BIOL 431 Unit 4 Lab Exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
kidney (4 fxn)
filter blood
regulate blood pH
regulate blood volume
regulate blood pressure
regulate blood pH
regulate blood volume
regulate blood pressure
2
New cards
renal hilium
indentation; where ureter, renal artery & renal vein are found
3
New cards
renal capsule
maintains shape & provides structure to kidney
4
New cards
adipose capsule
protection, insulation & holds kidney in place
5
New cards
renal fascia
anchors kidney & coverings to abdominopelvic wall
6
New cards
cortex
outer part; renal corpuscle & peritubular capillaries found here
7
New cards
medulla
inner part of kidney; contains loops of Henle & vasa recta
8
New cards
medullary pyramids
triangular structure in medulla; part of parenchyma
9
New cards
medullary papilla
tip of renal pyramid; bump like structure containing papillary ducts
10
New cards
medullary renal columns
part of cortex in between pyramids
11
New cards
pelvis/minor calyx/major calyx
passageway for urine
12
New cards
urine droplet tracing within kidney (minor calyx to ureter)
minory calyx
major calyx
renal pelvis
ureter
major calyx
renal pelvis
ureter
13
New cards
renal sinus
space within renal hylum
14
New cards
filtrate tracing (abdominal aorta to glomerular capillaries)
abdominal aorta
L & R renal arteries
segmental arteries
interlobar arteries
arcuate arteries
interlobular arteries
affarent arteriole
glomerular capillaries
L & R renal arteries
segmental arteries
interlobar arteries
arcuate arteries
interlobular arteries
affarent arteriole
glomerular capillaries
15
New cards
filtrate tracing (glomerular capillaries to inferior vena cava)
glomerular capillaries
efferent arteriole
peritubular capillaries/vasa recta
interlobular vein
arcuate vein
interlobular vein
segmental vein
L & R renal vein
inferior vena cava
efferent arteriole
peritubular capillaries/vasa recta
interlobular vein
arcuate vein
interlobular vein
segmental vein
L & R renal vein
inferior vena cava
16
New cards
renal corpuscle
glomerulus + bowman’s capsule
17
New cards
features of glomerulus
fenestrated endothelium
basal lamina
basal lamina
18
New cards
fenestrated endothelium
prevent filtration of blood cells & platelets
19
New cards
basal lamina
prevent filtration of large plasma proteins
20
New cards
features of Bowman’s capsule
parietal layer
visceral layer
podocytes & pedicels
filtration slits
slit membrane
basal lamina
visceral layer
podocytes & pedicels
filtration slits
slit membrane
basal lamina
21
New cards
podocytes & pediciels, filtration slits & slit membranes
prevent filtration of small/medium plasma proteins
22
New cards
filtration membrane
fenestrated glomerular capillary endothelial cells & slit membranes between podocytes of visceral layer of Bowman’s capsule
23
New cards
proximal coveted tubule
reabsorption of water, ions, & organic compounds
24
New cards
brush border on proximal convoluted tubule
increases surface area for reabsorption
25
New cards
Loop of Henle
sets up concentration gradient for countercurrent multiplication
26
New cards
descending limb of loop of henle
water reabsorption
27
New cards
ascending limb of loop of henle
active Na & Cl reabsorption
28
New cards
distal convoluted tubule
secretion of water, toxins, acids, drugs, etc
29
New cards
collecting duct
modifies filtrated based on body’s needs/hormones
30
New cards
juxtaglomerular apparatus
participates in tubuloglomerular feedback (regulates glomerular filtration rate)
macula densa cells + juxtaglomerular cells
macula densa cells + juxtaglomerular cells
31
New cards
macula densa cells
detect filtrate osmolarity
32
New cards
juxtaglomerular cells
modified smooth muscle cells; vasoconstrictor affarent arteriole & produces renin
33
New cards
ureter
transport urine via peristaltic waves
34
New cards
urinary bladder
temporary storage of urine
35
New cards
orifice of ureter
posterior inferior aspect of bladder
opening to ureter
opening to ureter
36
New cards
trigone
smooth region formed by 3 openings (2 orifice of ureter & internal urethral orifice)
37
New cards
detrusor muscle
smooth muscle structure of urinary bladder
involved in micturition
involved in micturition
38
New cards
rugae
ridges; allows expansion
39
New cards
urethra
passageway to expel urine
40
New cards
internal urethral orifice
opening at base of urinary bladder (to urethra)
41
New cards
internal urethral sphincter
smooth muscle; controls involuntary micturition
42
New cards
external urethral orifice
opens to expel urine to external environment
43
New cards
external urethral sphincter
skeletal muscle; controls voluntary micturition
44
New cards
prosthetic urethra
portion of urethra in prostate gland region
45
New cards
membranous urethra
portion of urethra in external urethral sphincter region
46
New cards
cavernous urethra
urethra that extends entire length of penis
47
New cards
urethra regions only in males
prostatic urethra
membranous urethra
cavernous/spongey/penile urethra
membranous urethra
cavernous/spongey/penile urethra
48
New cards
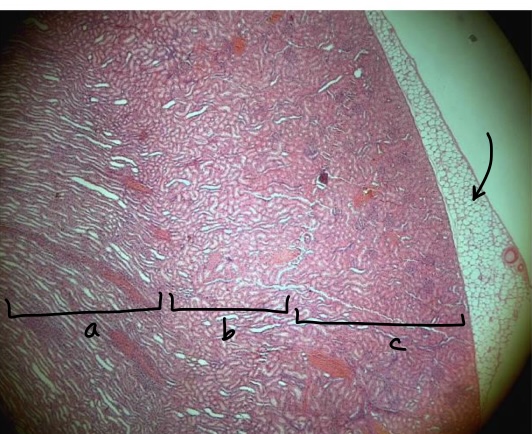
specimen in the field of view?
region a?
region b?
region c?
layer at the tip of the arrow?
region a?
region b?
region c?
layer at the tip of the arrow?
kidney
medulla
corticomedullary junction
cortex
renal adipose capsule
medulla
corticomedullary junction
cortex
renal adipose capsule
49
New cards
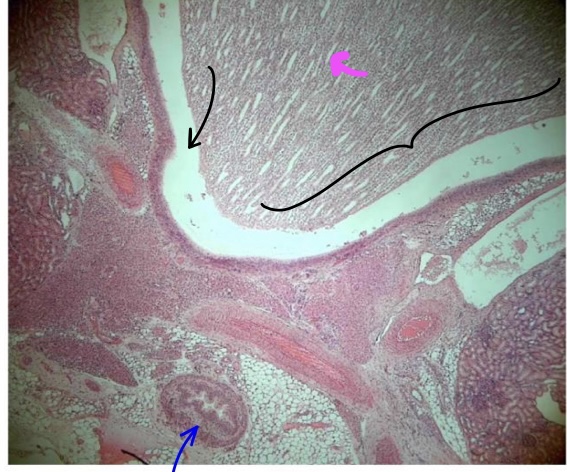
specimen in the field of view?
