Exam 2 MICROECON
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Elastic
Consumers are RESPONSIVE to price changes. Represented as a HORIZONTAL line on graph.

Inelastic
Consumers are UNRESPONSIVE to price changes. Represented as a VERTICAL line on graph.
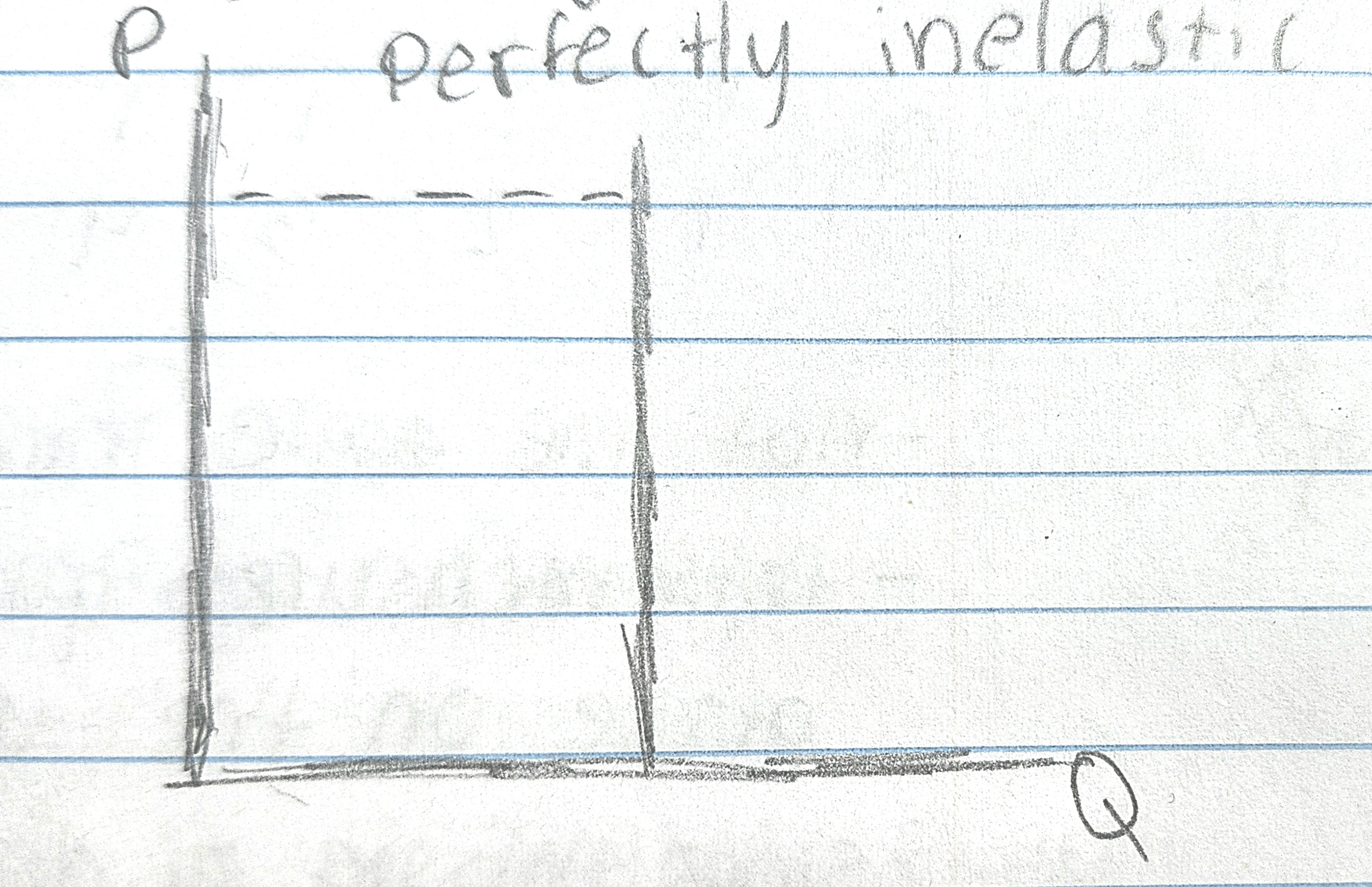

(ELASTIC) If there is an increase in price, how is quantity demanded affected?
Small increase in price, there will be a large reduction in quantity demanded that's perfectly ELASTIC.
(INELASTIC) If there is an increase in price, how is quantity demanded affected?
Consumers WILL buy even if the price goes up. Ex: medicine, people will buy no matter the price increases. This is INELASTIC demand.
Finding the percentage change formula.
The percentage change formula calculates the change in a value relative to its original value, expressed as a percentage. It is commonly used in economics to determine changes in price, quantity, or other variables.
