FMLec | M1: Introduction to Food Microbiology
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Study of microorganisms associated with food
Food microbiology
Divisions of the microbial world and how these are associated with Food Microbiology
Acellular
Virus: contaminated food or water can cause gastroenteritis
Subviral agents
Viroids: infect plants only; small, circular ssRNA
Plant pathogens, e.g., tomato
Prions: misfolded proteins that induce protein misfolding; infect only mammals
Mad cow disease (from animal meat)
Cellular
Prokaryotes
Archaea: hyperhalophiles, e.g., Halobacterium
Bacteria: Salmonella (Salmonellosis); Lactic acid bacteria
Eukaryotes
Fungi: Yeast, Molds, Mushrooms
Algae: Nori
Protists: Water molds (Oomycetes; plant pathogens), Red tide
2 subviral agents
Viroids = infect plants; small, circular ssRNA w/o protein coat
Composed of RNA only
Prions = infect mammals; cause protein misfolding
Composed of protein only
Food microbiology studies the _ on food and on consumers
actions and effects of microorganisms
Examples of actions of microorganisms on food
Beneficial
Fermentation
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) convert sugar → lactic acid
Yogurt, kimchi
Yeasts convert sugar → CO2, alcohol
Bread, wine, beer
Preservation
Propionibacterium produces propionic acid in Swiss cheese, inhibiting mold growth
Negative
Spoilage
Meat putrefaction due to protein breakdown by Pseudomonas
Souring of milk by LAB
Contamination
Salmonella in raw poultry
Clostridium botulinum in improperly canned goods
Effect of food microbes on consumers
Food poisoning
Illness caused by consuming food contaminated with toxins produced by microorganisms
Toxin, not the microorganism itself, causes symptoms
e.g., S. aureus produces enterotoxin > vomiting, diarrhea
e.g., C. botulinum produces botulinum toxin > paralysis
Food infection
Illness caused by consuming food contaminated with viable microorganisms that infect and multiply in the gastrointestinal tract
e.g., Salmonella, E. coli > diarrhea
e.g., L. monocytogenes > meningitis
T/F: B. cereus, C. perfringens, and all other bacteria can cause both food poisoning and infection
TRUE
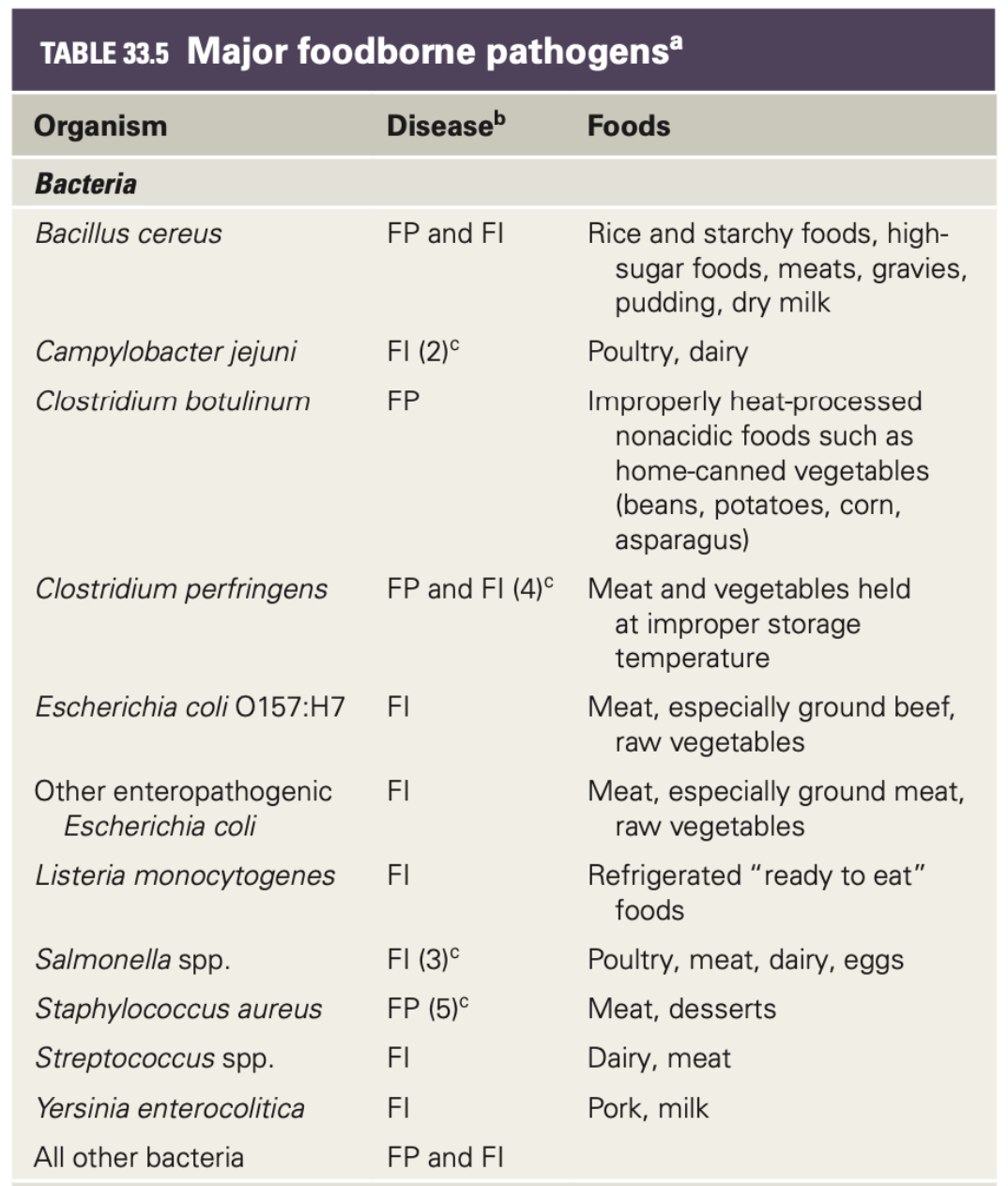
Food infection requires _
ingestion of living or viable cell
