Lab Practical Study Guide!
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/128
Earn XP
Last updated 9:55 PM on 11/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1
New cards
Ocular Lens(10x) x Objective Lens(... ,10,40,100)
calculation of total magnification
2
New cards
resolution
minimum distance at which 2 distinct points of a specimen can be seen
3
New cards
parfocal
being able to refocus with minimal effort when changing to a different objective lens
4
New cards
Resolving power by keeping light rays from refracting
What is the purpose of using immersion oil
5
New cards
Lens paper
With what do we clean the lenses?
6
New cards
to isolate bacterial colonies
What is the purpose of dilution streaking?
7
New cards
heat loop and swab the broth with loop → streak at 90 degree angles the loop with the agar plate → 4th side should show single colonies
Know how to aseptically perform this technique
8
New cards
identical bacteria that look the same as their mother colony
What is a colony?
9
New cards
shape, size, color, surface appearance, and texture
What are colony characteristics?
10
New cards
pure: one bacteria
mixed: 2 or more bacteria on a plate; will have different shapes and sizes on agar plate
contaminated: bacteria from different source have contaminated the agar plate
mixed: 2 or more bacteria on a plate; will have different shapes and sizes on agar plate
contaminated: bacteria from different source have contaminated the agar plate
What is the differences between a pure, mixed, and contaminated culture?
11
New cards
the lid can fall off the petri dish
Why label a plate on the bottom?
12
New cards
to lessen the risk of condensation compromising the colonies and lessen the risk of airborne contamination
Why incubate it in the inverted position?
13
New cards
to make them easily visible under microscope
Why do we stain cells?
14
New cards
adv: fixes bacteria on slide and preserves cells and kills microbes, disadvantage: inability to determine motility and distort cell shape and size
What are advantages and disadvantages to heat fixing slides?
15
New cards
basic: have positive charge so attract to cell wall and nuclei better than acid dyes: crystal violet, methylene blue, and Safranin
acidic: have negative charge and attach to positive components of cell); acid fuchsin
acidic: have negative charge and attach to positive components of cell); acid fuchsin
Know what basic and acidic dyes are and how they work
16
New cards
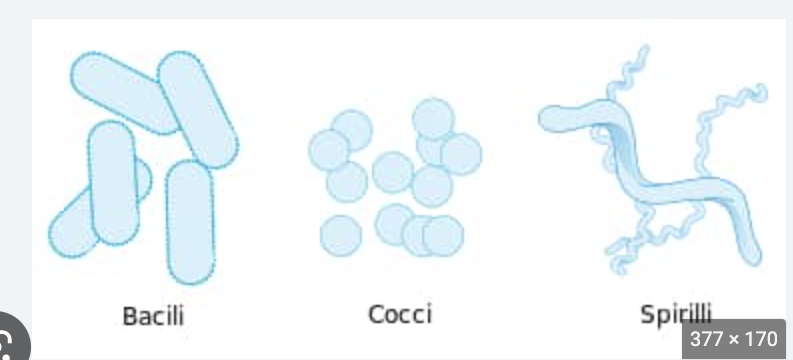
Bacillus, Coccus, or sprial
Know the basic shapes
17
New cards
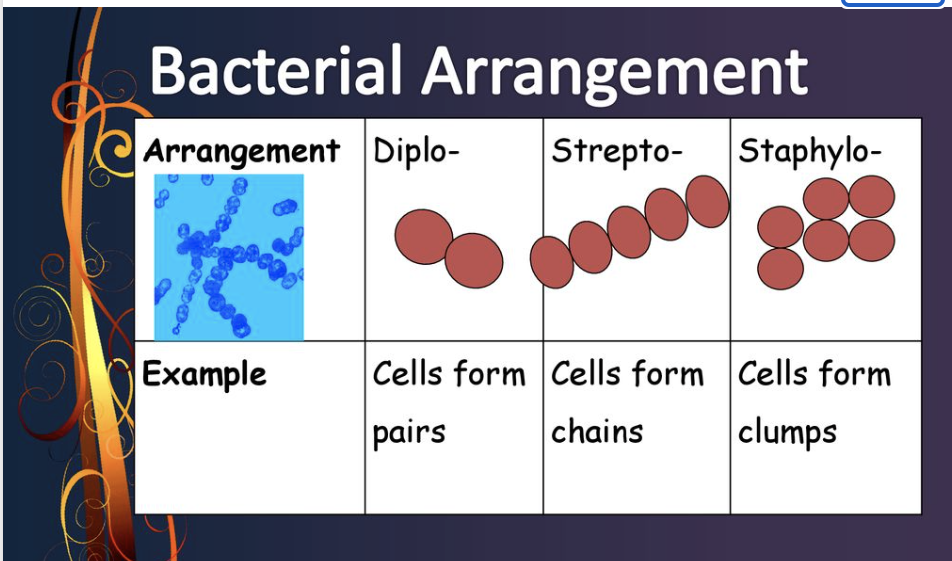
Staphylo, Strepto, Diplo
Arrangements of cells
18
New cards
1 to 2 uM diameter and 5 to 10 uM length
bacteria typically fall within the μm range?
