Cell membrane and passive transport (AP BIO)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
The plasma membrane.......
regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also aids in the protection and support of the cell
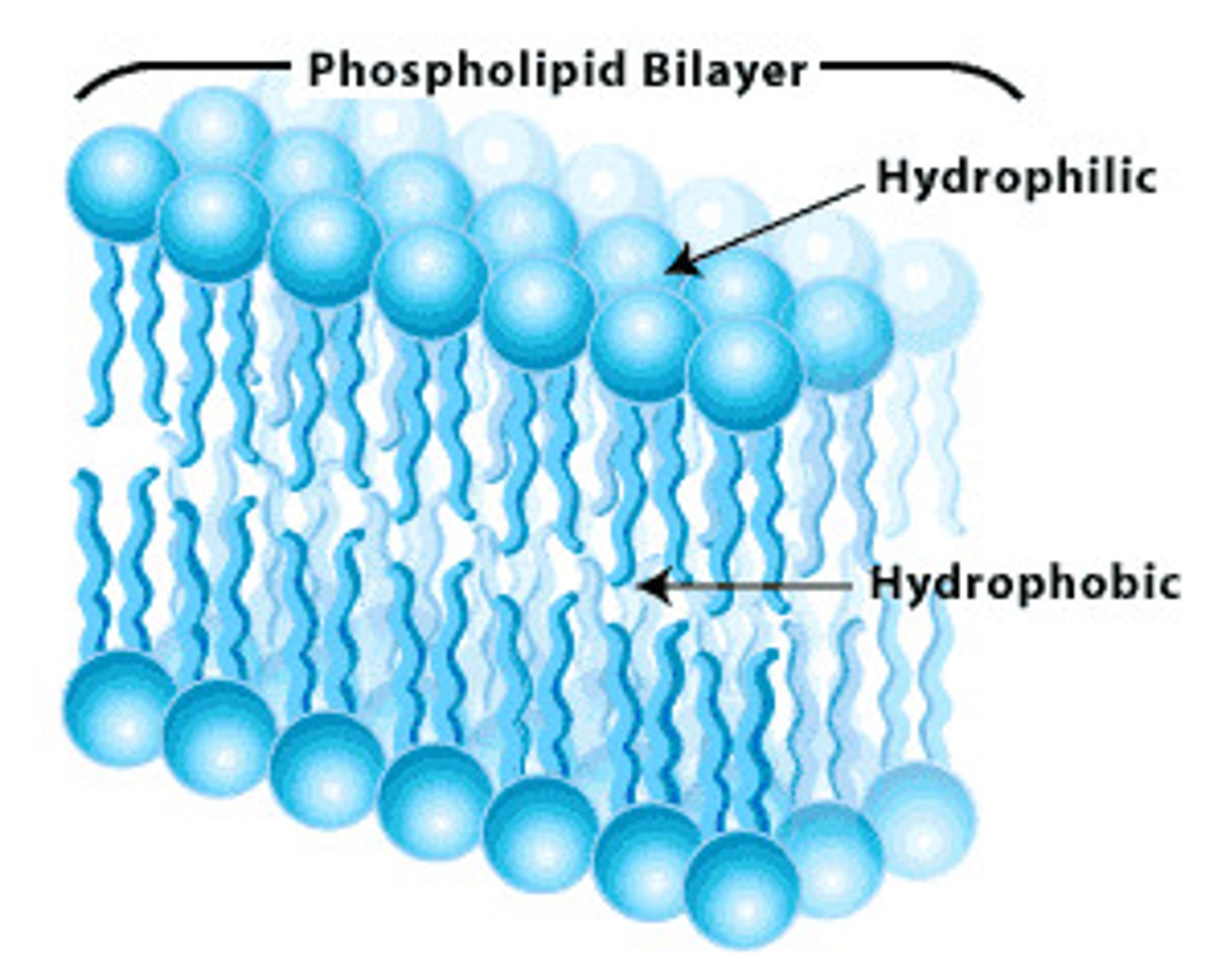
What is the lipid layer in the plasma membrane called?
phospholipid bilayer
The phospholipid bilayer has two different regions. What are the two regions and what is their relationship with water?
The head is hydrophilic (water loving) and the tail is hydrophobic (water fearing)
What molecules easily pass through the membrane?
non-polar and small particles
What are some examples of molecules that easily pass through the membrane?
CO2, O2, and steroids
What molecules have a hard time passing through the membrane?
Large polar molecules, one examples is glucose
What is the difference between polar and non-polar molecules?
Polar means there is unequal sharing of electrons, while nonpolar means equal sharing
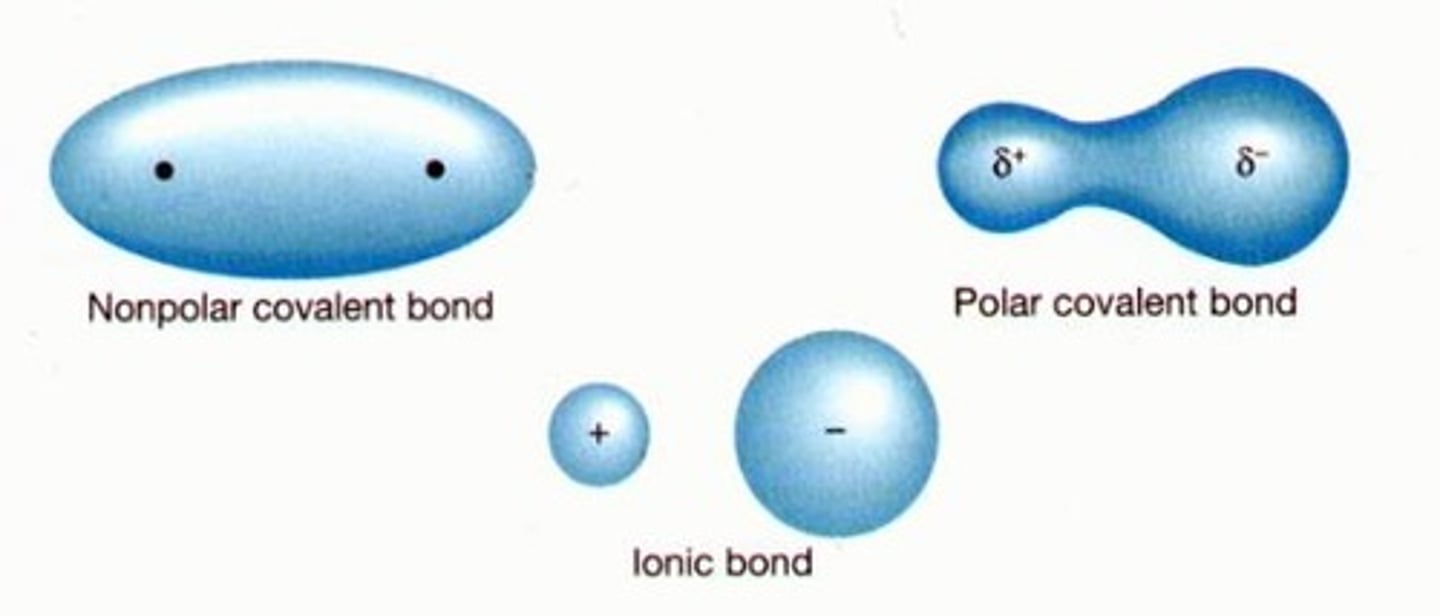
Why is it harder for polar molecules to pass through the membrane?
