4.2.2 (c.(i)(ii)) the features used to classify organisms into the five kingdoms: Prokaryotae, Protoctista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia . The evidence that has led to new classification systems, such as the three domains of life, which clarifies relationships
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
to include the use of similarities in observable features in original classification. To include the more recent use of similarities in biological molecules and other genetic evidence AND details of the three domains and a comparison of the kingdom and domain classification systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
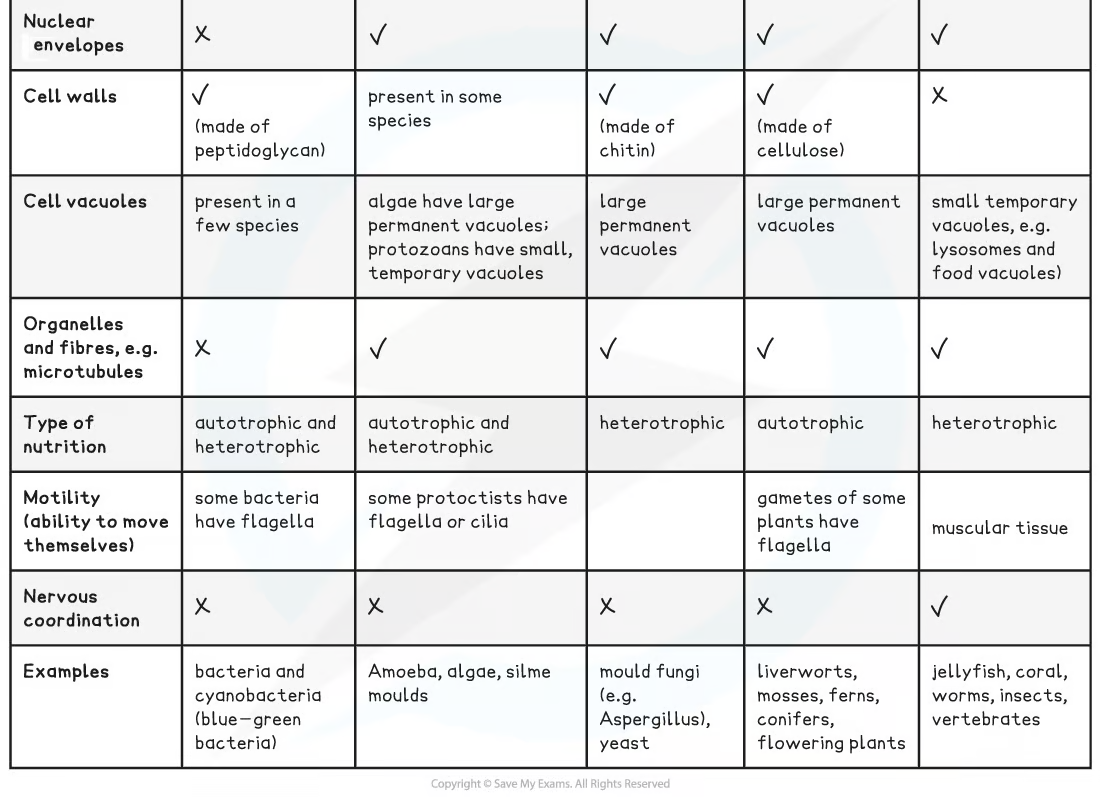
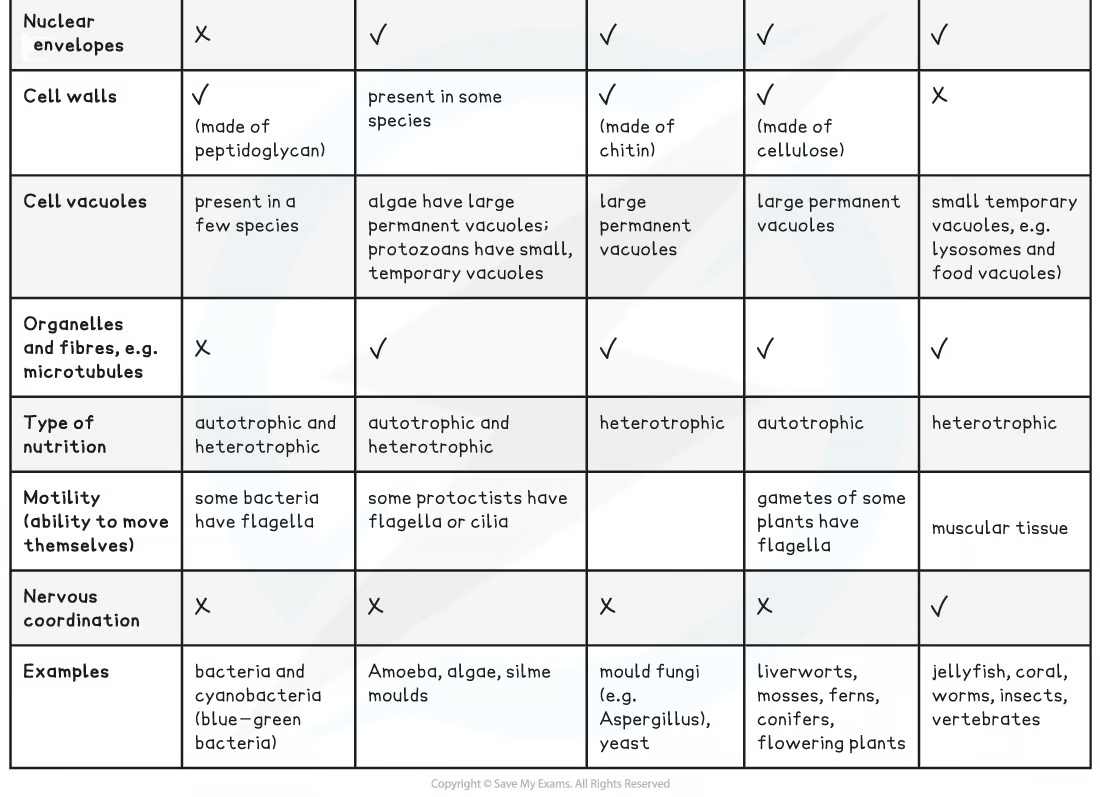
classification of the 5 kingdoms
most people thought there to be five kingdoms at the top of the classification hierarchy
Prokaryote
Protoctista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
Prokaryota
includes bacteria and blue-green bacteria
Most are unicellular (some can be found as filaments of cells or groupings of similar cells known as colonies)
cells have cell walls (not made of cellulose) and cytoplasm
no nucleus or mitochondria
cells divide by binary fission
Blue-green bacteria and some bacteria are autotrophic (they are photosynthetic)
Many bacteria are heterotrophic (feeding by decomposing living or dead organic materials)
Protoctista
are all eukaryotic
