Codes and Specs. Conceptual
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Three Materials in Slabs
Cement, Aggregates, Rebar
2 Examples of Ductile Material
Gold and Copper
2 examples of Brittle Material
Bismuth and Quartz
Name 3 Important Physical Properties of Materials
Density, Void Content, and Porosity
What is the Equation for Strain?
E= Change in Length/ Original Length
Define Poisson’s Ratio (word definition)
Poisson’s Ration is the ratio of lateral strain to the axial strain
Define Poisson’s Ratio (equation)
V= -Etrans / Elong
What is the Equation for Surface Moisture?
SM= Moisture Content - Absorption Content
What is Gap-Graded Aggregate?
A mix of aggregate where one or more intermediate sizes are missing
How does Fineness Modulus Work When Finding the Average Size of a Sample?
If given FM=#, we then move # from the smallest sieve tested up (We include the first sieve in the count and the last we count is the answer).
What is the Maximum Size of Fine Aggregate?
4.75 mm
What is the Equation for Moisture Content?
MC = (OG W- OD W) / (OD W)
What is the Maximum Size of an Aggregate That Will Be Used in a 5in Retaining Wall?
For Retaining Wall, Max Size is 1/5in of narrowest part. So for 5 in it will be 1 in.
What is the Nominal Aggregate Size?
It is the smallest sieve size that 95% of the sample passes through.
What is a Full vs Half size sieve?
A Full size sieve is half the size of the sieve before it whereas a Half size sieve does not follow this pattern.
How to Calculate FM given % Coarser?
FM = (Sum of % Coarser)/100
Sieve Analysis: Percent Coarser
% Coarser = Sum of larger samples retained including the current sample retained.
Sieve Analysis: Percent Finer
% Finer is all of the percent of the sample that passed the current sieve size (do NOT include current size retained).
Why add Gypsum to Cement?
It acts as a retardant, preventing flash setting.
What are The Four Major Compounds of Cement?
Tricalcium Silicate
Dicalcium Silicate
Tricalcium Aluminate
Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite
Which of The Four Major Compounds is Most Reactive To Cement?
Tricalcium Aluminate
What type of Cement Gives High Early Strength?
Type III
Define Consistency (cement)
Consistency is a property used in ASTM C187 to establish the setting properties of cement. It is also a measure of wetness and fluidity.
Define Workability (cement)
Workability is the ease of how a mixture can be handled from mixer to the fixed structure.
What is slump and how is it measured?
Slump is a result of a slump test that can be used to measure characteristics of workability. You fill and pack a mold, remove the mold, and measure the change in height due to the material “slumping”.
What is Air-Entrainment?
This is when a measured amount of air is added into a cement mix, usually 3-8%, to allow air pores to form. This results in a mixture resistant to freeze/thaw damage.
What is Freeze/Thaw Resistance?
This is a material’s characteristic to resist water entering voids and causing damage due to freezing/thawing cycles. It can be increased by air entrainment.
What is the average weight of a sack of cement in the US?
I sack = 94 lbs
If the W/C ratio = .55, with 270 lbs of water, how much cement is needed?
W/C = 270 lbs/ X lbs = .55
X lbs = 490.9 lbs
What is the primary reason to provide reinforcement in concrete?
Concrete has great compressive strength but has awful tensile strength. Therefore, reinforcing materials are added to improve the tensile capability of the concrete.
What is the bulk density of cement?
B = 1440 kg/m³ (from google)
Name two common chemical admixtures.
Calcium Chloride (accelerant)
Calcium Nitrite (accelerant)
What advantages come from adding fly ash to concrete?
Fly ash improves placement, workability, and pumping of concrete.
Give two reasons for adding superplasticizers to concrete?
They increase the slump/workability of concrete.
They reduce the W/C ratio, needing less water, while preserving high strength.
What are 3 considerations in mix design?
