Gene expression Eukaryotes - MCB
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Housekeeping genes ?
expressed in many cell types
GAPDH
pre-transcriptional switch
(before transcription)
Heterochromatin & Euchromatin
Gene re-arrangement
Modulating access transcription factors
Euchromatin
nucleosome separated by the naked DNA
actively transcribed
lightly packed for chromatin
Heterochromatin
Densely/tightly packed transcriptional form chromatin
Histone regulate gene expression
Methylation
Acetylation
Phosphorylation
Acetylation
Generated by adding acetyl group to N terminus (histone tail)
Unwind DNA - charged interactions and open up DNA
DNA methylation
Methyl group added cytosine base (5-methylcytosine)
Strongly affect gene expression not change DNA
CpG Islands
Active genes unmethylated regions
Lots nucleotides (lots potential methylated)
If methylated prevents transcription gene (can change toxin environment)
Methylation patterns inherited
Methyltransferase Dnmt1 scans new strand (add methyl group)
Inherited after cell division
Epigenetics
Information additional to gene sequence
e.g DNA methylation, histone modification
Transcription factor
Bind to specific DNA sequences
Can block/activate transcription
Protein-protein interactions lead to binding
Difference btwn prokaryotes and eukaryotes binding site
Eukaryotes: if binding site is further away than transcription factor can have indirect effect
Prokarytoes: closer and more stable
Eukaryotic gene
Proximal control elements: example CAAT box, GC box
Core promoter: TATA box to INR
INR (initiator element)
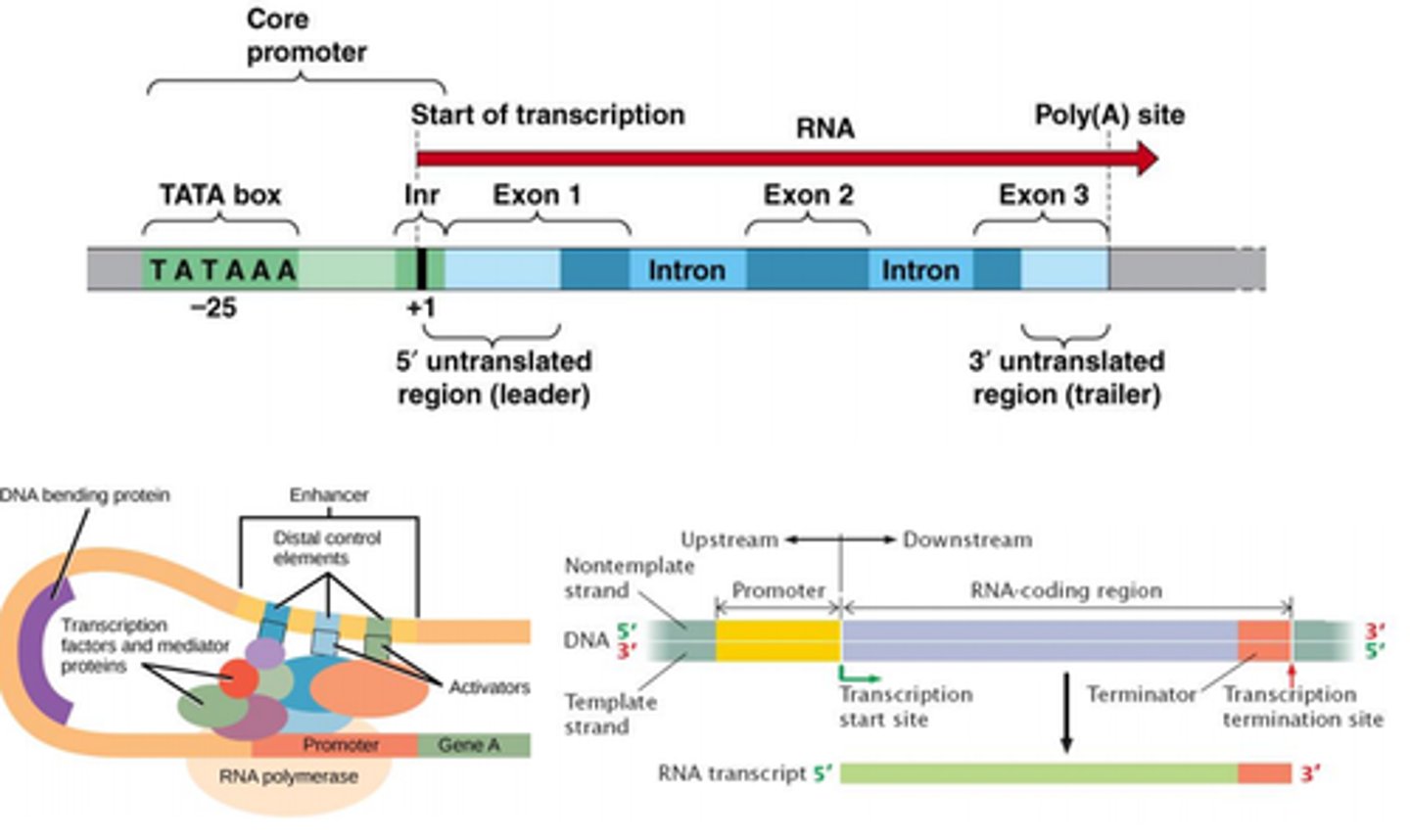
Proximal control element
bind to transcriptional activators
TATA box
binding & position RNA polymerase
in promoter region
Enhancer binding sites
Distant regulatory binding sites (indirect effects)
Bind transcription factors
Domain in Transcription Factors
Activation domain - bind RNA polymerase 2 (more variation)
DNA binding domain - bind DNA sequence
DNA binding factor
Usually binds to major grove
Mediator complex
DNA > RNA polymerase 2 > Mediator > Transcription Factor
Bridge - wen binding site not close RNA polymerase binding site
Signal
Goes nucleus transcription
Steroid
pass thru plasma membrane, bind intracellular receptors - dimerises enter nucleus
chain phosphorylation events
phosphorylation transcription factor bind regulatory DNA sequence (effect on gene)
Albumin gene
transcription factor bind
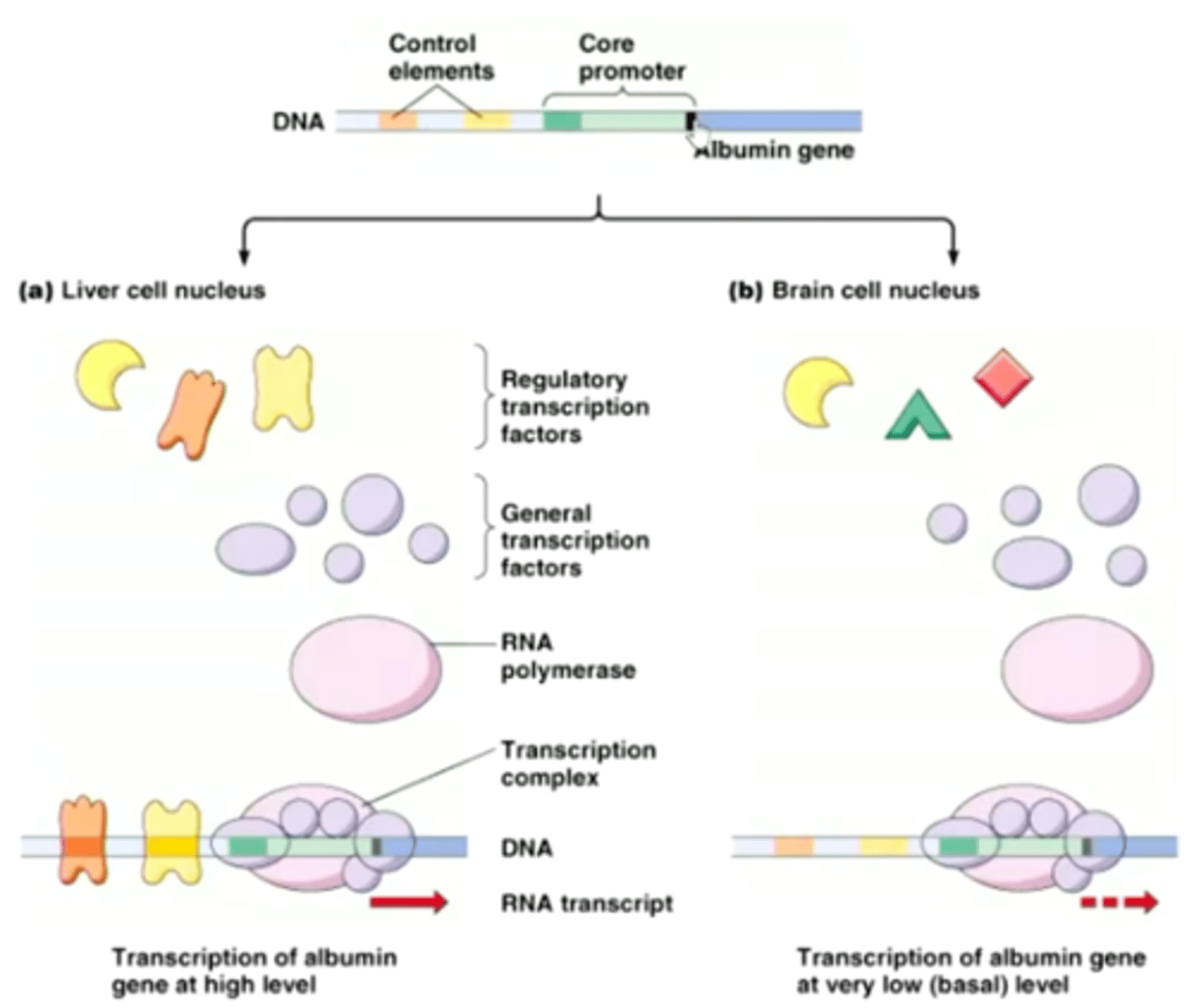
Splicing
Some introns spliced out
Splicing fibronectin gene
Exon EIIIA and EIIIB encode regions bind fibroblast to fibronectin gene
(lack hepatocytes)
