The kidney
1/32
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Describe the gross structure of a mammalian kidney
Fibrous capsule,cortex then the medulla
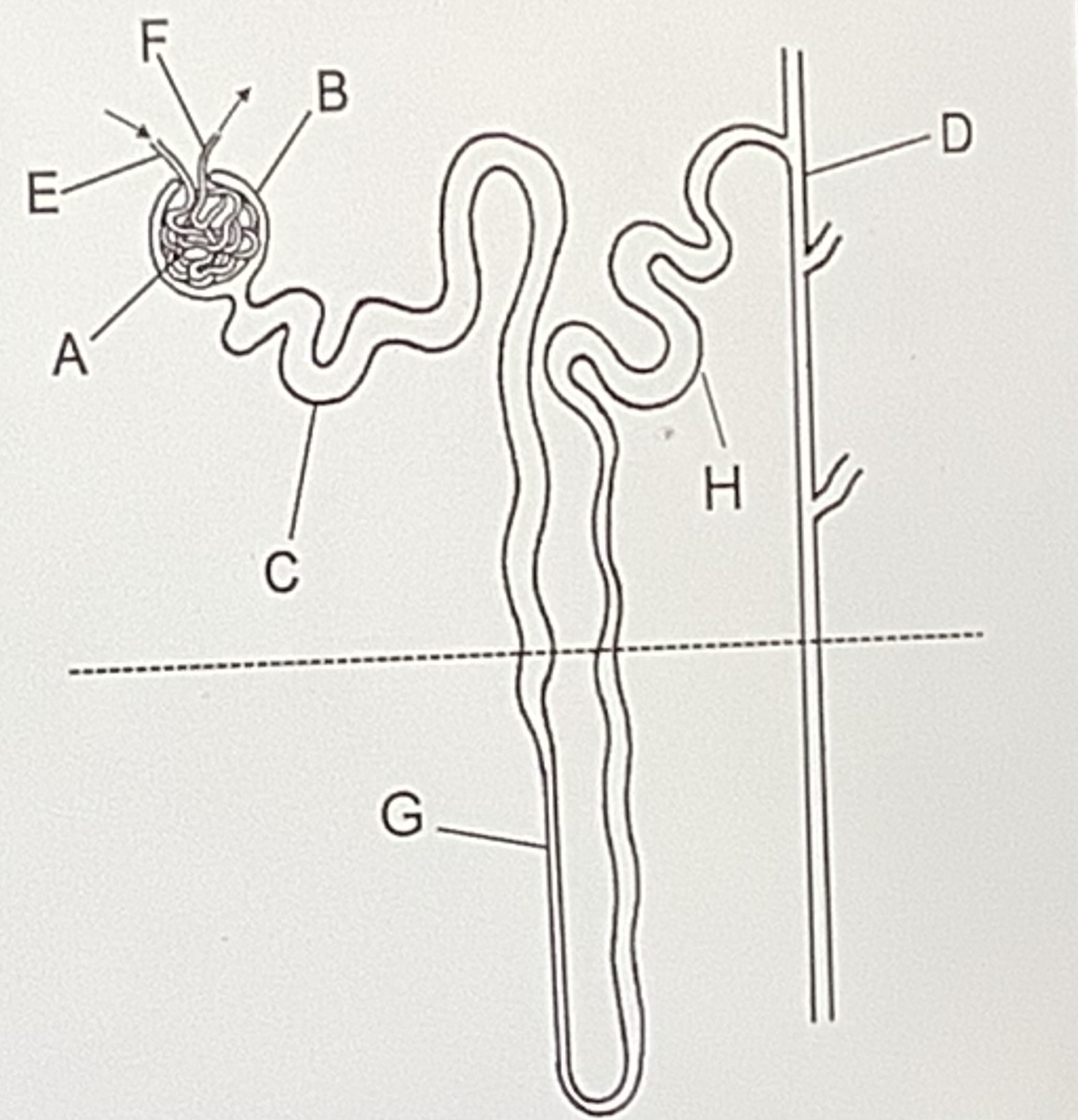
Label this diagram of a nephron

Describe the blood vessels associated with a nephron
Wide afferent arteriole-from renal artery-forms glomerulus
Narrow efferent arteriole-branched knot of capillaries
Capillary network formed by branches of the efferent arteriole
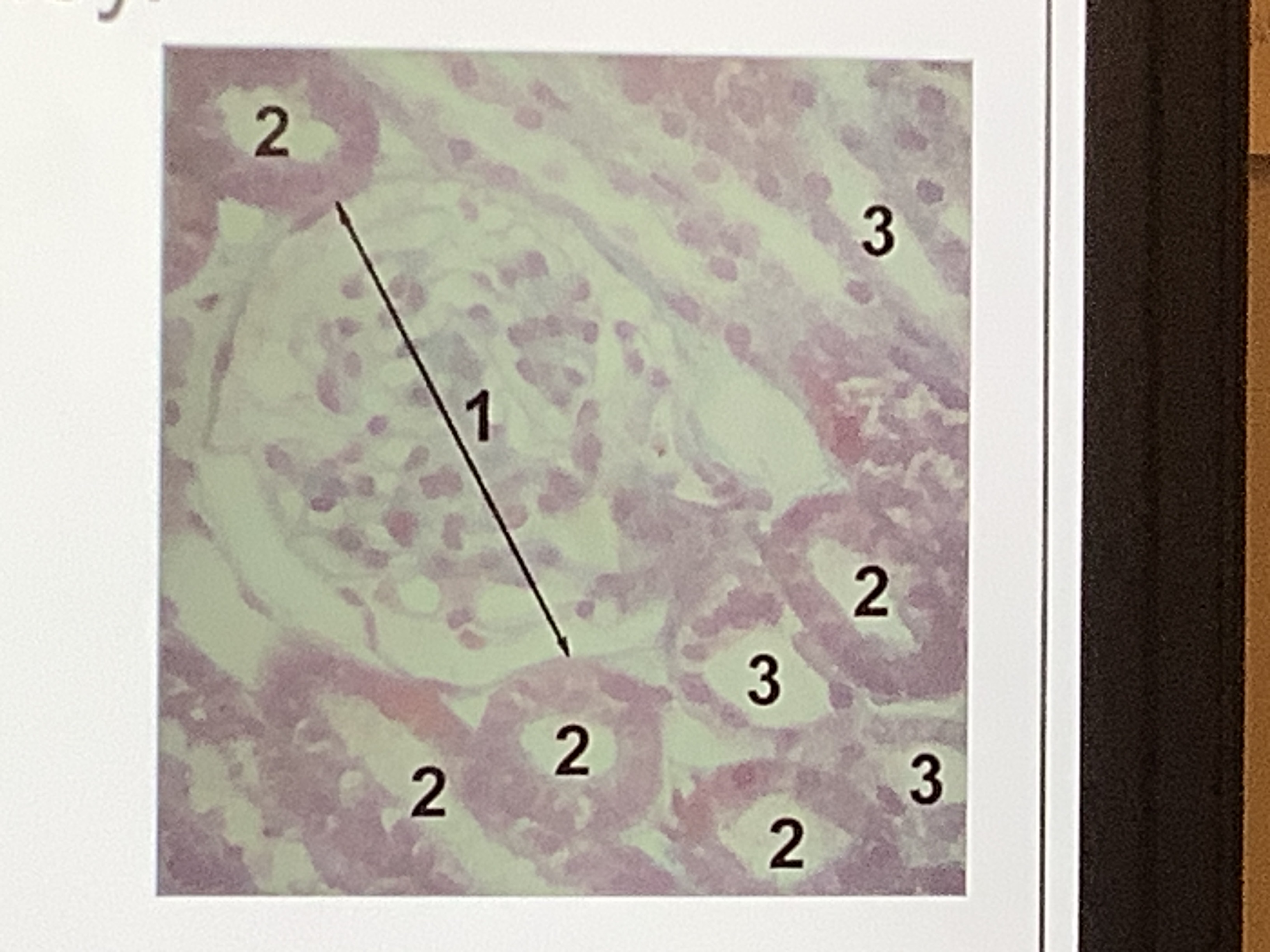
Describe the histology of the kidney using the diagram given

Describe the bowman’s capsule
Cup shaped, surrounds glomerulus,inner layer of podocytes
Describe the proximal convoluted tube-PCT
Series of loops surrounded by capillaries, walls lined with epithelial cells with villi
Describe the loop of henle
Hairpin loop extends from cortex to medulla
Distal convoluted tubule-DCT
Smaller PCT
Collecting duct
Site of emptying if the DCT, leading to the pelvis of the kidney
Where does ultrafiltration take place?
