Aggregate Demand
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Aggregate demand
The total demand for all goods and services in an economy at a given price level
Components of AD
Consumption(C) + Investment (I) + Government expenditure (G) + net trade (exports(X) - imports(M))
C+I+G+(X-M)
Reak balance effect
When the general price level falls, the real value of money increases.
That means people can buy more with the same amount of money
So they increase consumption (Real GDP rises)
Why is the AD curve downwards sloping
Wealth effect
Trade effect
Interest effect
A movement along the AD curve is caused by what
When there is a change in the price level caused by factors not related to AD i.e changes in AS
E.g a fall in oil prices(decrease in COP) would lead to an expansion in AD and a fall in the GPL
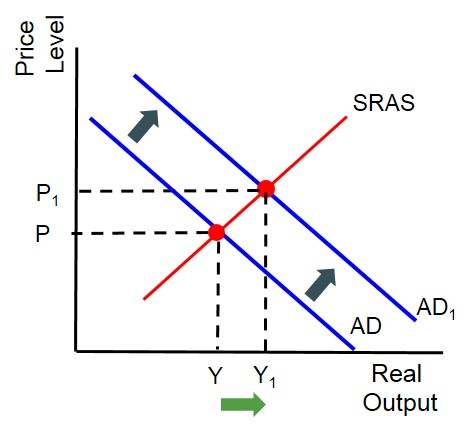
Shifts in AD curve
When any one of the components of AD changes.
If AD increases, we expect average level of prices to rise (inflation) and real output to rise (economic growth)
If AD decreases, we expect prices to fall (deflation) and real output to decrease (slowdown or recession)
Consumption
Spending by households on goods and services
(main component of AD)
Determinants of consumption
Interest rate
Consumer confidence
Wealth effects
The level of employment
Interest rate
If interest rates rise, it costs us more to borrow if we’re spending on credit
It also increases the opportunity cost of spending (saving)
Consumer confidence
If householders feel secure in jobs and future prospects in the economy, people will spend more. Because of this, what people think is going to happen in the economy has a big influence on what is actually going to happen
Wealth effects
An increase in share/ house prices mean that people are going to spend more
, For example, if my house is worth more I might take out a larger loan on my house
, and if my shares go up in value I might be more willing to book a foreign holiday
The level of employment
The higher the level of employment, the more thats spent in an economy (which might even lead to higher employment)
Investment
Defined as an increase in the capital stock (capital goods)
Influences of investment
The rate of economic growth
Confidence levels
Interest rates
Animal spirits
Risk
Access to credit
Gov decisions
Gov bureaucracy
The rate of economic growth
If there is an increase in real GDP, then firms need more capital to meet the increased demand,
So an increase in real GDP causes I to rise
And an increase in I causes GDP to rise
Animal spirits
Sometimes consumers and firms aren’t fully rational, investment doesn’t happen automatically and an additional boost may be needed by the government
Government decisions
Changes in gov decisions and rules can have a significant impact on capital spending
For example, a cut in coroporation tax would lead to more investment by firms
Government bureaucracy
If the gov relaxes planning restrictions, firms are more likely to invest in building projects
Access to credit
Low interest rates do not necessarily mean all firms can borrow cheaply, banks might not be willing to take risks in their lending
Risk
The higher the level of risk, the lower the investment
Interest rates
If interest rates rise, investment tends to fall as it costs more to borrow money to invest
Confidence levels
If firms think they will sell more in the future, they are more likely to invest today
Gross investment
Total amount of investment before any account is taken of depreciation of assets
Net investment
Takes account of the fall in value of capital assets
Fiscal policy
The governments position or set of decisions on government spending and taxation
Government expenditure
Spending by the government on goods and services that directly contribute to national output
Points about gov expenditure
If the government spends more than it earns, it is known as fiscal/budget deficit, this will increase flow of income, or Aggregate demand
If the government spends less than it earns, it is known as fiscal, or budget surplus and leads to a contraction of AD
The government automatically spends more in a recession as government spending increases on out-of-work benefits and taxation receipts fall as workers and firms earn less
The government automatically spends less in a boom as government spending decreases and taxation receipts rise as wages and employment rise.
Net trade (X-M)
Exports minus imports
Net exports
The exports of GS means money is flowing into the country, when the value of money flowing out of a country (imports) is deducted, a figure for net exports is the result
Exchange rate
The price of one currency in terms of another
Causes of changes in Net exports
Real income
Higher incomes in an economy reduces incentive for firms to export as they will sell domestically
Exchange rate
If the exchange rates rise, net exports are likely to fall as exports are less competitive abroad and imports are more competitive in the domestic economy
However in the short run, a strong ecxchange rate might increase the value of exports and decrease value of exports, because spending patterns do not change quickly
Changes in the state of world economy
Degree of protectionism
If there are high tarriffs, quotas or other restrictions on trade, firms will find it difficult to export to certain countries
Non price factors
Demand for exports and imports is determined by many things apart from price, such as quality of engineering, reliability, tarriffs, etc.
Wealth effect
As the price level decreases, people have more purchasing power, therefore increasing consumption, which therefore increases AD
Trade effect
When the price level decreases, exports become more competitive, because of lower COP, which increases X.
At the same time imports are less competitive as the domestic goods are more competitive, so there is less demand for them. This decreases M.
The increase in X and the decrease in M means that there is an increase in net trade
Interest effect
When the GPL falls, people and firms need less money for everyday transactions, so they save more
This leads to interest rates falling
This reduction in interest rates encourages greater consumption, and greater investment as it is cheaper to borrow