CHEM 40A Review
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
alkanes vs alkenes vs alkynes
hydrocarbons with only
a- single bonds
e- double bonds
y- triple bonds
straight chain alkanes (names)
methane CH4
ethane CH3CH3
butane
propane
pentane
hexane
heptane
octane
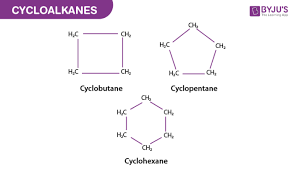
cycloalkanes
alkanes with ring structures (ie cyclohexane)
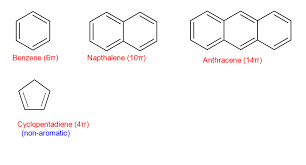
arenes (aka aromatic groups)
cyclic alkanes with alternating single and double bonds
(ie cyclohexane with alternating single and double bonds)
follows the 4n + 2pi rule & is conjugated
alcohol
OH group
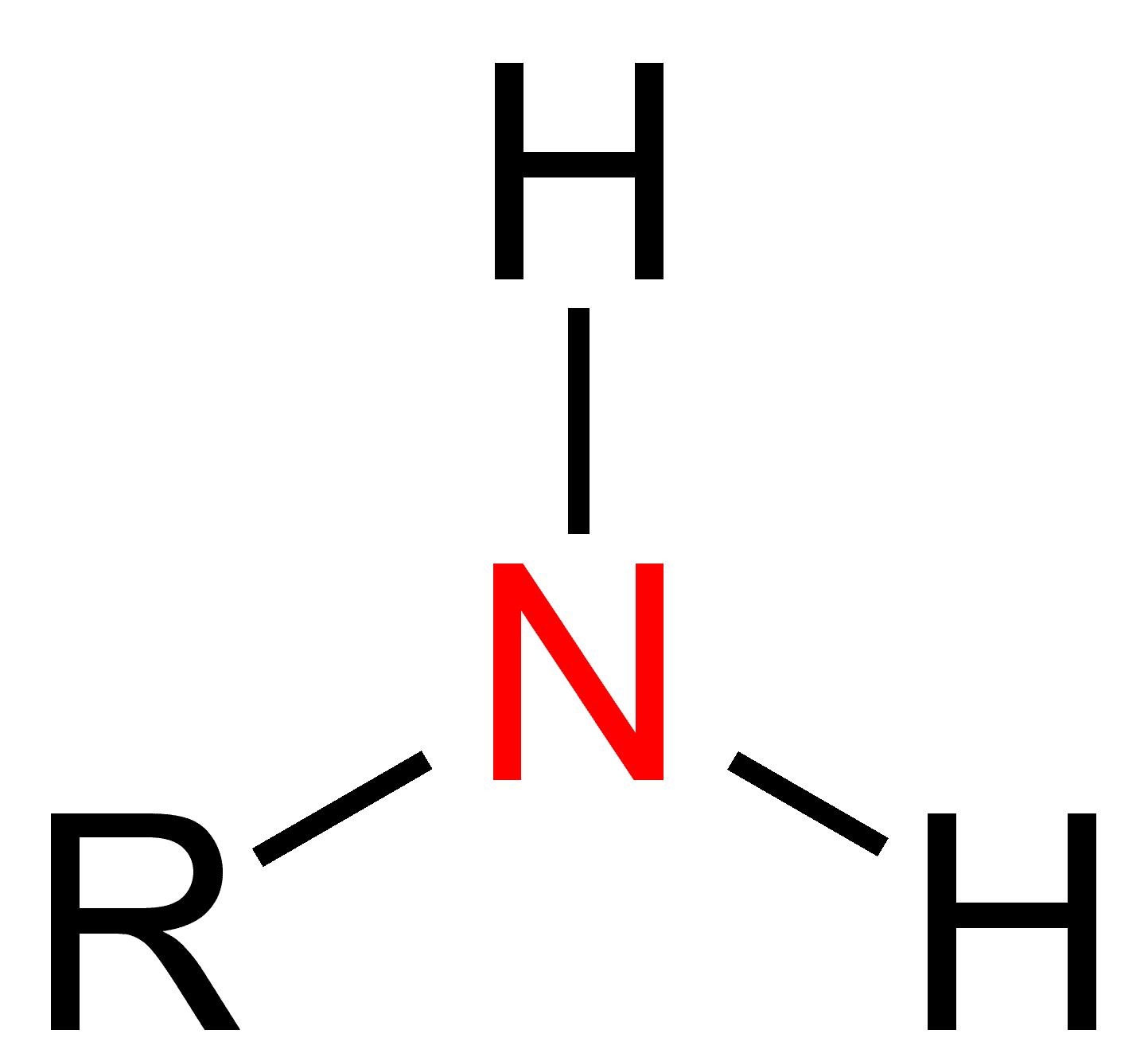
amines
NH2
ammonium compounds
NH4+
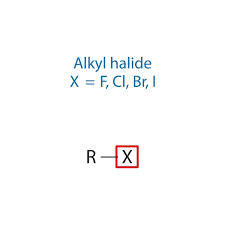
alkyl halides
alkane in which one of its H has been replaced by a halogen
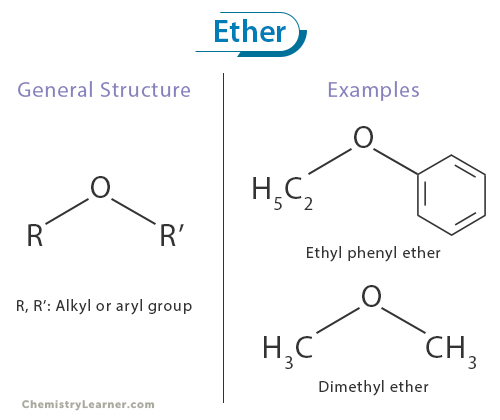
ethers
O attached to two C chains
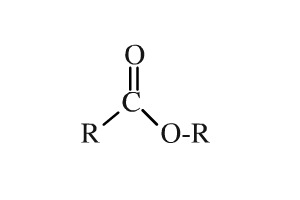
esters
C double bonded with an O and single bonded with another O that is attached to an alkyl group
RCOOR
ketone
C double bonded to O and also 2 single bonds to 2 C’s
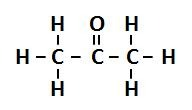
aldehyde
C double bonded to O and single bonded to H
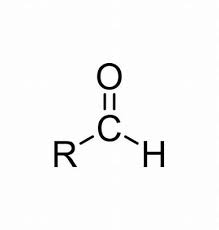
carboxylic acid
C double bonded to O and single bonded to OH
COOH
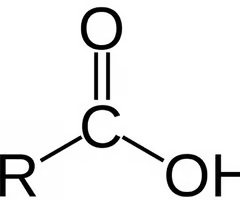
amides
C doubled bonded to O and single bonded to amine group (NH2)
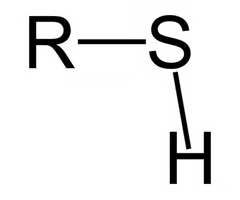
thiols
SH