The membrane is mostly made up of hydrophobic tails so certain molecules that are polar will be repelled
What is the function of cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
Maintaining the structural integrity and regulating the fluidity of cell membranes
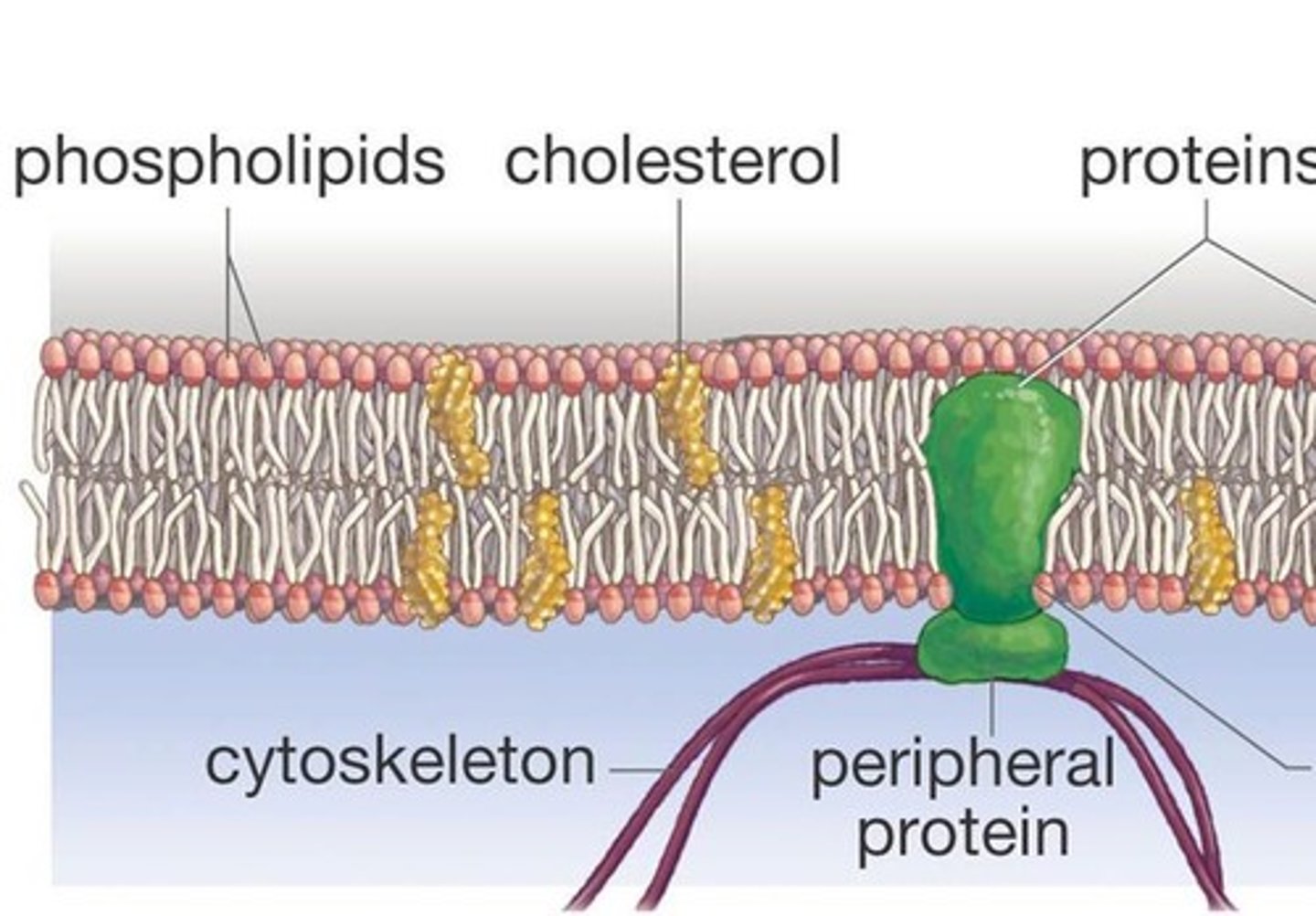
What do proteins do in the cell membrane?