19
New cards
live bacteria to see if they are motile; steps: cover jelly on all 4 sides of the cover slip, place loop of suspension in center of cover slip, and then place concave slide on top of cover slip
Know how to prepare a hanging drop specimen
20
New cards
motility
What characteristic of the live bacterial specimen was observed using this technique?
21
New cards
to avoid drying out the drop and killing the bacteria
Why do you have to reduce the amount of light with the diaphragm to see bacteria in a hanging drop slide?
22
New cards
Gram-positive: contain teichoic acid, LPS not present, very susceptible to antibiotics and produce exotoxin and stain Purple
Gram-negative: LPS present, and produce exo and endotoxins, stain pink
Gram-negative: LPS present, and produce exo and endotoxins, stain pink
Know the difference between a Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell wall
23
New cards
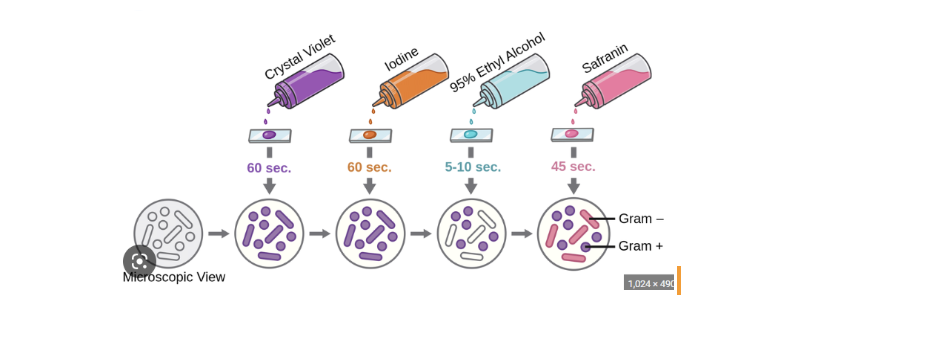
Primary stain: Crystal Violet
Mordant (fixes the dye): Iodine
Decolorizer agent: Ethyl Alcohol
Counter stain: Safranin
Mordant (fixes the dye): Iodine
Decolorizer agent: Ethyl Alcohol
Counter stain: Safranin
Know the basics of how to perform the Gram stain technique including the function of each component
24
New cards
not using morant-idoine properly
Under what circumstances might you get a false Gram-negative?
25
New cards
not using decolorizing agent: ethyl alcohol
Under what circumstances might you get a false Gram-positive result?
26
New cards
gram stain: differentiates gram positive and negative bacteria
acid-fast stain: differentiates mycobacteria (red) from non-mycobacteria (blue/green)
acid-fast stain: differentiates mycobacteria (red) from non-mycobacteria (blue/green)
Why is the Gram stain (and acid-fast stain) considered to be a differential staining technique?
27
New cards
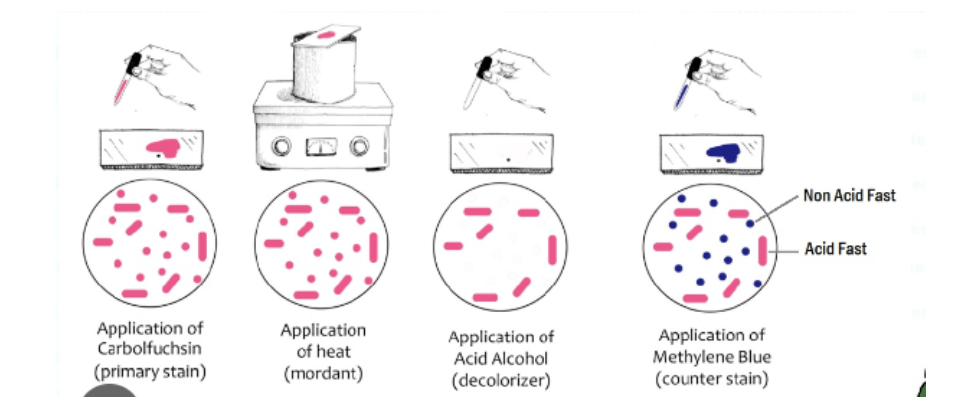
Carbolfuchsin (15 to 20 min) → Heat (3x hover over bunsen burner) → Acid Alcohol (20 sec) → Methylene Blue (60 seconds)
method for acid-fast staining.Know the staining procedure and function of each component
28
New cards
due to their lipid rich cell envelope
Why are mycobacteria acid-fast?
29
New cards
highly resistant to disinfectants and drying out
What advantages does this provide to the organism?
30
New cards
tuberculosis
What species cause important human diseases?
