Coding Midterm
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:39 PM on 12/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
What will this code segment output?
\
public class Printing
{
public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
System.out.println("\*\*\*\*\*"); System.out.println("\*\*\*\*"); System.out.println("\*\*\*"); System.out.println("\*\*"); System.out.println("\*");
}
}
\
public class Printing
{
public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
System.out.println("\*\*\*\*\*"); System.out.println("\*\*\*\*"); System.out.println("\*\*\*"); System.out.println("\*\*"); System.out.println("\*");
}
}
\*\*\*\*\*
\*\*\*\*
\*\*\*
\*\*
\*\*\*\*
\*\*\*
\*\*
2
New cards
\
What is the correct syntax for writing the **main** method in Java?
\
A) public void main()
{
}
B)public static void main()
{
}
C)
public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
}
D) public static void String(main)
{
}
What is the correct syntax for writing the **main** method in Java?
\
A) public void main()
{
}
B)public static void main()
{
}
C)
public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
}
D) public static void String(main)
{
}
C)
public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
}
public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
}
3
New cards
What will this code segment output?
System.out.println("Hello"); System.out.println("World");
System.out.println("Hello"); System.out.println("World");
Hello
World
World
4
New cards
\
Which code segment will print “Hello Karel” to the screen in Java?
\
1. System.out.printLine("Hello Karel");
2. print "Hello Karel";
3. System.out.println("Hello Karel");
4. System.println("Hello Karel");
Which code segment will print “Hello Karel” to the screen in Java?
\
1. System.out.printLine("Hello Karel");
2. print "Hello Karel";
3. System.out.println("Hello Karel");
4. System.println("Hello Karel");
3. System.out.println("Hello Karel");
5
New cards
Consider the following code snippet.
public static void main(String args\[\]){
final int z;
z = 20;
z = 30;
System.out.println(z);
}
public static void main(String args\[\]){
final int z;
z = 20;
z = 30;
System.out.println(z);
}
This code results in an error
6
New cards
What are the memory values associated with the variables x, y, and z after the code snippet below executes?
int x = 7;
double y = 2.0;
boolean z = false;
x = x + 3;
z = true;
int x = 7;
double y = 2.0;
boolean z = false;
x = x + 3;
z = true;
x holds the int value 10, y holds the double value 2.0 and z holds the boolean value true.
7
New cards
What will be the output of the following code snippet:
public class Variables { public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int totalBirds = 150;
double averageTime = 45.7;
String mostCommon = "Mallard Duck";
System.out.println("Bird Watching Results");
System.out.print("Total birds seen: ");
System.out.println(totalBirds); System.out.print("Average time between sightings: "); System.out.println(averageTime); System.out.print("Most common bird seen was "); System.out.println(mostCommon); } }
public class Variables { public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int totalBirds = 150;
double averageTime = 45.7;
String mostCommon = "Mallard Duck";
System.out.println("Bird Watching Results");
System.out.print("Total birds seen: ");
System.out.println(totalBirds); System.out.print("Average time between sightings: "); System.out.println(averageTime); System.out.print("Most common bird seen was "); System.out.println(mostCommon); } }
\
Bird Watching Results
Total birds seen: 150
Average time between sightings: 45.7
Most common bird seen was Mallard Duck
Bird Watching Results
Total birds seen: 150
Average time between sightings: 45.7
Most common bird seen was Mallard Duck
8
New cards
\
Which of the following is a proper way to declare and initialize a variable in Java?
\
1. myInteger = 100;
2. char = 'a';
3. int myNumber = 10;
4. "Variable"
Which of the following is a proper way to declare and initialize a variable in Java?
\
1. myInteger = 100;
2. char = 'a';
3. int myNumber = 10;
4. "Variable"
3. int myNumber = 10;
9
New cards
\
Which of the following variable names follows best practices for naming a variable?
\
1. 5apples
2. someVariable
3. applesnum
4. numApples
Which of the following variable names follows best practices for naming a variable?
\
1. 5apples
2. someVariable
3. applesnum
4. numApples
4. numApples
10
New cards
What will be the output of the following code snippet?
public class Calculator
{
public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int first = 7;
int second = 2;
int result = first / second; System.out.println(result);
}
}
public class Calculator
{
public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int first = 7;
int second = 2;
int result = first / second; System.out.println(result);
}
}
3
11
New cards
What is the result of this expression?