help materials cross the membrane
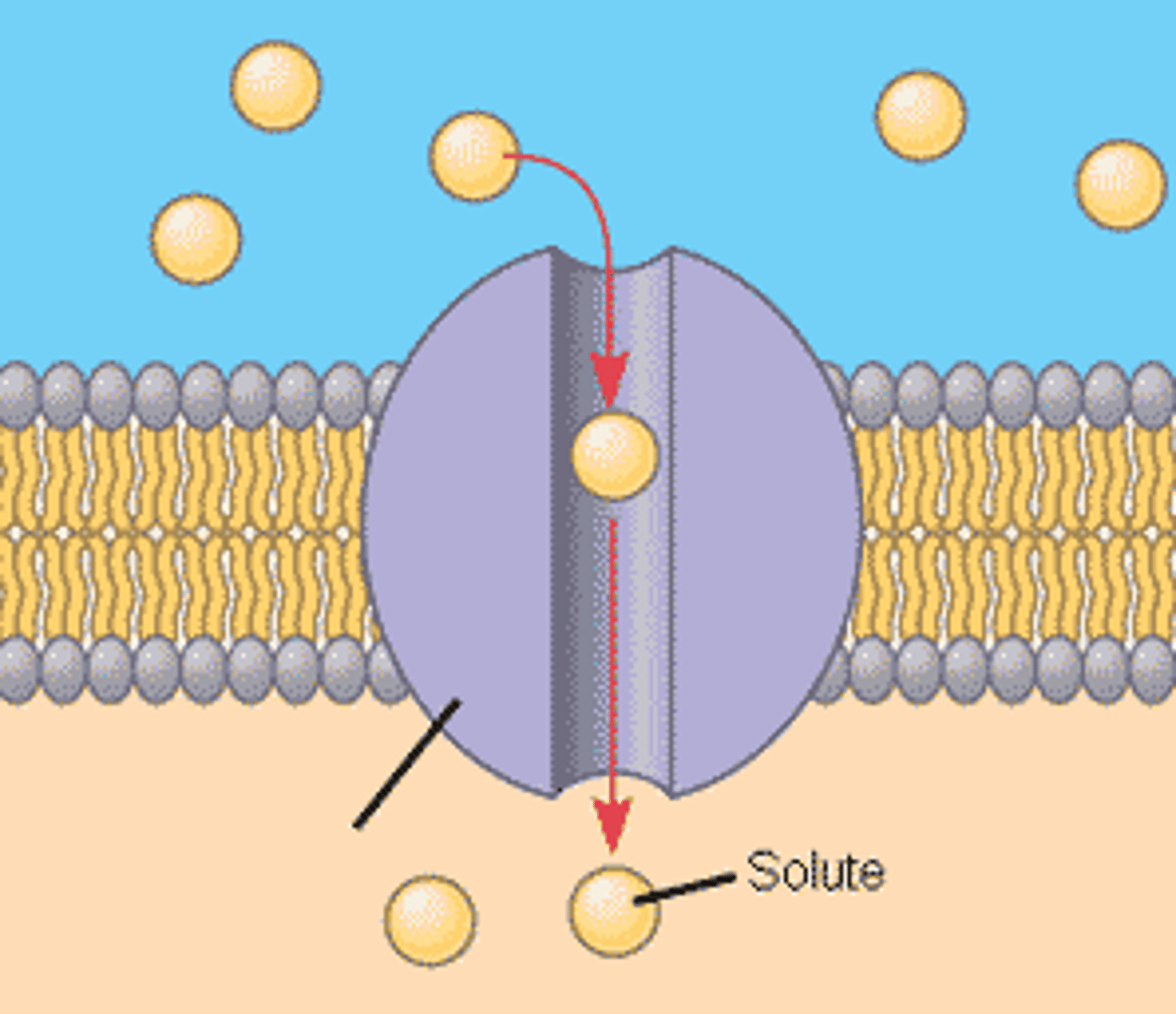
What do carbohydrates do in the cell membrane?
They help cells recognize eachother
Peripheral proteins
They are attached to the membrane but are not embedded in it. It helps with support, communication, enzymes, and molecule transfer in the cell
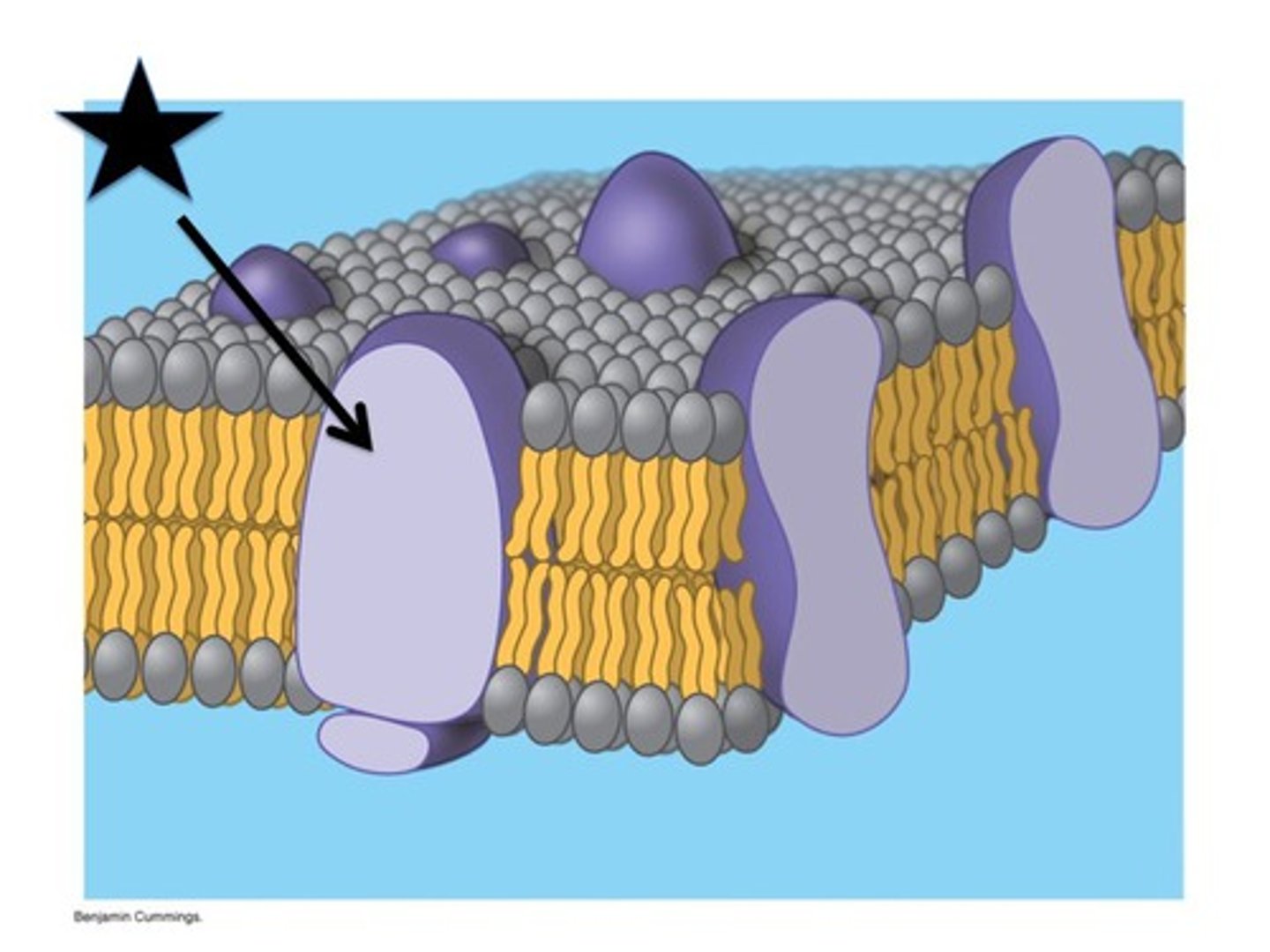
Integral proteins