can exist as single-celled organisms or a group of similar cells
A group of Protoctista known as protozoa possess cells similar to animal cells
Their cells have no cell wall
Another group of Protoctista known as algae possess cells similar to plant cells
Their cells have cellulose cell walls and chloroplasts
Fungi
All fungi are eukaryotic cells
Possess non-cellulose cell walls (often made of polysaccharide chitin)
Don’t have cilia
Fungi are heterotrophs:
use organic compounds made by other organisms as their source of energy + molecules for metabolism
They obtain this energy and carbon by digesting dead/decaying matter extracellularly or from being parasites on living organisms
fungi 2
Fungi reproduce using spores that disperse onto the ground nearby
Fungi have a simple body form:
They can be unicellular
Some consist of long threads called hyphae that grow from the main fungus body and form a network of filaments called the mycelium
Larger fungi possess fruiting bodies that release large numbers of spores (this is how many fungi reproduce)
The mould found on bread is actually a fungus: Rhizopus nigricans
Plantae
Plants are multicellular eukaryotic organisms
Plant cells:
have cell walls composed of cellulose
Possess large (and usually permanent) vacuoles that provide structural support
Are able to differentiate into specialized cells to form tissues and organs
Possess chloroplasts that enable photosynthesis (not all plant cells have chloroplasts)
