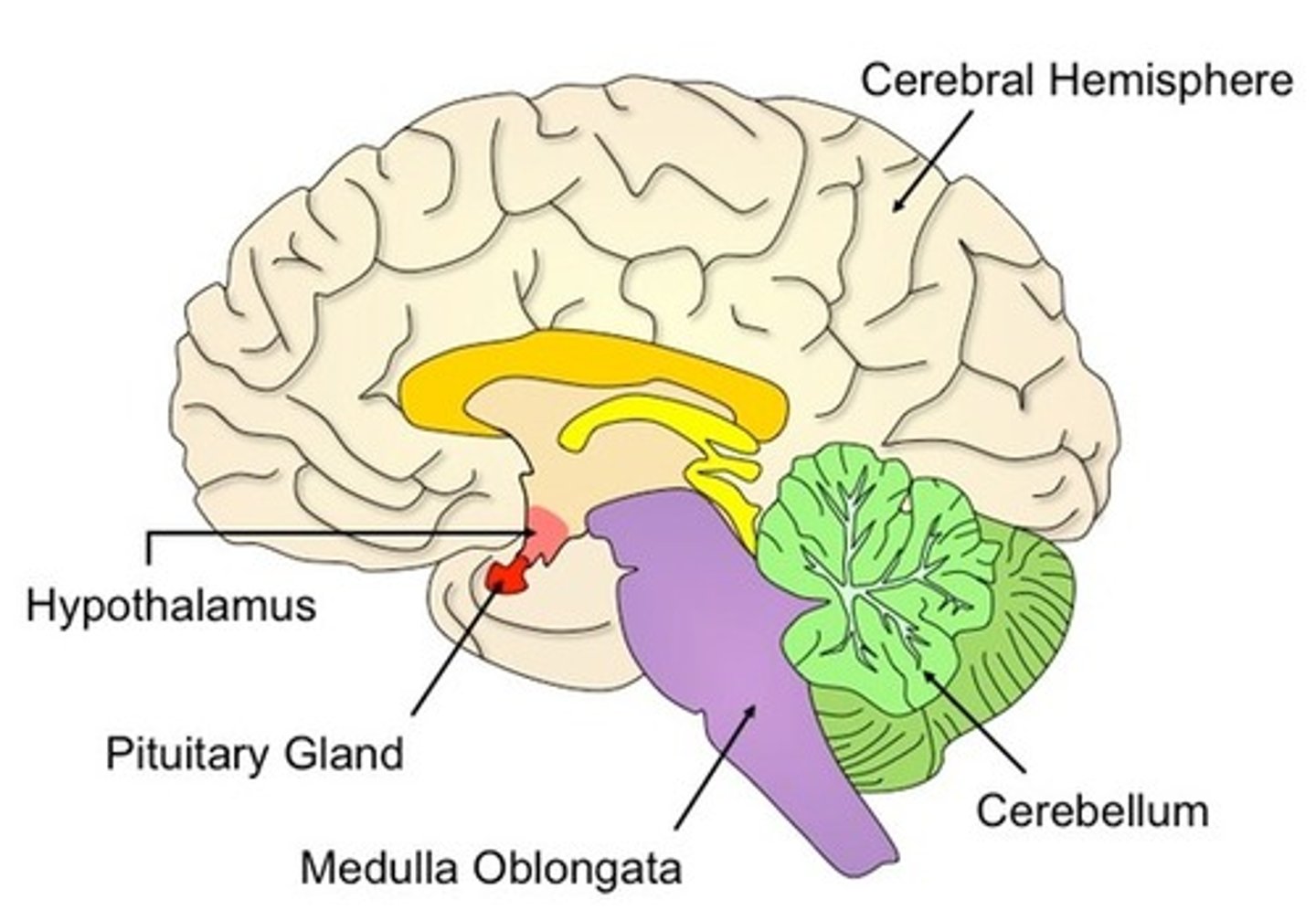
hypothalamus
coordination center for: autonomic NS, pituitary activity, hunger, thirst, body temp regulation, sleep, emotional activity, maternal behavior
- located above the pituitary gland and below the thalamus
reaches in each temporal lobe
- means "under the chamber"
pituitary gland
endocrine gland at the base of the brain
hypothalamus talks to pituitary -> pituitary release appropriate hormone
- located below the hypothalamus
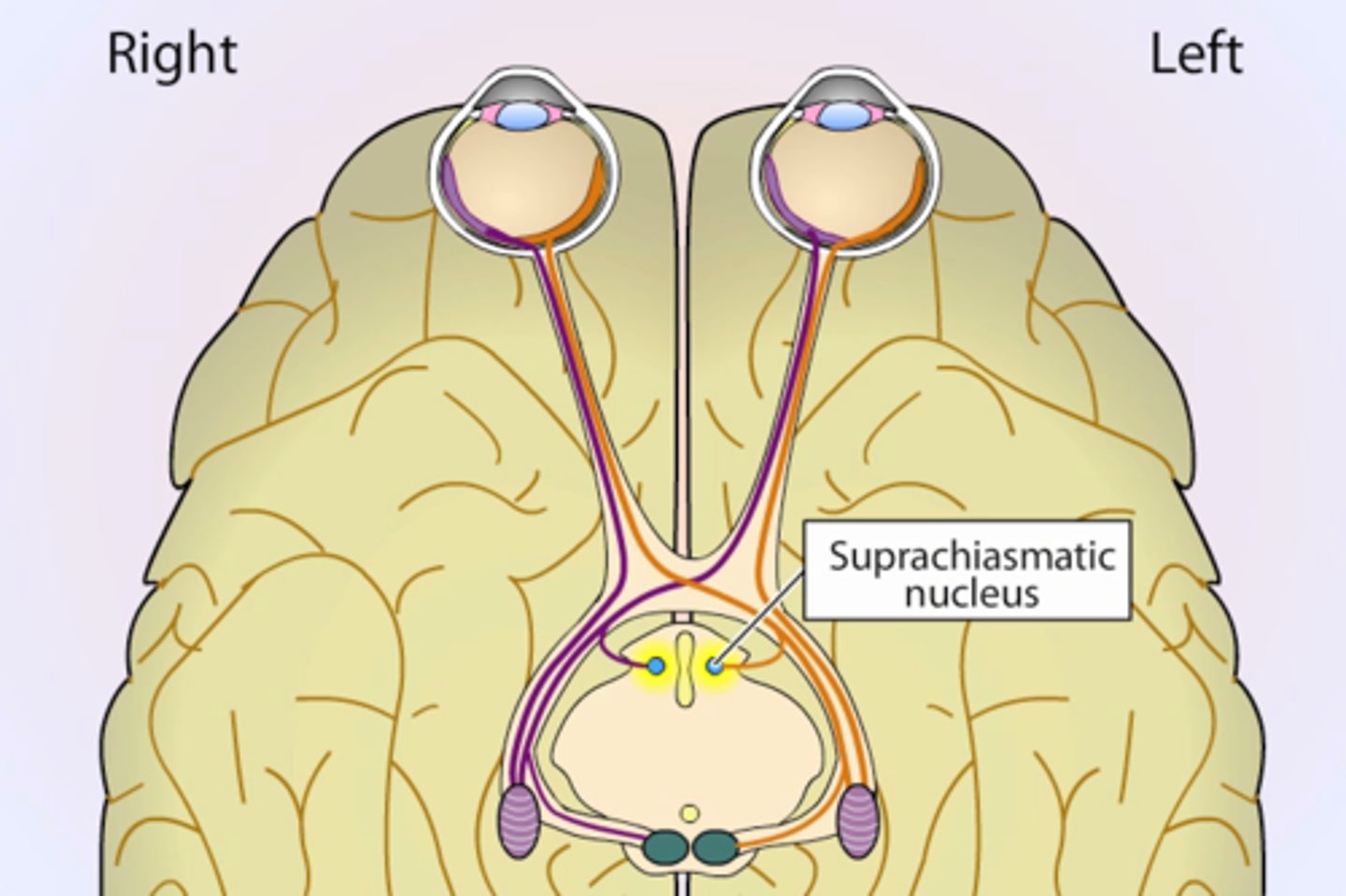
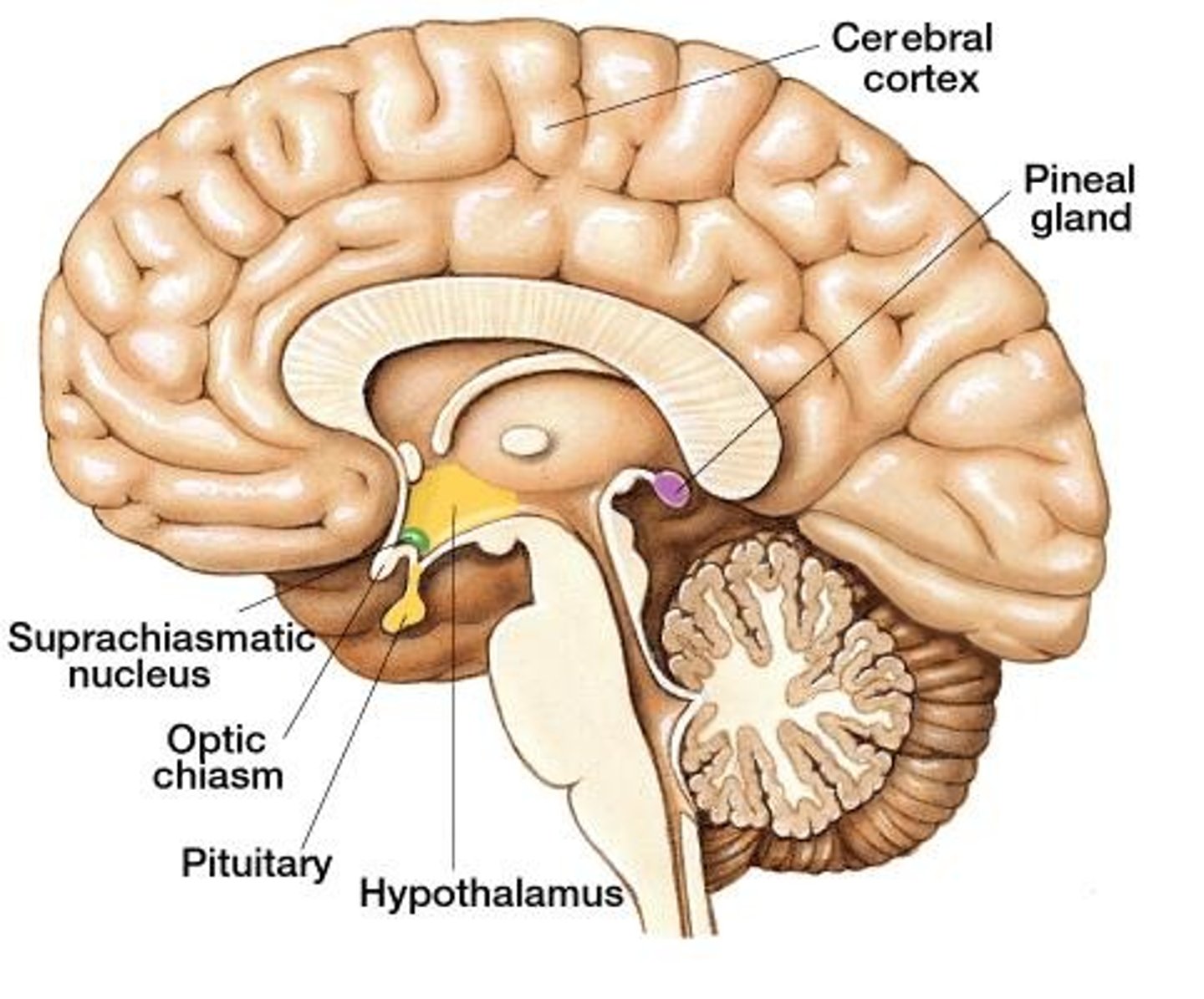
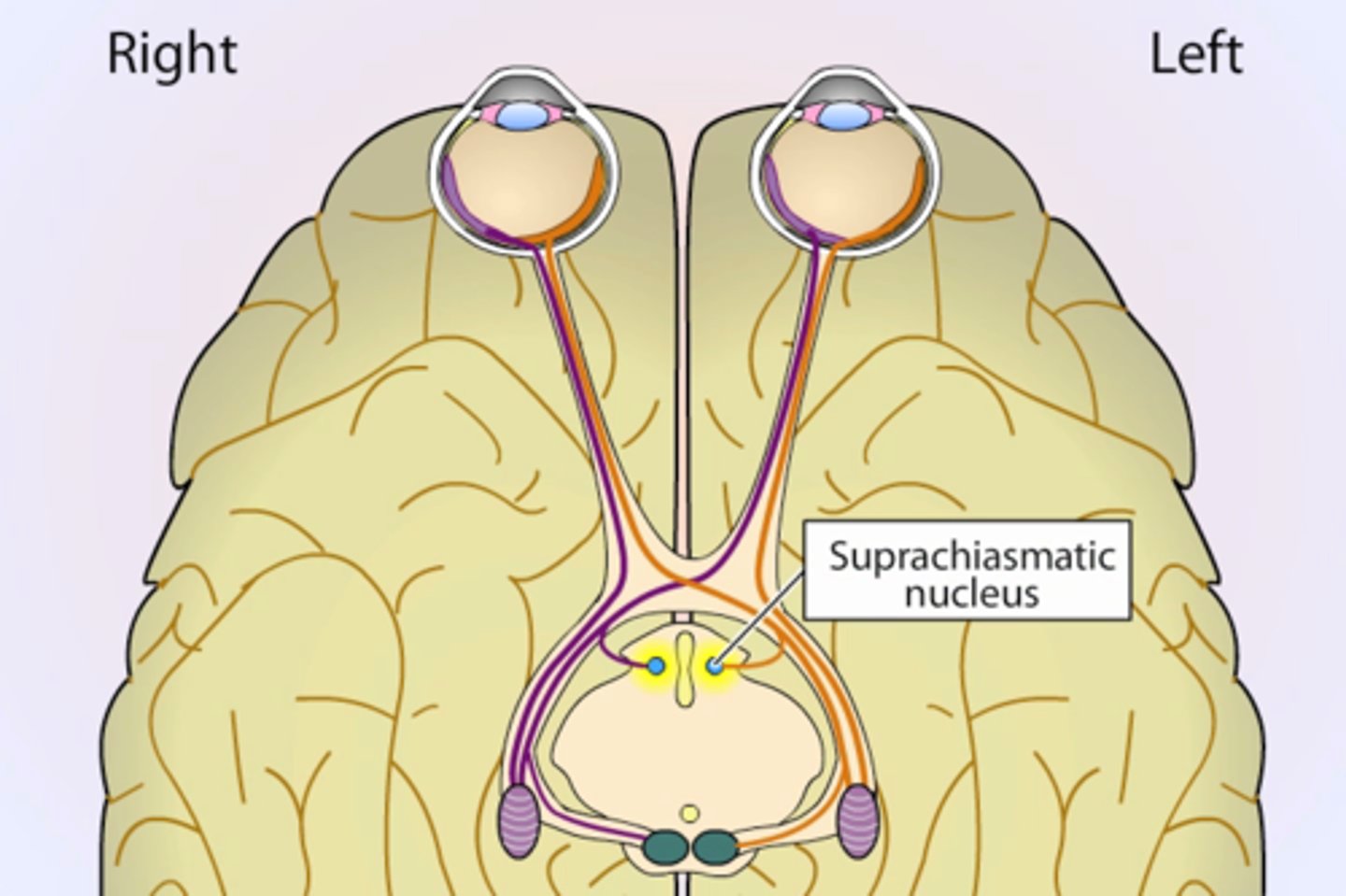
suprachiasmatic nucleus
circadian pacemaker "master oscillator", regulates pineal gland
- located in hypothalamus, above optic chasm
- means "nucleus above the optic chasm)
- consists of 20,000 neurons
pineal gland
secretion of melatonin, circadian rhythmicity
- located on midline of brain
- means "pine cone"
- only one!
