Introduction to Biochemistry: Cell Structure, Biomolecules, and Metabolic Processes
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
What is the idea of Vitalism in biochemistry?
Vitalism is the idea that substances and processes associated with living organisms do not behave according to the known laws of physics and chemistry.
What evidence supports the concept of Vitalism?
1) Only living things have a high degree of complexity. 2) Only living things extract, transform, and utilize energy from their environment. 3) Only living things are capable of self-assembly and self-replication.
Who was the first dead biochemist to challenge the fallacy that biochemicals can only be produced by living organisms?
Friedrich Wohler, who synthesized urea from ammonium cyanate in 1828.
What did Eduard Buchner demonstrate in 1897?
He showed that fermentation could occur in cell-free extracts, challenging the idea that living matter was necessary for biochemical processes.
What was Emil Fischer known for in biochemistry?
Emil Fischer contributed to the understanding of enzyme action and bioconversion of substances.
What did J.B. Sumner achieve in 1926?
He demonstrated that enzymes could be crystallized, proving they were proteins.
What significant discovery did Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty make in 1944?
They identified DNA as the molecule of heredity.
What is the central dogma of biology proposed by Crick in 1958?
The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
What are the main levels of organization of life in biochemistry?
1) Elements 2) Simple organic compounds (monomers) 3) Macromolecules (polymers) 4) Supramolecular structures 5) Organelles 6) Cells 7) Tissues 8) Organisms.
What does the term 'Biochemistry' refer to?
Biochemistry refers to the chemistry of living beings or the chemical basis of life.
What are the principal areas of biochemistry?
1) Structure and function of biological macromolecules 2) Metabolism (anabolic and catabolic processes) 3) Molecular genetics (replication and regulation of protein synthesis).
How does biochemistry impact medicine?
Medical biochemistry deals with the chemical basis of the human body and supports diagnosis, therapy, and research in clinical diseases.
What does clinical biochemistry focus on?
Clinical biochemistry focuses on the chemical processes related to clinical diseases and pathology.
What is bacterial biochemistry?
Bacterial biochemistry deals with the biochemical processes in microbes.
What is the significance of plant biochemistry?
Plant biochemistry studies the biochemical processes and compounds in plants.
What does animal biochemistry encompass?
Animal biochemistry deals with the biochemical processes in animals.
What is industrial biochemistry?
Industrial biochemistry involves the study of industrial products that involve microorganisms.
When did biochemistry emerge as a field?
Biochemistry emerged in the late 18th and early 19th century.
Who first introduced the term 'Biochemistry'?
The term 'Biochemistry' was first introduced by the German chemist Carl Neuberg in 1903.
What did Berzilus contribute to biochemistry?
Berzilus is known for his work on enzyme catalysis.
What discovery is associated with Louis Pasteur?
Louis Pasteur is known for his work on the fermentation process.
What is the TCA Cycle and who is associated with it?
The TCA Cycle, or Krebs Cycle, is a key metabolic pathway, and Hans Krebs is associated with its discovery.
What did Watson and Crick discover?
Watson and Crick discovered the double-stranded structure of DNA.
What is the role of ATP in biochemistry?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is crucial for energy transfer within cells.
What is the aim of studying biochemistry?
To understand the various biomolecules in the human body, their chemistry, structure, occurrence, functions, and the biochemical processes occurring at the molecular level.
What is Medical Biochemistry?
A branch of Biochemistry that deals with the biochemical constituents of the human body, their interactions in body cells, and their roles in maintaining normal health, growth, reproduction, and related diseases.
What are the key biochemical constituents studied in Medical Biochemistry?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, Minerals, and Water.
What is the primary role of carbohydrates in the human body?
They serve as the primary source of energy.
What is the secondary role of lipids in the human body?
They serve as a secondary source of energy.
What are the functions of proteins in the human body?
Proteins are structural and functional units that are essential for the survival of human beings.
What is the significance of vitamins in the human body?
Fat-soluble and water-soluble vitamins have specific functions that serve as accessory growth factors.
What role do minerals play in the human body?
Inorganic elements, both major and minor types, play important roles in building and functioning of human bodies.