\
150 % 100
\
150 % 100
50
12
New cards
\
Which of the below is NOT a Java arithmetic operator?
\
1. +
2. -
3. #
4. /
Which of the below is NOT a Java arithmetic operator?
\
1. +
2. -
3. #
4. /
\#
13
New cards
What will be stored in the variable modulo after running the following code snippet?
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
int num = 2;
int modulo = 15;
modulo %= num;
}
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
int num = 2;
int modulo = 15;
modulo %= num;
}
1
14
New cards
\
Which code snippet below will end with num holding the value 15?
\
A) public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int num = 14;
num++;
num--;
num++;
}
\
B) public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int num = 225;
num /= 15;
System.out.println(num);
}
\
C) public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int num = 31;
num %= 16; System.out.println(num);
}
\
D)All of the above
Which code snippet below will end with num holding the value 15?
\
A) public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int num = 14;
num++;
num--;
num++;
}
\
B) public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int num = 225;
num /= 15;
System.out.println(num);
}
\
C) public static void main(String\[\] args)
{
int num = 31;
num %= 16; System.out.println(num);
}
\
D)All of the above
D) All of the above
15
New cards
What will be stored in the variable age after this code snippet executes?
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
int age = 16;
age++;
age--;
age++;
}
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
int age = 16;
age++;
age--;
age++;
}
17
16
New cards
What will be the output of the following code snippet and why?
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
int num = 2;
int dividend = 5;
dividend /= num; System.out.println(dividend);
}
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
int num = 2;
int dividend = 5;
dividend /= num; System.out.println(dividend);
}
The output will be 2 because when two integers are divided in Java, the decimal portion is always truncated.
17
New cards
In Java, the = sign in a statement means
an assignment of the right hand side value to the left hand side variable.
18
New cards
What is the correct syntax for creating a Scanner object?
Scanner objectName = new Scanner(System.in);
19
New cards
What is the correct line of code needed to request a whole number from a user?
Assume a Scanner object called input has already been created.
Assume a Scanner object called input has already been created.
int num = input.nextInt();
20
New cards
What will be the output of the following code snippet?
public class Casting
{
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
int total = 100;
int numPeople = 40;
double average;
average = total / (double) numPeople; System.out.println("Average: " + average);
}
}
public class Casting
{
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
int total = 100;
int numPeople = 40;
double average;
average = total / (double) numPeople; System.out.println("Average: " + average);
}
}
Average: 2.5
21
New cards
What is casting in Java?
Casting is turning a value of one type into another type.
22
New cards
What will this java expression evaluate to?
(int) 9.9
(int) 9.9
9
23
New cards
\
Every class definition has each of the following EXCEPT
\
1. A name
2. Defined attributes
3. Defined behaviors to manipulate the state of the objects
4. Defined objects as copies of the class
Every class definition has each of the following EXCEPT
\
1. A name
2. Defined attributes
3. Defined behaviors to manipulate the state of the objects
4. Defined objects as copies of the class
4. Defined objects as copies of the class
24
New cards
describe the relationship between a class and an object
A class definition specifies the attributes and behavior of every object that will be made.
25
New cards
\
What is an object in Java?
\
1. An object is a template for how to make new programs in Java.
2. An object is something that contains both state and behavior.
3. An object is a single part of a computer program.
4. An object is a list of variables.
What is an object in Java?
\
1. An object is a template for how to make new programs in Java.
2. An object is something that contains both state and behavior.
3. An object is a single part of a computer program.
4. An object is a list of variables.
2. An object is something that contains both state and behavior.
26
New cards
\
Consider this class definition of a Pineapple.
public class Pineapple
{
private boolean isRipe;
private String color;
private double weight;
// Rest of class goes here
}
\
When we use this class to create Pineapple objects, which of the following is guaranteed to be true?
\
1. Every Pineapple object will be yellow
2. Every Pineapple object must choose which attributes it wants.
3. Every Pineapple object will have the same attributes.
4. It is impossible to know what attributes the Pineapple objects will have since the attributes are not listed here.
Consider this class definition of a Pineapple.
public class Pineapple
{
private boolean isRipe;
private String color;
private double weight;
// Rest of class goes here
}
\
When we use this class to create Pineapple objects, which of the following is guaranteed to be true?
