Chemical Building Blocks of Life
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Biological molecules
These consist primarily of carbon bonded to carbon, or carbon bonded to other molecules.
Carbon bonded to carbon, or
Carbon bonded to other molecules
Biological molecules consist primarily of (2):
4
Carbon can form up to how many covalent bonds?
True
(ADDITIONAL: Functional groups include hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, phosphate, and methyl.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Carbon may be bonded to functional groups with specific properties.
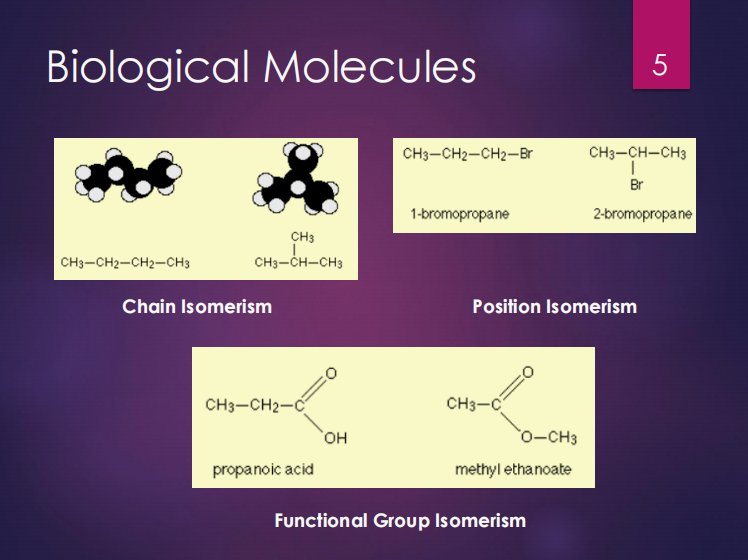
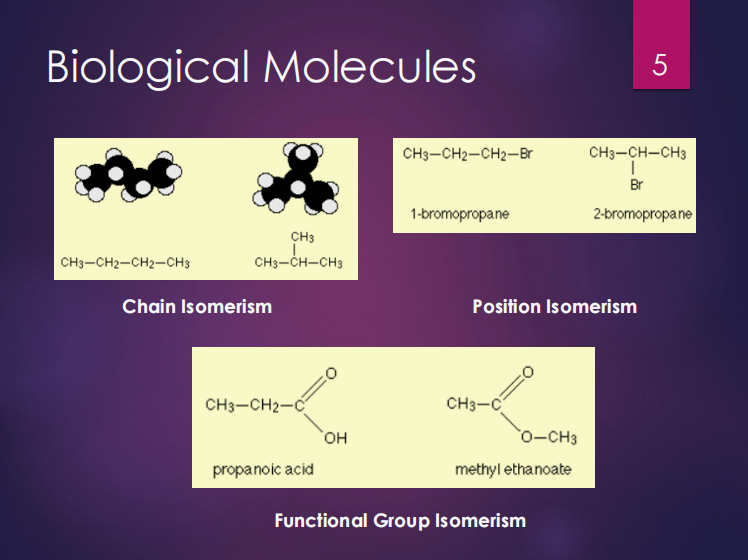
Isomers
These are molecules with the same chemical formula.
