Bio lab quiz Active and Passive Transport
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is the main function of the nephron?
To filter blood, reabsorb needed molecules, and secrete wastes, maintaining homeostasis.
What happens during filtration in the nephron?
Liquid is forced through Bowman's capsule; filtrate contains water, urea, glucose, amino acids, and ions.
What is the purpose of reabsorption?
To retain molecules needed to maintain homeostasis, such as water, ions, and nutrients.
What happens during secretion?
The nephron eliminates molecules not needed by the body, e.g., urea.
Where does filtration occur?
In the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule.
Which molecules are commonly reabsorbed in the nephron?
Water, glucose, amino acids, and ions.
What molecules are commonly secreted?
Urea, excess ions, and wastes
Why is secretion important in kidney function?
It helps remove toxins and maintain chemical balance in the blood.
Why does the cell prioritize glucose over maltose?
Glucose is the preferred energy source and metabolized more efficiently.
Name the functional unit of the kidney.
Nephron
Main structures to label in a nephron?
Glomerulus, Bowman's Capsule, Tubules
Role of the glomerulus?
Filters blood to form filtrate
Role of Bowman's Capsule?
Collects filtrate from the glomerulus
Role of tubules?
Reabsorb water/solutes and secrete wastes
True or False: Wash test tubes with soap after lab.
False—rinse only with water and return to rack
What is passive transport?
Movement of molecules across a membrane without energy, down the concentration gradient.
Types of passive transport?
Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
What is diffusion?
Molecules move from high to low concentration
What is osmosis?
Diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane
What is facilitated diffusion?
Molecules move through membrane proteins
Does passive transport require energy?
No
Example of facilitated diffusion?
Glucose or ions (Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻)
What is active transport?
Movement against a concentration gradient, requiring energy (ATP)
Types of active transport?
Primary active transport, secondary active transport
Primary active transport?
Uses ATP directly
Secondary active transport?
Uses energy from ion gradients set up by primary transport
Why do cells perform active transport?
To maintain homeostasis, uptake nutrients, remove wastes against gradients
Which transport type is studied in the Maltose Transporter Assay?
Active transport
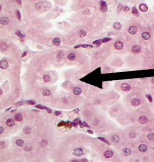
What is on the arrow
Tubules
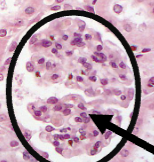
What is on the arrow
Glomerulus
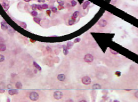
What is on the arrow
Bowman’s Capsule

What is this?
Renal Cortex
