Week 9: Survey Research in Social Sciences
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Respondent
A person who provides data by responding to a survey questionnaire.
Questionnaire
An instrument designed to elicit information.
Survey
A list of questions aimed for extracting specific data from a particular group of people.
Closed-ended question
A question where answers are usually provided, and the respondent chooses from among available options.
Open-ended question
A question that allows respondents to answer in their own words.
Survey Data: Quantitative
Data collected from surveys that can be quantified and analyzed statistically.
Survey Questionnaire
A highly structured list of questions and response categories that will be administered exactly to all respondents.
Measurement validity
The accuracy of survey data depends in large part on issues related to whether you are measuring what you think you're measuring.
Comprehensive
Provided answers (response categories) must ensure all individuals have a category.
Mutually exclusive
Only one category per individual must be ensured in the provided answers.
Homogeneous
Response categories must contain similar individuals.
Concise questions
Questions should be focused and straightforward.
Clear phrasing
Questions should avoid confusing terminology.
Explicit questions
Questions should be direct and unambiguous.
Neutral language
Questions should avoid politically or emotionally charged language.
Double-barreled questions
Questions that ask two things at once and should be avoided.
Guidelines for survey questions
1. Ask concise, focused questions; 2. Be simple and clear; 3. Be explicit; 4. Be neutral.
Example of a closed-ended question
Is this work mainly - Mark [X] ONE box: □Manufacturing? □Wholesale trade? □Retail trade? □Other?
