HGE Formulas 02
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Geotechnical Engineering
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Moisture Content
w = ww / ws
ww = weight of water
ws = weight of solids (dry soil)
Void Ratio
e = vv / vs
vv = volume of voids
vs = volume of soil solids
Degree of Saturation
S = vw / vv
vw = volume of water
vv = volume of voids
Porosity
n = vv / vT
vv = volume of voids
vT = total volume
Porosity, given void ratio
n = e / (1 + e)
Void Ratio, given porosity
e = n / (1 - n)
Relationship between Specific Gravity, Moisture Content, Degree of Saturation, and Void Ratio
Se = wGs
Air Void Ratio
ac = 1 - S = va / vv
Dry Unit Weight
γd = γw Gs / (1 + e)
γd = γm / (1 + w)
γd = wd / vT
Moist Unit Weight
γm = γw Gs (1 + w) / (1 + e)
γm = γw (Gs + Se) / (1 + e)
γm = γd (1 + w)
γm = wsoil / vT
Saturated Unit Weight
γsat = γw (Gs + e) / (1 + e)
Submerged Unit Weight
γ’ = γw (Gs - 1) / (1 + e)
γ’ = γsat - γw
Unit Weight of Water
γw = 62.4 lb/ft3 = 9810 N/m3
Specific Gravity from Laboratory Testing
Gs = (wf+s - ws) / ((wf+w - wf) - (wf+s+w - wf+s))
Relative Density
Dr = (emax - e) / (emax - emin) × 100%
Dr = (1 / γd,min - 1 / Dd) / (1 / γd, min - 1 / γd, max) × 100%
Relative Compaction
Rc = γd / γd, max × 100%
Coefficient of Uniformity
Cu = D60 / D10
Coefficient of Curvature
D302 / (D10 × D60)
Sorting Coefficient
S0 = √(D75 / D25)
Suitability Number
Sn = 1.7√ (3 / D502 + 1 / D202 + 1 / D102)
Shrinkage Limit
SL = (m1 - m2)/m2 - ρw (v1 - v2) / m2
SL = e / Gs
m = mass
v = volume
ρw = density of water = 1 g/cm3
Shrinkage Ratio
SR = m2 / ρwv2
Relationship between Shrinkage Ratio and Shrinkage Limit
1 / Gs = 1 / SR - SLL
Liquidity Index
LI = (w - PL) / (LL - PL)
w = moisture content
PL = plastic limit
LL = liquid limit
Consistency Index
CI = (LL - w) / (LL - PL)
Plasticity Index
PI = LL - PL
Shrinkage Index
SI = PL - SL
Flow Index
FI = (w1 - w2) / log (N2 / N1)
w = moisture content
N = number of blows (Liquid Limit Test)
Toughness Index
TI = PI / FI
Activity of Clay
A = PI / %Clay
%Clay = F200 or Fraction of Soil passing Sieve No. 200
USDA Classification
Gravel: > 2 mm
Sand: 0.05 mm - 2.00 mm
Silt: 0.002 mm - 0.005 mm
Clay: < 0.002 mm
AASHTO Classification
Gravel: 2 mm - 76.2 mm
Sand: 0.075 mm - 2 mm
Silt and Clay: Classified as Fines → < 0.075 mm
Group Index (GI) = (F - 35) [0.2 + 0.005(LL - 40)] + 0.01(F - 15)(PI - 10)
F = % Fines
LL = Liquid Limit
PI = Plasticity Index
Zero Air Voids Unit Weight
γzav = γwGs / (1 + wGs)
Discharge Velocity
v = ki
k = coefficient of permeability
i = hydraulic gradient
Hydraulic Gradient
i = h / L
h = head of sample
L = length of sample
Seepage Velocity
vs = ki / n
Constant Head Permeability Test
k = VL / Aht
V = volume of water
L = length of sample
A = cross-sectional area of sample
h = head of sample