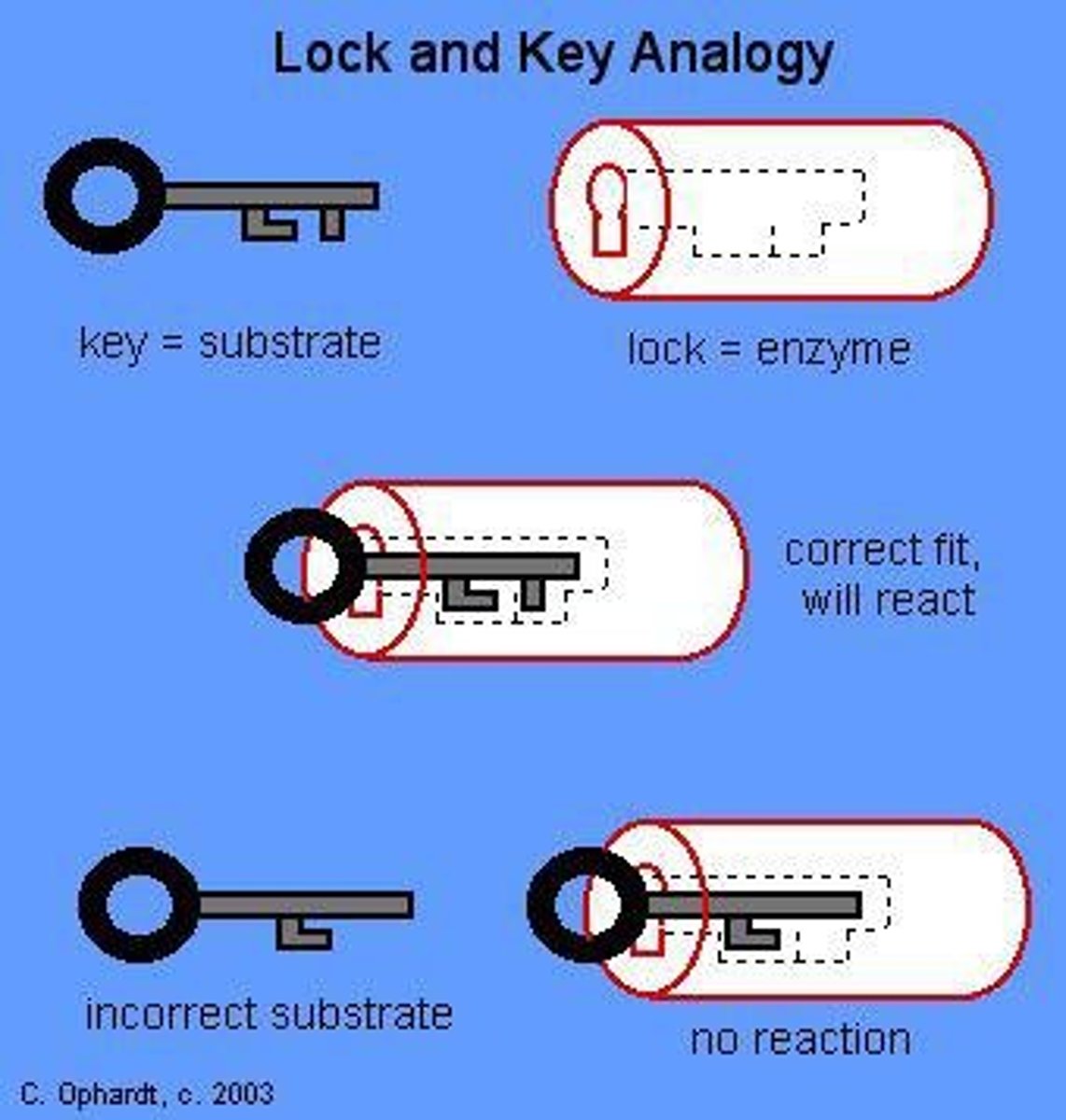
What are enzymes and their function in metabolism?
Enzymes are biomolecules that act as biocatalysts, catalyzing specific biochemical reactions in metabolic pathways.
What are hormones and their role in the human body?
Hormones are endocrine substances that act as chemical messengers, coordinating and regulating enzyme activities of metabolism.
What is the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms?
The cell.
Who invented the first compound microscope and when?
Robert Hooke in 1665.
What did Robert Hooke observe under the microscope?
He observed small box-like chambers in cork, which he called 'cells'.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
What are the three basic structures found in eukaryotic cells?
Nucleus, Cell Membrane, and Cytoplasm with organelles.
Where is the hereditary material (DNA) found in prokaryotic cells?