Structural isomers
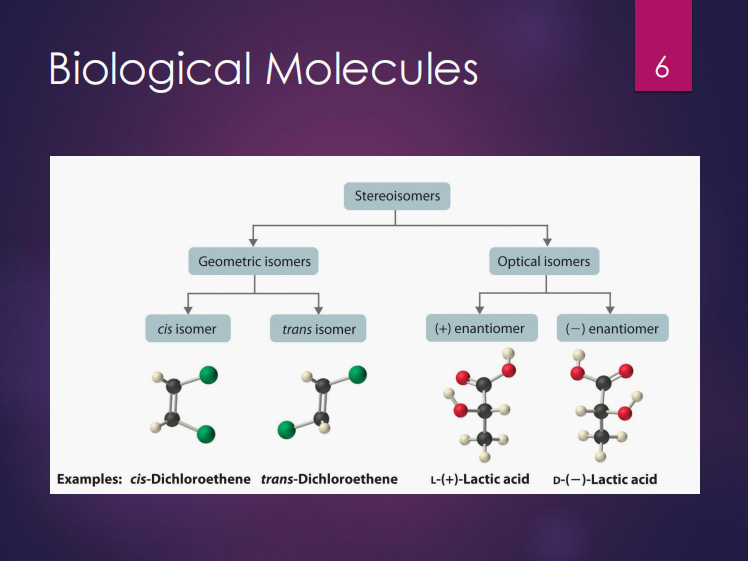
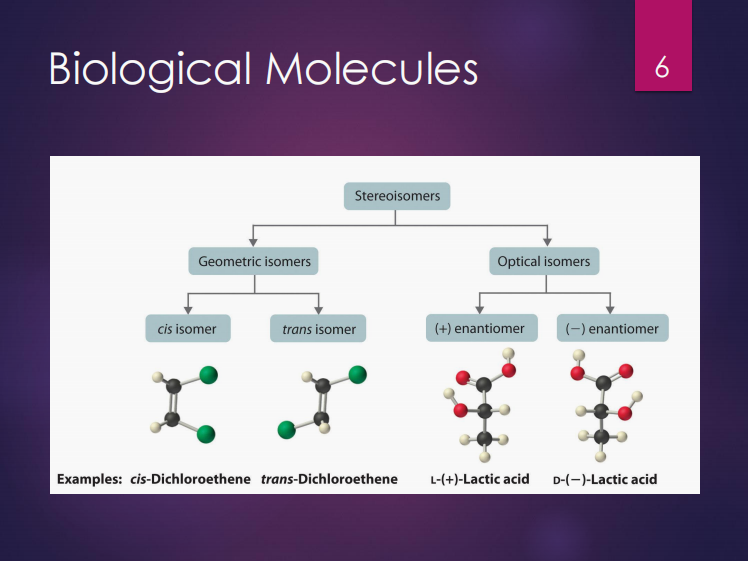
Stereoisomers
Isomers can either be (2):
Chain isomerism
Position isomerism
Functional group isomerism
Structural isomers can be (3):
Chiral molecules
These are mirror-images of each other.
Optimal isomers
Chiral molecules are also known as ___.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Biological molecules are typically large molecules constructed from smaller subunits.
Monomer
Polymer
Biological molecules are constructed from smaller subunits. Examples are (2):
Monomer
(ADDITIONAL: Mono = 1; mer = unit)
It is a small molecule.
Polymer
(ADDITIONAL: poly = many; mer = unit)
It is a long-chain molecule made up of a repeated pattern of monomers.
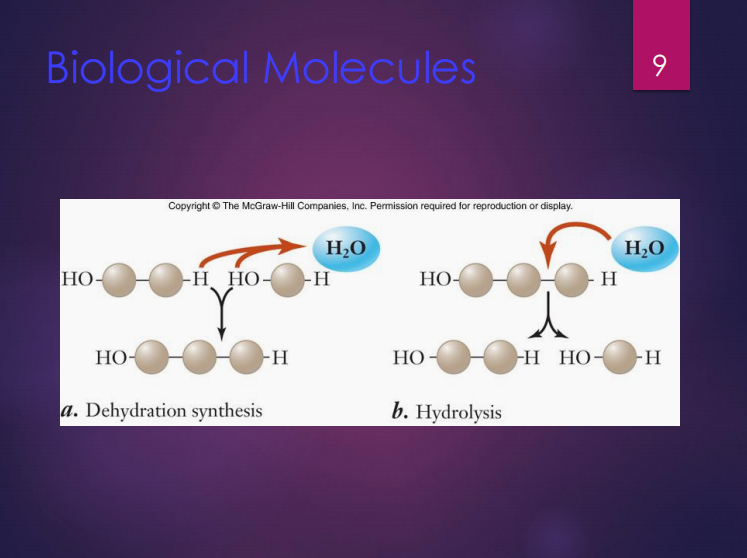
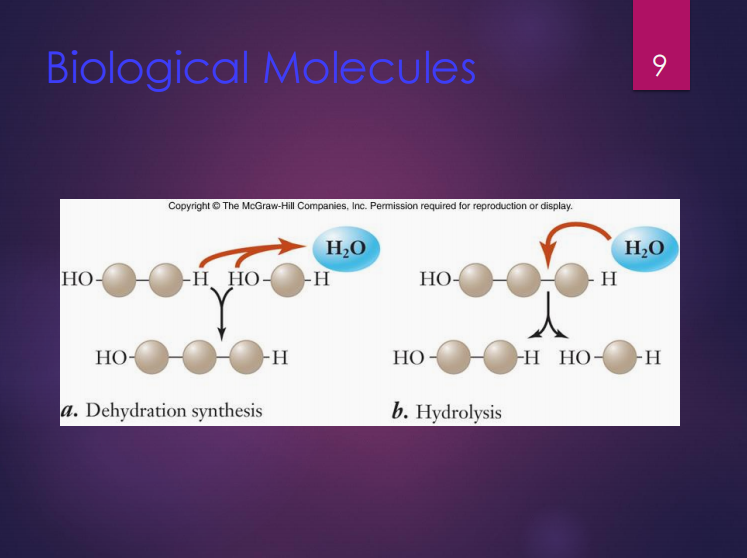
Dehydration synthesis
It is the formation of large molecules by the removal of water.