- consists of pinealocytes
brain stem
connects the brain and spinal cord
- consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
midbrain
(brain stem)
sensory and motor information, eye movement
pons
(brain stem)
REM sleep, autonomic regulation
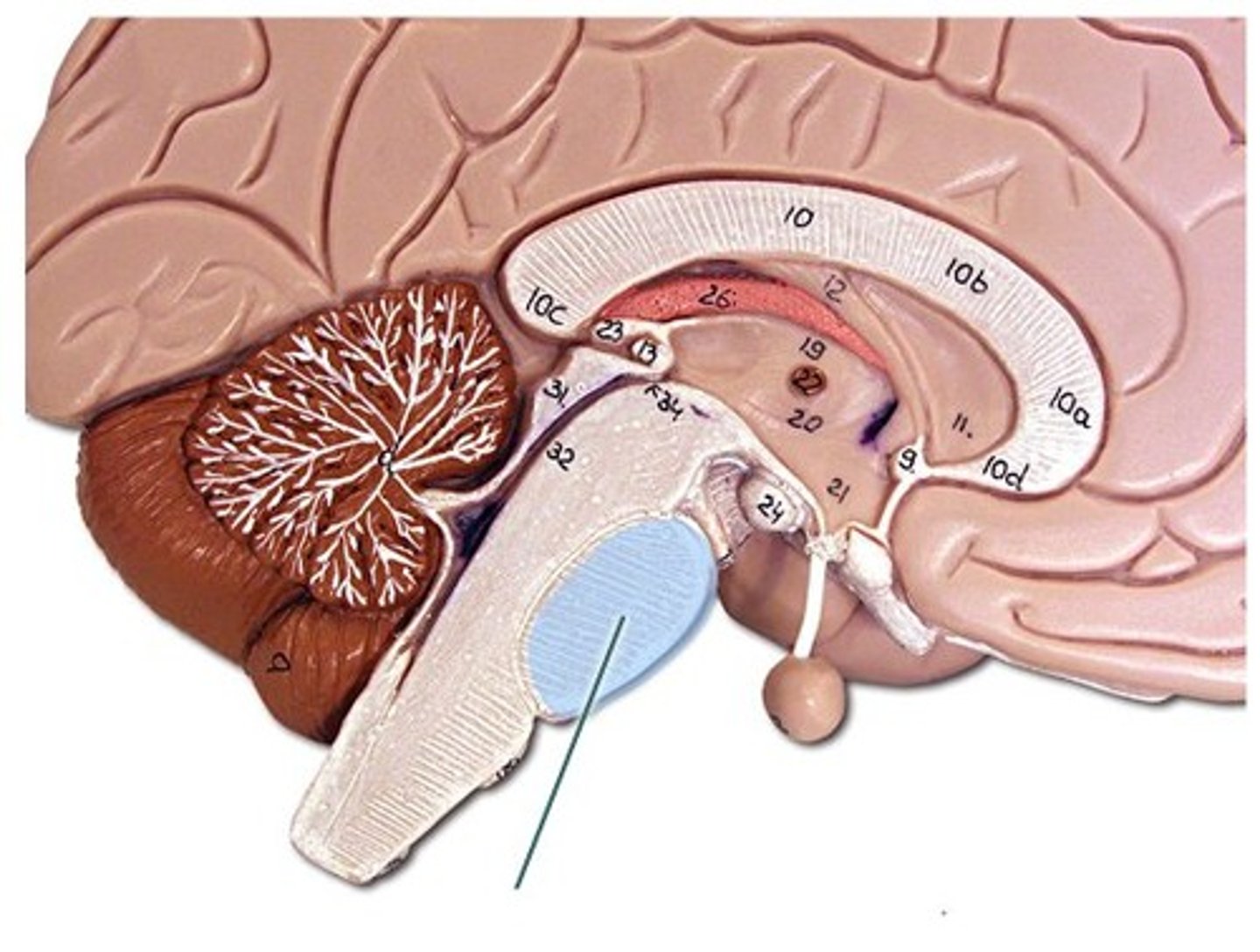
medulla oblongata
(brain stem)
blood pressure, breathing, heart rate, swallowing
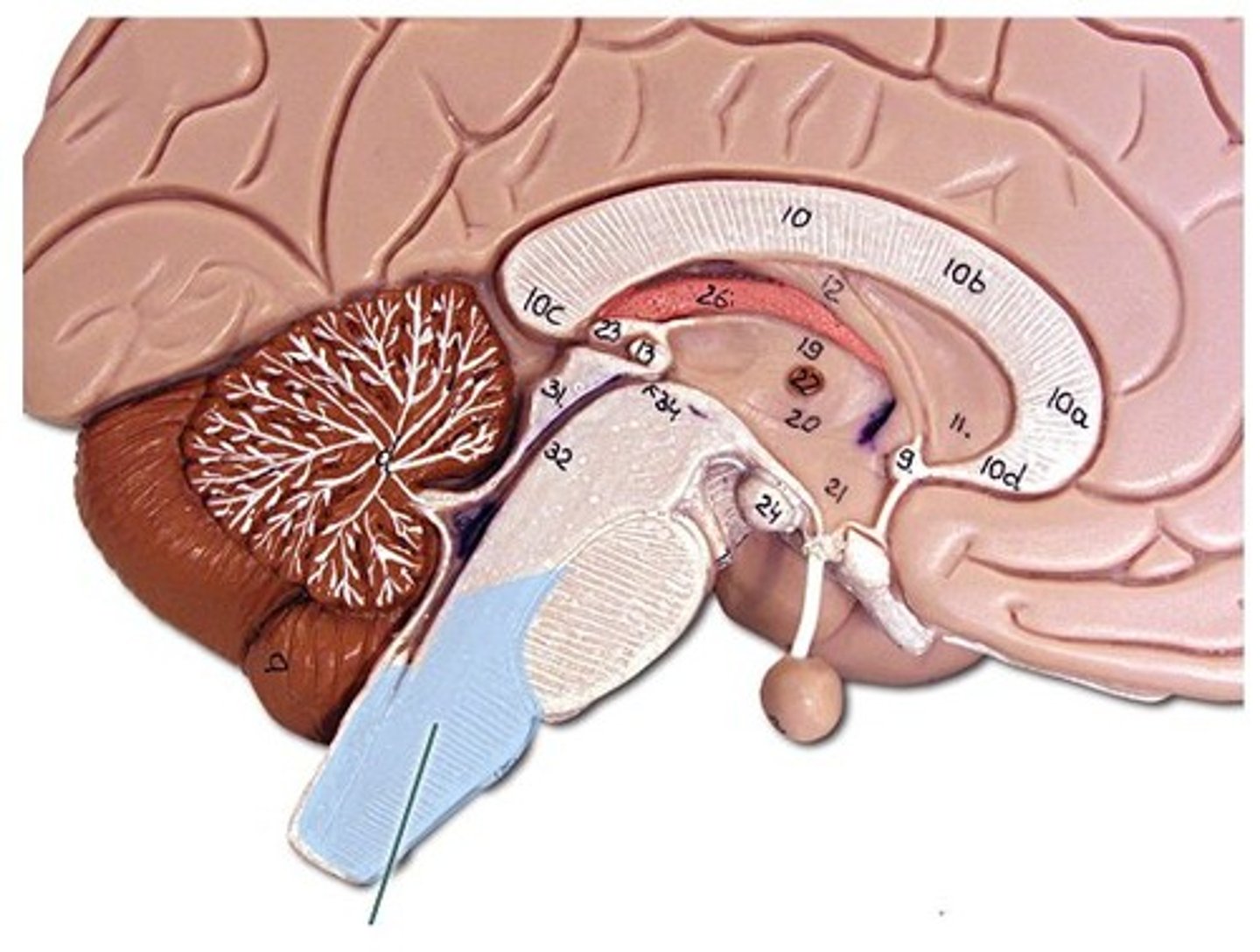
cerebellum
motor control system, balance, posture, coordination of muscles, finely adjusted movement
- lower area of the brain , close to pons
- means "little brain"
- consists of 2 hemispheres, tightly folded layers of gray matter
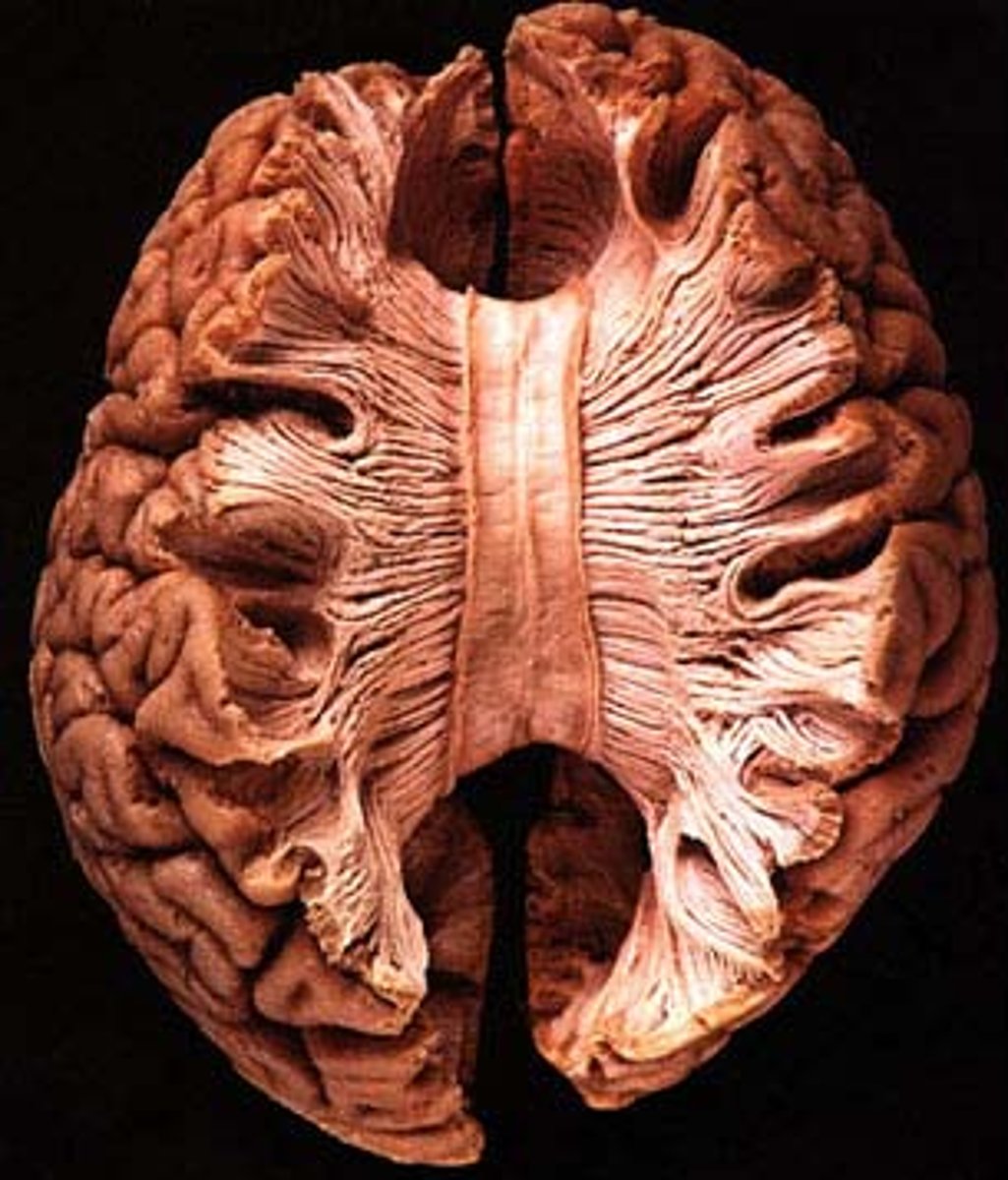
corpus callosum
communication between hemispheres
- located between the left and right hemispheres; above thalamus, under cortex
- means "tough body"
- largest white matter structure
- consists of 200-250 million axonal projections
cerebroventricular system
controls the synthesis, release, internal circulation, and drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- lateral ventricles (pair) - largest surface area
- third ventricle - diencephalon
- fourth ventricle - between the pons and medulla/ cerebellum
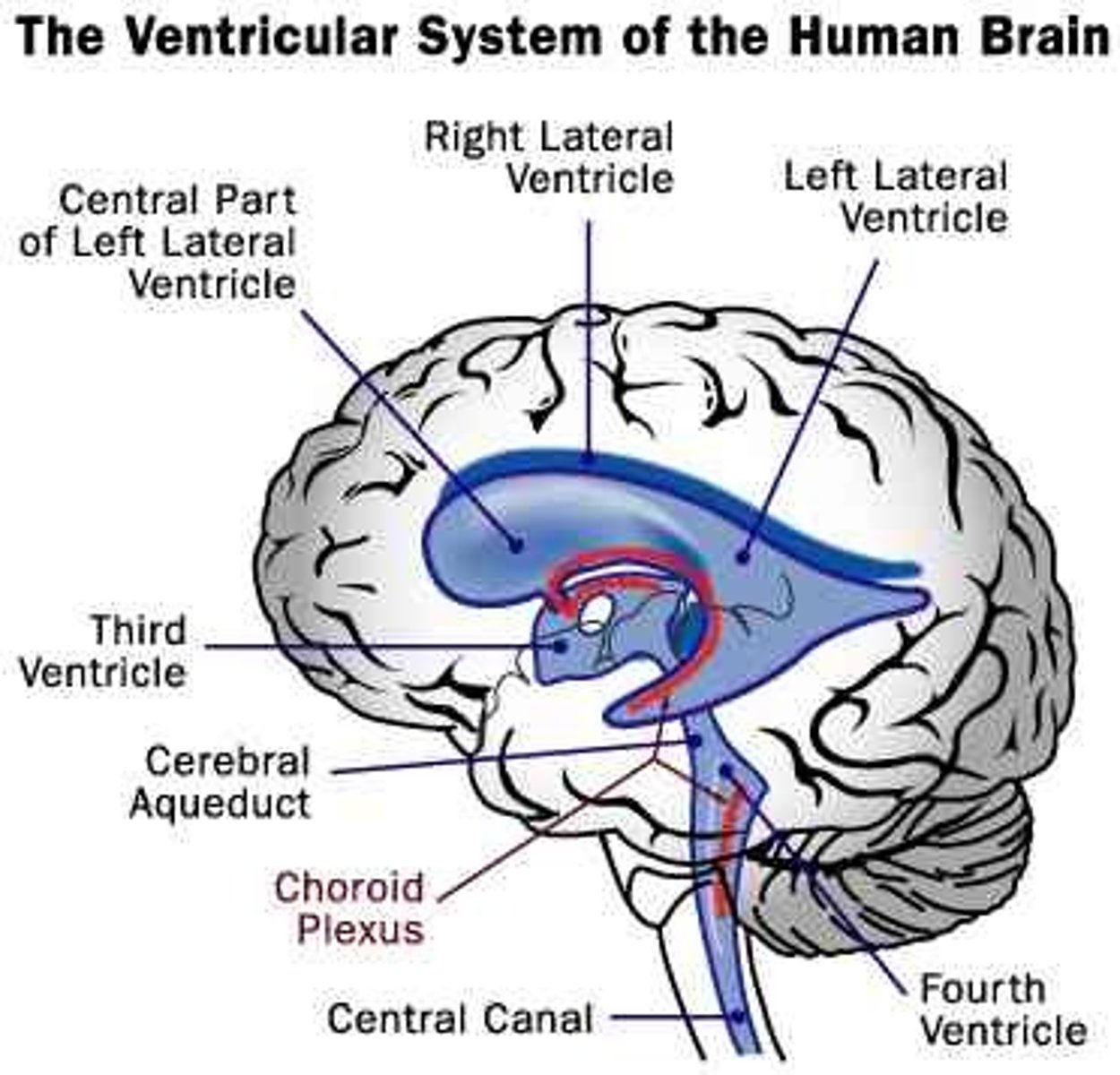