Food microbiology studies the actions and effects of microorganisms on _
food and consumers
_ of the cells in the human body do not contain our own DNA but instead belong to microbiota (i.e., bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and other unicellular organisms)
½ (Half)
Microbiota are most abundant in the _, where they aid in digestion, and, most amazingly, “talk” to our brain, influencing our mood, energy level, appetite, memory, and even personality meamp
Gut
Microbiota are most abundant in the gut, where they aid in digestion, and, most amazingly, “talk” to our brain, influencing our _
meamp
Mood
Energy level
Appetite
Memory
Personality
Mice raised in sterile facilities
Bubble mice
T/F: There are striking differences in terms of the behavior of a bubble mouse and normal mouse (i.e., colonized at birth with microbes)
TRUE
Normal mouse vs. Bubble mouse
Normal mouse
Quick & eager to learn
Show it a napkin ring and it will circle and sniff it with great interest
Place it in a maze and it will be keen to explore new passages and remember where it’s been
Bubble mouse
Lacks natural curiosity
Slow to learn but quick to forget
Just as inclined to favor the familiar over what’s new, exciting, or different
Don’t protest when separated from their mother, which is a trauma that, in a normal mouse, would result in life-long skittishness
Separating normal mouse from their mothers early in life results in _
life-long skittishness
T/F: When you colonize a bubble mouse with the normal microbiota for that strain (or microbiota of normal mouse), their behavior normalizes
TRUE
Give the 2 evidences proving that while humans are not mice, the effect of gut bacteria on humans is consistent with the effect of gut bacteria on animals/mouse
When they transferred gut bacteria from an overweight twin into a bubble mouse, bubble mouse fattened up
When they transferred gut bacteria from thin twin, bubble mouse stayed thin
When they transferred gut bacteria from depressed person into a bubble mouse, bubble mouse started exhibiting depressive-like symptoms, e.g., they stopped swimming sooner than a mouse transferred with gut bacteria from a non-depressed person
How can gut bacteria influence how we feel and act?