Hydrolysis
It is the breakdown of large molecules by the addition of water.
Dehydration synthesis
In this reaction, monomers are joined to form polymers.
Hydrolysis
In this reaction, polymers are broken down to monomers.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Carbohydrates
These are molecules with a 1:2:1 ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
(CH2O)n
What is the empirical formula for carbohydrates?
Sugars
Starch
Glucose
Enumerate three (3) examples of carbohydrates.
False
(EXPLANATION: C-H covalent bonds hold much energy. Hence, carbohydrates are good energy storage molecules.)
TRUE OR FALSE. C-H covalent bonds hold less energy. Hence, carbohydrates are bad energy storage molecules.
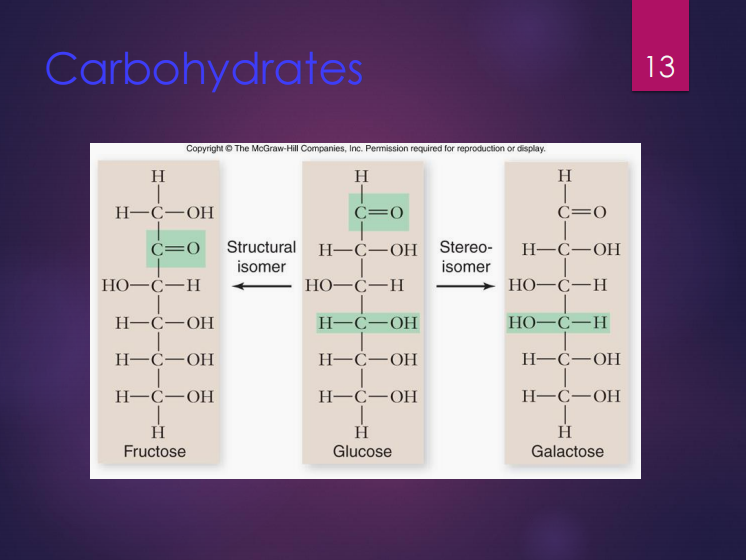
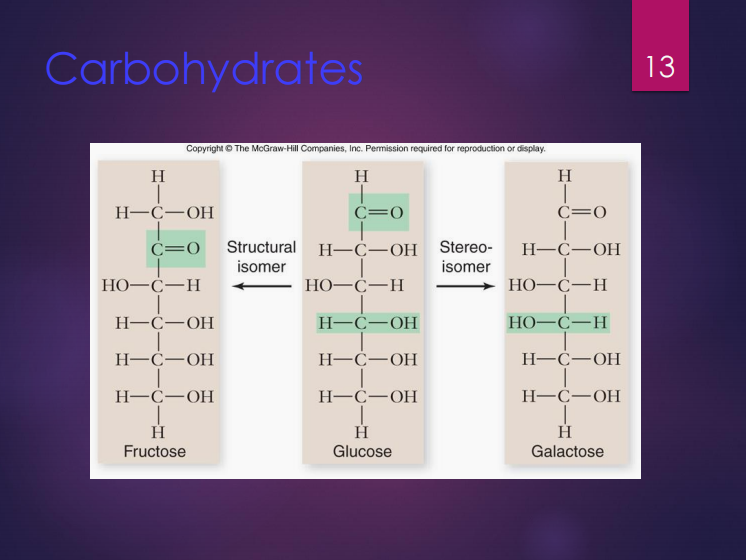
Glucose
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
It is a monosaccharide that contains 6 carbons and considered very important in energy storage.