Bowman’s capsule
Describe the process of ultrafiltration
High hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus forces small molecules out of capillary fenestrations/gaps AGAINST osmotic gradient
Basement membrane wars as a filter for blood cells and large molecules
Podocytes drains fluid into bowman’s capsule
How are cells in the bowman’s capsule adapted for filtration
Fenestrations between epithelial cells of capillaries
Fluid can pass between and under folded membranes of podocytes
Where does selective re absorption occur
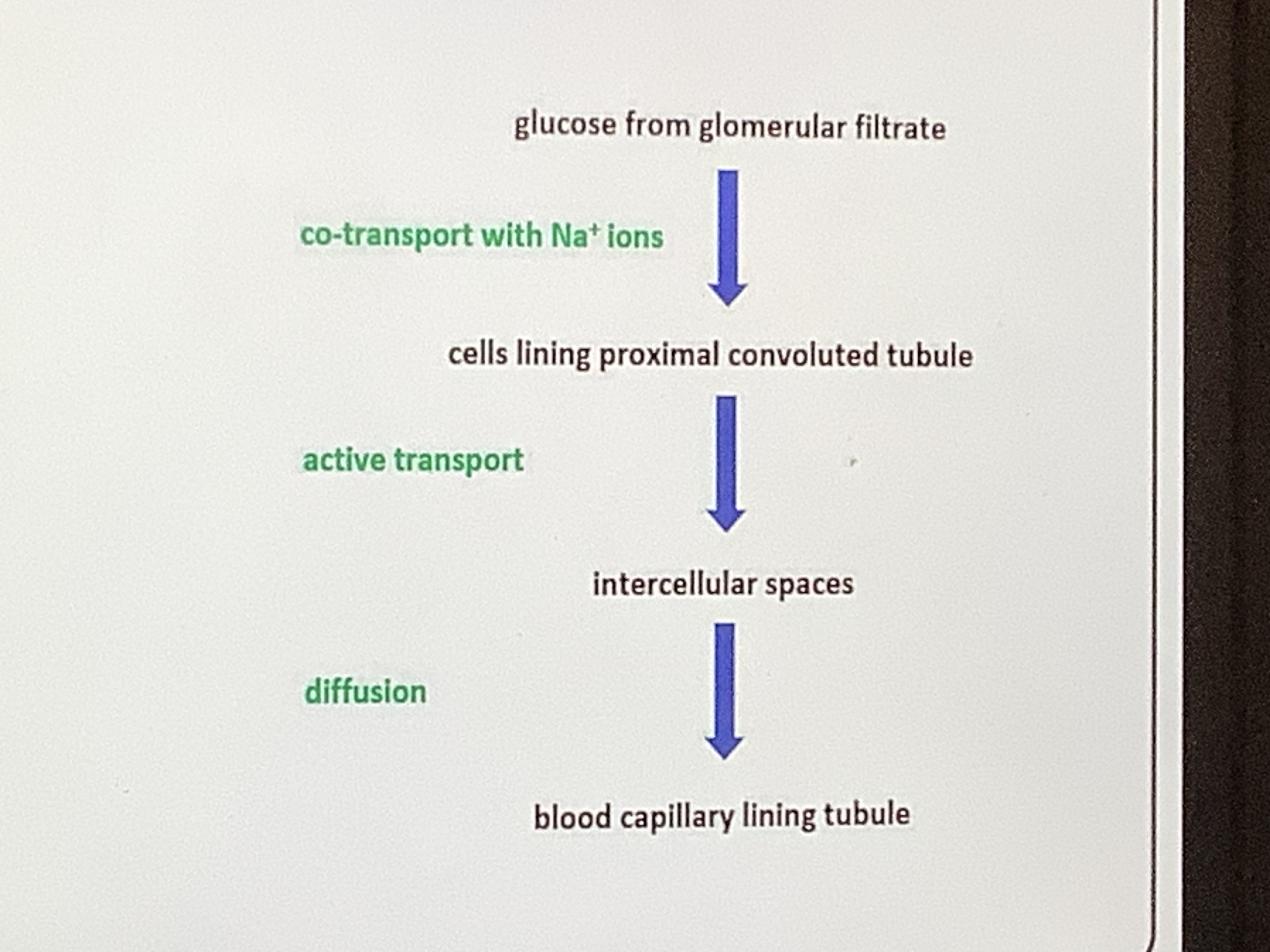
Occurs in PCT
What happens during selective reabsorption
Useful molecules from glomerular filtrate, e.g glucose are reabsorbed into blood
Outline the transport process involved in selective re absorption
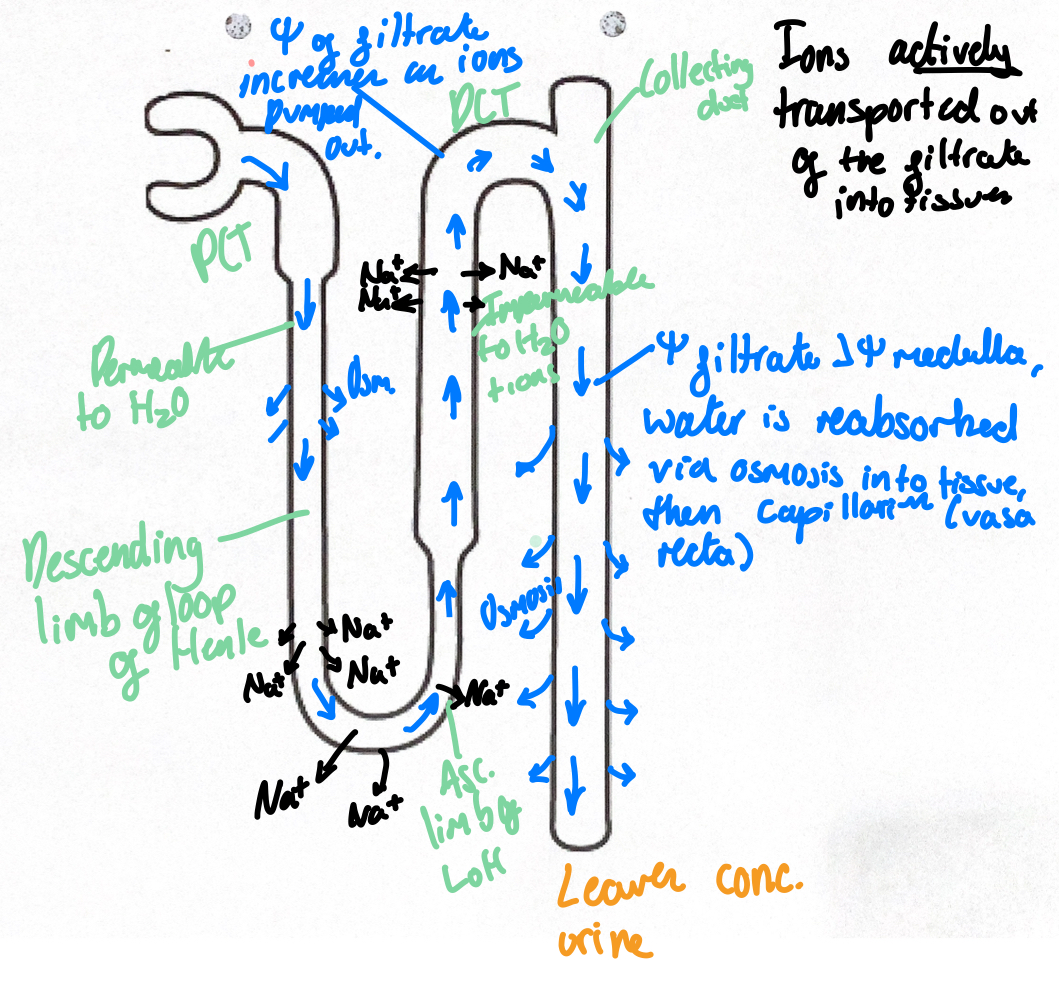
How does the kidney produce urine
By reabsorbing the water from the glomerular filtrate by passing it through the loop of henle,DCT and Collecting duct
What happens in the loop of henle
Active transport of Na + & Cl - out of ascending limb
Water potential of interstitial fluid decreases
Osmosis of water out of descending limb an ascending limb is impermeable to water
