Electronegativity + forces
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Define electronegativity
A measure of attraction of a bonded atom for the pair of electrons in a covalent bond
What is the trend of electronegativity across a period
the larger the nuclear charge and the smaller the atomic radius, the greater the attraction for the pair or electrons in a covalent bond
electronegativity increases
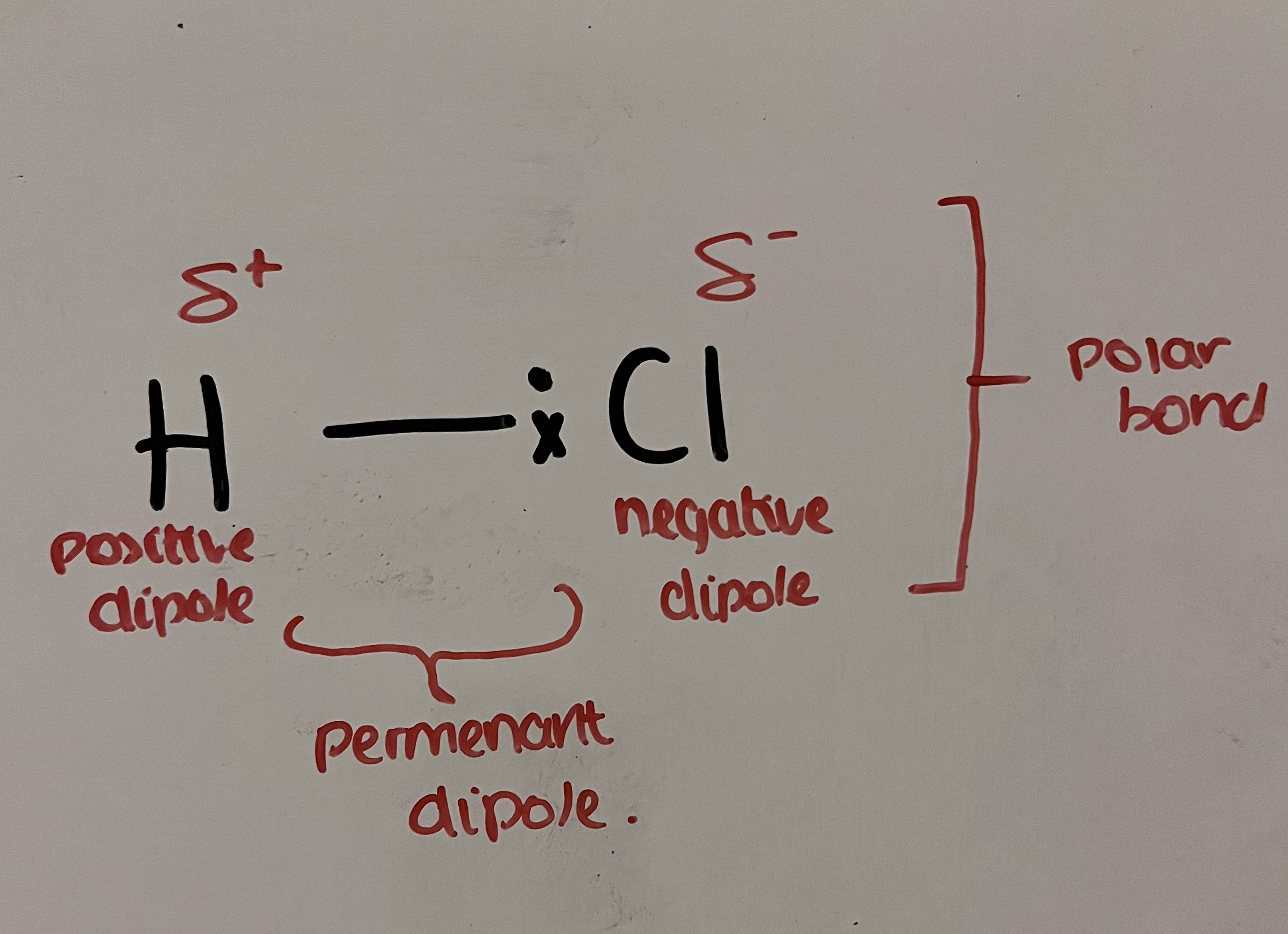
Explain the electronegativity in HCl
Cl is more electronegative than H
Cl atom has a greater attraction for the bonding pair of electrons than the H atom
bonding electrons attracted to the Cl atom which forms a polar bond
Cl has delta- (negative dipole)
H has delta+ (positive dipole)
charge difference is permanent dipole
Explain the electronegativity in H2 (any diatomic molecule)
the two atoms are identical
each H atom has an equal share of the pair of electrons in the bond
electrons are evenly distributed
What does it mean by a symmetrical molecule
( both rules must apply)
central atom has no lone pairs
outer atoms are identical
dipoles act in different directions = cancel out
NON-POLAR MOLECULE
What does it mean by an asymmetrical molecule
central atom has a lone pair
outer atoms are not identical
dipoles act in the same direction = dont cancel out
POLAR MOLECULE
Name all IMF in highest to lowest strength
hydrogen bonds
permanent dipole-permanent dipole
permanent dipole-induced dipole
london dispersion forces (induced dipole-dipole)
What are London Dispersion Forces
theres an uneven distributions of electrons and at any point, there will be an instantaneous dipole across the molecule
Instantaneous dipole induces a dipole in neighbouring molecule
small induced dipoles attract one another
present in all covalent molecules
Explain the pattern of BPs down group 7
BP increases
number of electrons increase down the group
greater instantaneous and induced dipoles, so stronger london dispersion forces between molecules
more energy required to break the LDFs
What are permanent dipole-induced dipole interactions
molecules with permanent dipoles approach non polar molecules which unevenly distributes the electrons in the non polar molecule
this causes it to become slightly polar and then an attraction occurs
molecule with permanent dipole induces a dipole in non-polar molecule
What are permanent dipole-permanent dipole forces
permanent dipole of one molecule attracts the permanent dipole of another polar molecule to form a weak permanent dipole-dipole force
permanent negative dipole is attracted to permanent positive dipole of other molecule
What is hydrogen bonding
occurd between H and either N, O, F
forms very polar bonds
Why is ice less dense than water
ice has an open lattice with hydrogen bonds holding H2O molecules further apart
when ice melts, H bonds collapse, allowing molecules to move closer together
Why does water have a higher MP and BP
has hydrogen bonds between molecules which are the strongest weak IMFs
requires a large amount of energy to break