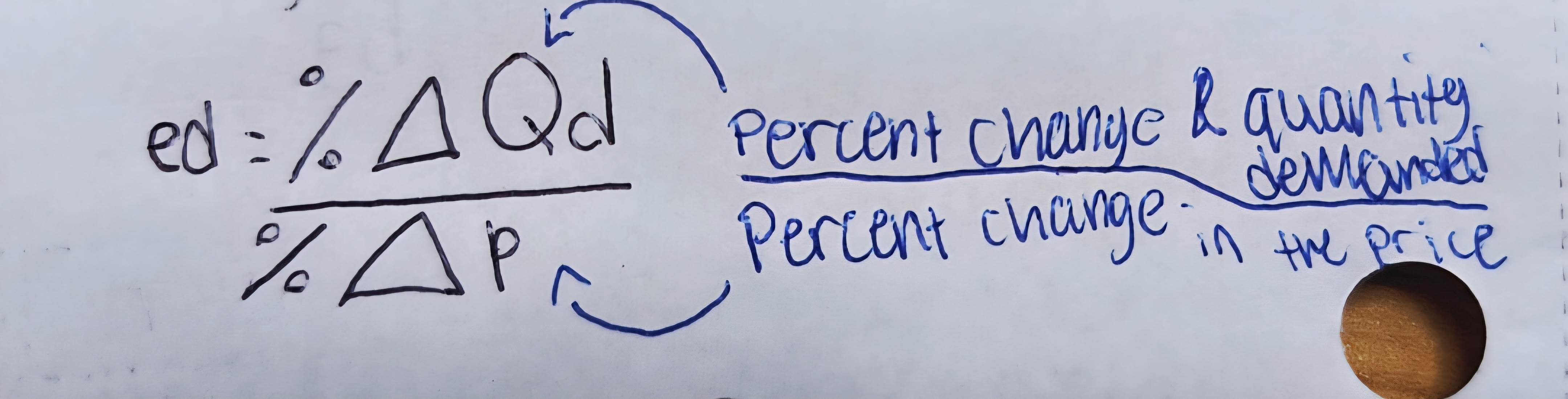
A number greater than 1 is _____?
A) Elastic
B) Unit Elastic
C) Inelastic
Elastic
A number equal to 1 is _____?
A) Elastic
B) Unit Elastic
C) Inelastic
Unit Elastic
A number between 0 and 1 is _____?
A) Elastic
B) Unit Elastic
C) Inelastic
Inelastic
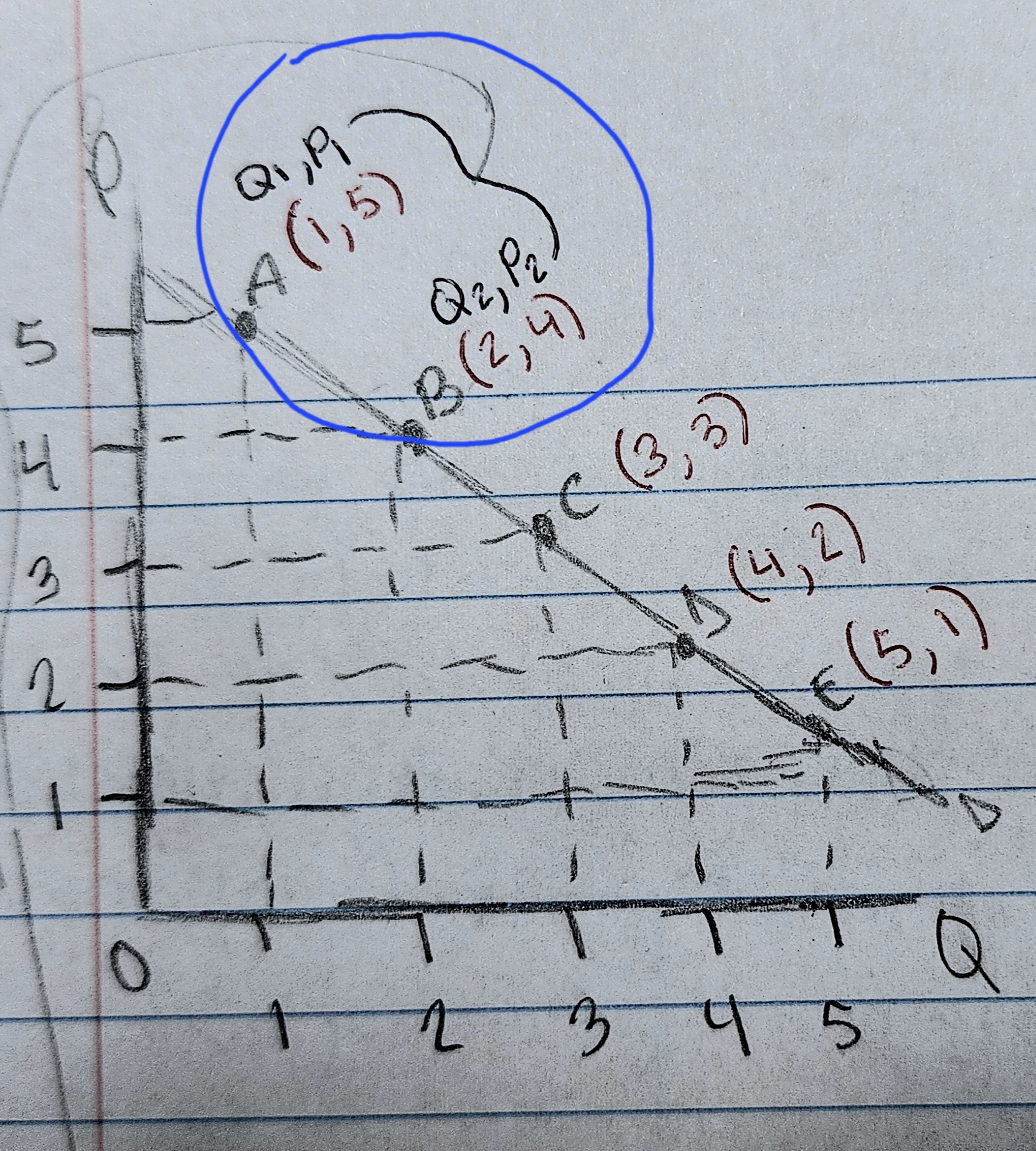
How would you solve this to find out if it's elastic or inelastic?