In the cytoplasm.
What is the size of an angstrom in nanometers?
1 angstrom = 0.1 nm.
What are the most abundant elements essential for all organisms?
Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), and Hydrogen (H).
What are trace elements essential for some organisms?
Vanadium (V), Chromium (Cr), Molybdenum (Mo), Boron (B), Aluminum (Al), Gallium (Ga), Tin (Sn), Silicon (Si), Arsenic (As), Selenium (Se), and Iodine (I).
What is the process by which monomers form polymers?
Through condensation.
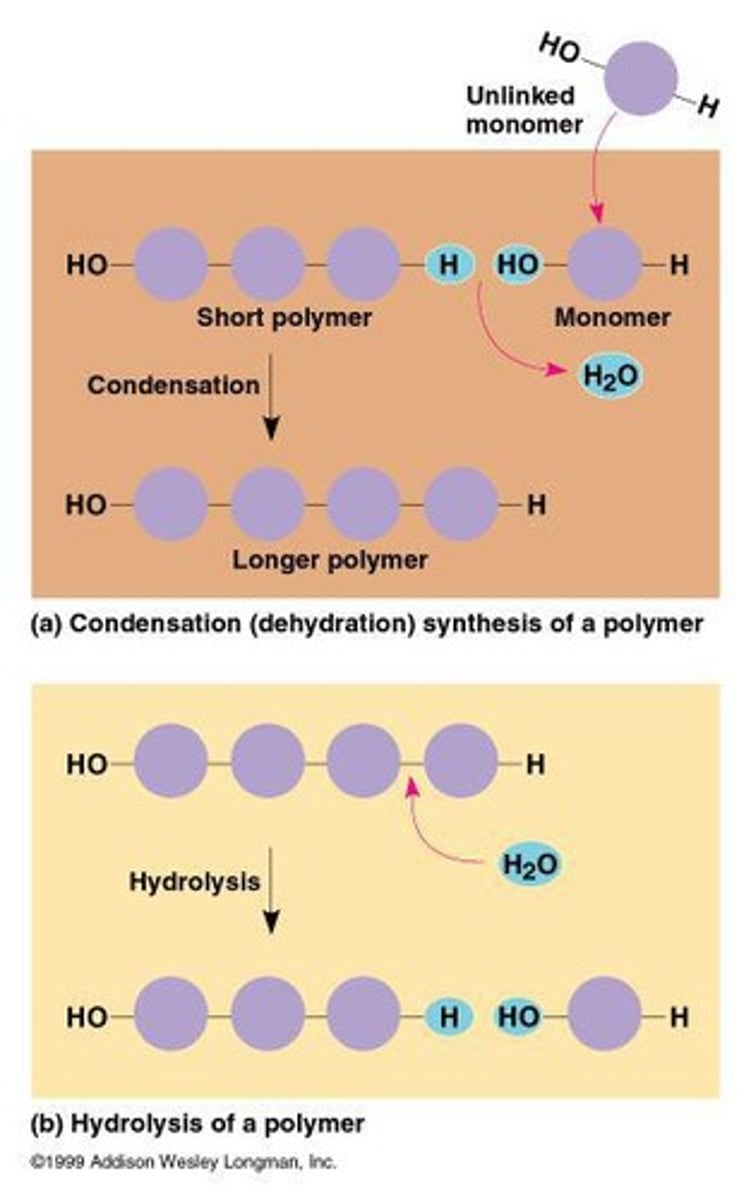
How are polymers broken down?
Through hydrolysis.
What is the definition of a cell?
The basic unit of all living things, composed of one or more cells.
What are the two main types of cells?
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic.
What is the function of ribosomes in prokaryotic cells?
To make proteins in their cytoplasm.
What is the nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells?
The area that contains the DNA.
What is the hereditary material found in prokaryotic cells?
DNA, found in the cytoplasm.
What type of organelles do prokaryotic cells lack?
Membrane-bound organelles.
What is the composition of the cell wall in prokaryotic cells?
Made up of peptidoglycan or murein.
What is the average size of prokaryotic cells?
0.5 - 10 nm in diameter.
What organisms are made of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotes, including animals, plants, fungi, and protista.
Where is the hereditary material found in eukaryotic cells?
Inside the membrane-bound nucleus.
What is the average size of eukaryotic cells?
10-100 nm in diameter.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
Provides a barrier and contains transport and signaling systems.