Gut bacteria produce hoards of psychoactive compounds, including half a dozen of neutrotransmitters
Gut bacteria can “talk” to our brain because the microbes and human cells in our body speak the same language
Some scientists even believe that this language they use to communicate was invented by bacteria
This long-distance conversation is facilitated by a major nerve cable running from gut to brain called vagus nerve, which can be directly activated by gut bacteria or the psychoactive compounds they produce
Incidentally, 80% of traffic on this cable is going from gut to brain, not the other way around as had long been assumed (only 20% goes from brain to gut)
Gut bacteria can also rely on circulatory system to transport their psychoactive compounds upstairs (to the brain)
One very important, indirect way that gut bacteria signal to the brain is by misbehaving
When aggressive bacteria invades the gut wall, immune cells rush to the scene, but these immune cells do not always stay localized in the gut but can travel to the brain, where they can trigger inflammation and depression
Inflammation & depression, for reasons not well understood, go hand-in-hand and are considered the “destructive duo,” thus influencing how we feel and act
Explain Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) therapy
Rapidly advancing treatment for mental disturbances
It entails electrically stimulating the vagus nerve via an electrode implanted in the chest
While VNS therapy evolved independently of microbiota research, some scientists think that the current may mimic the effects of gut bacteria on the vagus nerve (speculative)
What’s clear: VNS strengthens the gut barrier, preventing pathogenic bacteria from breaching it and from causing inflammatory responses that can spread to the brain
FDA has already approved Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) therapy for the treatment of _
Severe epilepsy
Depression unresponsive to standard therapy
Early clinical trials suggest that the VNS therapy may also be beneficial to people with _
ADHD, OCD, and PTSD
Parallel with the developments in early clinical trials showing that VNS therapy may be beneficial to ADHD, OCD, PTSD individuals, microbiota researchers are attempting to treat mental disturbances by _
Changing the composition of our gut microbiota, or
Alternatively by boosting or blocking the action of the chemicals produced by these microorganisms part of the gut microbiota
Cite 2 evidences that microbiota researchers are making progress in terms of pinpointing exactly which bacteria are good or bad factors in various neuropsychiatric conditions
People with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), for example, often have high amounts of a bacterial molecule in their blood and in rodents, this molecule has been shown to raise anxiety and alter brain connectivity
Axial Therapeutics (a company at the forefront of developing microbiota-based treatments) is currently conducting a clinical trial of a drug designed to prevent this destructive bacterial molecule from reaching the brain
Their goal is to treat irritability in children with ASD
A bacteria found in yogurt called Lactobacillus reuteri has been shown to promote social bonding in animal models of autism
Both good and bad bacteria have been similarly linked to Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), a neurodegenerative disease known for paralyzing baseball player Lou Gehrig at the peak of his career
Like him, most patients die within a few years after being diagnosed with ALS
A small minority live up to 10 years or longer
People with ASD are often found to have high amounts of a particular bacterial molecule in their blood, which, in rodents, has been shown to _
raise anxiety and alter brain connectivity
A company at the forefront of developing microbiota-based treatments, currently conducting clinical trial of a drug designed to prevent bacterial molecule from reaching the brain; aiming to treat irritability in ASD children
Axial Therapeutics
Bacterial species found in yogurt and shown to promote social bonding in animal models of autism
Lactobacillus reuteri
Both good and bad bacteria in ASD were similarly linked to this disease that’s known to have paralyzed baseball player Lou Gehrig at the peak of his career; die within few yrs after diagnosis except from a small minority who live up to 10 years or longer
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Axial Therapeutics aims to _ in children with ASD
treat irritability
In animal models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Israeli researchers have recently discovered 2 bacteria: _
One that accelerates the disease
One that slows down its development
In animal models of ALS, Israeli researchers recently discovered 2 bacteria: one that accelerates the disease, another that slows down its development
They suspect that the benefits of the good bacteria are due to the vitamin it produces called _
nicotinamide
Microbiota researchers are making even greater progress in unraveling _
root causes of Parkinson’s disease
Explain recent research discoveries on Parkinson’s disease
Microbiota researchers are making even greater progress in terms of unraveling the root causes of Parkinson’s disease
Michael J. Fox = actor known to have Parkinson’s, exhibiting characteristic symptoms: ssu
Shaking, stiffness, unsteady gait
It’s long known that Parkinson’s disease involves the misfolding of protein alpha-synuclein in substantia nigra part of the brain
As the misfolding spreads, brain cells start to die, symptoms worsen
Big mystery: What causes the alpha-synuclein (Parkinson’s protein) to misfold in substantia nigra in the first place?