\
1. Every Pineapple object will be yellow
2. Every Pineapple object must choose which attributes it wants.
3. Every Pineapple object will have the same attributes.
4. It is impossible to know what attributes the Pineapple objects will have since the attributes are not listed here.
3. Every Pineapple object will have the same attributes.
27
New cards
What is a constructor in Java?
A constructor allows us to create a new instance of a class, usually initializing instance variables.
28
New cards
Refer to the Card class shown below.
public class Card
{
private String suit;
private int value;
//13 values for each suit in deck (0 to 12)
public Card (String cardSuit, int cardValue)
{
/\* implementation \*/
}
// Rest of the class goes here }
\
Which of the following is the correct /\* implementation \*/ code for the constructor in the Card class?
public class Card
{
private String suit;
private int value;
//13 values for each suit in deck (0 to 12)
public Card (String cardSuit, int cardValue)
{
/\* implementation \*/
}
// Rest of the class goes here }
\
Which of the following is the correct /\* implementation \*/ code for the constructor in the Card class?
suit = cardSuit;
value = cardValue;
value = cardValue;
29
New cards
public class Shark
{
// Attributes
private String habitat;
private int age;
public Shark(String region, int sharkAge)
{
habitat = region;
age = sharkAge;
}
}
\
What is a formal parameter of the constructor?
{
// Attributes
private String habitat;
private int age;
public Shark(String region, int sharkAge)
{
habitat = region;
age = sharkAge;
}
}
\
What is a formal parameter of the constructor?
sharkAge or region
30
New cards
\
What is the purpose of overloading a class’ constructor?
\
1. It allows the user to create more than one object from the class.
2. It allows the user to make different types of objects from a single class type.
3. It allows the user to set the values of different combinations of the instance variables when the object is created.
4. It allows the user to call different constructors for the same object to initialize different instance variables.
What is the purpose of overloading a class’ constructor?
\
1. It allows the user to create more than one object from the class.
2. It allows the user to make different types of objects from a single class type.
3. It allows the user to set the values of different combinations of the instance variables when the object is created.
4. It allows the user to call different constructors for the same object to initialize different instance variables.
3. It allows the user to set the values of different combinations of the instance variables when the object is created.
31
New cards
\
A reference variable holds a special value. What is this special value?
\
1. The memory address of an object
2. The memory address of the reference variable
3. An object
4. The name of an object
A reference variable holds a special value. What is this special value?
\
1. The memory address of an object
2. The memory address of the reference variable
3. An object
4. The name of an object
1. The memory address of an object
32
New cards
Suppose a program is a client of the Player class. Here is a snippet of code contained in the program
Player firstPlayer = new Player("Karel", "Warrior", "Mote Prime", 90);
\
Looking at the documentation of the class, you find the signature for the constructor, shown below.
public Player(String name, String role, String location, int health);
\
Where would you find the formal parameters?
Player firstPlayer = new Player("Karel", "Warrior", "Mote Prime", 90);
\
Looking at the documentation of the class, you find the signature for the constructor, shown below.
public Player(String name, String role, String location, int health);
\
Where would you find the formal parameters?
In the documentation
33
New cards
\
Which of the following is NOT a valid way to overload this constructor? For brevity, only the signature is given.
Pineapple(String color)
\
1. Pineapple()
\
2. Pineapple(String color, int age)
\
3. Pineapple(int age, String species)
\
4. FancyPineapple(String color, int age)
Which of the following is NOT a valid way to overload this constructor? For brevity, only the signature is given.
Pineapple(String color)
\
1. Pineapple()
\
2. Pineapple(String color, int age)
\
3. Pineapple(int age, String species)
\
4. FancyPineapple(String color, int age)
4. FancyPineapple(String color, int age)
34
New cards
\
Which of the following is NOT part of the constructor signature?
\
1. Which instance variables are initialized
2. The parameter types
3. The order of the parameters
4. The name of the constructor
Which of the following is NOT part of the constructor signature?
\
1. Which instance variables are initialized
2. The parameter types
3. The order of the parameters
4. The name of the constructor
1. Which instance variables are initialized
35
New cards
\
What does it mean to be a client of a class?
\
1. Being a client of a class means that there a single method that we can use.
2. Being a client of a class means that we are the author of the class implementation.
3. Being a client of a class means that we can use its methods and functionality without necessarily understanding how it works.
4. Being a client of a class means that the class has documentation.
What does it mean to be a client of a class?
\
1. Being a client of a class means that there a single method that we can use.
2. Being a client of a class means that we are the author of the class implementation.
3. Being a client of a class means that we can use its methods and functionality without necessarily understanding how it works.