These proteins are permanently embedded in the membrane and its functions include channeling or transporting molecules across the membrane
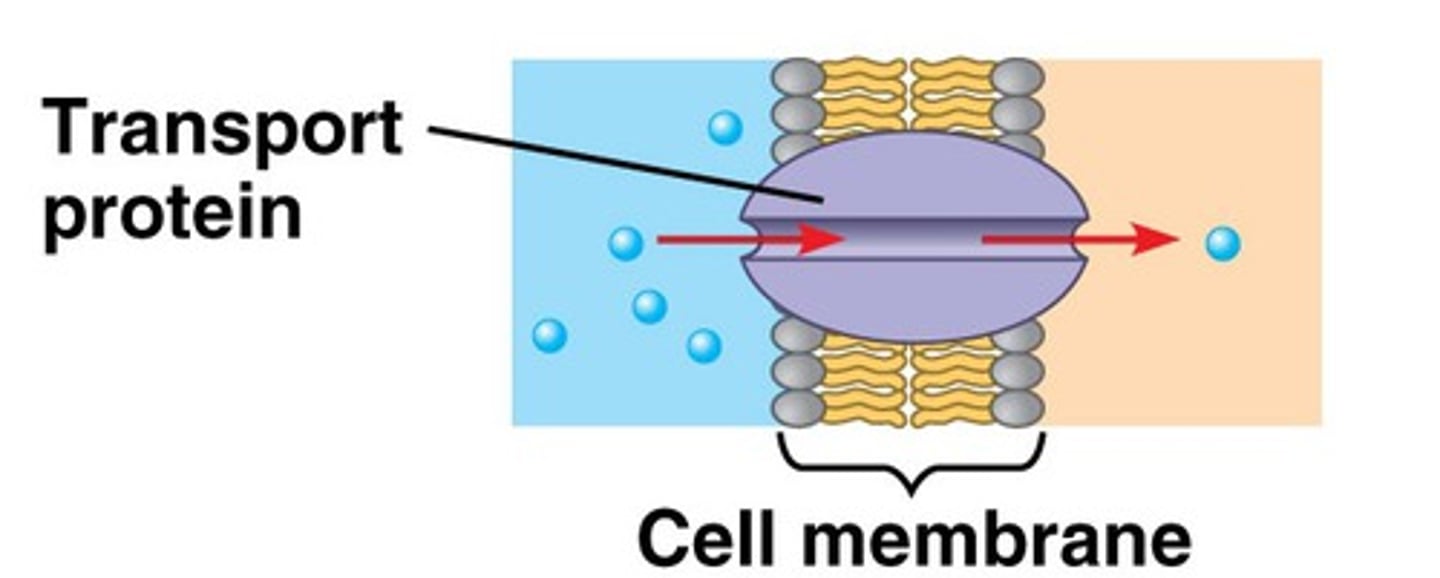
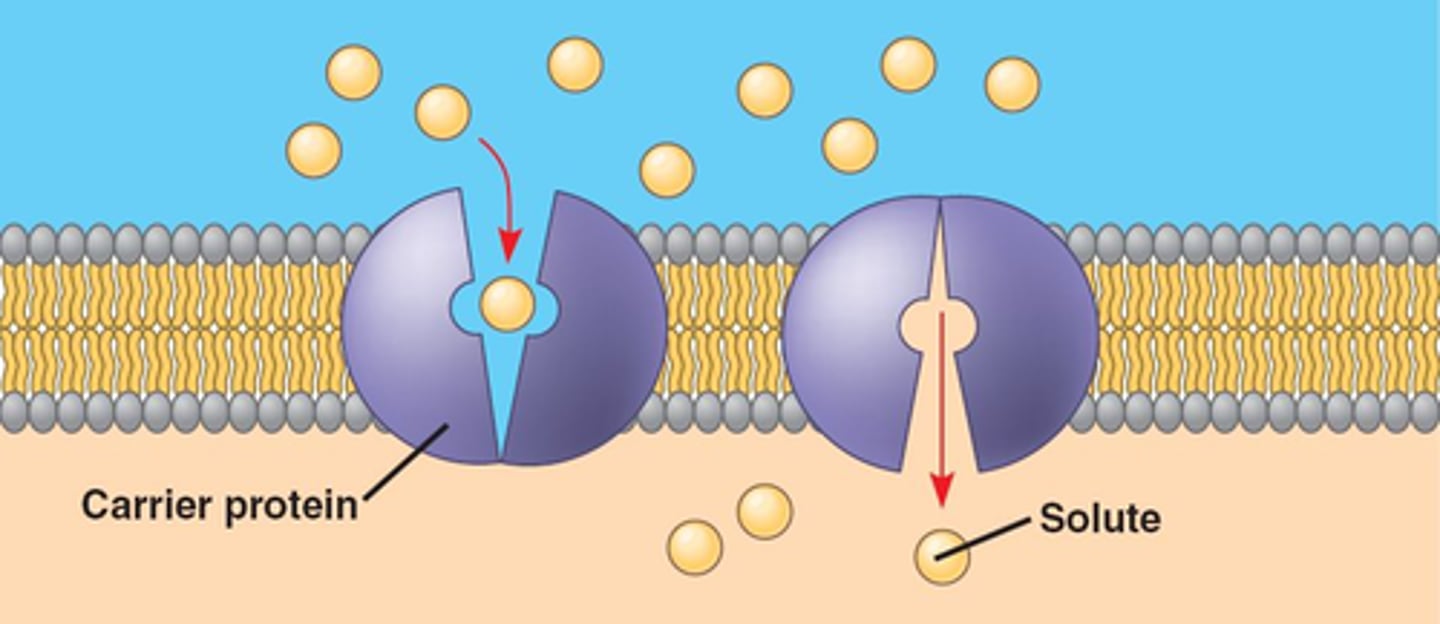
Transport proteins
allow passage of hydrophilic substances across the membrane
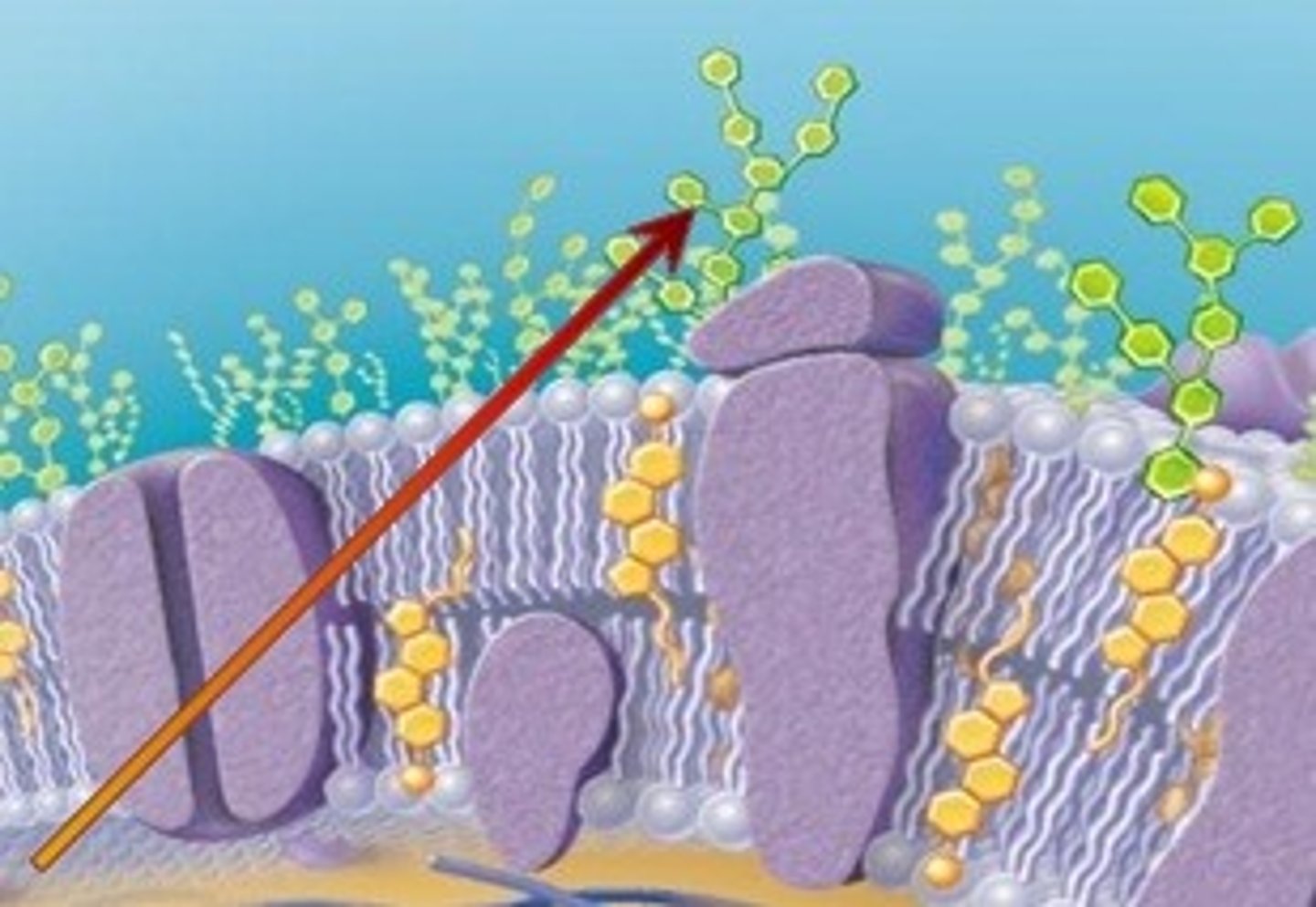
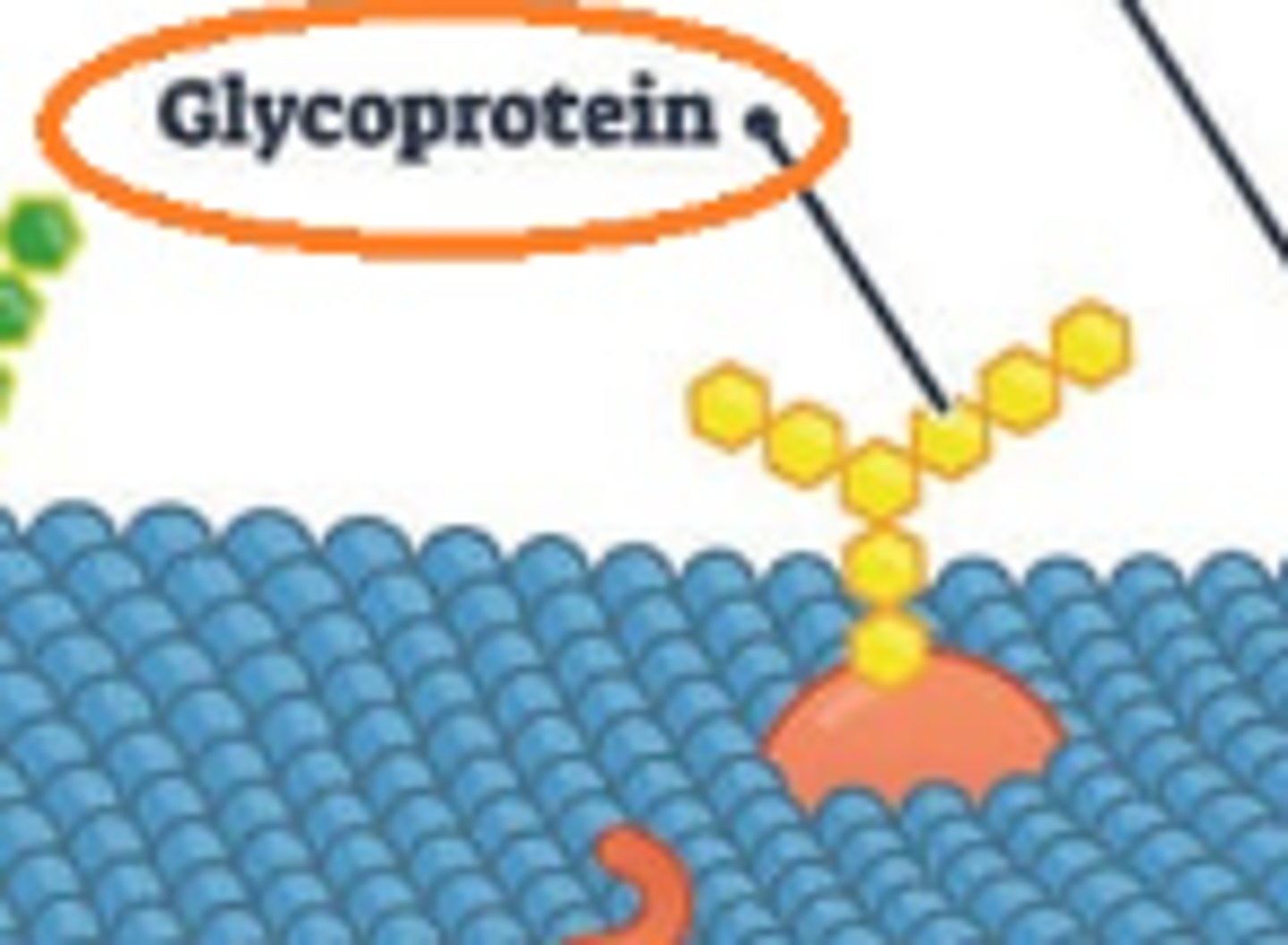
Glycoprotein
Heavily involved in the immune system, where they allow white blood cells to move around the body, initiate immune responses, and identify other cells