Water potential of filtrate decreases as filtrate passes through descending limb,lowest as it passes into medulla
Explain the role of the DCT
Reabsorption of water and ions
Define osmoregulation
Control of plasma water potential via negative feedback homeostatic mechanisms
Explain the role of the hypothalamus in osmoregulation
Osmosis of water out of osmoreceptors, causing them to shrink
This triggers the release of ADH from neurosecretary cells in the posterior pituitary gland
Explain the role of ADH in osmoregulation
Binds to receptors on membranes of cells in the DCT and the collecting duct,triggering the activation of cAMP as a secondary messenger
How does the activation of cAMP increase re absorption of water
Phosphorylase vesicles bind to membrane, which contain aquaporins, allowing more water to pass through the channel proteins on the cell surface membrane
Also increases permeability of cells to urea
What can cause kidney failure? [4]
Kidney infections causing inflammatory damage
Kidney Stones
Uncontrolled Diabetes
High blood pressure
Describe the effects of kidney failure, and their consequences [3]
Build up of toxic waste products causes vomiting
Kidneys cannot remove excess water, so fluid accumulation leads to swelling
Disruption to electrolyte balance can cause bones to become more brittle or increase water retention
Name potential treatments for kidney failure [2]
Renal dialysis
Kidney transplant
Describe haemodialysis [4]
Removes blood from body and pumps through a machine
Blood runs countercurrent to dialysis fluid
An artificial membrane separates the fluids, allowing for diffusion of molecules across the membrane
A blood thinner is used to prevent clotting
Describe peritoneal dialysis [3]
Dialysis fluids is put into body cavity
Exchange of molecules happen across body’s own peritoneal membrane
Fluid must be drained and replaced
How can urine samples be used to test for pregnancy?
Monoclonal antibodies in the test bind to hCG in the urine of pregnant women
How can urine samples be used to test for drugs such as anabolic steroids
Gas chromatography measures the time taken for the urine sample to pass through the column compared to the time it takes for a steroid to pass through
What are anabolic steroids?
Drugs used to build muscle mass
![<p>What part of the kidney is this from and why? [2]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/12b25217-a794-4fe2-9002-445897f7136c.jpg)
What part of the kidney is this from and why? [2]
Cortex [1]
Shows glomerulus/Bowman’s capsule [1]