(like alcohols but with S instead of O)
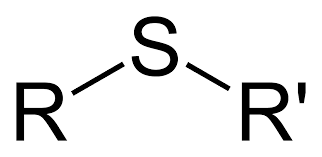
sulfides
S
disulfide
SS
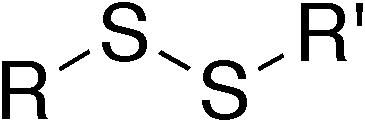
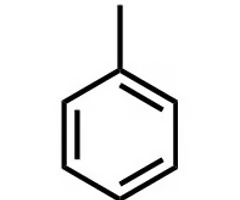
phenyl
has benzene as a substituent
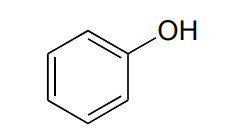
phenol
hydroxyl group directly attached to aromatic group
imine (aka Schiff base)
C doubled bonded to N
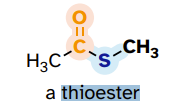
thioester
like an ester but single bonded to S (instead of O) that is attached to an alkyl group
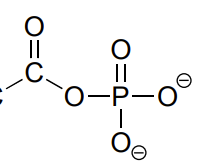
acyl phosphate
C double bonded to O and single bonded to an O that is part of a phosphate group
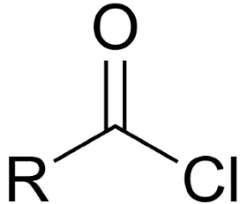
acid chloride
C double bonded to O and single bonded to Cl
phosphate ester
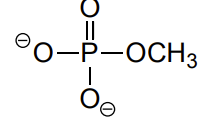
phosphate diester
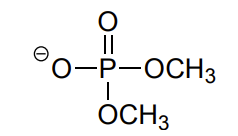
constitutional isomers def
same MF but different connectivity of atoms
naming: halides
-o
naming: OH
hydroxy-
naming: ketone
no e & -one
naming: aldehyde
-al
naming: carboxylic acids
-oic acid
naming: deprotonated carboxylic acid
-oate
naming: amide
-amide
how to identify
lipids
carbohydrates
amino acids
nucleic acids
lipids (long hydrocarbon chains with phosphate group)
carbs (C with H2O)
amino acids (H, NH3, COOH group with side chain)
nucleic acids (rings/bases with lines b/w connecting them)
sigma bonds have AOs overlapping - the internuclear axis
pi bonds have AOs overlapping - the internuclear axis
