ANSC 625 - Important Bacterial Diseases
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Bacillus anthracis (rod bacteria, spore-forming)
What pathogen causes anthrax?
worldwide, enzootic in Texas and Minnisota but not seen east of Mississippi river
Where is anthrax mostly found?
wild and domestic cloven-hoofed herbivores
What animals get anthrax?
ingestion of spores from soil or contaminated feed/animal tissue, cutaneous wound contamination, inhalation
How is anthrax transmitted?
vegetative bacteria are released by carcass bloating, scavengers, or necropsy and sporulated when in contact with air
What happens to the anthrax bacteria after the animal dies?
septicemia with high fatality and hemorrhagic, swollen lymph nodes, necrosis
How does anthrax present in ruminants?
rapid death, staggering-> collapse, dyspnea, seizures
What are the signs of very acute anthrax?
fever, depression, respiratory and cardiac distress, staggering, seizures, death, bloody discharge from nose, mouth and anus, abortion, edematous swelling of ventral neck thorax and shoulders
What are the signs of acute anthrax?
chronic ill, septicemia with sudden death and oropharyngitis in pigs
How does anthrax present in humans, horses and pigs?
rigor mortis is absent or incomplete, blood fails to clot
In animals that have died from anthrax, what is characteristic?
optimal sample is cotton swab dipped in blood and dried to sporulate bacteria to then culture and PCR (warn lab)
How is anthrax diagnosed?
lymphatic tissue submitted for bacterial culture and PCR
How is anthrax diagnosed in animals that don't develop septic disease?
long-acting antibiotic, vaccination after treatment, cull
How is anthrax treated?
annual vaccination in endemic areas, rigid enforcement of quarantine, rapid detection and reporting of cases, isolation of sick animals and removal of well animals from contamination, treatment of asymptomatic animals, promt disposal of bodies, cleaning and disinfection of environment and equipment, insect repellents, decontaminate soils
How is anthrax controlled?
zoonotic, reportable
Anthrax is both ___ and ___
presents as primarily cutaneous disease following contact with carcasses, consuming raw/undercooked meat (GI), inhaling in labs, animal processing facilities, or bioterrorism, injected with contaminated needle
How do people get anthrax?
Anaplasma phagocytophilum (develops in cytoplasmic vacuoles of neutrophils)
What pathogen causes equine granulocytic anaplasmosis?
horses, burros, dogs, llamas, rodents
There are naturally recurring infections of equine granulocytic anaplasmosis in what animals?
vector borne through ixodes tick primarily
How is equine granulocytic anaplasmosis transmitted?
yes through tick bites only
Is equine granulocytic anaplasmosis zoonotic?
destruction of RBCs, WBCs, and platelets
What does equine granulocytic anaplasmosis cause?
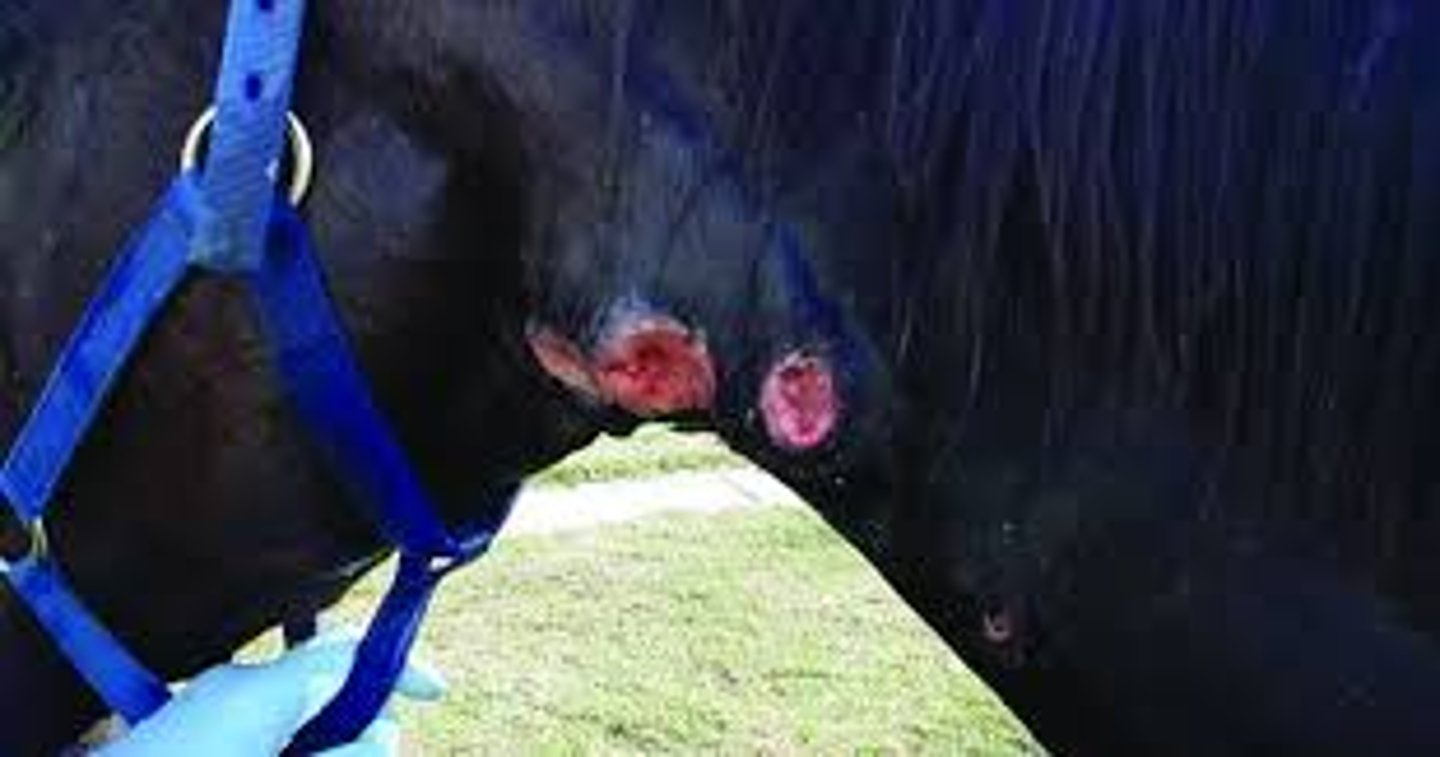
fever, depression, mild limb edema, ataxia, anorexia, petechiation, jaundice
What are the signs of equine granulocytic anaplasmosis?