Several research labs recently converged on 1 likely culprit
Their research suggests that the guts of some people harbor a strain of E. coli that churns out a misfolded compound very similar to Parkinson’s protein
When misfolded variants of this protein are injected into guts of susceptible rodents, it causes normal proteins in the intestinal lining to misfold in turn
This wave of misfolding proteins slowly spreads up to the vagus nerve and, in about 2 months, you’d see clumped-up proteins in exactly the part of the brain that degenerates in Parkinson’s patients (i.e., substantia nigra)
3 common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease
ssu
Shaking
Stiffness
Unsteady gait
T/F: It’s long been known that ALS involve the misfolding of the alpha-synuclein protein in the substantia nigra part of the brain
FALSE
It’s long been known that Parkinson’s disease involve the misfolding of the alpha-synuclein protein in the substantia nigra part of the brain
Name disease based on symptoms
Shaking, stiffness, unsteady gait
Irritability
Paralysis
Shaking, stiffness, unsteady gait = Parkinson’s (MJ Fox)
Irritability = ASD
Paralysis = Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (Lou Gehrig)
Name disease based on cause
Alpha-synuclein protein misfolding in substantial nigra
Parkinson’s disease
T/F: VNS therapy evolved independently of microbiota research
TRUE
But some scientists think that the current may mimic the effects of gut bacteria on the nerve (still speculative)
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) entails electrically stimulating the vagus nerve via _
an electrode implanted in the chest
Explain recent consensus of several research labs regarding the cause of alpha-synuclein misfolding in substantia nigra
Their research suggests that the guts of some people harbor a strain of E. coli that churns out a misfolded compound very similar to Parkinson’s protein (alpha-synuclein)
When misfolded variants of this protein were injected into the guts of rodents, it caused normal proteins to misfold in turn
This wave of misfolding proteins slowly spreads to the vagus nerve and, in about 2 months, one would observe clumped-up proteins in exactly the part of the brain that degenerates in Parkinson’s patients
Kathleen McAuliffe’s main point in her TED Talk “Do Gut Microbes Control Your Personality?”
Most importantly, these fresh glimpses into the origin of the disease (Parkinson’s) is suggesting new ways of intervening in its progression
Behavior is controlled not just top-down but also bottom-up
I is really We
If microbes have effect on food and consumers, the ability of microbes to grow will also be affected by _
food system
Rapidly advancing treatment for mental disturbances
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
Apart from food microbiology being the study of microorganisms associated with food and talking about the actions and effects of microorganisms on food and on consumers, food microbiology also tackles _
how food environment influences microbes
If the food is acidic, what kind of microorganisms do you expect to grow or contaminate this food?
Acidophiles
When you’re manufacturing vinegar, what you have to consider when designing your production line is _
how to prevent the growth of acidophilic organisms
If the food is basic, what kind of microorganisms do you expect to grow or contaminate this food?
Alkaliphiles
If the food has a high salt or NaCl concentration, what kind of microorganisms do you expect to grow or contaminate this food?
Halophiles
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) therapy strengthens _, preventing pathogenic bacteria from breaching it and from causing inflammatory responses that can spread to the brain
gut barrier
In ice cream, what kind of microorganisms do you expect to grow or contaminate this food?
