1.1 The market system
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
166 Terms
What is the problem of scarcity?
where there are unlimited wants and finite resources, leading to the need to make choices
What three factors must businesses consider?
-What to produce?
-How to produce?
-For whom to produce?
What is the basic economic problem?
unlimited wants and limited resources (scarcity)
why does scarcity lead to choice
Scarcity means there are unlimited wants but limited resources. This means people cannot have everything they want, so they must make choices about what to buy or use. When one option is chosen, another must be given up
What does opportunity cost mean?
The foregoing of the next best alternative
Who are economic agents?
consumers, producers, government
What is a consumer?
The person who uses the product/service
What is a production possibility curve (PPC
)?
a curve measuring the maximum combination of outputs that can be obtained from a given number of inputs.
-D = unemployed resources
-A,B,C = maximum productive potential of an economy
-E = impossible to obtain unless there is a shift
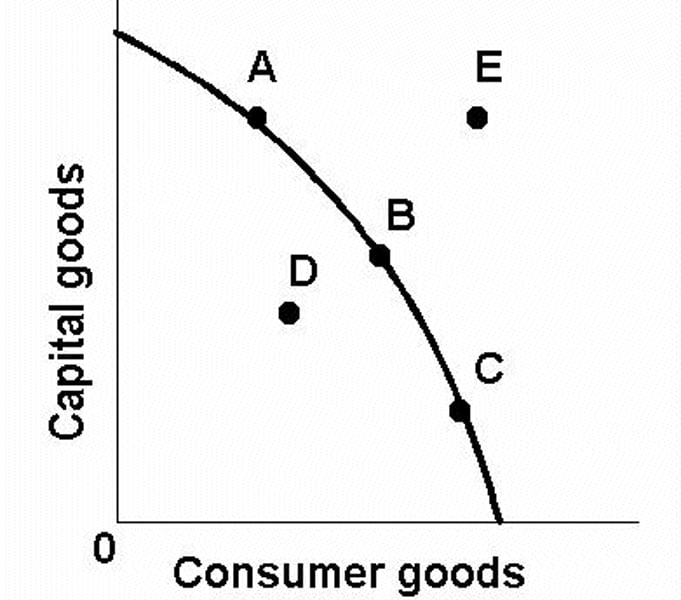
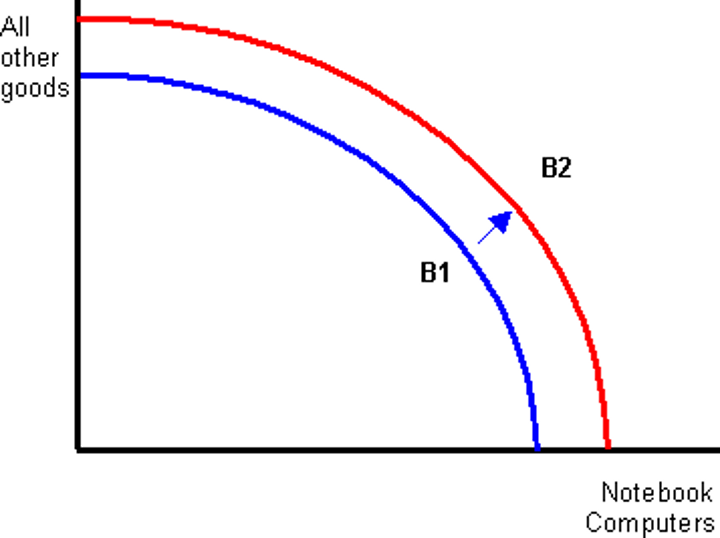
What does a positive shift of a PPC look like?
How is economic output measured?
-GDP (Gross domestic product)
-GNI (Gross national income)
What is positive economic growth?
an increase in GDP
What is a negative economic growth?
A decrease in GDP
What are the causes of positive economic growth?
-More money invested in economy
-Increase in FDI (Foreign Direct Investment)
-Increased immigration (workforce grows in size)
-Discovery of a new resource
-Increase the national minimum wage (attracts people in workforce)
Causes of Negative economic growth?
-War
-Natural disaster
-Brexit
-Global viruses (Covid)
-Financial Crash (2008)
What do consumers aim to maximise?
Consumers aim to maximise benefit
What do businesses aim to maximise?
Businesses aim to maximise profit
What does it mean to maximise benefit?