Can sometimes have flagella
They are autotrophs
meaning they can synthesize their organic compounds and molecules for energy use and build biomass from inorganic compounds
Plants have complex body forms
They have branching systems above and below the ground
Animalia
are also multicellular eukaryotic organisms
cells able to differentiate into many different specialised cell types that can form tissues and organs
Have small temporary vacuoles (for example, lysosomes)
Have no cell walls
Sometimes have cilia
They are heterotrophs and have a wide range of feeding mechanisms
Communication within their complex body forms takes place through a nervous system and chemical signalling
what are the three domians of life
Bacteria (prokaryotes)
Archaea (prokaryotes)
Eukarya (eukaryotes)
Bacteria
These are organisms that have prokaryotic cells which contain no nucleus
Bacterial cells divide by binary fission
Example: Staphylococcus pneumoniae is a species of bacteria that causes pneumonia
Archaea
often referred to: extremophile prokaryotes as they were first found living in extreme environments (although not all archaea do)
they have no nucleus
Archaea have a similar size range as bacteria
in many ways metabolism is similar between the two
DNA transcription is more similar to that of eukaryotes
Example: Halobacterium salinarum is a species of the archaea domain that can be found in environments with high salt concentrations like the Dead Sea
Eukarya
Organisms that have eukaryotic cells with nuclei and membrane-bound organelles.
divide by mitosis
can reproduce sexually or asexually
why is classifying organisms using cell type, insufficient?
Based on molecular analyses of RNA genes in particular, and by looking at features:
ribosomal RNA (rRNA),
aspects of protein synthesis
structure of cell membranes and flagella
found that prokaryotes could be divided into two separate groups (domains)
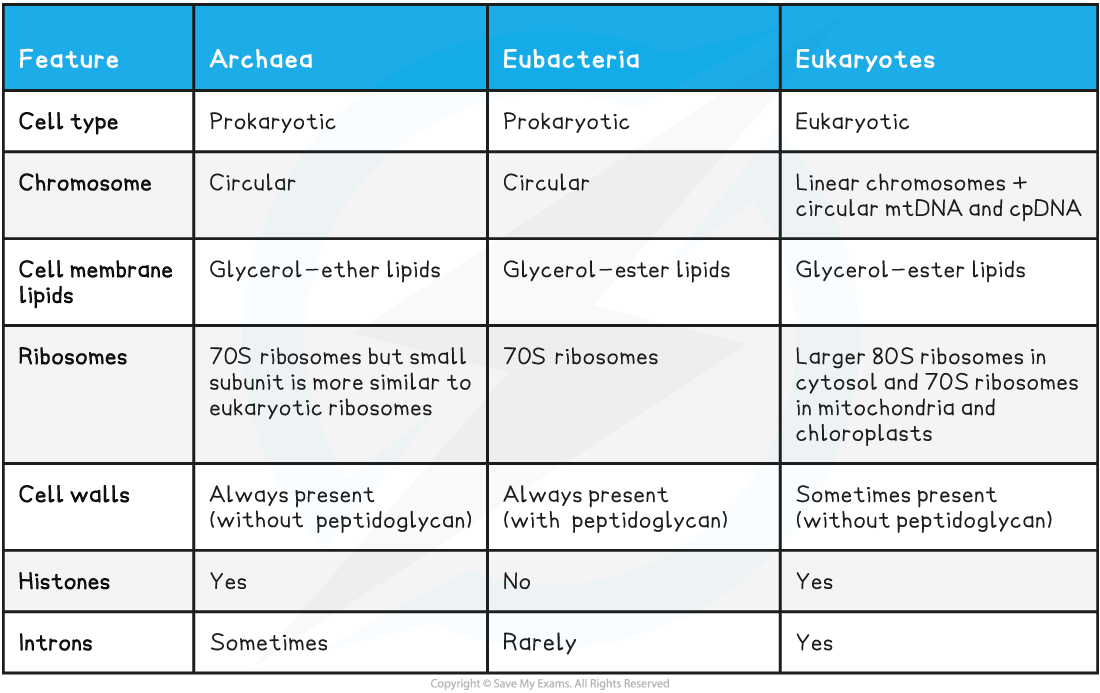
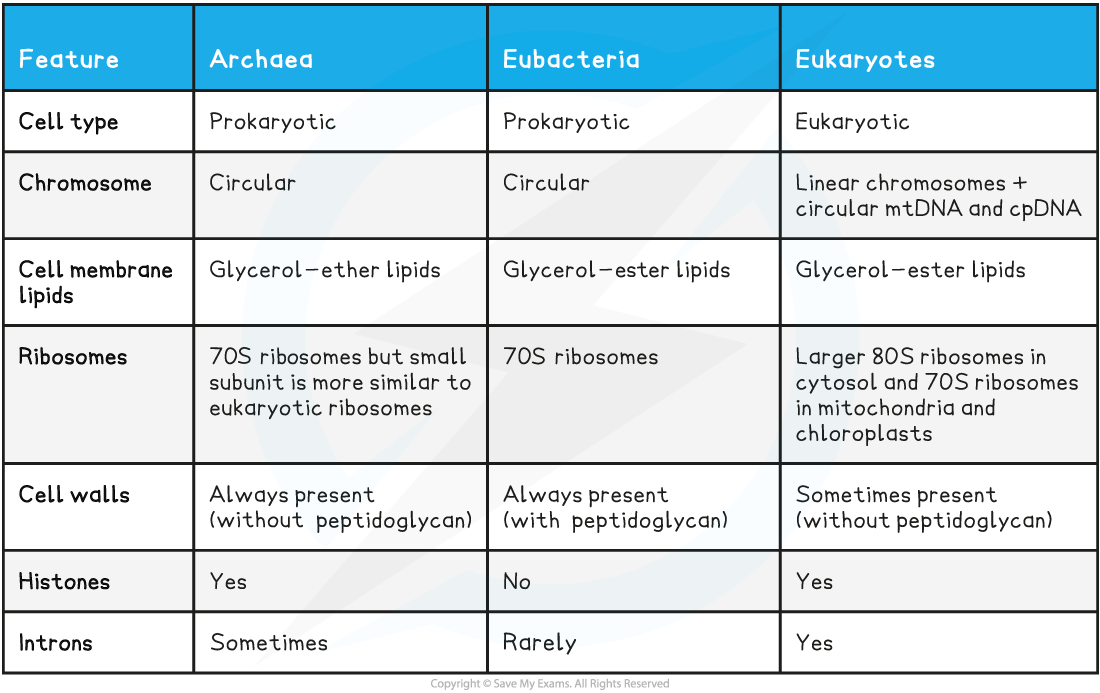
membrane lipid differences
The membrane lipids of Archaea consist of branched hydrocarbon chains bonded to glycerol by ether linkages
The membrane lipids of Bacteria consist of unbranched hydrocarbon chains bonded to glycerol by ester linkages
Ribosomal RNA
Archaea and Bacteria possess 70S ribosomes
The 70S ribosomes in Archaea possess a smaller subunit that is more similar to the subunit found in Eukaryotic
The base sequences of ribosomal RNA in Archaea show more similarity to the rRNA of Eukarya than Bacteria
The primary structure of ribosome proteins in Archaea show more similarity to the ribosome proteins in Eukarya than Bacteria
cell wall differences
bacteria domain have cells that always possess cell walls with peptidoglycan
Archaea domain also have cells that always possess cell walls, however these do not contain peptidoglycan