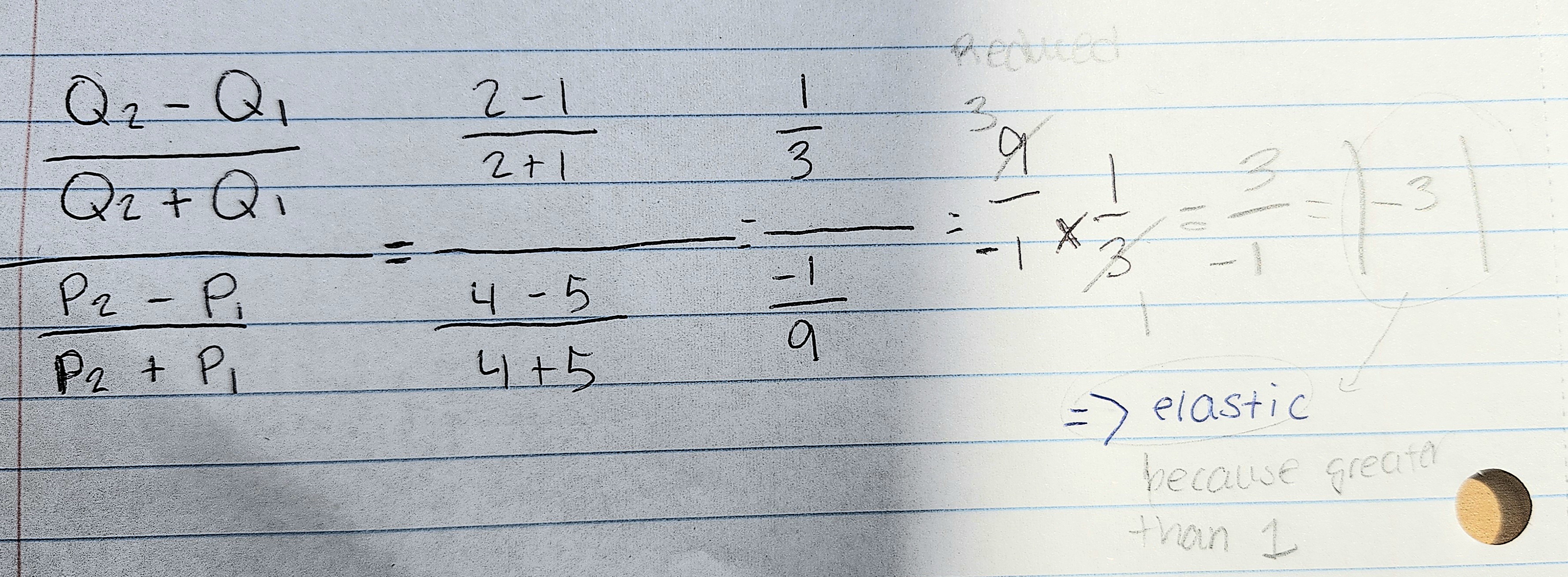
If you're in the inelastic range, an increase in price leads to an increase or decrease in TR (total revenue)?
increase in total revenue
If you're in the inelastic range, a decrease in price leads to an increase or decrease in TR (total revenue)?
decrease in total revenue
If you're in the elastic range, an increase in price leads to an increase or decrease in TR (total revenue)?
Decrease in total revenue
If you're in the elastic range, a decrease in price leads to an increase or decrease in TR (total revenue)?
Increase in total revenue
When unit elastic, TR is at it's what?