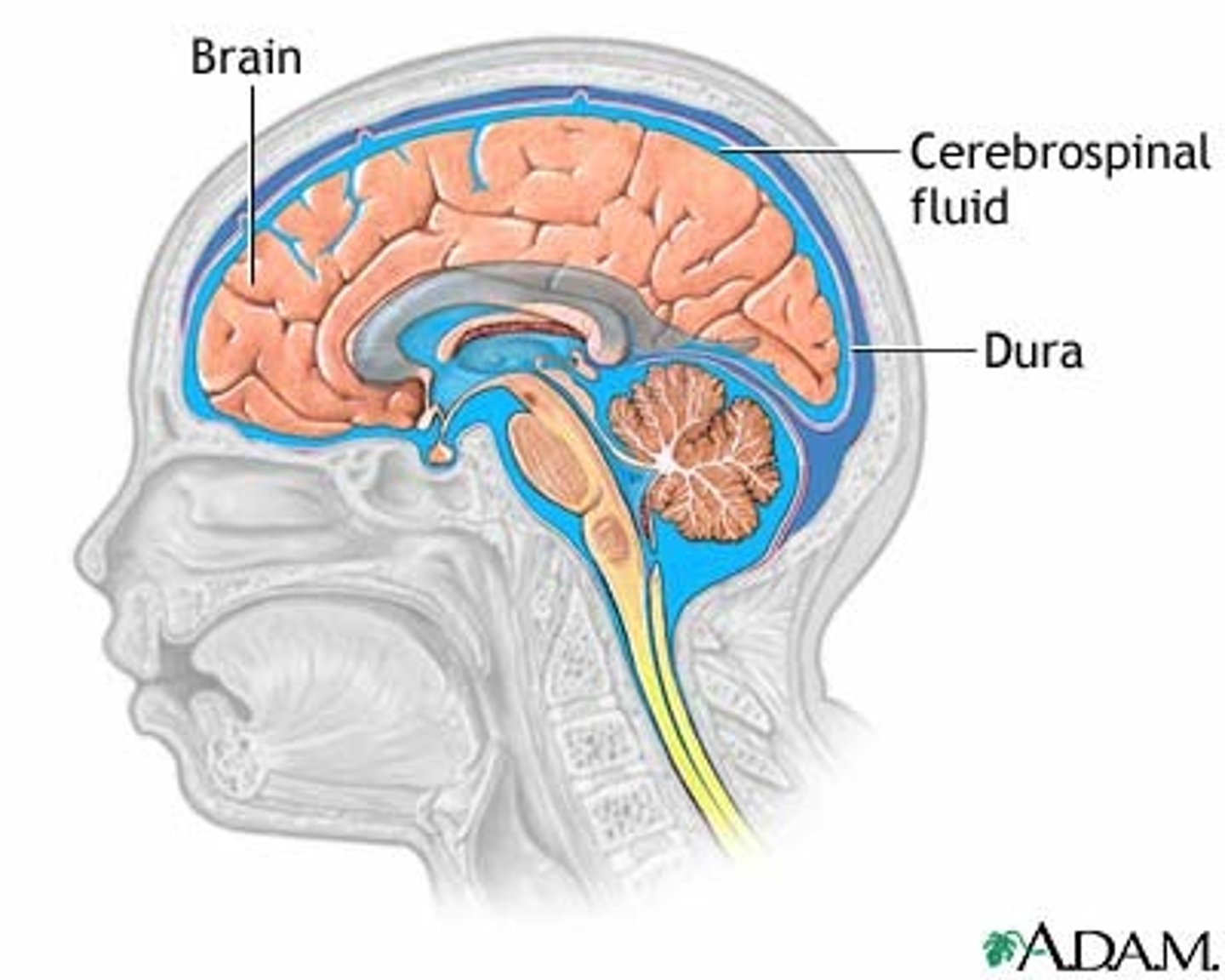
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
a highly modified filtrate of plasma that is produced and released by epithelial cells in the choroid plexus
- the brain circulates a total volume of about 150 mL
- 700 mL is secreted each day in humans
- entire volume turns over every 5-7 hours
functions:
1. cushion and support the brain
2. regulation of ion composition/ hormone distribution
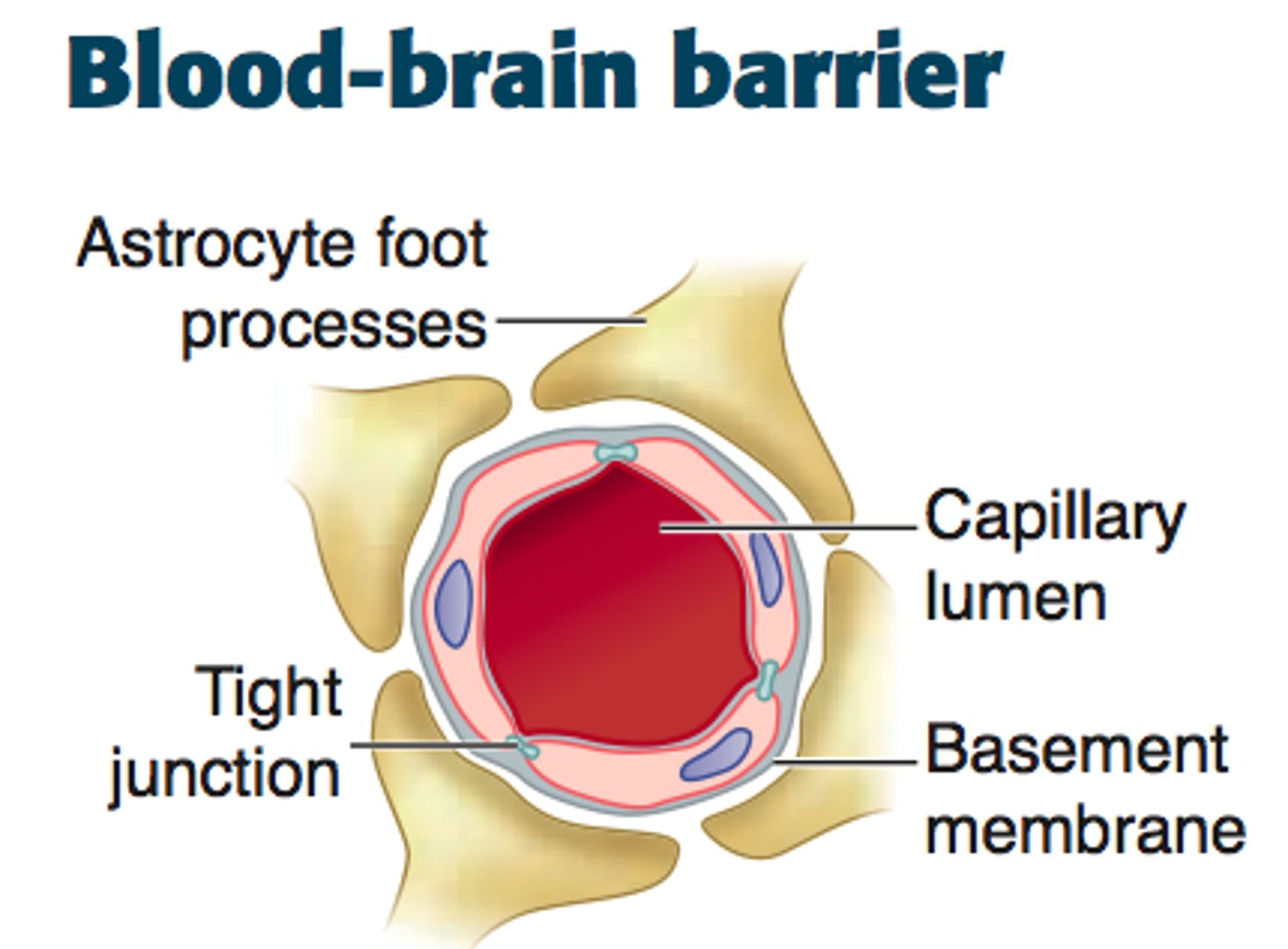
blood brain barrier
blood vessels (capillaries) that selectively let certain substances enter the brain tissue and keep other substances out
- 100 billion capillaries
- 100% of large molecule drugs and 98% of small molecules do NOT cross the BBB
functions:
- provide brain with O2/ glucose, clear waste, prevent xenobiotic entry, maintain brain homeostasis, protect from abrupt changes in peripheral blood
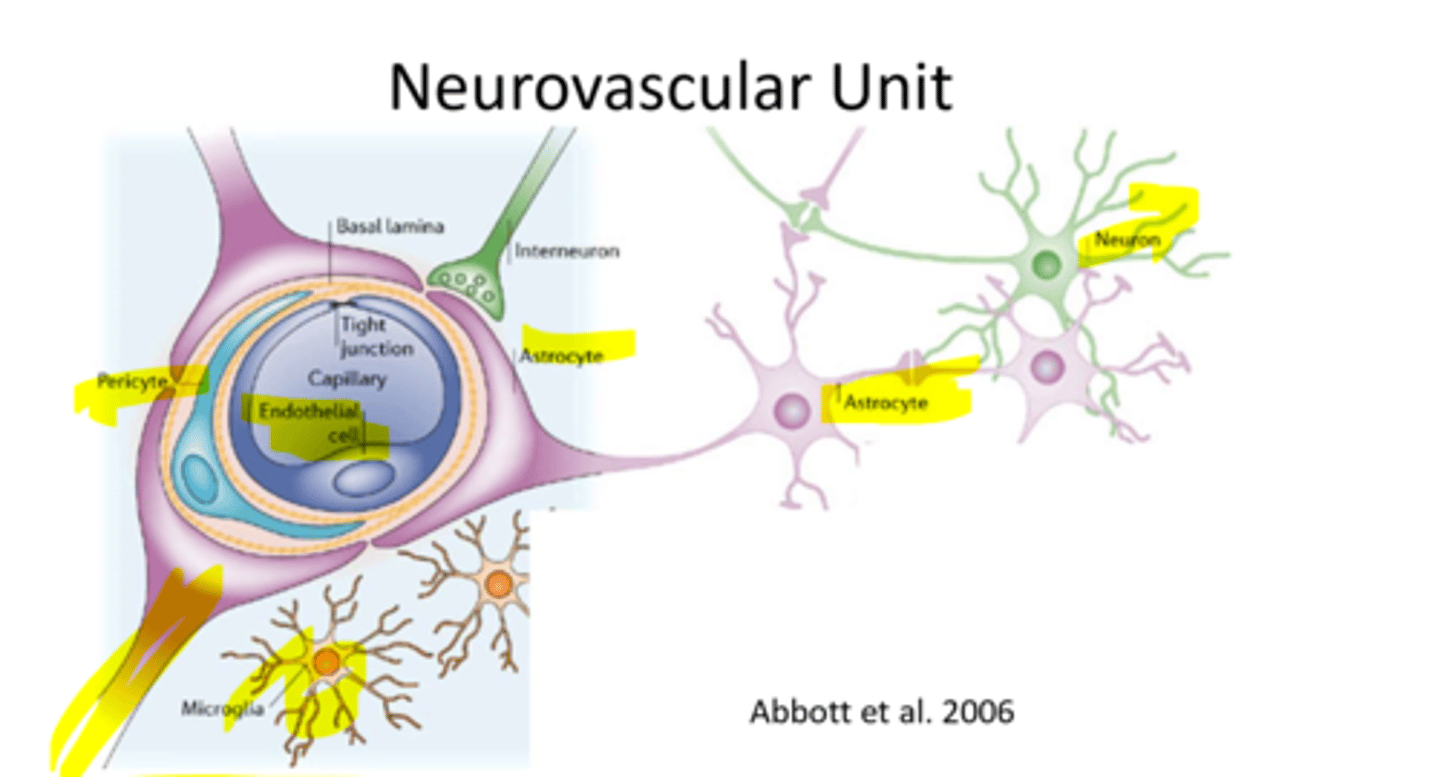
neurovascular unit
an active barrier consisting of influx transporters, efflux transporters, and metabolic enzymes in endothelial cells
cirumventricular organs
brain regions that are in close contact with CSF and must respond quickly to factors present in systemic circulation (fluid/ electrolyte balance, endocrine feedback, emesis)
- lack an organized BBB