What surrounds the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
A double membrane.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Energy production through metabolism.
What is unique about mitochondria and chloroplasts?
Both contain their own DNA and are believed to have originated as captured bacteria.
What is the role of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
Synthesis of proteins for secretion or localization in membranes.
What does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) synthesize?
Lipids and detoxifies chemicals.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
Processes proteins and sends them to their final destinations.
What do lysosomes do?
Degrade proteins and membranes, and materials ingested by the cell.
What do vacuoles store in plant cells?
Water and storage materials.
What is the function of peroxisomes?
Produce and degrade hydrogen peroxide.
What is the composition of the plant cell wall?
Rigid structure in addition to the cell membrane.
What is the cytoplasm?
The liquid portion enclosed by the plasma membrane, housing organelles.
What is the cytoskeleton?
Arrays of protein filaments that give the cell its shape and basis for movement.
What percentage of a cell's content by weight is water?
50-95%.
What elements are most bio-molecules derived from?
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Phosphorus (P), and Sulfur (S).
What determines the chemical properties of organic bio-molecules?
Their functional groups.
What are the four major classes of biomolecules?
Lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids.
What is a monomer?
A basic building block of polymers.
What is a polymer?
A large molecule composed of repeating structural units (monomers).
What is a supramolecular structure?
A complex arrangement of multiple molecules held together by non-covalent interactions.
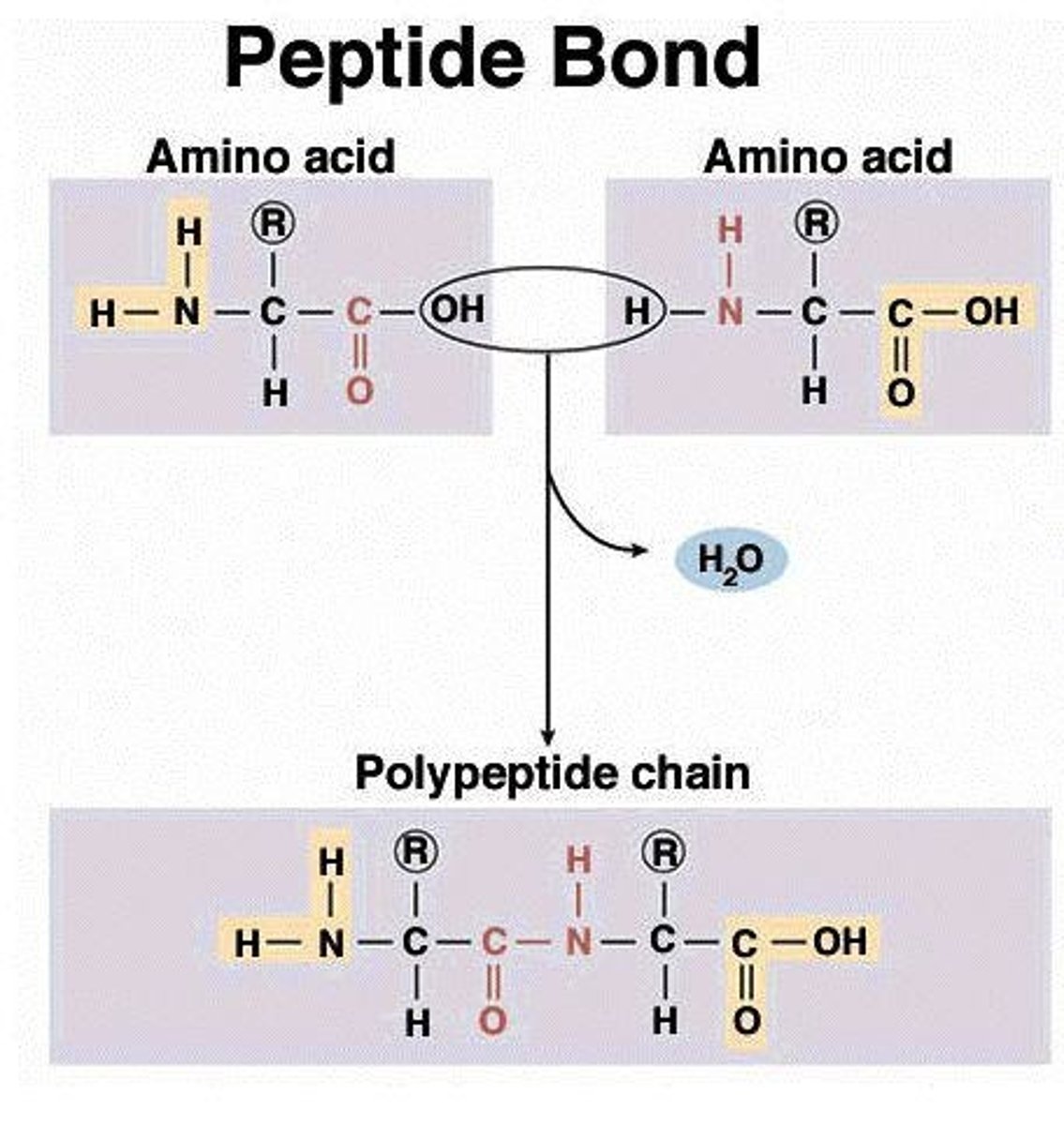
What are proteins made of?