31
New cards
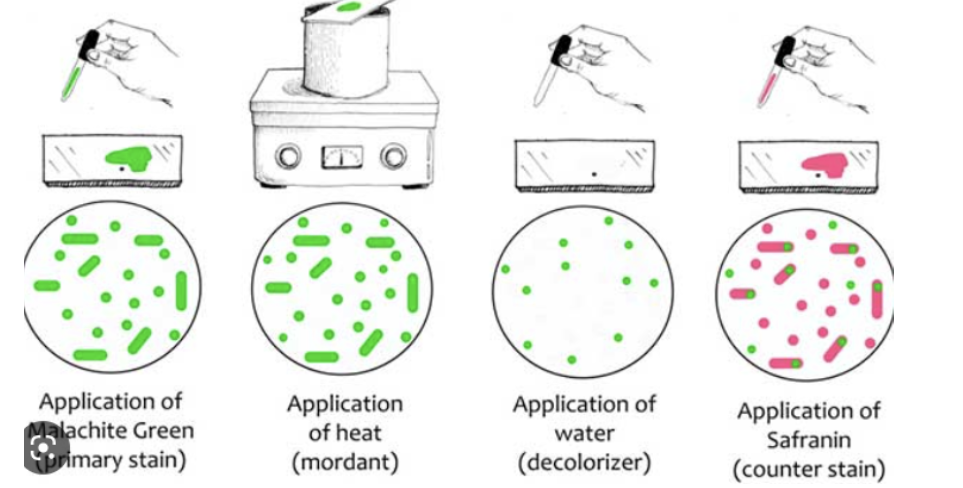
Primary stain: malachite green
Mordant: heat
Decolorizer: water
Counter stain: Safranin
Mordant: heat
Decolorizer: water
Counter stain: Safranin
The endospore-staining procedure was provided in a handout. Know the staining procedure and function of each component.
32
New cards
non-growing cell;dormant; green color
What are endospores?
33
New cards
growing cell; pink color
What are vegetative cells?
34
New cards
germination: the process by which the dormant spore is converted into a vegetative cell.
sporulation: the formation of spores
sporulation: the formation of spores
Define germination and sporulation?
35
New cards
bacillus and clostridium
What two genera characteristically produce endospores?
36
New cards
antrax, bolutlism, and tetanus
What human diseases discussed in lab are associated with spore-formers?
37
New cards
A steam-pressure sterilizer; uses high heat
What is an autoclave?
38
New cards
steam forms at 100 celsius, it’s temp inc. → inc. pressure; inc in pressure or temp= dec.(less time) to kill exposed heat-resistant endospores
How are steam, pressure, temperature, and time used in the sterilization process
39
New cards
hospital sterilization= 25 to 30 lb pressure, 133-135 celsius, and 5 to 25 min
What pressure, temperature, and time were used in the demonstrations?
40
New cards
if we can sterilize endospore cell walls(control) then we can sterilize everything else
Why is an endospore sample a valid sterilization control?
41
New cards
We did streaking technique. We mixed E. coli with each different disinfectant to see which one will kill the bacteria. Thick walls surrounding endospores are more resistant to adverse conditions than the vegetative bacterial cells.
Understand how you tested disinfectant (and antiseptic) activities on vegetative and endospore-forming bacteria in a time-dependent fashion. What was the overall outcome?
42
New cards
We labeled a blood agar plate and divided it in half to test before and after results. We use our fingers from tapping the before to then tapping the after section
How did you test the effectiveness of hand hygiene practices?
43
New cards
concentration of disinfectant, nature of material being disinfected {organic matter, biofilms}, pH/ temp, contact between disinfectant/ area to be disinfected, time of exposure, # of microbes, microbial characteristics
What are the principles of effective chemical disinfection?
44
New cards
Most resistant: Prions
Least resistant: viruses w/ lipid envelopes
Least resistant: viruses w/ lipid envelopes
Which types of organisms are most or least resistant to chemical biocides?
45
New cards
1.Sodium hypochlorite, ethyl alcohol: alcohols, determining of ethanol
2.Hydrogen peroxide: peroxygen, cleanse wounds
3.Lysol, Iodophor: halogens, skin disinfection/wound treatment
4.Antiseptic mouthwash, chlorhexidine gluconate: biguanide, surgical scrubs/ preoperative skin preparation
2.Hydrogen peroxide: peroxygen, cleanse wounds
3.Lysol, Iodophor: halogens, skin disinfection/wound treatment
4.Antiseptic mouthwash, chlorhexidine gluconate: biguanide, surgical scrubs/ preoperative skin preparation
As for the quiz, you should know the disinfectants and antiseptics used in lab.
46
New cards
Avoid cross contamination of germs
In a clinical setting, why do you wash your hands before and after wearing gloves?
47
New cards
Infections acquired during the process of receiving health care that was not present during the time of admission.
What is a nosocomial infection?
48
New cards
It physically destroys germs/ removes germs and chemicals from skin.
Why is hand-washing an effective way to break the transmission of infection?
49
New cards
Microorganisms that are usually not found in the body
What are transient bacteria?
50
New cards
Transient flora colonizes the superficial layers of the skin, and is more amenable to removal by routine hand hygiene.
Are normal flora or transient bacteria easier to remove via hand-washing?
51
New cards
The test helps healthcare practitioners to determine which drugs are likely to be most effective in treating a person’s infection.
In a clinical setting, why is it important to perform antimicrobial susceptibility testing?
52
New cards
Take swab that has bacteria and swab a plate to create a uniform layer, divide plate into 4 quadrants, then place a disk in quadrants.
Understand the basics of how to perform the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test.
53
New cards
Appearance of bacterial colonies when all individual colonies on a dish agar plate merge to form a field of bacteria.
What is a bacterial lawn?