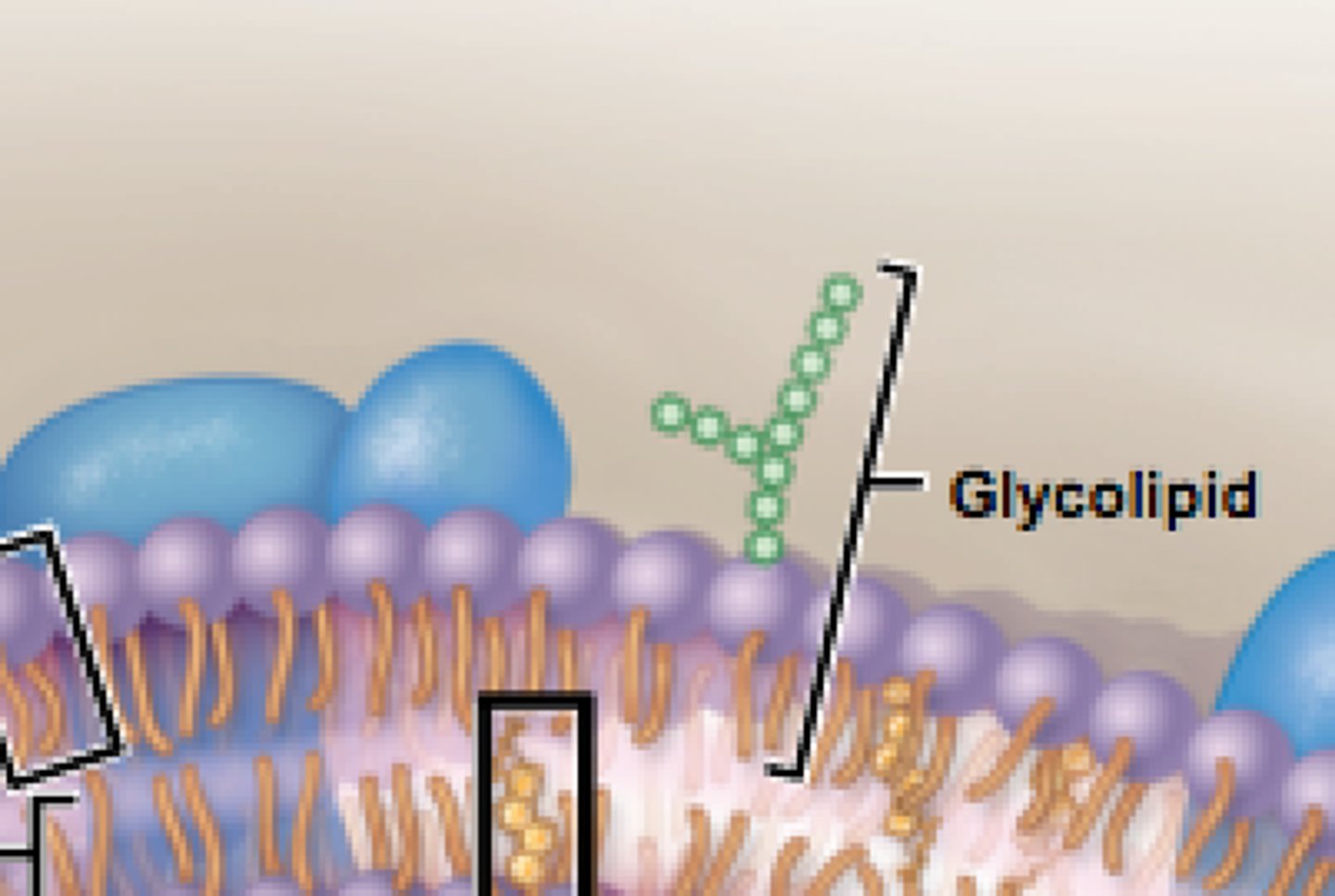
Glycolipid
Maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues
Why is the cell membrane called the fluid mosaic model?
It is often described this because it is made up of many different workings parts which correlates with the word mosaic and fluid part means it is flexible and shifts
What is are some possible message that one cell might send to another cell?