4. Being a client of a class means that the class has documentation.
3. Being a client of a class means that we can use its methods and functionality without necessarily understanding how it works.
36
New cards
\
What is the importance of the null value?
\
1. null allows a reference variable to hold every object’s address simultaneously.
2. null prevents the reference variable from referring to another object again.
3. null restricts the class to only making one object.
4. null allows a reference variable to be empty and not hold any memory address.
What is the importance of the null value?
\
1. null allows a reference variable to hold every object’s address simultaneously.
2. null prevents the reference variable from referring to another object again.
3. null restricts the class to only making one object.
4. null allows a reference variable to be empty and not hold any memory address.
4. \`null allows a reference variable to be empty and not hold any memory address.
37
New cards
\
int roomHeight = 40;
int roomWidth = roomHeight \* 3; Rectangle room = new Rectangle(roomHeight, roomWidth);
\
Which of the following is a reference variable?
\
1. room
2. roomHeight
3. roomWidth
4. Rectangle
int roomHeight = 40;
int roomWidth = roomHeight \* 3; Rectangle room = new Rectangle(roomHeight, roomWidth);
\
Which of the following is a reference variable?
\
1. room
2. roomHeight
3. roomWidth
4. Rectangle
1. room
38
New cards
\
You are using a class as a client. What would you need to know in order to create an object of the class you intend to use?
\
1. You need to know how the class you are a client of was implemented.
2. You need to know the formal parameters in order to pass in actual parameters.
3. You need to know what other programs are using the class as a client.
4. You need to know the programmer who wrote the class.
You are using a class as a client. What would you need to know in order to create an object of the class you intend to use?
\
1. You need to know how the class you are a client of was implemented.
2. You need to know the formal parameters in order to pass in actual parameters.
3. You need to know what other programs are using the class as a client.
4. You need to know the programmer who wrote the class.
2. You need to know the formal parameters in order to pass in actual parameters.
39
New cards
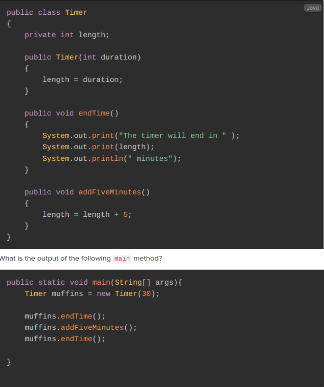
What is the output?
The timer will end in 30 minutes
The timer will end in 35 minutes
The timer will end in 35 minutes
40
New cards
\
What is an instance method?
\
1. An instance method is a piece of code called on a specific instance (an object) of the class.
2. An instance method is a piece of code that does not depend on any specific instances (objects), just on the general class.
3. An instance method adds functionality to a class by creating private fields.
4. An instance method adds functionality to the class by printing out a result.
What is an instance method?
\
1. An instance method is a piece of code called on a specific instance (an object) of the class.
2. An instance method is a piece of code that does not depend on any specific instances (objects), just on the general class.
3. An instance method adds functionality to a class by creating private fields.
4. An instance method adds functionality to the class by printing out a result.
1. An instance method is a piece of code called on a specific instance (an object) of the class.
41
New cards
\
Suppose the class Timer has a method called startTime that prints out the starting time of the Timer. \n Which of the following correctly uses this method to print out the start time of a Timer object called laundry?
\
1. System.out.println(laundry.startTime());
2. System.out.println(laundry.startTime);
3. int start = laundry.startTime();
4. laundry.startTime();
5. laundry.startTime;
Suppose the class Timer has a method called startTime that prints out the starting time of the Timer. \n Which of the following correctly uses this method to print out the start time of a Timer object called laundry?
\
1. System.out.println(laundry.startTime());
2. System.out.println(laundry.startTime);
3. int start = laundry.startTime();
4. laundry.startTime();
5. laundry.startTime;
4. laundry.startTime();
42
New cards
\
Which of the following correctly calls the method addFiveMinutes on an object of the Timer class called kitchenTimer?
\
1. kitchenTimer(addFiveMinutes);
2. Timer.addFiveMinutes();
3. kitchenTimer.addFiveMinutes();
4. kitchenTimer.addFiveMinutes;
Which of the following correctly calls the method addFiveMinutes on an object of the Timer class called kitchenTimer?