Monosaccharide
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
It means ‘single sugar’.
Fructose
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
It is a structural isomer of glucose.
Galactose
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
It is a stereoisomer of glucose.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Disaccharides
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
These are two (2) monosaccharides linked together by dehydration synthesis.
Disaccharides
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
These are used for sugar transport or energy storage.
Sucrose
Lactose
Maltose
Enumerate three (3) examples of disaccharides.
Polysaccharides
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
These are long chains of sugars that are used for energy storage.
Starch
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
In plants, a polysaccharide that is used for energy storage is ___.
Glycogen
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
In animals, a polysaccharide that is used for energy storage is ___.
Cellulose
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
In plants, a polysaccharide that is used for structural support is ___.
Chitin
CARBOHYDRATES. Determine what is being described below.
In animals, a polysaccharide that is used for structural support is ___.
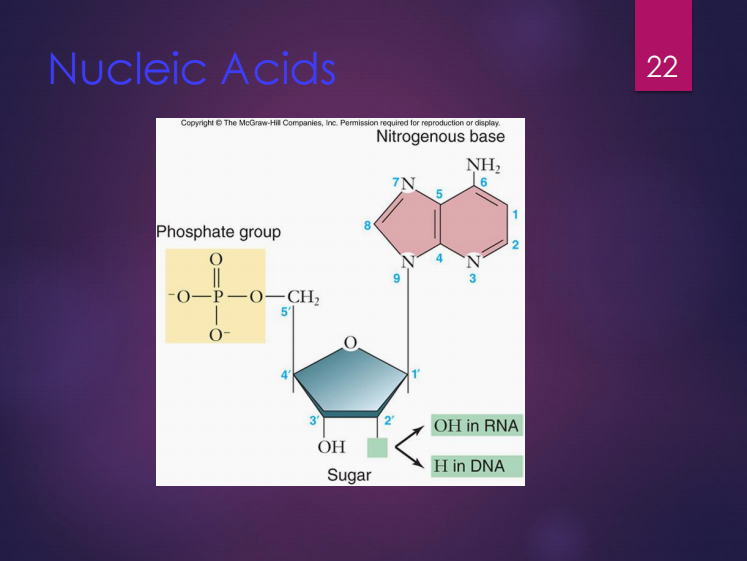
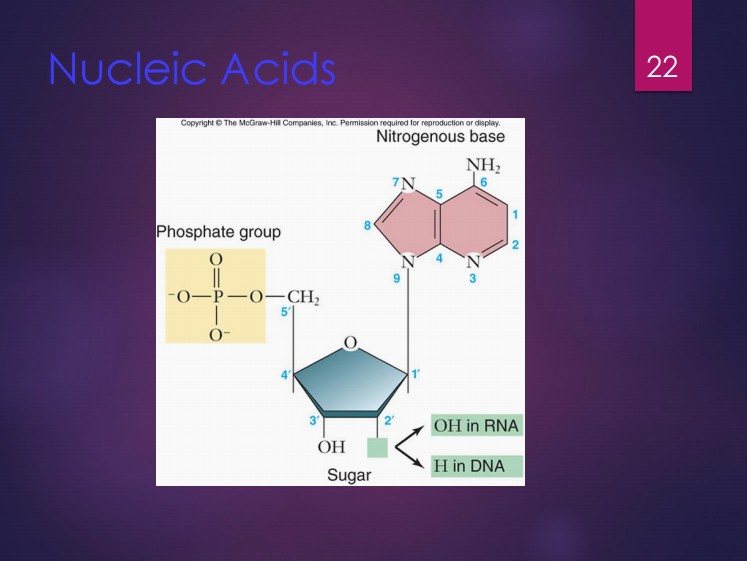
Nucleic acids
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
These are polymers of nucleotides.
Sugar
Phosphate
Nitrogenous base
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
Nucleotides are composed of three (3) components which are:
Deoxyribose
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
It is the sugar found in DNA.
Ribose
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
It is the sugar found in RNA.
