biology 10: exam review (chapters 1-11)
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
KSJDNKJSNDSKDL im done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
organism
any living things
botany
the study of plants
biology
the study of living things
herbaceous
nonwoody (green) stems
taproot
one main root (stores food)
angiosperms
flowering seed plants (half of population of plants)
annual
lives for one growing season
perennial
lives for several growing seasons
nitrogen cycle
the movement of nitrogen from air, into the soil, and back into the air
grass family
considered the most important group of plants on earth
deciduous
when trees lose their leaves
crown
leaves of the tree
bracts
special leaf that looks like a flower petal
samara
fruit consisting of a small dry seed with one or more wing-like structures attached to it
system
a group of structures designed to function together as a unit to perform a particular job for an organism
organ
a structure within a system that has a definite form and performs a definite function or functions for the system
shoot system
the part of the plant that is usually found above ground, holding the leaves toward the sun for the manufacturing of food and providing for the production of flowers, fruits, and seeds
root system
part of a plant that is ordinarily underground, anchoring the plant, and that functions in absorption of nutrients and storage of food
buds
contain developing leaf or stem structures
opposite
when two leaves grow from each node
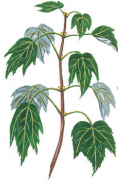
alternate
only one leaf grows from each node in an alternating pattern up the branch

whorled
when there are three or more leaves growing from each node

tissue
living material that is constructed in such a way as to perform a particular task for the organs of an organism
xylem
transports water and dissolved minerals upward from the roots to the leaves
phloem
transports food manufactured in the leaves downward
parallel venation
leaf venation in which the veins are usually parallel to each other along the length of the leaf; monocots
palmate
leaf venation in which two or more major veins extend outward from one point
pinnate
leaf venation in which the veins are in a branching pattern characterized by a midrib with smaller veins extending out from it
cell
the basic structural unit of all living things
cell wall
found around the outside of the cell membrane
cellulose
a complex carbohydrate made up of long chains of glucose (a simple sugar) molecules
chlorophyll
the green pigment that gives plants their color and enables them to capture the energy of light
autotrophs (producers)
organisms, such as green plants, that can make their own food
heterotrophs (consumers)
organisms that cannot make their own food and must obtain it from other organisms
photosynthesis
the process whereby a plant’s chloroplasts capture the radiant energy of light and convert it into the chemical energy of food
glucose
a simple sugar
produce seeds
fill in the blank
the primary function of flowers is to ________ ________ for reproduction
complete flower
has sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils
daylight
night
two answer fill in the blank
the chief factor controlling flowering in most plants is the length of _________ and ______
pollination
the process by which pollen reaches the pistil
nectar
a sweet-tasting, watery liquid produced by plants
fertilization
a sperm cell brought by a pollen grain fuses with the egg cell within the ovule
gametes
sperm cell and egg cell
radicle
will develop into the root system of the plant
plumule
a tiny shoot that will develop into the stem and leaves of the plant
dormancy
a period of inactivity
sexual reproduction
reproduction in which sperm and egg unite
primary growth
growth of a stem in length
xylem
wood; located toward the center of the stem
phloem
bark; located toward the outside of the stem
heartwood
inner portion of a woody stem, made of older xylem tubes that have become clogged and been sealed off
annual growth rings
distinct layer in the xylem of a woody stem formed by annual variation in the rate of secondary growth
rind
outer covering of a monocot stem
asexual reproduction
no union of sex cells
tropism
response in which an organism turns either toward or away from a stimulus
rhizomes
thick stems that grow horizontally under the ground providing food storage and a means of vegetative reproduction
thorns
long, sharp special stem that provides protection to a plant
root cap
cone-shaped structure that covers and protects the tip of a plant root
osmosis
one-way diffusion through a semipermeable membrane
sap stream
upward flow of water and minerals through the xylem
kind
group of similar organisms that are all descended from a single group of originally created organisms
kingdom
one of the main groups into which all organisms are divided in the linnaean system of classification
domain
any of the three larger groups into which kingdoms are placed
gymnosperms
plants that produce seeds but do not produce flowers
angiosperms
plants that reproduce by seeds formed in flowers
ginkgo
an oriental gymnosperm with two-lobed, fan shaped leaves
cycad
resemble palm trees; grow today only in certain tropical and subtropical regions
conifers
the very familiar cone-bearing gymnosperms
alternation of generations
the life cycle of a fern; involves both asexual (no union of sex cells) and sexual (union of sex cells) reproduction
rhizoids
tiny hair like threads; grow into the soil to absorb water and minerals
bryophytes
mosses and liverworts; literally means “mosslike plants”
algae
the smallest of the green, chlorophyll-containing organisms
yellow algae
yellow-green or golden-brown in color; unicellular, but they often live in colonies or clusters; dynamite
kelp
the largest of the brown algae
saprophytes
obtain their nutrition from dead organisms
parasite
an organism that lives on or in another living organism and derives its nutrition from that organism
lichen
fungus and an alga live together in a close relationship that combines the two organisms into a single unit
system
a group of structures that function together as a unit to perform a definite job for the body
eleven
how many functional body systems are there?
vestigial
describes organs that allegedly serve no useful purpose today
skeletal system
body system that provides support and rigidity and serves as the framework of the body
hyoid
u-shaped bone hidden in the upper neck, just above your larynx
sinuses
hollow spaces certain bones in the skull
cartilage
a tough, rubbery connective tissue that cushions the joints between bones
sternum
also called the breast-bone
humerus
largest bone of the arm
femur
largest bone in the body; composes the thigh; attaches to the pelvic girdle at the hip joint
tibia
shin bone; extends from the knee joint to the ankle
phalanges
correspond to those of the fingers and thumb
tendon
strong “cable” of tough fibers that attaches a muscle to a bone
flat bones
ribs and cranial bones; often have the job of protecting vital organs
red marrow
special tissue that manufactures red blood cells and white blood cells for the body’s circulatory and immune systems
ligament
tissue that joins bones to other bones
joints
places where bones join, or articulate
arthritis
inflammation of the joints
homeostasis
built-in maintenance of a stable internal environment
integumentary system
system of the body designed specifically for homeostasis
skin
organ that covers the outside of the body
epidermis
part of the skin that is exposed to the environment
melanin
the main pigment responsible for skin color