module 7- action potentials
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
knock on mechanism in potassium voltage-gated channels
selectivity filter strips hydration shell from ion → ion moved into channel
the entry of one 1 K ion into the channel pushes one of the other ions occupying the channel out of the other side
oxygen atoms help stabilise the ion as it passes through the membrane (because potassium ions are the right size for interaction)
when do sodium voltage-gated channels innactivate
1msec after membrane potential reaches the threshold (action potential)
how does sodium voltage-gated channel open during depolarisation
voltage sensor moves & pulls the channel open
inactivation gate in sodium voltage-gated channels
found between 3rd & 4th psuedosubunits
ball & chain like structure on sodium voltage-gated channels swing up & blocks the gate which causes channel inactivation (no more Na ions can leave cell)
duration of action potential in neurones
2 msecs
duration of action potential in skeletal muscle
5 msecs
duration of action potential in the heart
200 msecs
anatomy of an action potential (draw)
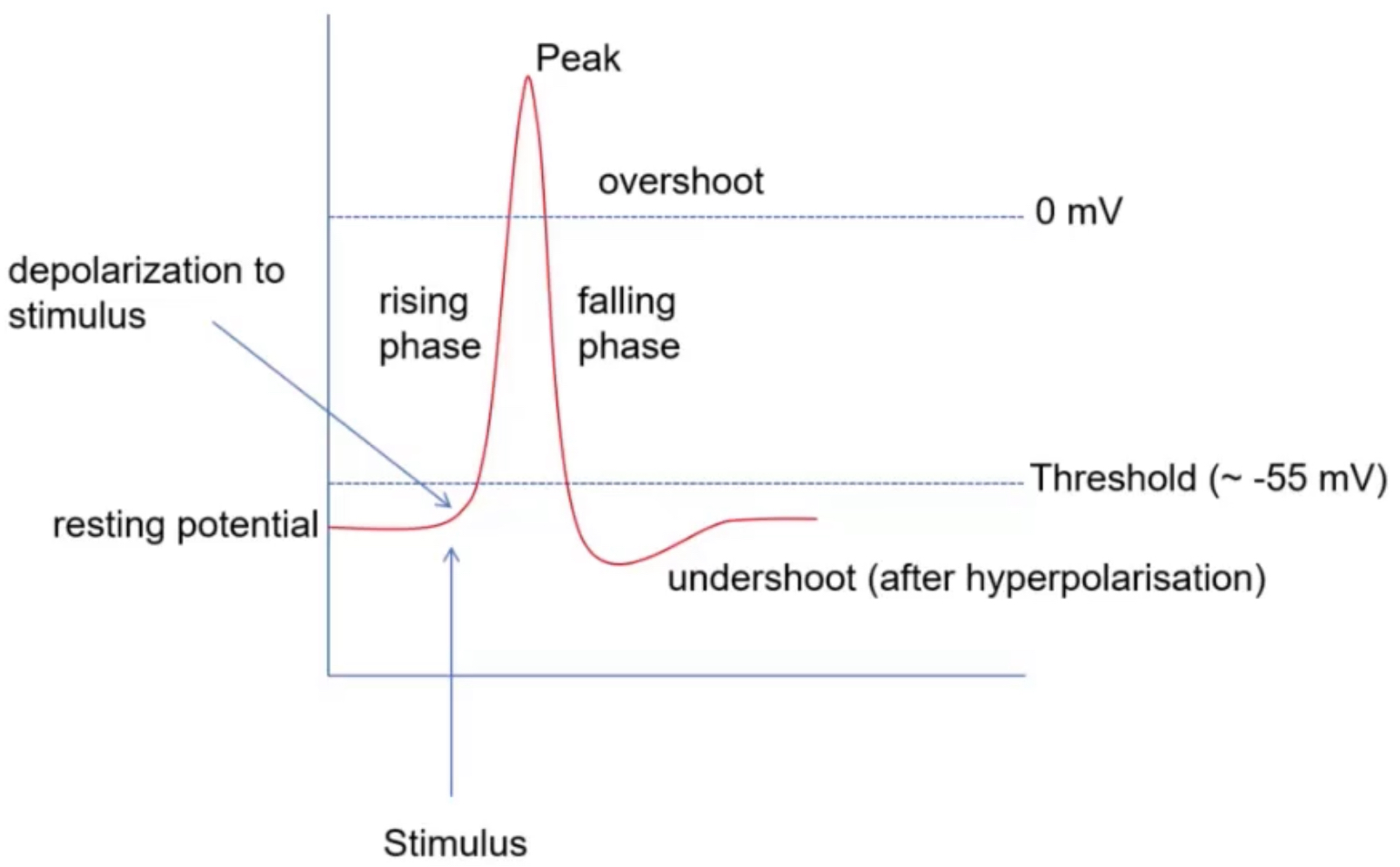
Na voltage-gated channels at resting potential
probability of closing >> probability of opening
Na voltage-gated channels at below threshold stimulus
probability of closing > probability of opening
Na voltage-gated channels at above threshold stimulus (depolarisation)
probability of closing << probability of opening
what is dravet syndrome
form of epilepsy
inheritable
mutation of SCN1A gene that codes for a sodium channel → mutation prevents action potentials in inhibitory neurons so lack of inhibition in some brain regions
Nav1.1 is mutated → main sodium channel expressed in inhibitory neurons
how can dravet syndrome be treated
cannabinoids (CBD)
NICE guidelines → since 2019 its been legal to prescribe cannabinoids for treatment resistant epilepsies
what does the relative refractory period prevent
prevents action potential from spreading backwards across axon