Purines (Ex.: adenine, guanine)
Pyrimidines (Ex.: thymine, cytosine, uracil)
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
Nitrogenous bases include (2):
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
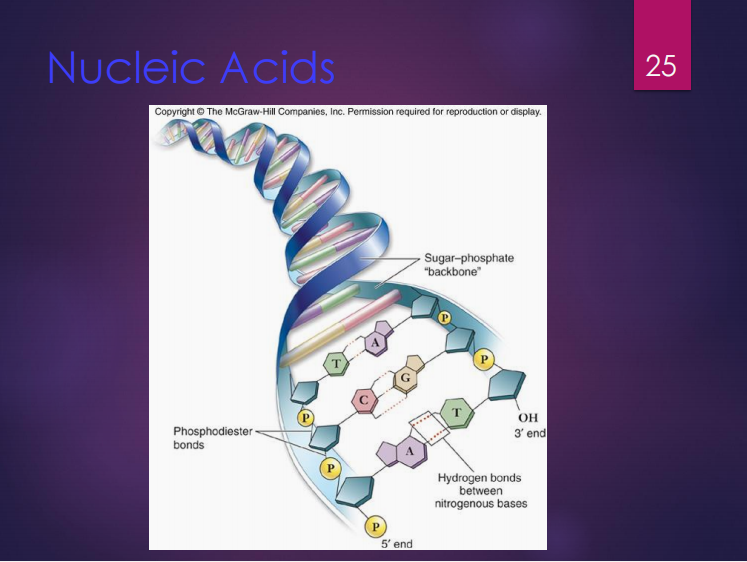
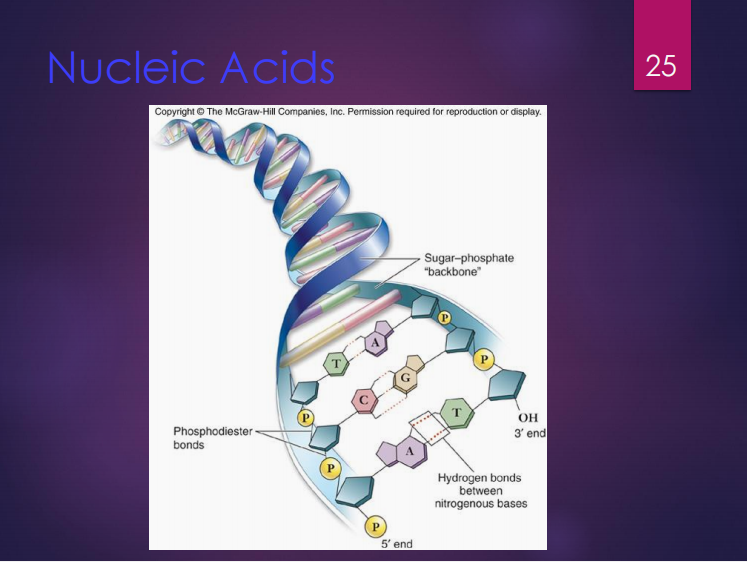
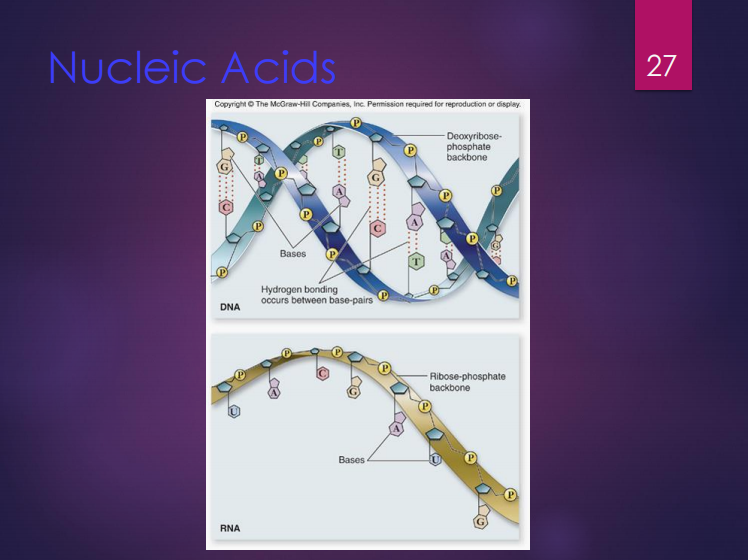
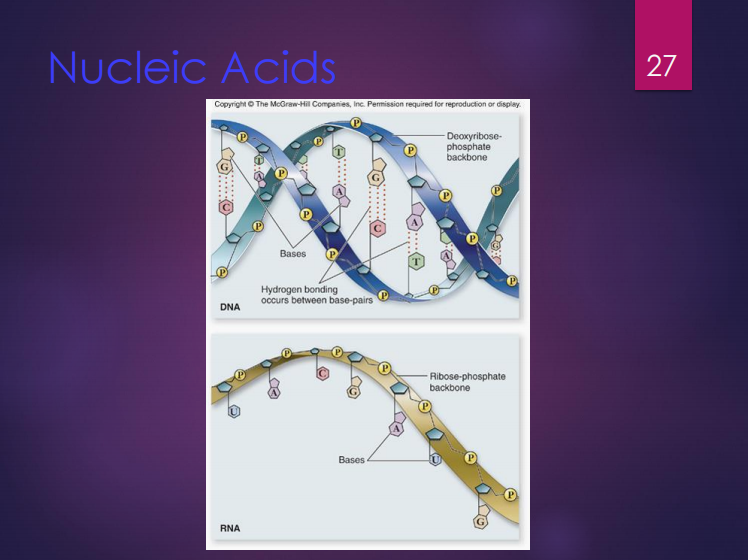
DNA
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
It is composed of nucleotides connected by phosphodiester bonds.
DNA
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
Its shape is a double helix with 2 polynucleotide strands connected by hydrogen bonds.
DNA
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
Genetic information is carried in the sequence of its nucleotides.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Polynucleotide strands are complementary.
Phosphodiester bonds
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
DNA is composed of nucleotides connected by what bonds?
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
RNA
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
It contains ribose instead of deoxyribose and uracil instead of thymine.
RNA
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
It is a single polynucleotide strand.
RNA
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
Its functions include reading the genetic information in DNA and directing the synthesis of proteins.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of function.
Long-term storage of genetic information; transmission of genetic information to make other cells and new organisms
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of function.
Used to transfer the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes to make proteins; used to transmit genetic information in some organisms
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of function.
May have been the molecule used to store genetic blueprints in primitive organisms
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of structural features.
B-form double helix
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of structural features.
A double-stranded molecule consisting of a long chain of nucleotides
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of structural features.
A-form helix
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of structural features.
A single-strand helix consisting of shorter chains of nucleotides
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of composition of bases and sugars.
Deoxyribose sugar phosphate backbone
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of composition of bases and sugars.
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine bases
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of composition of bases and sugars.
Adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil bases
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of composition of bases and sugars.
Ribose sugar phosphate backbone
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of propagation.
It is synthesized on an as-needed basis.
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of propagation.
It is self-replicating.
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of base pairing.
A-T (adenine-thymine)
G-C (guanine-cytosine)
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of base pairing.
A-U (adenine-uracil)
G-C (guanine-cytosine)
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of reactivity.
The C-H bonds make it fairly stable, and the body destroys enzymes that would attack it.
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of reactivity.
The O-H bond in the ribose makes the molecule more reactive.
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of reactivity.
It is not stable under alkaline conditions, and the large grooves in the molecule make it susceptible to enzyme attack.
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of reactivity.
The small grooves in the helix serve as protection, providing minimal space for enzymes to attach.
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of reactivity.
It is constantly produced, used, degraded, and recycled.
DNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of ultraviolet damage.
It is susceptible to UV damage.
RNA
DNA OR RNA. Determine what is being described below in terms of ultraviolet damage.
It is relatively resistant to UV damage.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
It is the primary energy currency of the cell.
NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
It is a redox coenzyme that can oxidize a metabolite by accepting two electrons and a hydrogen ion or can reduce a metabolite by giving up electrons.
FAD (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide)
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
It is a redox coenzyme that accepts two electrons and two hydrogen ions.
NADH
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
NAD+ can oxidize a metabolite by accepting two electrons and a hydrogen ion which results in ___.
FADH2
NUCLEIC ACID. Determine what is being described below.
FAD accepts two electrons and two hydrogen ions to become ___.
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE. Each metabolic reaction in cellular respiration is catalyzed by its own enzyme.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Electrons received by NAD+ and FAD are high-energy electrons and are usually carried to the electron transport system.
False
(EXPLANATION: Only a small amount of NAD+ is needed in cells, because each NAD+ molecule is used over and over again.)