\
1. kitchenTimer(addFiveMinutes);
2. Timer.addFiveMinutes();
3. kitchenTimer.addFiveMinutes();
4. kitchenTimer.addFiveMinutes;
3. kitchenTimer.addFiveMinutes();
43
New cards

Which of the following is a correctly written method for the class below?
1. public void addFiveMinutes()
{
length = length + 5;
}
\
2. public addFiveMinutes()
{
length = length + 5;
}
\
\
3. addFiveMinutes()
{
length = length + 5;
}
\
4. public void addFiveMinutes
{
length = length + 5;
}
1. public void addFiveMinutes()
{
length = length + 5;
}
\
2. public addFiveMinutes()
{
length = length + 5;
}
\
\
3. addFiveMinutes()
{
length = length + 5;
}
\
4. public void addFiveMinutes
{
length = length + 5;
}
1. public void addFiveMinutes()
{
length = length + 5;
}
44
New cards
\
What are parameters?
\
1. The value that a method returns.
2. The values that a method prints to the screen.
3. The formal names given to the data that gets passed into a method.
4. The type that is given to a variable.
What are parameters?
\
1. The value that a method returns.
2. The values that a method prints to the screen.
3. The formal names given to the data that gets passed into a method.
4. The type that is given to a variable.
3. The formal names given to the data that gets passed into a method.
45
New cards

1. karel.setHonorStatus(isHonors = true);
2. karel.isHonors = true;
3. karel.setHonorStatus(status=true);
4. karel.setHonorStatus(true);
4. karel.setHonorStatus(true);
46
New cards

What is the output?
\
\
24\.0
20\.0
20\.0
47
New cards
public class Rectangle
{
private int width;
private int height;
public Rectangle(int rectWidth, int rectHeight)
{
width = rectWidth;
height = rectHeight;
}
\
public int getArea()
{
return width \* height;
}
}
{
private int width;
private int height;
public Rectangle(int rectWidth, int rectHeight)
{
width = rectWidth;
height = rectHeight;
}
\
public int getArea()
{
return width \* height;
}
}
int area = shape.getArea();
48
New cards
\
Which of the following methods is implemented correctly with respect to the method’s return type?
\
1. public String getColor()
{ return "Red"; }
2. public int getColor()
{ return "Red"; }
3. public void getColor()
{ return "Red"; }
4. public Color()
{ return "Red"; }
Which of the following methods is implemented correctly with respect to the method’s return type?
\
1. public String getColor()
{ return "Red"; }
2. public int getColor()
{ return "Red"; }
3. public void getColor()
{ return "Red"; }
4. public Color()
{ return "Red"; }
1. public String getColor()
{
return "Red";
}
49
New cards
\
The value that a method outputs is called
\
1. a print statement.
2. an argument.
3. a parameter.
4. a return value.
The value that a method outputs is called
\
1. a print statement.
2. an argument.
3. a parameter.
4. a return value.
4. a return value.
50
New cards
\
Suppose you have a class called Elevator. The Elevator class has a method called goingUp, partially defined below
public boolean goingUp()
{
// code omitted
}
Which of the following statements correctly stores the return value of goingUp when it is called on the Elevator object called hotel?
\
1. int up = hotel.goingUp();
2. double up = hotel.goingUp();
3. boolean up = hotel.goingUp();
4. String up = hotel.goingUp();
Suppose you have a class called Elevator. The Elevator class has a method called goingUp, partially defined below
public boolean goingUp()
{
// code omitted
}
Which of the following statements correctly stores the return value of goingUp when it is called on the Elevator object called hotel?
\
1. int up = hotel.goingUp();
2. double up = hotel.goingUp();
3. boolean up = hotel.goingUp();
4. String up = hotel.goingUp();
3. boolean up = hotel.goingUp();
51
New cards
\
What would be printed by this code snippet?
String language = "Java"; String opinion = " is fun!"; System.out.println(language + opinion);
\
1. Java
2. Javais fun!
3. Java is fun!
4. This code would not compile. You can’t add Strings.
What would be printed by this code snippet?
String language = "Java"; String opinion = " is fun!"; System.out.println(language + opinion);
\
1. Java
2. Javais fun!
3. Java is fun!
4. This code would not compile. You can’t add Strings.
3. Java is fun!
52
New cards
Which of the following statements will not compile? You may assume any text in this font is an initialized variable.
