LEC 2: Reproductive and Sexual Health
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
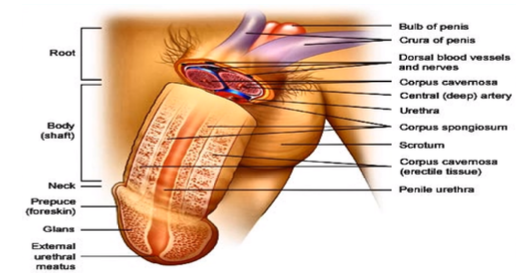
root, body (shaft), glans
What are the parts of the penis?
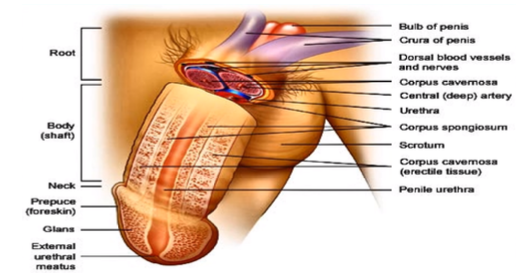
bundle of blood vessels in the nerves to support the penis
What do you see in the root of the penis?
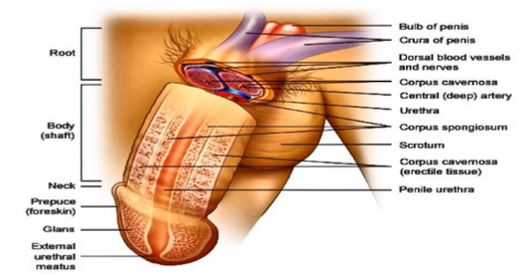
prepuce
What is another name for the “foreskin”?
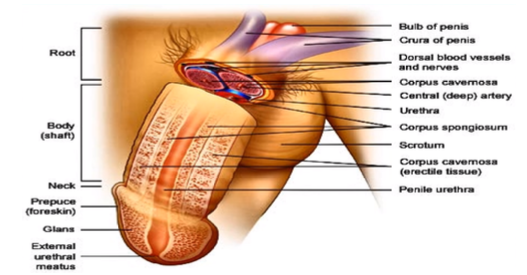
external urethral meatus
What is the opening from the male urethra?
innermost portion of the body body (shaft) where the urine and the semen travels through, coming out of the penis
What is the urethra and what occurs there?
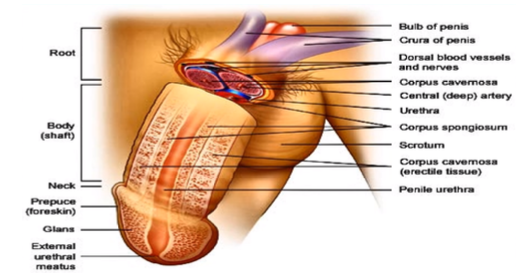
corpus cavernosa, corpus spongiosum
What is the erectile tissue surrounding the penis called? What is it inside of?
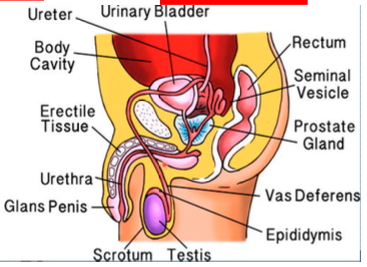
scrotum
What houses the testes?
testosterone (the primary male sex hormone)
What are the testes responsible for?
bringing sperm to maturity
What is the job of the epididymis?
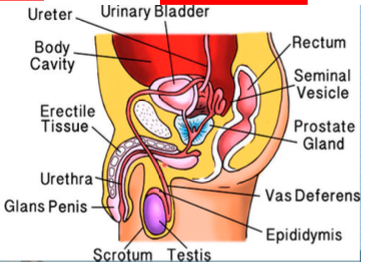
vas deferens, seminal vesicle
from the epididymis, sperm travels up through the ____ and it meets with the fluid produced by the ____
provides sperm the source of energy and houses sperm’s motility or ability to move
What does fructose do for the sperm?
ejaculatory duct, prostate gland
from the seminal vesicle, the fluid fuses within the ____ wherein it combines with the fluid produced by the ____
more basic, the fluid lessens the acidity of the urethra
Is the fluid produced by the Cowper’s Gland or the Bulubourethral Gland more acidic or basic?