bracketed structure?
space at tip of black pointer
liquid found in that space?
specific tissue lining the lumen
structure at tip of magenta pointer
structure at tip of blue pointer
bracketed structure?
space at tip of black pointer
liquid found in that space?
specific tissue lining the lumen
structure at tip of magenta pointer
structure at tip of blue pointer
kidney
renal papilla
calyx
urine
transitional epithelium
papillary duct
ureter
renal papilla
calyx
urine
transitional epithelium
papillary duct
ureter
50
New cards
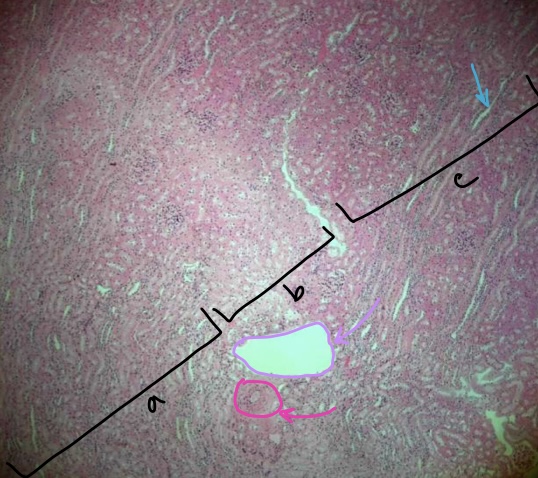
specimen in field of view
region a
region b
region c
structure at tip of light blue arrow
structure at tip of purple arrow
structure at tip of pink arrow
region a
region b
region c
structure at tip of light blue arrow
structure at tip of purple arrow
structure at tip of pink arrow
kidney
medulla
corticomedullary junction
cortex
medullary ray
arcuate vein
arcuate artery
medulla
corticomedullary junction
cortex
medullary ray
arcuate vein
arcuate artery
51
New cards
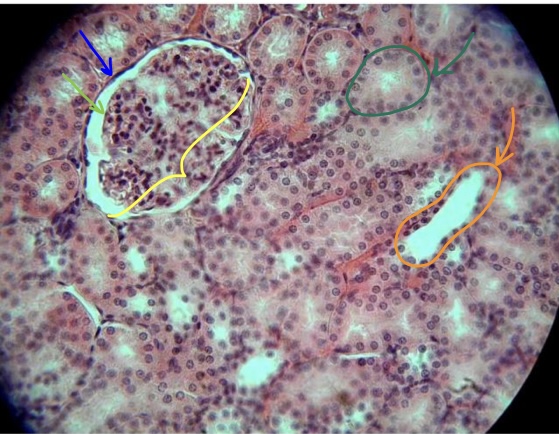
structure in yellow bracket
structure at tip of dark green arrow
structure at tip of orange arrow
structure at tip of blue arrow
structure of light green arrow
space between the green & blue arrows
structure at tip of dark green arrow
structure at tip of orange arrow
structure at tip of blue arrow
structure of light green arrow
space between the green & blue arrows
renal corpuscle
proximal convoluted tubule with brush border
distal convoluted tubule
parietal layer of bowman’s capsule
visceral layer of bowman’s capsule
bowman’s space
proximal convoluted tubule with brush border
distal convoluted tubule
parietal layer of bowman’s capsule
visceral layer of bowman’s capsule
bowman’s space
52
New cards
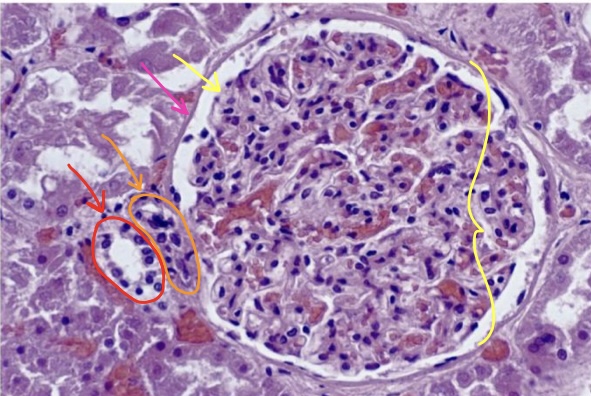
structure in yellow bracket
structure at tip of yellow arrow
structure at tip of pink arrow
specific cells at tip of orange arrow
specific cells at tip of red arrow
structure at tip of yellow arrow
structure at tip of pink arrow
specific cells at tip of orange arrow
specific cells at tip of red arrow
renal corpuscle
visceral layer of bowman’s capsule
parietal layer of bowman’s capsule
juxtaglomerular cells
macula densa cells
visceral layer of bowman’s capsule
parietal layer of bowman’s capsule
juxtaglomerular cells
macula densa cells
53
New cards
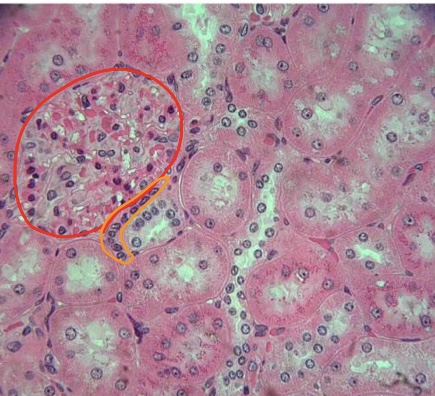
specimen in field of view
structure circled in red
specific cells circled in orange
structure circled in red
specific cells circled in orange
kidney
renal corpuscle
macula densa cells
renal corpuscle
macula densa cells
54
New cards
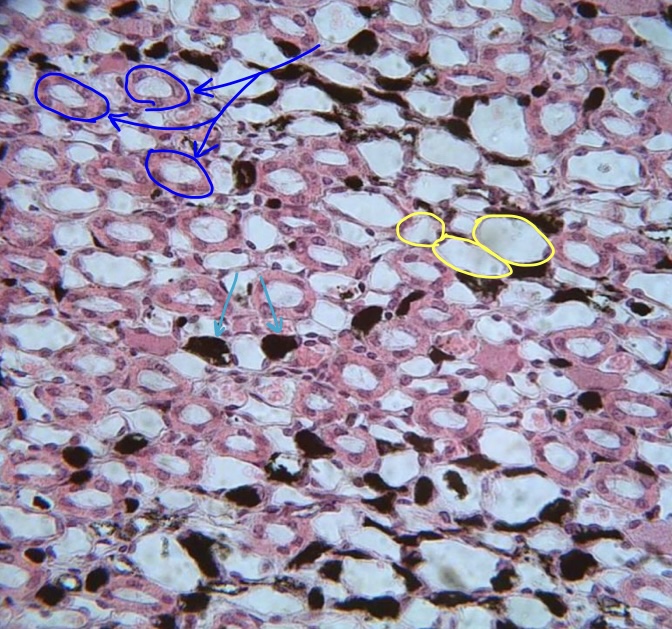
specimen in field of view
structures at tip of dark blue arrow
structure encircled in yellow
structure & function at tip of light blue arrow
structures at tip of dark blue arrow
structure encircled in yellow
structure & function at tip of light blue arrow
vascular injected kidney
thick limb of loop of henle
thin limb of loop of henle
vasa recta (maintain concentration gradient)
thick limb of loop of henle
thin limb of loop of henle
vasa recta (maintain concentration gradient)
55
New cards
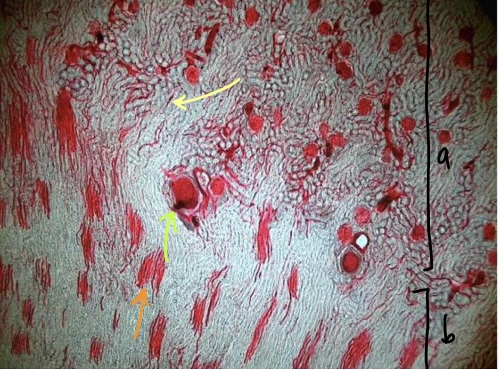
specimen in field of view
region a
region b
structure at tip of yellow arrow
structure at tip of orange arrow