Unit Elastic = TR max
Income elasticity formula
% change in quantity demanded / % change in income
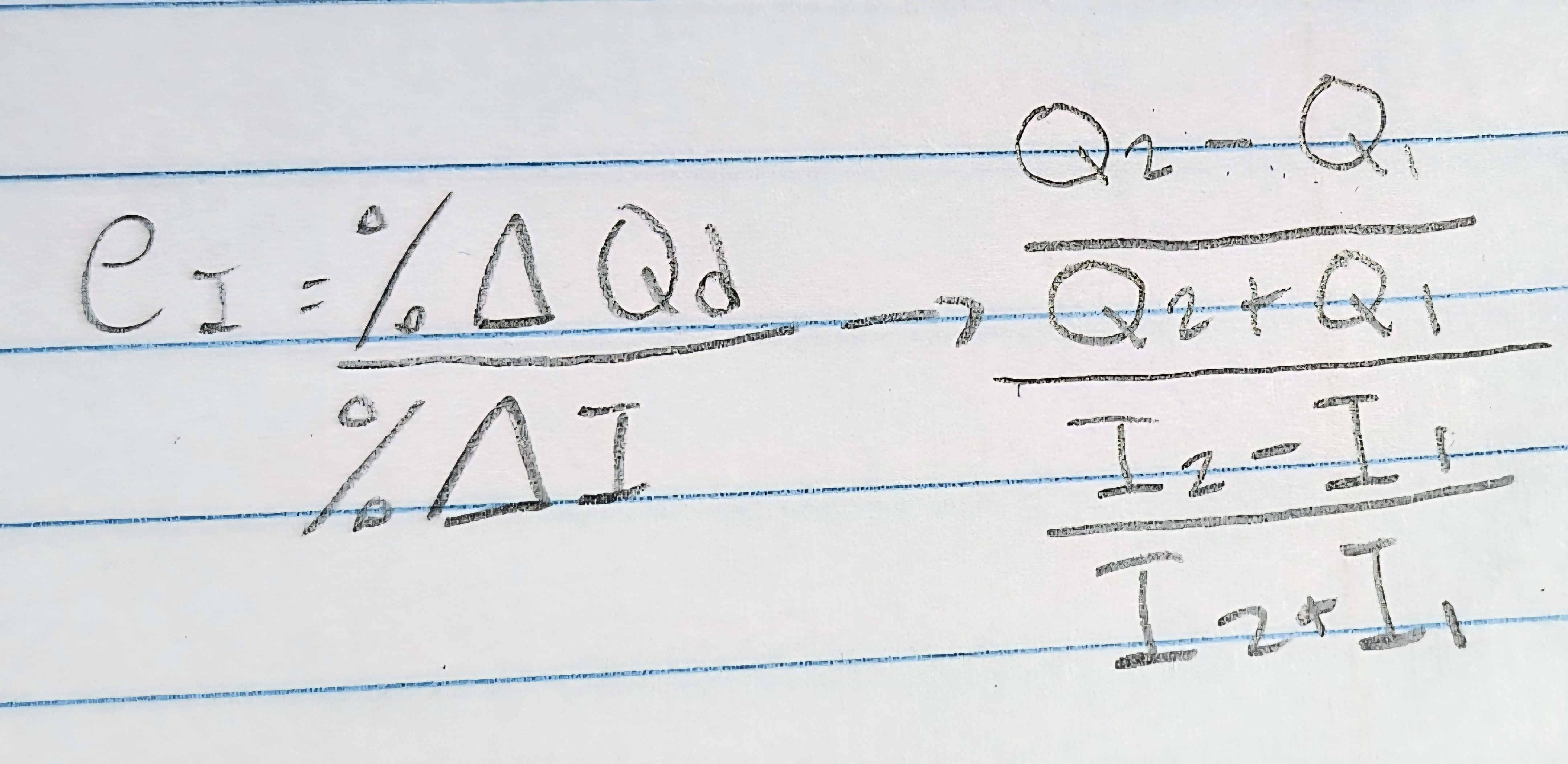
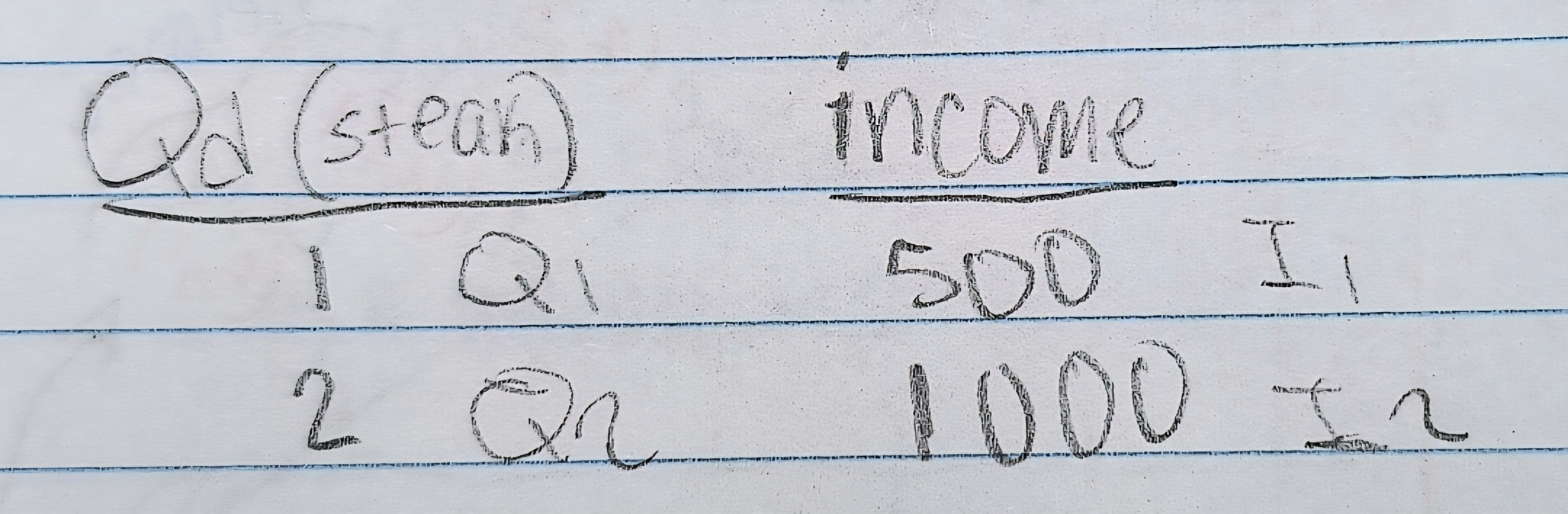
Use the income elasticity formula to know if it's a normal or an inferior good