Workability, Strength/Durability, and Economics
Draw a typical graph of Compressive Strength VS W/C Ratio
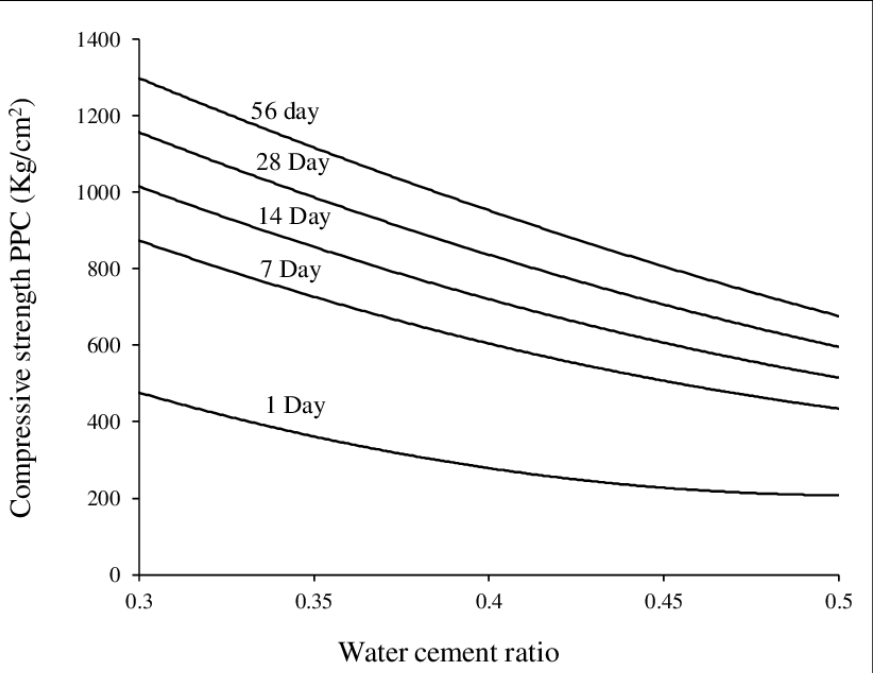
Do and example of cement ratio and weight calculations.
In the mix procedure, which property controls the w/c ratio?
The main property that controls w/c ratio is needed compressive strength.
What property controls the amount of cement?
The W/C ratio
Define Curing
Curing is any procedure that maintains proper moisture and temperature to insure continuous hydration for proper strength development.
What is the tensile strength of concrete of a compressive strength of 4,000 psi?
ft = 6.7(fc)^1/2 , ft = 423.7 psi
Calculate Modulus Elasticity given compressive strength?
example on hw 2
Calculate 28 day strength from 7 day strength
example on HW 2
Calculate expected average strength given specified strength.
example HW 2
Show position of reinforcement in a concrete cantilever beam.
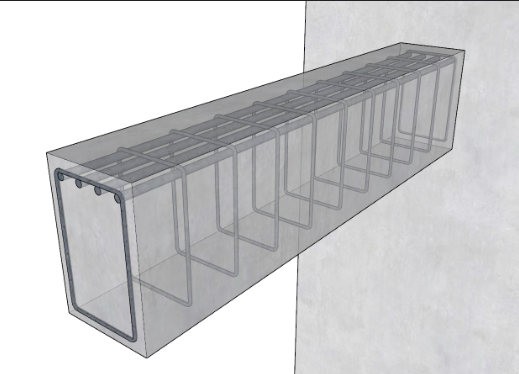
What are the two most important pieces of information inscribed on the surface of a reinforcing steel bar?
Steel Type and Bar Size
What is the purpose of adding fibers to concrete?
Fibers are added to reduce early age shrinkage cracks.
Describe the effects of creep and shrinkage.
Creep causes the concrete to deform over a period of time due to a constant load. Shrinkage causes the concrete to crack and may cause differential volume throughout project.
Go through all 10 Steps of calculating Concrete Mix
What are the three commercial forms of iron products?
Wrought Iron, Steel, Cast Iron
Explain the differences between wrought iron and cast iron.
Wrought iron has the least amount of iron whereas cast iron has the highest amount. Wrought iron is the only iron containing slag in its final form.
Explain the effect of carbon on steel and ductility of steel.
As carbon content increases within steel, its hardness, strength, and abrasion resistance also increases. But, ductility, toughness, and impact resistance all decrease with increase in carbon.
Define Yield Point
Yield point is the first stress at which an increase in strain occurs without an increase in stress.
Define Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is the maximum stress that a material can bear before breaking.