structure at tip of green arrow
region a
region b
structure at tip of yellow arrow
structure at tip of orange arrow
structure at tip of green arrow
vascular injected kidney
cortex
medulla
peritubular capillaries
vasa recta
glomerulus
cortex
medulla
peritubular capillaries
vasa recta
glomerulus
56
New cards
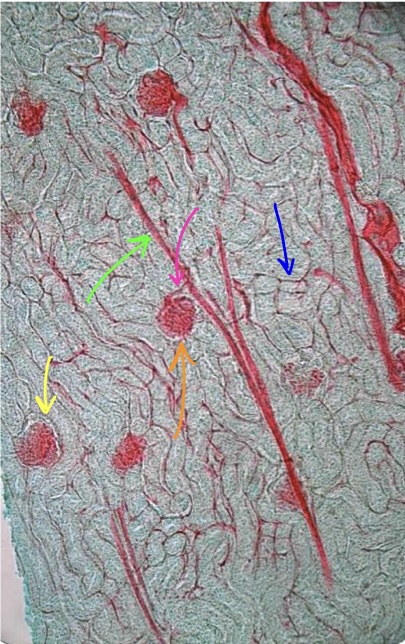
specimen in field of view
structure at tip of blue arrow
structure at tip of pink arrow
structure at tip of orange arrow
structure at tip of green arrow
structure at tip of yellow arrow
structure at tip of blue arrow
structure at tip of pink arrow
structure at tip of orange arrow
structure at tip of green arrow
structure at tip of yellow arrow
vascular injected kidney
peritubular capillaries
affarent arteriole
glomerulus
interlobular artery
glomerulus
peritubular capillaries
affarent arteriole
glomerulus
interlobular artery
glomerulus
57
New cards
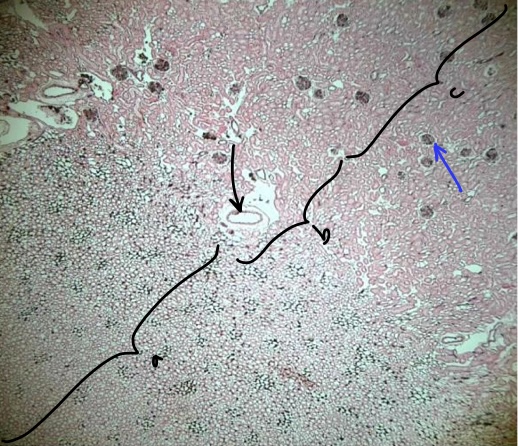
region a
region b
region c
structure at tip of black arrow
structure at tip of blue arrow
region b
region c
structure at tip of black arrow
structure at tip of blue arrow
medulla
corticomedullary junction
cortex
arcuate vessel
glomerulus
corticomedullary junction
cortex
arcuate vessel
glomerulus
58
New cards
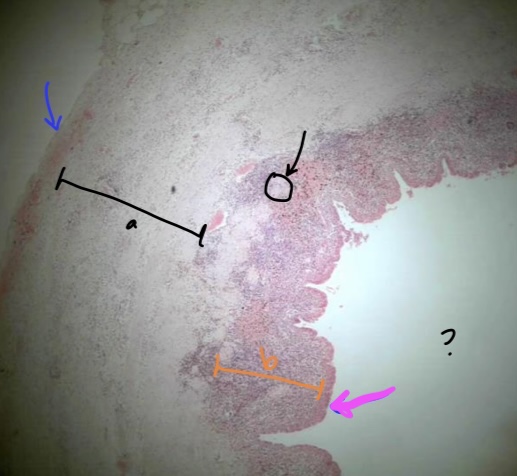
specimen in the field of view
layer at tip of blue arrow
region a
structure at tip of black arrow
specific in orange bracket (b)
specific tissue at tip of magenta arrow
space where ? is at
layer at tip of blue arrow
region a
structure at tip of black arrow
specific in orange bracket (b)
specific tissue at tip of magenta arrow
space where ? is at
ureter
adventitia
muscularis
mucosa associated lymphatic tissue
lamina propria
transitional epithelium
lumen
adventitia
muscularis
mucosa associated lymphatic tissue
lamina propria
transitional epithelium
lumen
59
New cards
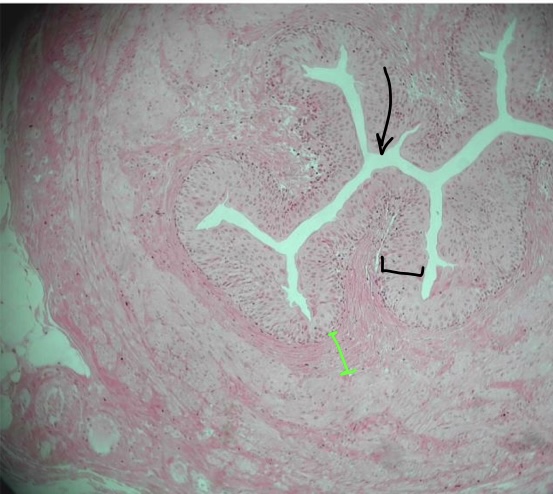
specimen in field of view
space at tip of black arrow & what it holds
specific tissue in black bracket
specific tissue in green bracket
space at tip of black arrow & what it holds
specific tissue in black bracket
specific tissue in green bracket
ureter
lumen & urine
transitional epithelium
lamina propria
lumen & urine
transitional epithelium
lamina propria
60
New cards
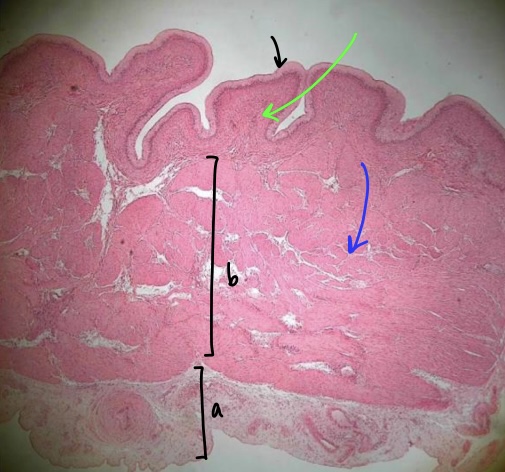
specimen in field of view (& position)
specific layer at tip of black arrow
specific tissue at tip of green arrow
specific layer in bracket b
specific layer in bracket a
specific structure at tip of blue arrow
specific layer at tip of black arrow
specific tissue at tip of green arrow
specific layer in bracket b
specific layer in bracket a
specific structure at tip of blue arrow
contracted/empty urinary bladder
mucosa
areolar connective tissue
muscularis
adventitia
detrusor muscle
mucosa
areolar connective tissue
muscularis
adventitia
detrusor muscle
61
New cards
3 layers of muscularis (urinary bladder)
inner longitudinal
middle circular
outer longitudinal
middle circular
outer longitudinal
62
New cards
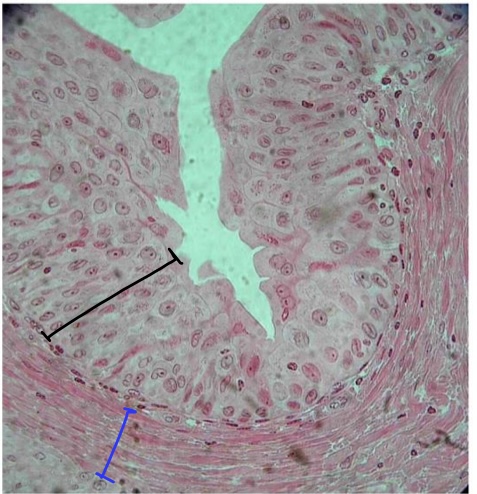
specimen in field of view
specific tissue in black bracket
specific layer & tissue in blue bracket
specific tissue in black bracket
specific layer & tissue in blue bracket
ureter
transitional epithelium
lamina propria (areolar connective tissue)
transitional epithelium