what do all neurons do?
- detect and summate all incoming stimuli
- process and integrate the information received
- conduct an electrical signal along the cell
- transfer chemical information to other cells
dendrites
a neuron's bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
- detect and summate all incoming stimuli
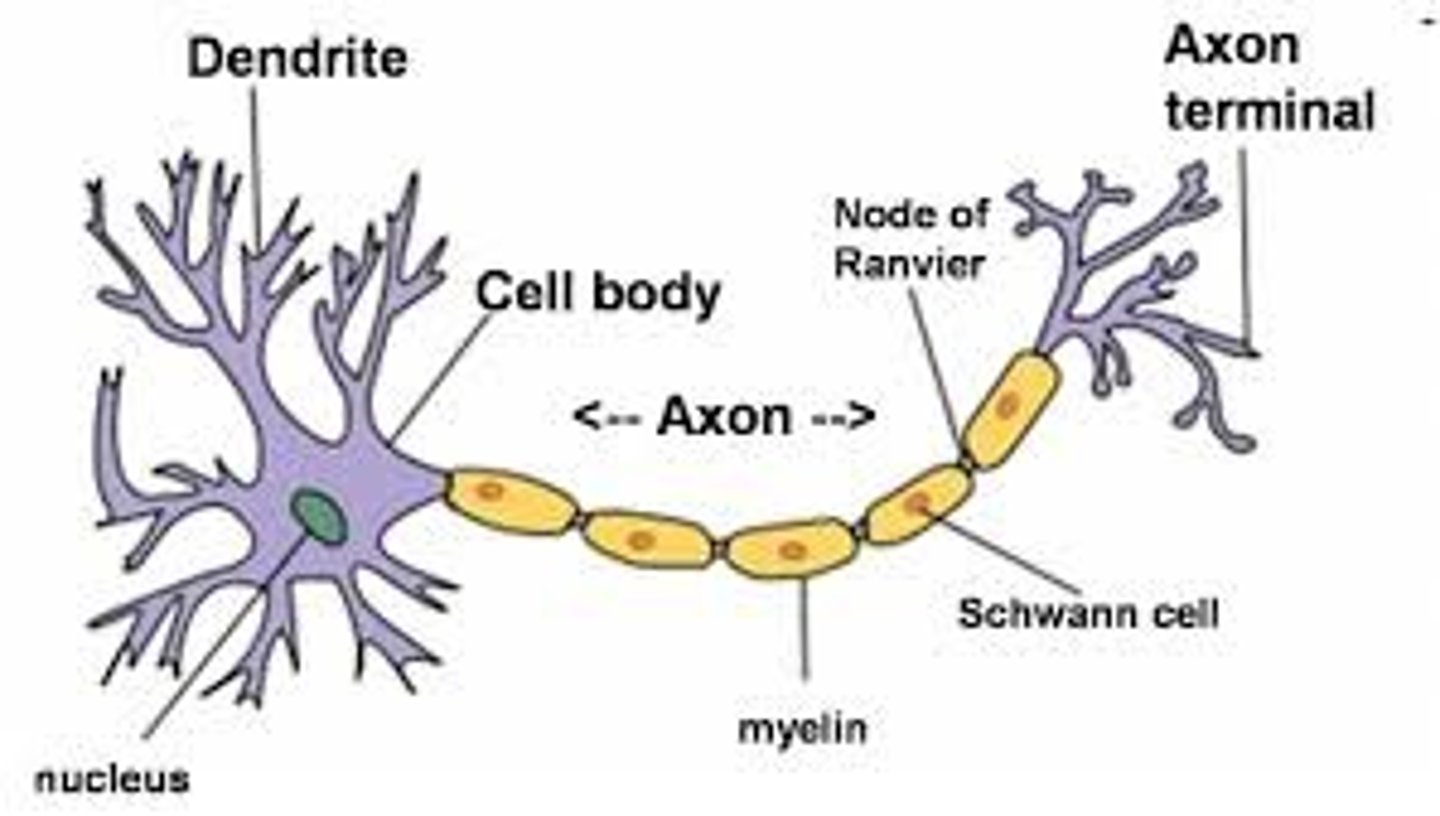
cell body (soma)
contains the nucleus and other parts of the cell needed to sustain its life
- process and integrate information receieved
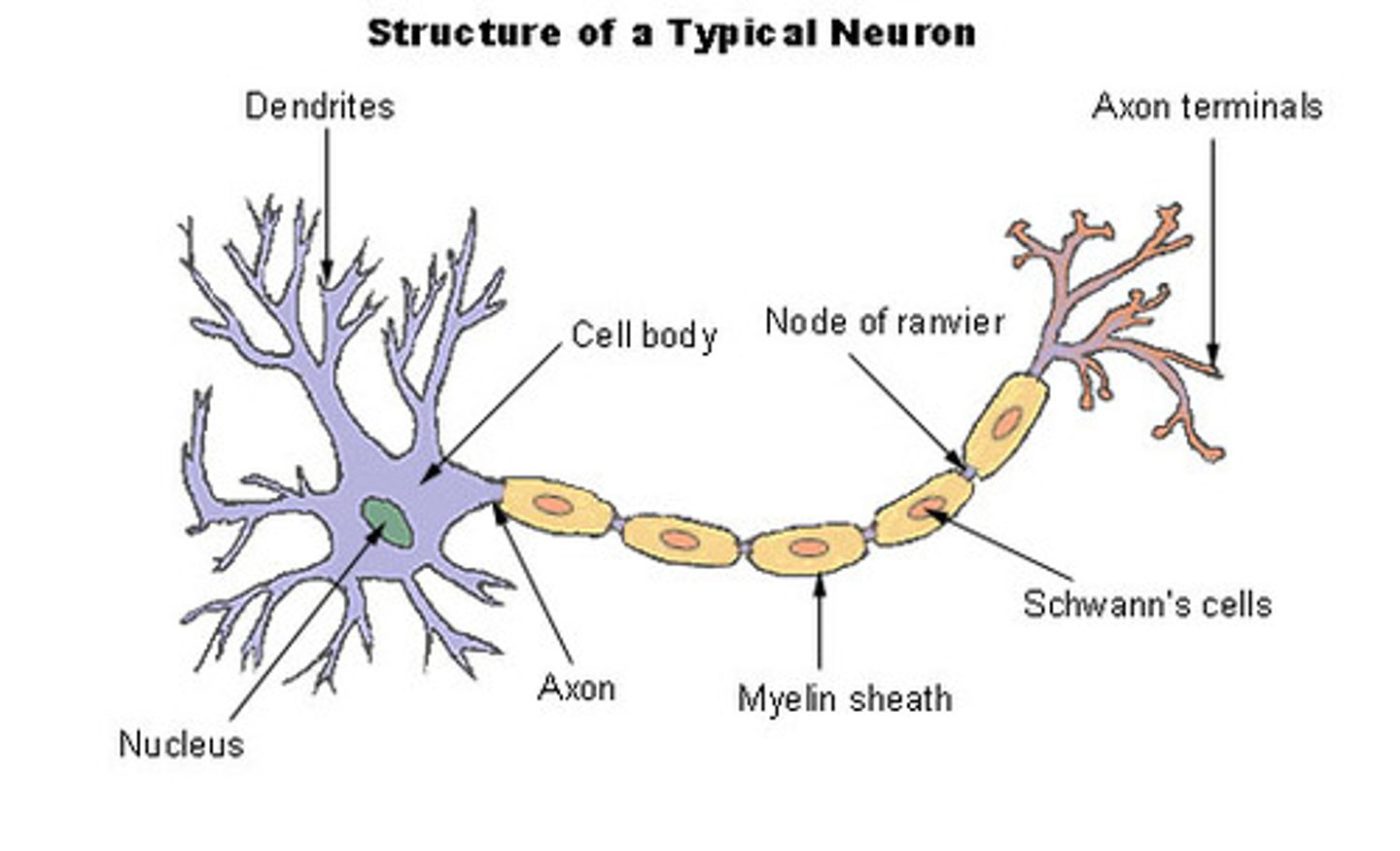
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
- conduct an electrical signal along the cell
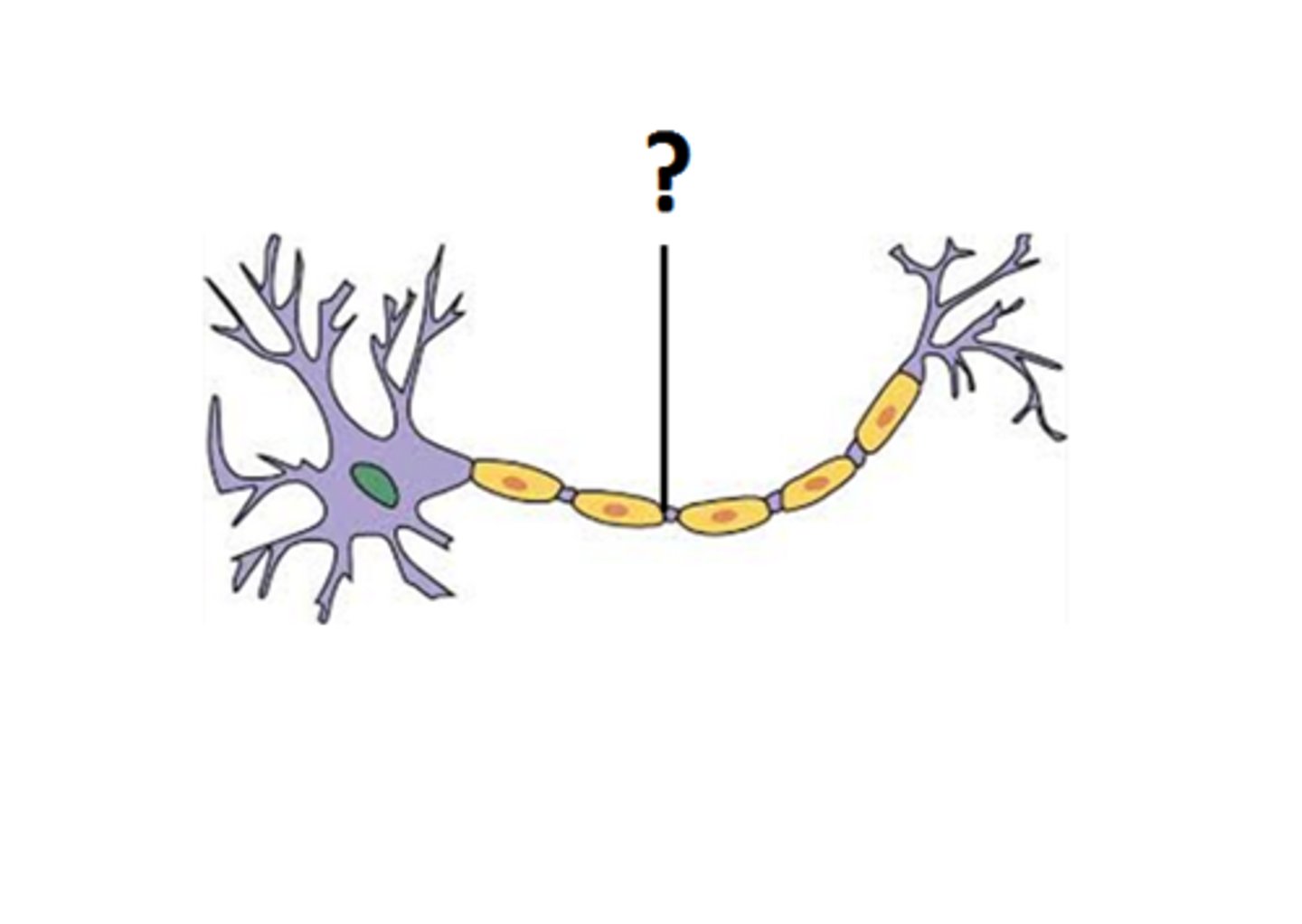
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
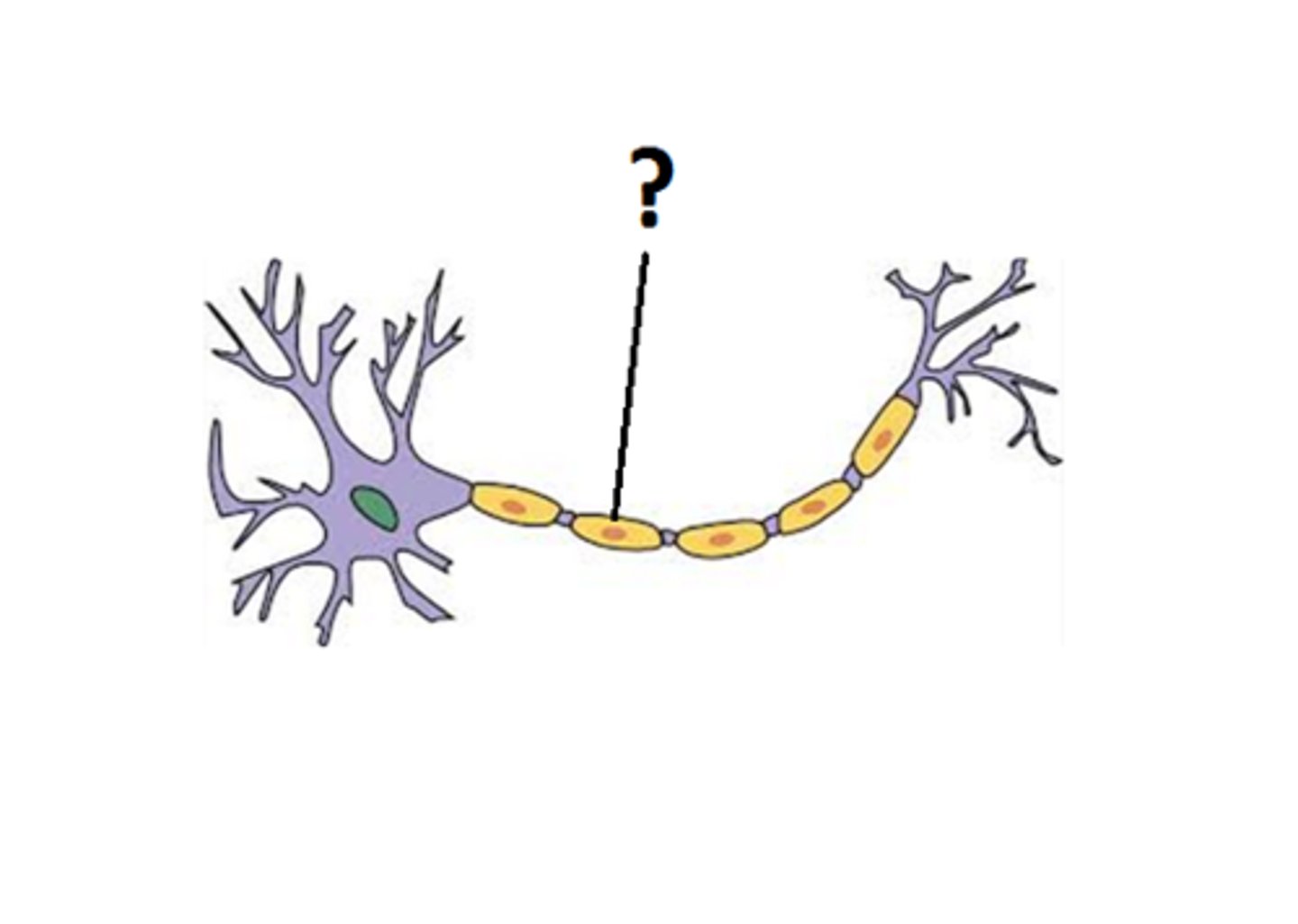
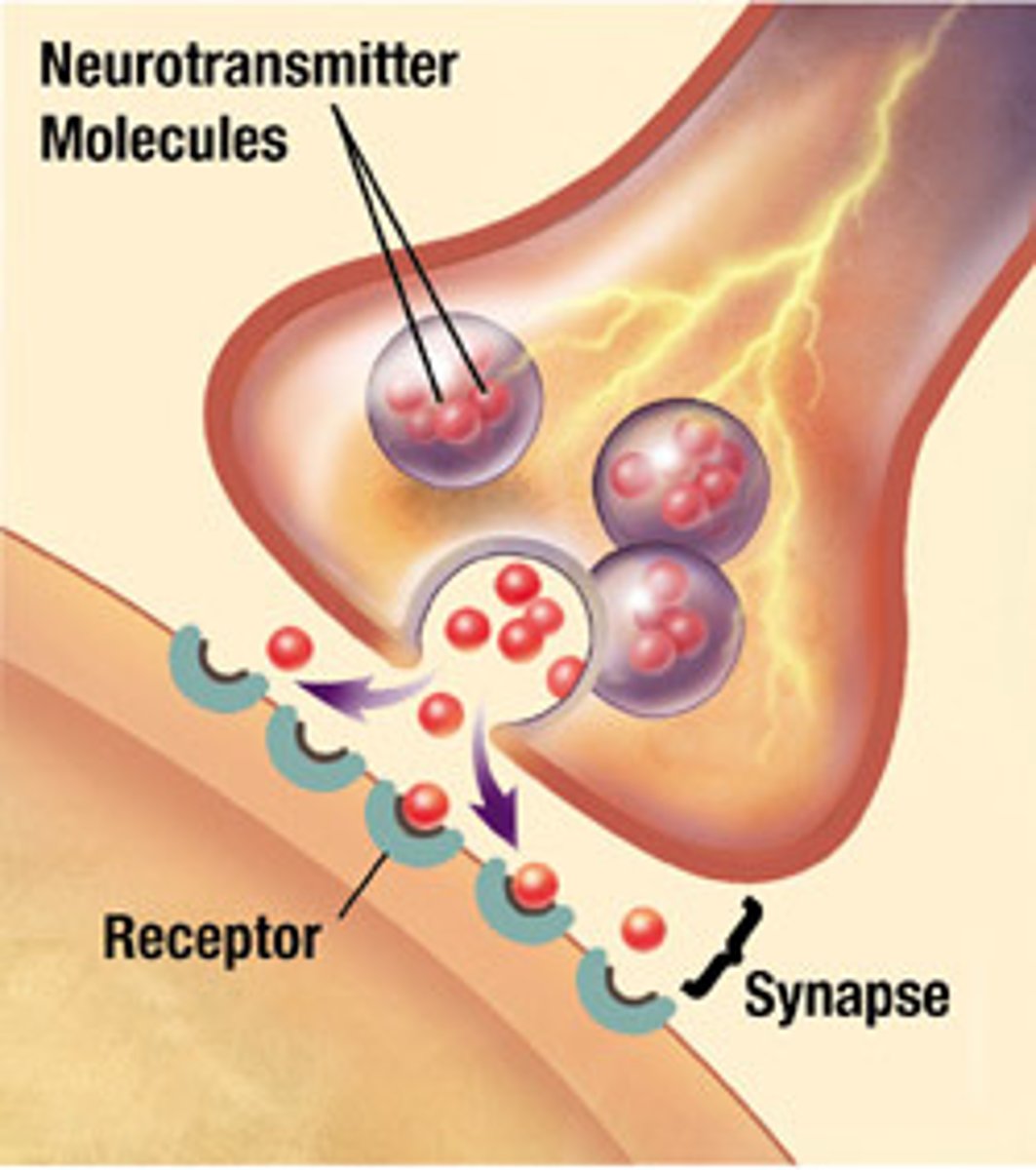
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
- transfer chemical information to other cells or tissues
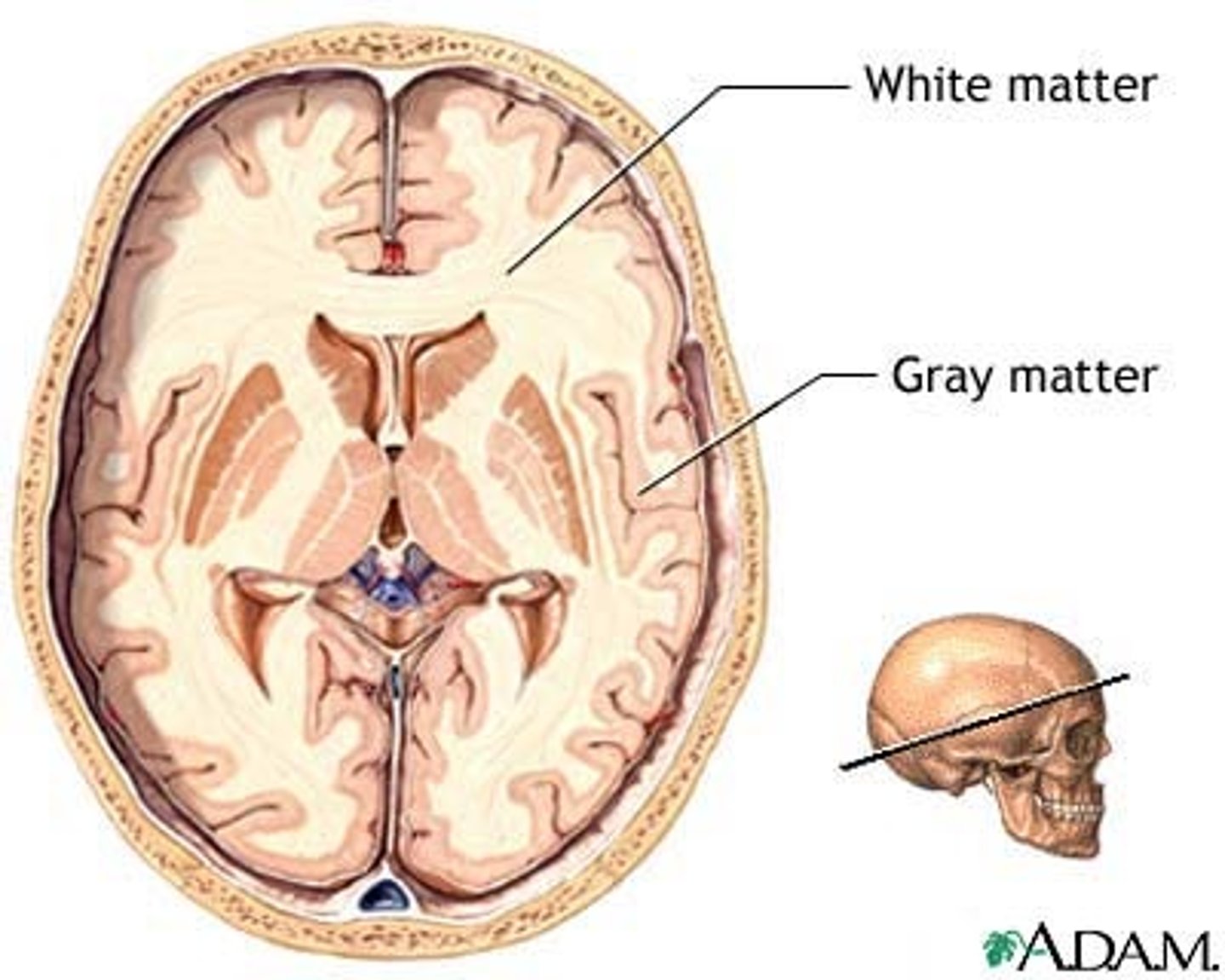
gray matter
consists of the cell bodies and dendrites of neurons and glia
- pink outer layer
- sensory perception, muscle control, self-control, decision making, memory, data processing
white matter
consists of neuronal axons ensheathed in myelin
- learning and cognition