Example of an open-ended question
What kind of work was this person doing? (For example: registered nurse, personnel manager, etc.)
Survey Steps
Preparing the questionnaire is a major and crucial task when collecting primary survey data.
Survey Measurement
The accuracy of survey data depends on measurement validity.
Explicit frequencies
Specific time intervals used in surveys, such as 'once a week', instead of vague terms like 'regularly' or 'often'.
Leading questions
Questions that suggest a particular answer or bias the respondent's response.
Social desirability
The tendency of respondents to answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others.
Question order effect
The impact that the sequence of questions has on respondents' answers.
Item non-response
When respondents fail to answer specific questions in a survey.
Survey measurement problems
Potential issues that can arise in the process of collecting data through surveys.
Percentage of respondents
A statistical measure indicating the proportion of survey participants who provided a specific response.
Gallup
A research-based company known for its public opinion polls.
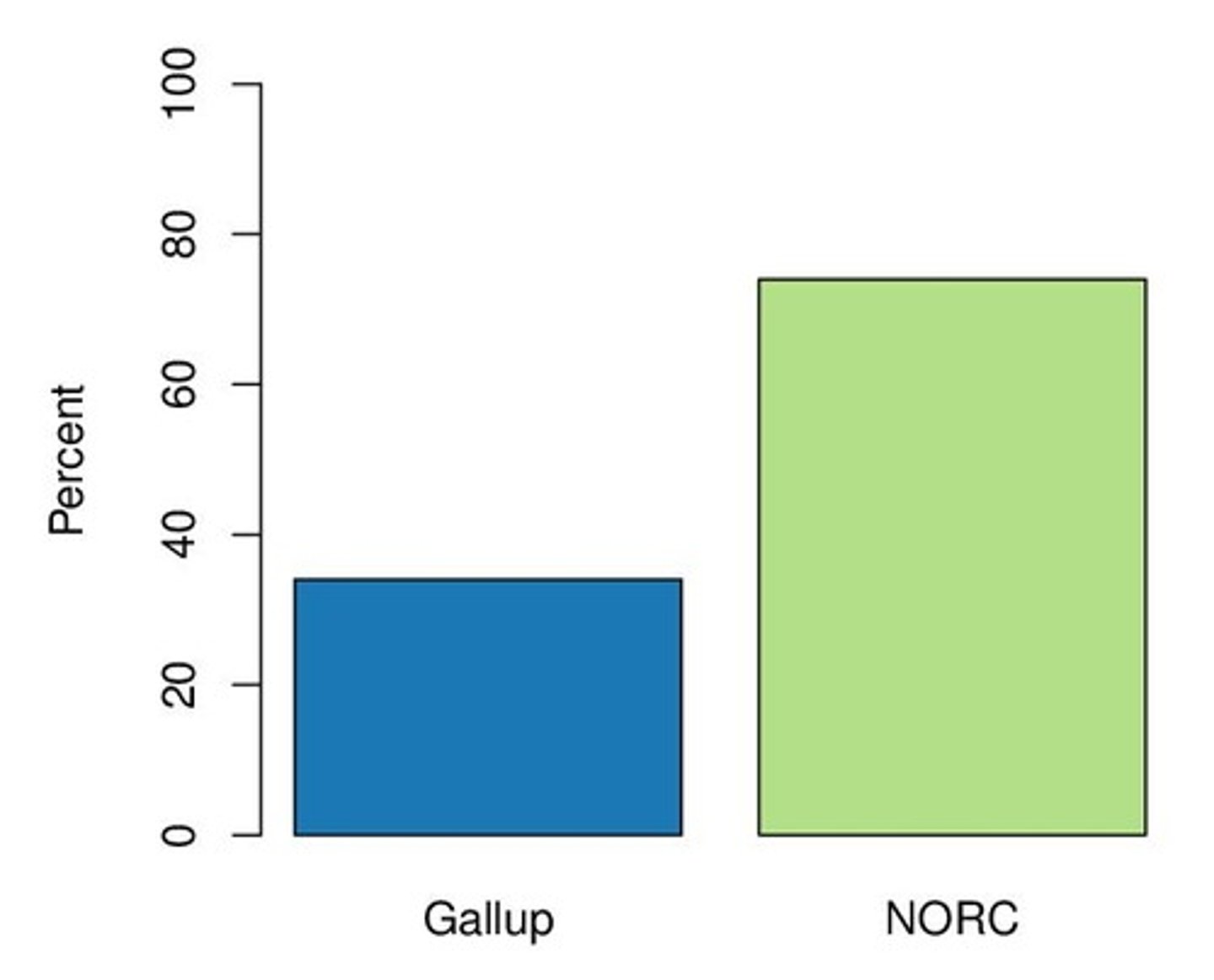
NORC
The National Opinion Research Center, known for conducting social research.
General Social Survey (GSS)
A sociological survey used to collect data on demographic characteristics and attitudes of residents of the United States.
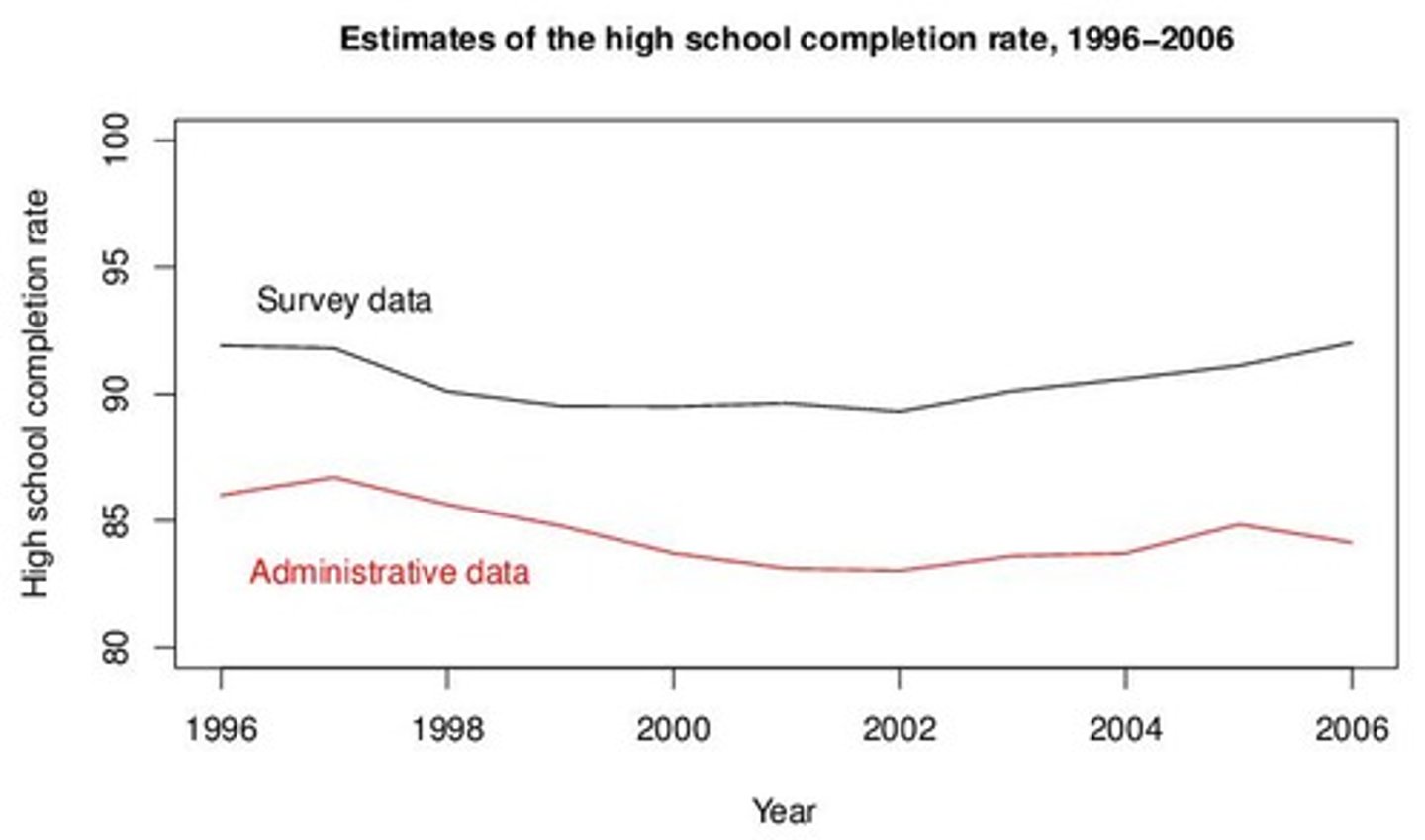
High school completion rate
The percentage of individuals who have completed high school within a specified time frame.
Korean War survey questions
Questions designed to gauge public opinion on the United States' involvement in the Korean War.

Alcohol consumption questions
Survey questions aimed at assessing individuals' drinking habits over a specified period.
Effect of question wording
How the phrasing of survey questions can influence the responses given by participants.
Respondent grouping
The categorization of survey participants based on specific characteristics, such as gender.
Residual effect
The lingering impact of a previous question on the response to a subsequent question.
Pregnant woman abortion questions
Survey questions regarding opinions on the legality of abortion for pregnant women under various circumstances.
Opposite sex partners
Refers to sexual partners of a different gender.
Survey data
Information collected through questionnaires or interviews from respondents.
Administrative data
Data collected through administrative records rather than through direct surveys.
Closed population
A population where there is no migration in or out, affecting the dynamics of survey responses.
Percent in favor
The proportion of respondents who express support for a particular issue or question.
Interviewer effects
Interviewer effects occur when the answers respondents provide are affected by the characteristics of the person who is interviewing them.
Probability sampling
The probability of selection into the sample is known for all members of the population.
Non-probability sampling
Data from a non-probability sample cannot be used to make inferences about the larger population.
Survey Sampling
Generally, survey samples are probability samples representative of populations.
Sampling and Error
A large unbiased sample gives good information about the population.
Census
Entire population.
Selection Bias
Systematic error can happen because of selection bias, where some people are systematically not included in the sample.