I. “Tilly is ” + age + ” years old” \n II. “My favorite letter is ” + ‘k’ \n III. greeting + name \n IV. “Our team, ” + teamName + ” has ” + numPlayers
I. “Tilly is ” + age + ” years old” \n II. “My favorite letter is ” + ‘k’ \n III. greeting + name \n IV. “Our team, ” + teamName + ” has ” + numPlayers
all of the above
53
New cards
\
Strings are immutable. This means that
\
1. Once a String variable has been assigned a value, the value of the variable must always have the same value.
2. Once a String variable has been assigned a value, the value cannot be modified but the variable can be assigned to a different value.
3. The value of a String variable can be modified, but the variable cannot be reassigned.
4. The value of a String variable cannot be modified and the variable cannot be reassigned.
Strings are immutable. This means that
\
1. Once a String variable has been assigned a value, the value of the variable must always have the same value.
2. Once a String variable has been assigned a value, the value cannot be modified but the variable can be assigned to a different value.
3. The value of a String variable can be modified, but the variable cannot be reassigned.
4. The value of a String variable cannot be modified and the variable cannot be reassigned.
2. Once a String variable has been assigned a value, the value cannot be modified but the variable can be assigned to a different value.
54
New cards
\
Which of the following would properly print this quote by Edsger W. Dijkstra (an early pioneer of Computer Science) as shown below?
"Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs" --- Edsger W. Dijkstra
\
1. System.out.println('"Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs"');
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
2. System.out.println("Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs");
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
3. System.out.println("\\"Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs\\"");
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
4. System.out.println(""Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs"");
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
Which of the following would properly print this quote by Edsger W. Dijkstra (an early pioneer of Computer Science) as shown below?
"Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs" --- Edsger W. Dijkstra
\
1. System.out.println('"Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs"');
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
2. System.out.println("Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs");
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
3. System.out.println("\\"Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs\\"");
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
4. System.out.println(""Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs"");
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
System.out.println("\\"Testing shows the presence, not the absence of bugs\\"");
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
System.out.println("--- Edsger W. Dijkstra");
55
New cards
What is the output of the following code snippet?
String forest = "Amazon Rainforest"; System.out.println(forest.indexOf('a')); System.out.println(forest.indexOf('g')); System.out.println(forest.indexOf('n'));
String forest = "Amazon Rainforest"; System.out.println(forest.indexOf('a')); System.out.println(forest.indexOf('g')); System.out.println(forest.indexOf('n'));
2
\-1
5
\-1
5
56
New cards
Consider the following code snippet. What would the output be?
String school = "Rydell High School"; System.out.println(school.substring(8));
System.out.println(school);
String school = "Rydell High School"; System.out.println(school.substring(8));
System.out.println(school);
igh School
Rydell High School
Rydell High School
57
New cards
What method must a class implement in order to concatenate an object of the class with a String object?
toString
58
New cards
\
What would be printed by the following code snippet?
String lastName = "Vu";
String otherLastName = "Lopez";
int comparison = lastName.compareTo(otherLastName);
System.out.println(comparison);
\
1. Zero because both strings start with capital letters
2. A positive number because “Vu” comes before “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
3. A negative number because “Vu” comes before “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
4. A positive number because “Vu” comes after “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
5. A negative number because “Vu” comes after “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
What would be printed by the following code snippet?
String lastName = "Vu";
String otherLastName = "Lopez";
int comparison = lastName.compareTo(otherLastName);
System.out.println(comparison);
\
1. Zero because both strings start with capital letters
2. A positive number because “Vu” comes before “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
3. A negative number because “Vu” comes before “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
4. A positive number because “Vu” comes after “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
5. A negative number because “Vu” comes after “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
4. A positive number because “Vu” comes after “Lopez” in lexicographical order.
59
New cards
\
The purpose of a wrapper class is to
\
1. Allow methods to be called on a primitive value
2. “Wrap” an object to convert it to a primitive value
3. Allow primitive to be passed to methods
4. “Wrap” a primitive value to convert it to an object
The purpose of a wrapper class is to
\
1. Allow methods to be called on a primitive value
2. “Wrap” an object to convert it to a primitive value
3. Allow primitive to be passed to methods
4. “Wrap” a primitive value to convert it to an object
4. “Wrap” a primitive value to convert it to an object
60
New cards
\
Java automatically converts between objects and primitives in the process of autoboxing and unboxing.
What happens when an int is autoboxed?
