Unit 2: The periodic table
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Element Symbol
A one or two lettered symbol for the element name. First letter is always capitalized, and the second letter is always lowercase.
Electrons
Negatively charged particles outside of the nucleus
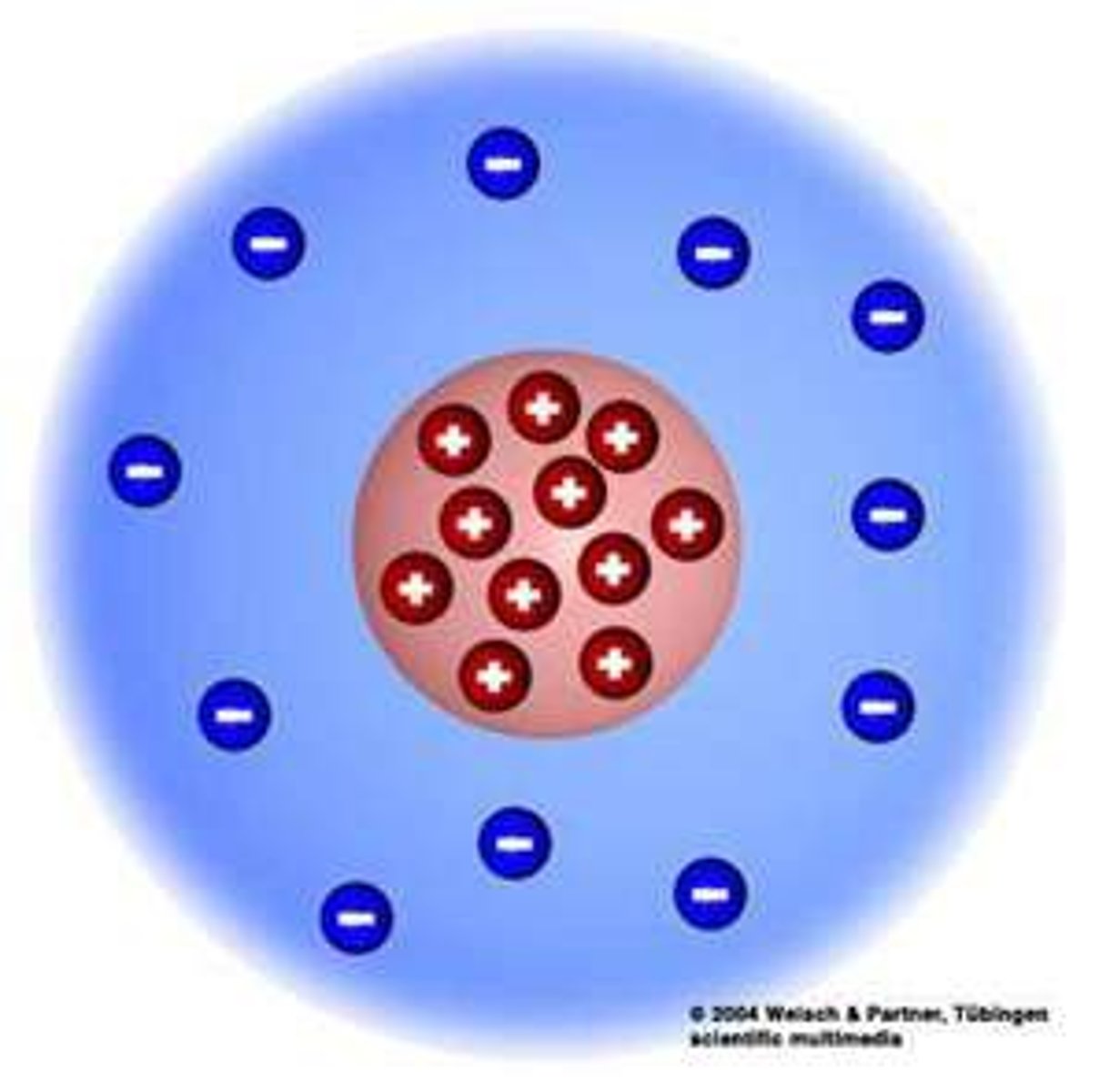
Nuclear Atom
Three subatomic particles, protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons are located outside of the nucleus
Proton
Positively charged subatomic particle. Mass of 1 amu, and is located in the nucleus
Neutron
Neutral subatomic particle. Mass of 1 amu, and it is located in the nucleus.
Isotopes
An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. For example, C-12 and C14
Atomic Number
The number above the symbol on the periodic table. Also, the number of protons in an element.