Psychrophiles
T/F: The food that we eat also affect the microbes we nurture in our gut
TRUE
T/F: Billions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi live on or inside of us, thus maintaining a good, balanced relationship with them is to our advantage
FALSE
Trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi live on or inside of us, thus maintaining a good, balanced relationship with them is to our advantage
_ is a rich ecosystem consisting of bacteria, fungi, viruses, etc. that perform a variety of functions in our body
Gut microbiome
Bacteria in our gut performs 4 main functions
bprp
Break down food the body can’t digest
Produce important nutrients
Regulate immune system
Protect against harmful germs
There is no blueprint yet on which good bacteria a robust gut needs, but we do know that _
it is important for a healthy microbiome to have a variety of bacterial species
Many factors affect our microbiomes, including _
emcd
Our environment
Medications (e.g., antibiotics)
Whether we’re delivered via C-section or not
Diet
_ is emerging as one of the leading influences on our gut health
Diet
While we can’t control all these factors (emcd), we can manipulate the balance of microbes in our gut by _
paying attention to what we eat
Dietary fibers from foods such as _ are the best fuel for gut bacteria
fv nlw
Fruits
Vegetables
Nuts
Legumes
Whole grains
T/F: The more fibers you ingest, the less fiber-digesting bacteria colonize your gut
FALSE
The more fibers you ingest, the more fiber-digesting bacteria colonize your gut
Explain the study emphasizing the importance of high-fiber diets in nourishing your gut microbiome
In a recent study, scientists exchanged the regular high-fiber diets of a group of rural South Africans with the high-fat, meat-heavy diets of a group of African Americans
After just 2 weeks of high-fat, low-fiber, Western style diet, the rural South African group showed increased colon inflammation and decreased butyrate levels (short-chain fatty acid known to lower colon cancer risk)
Opposite results were found in the African American group who consumed high-fiber diets → decreased colon inflammation and higher butyrate levels
What goes wrong with our gut bacteria when we consume low-fiber processed foods?
Consuming low-fiber processed foods provides less fuel for our gut bacteria, essentially starving them until they die off
Low-fiber diet results in less diversity and hungry bacteria; some even starts feeding on mucus lining
Enumerate specific foods that affect gut bacteria
Fruits, vegetables, tea, coffee, red wine, dark chocolate fvt crd
correlated with increased bacterial diversity because they contain polyphenols, which are naturally occurring antioxidant compounds
Foods rich in dairy fat, e.g., whole milk, sugar-sweetened soda
correlated with decreased bacterial diversity
Naturally occurring antioxidant compounds present in certain food that lead to increased bacterial diversity in human gut
Polyphenols
Cite a situation showing why food preparation matters also when maintaining gut health
Minimally processed fresh foods generally have more fiber and thus provide more fuel for our gut bacteria, thus lightly steamed, sauteed, and raw vegetables are typically more beneficial than fried dishes
There are ways of preparing food that can actually introduce good bacteria (AKA probiotics) into our gut, including _
Fermentation
Fermented foods (e.g., kimchi, sauerkraut, tempeh, kombucha) are teeming with helpful probiotic bacteria like _
Lactobacillus, Bifidobacteria
There are ways of preparing food that can introduce good bacteria, also known as _, into our gut
probiotics
Originally used as a way of preserving food before the invention of refrigeration, _ remains a traditional practice all over the world
fermentation
Short-chain fatty acid produced by bacteria when they digest fiber
3 important things it does
Butyrate
Nourish gut barrier, improve immune function, and help prevent inflammation, which generally reduces cancer risk nip
Fermented foods, e.g., _, provide variety and vitality into our diets
Kimchi, sauerkraut, tempeh, kombucha, yogurt
T/F: All yogurt is good for us
FALSE
Not necessarily. There are brands with too much sugar but not enough good bacteria.
T/F: Today, it is sufficiently understood how any of these food interact with our microbiomes
FALSE
We only see positive correlations, but the inside of our gut is a difficult place to make direct observations
Example of situation proving that we only see positive correlations (but inside of gut is a difficult place to make direct observations)
We currently don’t know whether any of these foods are directly responsible for the changes in diversity in our gut or something more complicated is happening
3 Fs you need to consume to support your gut microbiota
Consume Fibers, Fresh, and Fermented foods
5 major roles of microbiology in the food industry
ppqle
Product development
Public health
Quality and safety control
Establishing legislations
Extension / education
What is the best fuel for gut bacteria? Why?