Coverage error
Some people are in the population and not on the list.
Non-response
Not everyone in the sample answers the questions.
Survey non-response
The number of individuals who completed the survey divided by the number of individuals selected for the sample.
Response rate
The proportion (or percentage) of individuals selected into the sample who complete the survey.
Survey Response Rate
An important measure of the quality of the survey; low response rates are problematic.
Effect of question order
The order of questions can influence the responses given by participants.
Effect of examples
The examples provided can affect the responses of interviewees.
Data Collection for Surveys
When collecting primary survey data, a major and crucial task is sampling respondents and then checking and tracking the quality of the sample.
Survey Sample Size Tradeoffs
LARGE sample size reduces random error; an UNBIASED or PROBABILITY sample eliminates systematic error.
Generalizable
Data from a probability sample can be used to make inferences about the larger population.
American Community Survey
A survey that collects data from 50,000 households per month.
General Social Survey
A survey that provides local representativeness and flexibility.
Current Population Survey
A survey that samples 3,000 households.
Survey method
The survey method is tailored to extracting data from large numbers of people.
Attitudes toward interracial marriage
An example of data collected that can be influenced by the race of the interviewer.
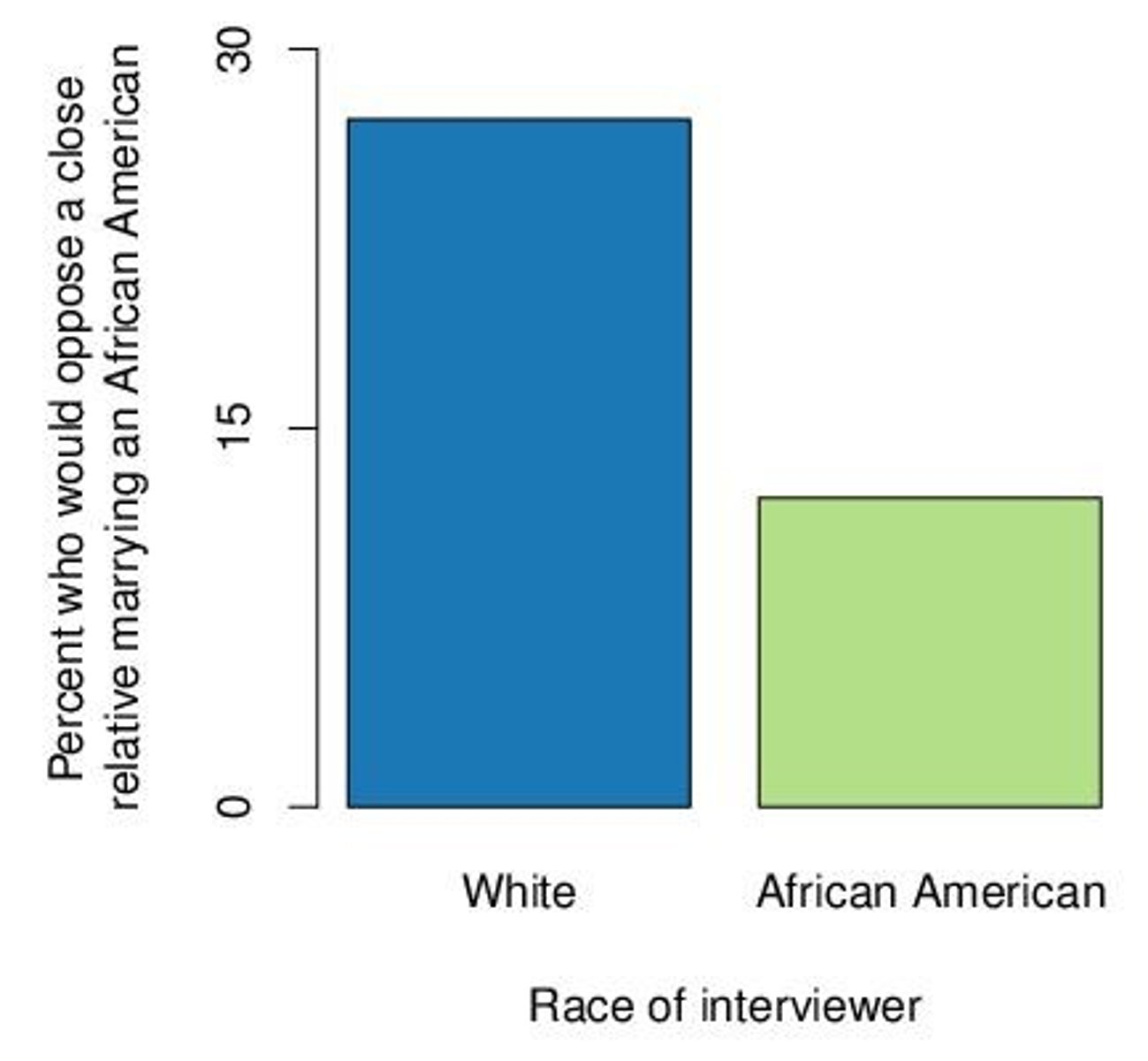
High Quality Surveys
Surveys that are representative of the same population and provide a standard for comparison.
Population Generalization
The population you can generalize to is the population from the sampling frame.
Subnational Samples
Samples of smaller populations that may not hold findings for national or regional populations.
Data Processing Lag
Considerable delays in data processing and release may make data out-dated.
Item Non-Response
When people choose not to answer a specific question in a survey.
Impute Values
The process of guessing at a non-response answer or not using the person's whole survey.