54
New cards
Measure the diameter of inhibition zones around the antimicrobial disk, measured in millimeters. To read resistance/ susceptibility: < 10mm: resistant, 11-15mm: intermediate, >16mm: sensitive
Know how to measure the diameter of the zone of inhibition as well as how to interpret the reading regarding resistance and susceptibility for a particular antibiotic.
55
New cards
Determine the minimum inhibitory concentrations of antimicrobial agents.
What is an E-test?
56
New cards
Place a continuous concentration gradient strip on blood agar plate, after you incubate it would show how much of ampicillin diffuses into the agar.
How did you determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)?
57
New cards
Explaining the meaning of something
What is the interpretation?
58
New cards
Plasmid play a central role as the vehicles for resistance gene capture/ their subsequent dissemination.
How did a plasmid confer resistance to ampicillin?
59
New cards
Have sterile nutrient broth, then add ampicillin to the first tube, then transfer to another tube, then transfer to the third, and continue this process till you fill all your tubes. Then transfer e.coli into the tube, mix content, then add the organism suspension to the antibiotic containing broth. You interpret the MIC by the qualitative categories (susceptible, intermediate, and resistant)
Know how to perform the “Broth Dilution Method” and how to interpret the MIC.
60
New cards
Growth controls help to check bacterial growth and sterility control is monitor/ control time, temp, pressure.
What are the purposes of the growth and sterility controls?
61
New cards
Cell wall, protein synthesis, nucleic acid synthesis.
What are antibiotic targets of the bacterial cell?
62
New cards
Limiting uptake of a drug, modification of a drug, inactivation of a drug.
What are the modes of resistance developed by bacteria?
63
New cards
Conjugation, transformation, transduction
Know the three mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer.
64
New cards
Cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, DNA Gyrase, folic acid synthesis
What were the general modes of action of the antibiotics studied in lab?
65
New cards
1.Staphylococci: gram positive non-spore-forming spherical, appearance of “grape: clusters.
2.Streptococci: gram-positive facultative anaerobes, round shape, chain like (diplococci).
3.Pneumococci: gram-positive, lancet-shaped, chains.
4.Enterococci: gram-positive, spherical, short chains.
2.Streptococci: gram-positive facultative anaerobes, round shape, chain like (diplococci).
3.Pneumococci: gram-positive, lancet-shaped, chains.
4.Enterococci: gram-positive, spherical, short chains.
What are the Gram reaction, cell shape, and arrangements of these genera?
66
New cards
Catalase enables bacteria to metabolize harmful hydrogen peroxide and oxygen (bubbles).
Staphylococcus are catalase +, Streptococcus are catalase -
Staphylococcus are catalase +, Streptococcus are catalase -
Know the catalase reaction and how this can differentiate between the two genera.
67
New cards
Staphylococcus aureus, Epidermidis, Saprophyticus.
What are the three medically important staphylococci studied in lab?
68
New cards
1. Staphylococcus aureus is an opportunistic pathogen that typically inhabits the skin and mucous membranes of the nose as a commensal.
2. Staphylococcus epidermidis Like S. aureus inhabits the skin and mucous membranes. Can cause biofilms to grow on plastic devices in the human body.
3. Staphylococcus saprophyticus is often associated with urinary tract infections in women.
2. Staphylococcus epidermidis Like S. aureus inhabits the skin and mucous membranes. Can cause biofilms to grow on plastic devices in the human body.
3. Staphylococcus saprophyticus is often associated with urinary tract infections in women.
now how the following selective / differential media and tests are used to distinguish between the species.
69
New cards
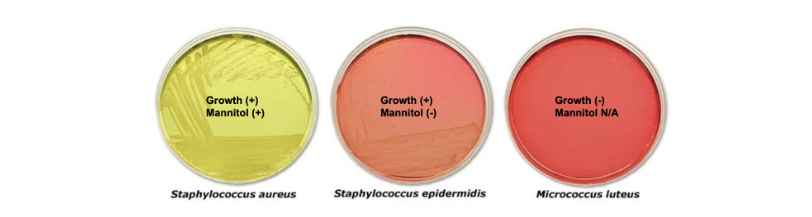
used as a selective media for the isolation of pathogenic Staphylococci.
What is Mannitol Salt Agar?
70
New cards
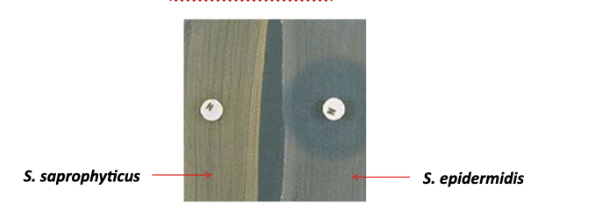
used to differentiate coagulase-negative staphylococci and identify the isolate as staphylococcus saprophyticus.
What is Hemolytic reactions as well as colony morphology on blood- agar Novobiocin disk test?
71
New cards

use to different potential pathogenic Staphylococci such as Staphylococcus aureus from other gram-positive catalase-positive cocci.
What is a Coagulase test?
72
New cards

used to check for certain antibodies or antigens in body fluids including saliva, urine, cerebrospinal fluid or blood.
What is a Latex Agglutination Test?