Dietary fiber from foods like fruit, vegetables, nuts, legumes, and whole grains are the best fuel for gut bacteria because when bacteria digest dietary fibers, they produce the short-chain fatty acid called butyrate that: nip
nourish the gut barrier,
improve immune function, and
help prevent inflammation, which generally reduces cancer risk
_ is a single-celled fungi used to make beer, bread, wine, among other products
Yeasts
Yeasts break down _ such as _ to get the energy and the molecules they need to function
carbohydrates, sugars
Yeasts can break down carbohydrates (sugars) in 2 ways: _
Oxygen-dependent aerobic pathway
Oxygen-independent anaerobic pathway (fermentation)
T/F: Only anaerobic pathway can be used by yeast in baking bread
FALSE
Both anaerobic & aerobic pathways may be used by yeast in baking bread, but they normally prefer to start with anaerobic fermentation
T/F: Oxygen-dependent aerobic pathway of yeasts produce ethanol as byproduct
FALSE
Oxygen-independent anaerobic pathway of yeasts produce ethanol as byproduct
Products of aerobic O2-dependent pathway in yeasts = _
Products of anaerobic O2-independent pathway in yeasts = _
Aerobic = CO2, H2O, ATP
Anaerobic = CO2, Ethanol, ATP
T/F: No bread is not alcoholic because the small amounts of alcohol secreted evaporate during baking
TRUE
T/F: In the aerobic oxygen-dependent pathway, yeast consume some of the sugar and produce CO2 + ethanol + ATP
FALSE
In the aerobic oxygen-dependent pathway, yeast consume some of the sugar and produce CO2 + H2O + ATP
What gives the bread its soft texture?
During either aerobic/anaerobic pathway, CO2 accumulates, creating tiny bubbles
These bubbles get trapped by gluten and create a sponge-like structure that gives the bread its soft texture
T/F: Wine also relies on yeast, but wine-making setup keeps O2 levels high so yeast would consume sugar via fermentation/anaerobic pathwaythe
FALSE
Wine also relies on yeast, but the wine-making setup keeps O2 levels low, so yeast would consume sugar via fermentation/anaerobic pathway
Explain process of wine-making
Starts with wild yeasts already hanging out on the grapes, but to get consistent results, most winemakers would carefully add selected strains of yeast that can tolerate high levels of alcohol
Yeasts would then consume sugar in grapes, causing sugar level to drop and alcohol level to rise
But this doesn’t necessarily mean that sweeter wines have less alcohol because (1) different grape types start with different amounts of sugar and (2) sugar can also be added
CO2 then bubbles away through a vent
But in carbonated alcoholic beverages like beer and champagne, sealed containers are used in primary / secondary fermentation to keep CO2 inside the bottle
In carbonated alcoholic beverages like beer and champagne, _ are used in primary / secondary fermentation to keep CO2 inside the bottle
sealed containers
What happens to CO2 in wine-making setup?
It bubbles away through a vent
What do most winemakers add initially to get consistent results?
Selected strains of yeast that can tolerate higher levels of alcohol
T/F: Sweeter wines always have less alcohol
FALSE
Bc different grape types start with different amounts of sugar and sugar can also be added
_ are key for cheese
Bacteria
Explain how to make cheese
To make cheese, milk is inoculated with bacteria that consumes lactose (a kind of sugar), producing lactic acid + many other chemicals
As milk gets more and more acidic, its proteins aggregate and curdle, hence spoiled milk is clumpy
Cheesemakers usually add the enzyme rennet, which is naturally found inside cows, goats, and other mammals, to help this process along
Eventually, those little curdles turn into bigger curds, which are then pressed to squeeze out water and create firm cheese
T/F: Different strains of bacteria make different kinds of cheese
TRUE
Bacterial species that emits CO2 and gives Swiss cheese its characteristic wholes
Propionibacterium sp.
_ is the microorganism used to make brie and camembert cheese
Mold
What was Mr. Lang’s foodborne illness in CDC video?
Salmonella infection
Name of (1) epidemiologist and (2) lab personnel in CDC video
Dr. Hayes
Dr. Grey