Proteins are made of amino acids.
How many commonly occurring amino acids are there?
20
What functional groups are found in amino acids?
Amino group and carboxyl group.
What determines the chemical properties of amino acids?
The R group (side chains) of each amino acid.
What type of bond connects individual amino acids in proteins?
Peptide bond.
What are the functions of proteins?
Transport, structural support, enzymes, antibodies, and cell receptors.
What is the basic unit of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides.
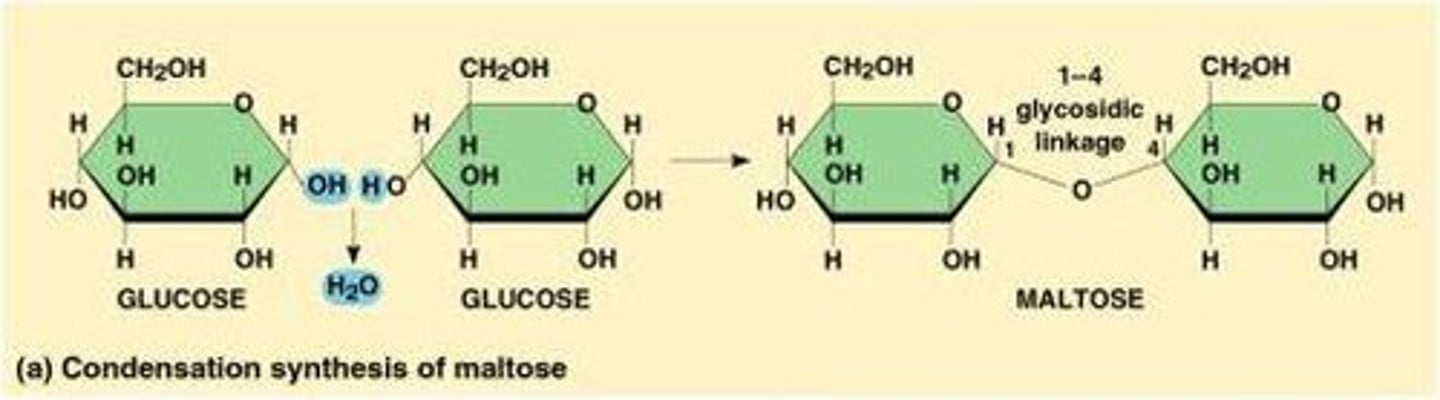
What are the larger molecules formed from monosaccharides?
Glycogen, plant starch, and cellulose.
What are the primary functions of carbohydrates?
Store energy, provide energy through metabolism, supply carbon for synthesis, and form structural components.
What are fatty acids?
Monocarboxylic acids containing an even number of carbon atoms.
What are the two types of fatty acids?
Saturated (single bonds) and unsaturated (double bonds).
What are some examples of lipids?
Triacylglycerol, steroids (cholesterol, sex hormones), and fat-soluble vitamins.
What are the functions of lipids?
Energy storage, membrane structure, insulation, and hormone synthesis.
What is metabolism?
The total sum of chemical reactions occurring in a living organism.
What are the two main pathways of metabolism?
Anabolism (biosynthetic pathways) and catabolism (degradation of fuel molecules).
What is the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions?
Enzymes catalyze all biochemical reactions.
What are some common types of biochemical reactions?
Nucleophilic substitution, elimination reactions, addition reactions, isomerization reactions, oxidation-reduction reactions, and hydrolysis reactions.
