B2.3.7 Adaptations to increase surface area to volume ratios of cells
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
adaptations to increase SA:V ratio
forming long, thin extensions
having a thin, flat shape
forming invaginations or microvilli
long and thin extensions of the cell membrane
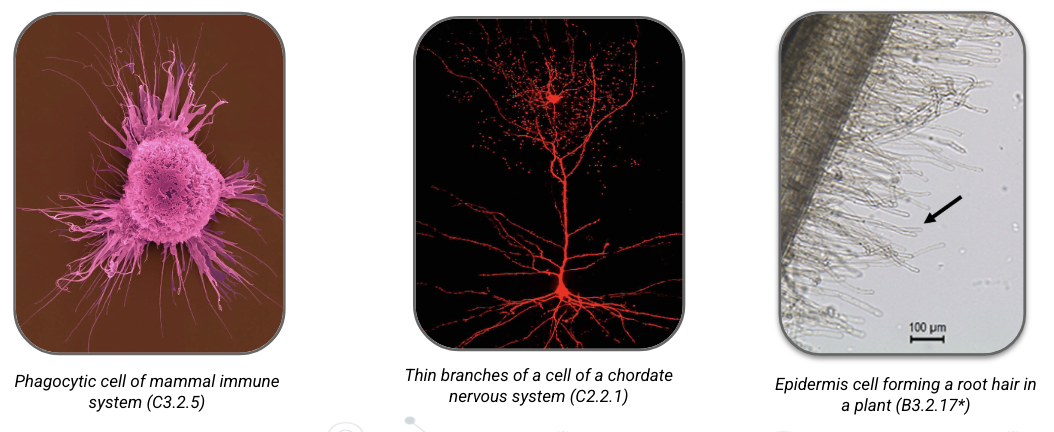
significantly expand cell’s surface area while adding only a small amount to overall volume
examples: phagocytic cell of mammal immune system, branches of cell of chordate nervous system, epidermis cells form root hairs in plants
thin and flat shape of cell
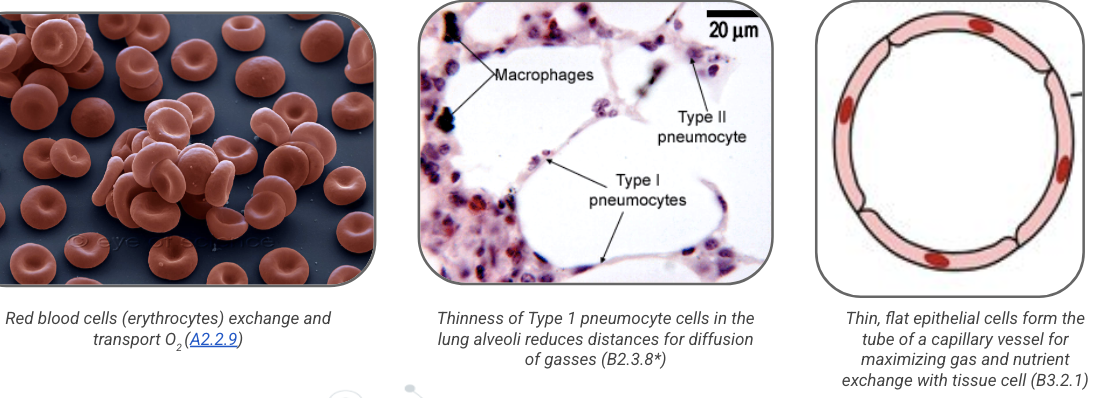
maximizes amount of surface area exposed relative to the volume it occupies more than a thicker/more rounded shape
red blood cells (erythrocytes) exchange and transport O2