12-20 days
How long does it take for the sperm to travel from the testes to epididymis?
65-75 days
How long does it take for the sperm to mature?
endocrine gland
What is the hormonal component that affects the male reproductive system?
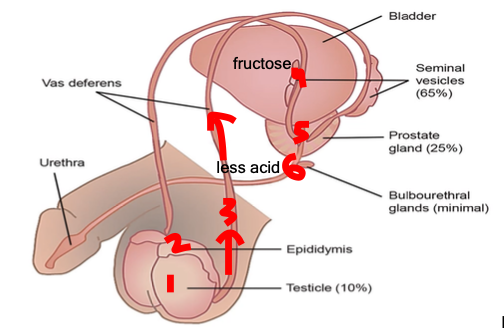
testes, epidydymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, prostate, bulbourethral gland
What is the route of the sperm?
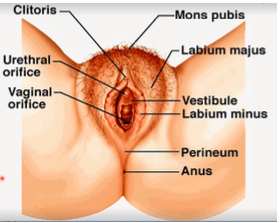
mons pubis
Where does the appearance of secondary female sex characteristics initially occur?
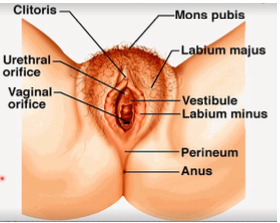
superior portion beneath the mons pubis
Where is the “clitoris” located?
urethral orifice
Where should the Foley catheter be inserted?
posterior structure where labia minora meets. this is important because this tears apart during vaginal delivery or where doctors surgically makes an incision or episiotomy to increase passageway of the fetus
What is the fourchette? Why is it important?
thin piece of mucosal tissue that surrounds or partially covers the external vaginal opening
What is the hymen?
occurs when hymen can’t be perforated; this is the accumulation of blood in the vagina and uterus, especially during menstruation
When does hematocolpoometra occur? What is it?
hymnectomy
What intervention is done when hematocolpometra occurs?
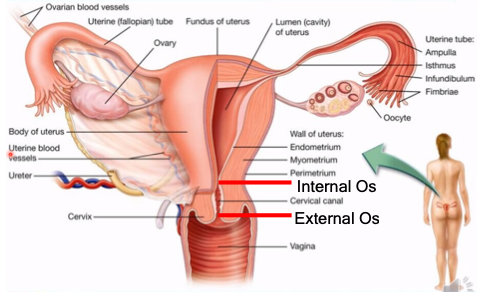
port of entry from the external structures to the internal
What is the vaginal canal?
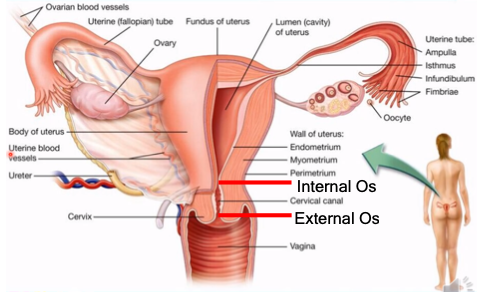
external os, internal os
What is the cervix divided into?
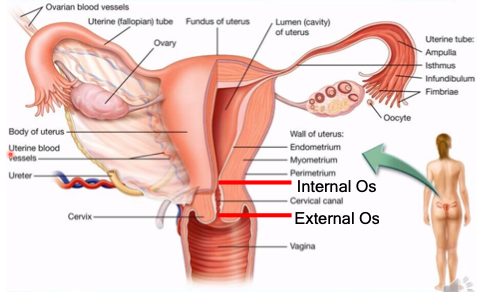
important in keeping pregnancy intact all throughout the 9 months of gestation
Why is the cervix important in pregnancy?
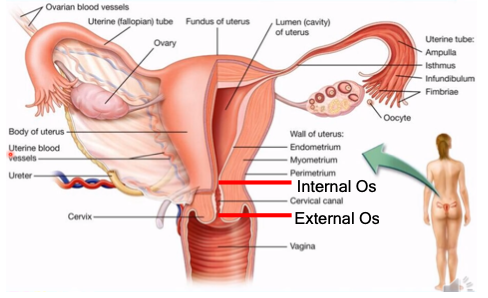
endometrium, myometrium, perimetrium
What are the walls of the uterus?