\
1. A int is autoboxed when it is converted to a primitive value.
2. A int is autoboxed when it is converted to a Double
3. A int is autoboxed when it is passed to a method.
4. A int is autoboxed when it is converted to a Integer
Java automatically converts between objects and primitives in the process of autoboxing and unboxing.
What happens when an int is autoboxed?
\
1. A int is autoboxed when it is converted to a primitive value.
2. A int is autoboxed when it is converted to a Double
3. A int is autoboxed when it is passed to a method.
4. A int is autoboxed when it is converted to a Integer
4. A int is autoboxed when it is converted to a Integer
61
New cards
\
Which of these is *not* true about primitives and objects?
\
1. An object stores an address as a value while a primitive stores a literal value.
2. An object has data and methods associated with it while a primitive only stores data.
3. When passed to a method, changes made to the object will show in the calling method, but changes to the primitive will not.
4. A primitive has data and methods associated with it while an object only stores data.
Which of these is *not* true about primitives and objects?
\
1. An object stores an address as a value while a primitive stores a literal value.
2. An object has data and methods associated with it while a primitive only stores data.
3. When passed to a method, changes made to the object will show in the calling method, but changes to the primitive will not.
4. A primitive has data and methods associated with it while an object only stores data.
4. A primitive has data and methods associated with it while an object only stores data.
62
New cards
\
Java automatically converts between objects and primitives in the process of autoboxing and unboxing.
What happens when a Double is unboxed?
\
1. A Double is unboxed when it is converted to a primitive value.
2. A Double is unboxed when it is converted to an Integer
3. A Double is unboxed when it is passed to a method.
4. A Double is unboxed when it is converted to a Double value.
Java automatically converts between objects and primitives in the process of autoboxing and unboxing.
What happens when a Double is unboxed?
\
1. A Double is unboxed when it is converted to a primitive value.
2. A Double is unboxed when it is converted to an Integer
3. A Double is unboxed when it is passed to a method.
4. A Double is unboxed when it is converted to a Double value.
1. A Double is unboxed when it is converted to a primitive value.
63
New cards
What would this program print?
\
double sideLength = Math.sqrt(64); double height = Math.pow(3, 2); double difference = Math.abs(sideLength - height);
System.out.println(difference);
\
double sideLength = Math.sqrt(64); double height = Math.pow(3, 2); double difference = Math.abs(sideLength - height);
System.out.println(difference);
1\.0
64
New cards
What range of numbers would be generated by using
int num = (int) (Math.random() \* 501);
1. 1 - 500
2. 1 - 501
3. 0 - 501
4. 0 - 500
int num = (int) (Math.random() \* 501);
1. 1 - 500
2. 1 - 501
3. 0 - 501
4. 0 - 500
4. 0 - 500
65
New cards
\
Which of these is an example of calling a static method?
\
1. point.setX(x)
2. Math.abs(x)
3. student.getName()
4. square(x)
Which of these is an example of calling a static method?
\
1. point.setX(x)
2. Math.abs(x)
3. student.getName()
4. square(x)
2. Math.abs(x)
66
New cards
\
Which of the following describes the difference between static methods and instance methods?
\
1. Static methods cannot return a value while instance methods may or may not return a value
2. Static methods can be called without using an object while instance methods need to be called on an object
3. A class can only have one static method.
4. Static methods must be called using an object while instance methods can be called without using an object
Which of the following describes the difference between static methods and instance methods?
\
1. Static methods cannot return a value while instance methods may or may not return a value
2. Static methods can be called without using an object while instance methods need to be called on an object
3. A class can only have one static method.
4. Static methods must be called using an object while instance methods can be called without using an object
2. Static methods can be called without using an object while instance methods need to be called on an object
67
New cards
\
Which of the following is NOT a relational operator?
\
1. <
2. ?
3.
4.
Which of the following is NOT a relational operator?
\
1. <
2. ?
3.
4.
2. ?
68
New cards
String name = "Karel";
String checkName = new String("Karel");
boolean nameMatches = name == checkName;
Note that we forced Java to create a new String object by using new and calling the String constructor. \n Recall that if you set two String variables to the same String literal, Java tries to be efficient and uses the same object.
With this in mind, what will the value of nameMatches be?
String checkName = new String("Karel");
boolean nameMatches = name == checkName;
Note that we forced Java to create a new String object by using new and calling the String constructor. \n Recall that if you set two String variables to the same String literal, Java tries to be efficient and uses the same object.