lamina propria (areolar connective tissue)
63
New cards
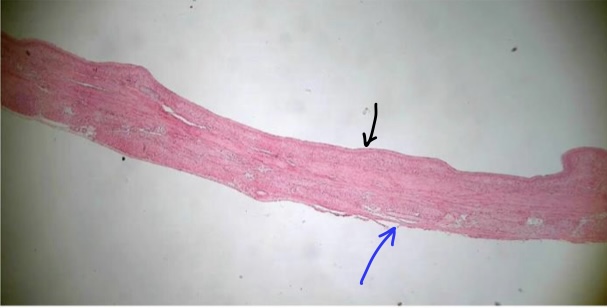
specimen in field of view (& position)
specific layer at tip of black arrow
specific layer at tip of blue arrow
space touching black arrow’s layer
specific layer at tip of black arrow
specific layer at tip of blue arrow
space touching black arrow’s layer
relaxed/full urinary bladder
mucosa
adventitia
lumen
mucosa
adventitia
lumen
64
New cards
urinary formation rate formula & typical formation rate
volume/time elapsed
\~1 mL/min
\~1 mL/min
65
New cards
what causes urine turbidity
presence of glucose, bacteria, pus, etc
66
New cards
normal urine pH & factors that can change the pH
4\.6-8
diet & amount of H+ secreted (meat = acidic, vegetables = basic)
diet & amount of H+ secreted (meat = acidic, vegetables = basic)
67
New cards
urinometer
measures specific gravity of urine
68
New cards
specific gravity of water
1\.0000
69
New cards
normal specific gravity of urine
1\.001-1.035
70
New cards
high specific gravity indicative of
hypertonic urine (more concentrated)
potential causes: fevers, diabetes mellitus & adrenal diabetes
potential causes: fevers, diabetes mellitus & adrenal diabetes
71
New cards
most abundant solute found in urine
urea
72
New cards
second most abundant solute found in urine
chloride (found as NaCl)
73
New cards
leukocytes in urine (name, non pathological cause & pathological cause)
pyuria
pregnancy
urinary tract infection, kidney infection
pregnancy
urinary tract infection, kidney infection
74
New cards
blood in urine (name, non pathological causes & pathological cause)
hematuria
menstruation
glomerulonephritis, kidney stones & kidney trauma
menstruation
glomerulonephritis, kidney stones & kidney trauma
75
New cards
nitrites in urine (name, non pathological causes & pathological causes)
nitrituria
excessive nitrite ingestion
urinary tract infection, kidney infection
excessive nitrite ingestion
urinary tract infection, kidney infection
76
New cards
protein in urine (name, non pathological causes & pathological causes)
proteinuria
pregnancy, excessive physical exertion & hypertension
glomerulonephritis, kidney disease & renal failure
pregnancy, excessive physical exertion & hypertension
glomerulonephritis, kidney disease & renal failure
77
New cards
glucose in urine (name, non pathological causes & pathological causes)
glucosuria/glycosuria
increased sugar intake, increased stress & pregnancy
diabetes mellitus
increased sugar intake, increased stress & pregnancy
diabetes mellitus
78
New cards
ketone in urine (name, non pathological causes & pathological causes)
ketonuria
stress, pregnancy
diabetes mellitus
stress, pregnancy
diabetes mellitus
79
New cards
kidney (juxtaglomerular cells) produce what hormone & its effects
renin
converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I
converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I
80
New cards
liver produces what hormone/substance & its effects
angiotensinogen (plasma protein)
precursor to angiotensin I
precursor to angiotensin I
81
New cards
blood vessels produce what hormone/substance & its effects
ACE; converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II
angiotensin II: increase thirst, system vasoconstriction, vasoconstrict affarent arteriole & stimulate adrenal gland to produce aldosterone