-Chemical compounds
-immune system
-nerves to your brain
-growth hormones
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) function?
ECM provides a stable microenvironment that supports the adhesion, migration, proliferation, and differentiation of cell
Diffusion
The tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into open space
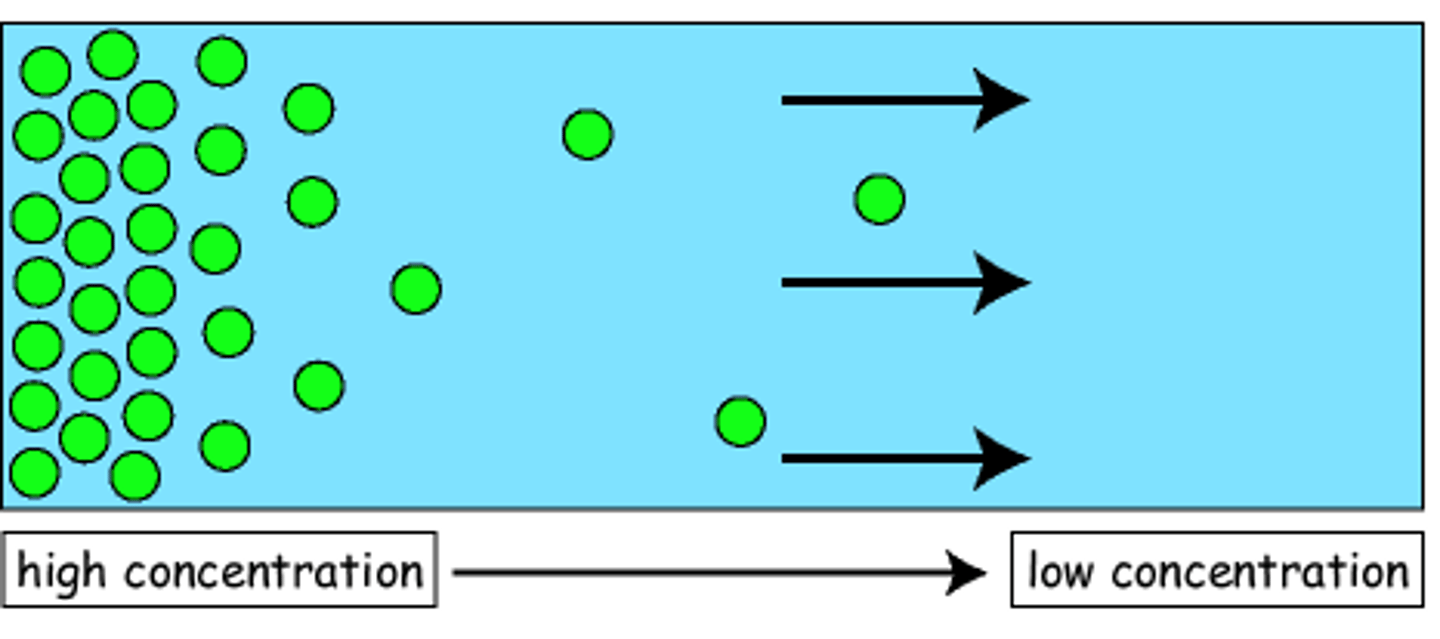
What is passive transport (3 important things)?