Making the most out of something/buying an item that is likely to provide the greatest satisfaction
What is profit?
When revenue exceeds total costs
Why is profit likely to be a key objective for a business?
-So shareholders/investors return a greater dividend (return)
-Reinvest back into the business
Why are consumers not always good at calculating benefit?
-It's difficult to calculate
-It can only be decided once the product has been consumed
Why do consumers have habits that are hard to give up?
-They may be addicted to a product/service
-It could be hard to swap (eg. switching banks)
-Their perceived benefit is greater than their actual benefit
What are reasons consumers may not maximise benefit?
-They may copy others' behaviour
-They have habits that are hard to give up
-They are not always good at calculating their benefit
What are reasons why producers may not maximise profit?
-They may have managers that revenue maximise or sales maximise
-Charitable work
-May prioritise caring for customers
Who owns a business?
shareholders (if a public limited company)
Who runs a business?
An elected board of directors
What is revenue?
money obtained from goods or services (aka: income)
What is revenue maximising?
An alternate way of saying maximising profit
What are likely objectives for businesses that don't aim to maximise profit?
-They may have managers that revenue maximise or sales maximise
-They may prioritise caring for customers -producers may complete charitable work
What is demand?
the amount of a good/service that a consumer is willing & able to purchase at a given price in a given time period
What is a demand curve?
a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
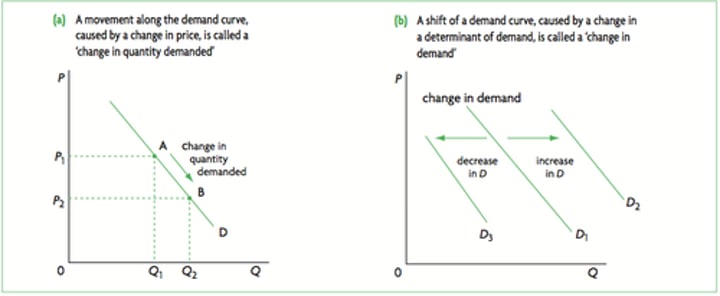
factors that may cause a shift in demand curve?
-Advertising
-Income
-Fashion and tastes
-Price of substitute goods
-Price of complementary goods
-Demographic changes
What is advertising and how will it impact a demand curve?
A form of promoting a product. Used to increase desirability of something by raising awareness. Cause outward shift in demand/increase in demand
What is income and how will it impact a demand curve?
The inflow of money to a person. Can come from work/investments/rental. Cause a positive shift - the more income consumers have, the more they'll demand products/services
How can fashion/tastes impact demand?
If there is a new trend then it'll cause a shift in demand
What is a substitute good?
a good that can be used in place of another good
How would an increase In price affect demand?
It would decrease demand
How would a decrease In price affect demand?
It would increase demand
If the price of a substitute increases, what happens to demand for the original product?
Demand will increase
What is a complementary good?
Products that are used all together, an increase or decrease in demand for one will result in the same affect for demand in the other.
What are demographic changes?
Changes to the size and structure of the population
What is technology?
The use of automated processes to speed up production
How does technology affect business's output?
Increase output potential
What are indirect taxes?
A tax that can be passes on another economic agent
Examples of Indirect tax?
-VAT
-congestion charge
-Stamp duty (based on buying a house)
What is a subsidy?
A government payment that supports a business and increases output
How do subsidies affect supply?
increase in supply/supply will shift outwards
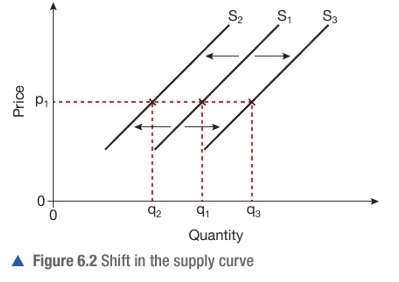
What are factors that shift supply?
-Cost of production
-Changes in technology -Indirect taxes
-Subsidies
-Natural factors
How will natural factors affect supply?
A natural disaster will destroy supply. Cause an inward shift In supply.
How does the cost of production shift the supply curve?
The quantity supplied will decrease if production costs increase, leading to a leftward shift in the supply curve.
How can weather affect supply?