sigma (along)
pi (outside)
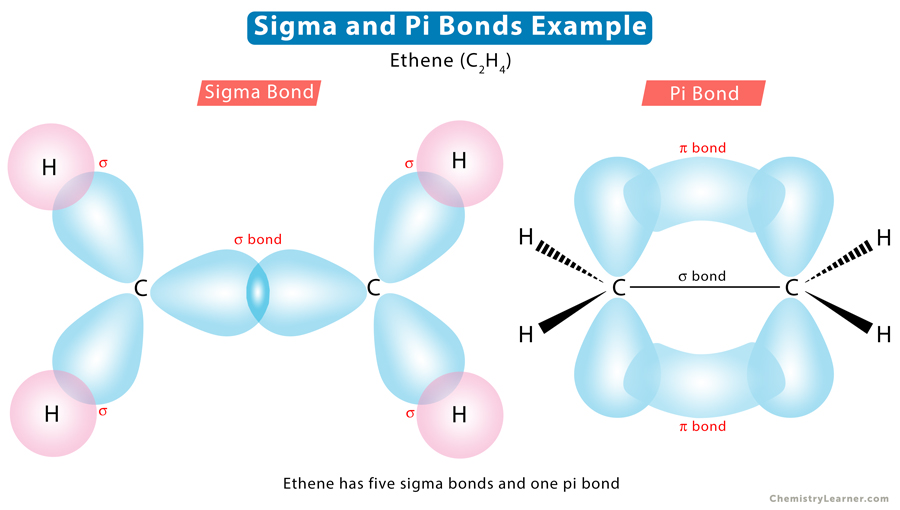
why are pi bonds weaker than sigma bonds
areas of overlap in pi bonds are not as extensive
they have less overlap between atoms (b/c is outside internuclear axis)
how to determine which is major or minor resonance contributor in non-equivalent resonance structures?
minor: not full octet
if both have full octet, then look at which atom has the negative FC, whichever atom is more electronegative is the major resonance contributor (other is minor)
solubility in water
has OH group
more soluble = less carbons
nonpolar is poorly soluble
higher boiling point = to
larger compounds
IMF and dipole-dipole interactions strengths
torsional strain def & steric strain
torsional - e- repulsion between bonds on adjacent atoms (close)
steric - close and between large groups
staggered anti vs gauche
anti- largest group on front and back C’s that are 180 degrees apart
gauche - largest groups on front and back C’s are 60 degrees apart and are adjacent
alkyl groups list
me - methyl CH3
Et - ethyl CH2CH3
pr - propyl CH2CH2CH3
Bu - butyl CH2CH2CH2CH3
iPr - isopropyl CH(CH3)2
t-Bu - tert-butyl C(CH3)3
rotational isomers def
interchangeable when rotate around single bonds
stereoisomers def
can only interconvert by breaking covalent bonds
more stable when larger/bulkier group is -
equatorial
what 2 conf. have steric hindrance
eclipsed when two large are adjacent
staggered gauche