angiotensin II: increase thirst, system vasoconstriction, vasoconstrict affarent arteriole & stimulate adrenal gland to produce aldosterone
82
New cards
adrenal gland produce what hormone/substance & its effects
aldosterone
inserts Na+/K+ pump to increase Na reabsorption & K secretion at principal cells of DCT/CD
inserts Na+/K+ pump to increase Na reabsorption & K secretion at principal cells of DCT/CD
83
New cards
posterior pituitary gland produces what hormone/substance & its effects
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
inserts aquaporin II in collecting duct/late DCT to increase water reabsorption
inserts aquaporin II in collecting duct/late DCT to increase water reabsorption
84
New cards
heart produces what hormone/substance & its effects
atrial natriuretic peptide
decrease Na+ reabsorption, decrease water reabsorption
decrease Na+ reabsorption, decrease water reabsorption
85
New cards
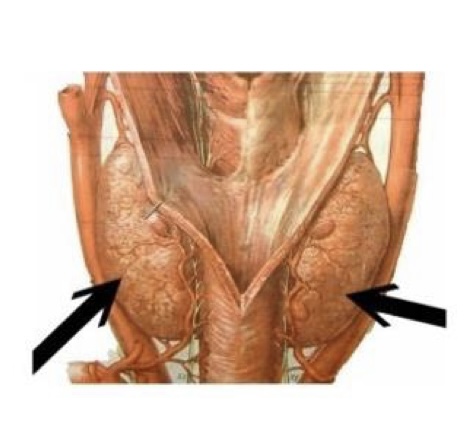
gland & hormone
thyroid gland & calcitonin
86
New cards
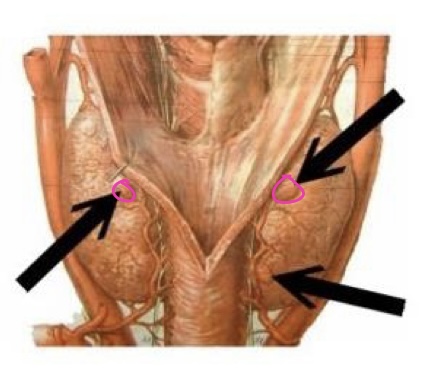
gland & hormone
parathyroid gland & parathyroid hormone
87
New cards
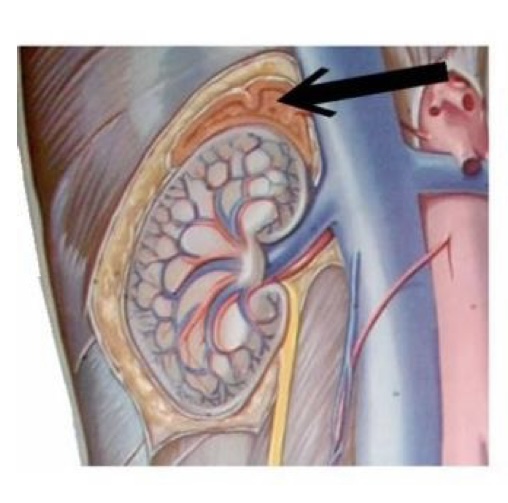
gland & hormone
adrenal gland & aldosterone
88
New cards
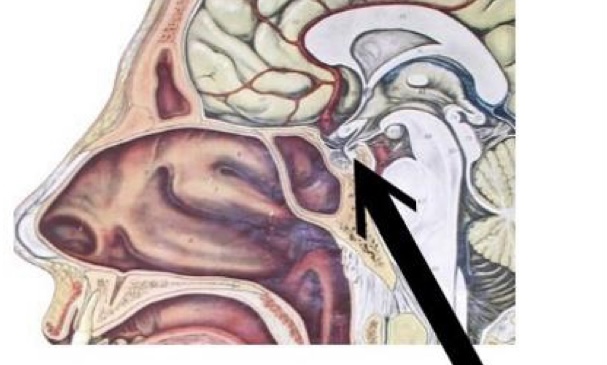
gland & hormone
posterior pituitary gland & ADH
89
New cards
4 acid base imbalances
metabolic alkalosis
metabolic acidosis
respiratory akalosis
respiratory acidosis
metabolic acidosis
respiratory akalosis
respiratory acidosis
90
New cards
acid base (normal pH, \[HCO3-\], PCO2)
pH: 7.4
\[HCO3-\]: 24
PCO2: 40 mmHg
\[HCO3-\]: 24
PCO2: 40 mmHg
91
New cards
metabolic alkalosis (change, causes, compensation)
change: increased pH & \[HCO3-\]
cause: alkaline tide, ingestion of tums & baking soda, vomiting
compensation: respiratory; hypoventialtion
cause: alkaline tide, ingestion of tums & baking soda, vomiting
compensation: respiratory; hypoventialtion
92
New cards
metabolic acidosis (change, causes, compensation)
change: decreased pH, decreased \[HCO3-\]
causes: increased ketone bodies (starvation, keto diet, diabetes mellitus), increased anaerobic exercise, diarrhea
compensation: respiratory; hyperventilation
causes: increased ketone bodies (starvation, keto diet, diabetes mellitus), increased anaerobic exercise, diarrhea
compensation: respiratory; hyperventilation
93
New cards
respiratory alkalosis (change, causes & compensation)
change: increased pH, decreased PCO2
causes: high altitude, mechanical ventilation, hyperventilation, sever anxiety
compensation: renal; decreased H+ secretion & decreased HCO3 reabsorption (occurs at intercalated cell & proximal convoluted tubule)
causes: high altitude, mechanical ventilation, hyperventilation, sever anxiety
compensation: renal; decreased H+ secretion & decreased HCO3 reabsorption (occurs at intercalated cell & proximal convoluted tubule)
94
New cards
respiratory acidosis (change, causes & compensation)
change: decreased pH, increased PCO2
causes: sleep apnea, asthma, COPD/emphysema, alcohol/CNS depressant
compensation: renal; increased H+ secretion & increased HCO3- reabsorption
causes: sleep apnea, asthma, COPD/emphysema, alcohol/CNS depressant
compensation: renal; increased H+ secretion & increased HCO3- reabsorption
95
New cards
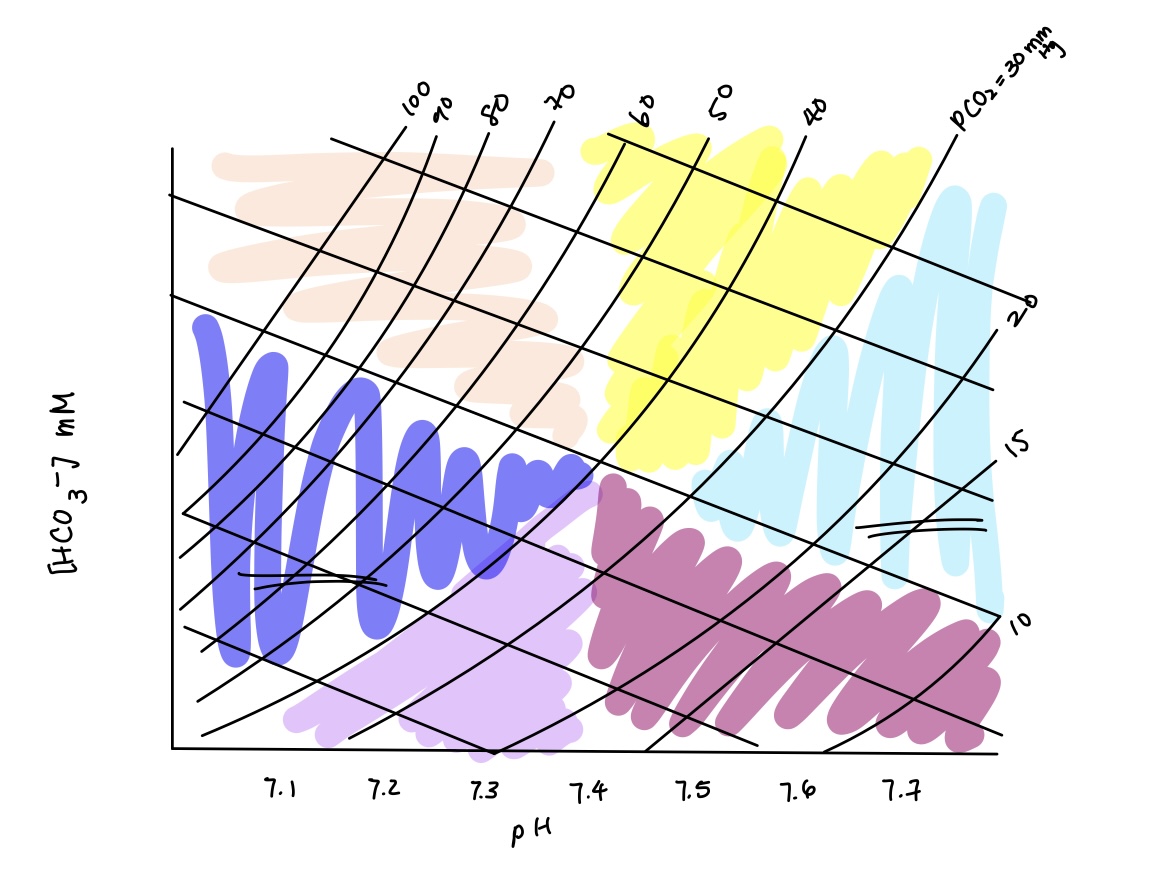
acid base imbalance in orange? causes? compensation?