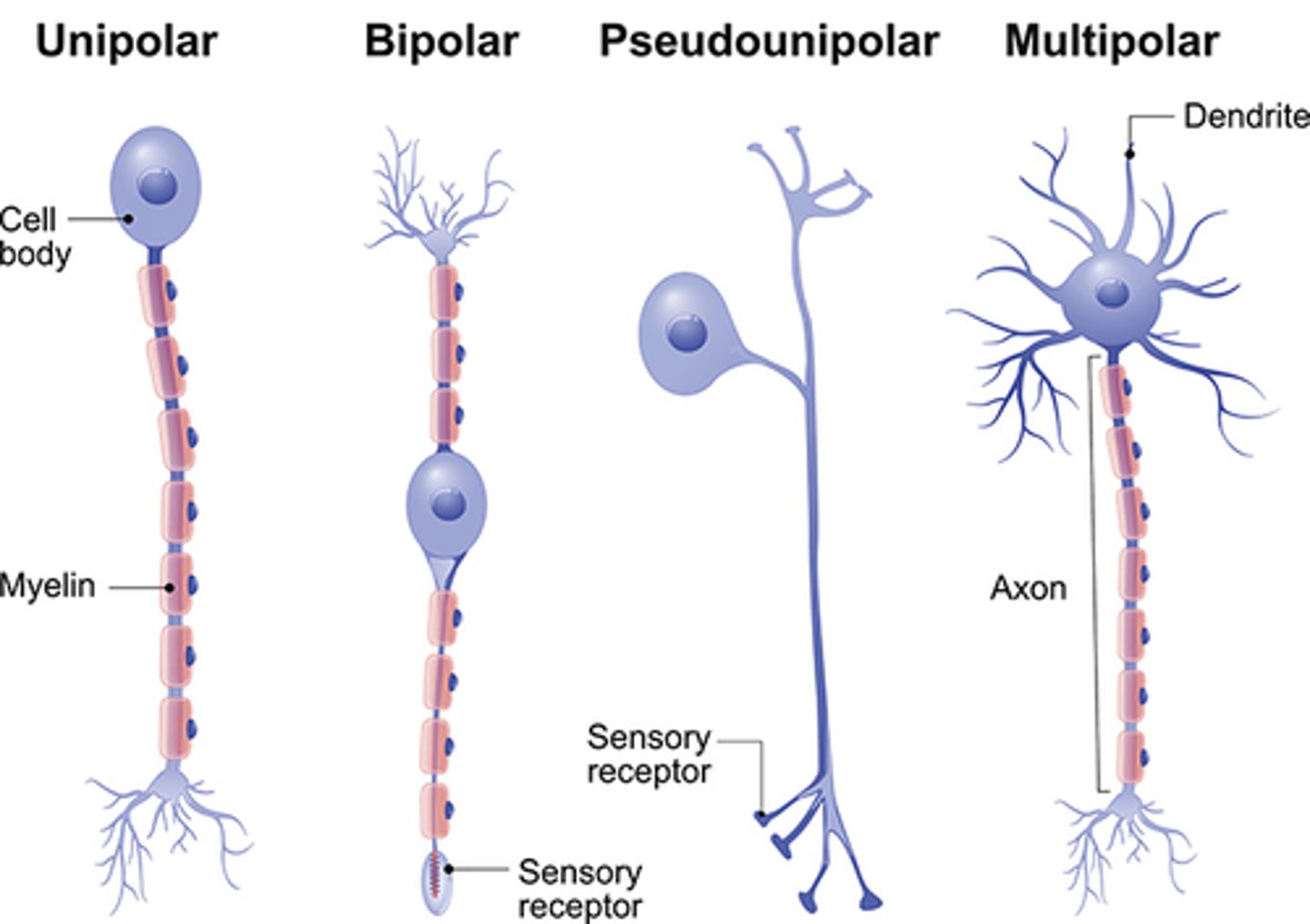
4 basic types of neurons
1. multipolar - motor neuron, most common in CNS
2. bipolar - eyes & ears, processes precise info
3. pseudo-unipolar - sensory neurons in PNS, important in pain
4. unipolar - mostly in invertebrates
ganglion
a collection of nerve cell bodies that are located outside the CNS
- autonomic ganglia, Trigeminal ganglia
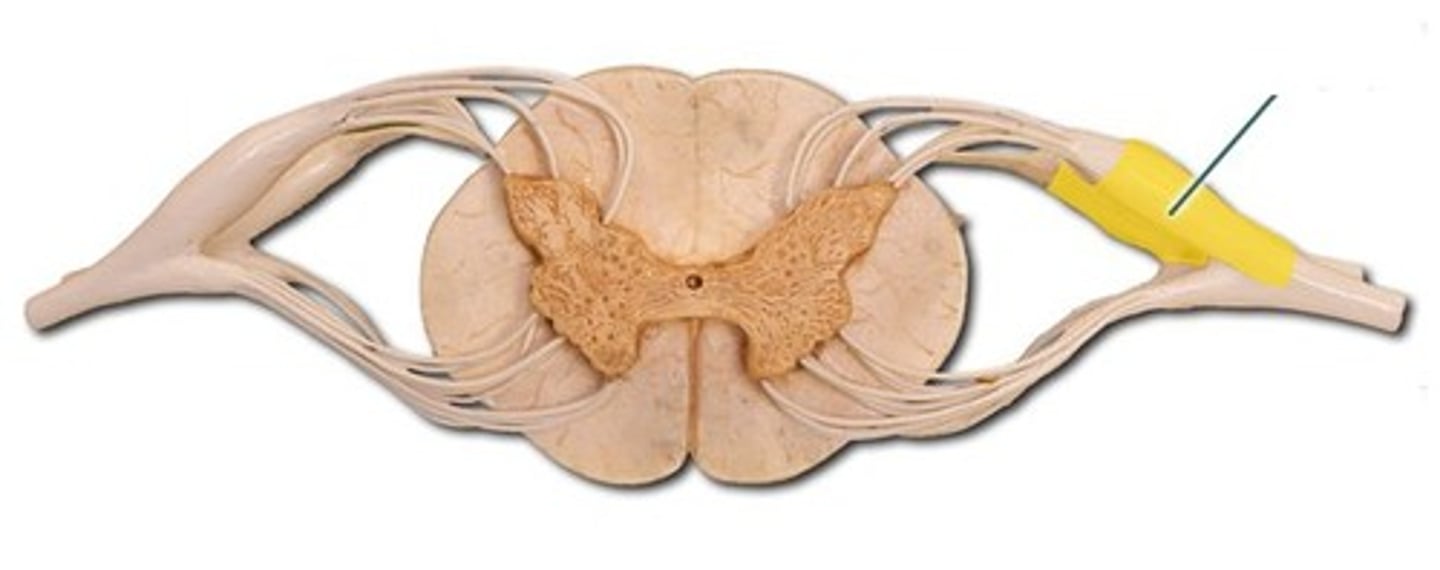
nucleus
a collection of neuronal cell bodies that are located inside the CNS
- suprachiasmatic nucleus, nucleus acumbens
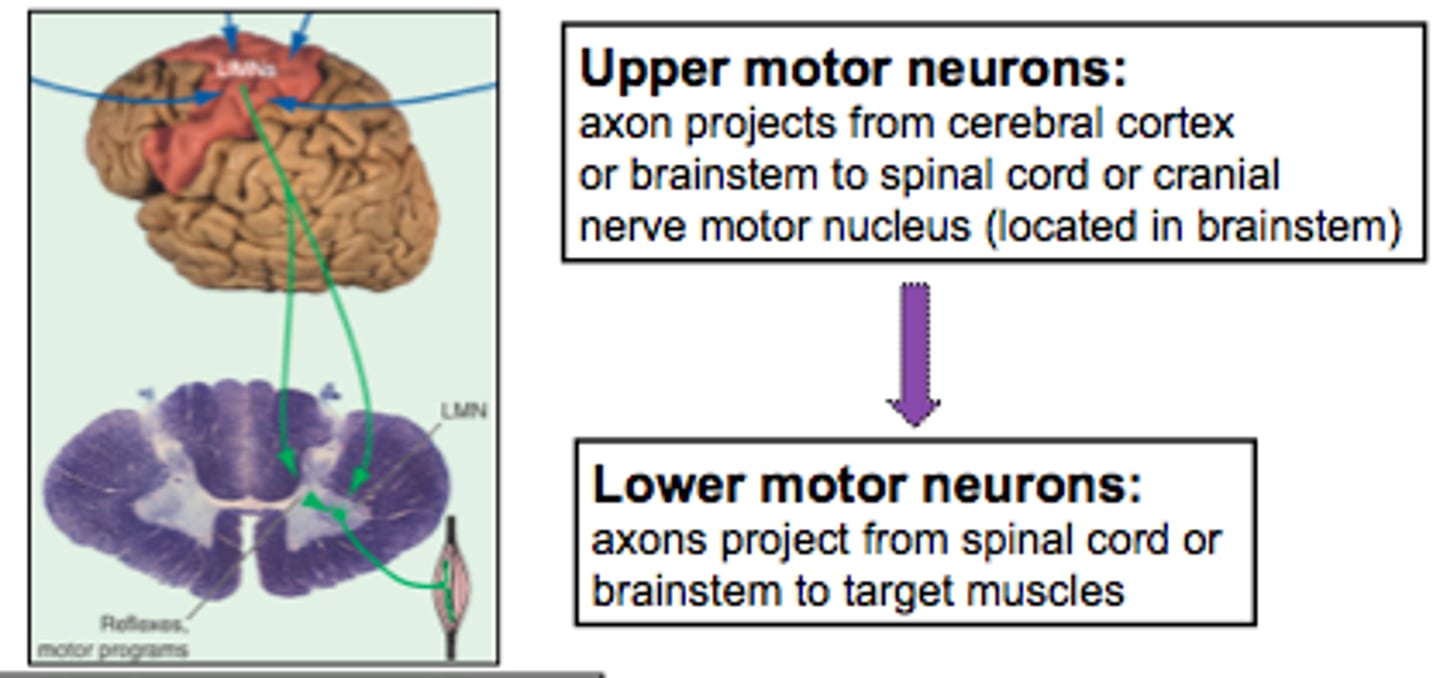
upper motor neurons
NCBs (nerve conduction bundles) in the motor control areas of the cerebral cortex or brainstem
- damage to upper motor neurons leads to excess muscular movement (spasticity)
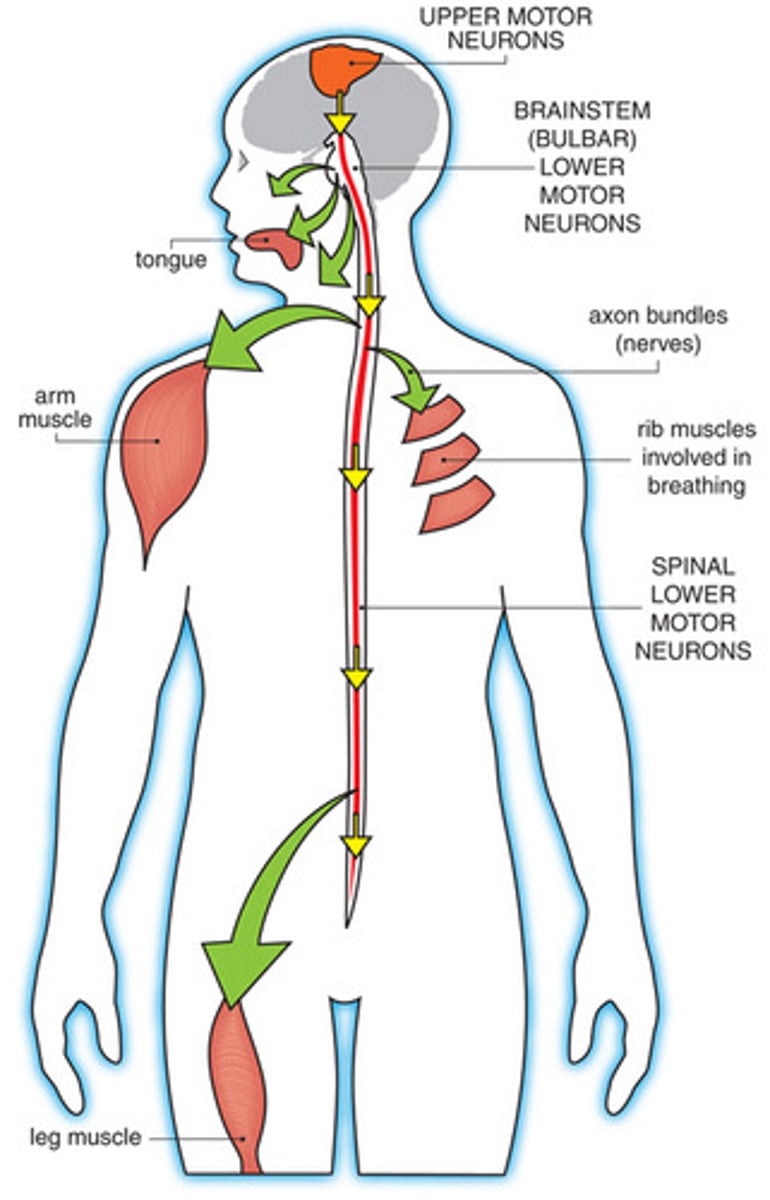
lower motor neurons
neurons that directly innervate skeletal muscles
- somatic - NCBs in the spinal cord + presynaptic nerve terminals on skeletal muscle
> damage leads to muscular weakness and paralysis
- autonomic - NCBs in the spinal column + presynaptic nerve terminals on smooth muscle (vascular, glandular, lining of hollow organs)
- special visceral motor neurons - cranial nerves (facial movement)
motor neuron