Systematic Differences
Differences between non-responders and those who answer every question that may affect results.
Average Income for White Respondents
$51,000.
Average Income for Black Respondents
$45,500.
Example Respondent Data
A table showing race, gender, and income for various respondents.
Consequences of Item Non-Response
If item non-response is a function of the variables in analyses, the consequences can be large.
Orthogonal Item Non-Response
If item non-response is unrelated to the variables in analyses, the consequences are trivial.
Ethical Issues in Surveys
Concerns that arise regarding the conduct and implications of survey research.
Change Over Time
Populations change over time, affecting the relevance of survey findings.
Survey of Maryland Residents
Findings from this survey do not hold for all of the US or North America.
Latest Available Survey
Results from surveys collected in 2015 may no longer hold for 2021.
Missing Data Concerns
Researchers spend time worrying about missing data due to its potential impact on results.
Respondent Characteristics
Demographic details such as race, gender, and income of survey participants.
Income Variability
Income levels can vary significantly among respondents of different races.
Survey Sampling Frame
The source from which a sample is drawn for a survey.
Data Out-Dated
Data may no longer be relevant due to changes in the population over time.
Consequences of Non-Response
The implications of having missing responses in survey data.
Informed consent
The process of obtaining permission from participants after disclosing who the researcher is and what they are doing.
Confidentiality
The principle that ensures the privacy of participant data and results.
Panel Study
A study that shows change over time in individuals by using the same sample.
Longitudinal Study
Data collected at more than one point in time.
Trend Study
Repeated cross-sectional surveys with different samples that show change over time in a population.
Cross-sectional Study
Data collected at one point in time.
Retrospective Study
Data collected at one point in time, but asks about times in the past.