respiratory acidosis
causes: sleep apnea, asthma, COPD/emphyema, alcohol/CNS depressant
compensation: renal compensation (increased H+ secretion & HCO3- reabsorption)
causes: sleep apnea, asthma, COPD/emphyema, alcohol/CNS depressant
compensation: renal compensation (increased H+ secretion & HCO3- reabsorption)
96
New cards
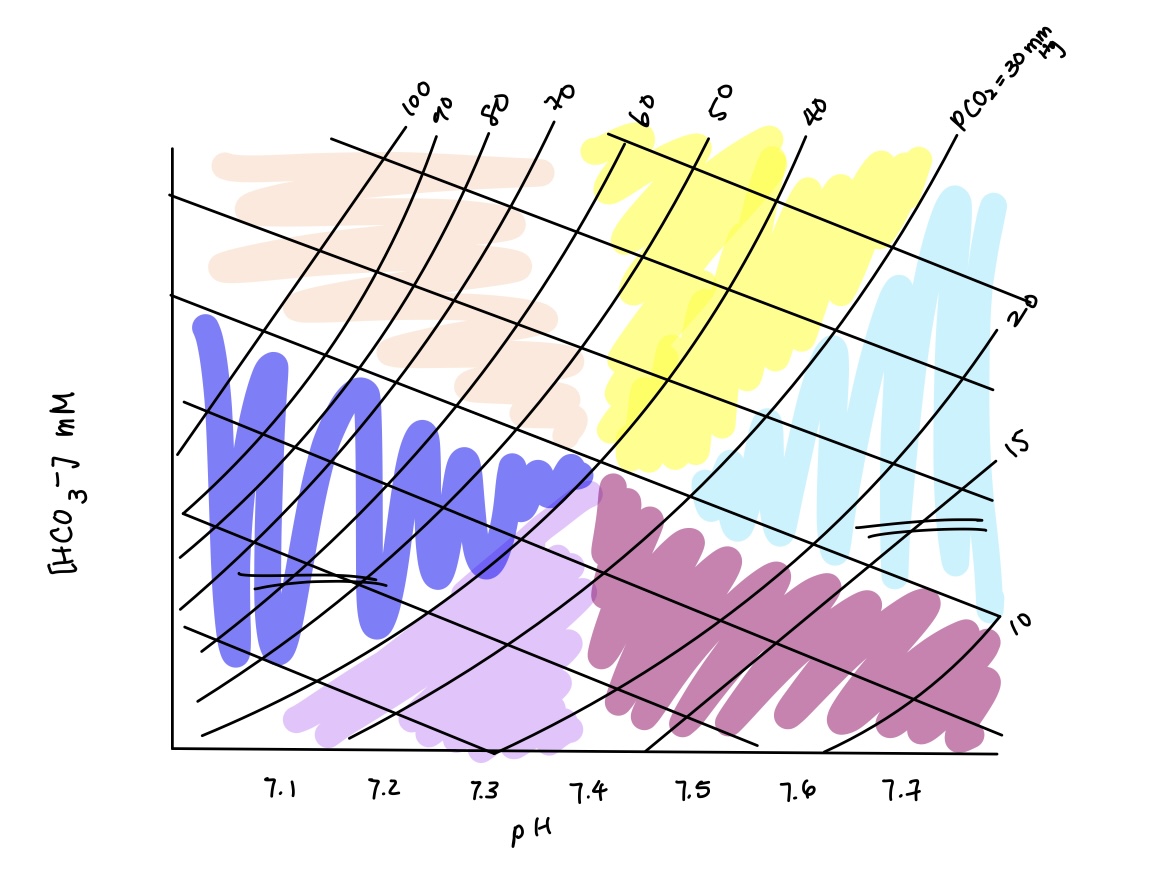
acid base imbalance in dark blue? causes? compensation?