Define Modulus of Elasticity
Modulus of Elasticity is the ration of stress to strain below the proportional limit.
What is the yield stress of grade 50 steel? (Can use tables)
Sigma y = 50 ksi
What are the advantages of using high strength steel?
Designs tend to be more economical and will lead to lighter sections.
What are the three forms of reinforcing steel?
Plain Bars, Deformed Bars, Plain and Deformed Wire Fabric
What is the cross-sectional area of a No. # bar?
Diameter = #/8 in, so the area without the ribs uses this. For nominal area, tables give values.
Aggregate Definition
Granular material when bounded together into a conglomerate mass by cement forms concrete or mortar or alone as a base course.
Define the material property, Hardness
Hardness is the resistance to penetration
Fine Aggregate Diameters Range (#<x<#)
75 microns < x < 4.75 mm
Coarse Aggregate Diameter Range ( # < x < #)
4.75 mm < X
Example of a Fine Aggregate
Sand
Example of Coarse Aggregate
Gravel
Define the material property, Durable
Ability to withstand deterioration from weathering elements ( mainly water and other chemicals)
Define the material property, Porosity
Relates the number of pores to the total volume of rock
Define the material property, Absorption
Ability to retain water
Define the material property, Density
Relates mass to volume
Define the material property, Specific Gravity
Relates density of material to density of water
Absorbed Moisture
Moisture within pores
Surface Moisture
Moisture on the surface
Define Saturated Surface Dry (SSD)
When the pores are filled with water and the surface is dry.
What is Void Content?
It is the volume of voids out of the total volume of a sample.
What happens to the elastic modulus of concrete as the elastic modulus of aggregate increases?
E of concrete also increases.
Define Strength
Maximum compressive and tensile strength
Define the characteristic, Freeze Thaw
Resist cyclic freezing and melting
Define the characteristic, Abrasion Resistance
Resist wear and won’t erode
Define Well Graded Aggregates
Contains high, intermediate, and smaller sizes of aggregate.
Define Poorly Graded Aggregates
Consists of only one size of aggregate.
Define Maximum Aggregate Size (sieve analysis)
Smallest opening size through which the entire sample passes
What is the max aggregate size for non-reinforced plain concrete?
1/5 in of the narrowest dimension.
What is the max aggregate size for reinforced concrete?
¾ X the clearance distance between bars
Define Fineness Modulus
Average size of the aggregate in the sample.
Why do we use concrete?
Resistant to water and chemicals, easy to form, economical, less energy input, waste can be used as aggregates and fillers, sustainable
What are some uses of concrete?
Foundations, Pavements, Walkways, Storage Tanks, Dams, etc.
What is the three requirements for good concrete?
Quality
Workability
Economical
What makes concrete quality?
Strength, Durability, and Dimensional Stability
What is included in the workability of good concrete?
Transportation, plasticity, mobility, and slump
What can make good concrete economical?
Reduce cement and admixture, workable and quality at low cost, local materials, and low energy demand
Define Cement
A material that binds/unites like glue concrete, mortar, and grout
What can be a drawback of Portland Cement use?
High CO2 emissions resulting in green house gases
What are the characteristics of the compound Tri-Calcium Silicate when used in Portland Cement?
Early strength, early heat of hydration, and rapid hydration
What are the characteristics of the compound Di-Calcium Silicate when used in Portland Cement?
Hardens slowly, responsible for strength increase at later stages, and gives off the least heat during hydration
What are the characteristics of the compound Tri-Calcium Aluminate when used in Portland Cement?
Rapid hydration, gives off most heat during hydration, can not be used if hydration is not controlled
What are the characteristics of the compound Tetra-Calcium Aluminoferrite when used in Portland Cement?
lowers heat required during manufacturing, reduces needed amount of tri-calcium aluminate
What is the order of hydration speed for the Portland Cement Compounds (slowest to fastest)?
Di-calcium Silicate (Slowest)
Tri-calcium Silicate
Tetra-calcium Aluminoferrite
Tri-calcium Aluminate (Fastest)
What is Hydration?
Hydration is when water mixes with cement, causing hydrates of compounds to from giving hardness and strength to the mix
What compounds does the strength from hydration depend on?
Tri-calcium Silicate and Di-calcium Silicate