Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
1/25
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Know the chemical equation for photosynthesis.
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
carbon dioxide + water + energy --> glucose + oxygen
What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis?
light intensity, temperature, and water (and color of light from the gizmo)
Know the chemical equation for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ---> 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy
glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + energy
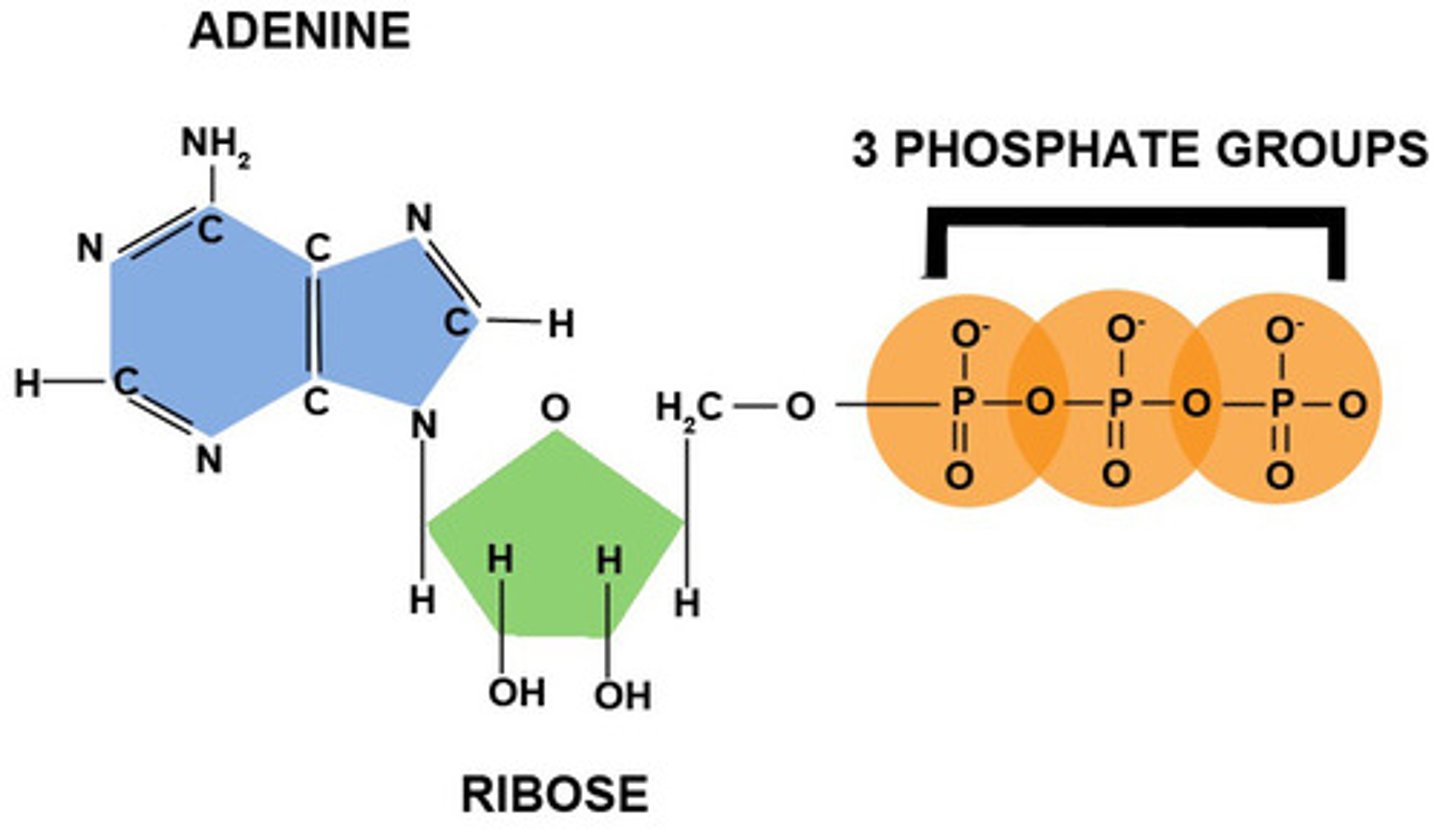
Be able to label an ATP molecule
Define autotroph and heterotroph
Autotroph: make their own food such as plants and bacteria
Heterotroph: get their food from eating plants and/or animals such as animals and fungus.
What do your cells need energy for?
Growth
Building new molecules
Movement
Responding to the environment
Maintaining homeostasis
How does ATP release energy?
Cells release energy by breaking bonds between phosphate groups.