combined respiratory & metabolic acidosis
causes: respiratory + metabolic acidosis causes
compensation: no
causes: respiratory + metabolic acidosis causes
compensation: no
97
New cards
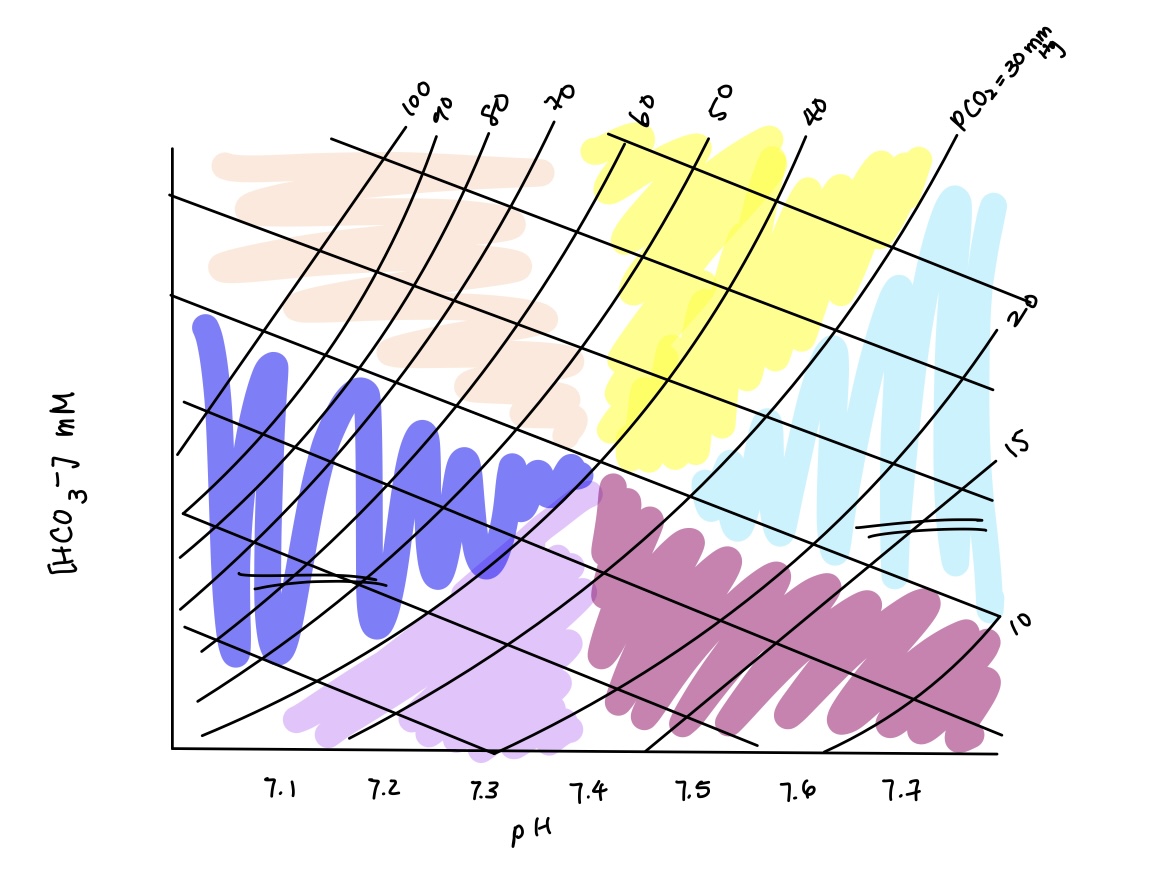
acid base imbalance in purple? causes? compensation?
metabolic acidosis
causes: starvation (increased ketone bodies), increased anaerobic exercise & diarrhea
compensation: respiratory compensation (hyperventilate)
causes: starvation (increased ketone bodies), increased anaerobic exercise & diarrhea
compensation: respiratory compensation (hyperventilate)
98
New cards
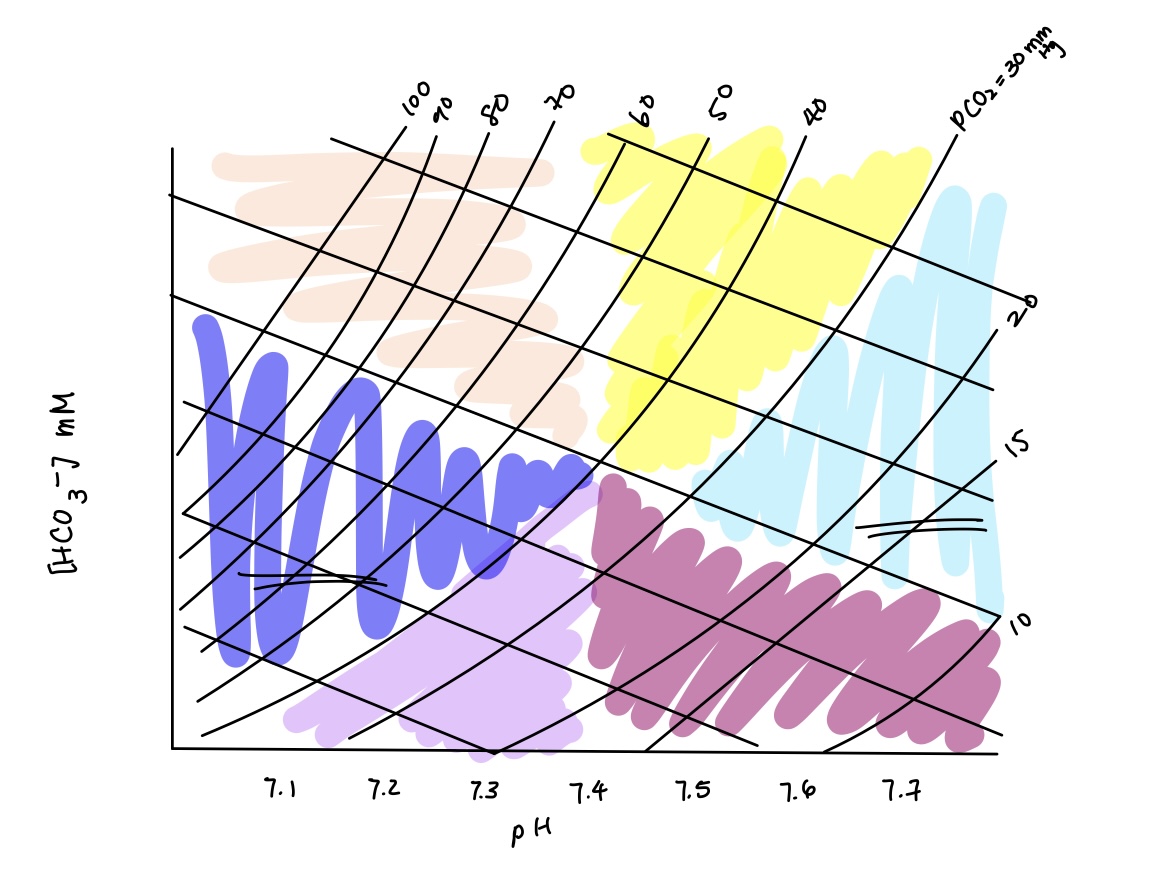
acid base imbalance in yellow? cause? compensation?