73
New cards
Streptococcus pyogenes, Agalactiae, Pneumoniae.
What are the three medically important streptococci studied in lab?
74
New cards
Yes, it is the normal flora of the mouth
Is viridans part of the normal flora?
75
New cards
The human intestines/ female genital tract.
Where do enterococci normally reside?
76
New cards
Opportunistic pathogen that can cause UTI, bacteremia, endocarditis.
What is their primary role in disease?
77
New cards
To remove O2 and increase CO2
Why was S. pneumoniae incubated in the candle jar?
78
New cards
Collect the throat culture by rubbing the sterile swab tip on the surface of one tonsils and swab in the culture medium, then incubate.
Know how to obtain a throat culture.
79
New cards
Alpha Hemolysis: Green-presence of biliverdin, by-product of the breakdown of hemoglobin (S. pneumoniae)
Beta Hemolysis: Yellow-complete lysis of RBCs. A clear zone appears around the bacteria (S. pyogenes)
Gamma Hemolysis: lack of hemolysis (E. faecalis)
Beta Hemolysis: Yellow-complete lysis of RBCs. A clear zone appears around the bacteria (S. pyogenes)
Gamma Hemolysis: lack of hemolysis (E. faecalis)
Know how the following selective/differential media and tests are used to distinguish between species of these organisms.
80
New cards
a differential test used to distinguish between organisms sensitive to the antibiotic optochin and those not.
What is TAXO A (bacitracin)?
81
New cards
a differential test used to distinguish between organisms resistant to the antibiotic optochin and those not.
What is TAXO P (optochin)?
82
New cards
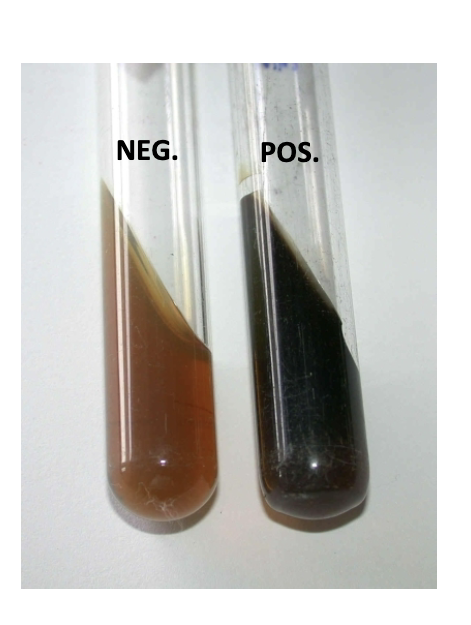

identify members of the group D streptococci. Enterococcus faecalis can grow in bile salt and hydrolyze esculin, forming a black slant.
What is Bile-esculin?
83
New cards
Add four drops of reagent A and B to the extraction tube, place specimen sample in test tube, place strip into solution then interpret your results
Steps of a Rapid Strep A test kit?
84
New cards
Gram-negative rods; Some normally inhabit the human intestine and are non-pathogenic while others are pathogens that are transmitted via the fecal-oral route.
Members of Enterobacteriaceae are?
85
New cards
glucose fermenters, nitrate reducers, and oxidase negative. Typically non-lactose fermenters are pathogenic while lactose fermenters are non-pathogenic.
Enterobacteriaceae members are?
86
New cards
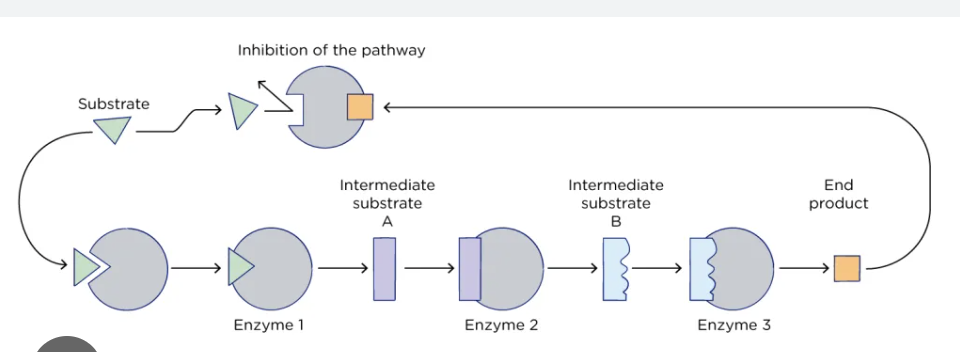
...
Know the substrates, enzymes, products, and how to read a positive reaction.