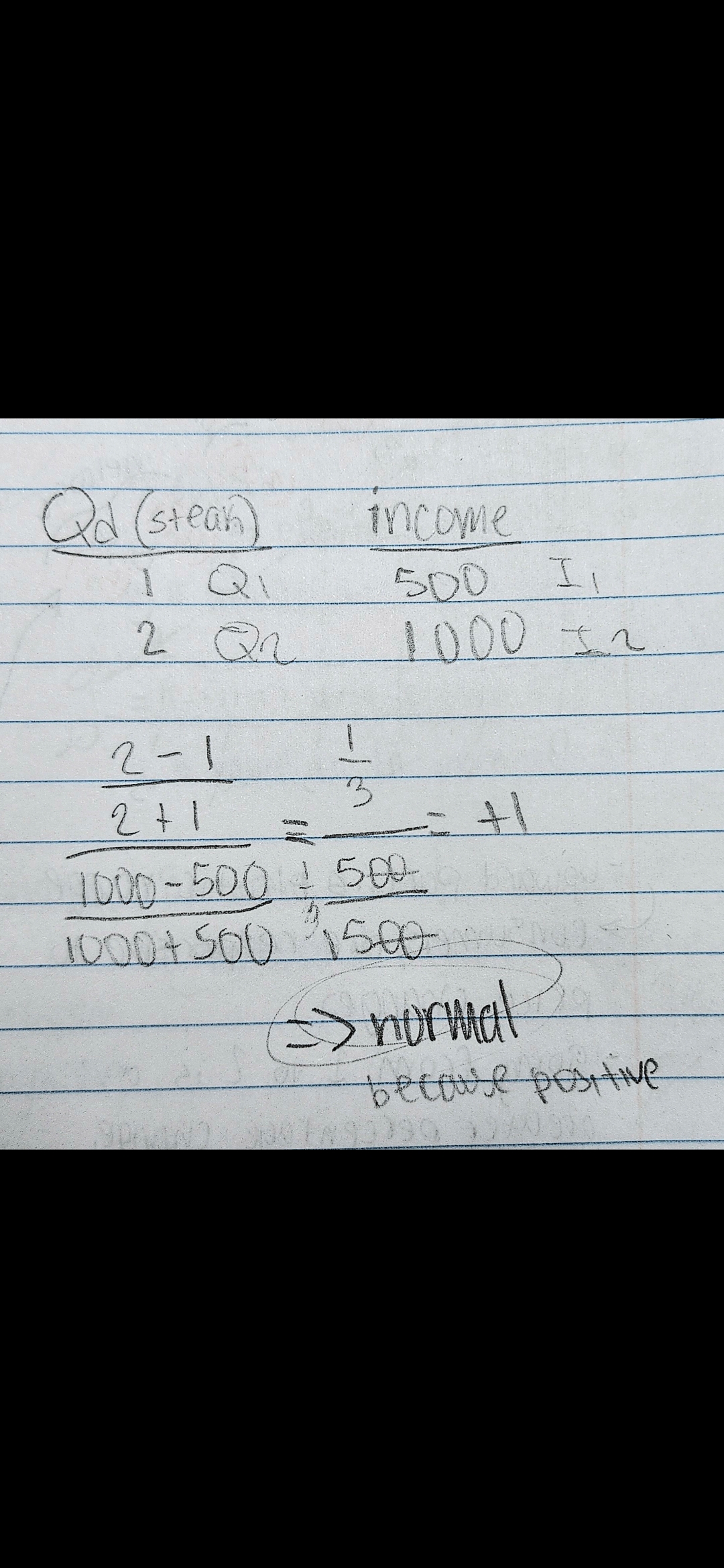
Positive is ____?
A) Normal good
B) Inferior good
Normal good
Negative is _____?
A) Normal good
B) inferior good
Inferior good
Cross price elasticity formula
Measures the responsiveness of demand for one good to the price change of another good.