No energy is required, goes with concentration gradient, and goes from a high to low concentration until equilibrium
What are examples of passive transport?
Examples of passive transport are diffusion, osmosis, and facilitate diffusion
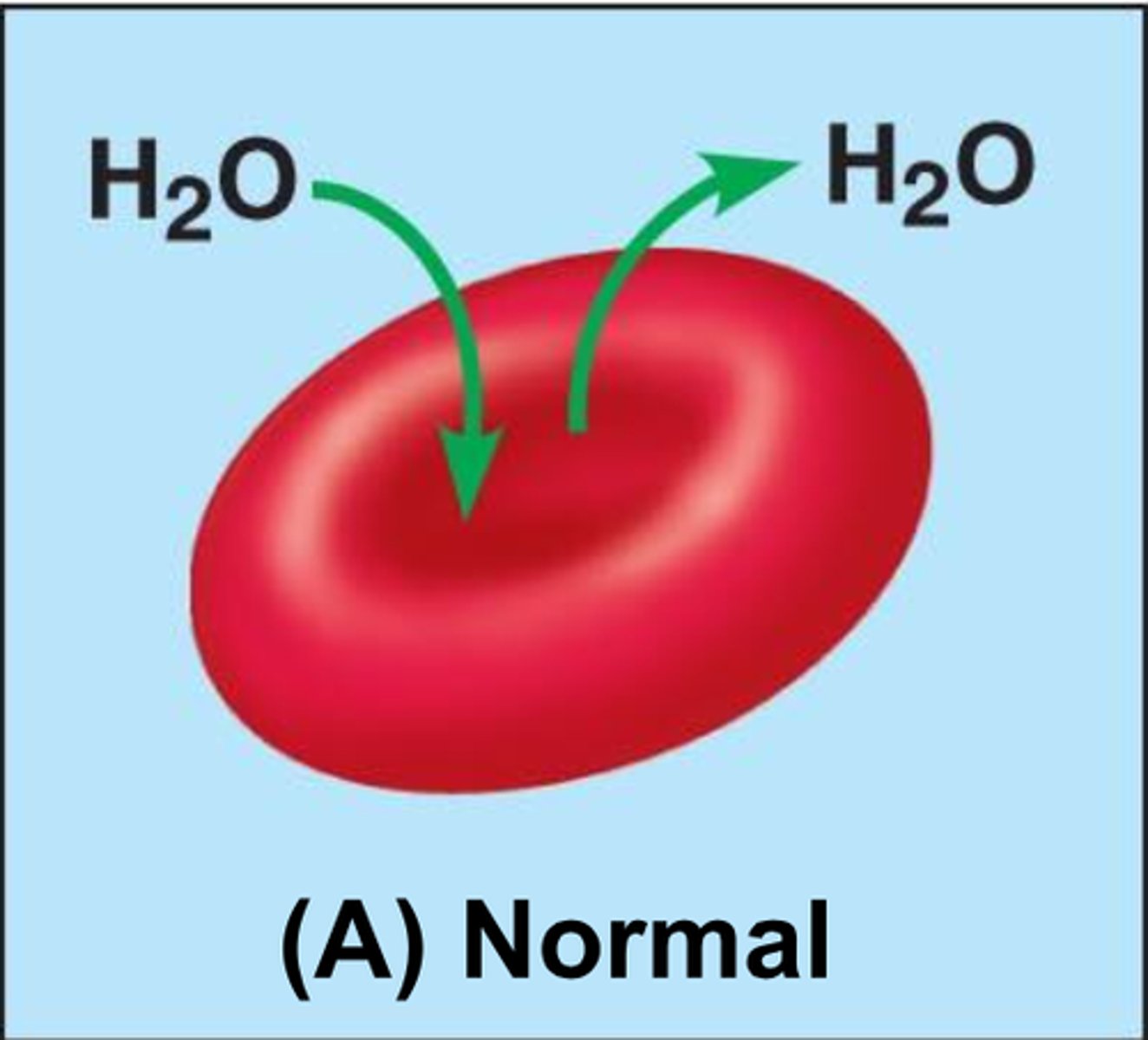
What is osmosis?
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
What is facilitated diffusion?