t = time of collection of water
Falling Head Permeability Test
k = aL / At × ln (h1 / h2)
a = cross-sectional area of standpipe
L = length of sample
A = cross-sectional area of sample
t = time of collection of water
h = head of sample before and after time was recorded
Unconfined Aquifer
k = Q ln(R1 / R2) / (π(h12 - h22))
Q = Discharge
R1 = Radial distance from the center of the well to observation point 1
R2 = Radial distance from the center of the well to observation point 2
H1 = Hydraulic Head of Groundwater at R1
H2 = Hydraulic Head of Groundwater at R2
Discharge
Q = kiA = Av
Confined Aquifer
k = Q ln(R1 / R2) / (2πt (h1 - h2))
Q = Discharge
R1 = Radial distance from the center of the well to observation point 1
R2 = Radial distance from the center of the well to observation point 2
H1 = Hydraulic Head of Groundwater at R1
H2 = Hydraulic Head of Groundwater at R2
t = saturated thickness of the confined aquifer
Equivalent Coefficient of Permeability
k|| = Σ(kh) / Σh
k⟂ = Σh / (Σ (h/k))
Transmissivity
T = kt
Seepage Force
j = i γw
Seepage Flow Rate (Flow Nets)
Q = kH Nf / Nd
Nf = number of flow channels
Nd = number of drops
Mnemonic: Kathryn, Hindi Na Forever Ni Daniel
Total Stress
σ = Σγh
Porewater Pressure
µ = γwhw
Effective Stress
σ’ = σ - µ
Capillary Height
hc = c / eD10
c = Capillary constant
e = void ratio
D10 = effective grain size of soil
Porewater pressure at capillary zone
µ = Sγwhz
S = degree of saturation
hz = height from GWT
Seepage: Head Loss per Drop
∆h = H / Nd
Seepage: Pressure Head
hp = H ± hz
Seepage: Total Head
Hj = H - ∆h(Nd)j
Seepage: Porewater Pressure
uj = (hp)j γw
Seepage: Uplift Pressure
pw = Σuj ∆xj
Primary Settlemnt: Normally Consolidated Soil
Sc = CcH / (1 + e) × log ((Po + ∆P) / Po)
Cc = Compression index
H = height to middle of clay layer
e = void ratio of clay
Po = Effective stress at middle of clay layer
∆P = Load applied above ground surface
Primary Settlement: Po + ∆P < Pc
Sc = CsH / (1 + e) × log ((Po + ∆P) / Po)
Cs = Swell index
H = height to middle of clay layer
e = void ratio of clay
Po = Effective stress at middle of clay layer
∆P = Load applied above ground surface
Primary Settlement: When Po + ∆P > Pc
Sc = CsH / (1 + e) × log (Pc / Po) + CcH / (1 + e) × log ((Po + ∆P) / Pc)
Cc = Compression index
Cs = Swell index
H = height to middle of clay layer
e = void ratio of clay
Po = Effective stress at middle of clay layer
∆P = Load applied above ground surface
Pc = Preconsolidation pressure
Swell Index (if not given)
Cs = Cc / 5
Compression Index
Cc = 0.009 (LL - 10)
Cc = (e1 - e2) / log (P2 / P1)
Overconsolidation Ratio
OCR = Pc / Po
Coefficient of Compressibility
av = (e1 - e2) / (P2 - P1)
Coefficient of Volume Compressibility
mv = av / (1 + eave)
Coefficient of Consolidation
Cv = Hdr2 Tv / t
Hdr = drainage height*