With this in mind, what will the value of nameMatches be?
false
69
New cards
What does this Java expression evaluate to?
80 >= 80
80 >= 80
true
70
New cards
What is the difference between == and =?
= is used for assignment, while == is used to check for equality.
71
New cards
\
Which of the following symbols is the “not equal” symbol?
1.
2.
3.
4.
Which of the following symbols is the “not equal” symbol?
1.
2.
3.
4.
3. !=
72
New cards
What is the output of this program?
int numTreeRings = 50; System.out.println("How old is the tree?");
if(numTreeRings < 20)
{
System.out.println("Still young!");
}
if(numTreeRings < 50)
{
System.out.println("Pretty old!");
}
if(numTreeRings < 100)
{ System.out.println("Very old!");
}
int numTreeRings = 50; System.out.println("How old is the tree?");
if(numTreeRings < 20)
{
System.out.println("Still young!");
}
if(numTreeRings < 50)
{
System.out.println("Pretty old!");
}
if(numTreeRings < 100)
{ System.out.println("Very old!");
}
How old is the tree? \n Very old!
73
New cards
What is the output of this program?
int numTreeRings = 50; System.out.println("How old is the tree?");
if(numTreeRings > 10)
{
System.out.println("Still young!");
}
if(numTreeRings > 40)
{
System.out.println("Pretty old!");
}
if(numTreeRings > 150)
{
System.out.println("Very old!");
}
int numTreeRings = 50; System.out.println("How old is the tree?");
if(numTreeRings > 10)
{
System.out.println("Still young!");
}
if(numTreeRings > 40)
{
System.out.println("Pretty old!");
}
if(numTreeRings > 150)
{
System.out.println("Very old!");
}
How old is the tree? \n Still young! \n Pretty old!
74
New cards
What is the output of this program?
int phLevel = 9;
if(phLevel < 7)
{
System.out.println("It is acidic!");
}
if(phLevel > 7)
{
System.out.println("It is basic!");
}
if(phLevel == 7)
{
System.out.println("It is neutral!");
}
\
int phLevel = 9;
if(phLevel < 7)
{
System.out.println("It is acidic!");
}
if(phLevel > 7)
{
System.out.println("It is basic!");
}
if(phLevel == 7)
{
System.out.println("It is neutral!");
}
\
It is basic!
75
New cards
\
Why do we use if statements in Java?
\
1. To break out of some block of code
2. To do something only if a condition is true
3. To do something while a condition is true
4. To repeat something for a fixed number of times
Why do we use if statements in Java?
\
1. To break out of some block of code
2. To do something only if a condition is true
3. To do something while a condition is true
4. To repeat something for a fixed number of times
2. To do something only if a condition is true
76
New cards
Consider the following code snippet
if (x == y)
{
// Statement A
}
else
{
// Statement B
}
Which statement will be executed if x = 3 and y = 3?
\
if (x == y)
{
// Statement A
}
else
{
// Statement B
}
Which statement will be executed if x = 3 and y = 3?
\
statement A
77
New cards
Consider the following code snippet
if (x == y)
{
// Statement A
}
else
{
// Statement B
}
Which statement will be executed if x = 15 and y = 20?
if (x == y)
{
// Statement A
}
else
{
// Statement B
}
Which statement will be executed if x = 15 and y = 20?
Statement B
78
New cards
What is the output of this code?
String firstName = "Karel";
String lastName = "The Dog";
if (firstName.length() > lastName.length())
{
System.out.println(firstName + " is longer than " + lastName);
}
else
{
System.out.println(lastName + " is longer than " + firstName);
}
String firstName = "Karel";
String lastName = "The Dog";
if (firstName.length() > lastName.length())
{
System.out.println(firstName + " is longer than " + lastName);
}
else
{
System.out.println(lastName + " is longer than " + firstName);
}
The Dog is longer than Karel
79
New cards
What is the output of the following code snippet?
char combo = 'B';
if(combo == 'A')
{
System.out.println("Tamale it is!");
}
else if (combo == 'B')
{
System.out.println("Quesadilla it is!"); }
else { System.out.println("That is not a combo of ours"); }
char combo = 'B';
if(combo == 'A')
{
System.out.println("Tamale it is!");
}
else if (combo == 'B')
{
System.out.println("Quesadilla it is!"); }
else { System.out.println("That is not a combo of ours"); }
Quesadilla it is