What is the source of all energy on earth?
the sun
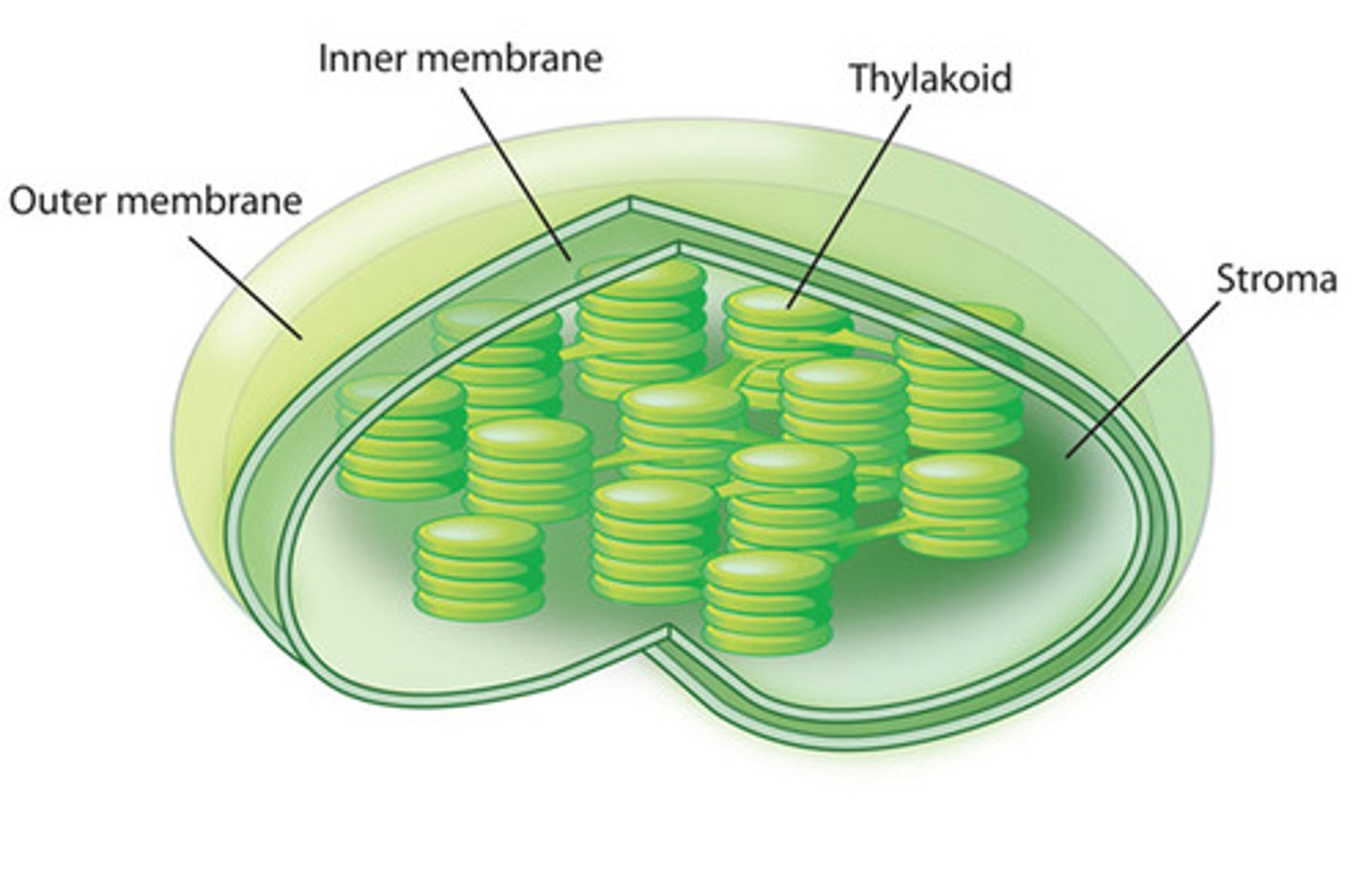
Label a chloroplast
Chlorophyll is in the thylakoid
Granum is a stack of thylakoids
Compare light and dark reactions.
Light: Take place in the thylakoids, need sunlight, the H2O and sunlight produce oxygen and turns ADP into ATP
Dark: takes place in the stroma, ATP combines with CO2 and H2O to produce glucose
What are stoma, where are they and why are they important to maintain homeostasis in a plant?
Stoma are the holes that let in CO2 and O2 out. They are on the underside of the leaf. They regulate CO2 and O2 and regulate water loss when they close.
Where are the guard cells and when do they open and close?
They are surrounding the stoma. They open in the day and normal temp. They close at night and when it gets too hot.
How do the reactants of photosynthesis enter a leaf?
Water goes in through the veins, CO2 comes in through the stoma. The leaves absorb the sunlight.
How do the products of photosynthesis leave a leaf?
Oxygen leaves through the stoma and glucose goes through the veins to the other parts of the plant.
How do the reactants of cellular respiration enter your body?
Oxygen enters through inhalation. Glucose enters through food/eating.
How do the products of cellular respiration leave your body?
CO2 leaves through exhalation. Water leaves through sweat and exhalation. Energy leaves through body heat.
Know the 3 stages of cellular respiration.
Glycolysis
Kerbs Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Which stage occurs in the cytoplasm?
glycolysis
Which occur in the mitochondria?
kerbs cycle and electron transport chain
Which stage does not require oxygen?
glycolysis
Which stage produces the most molecules of ATP?
electron transport chain- 32 ATP
Why do plant cells need mitochondria?
They need it for cellular respiration which creates the ATP energy
How many calories does 1g of fat give you?
9 calories
How many calories does 1g of protein and carbohydrates give you?
4 calories
What does yeast produce as a byproduct of alcoholic fermentation?
CO2 and alcohol.
When do our bodies use lactic acid fermentation? How is it different from cellular respiration?
We use it when you need a short burst of energy such as sprinting. It is different because it does not require oxygen, but cellular respiration does.