-Good weather can increase crop yield - causing outward shift in supply
-Bad weather can damage supply of crops - causing inward shift in supply
What is a Supply curve?
a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
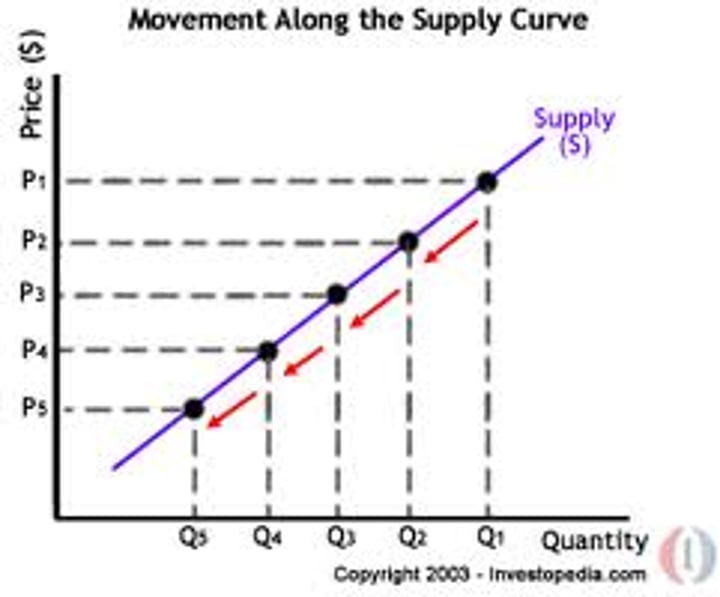
What is excess demand?
when quantity demanded is more than quantity supplied (shortage of supply)
What is excess supply?
when quantity supplied is more than quantity demanded (surplus of supply)
What is national minimum wage?
Lowest amount a worker can legally be paid for at their age
What are market forces?
When the market correct itself to remove either excess supply or demand, also known as the 'invisible hand'
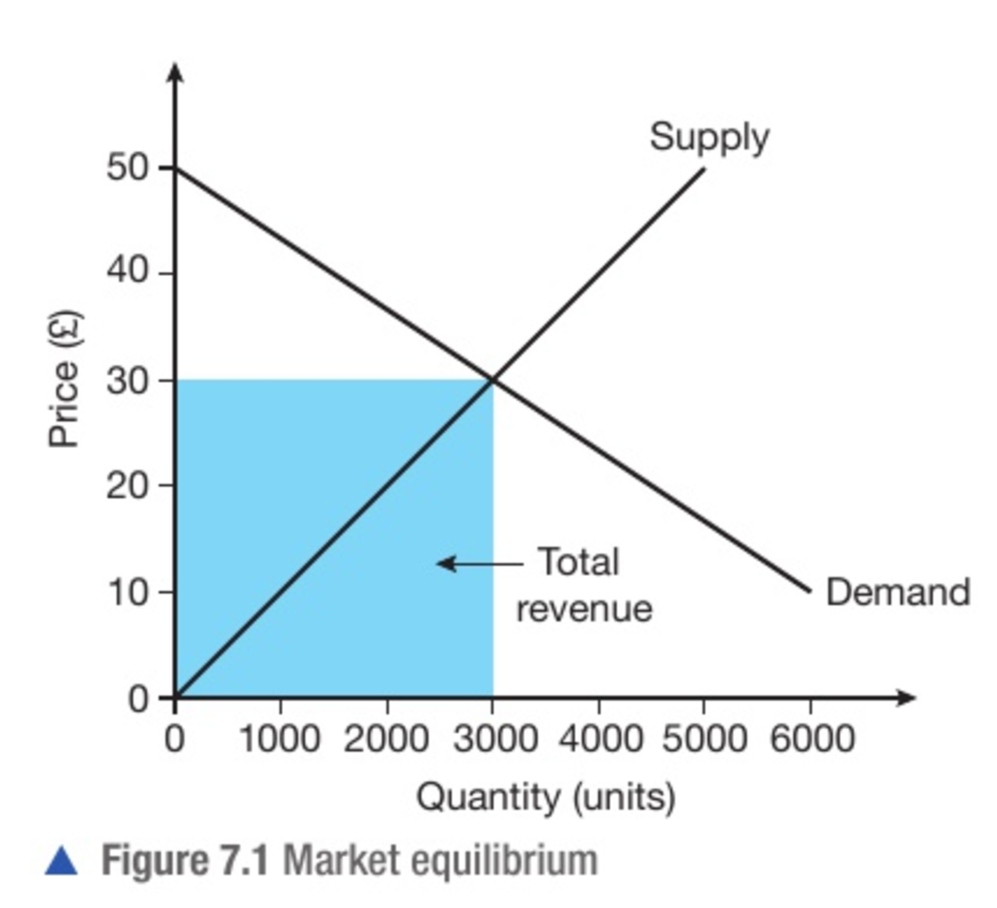
market clearing price(aka equilibrium )
price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. there are no buyers left without goods and no sellers left with unsold stock
What is equilibrium?