thinness of type 1 pneumocyte cells in lung alveoli reduces distances for diffusion of gases
thin, flat epithelial cells form the tube of a capillary vessel for maximizing gas and nutrient exchange with tissue cell
invaginations
cavity formed when a surface folds inward to create an indentation
microvilli
small finger-like projections that are tiny invaginations of the cell membrane of a single cell; drastically increase overall surface area available without significantly increasing cell’s volume
on the surface of cells in small intestine - increase surface area for absorbing nutrients from digested food
on the surface of cells in kidney proximal convoluted tubule - increase surface area for reabsorbed useful substances before excretion in urine
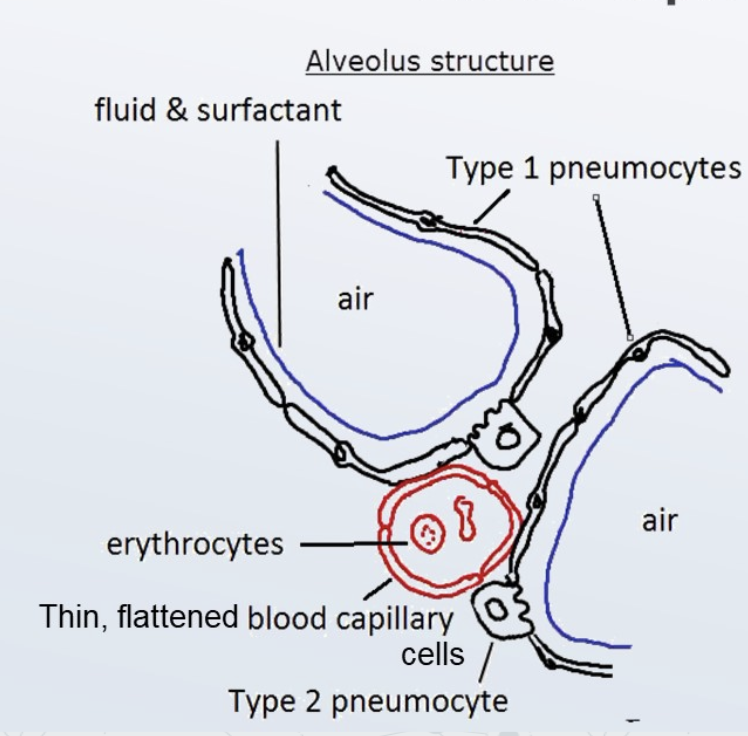
alveolar epithelium