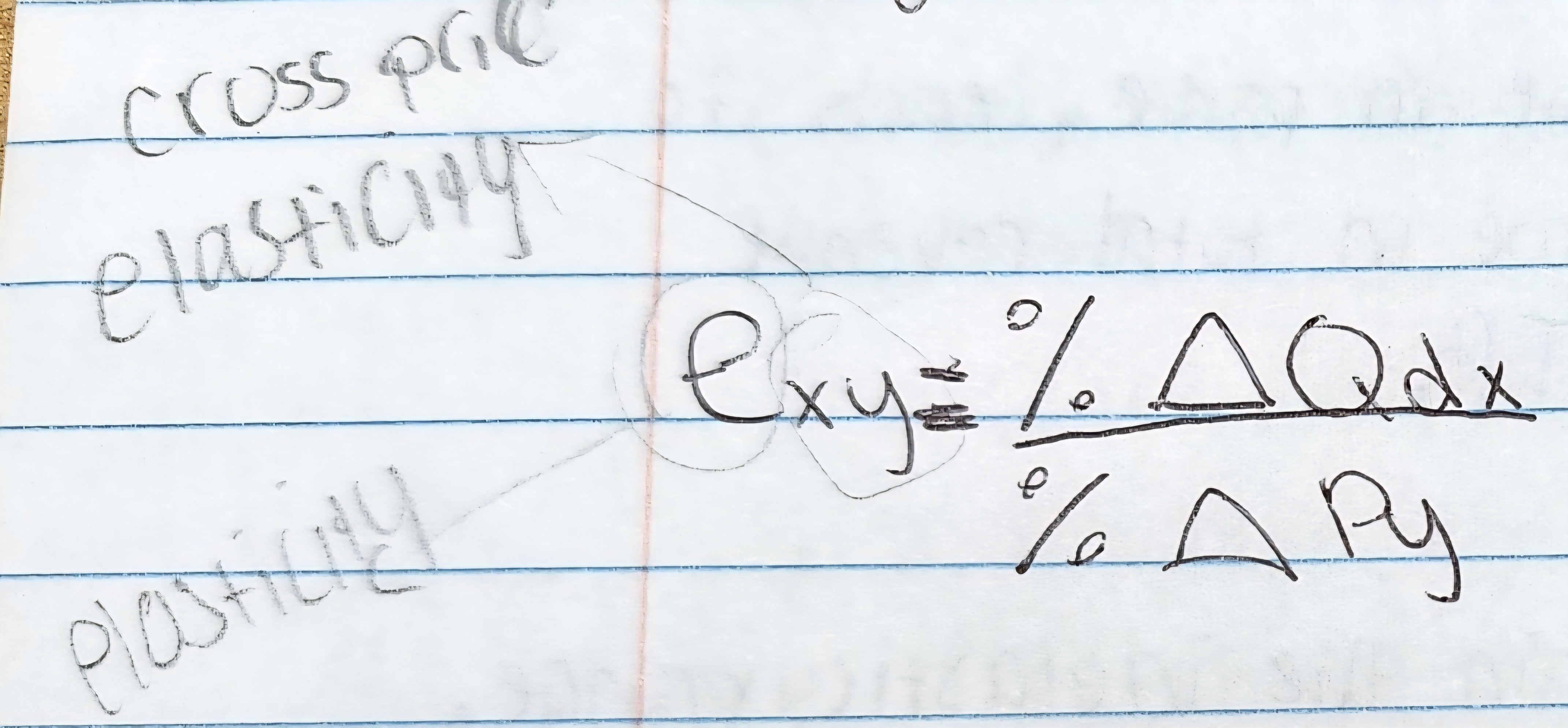
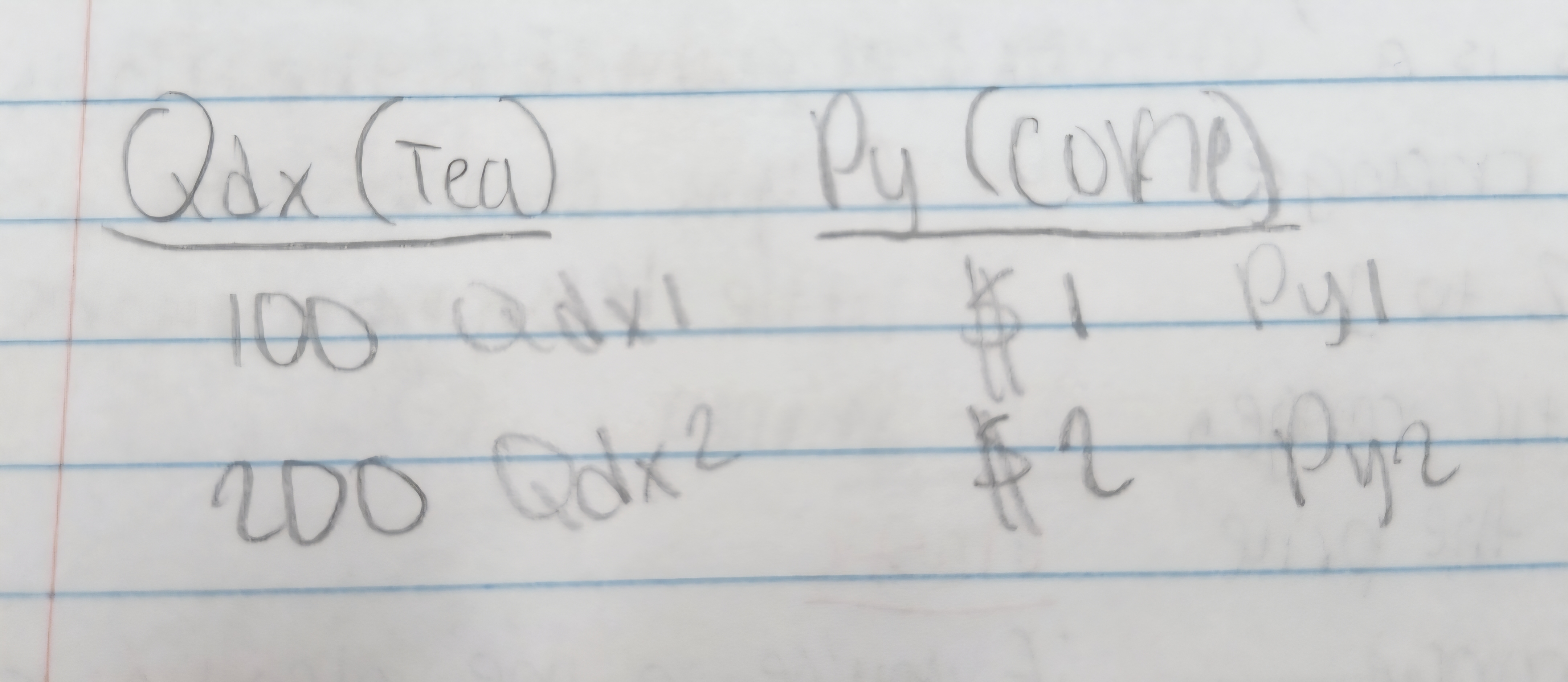
Use the cross price elasticity formula