The pont of balance, where supply equals demand
What is PED? (Price Elasticity of Demand)
the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in price
What is the formula for PED?
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
What numerical value does PED have if it's inelastic?
PED < 1
What numerical value does PED have if it's elastic?
PED > 1
If PED is 0, demand is?
perfectly inelastic
If PED is infinity, demand is?
Perfectly elastic
What numerical value is PED if ir's unitary?
-1 or 1
What does perfectly inelastic demand mean?
A change in price will result in no change in quantity demanded
Factors affecting PED?
-Availability of substitutes
-Degree of necessity
-Proportion of income spent on a product
-Time
How does Availability of substitutes affect PED?
products with a large number of available substitutes generally have a elastic PED, because if the price of the original product were to rise, consumers would just switch to the available substitutes which are presumably cheaper.
How does Degree of necessity affect PED?
products that are considered necessities generally have inelastic PED, this is because even if the price were to rise, consumers would still need to buy the product because by definition, they are necessities.
How does Proportion of income spent on a product affect PED?
Products which cost very little in relation to income are more price inelastic and vice versa
How does Time affect PED?
The longer the time period, the easier it is for consumers to adjust their spending. Therefore demand is inelastic in the short-run but elastic in the long-run.
What is supply?
The output from a business at any given price point over a period of time
What is PES? (price elasticity of supply)
responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price
What is the formula for PES?
% change in quantity supplied / % change in price
What are the factors of production?
-Land (To locate a business and natural resources)
-Labour (people employed)
-Capital (Funding/money)
-Enterprise (coming up with business ideas)
How are the factors of production likely to impact PES?
-If there is limited land available, PES will be inelastic
-If there is high unemployment, PES will be elastic
What are stocks?
Raw materials/components that are required to produce a good or service
How can stocks impact PES?
The more stock available, the more elastic supply is likely to be
What is capacity for a business?
The total output a business can produce
What is spare capacity?
The difference between actual output and potential output
Factors affecting PES?
-Factors of production
-Availability of stocks
-Spare capacity
-Time
How will spare capacity impact PES?
More spare capacity = greater elasticity because there are more available resources to make more
How does time impact PES?
If a business has limited time to produce more items, supply will be likely to be inelastic
What is PES likely to be for manufactured goods?
Elastic as firms can produce more if price increases quickly
What is PES for primary products likely to be?
Inelastic as it takes more time and resources to find.
What is income elasticity of demand?
The responsiveness of demand to a change in income
What is the formula for YED? (income elasticity of demand)
%change in quantity demanded / %change in income
IF YED >1, the good is.....
A luxury good
If YED = 0-1, the good is...
A normal good
If YED < 0, what type of good is it?
An inferior good
What is a mixed economy?
an economic system combining the private and public sector
What is an economy?
the wealth and resources of a country or region, especially in terms of the production and consumption of goods and services.
What is the public sector and what are their goals?
the part of the economy that is controlled by the government (like the NHS). Their goals are to improve quality of services, minimise costs and profit
What is the private sector and what are their goals?
the part of the economy that is controlled by individuals or groups of individuals (like Cadburys). Their goals are profit maximisation, survival and growth
What does the private sector produce?
Consumer goods such as clothes/food and services like in restaurants
What does the public sector 'produce'?
Essential services that may not be provided to all by the private sector such as education. street lighting and medical access
What is tendering?
Government allocating work to a business
What is privatization?
the transfer of a business, industry, or service from public to private sector
What is market failure?
Where markets lead to an inefficient distribution of goods and services
Factors leading to market failure?
-Externalities
-Lack of competition
-Missing markets
-Lack of information
-Factor immobility
What is an externality?
a benefit or cost that affects someone who is not directly involved in the production or consumption of a good or service