location: motor cortex, brain stem, and spinal cord
composed of: long axons and dendrites
functions: project to spinal cord or effector organs (muscles, glands) and movement of muscles
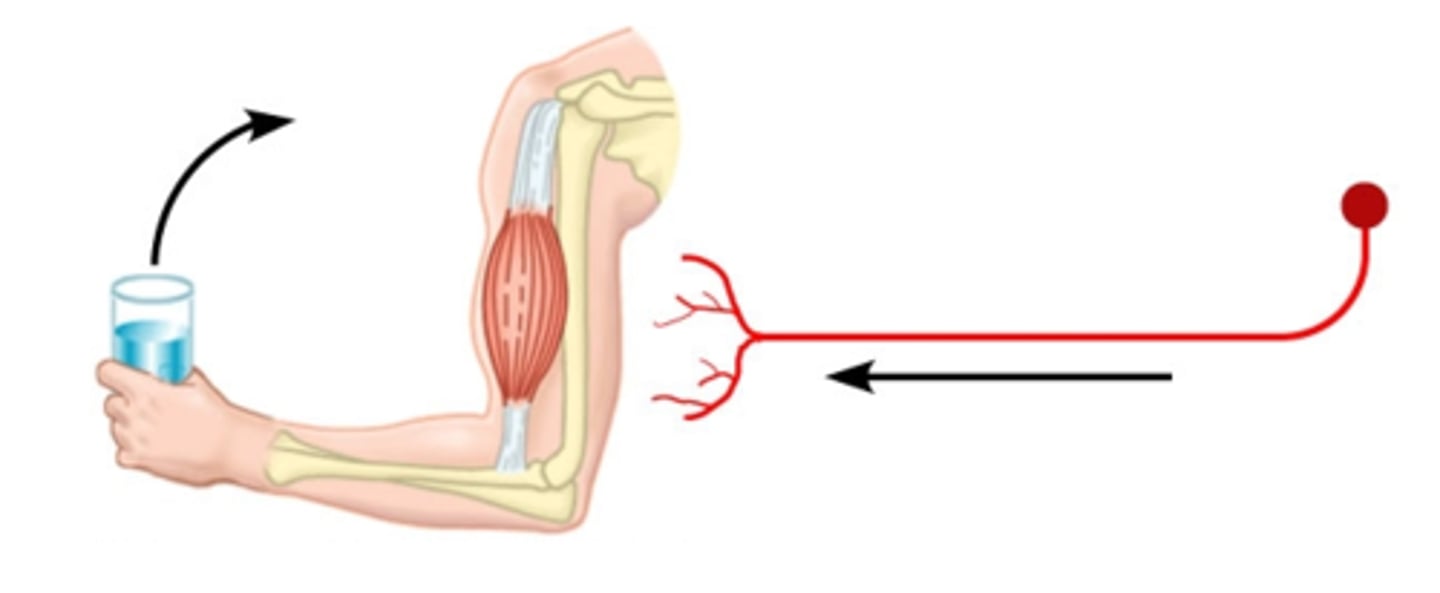
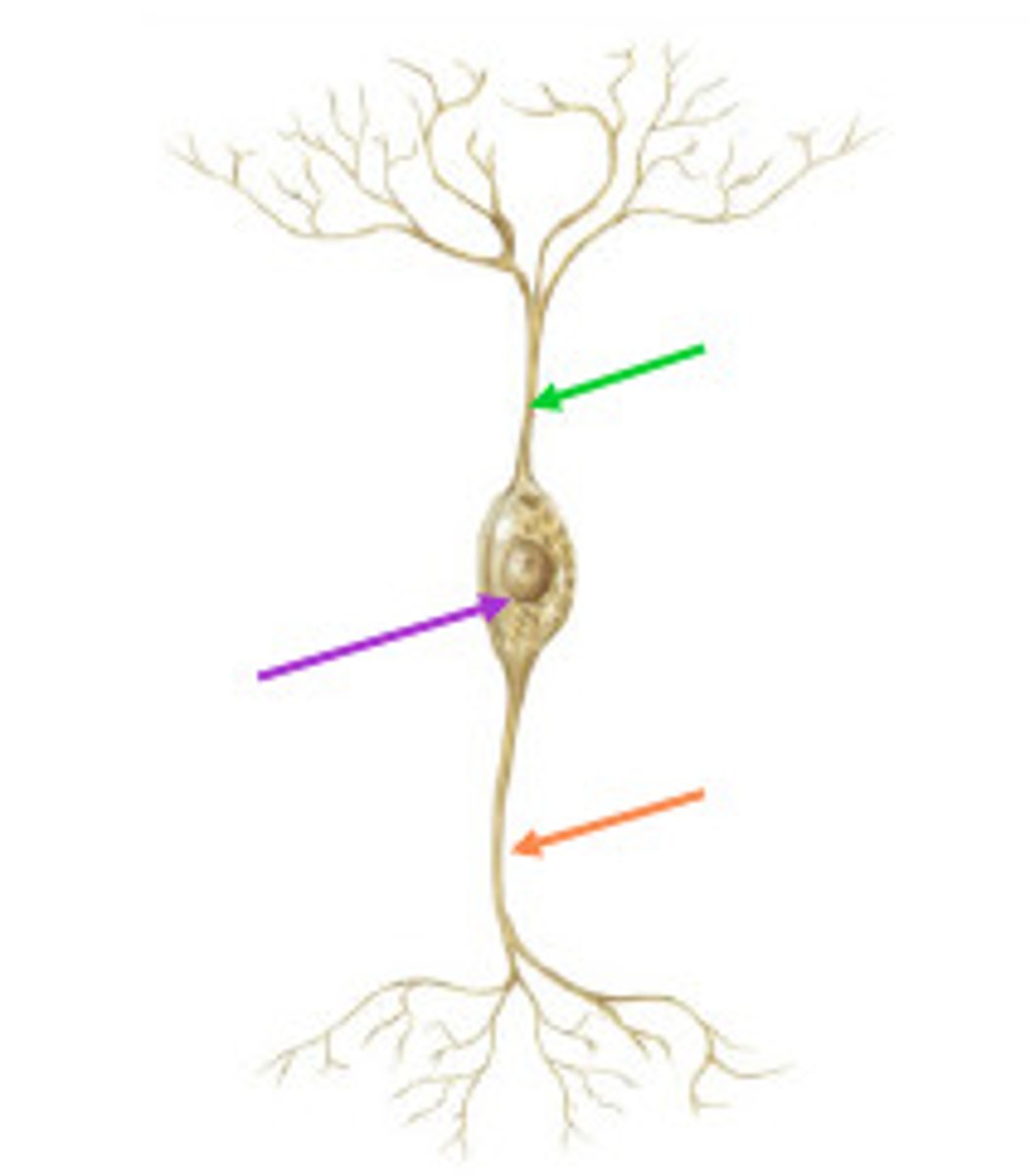
sensory neuron
location: dorsal root ganglia, peripheral axons that extend to receptors in the periphery, central axon projections into the spinal cord
composed of: short axons, receptors, dendrites receiving information straight from the source, cell body is on the side
functions: response to external stimuli (touch, odor, taste, vision) and activate motor neurons
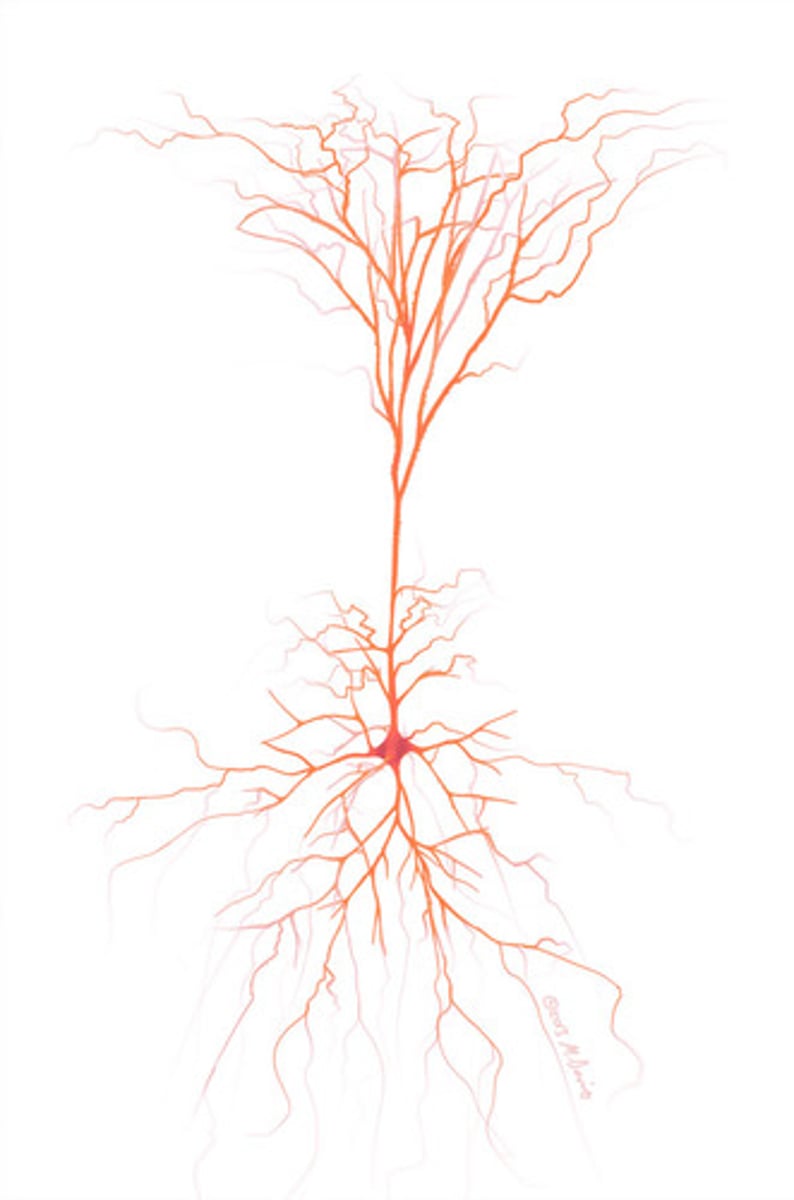
pyramidal neurons
location: hippocampus, cerebral cortex, amygdala
composed of: neuron with apical and basal dendritic branches
functions: synaptic integration and neuroplasticity
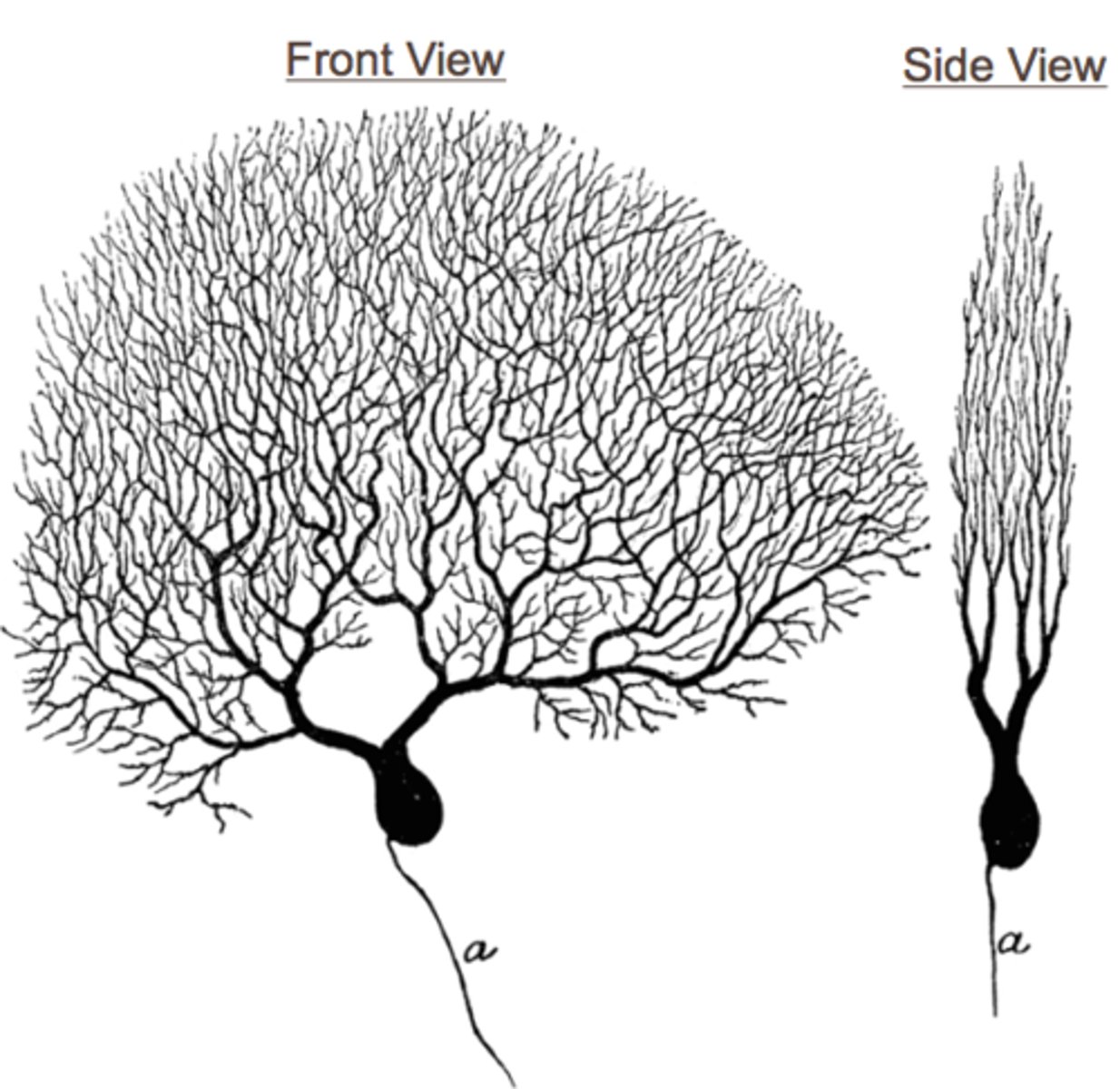
purkinje cells
GABAinergic neurons
location: cerebellum
composed of: neuron with many branching extensions
function: motor movement control
- needs to be very precise = many branches
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
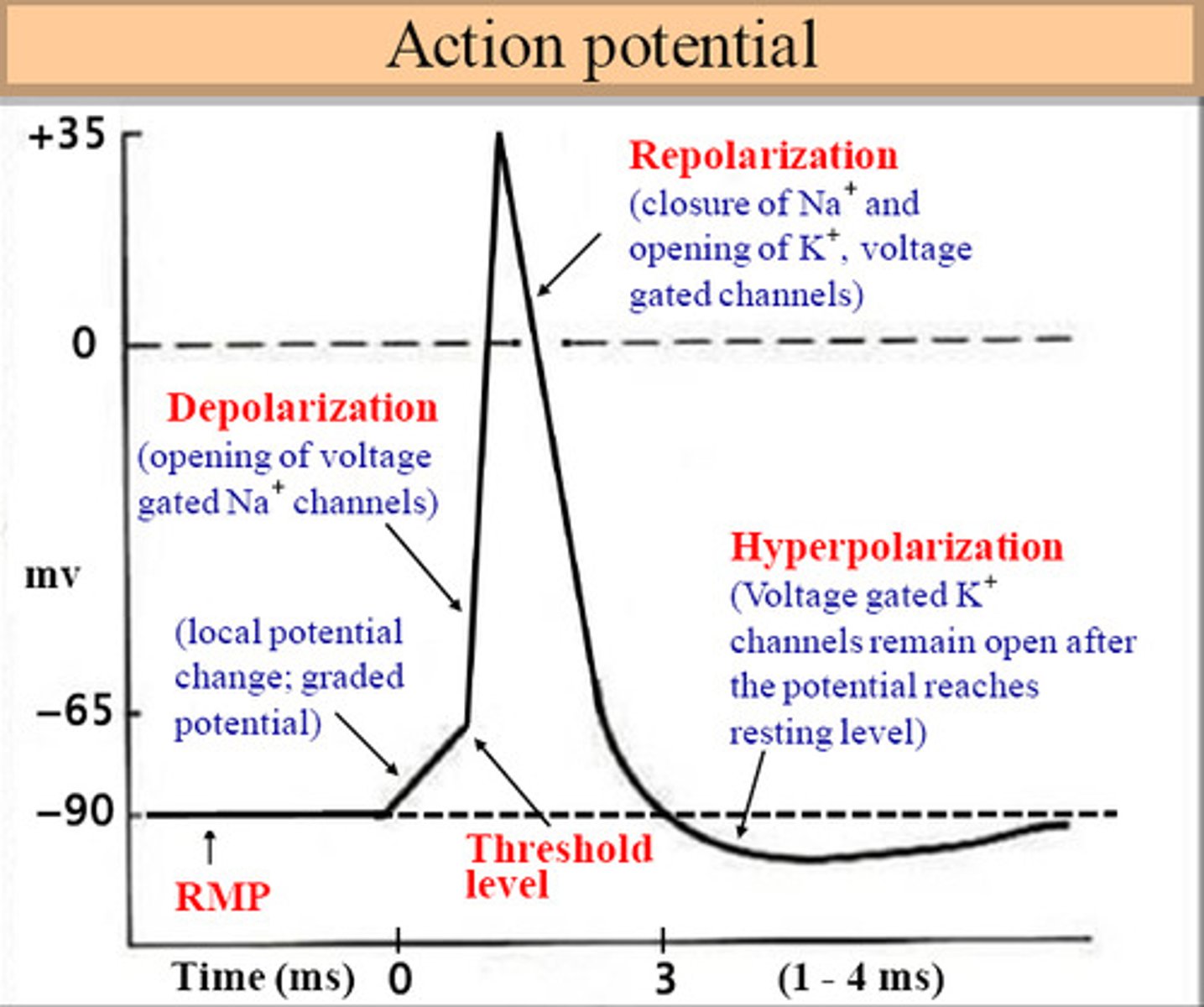
electrical neurotransmission
following sufficient excitatory stimulation of the neuron, an action potential is generated at the origin of the axon