to know if it's a substitute or a complement
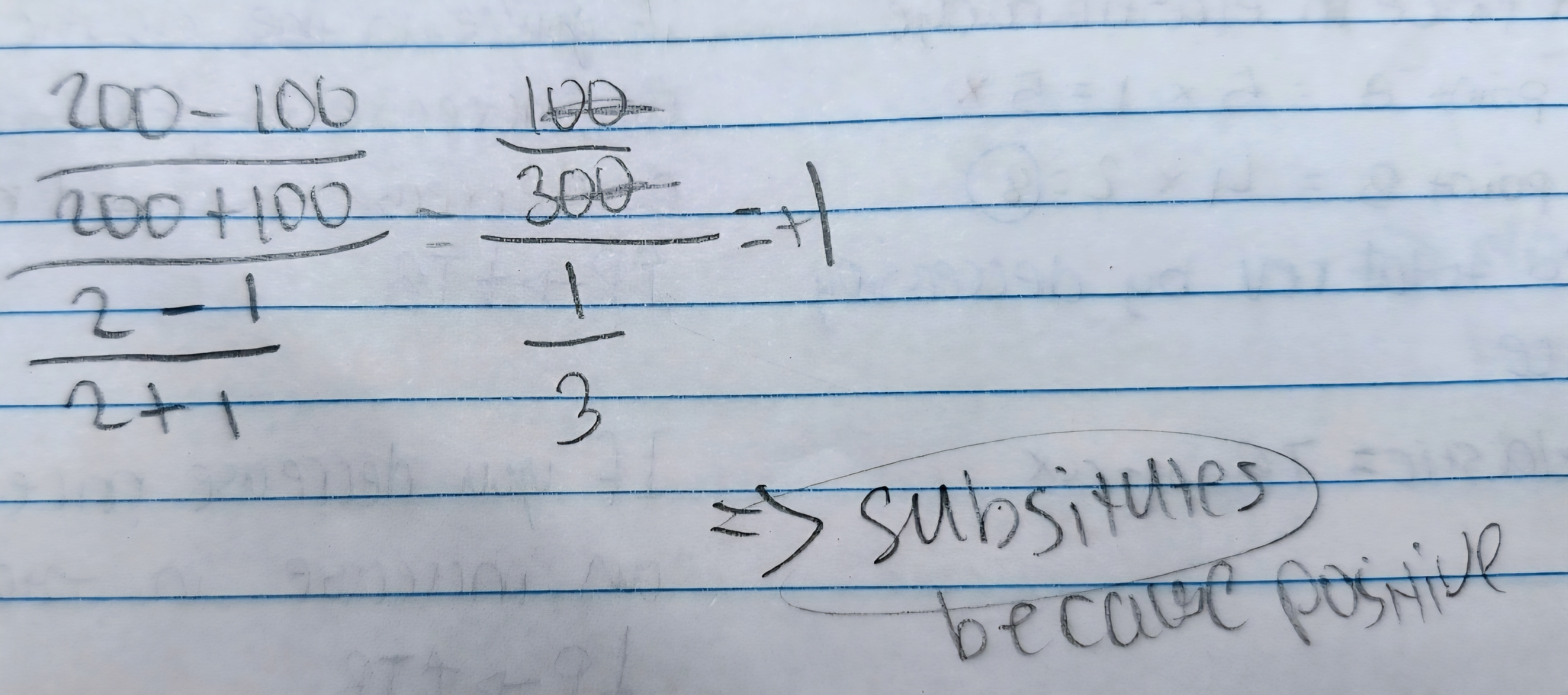
How to get MC (Marginal Cost)?