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
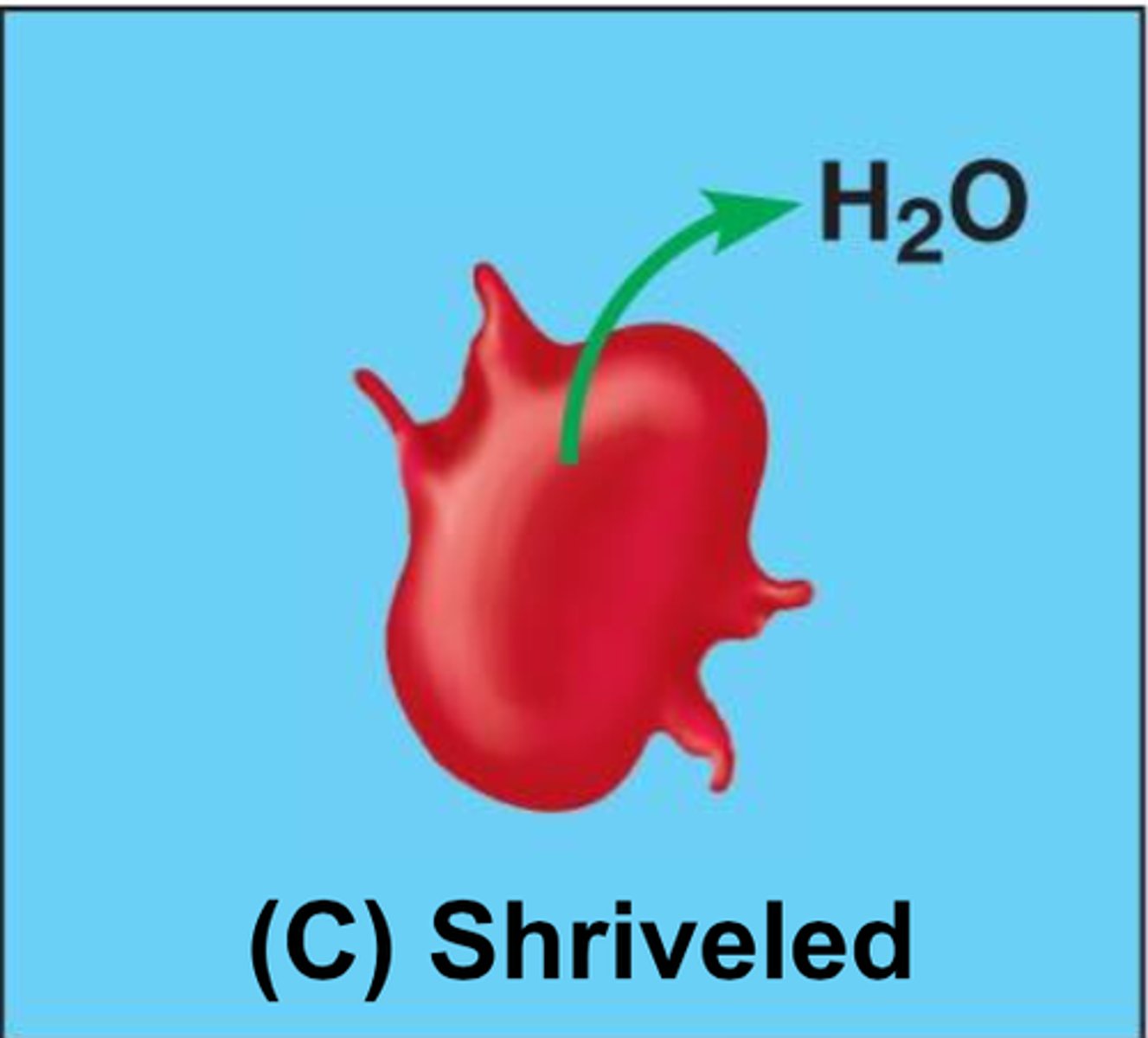
What is hypertonic?
Solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell; cell loses water
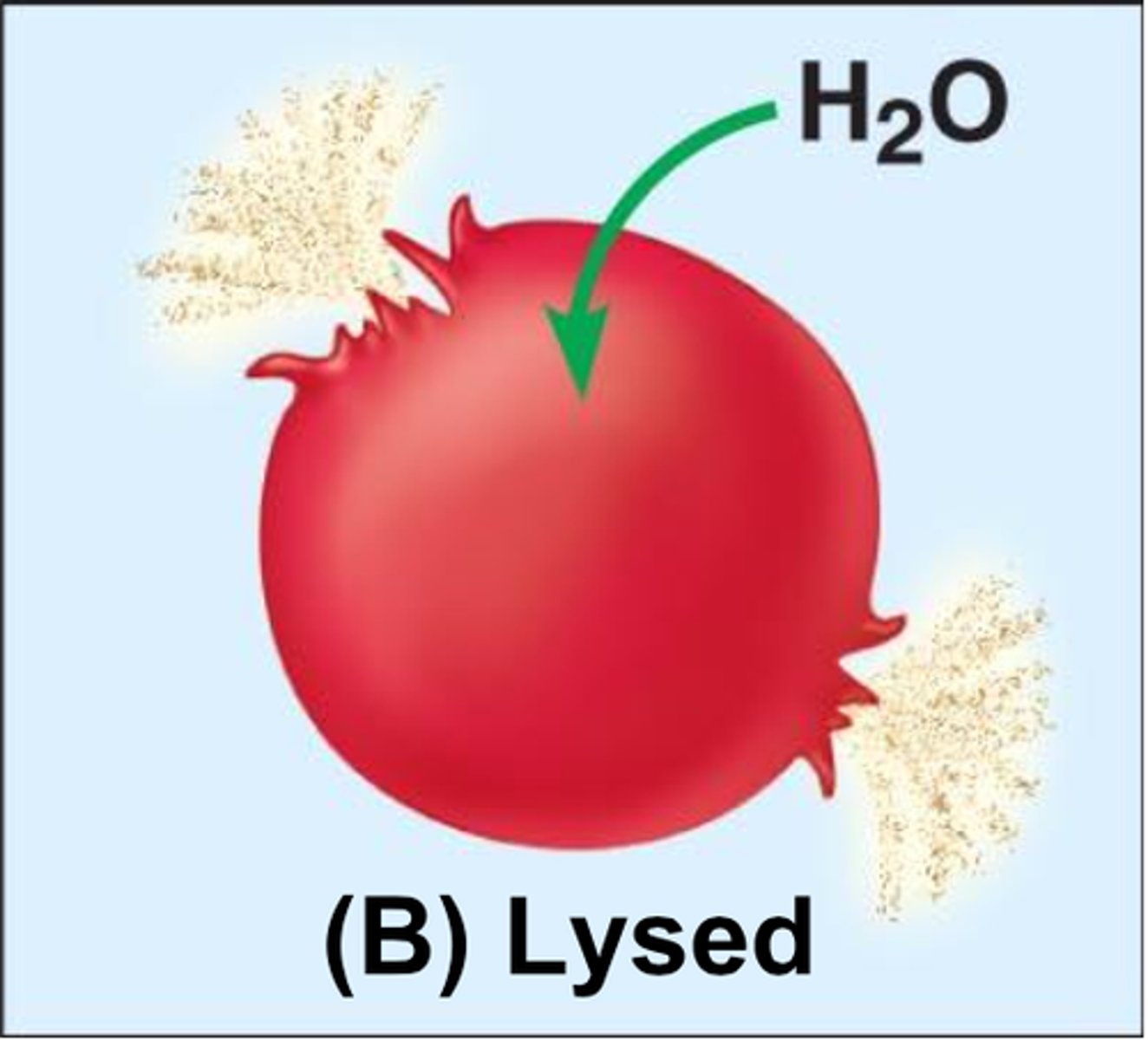
What is hypotonic?
Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
What is isotonic?
Solute concentration is the same as inside the cell; no net water movement across the membrane (humans want this)