Chapters 4-5: Mercury
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Surface characteristics
heavily cratered ancient terrain like Moon and parts of Mars
Lava flow properties
similar to the moon
high eruption rates
great travel distances
drown their own vents
explosive volcanic activity
evidence: >30 rimless depressions up to ~40km diameter
distinctive deposits
volatile content interference: up to ~1wt% volatiles in erupting magmas
nature of volatiles: high abundance of sulfur
more volcanic evidence
irregularly shaped, rimless, steep-sided pits up to ~30km diameter
common location: floor of impact craters

long sheet-like lava flows flooded much of northern hemisphere early in geologic history
almost completely buried an old impact crater
mercury atmospheric pressure
zero atmospheric pressure
miniscule amount of magmatic volatiles
<1Pa
convecting eruption clouds cannot form
shock waves form in region above vent
io and moon too (no pressure, no atmosphere)
mercury volcanic composition is
basaltic lava flows
mercury eruption style is
high rate, long distance flows that drown their vents
Mercury impact velocities
highest mean impact velocity among terrestrial planets for asterodial bodies: over ~25km/s
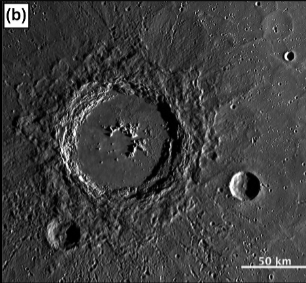
Hokusai Crater
100km diameter
transitional between central peak crater and peak ring basin
continuous (lobate) and discontinuous ejecta
secondary craters surrounding
MOST EXTENSIVELY RAYED CRATER ON MERCURY
rays extend over 1000km from the rim
simple crater dimensions on mercury
D/d: 0.98
coefficient: 0.18
surface gravity 3.78m/s²
mercury impact craters compared to mars
similar surface gravities (mercury = 3.78, mars = 3.72)
Martian complex craters SHALLOWER tha equivalent sized Mercurian
due to: target material properties - mars weaker target, mars also has wind/water processes that reduce crater-related topography through erosion and sedimentary infilling

Rachmaninoff Basin
290km diameter
peak ring basin structure
dark, smooth fractured deposits interior to the inner ring
represent extensive deposits rich in impact melt that were emplaced during crater formation
Peak ring basin formation hypothesis on mercury
has largest population of peak ring structures
on large impact events: depth of impact melting may reach and even exceed depth of cavity floor
when transient cavity uplifted - central, melted part has no strength
only rings from unmelted portion can form out from crater
explains why theres rings but no central peaks
key mercury values/stats
gravity 378cm/s²
mean impact velocity >25km
has most peak ring basins per area of all terrestrial planets
notable craters: Hokusai (~100km), Rachmaninoff (~290km)