How do cells obtain energy?
By the oxidation of biomolecules.
What are the four components of cellular membranes?
Phospholipid bilayer, transmembrane proteins, interior protein network, and cell surface markers.
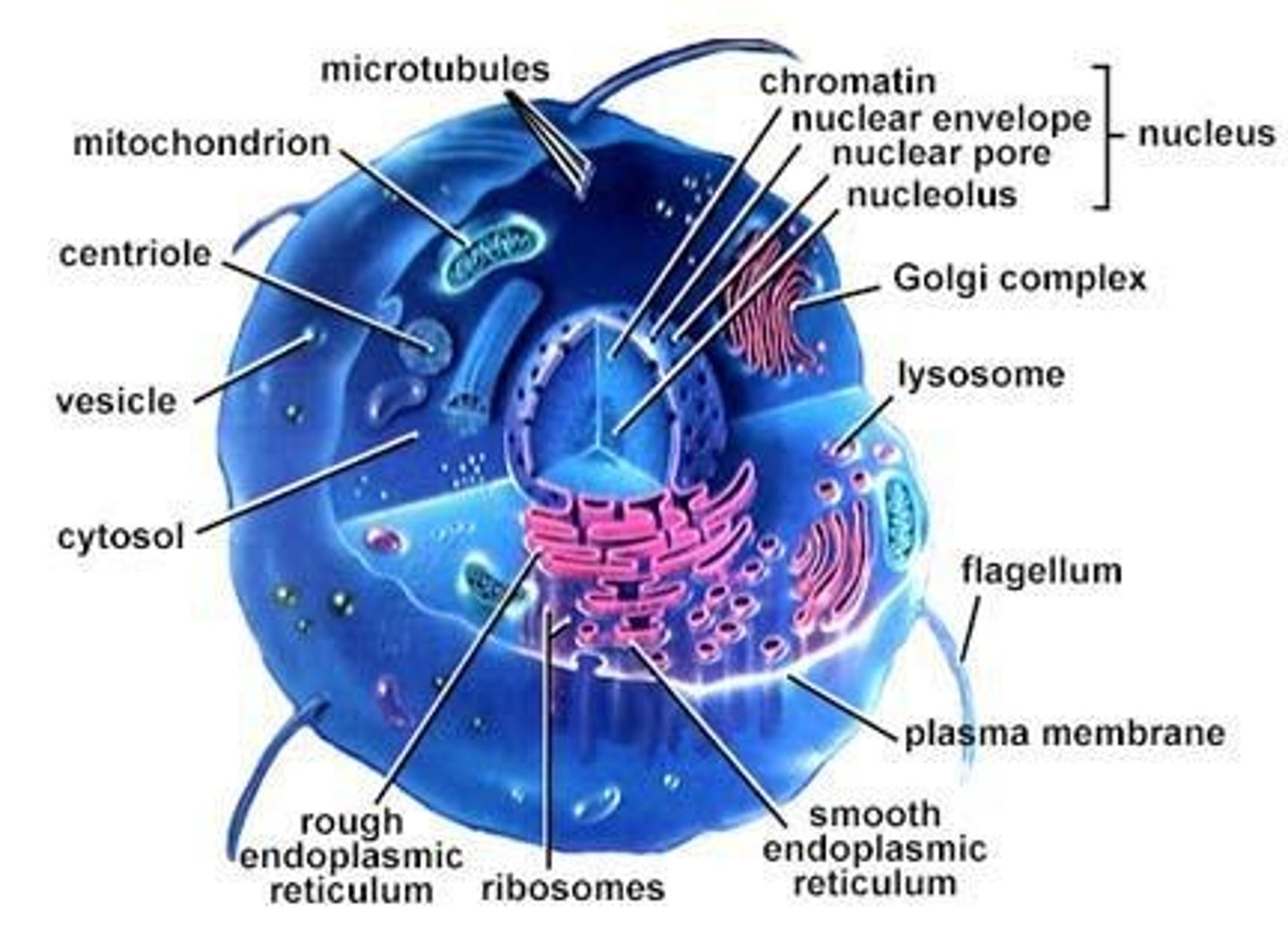
What is the function of the cell membrane?
It is selectively permeable, communicates with other cells, and controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
What is the significance of organized movement in cells?
It is essential for sustaining life and requires coordinated activities of cell components.
What happens if waste products are not removed from animal cells?
They can become toxic.