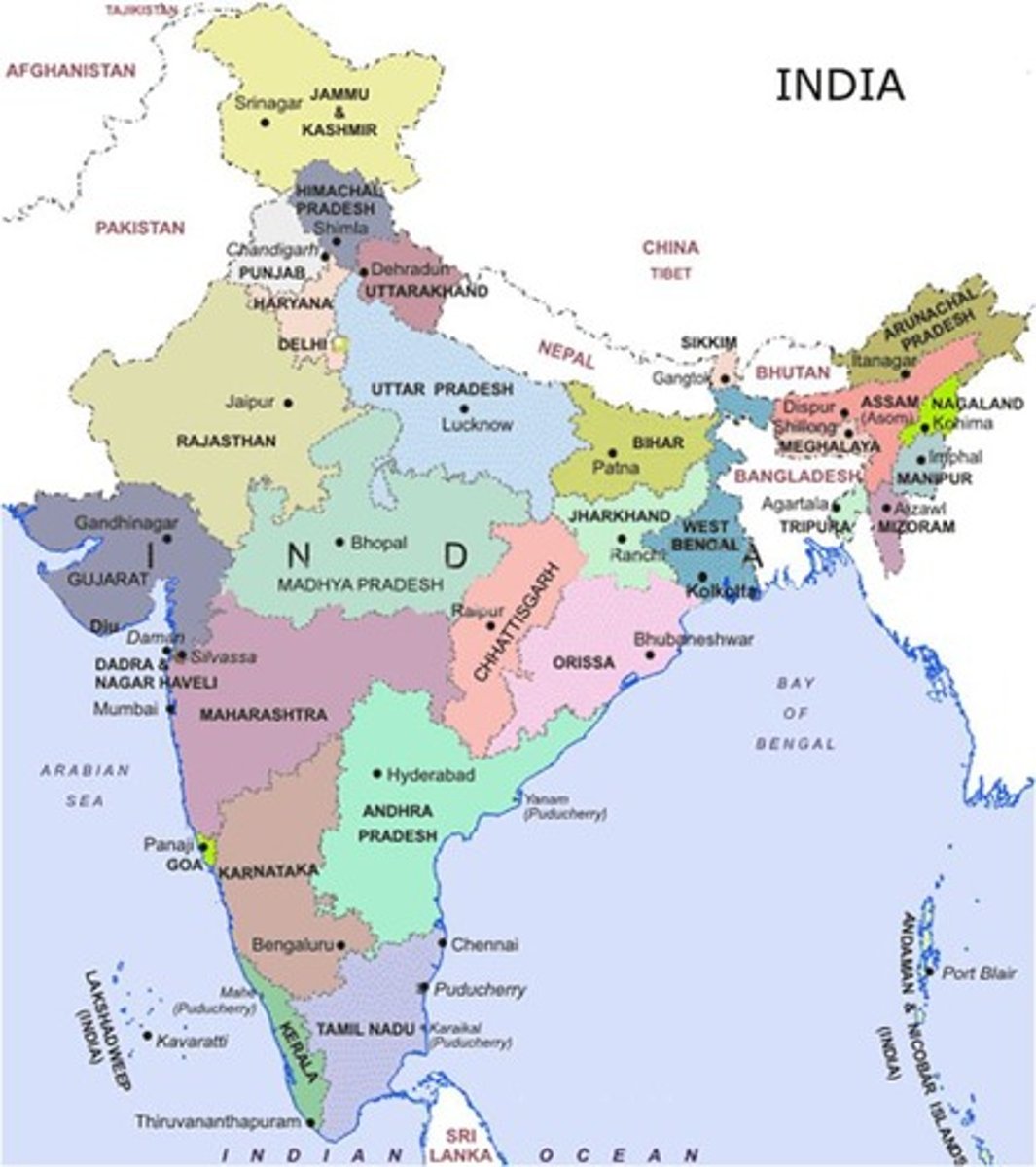
Indian National Family Health Survey
A survey of over 90,000 India households collected in four different times (waves): 1992-93, 1998-99, 2005-06, & 2014-15.
Primary Data
Data that you collect yourself.
Secondary Data
Data collected by others.
Secondary Survey Analysis
The analysis of surveys collected by one group but analyzed by many others.
Example Survey: India Human Development Survey
A survey involving 41,554 households, 215,754 household members, and various assessments including health and education.
Analytical Sample
The sample actually analyzed in a particular study, derived from the target population.