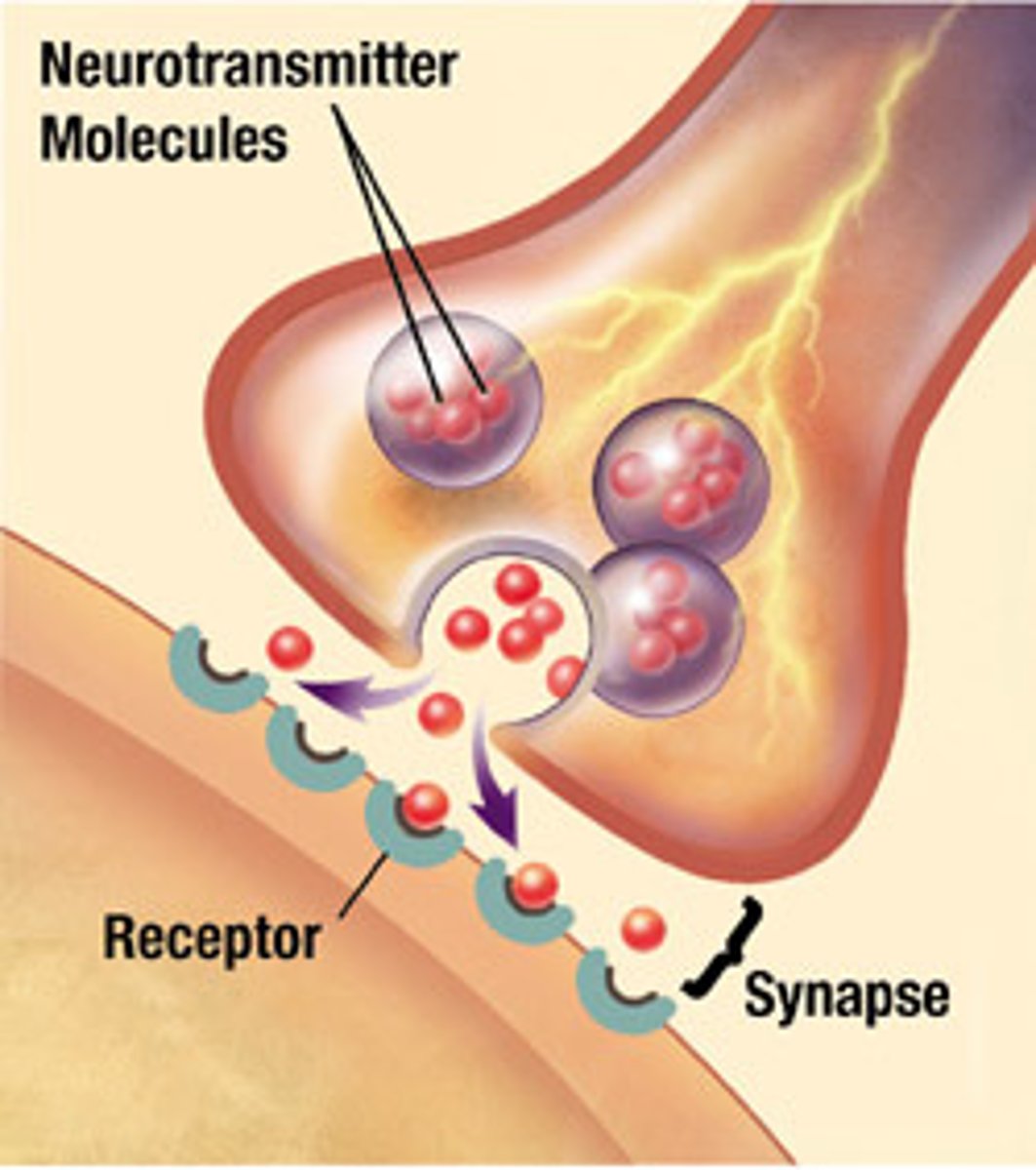
chemical neurotransmission
when the action potential reaches the axon terminal, it stimulates the release of chemical neurotransmitters
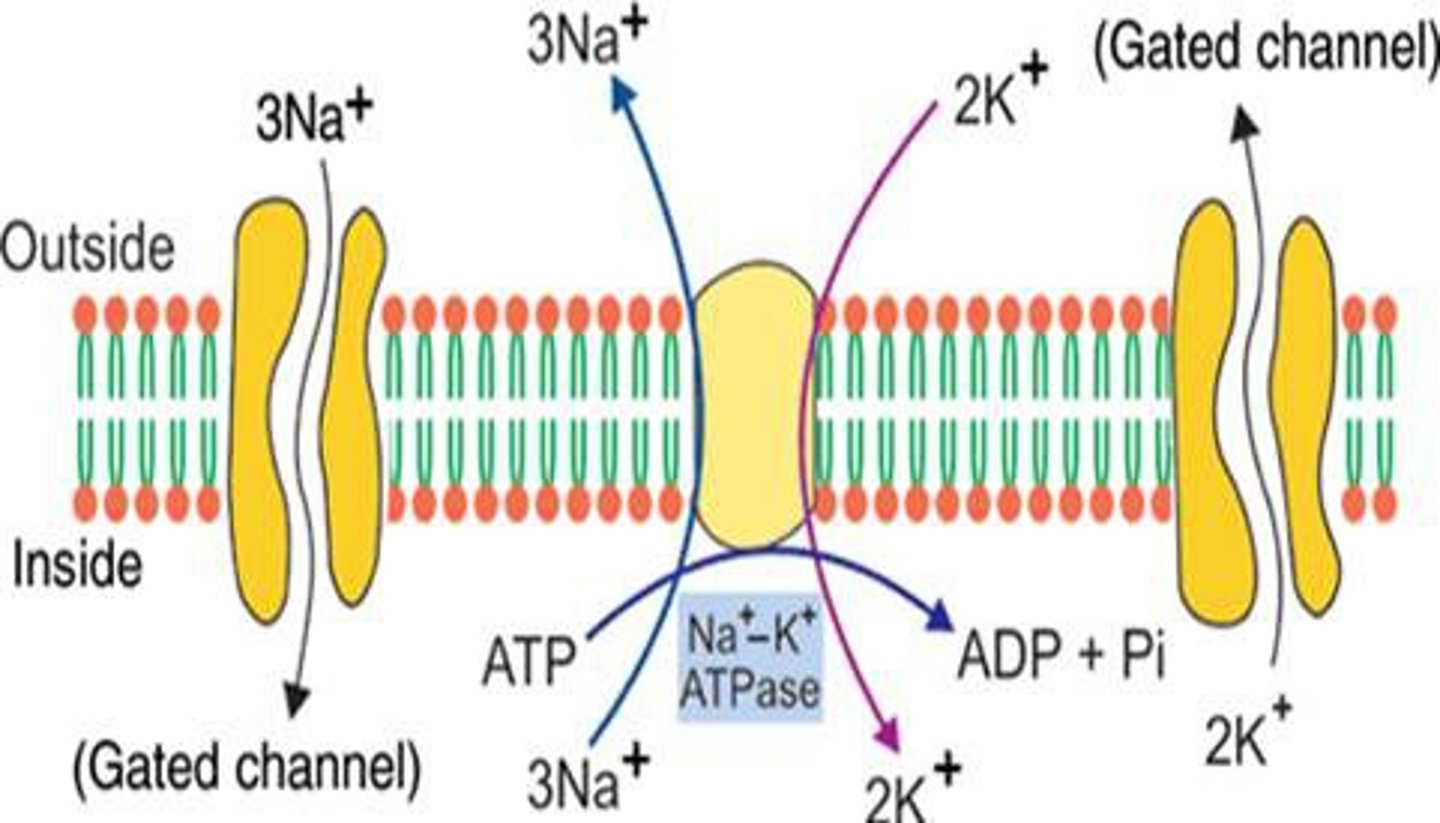
sodium potassium ATPase
powered by ATP
carries 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in
balances passive forces of diffusion
what is calcium's role in neurotransmission?
triggers neurotransmitter release
voltage-gated ion channels
transmembrane proteins important in electrical signaling of cells
- activity is regulated by the membrane potential of a cell
- open channels allow the movement of ions along an electrochemical gradient across cellular membranes
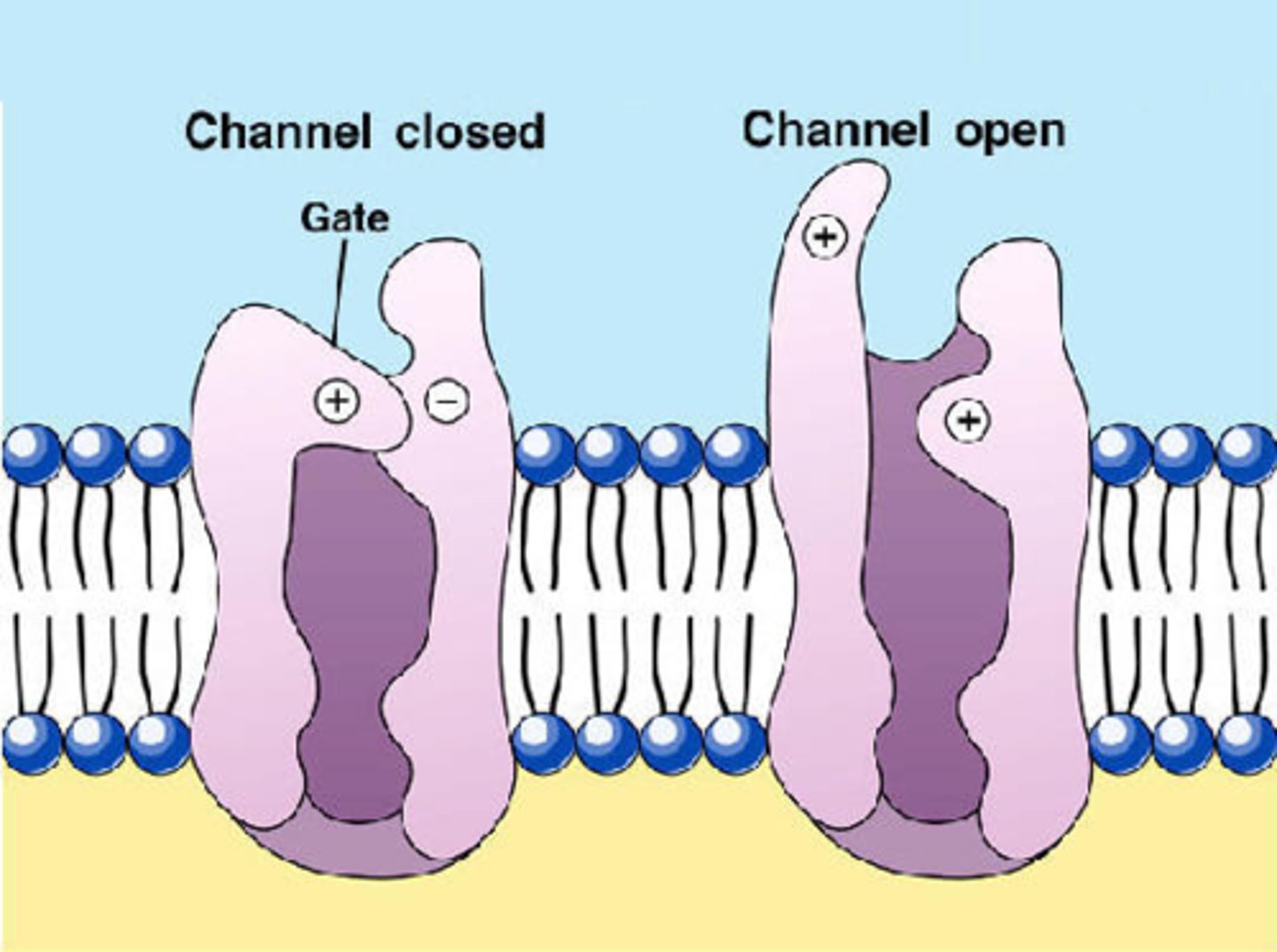
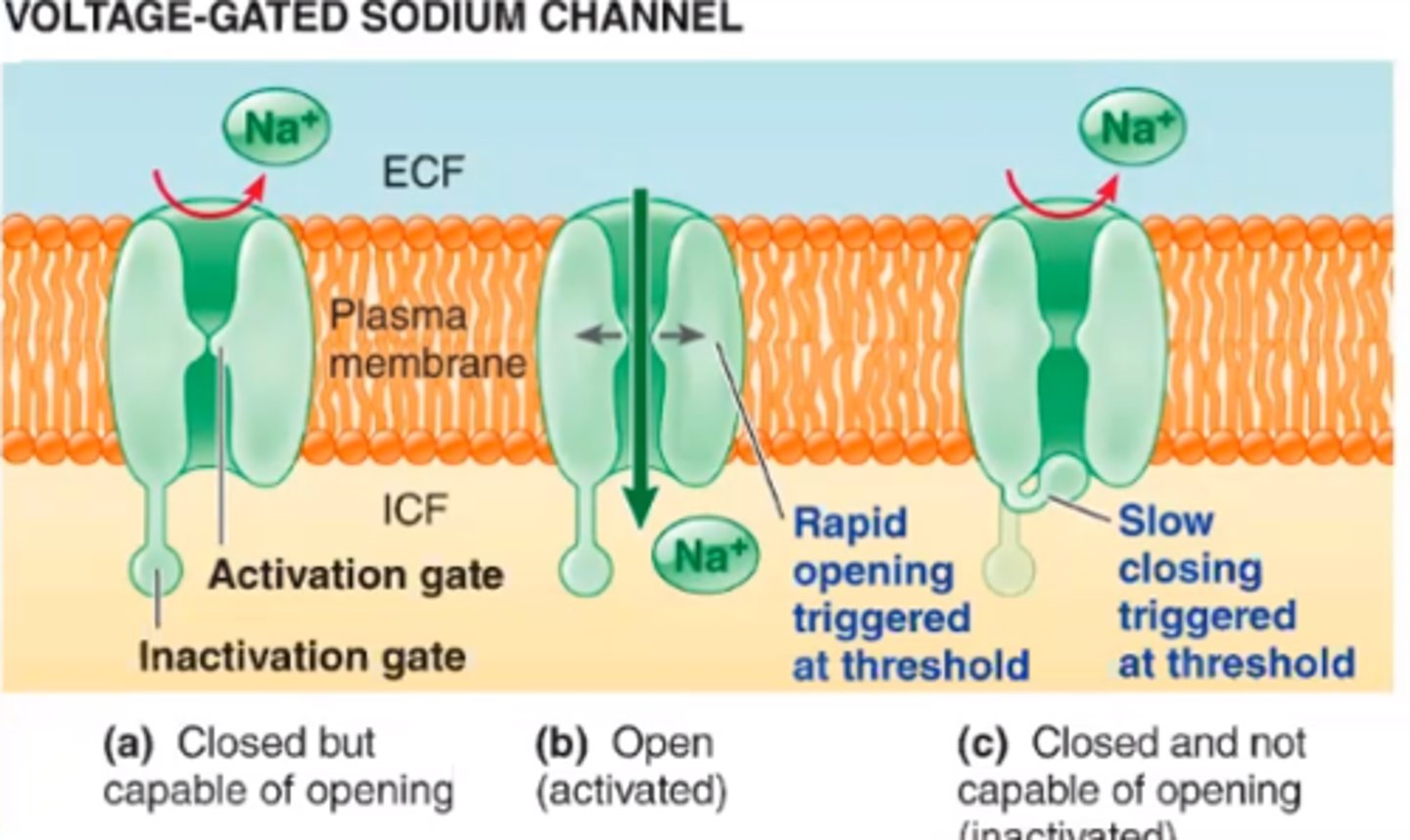
voltage-gated sodium channels
membrane proteins that open sodium channels in response to a sufficient voltage change, and initiate and transmit the action potential as Na+ enters through the channel
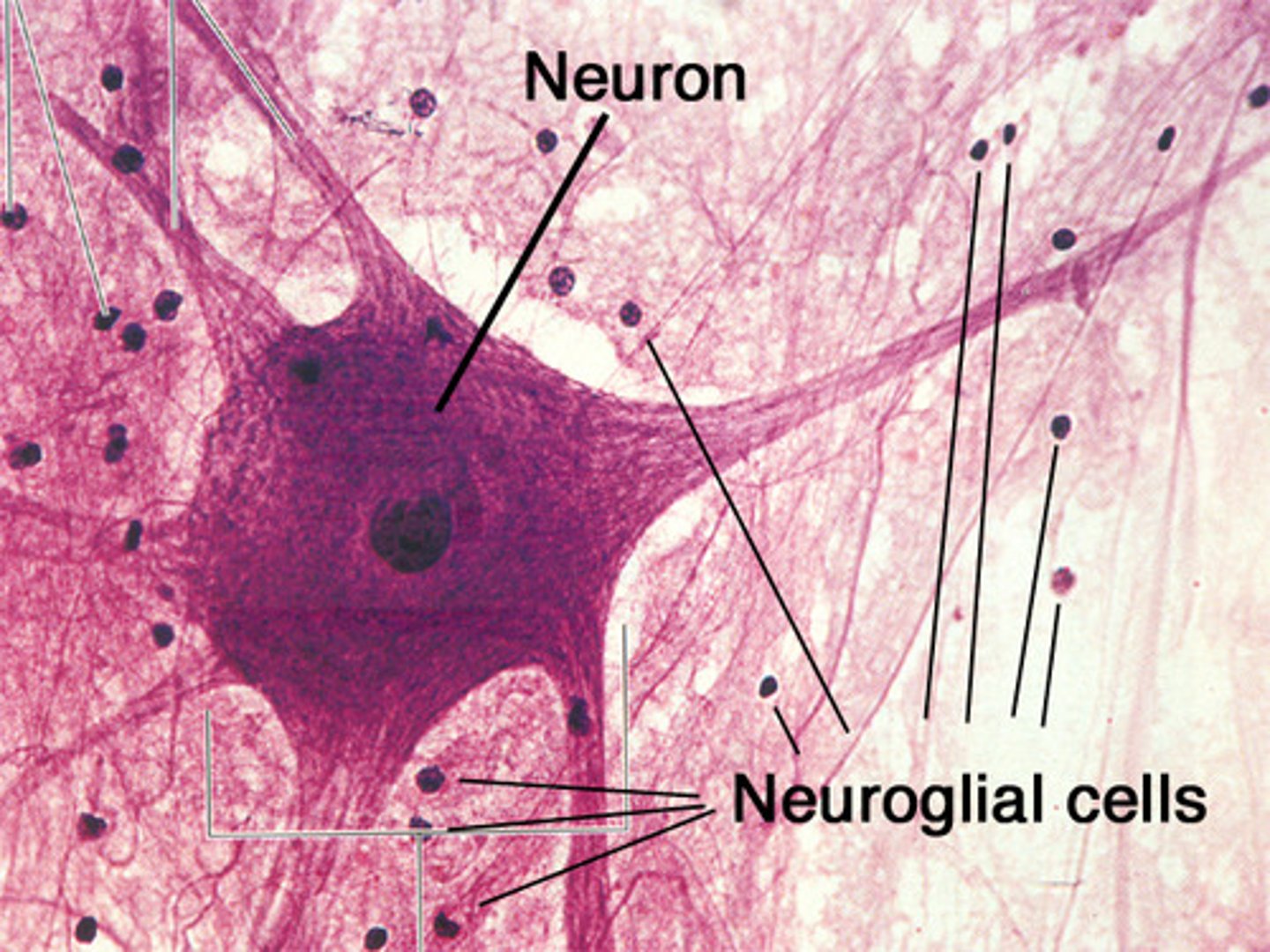
neuroglia
cells that support and protect neurons
can be in the CNS and PNS
CNS:
- ectodermal origin: astrocytes (BBB formation) and oligodendrocytes (myelin sheath)
- mesodermal origin: microglia (neuro-immune)