TRUE OR FALSE. A large amount of NAD+ is needed in cells.
Enzyme catalysts
Defense
Transport
Support
Motion
Regulation
Storage
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
Protein functions include (7):
Proteins
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
These are polymers of amino acids.
20 amino acids
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
How many common amino acids are there?
Dehydration synthesis
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
Amino acids are joined by what reaction?
Peptide bonds
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
What bonds form between adjacent amino acids?
Amino group
Carboxyl group
Single hydrogen
Variable R group
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
In the structure of an amino acid, the central carbon atom is surrounded by (4):
R group
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
The structure of the ___ dictates the chemical properties of the amino acid.
Nonpolar
Polar
Charged
Aromatic
Special function
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
Amino acids can be classified as (5):
True
TRUE OR FALSE. The shape of a protein determines its functions.
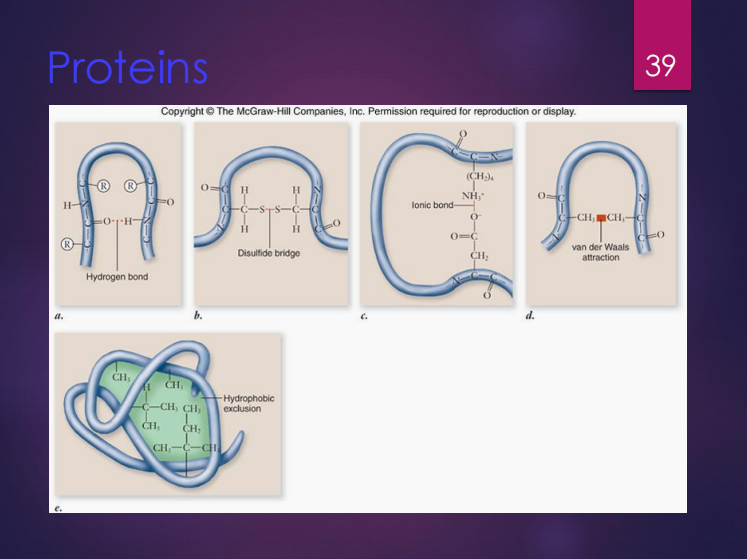
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Ternary structure
Quaternary structure
PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
The shape of a protein has four (4) types of structures which are:
Primary structure
STRUCTURES WITHIN PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
It refers to the sequence of amino acids.
Secondary structure
STRUCTURES WITHIN PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
It refers to the interaction of groups in the peptide backbone.
α- helix, β-sheet
STRUCTURES WITHIN PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
A protein’s secondary structure can either be (2):
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
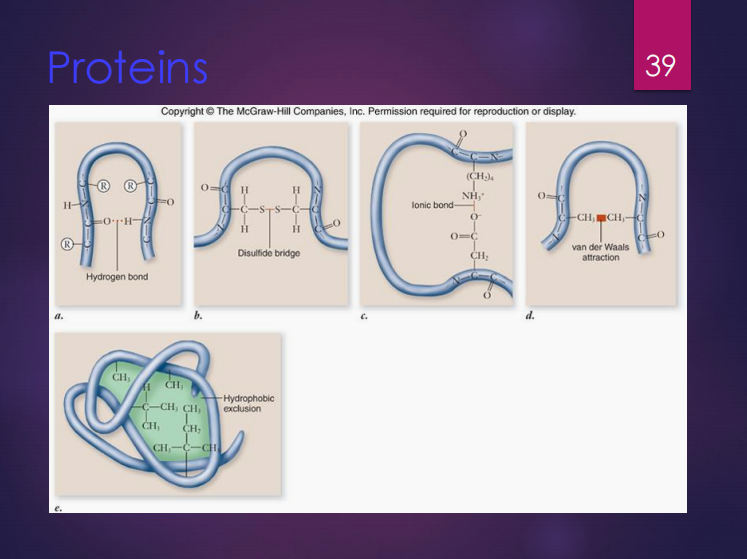
Tertiary structure
STRUCTURES WITHIN PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
It refers to the folded shape of the polypeptide chain.
Quaternary structure
STRUCTURES WITHIN PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
It refers to the interactions between multiple polypeptide subunits.
Chaperone proteins
STRUCTURES WITHIN PROTEINS. Determine what is being described below.
Protein folding is aided by ___.