example of tissue where more than one cell type is present
type I and II pneumocytes, blood capillary cells, erythrocytes
different adaptations required for overall function of tissue
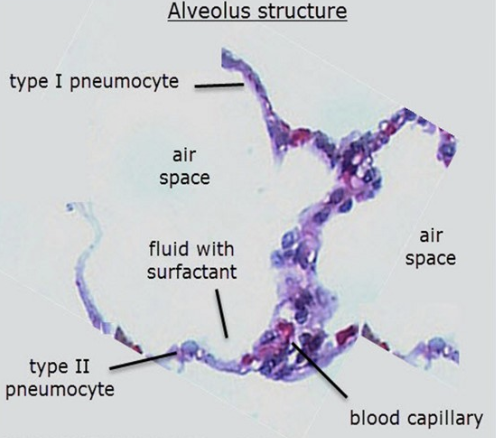
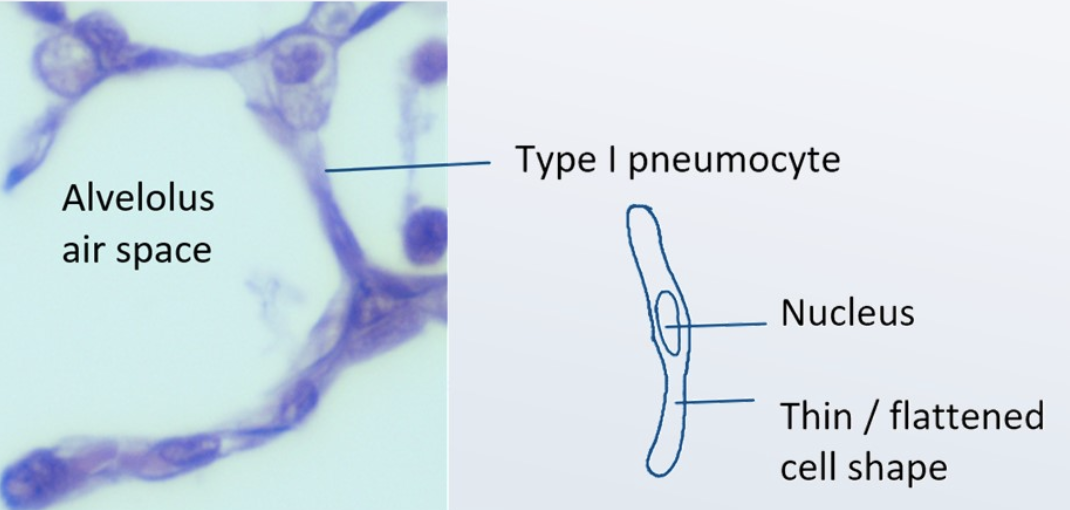
adaptation of type I pneumocytes
extreme thinness to reduce distance for diffusion
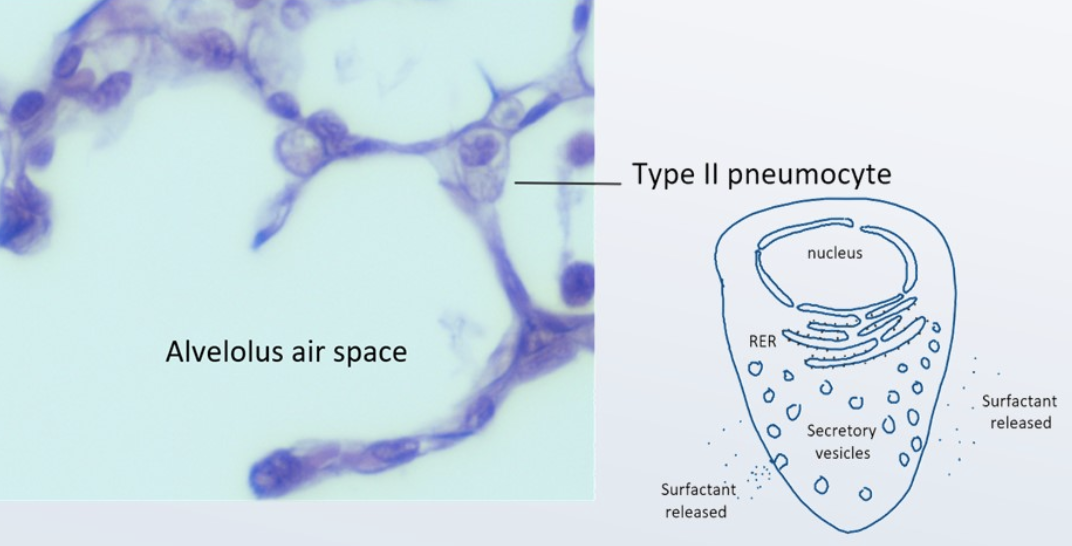
adaptation of type II pneumocytes
many secretory vesicles (lamellar bodies) in their cytoplasm, make and release surfactant to alveolar lumen
adaptation of blood capillary cells
thin to enable diffusion
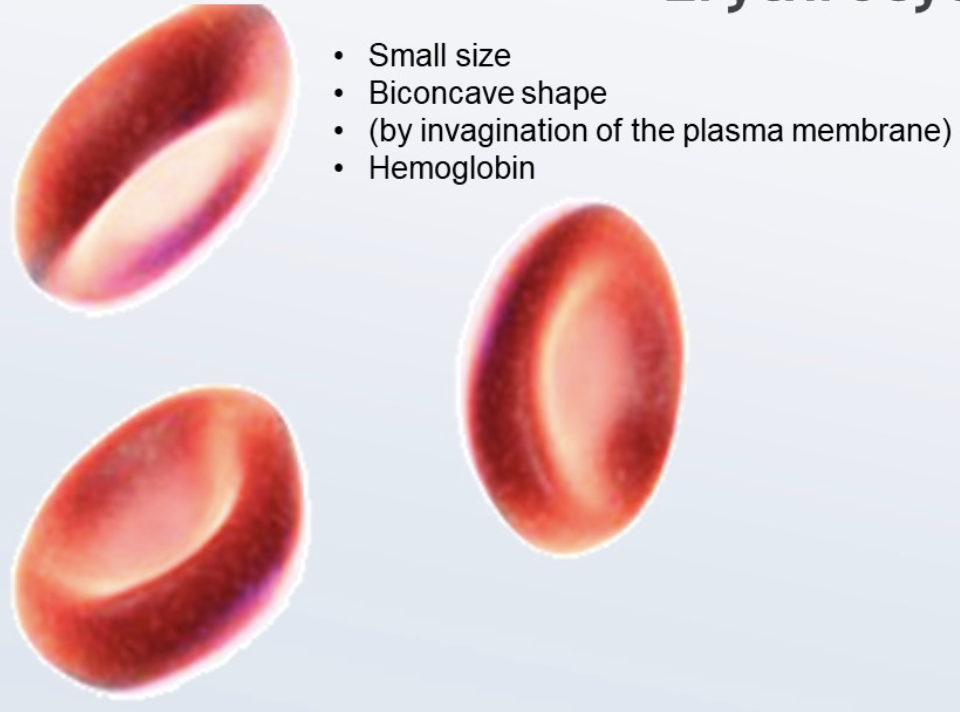
adaptation of erythrocytes
small size to allow them to flow in capillaries
biconcave shape to increase surface area
contain hemoglobin to carry oxygen as oxyhemoglobin