Regulation genes associated Iron Metabolism
Transferrin
Transferrin Receptor
Ferritin
Transferrin
transport protein carries iron in serum
Transferrin receptor
Membrane protein binds transferrin to enter cell
Ferritin
efficient iron storage protein in liver and kidney
High iron
need less ferritin and less transferrin receptor
Iron response element (IRE)
Ferritin mRNA - stem hairpin loop structure
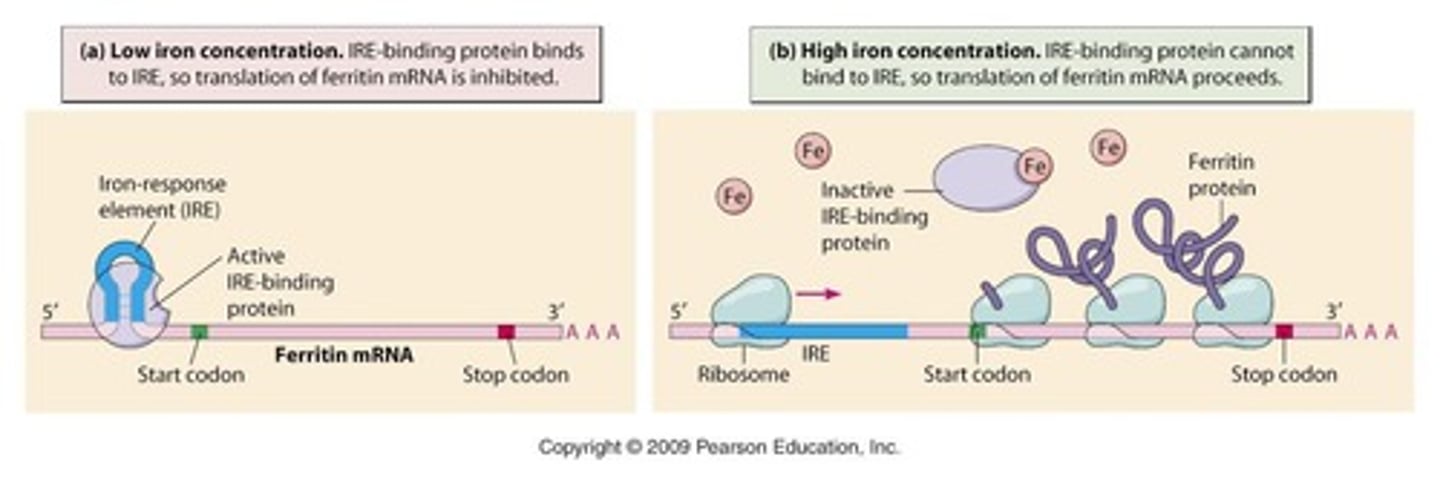
Low iron concentration - translation
Ferritin mRNA binds to IRE-binding protein (IRP) blocks initiation
Iron level high - translation
High level iron bind IRP - can no longer bind to ferritin
What disadvantage high iron concentration
As IRP can't bind to mRNA
transferrin receptor mRNA is rapidly degraded and not expressed
Micro-RNA (miRNA)
Class regulated RNA molecules
Cleaved into small fragment (20 nucleotides)
Bind mRNA molecules with complementary binding sequence - double stranded
miRNA targets mRNA degradation
How are proteins digested by proteosomes
Protein - added ubiquitin molecule to lysine
U recognised by proteosome complex
Degrades into short peptides
Protein phosphorylation
Phosphate transferred from ATP to amino acid side chain (protein kinase)
Removal phosphate - protein phosphatase
Protein glycosylation
Attach carbohydrates form glycoprotein