Tv = time factor for consolidation
t = time of consolidation
* Single drainage: Hdr = H; Double drainage: Hdr = H / 2
Hydraulic Conductivity
k = Cv mv γw

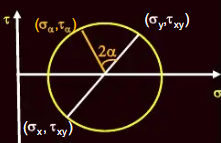
Mohr’s Circle for Stresses in Soil
C = ½ (σx + σy)
R = √ (½ (σx - σy)2 + τxy2)
σ1 = C + R; σ2 = C - R; τmax = R
C = center of circle
R = radius
σx and σy = stress along x-face and y-face
σ1 and σ2 = principal normal stresses
Sign Convention: (+) = Compression, CCW shear; (-) = Tension, CW Shear
Triaxial Test
σ3 + ∆σ = σ1
θ = 45° + Φ/2
σ3 = minimum principal stress (confining pressure)
∆σ = additional /deviator stress
σ1 = maximum principal stress
θ = angle of failure in shear
Φ = angle of internal friction
Lateral Earth Pressure: Compoments
Ps = kγ’h
Pc = 2c√k
Pq = kq
Pw = γwhw
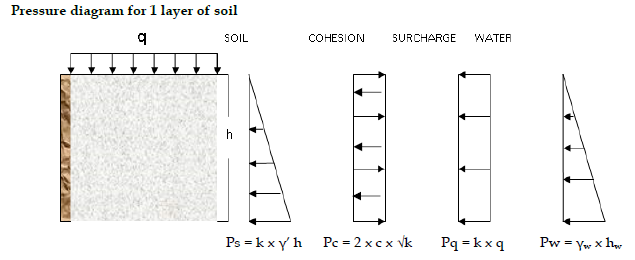
Lateral Earth Pressure: Active Soil Pressure
Active → away from soil
Active: (-) Pc
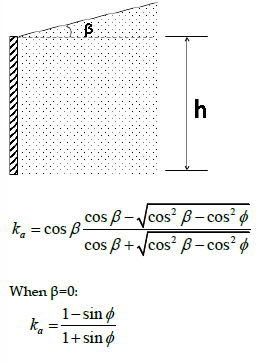
Lateral Earth Pressure: Passive Soil Pressure
Passive → push towards soil
Passive: (+) Pc
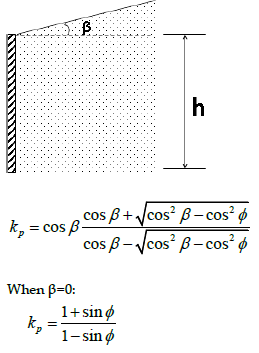
Lateral Earth Pressure: At-Rest Earth Pressure
ko = 1 - sinΦ
Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity: General Shear Failure
Circular Footing: qult = 1.3cNc + qNq + 0.3γBNγ
Square Footing: qult = 1.3cNc + qNq + 0.4γBNγ
Strip Footing: qult = cNc + qNq + 0.5γBNγ
Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity: Local Shear Failure
Circular Footing: qult = 1.3c’Nc + qNq’ + 0.3γBNγ’
Square Footing: qult = 1.3c’Nc + qNq’ + 0.4γBNγ’
Strip Footing: qult = c’Nc + qNq’ + 0.5γBNγ’
c’ = 2/3 × c
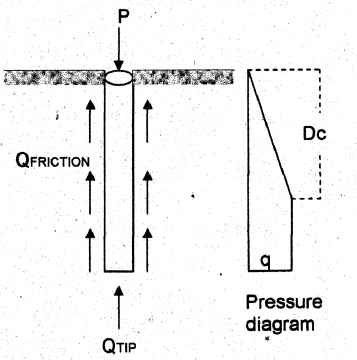
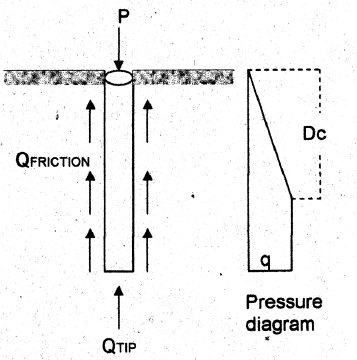
Piles in Sand
Qfriction = (Apressure diagram) k tanα P
Qtip = q Nq Atip
Qtotal = Qfriction + Qtip
Dc = Critical Depth = 10 x (size of pile) for loose sand; 20 x (size of pile) for dense sand
P = Perimeter of pile
k = coefficient of lateral pressure
Nq = soil bearing factor
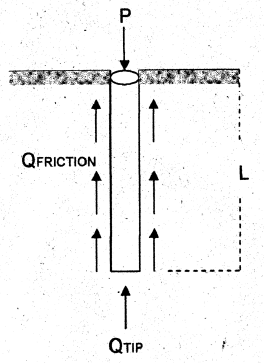
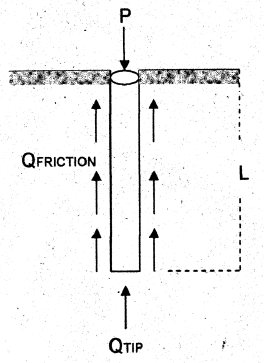
Piles in Clay
Qfriction = α Cu P L
Qtip = ctip Nc Atip
Qtotal = Qfriction + Qtip
α = friction factor = f / c
f = adhesion between pile and soil
c = cohesion
P = perimeter of pile
L = embedded length of pile
Nc = soil bearing factor

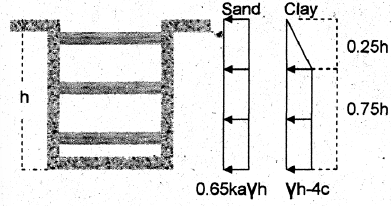
Braced Cuts
Soft to Medium Clay: γH / c > 4
Stiff Clay: γH / c < 4
S = Mmax / σall
Mmax = wL2 / 8 from shear/moment diagram
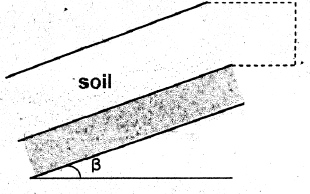
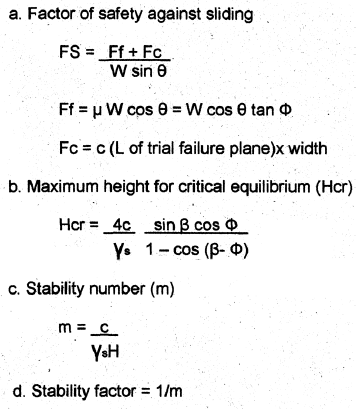
Infinite Slope: Factor of Safety
c = cohesion
ß = angle of backfill from horizontal
Φ = angle of internal friction
H = thickness of soil layer

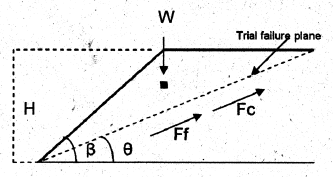
Fixed Slope
Ff = Friction Force
Fc = Cohesion Force
W = weight of soil above trial plane
c = cohesion
Φ = angle of internal friction