19 Low unemployment
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is unemployment
Unemployment: “people of working age who are without work, available for work, and actively seeking employment
Unemployment rate
(Number of unemployed // Total labour force) x 100
who is not counted in labour force
people outside of working age, children and retired
students attending school
parents at home who are looking after children
choose not to/can’t work
Difficulties in measuring unemployment
inaccuracies
incentive to register as unemployed depends on unemployment benefits
alternatives in how countries measure unemployment
those registered as unemployed
those receiving unemployment benefits
“Hidden unemployment“ - different groups of people
unemployed for long, given up search
people who have part-time work, or temporary contracts
people working jobs they are over qualified for
Typical disparities amongst groups of people
geographical location: varies across regions
Age disparities: higher unemployment rate for those under 25 generally
ethnic differences: minorities often suffer more
gender disparities: women generally
Unemployment effect on people themselves
receive less income, assuming they get benefits
lower living standard
costs worsen the longer the unemployment
cause mental health problems
Cost of unemployment on society
areas of increased unemployment
poverty, homelessness, increase criminal activity, increased gang activities
Cost of unemployment on economy
if actual output less than potential due to unemployment, economy producing under ppc
gov erans less in tax - spend more on solving social problems
What is the flow concept
relationship between becoming unemployed while others gain employment
Labour market diagrams
y-axis, price of labour, average real wage rate
average level of wages adjusted for inflation
x-axis, quantity/number of worker
AD for labour
labour for whole economy
demand for labour at every wage
Types of unemployment
cyclical (demand-deficient)
structural
frictional
seasonal
Cyclical unemployment
Cyclical downturns in economy
slower growth, AD decreases as consumers spend less
fall in spending, less demand for labour
What is wage stickiness
less likely that wages fall
firms realise if they lower wage, less motivation
Can’t - labour contracts and trade union power
AS for labour greater than AD
Cure cyclical - fiscal/monetary
Since AD is low, G intervenes
Fiscal - AD increase, increase G spending/lower tax rates
Monetary - lower interest rates or increase money supply
What casues for structural unemployment generally and the two types
changing structure of economy, two forms
permanent fall in D for a particular type of labour
change in institutional framework
Permanent fall in D for particular labour type
natural in growing economy, new types of jobs, others dissapear
long term unemployment - those who lose job do not have the skills for the new job
lack occupational mobility
What is occupational mobility
ability to change jobs
Causes of structural unemployment - type 1, change in d for labour
technological changes
Globalisation made possible for companies. Set up in cheaper countries
Change in consumer taste, decreases demand for particular labour
people increasingly concerned about effects of coal for example. Less coal miners needed
Change in institutional framework
laws governing labour market
law which states firms may not fire without lengthy documentation of malpractice
prevent firms from hiring workers, costs of dismissing not worth it
min wage legislation
increase COP
creates price floor graph
laws governing trade union
union contribute to unemployment
Interventionist policies for structural unemployment
long term- education system that trains more occupationally flexible. People in more developed economies change jobs
improve occupational mobility - spend on adult upskilling or retraining
subsidies to firms who provide training
job in other parts of countries, provide subsidies or tax breaks to encourage people to move
gov support apprenticeship programmes
job centres providing info about job vacancies, training opportunities and interview-training
Disadvantages in intervensionist policies for structural
involves increased opportunity costs, forego spending on other areas
only effective in long run
Market based policies for structural and their problem
lower unemployment benefits. encourage unemployed to take available jobs
PROBLEM: people who lose benefits have lower living standard, increase inequity
Felt that gov intervention, reduces “labour market flexibility” and discourages firms from hiring
argue un favour of deregulation of labour market
PROBLEM: worsen working conditions
Frictional unemployment
short term unemployment when people are between jobs or left education and are waiting for job
how to reduce frictional unemployment
decrease unemployment benefits
improve flow of information from employers to people searching for jobs
Seasonal unemployment
workers who are employed on a seasonal basis
reduce seasonal unemployment
encourage peopel to take other jobs in off season
Natural rate of unemployment
encourage people to look for jobs off season
Natural rate of unemployment
some types of unemployment occur even when labour market is in eq.