PNS:
- Schwann cells (myelin sheath)
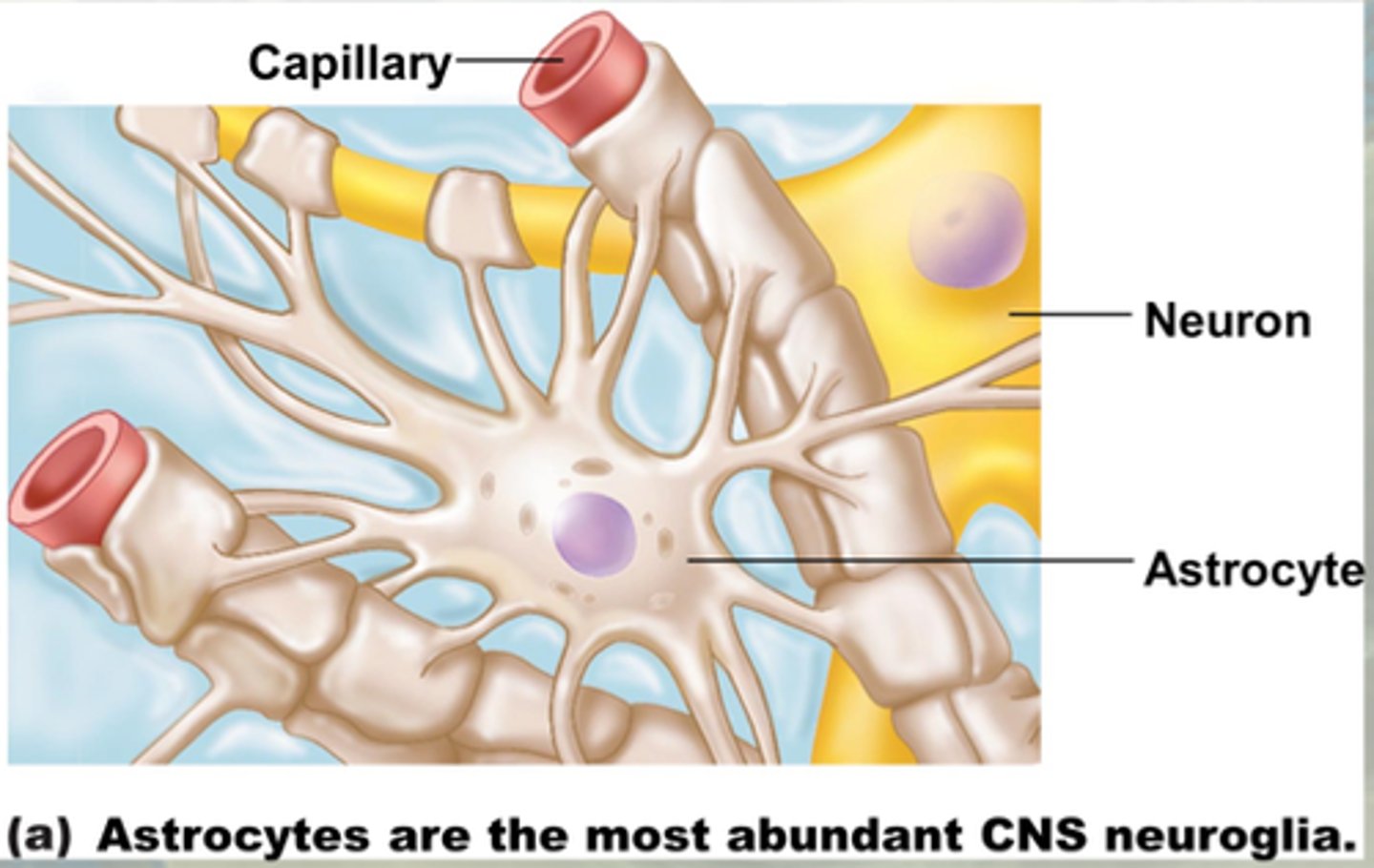
astrocytes
glia cells (CNS)
"star-shaped cells"
location: whole brain
functions: part of the neurovascular unit (BBB), provide nutrients to nervous tissue, maintain ion balance, repair/ scarring process following traumatic injuries, synthesis and degradation of glutamate
microglia
glia cell (CNS)
primary immune cells of the CNS
location: whole brain
functions: overall brain maintenance, scavenge plaques/ damaged cells/ infectious agents
- they become activated when they detect pathogens
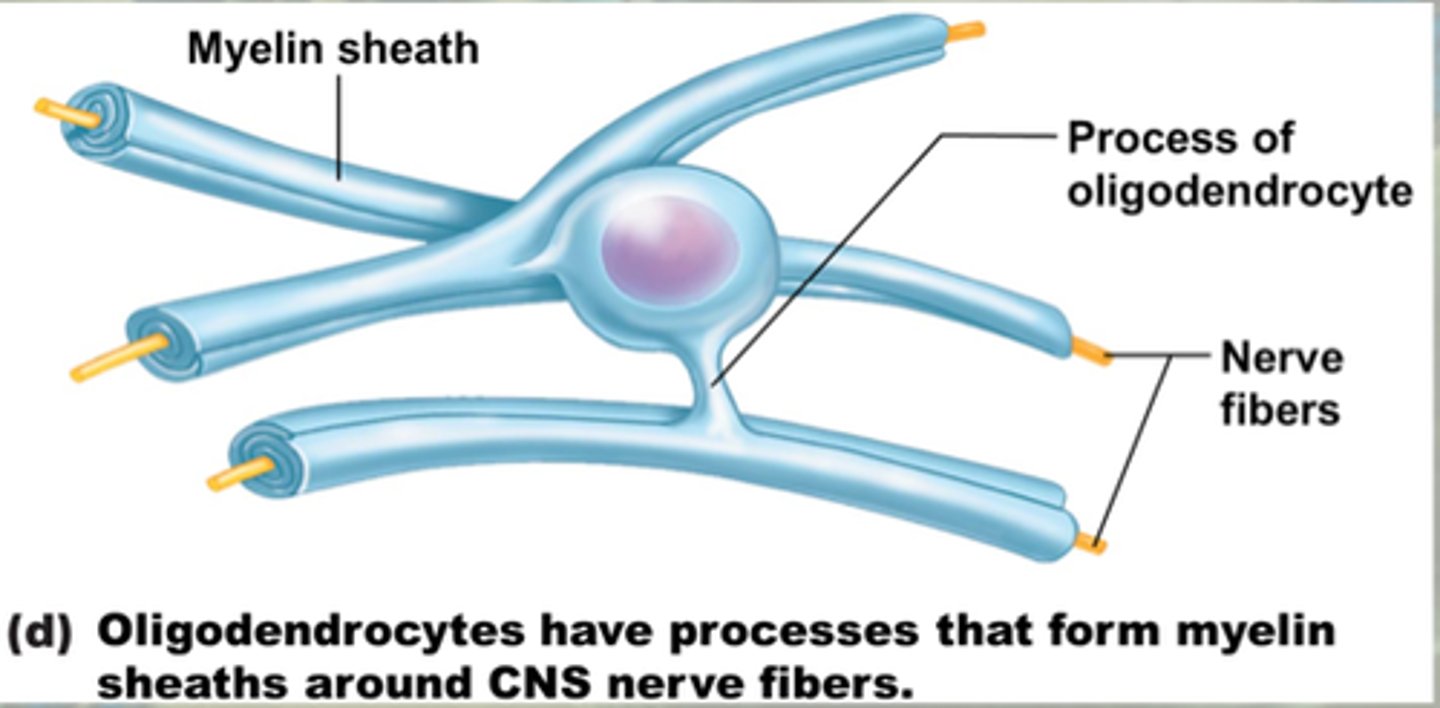
oligodentrocytes
glia cell (CNS)
"cells with a few branches"
location: whole brain
functions: support for axons, create myelin sheath for axons
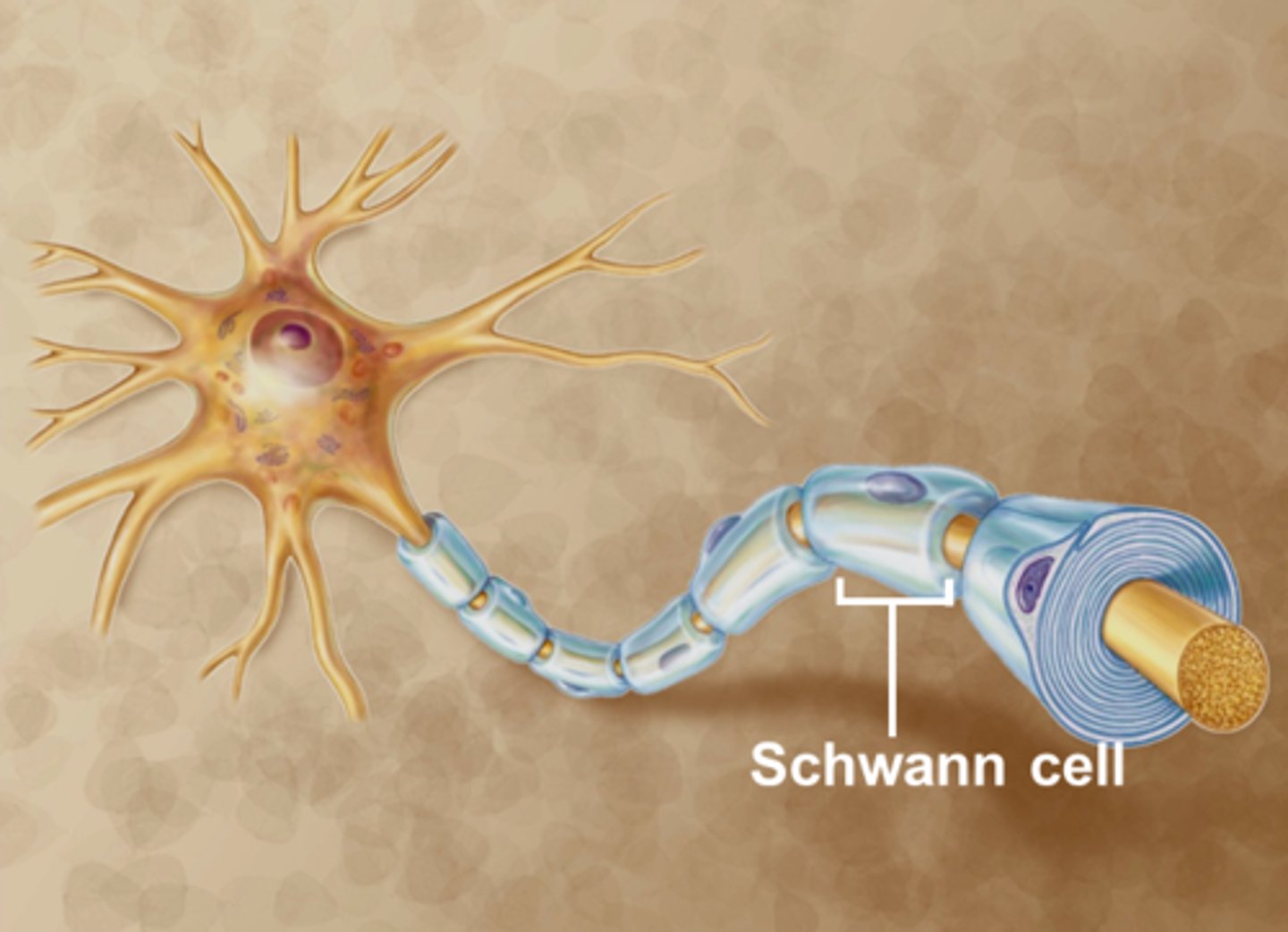
Schwann cells
glia cell (PNS)
functions: create myelin sheath for axons
- can only wrap around ONE axon
mast cells
immune cell (WBC)
"master regulator" of the immune system
location: brain
functions: interact with astrocytes/ microglia/ BBB, neuroinflammation, brain injury, stress
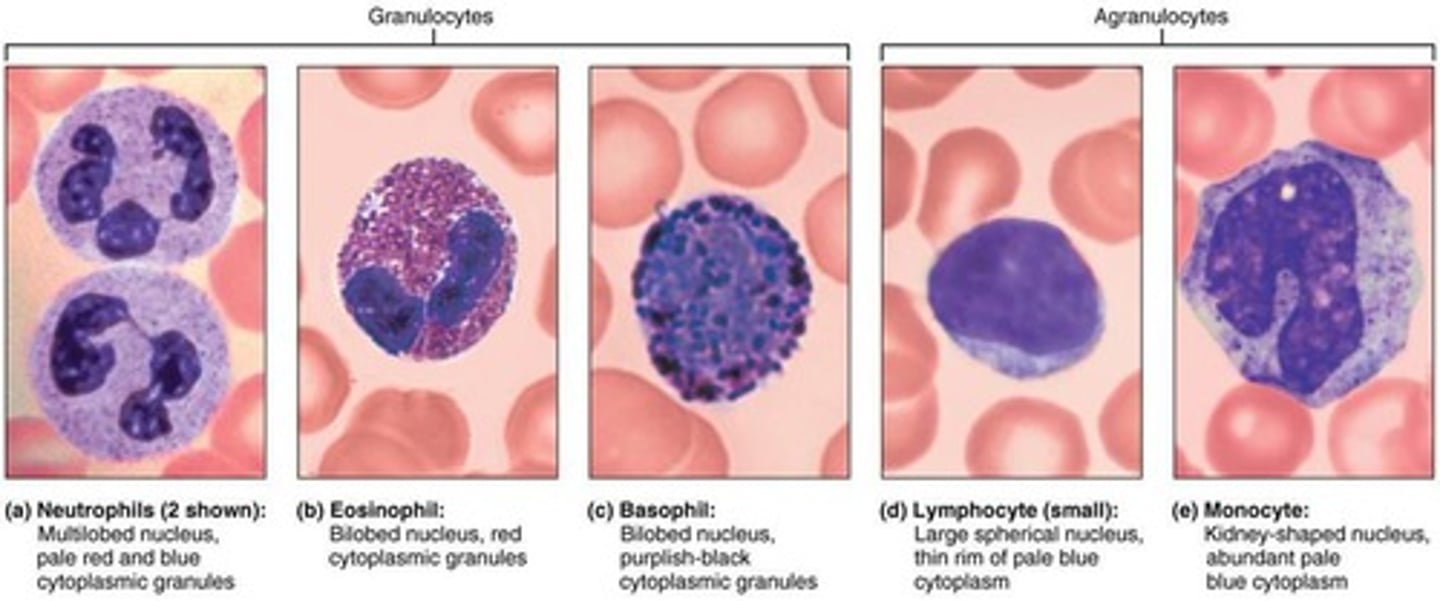
leukocytes
immune cells (WBC)
location: brain
- enter brain through the BBB
functions: immune surveillance of the CNS, neuroinflammation