metabolic alkalosis
causes: alkaline tide, vomiting, ingestion of tums/baking soda
compensation: respiratory compensation (hypoventilate)
causes: alkaline tide, vomiting, ingestion of tums/baking soda
compensation: respiratory compensation (hypoventilate)
99
New cards
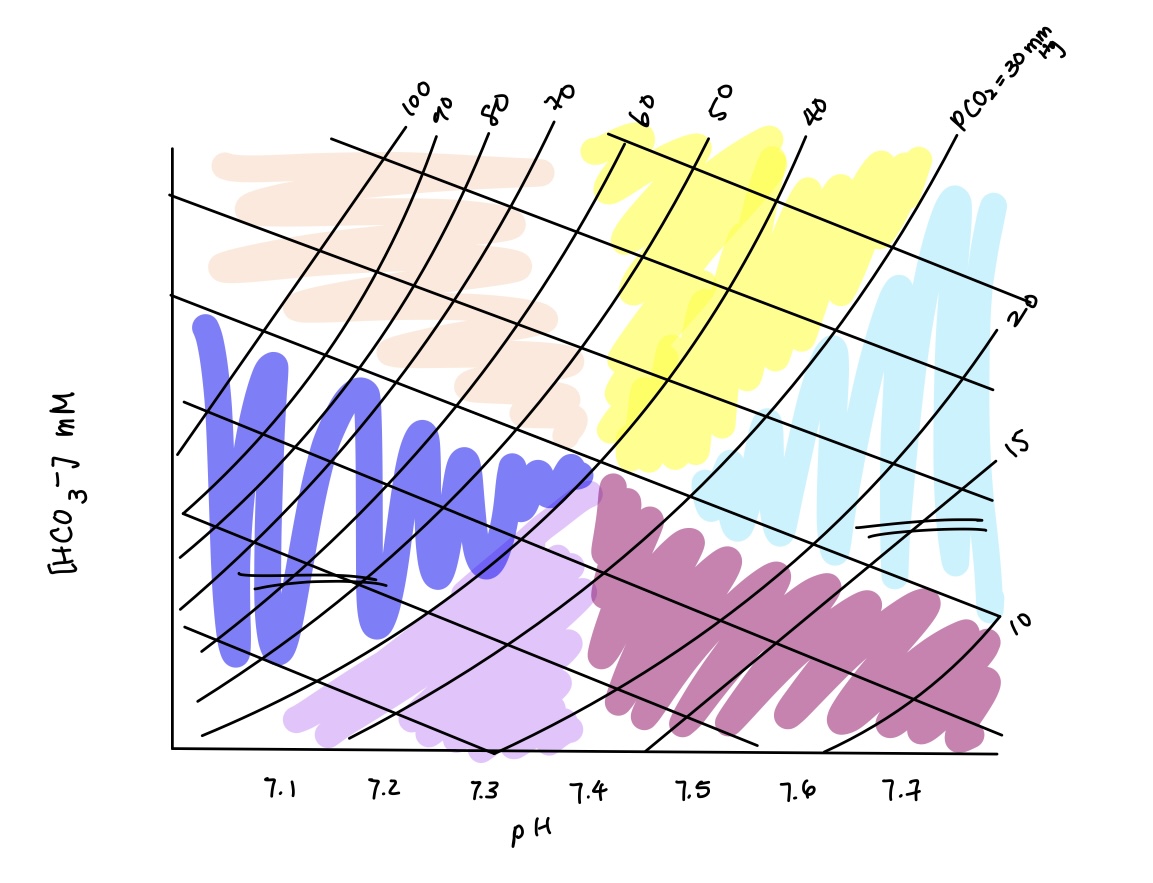
acid base imbalance in light blue? causes? compensation?
combined respiratory & metabolic alkalosis
causes: respiratory & metabolic alkalosis causes
compensation: none
causes: respiratory & metabolic alkalosis causes
compensation: none
100
New cards
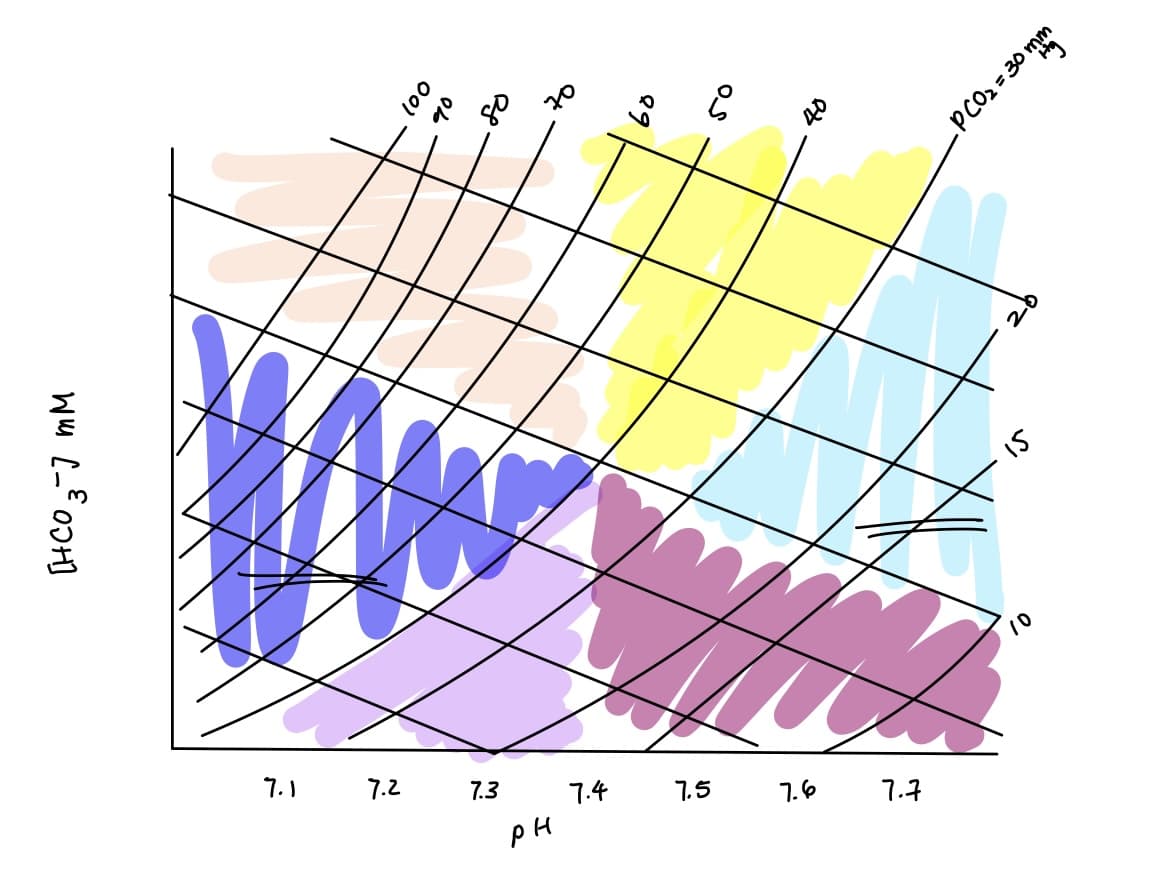
acid base imbalance in dark magenta? causes? compensation?
respiratory alkalosis
causes: high altitude, hyperventilation, severe anxiety & mechanical ventilation
compensation: renal compensation (decrease H+ secretion & HCO3- reabsorption)
causes: high altitude, hyperventilation, severe anxiety & mechanical ventilation
compensation: renal compensation (decrease H+ secretion & HCO3- reabsorption)