Atomic Mass
The number below the symbol on the periodic table. The average for all of the different isotopes of that element
Dalton's Atomic Theory
Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms, matter can not be created or destroyed

JJ Thomson's experiment
Used the cathode ray tube, and discovered a negatively charged particle in the atom - the electron
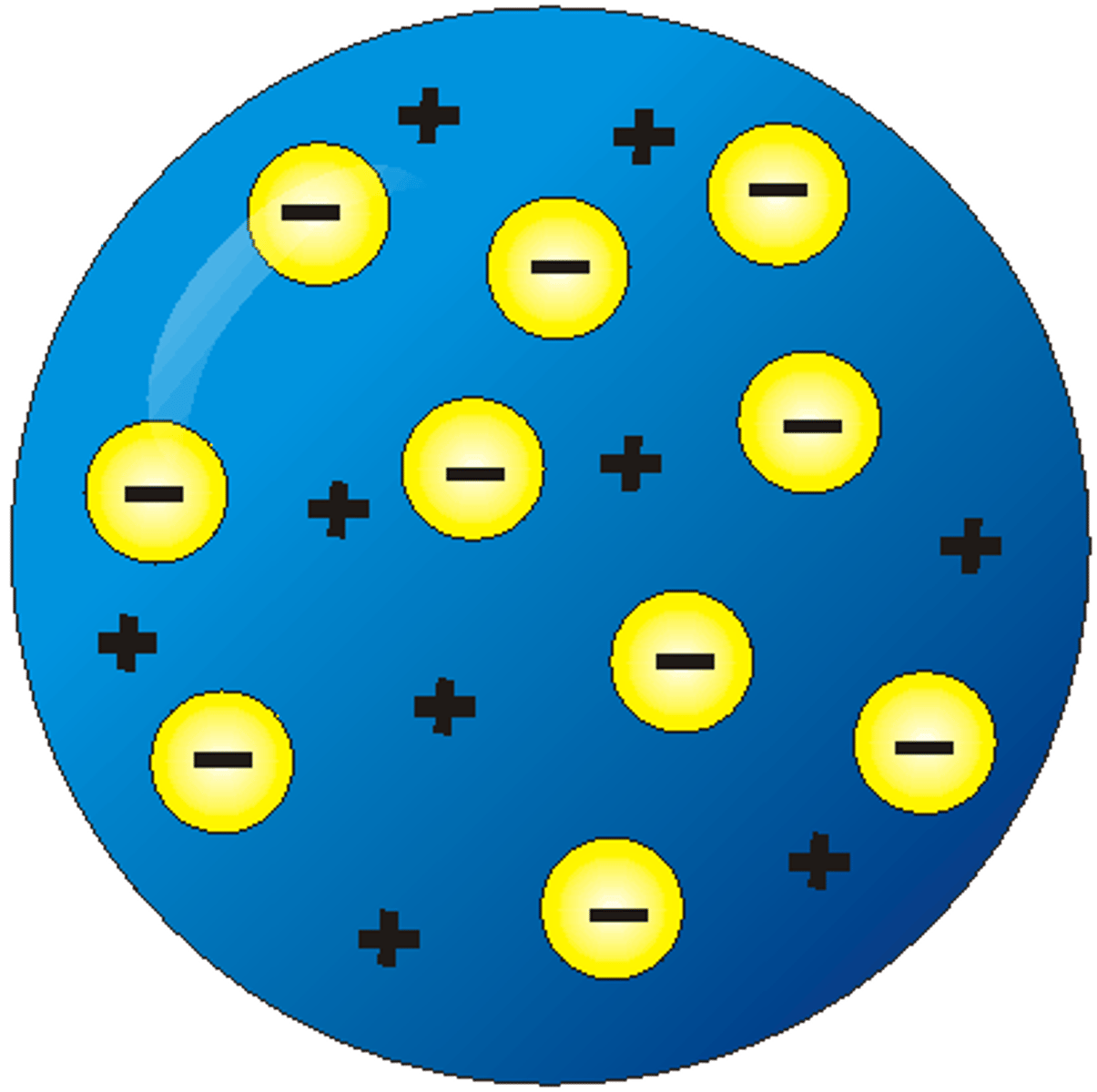
Rutherford's experiment
Used the gold foil experiment, discovered a small dense positively charged nucleus
Law of conservation of matter/mass
Matter/mass can not be created or destroyed, it is conserved
Mass number
The protons and neutrons in an atom
Periodic table
A table used to arrange elements by increasing atomic number.
Groups/Families
Alkali (Group 1A), Alkaline earth metals (2A), Transition metals, Metalloids, Halogens (7A), Noble gas (8A)
Alkali metals
Group 1A metals
Alkaline earth metals
Group 2 A metals
Halogens
Group 7 a nonmetals
Noble gases
Group 8A nonmetals- nonreactive
Transition metals
Metals to the left of the stair case
Metals
Luster, malleable, ductile, and conducts electricity
Nonmetals
Dull, brittle, not ductile, not able to conduct electricity
Metalloids- Semi metals
along the stair case- characteristics of both a metal and a nonmetal
Density
The amount of matter in a given amount of space
Fluorine
The most electronegative element on the periodic table