87
New cards
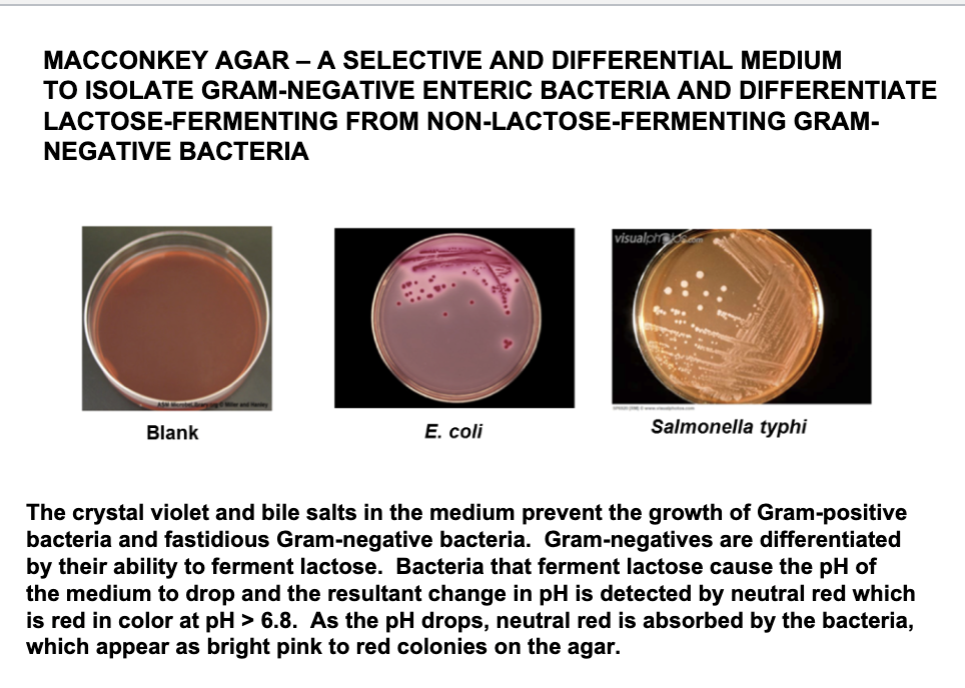
A selective and differential medium to isolate gram - enteric bacteria and differentiate lactose-fermenting from non-lactose -fermenting gram - bacteria
Define MacConkey agar?
88
New cards

A selective and differential medium to recover gastrointestinal pathogens
What is Hektoen enteric (HE) agar ?
89
New cards
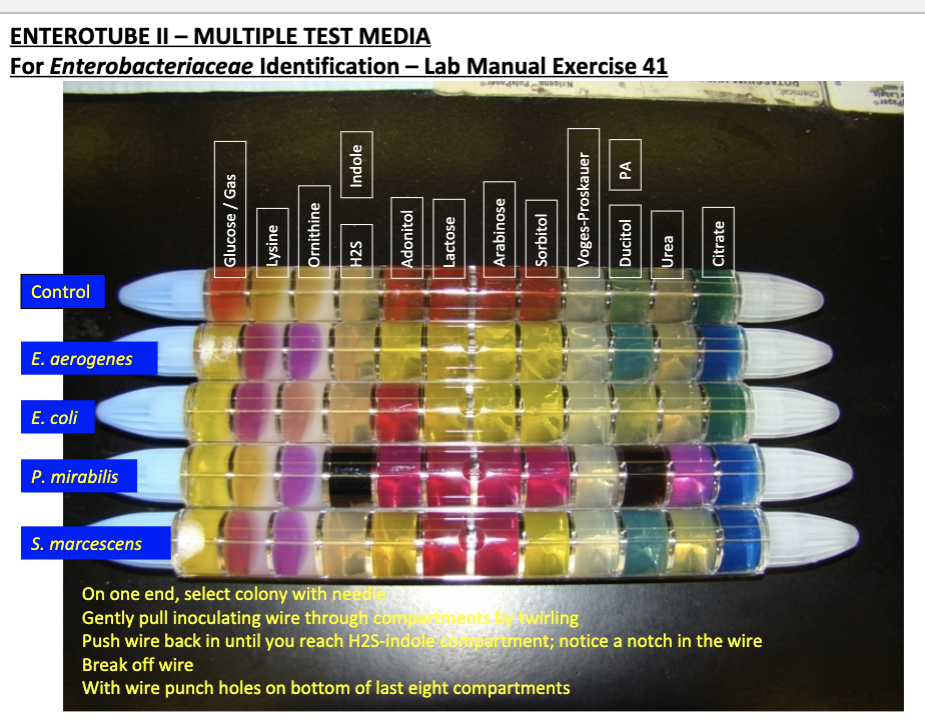
1. On one end, select colony with the needle
2. Gently pull inoculating wire through by twirling
3. Push wire in until you reach H2S-indole compartment; notice a notch in the wire
4. Break of wire
5. With the wire punch holes on the bottom of last eight compartments
2. Gently pull inoculating wire through by twirling
3. Push wire in until you reach H2S-indole compartment; notice a notch in the wire
4. Break of wire
5. With the wire punch holes on the bottom of last eight compartments
Understand how to perform the Enterotube II System test to identify members of Enterobacteriaceae.