What is the same when the labour market is at equilibrium
number of job vacancies is same as n of people looking for work
what is natural unemployment greater than
greater than eq. level of unemployment, which is known as equilibrium level of output
what does natural rate of unemployment consist of
structural, frictional, seasonal
natural rate = Structural + frictional + seasonal
What do demand side policies do in unemployment
manipulate interest rates, narrow business cycle fluctuations and reduce output gaps
What do supply side policies do in unemployment
ensure labour suitably skilled and flexible to adapt to changing economic conditions. LRAS shifts right
What is crowding out
when government runs a budget deficit to stimulate economy and decrease unemployment, potential problem - crowding out
What must gov do to run budget deficit and what do they aim to do
must borrow money
sell bonds to financial institutions who sell them on
increases demand for saving
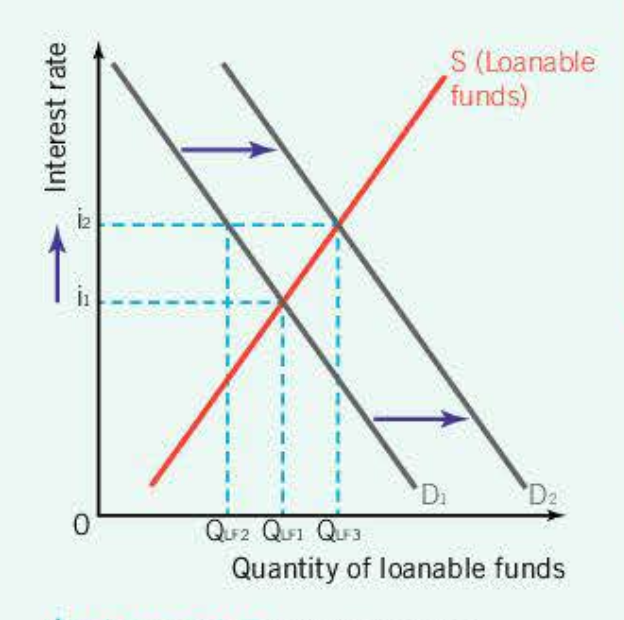
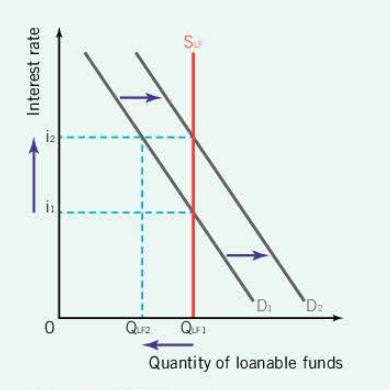
How does crowding out look on a diagram and the effects it has
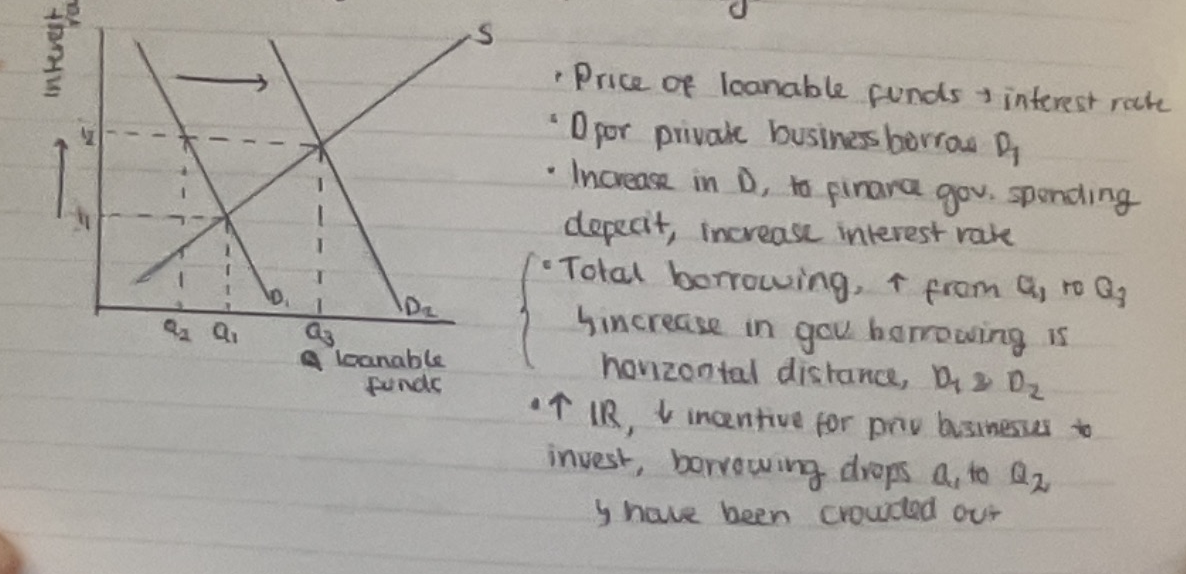
Effect of crowding out on investment
By G spending increasing, AD increases- higher interest rates cause interest sensitive private investments to fall. Final Ad depends on size of spending
Keynesian VS New classical - crowding out
keynesian: will not occur if economy producing at less than full employment
new classical: opposed. to demand side policies. argue crowding out is a problem
extreme: Supply loanable funds is fixes. Increase in gov spending, leads to increase IR, but none in total borrowing