The change of TC (Total Cost) or the change of VC (Variable Cost)
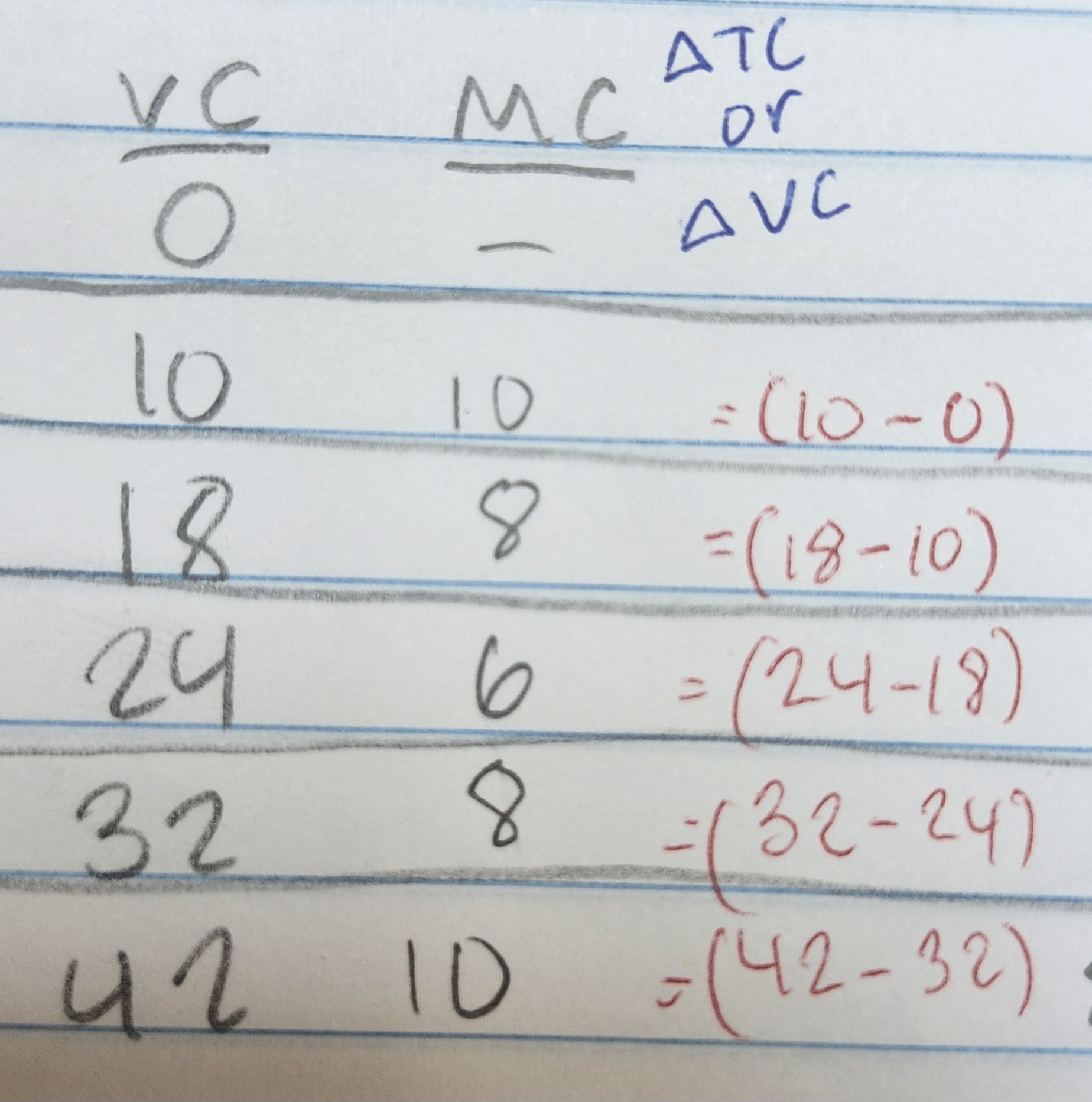
How to get the AVC?
VC/Q (variable cost divided by quantity)
How to get TC (total cost)?
FC+VC (Fixed Cost + Variable Cost)
How to get the AFC (Average Fixed Cost)?
FC/Q (Fixed Cost divided by quantity)
How to get the ATC (Average Total Cost)?
AFC+AVC (Average Fixed Cost + Average Variable Cost) or TC/Q (Total Cost divided by Quantity)
Two types of profit
Accounting Profit & Economic Profit
What is the difference between AP (accounting profit) and EP (economic profit)?
AP is the total revenue minus explicit costs, while EP accounts for both explicit and implicit costs, reflecting opportunity costs.
When asking a business owner how much they make, will they tell you their economic profit or their accounting profit?
Accounting Profit
Economic profit is a…
Signal to enter or exit, to see what they should do what their business.
Positive economic profit means to…
Enter
Negative economic profit means to…
Exit (this means you're not covering your opportunity cost, you can make more money doing something else)
Formula to find profit
Profit = TR - TC
Formula to get TR
TR = P × Q
How to get accounting profit?
TR (Total Revenue) - EC (Explicit Cost) = Accounting Profit
Scale deals with…
The size of the business
Economics of Scale
As you increase the size of your business, your cost per unit goes down
Constant returns to scale
As businesses get larger, it starts to level-off
Diseconomies of scale
When get too large, the cost of unit goes up. What causes this? As get larger there's distribution costs, redundant layers of middle management, diffculg to keep employee morality. When in this range, they want to cut thr size of the business to get into the more competitive range.