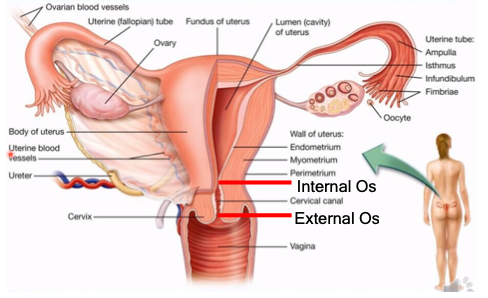
inner lining; sheds off the cervical canal and out of the vagina during menstruation
What is the endometrium?
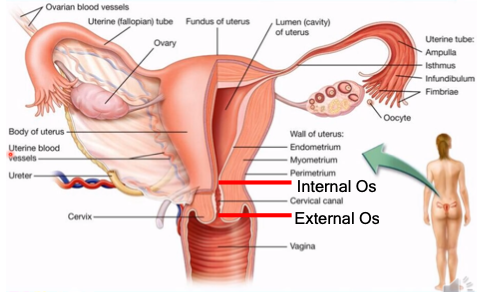
contraction of the uterus during labor and delivery
What is the myometrium?
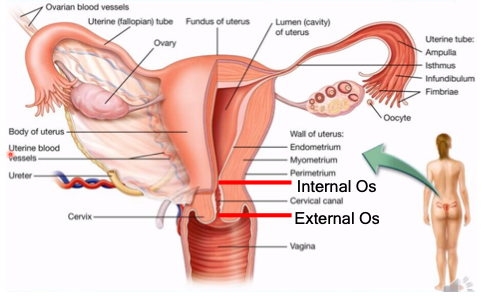
outer layer (body of the uterus)
What is the perimetrium?
landmark that gives the information about fetal growth
What is the importance of the fundus of the uterus relating to pregnancy?
isthmus, ampulla, infundibulum
What are the parts of the fallopian tube?
narrowest part (tubal ligation)
What is the isthmus?
fertilization occurs, sperm and egg meets
What happens at the ampulla?
holds ciliated finger-like projections which capture the ovum from the ovary
What is the purpose of the infundibulum?
fibriae
What is another name for the finger-like projections held by the infundibulum?
oogenesis - production of egg cells
What occurs in the ovary?
(1) round, (2) broad, (3) ovarian, (4) cardinal, (5) uterosacral
What are the different ligaments maintaining the uterus?
remnant of the gubernaculum extending from uterine horns to the labia majora via inguinal canal
What is the “round ligament”?
double layer of peritoneum attaching sides of uterus to pelvis. it acts as a mesentery of the uterus, and contributes in maintaining the position of it
What is the “broad ligament” and what does it do?
holds the ovary
What does the “ovarian ligament” do?
located at the base of broad ligament. it extends from the cervix to the lateral pubic walls, and contains the uterine artery and vein in addition to providing support to the uterus
What is the “cardinal ligament” and what does it do?
extends from cervix to sacrum, and provides support to the uterus
What is the “uterosacral ligament” and what does it do?
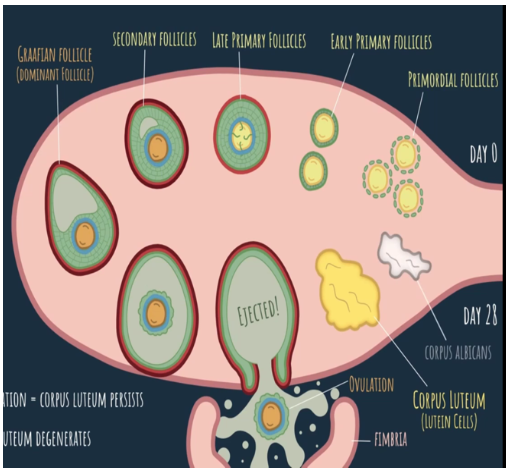
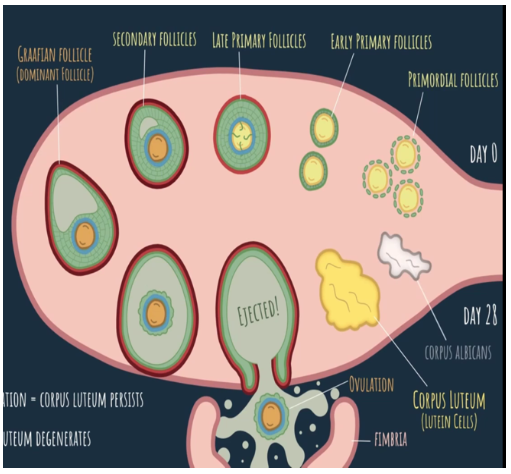
day 0
What is the beginning of the ovarian cycle called?
day 28
When does the ovarian cycle end?