90
New cards
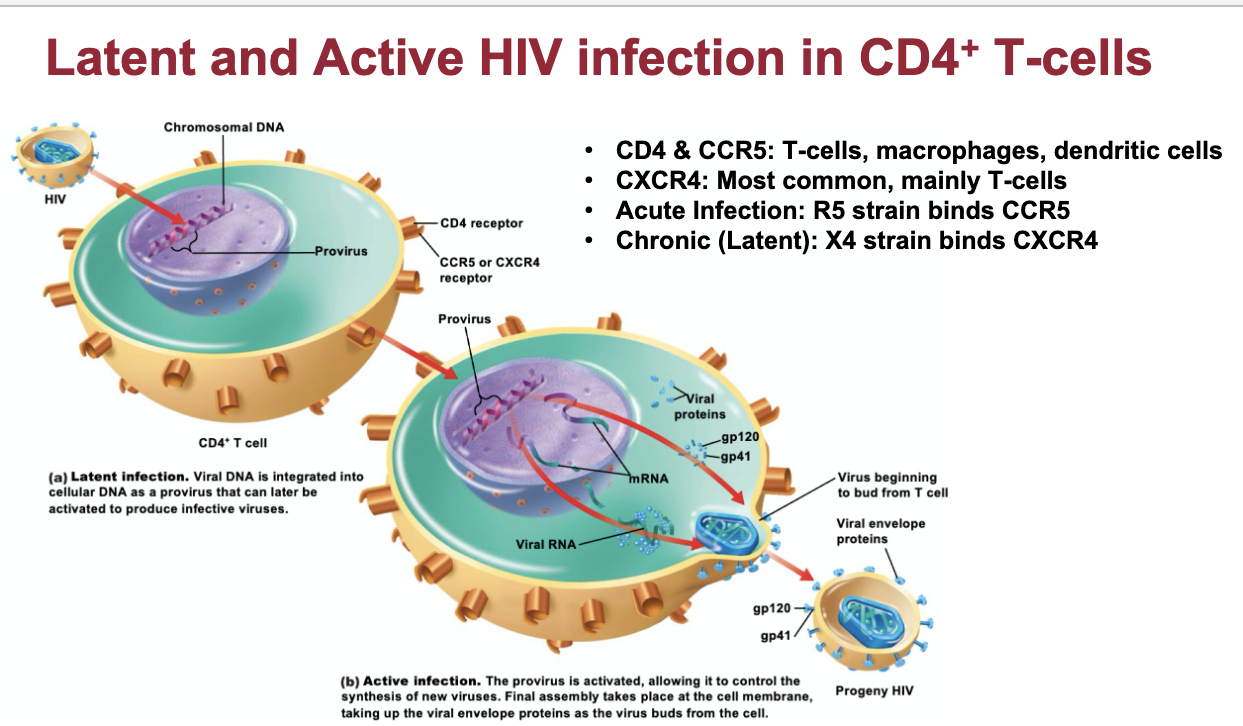
is a retrovirus that uses reverse transcriptase to convert ss RNA to dsDNA
What is HIV-1?
91
New cards
Recognized as a distinct disease in 1981, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the causative agent.
What is AIDS?
92
New cards
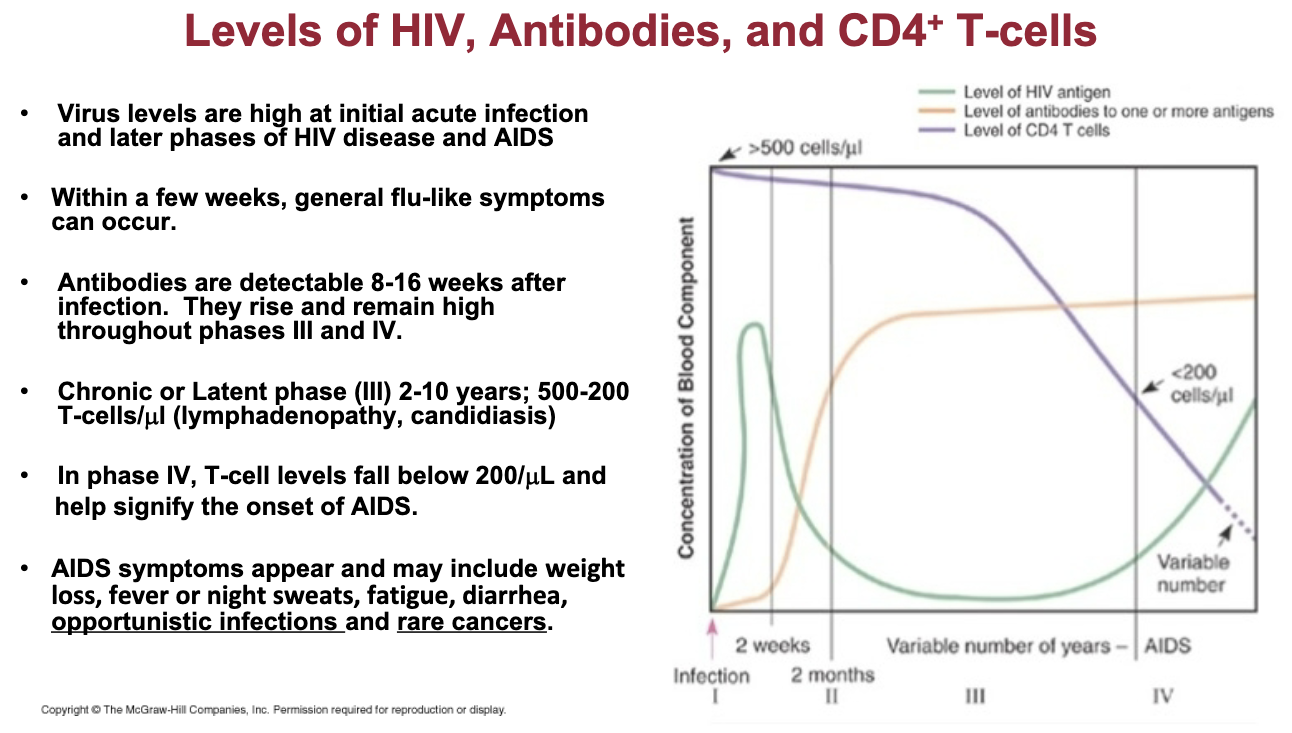
...