no
Is there a carrier state for equine granulocytic anaplasmosis?
demonstration of characteristic intracelullar inclusion bodies in blood smear, PCR/serology on blood
How is equine granulocytic anaplasmosis diagnosed?
antibiotics
How is equine granulocytic anaplasmosis treated?
tick control
How is equine granulocytic anaplasmosis controlled?
no
Is there a vaccine for equine granulocytic anaplasmosis?
equine granulocytic anaplasmosis
This horse has been anorexia and has petechiation on membranes. What disease does it likely have?
Streptococcus equi
What pathogen causes strangles?
only equids, high morbidity low mortality
What animals develop strangles?
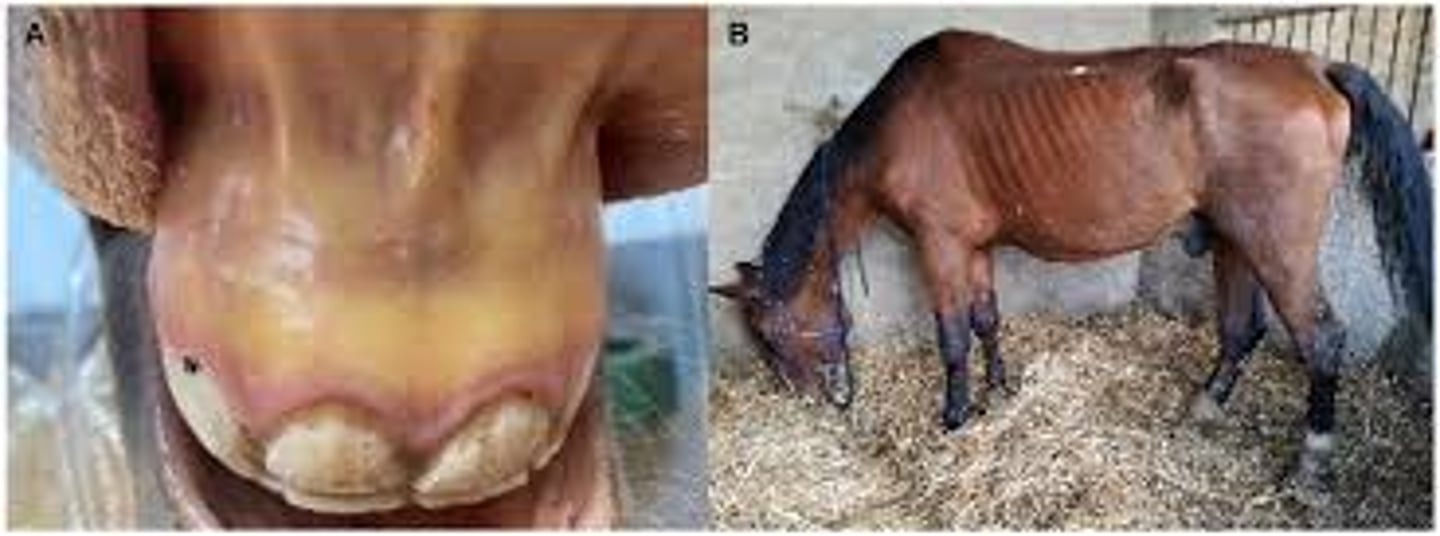
fever, nasal discharge/pus, depression, enlargement of lymph nodes on head, abscesses in lymph nodes, pneumonia
What are the signs of equine strangles?
enlargement of retropharyngeal lymph nodes can cause respiratory distress
Why is it called strangles?
direct and indirect contact with exudate (pus)
How is Streptococcus equi transmitted?
bacterial culture of abscesses or nasal discharge
How is strangles diagnosed?
local therapy of abscesses, anti-inflammatory meds, +/-antibiotics
How is strangles treated?
good biosecurity between horses, vaccination based on risk
How is strangles prevented?
strangles
This horse also has nasal discharge. What disease does it likely have?