15-20 primordial follicles begin maturation, making their way to ovulation
What happens at the beginning of the ovarian cycle?
when the other follicles degenerate along the way to ovulation, turning them into atretic follicles
What is atresia?
early primary follicles
What is the term for the primordial follicles that survived the first step of the ovarian cycle?
squamous, cuboidal
Early primary follicles change from ____ cells to ____ cells
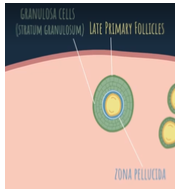
granulosa cells (entire structure of cells is called stratum granulosum)
What is formed when the follicular cells proliferate and form a row of cells?
glycoproteins; zona pellucida (transparent zone) which plays an important role in fertilization
What do the granulosa calls and oocyte begin to secrete? What does it form?
this makes it difficult for the oocyte to receive its nutrients
What is the significance of the Zona Pellucida separating the oocyte from its surrounding granulosa cells?
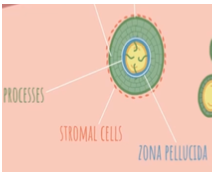
granulosa cells send “finger-like” processes through the zona pellucida to reach the oocyte and feed it
How is the oocyte “fed”?
Stromal Cells: these cells are part of the connective tissue of the ovary
What are the changes in the cell surrounding the follicle called?
Theca Folliceculi (these features characterize the late primary follicle)
What is the layer formed when stromal cells begin to organize themselves around the follicle called?
proliferate, enlarge
as the ovarian cycle continues, the granulosa cells also continue to ____ and ____ the follicle
Antrum
What is the vesicle in which granulosa cells begin to secrete fluids into called?
Theca Interna - highly vascularized to supply follicles with nutrients, secretes hormones vs Theca Externa - contracts (important in ovulation)
What are the 2 layers of the Theca Folliculi and how can they be differentiated?
oocyte completes meiosis I, enters meiosis II, and is arrested at metaphase II; secondary oocyte
What happens at the end of the secondary follicular stage? What is the oocyte known as at the end of these changes?
almost all
The secondary oocyte gets ____ ____ the cytoplasm
has nothing, tiny, no function, and will degenerate & disappear
What is the significance of the polar body as it relates to the secondary oocyte?
the granulosum cells continue to secrete fluid causing the antrum to grow
What is the significance of an enlarged antrum?
the follicle after meiosis I and before ovulation
What is the graafian/dominant follicle?
the structure of cells that surrounds the floating oocyte
What is the corona radiata?
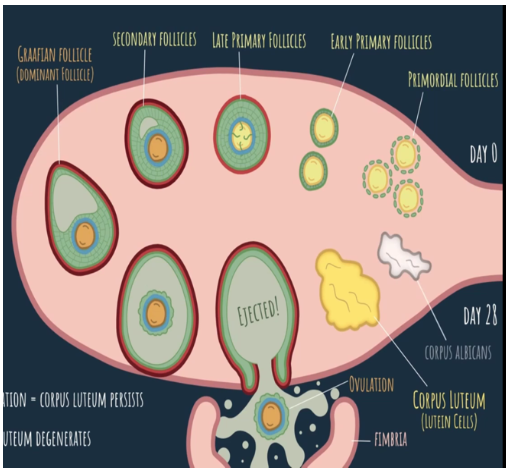
tentacle-like that helps the oocyte out of the ovary
What is the fimbria?
14
Ovulation occurs at ____ days in a 28 day cycle.
persists, growing bigger to support the embryo
Fertilization and Implantation = Corpus Luteum ____
degenerates, becoming a structure called corpus albicans
No Fertilization = Corpus Luteum ____
corpus luteum or yellow body
What structure do lutein cells form?
maintenance of the growing emrbyo and the uterus
What is the significance of the corpeus luteum?
the process of formation of female gametes; begins inside the fetus before birth
What is oogenesis and when does it occur?