Understand the stages of disease progression and signs and symptoms of HIV infection and AIDS discussed in lab.
93
New cards
HIV kills immune system cells that help the body fight infections and diseases.
*Know that individuals with AIDS typically succumb to opportunistic infections and/or rare cancers.
*Know that individuals with AIDS typically succumb to opportunistic infections and/or rare cancers.
How does HIV challenge the immune system?
94
New cards
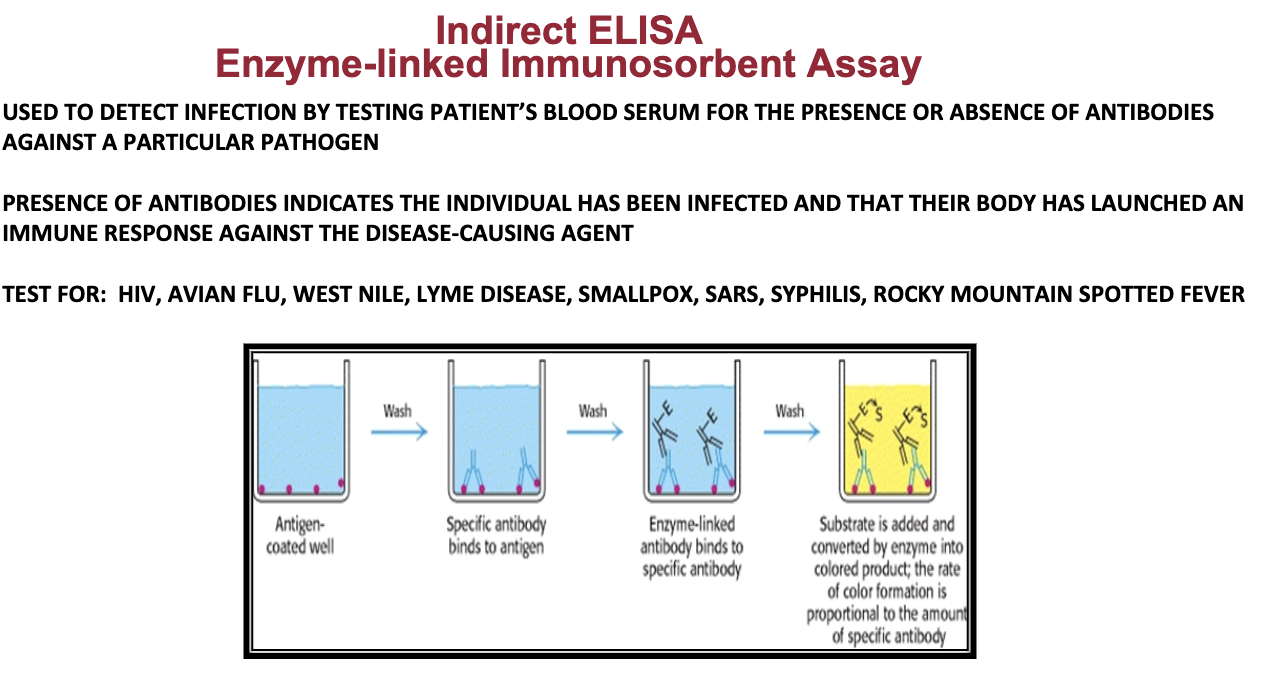
...
Understand how an indirect ELISA was used to detect the presence of anti-HIV IgG antibodies in hypothetical patient serum samples. Know the steps of the assay and their importance.
95
New cards
if the patient has not yet developed antibodies to HIV
Are there any limitations of the ELISA for HIV testing?
96
New cards
Know that alleles for blood types A and B are codominant while the allele for blood type O is recessive.
Blood Grouping
97
New cards
is an inherited protein found on the surface of red blood cells. a woman with Rh-negative blood is impregnated by a man with Rh-positive blood and conceives a fetus with Rh-positive blood, sometimes resulting in hemolysis.
What is the Rh factor? How is it implicated in erythroblastosis fetalis?
98
New cards
A -> B Antibodies
B -> A Antibodies
O -> All antibodies
AB -> No antibodies
B -> A Antibodies
O -> All antibodies
AB -> No antibodies
For a person with a specific blood type, what antibodies is he producing?
99
New cards
Universal Donor: O -> A, B
A,B -> AB (Universal Recipient)
A,B -> AB (Universal Recipient)
For someone with a specific blood type, who can she donate to or receive blood from?
100
New cards
Rh + -> receive + or -
Rh - -> receive ONLY -
Rh - -> receive ONLY -
For someone with a specific blood type, who can she donate to or receive blood from?