BIOL 2402 A&P-2 UNIT 1 Lecture Exam Study Guide
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
237 Terms
What is a hormone?
a long distance chemical signal that travels in the blood or lymph
What are a hormone's main functions?
serve as messengers, controlling and coordinating activities throughout the body
What are endocrine glands?
ductless glands that produce hormones.
have a rich vascular and lymphatic drainage that receives the hormones and are in cords and branching networks.
What do endocrine glands secrete?
hormones directly into the bloodstream
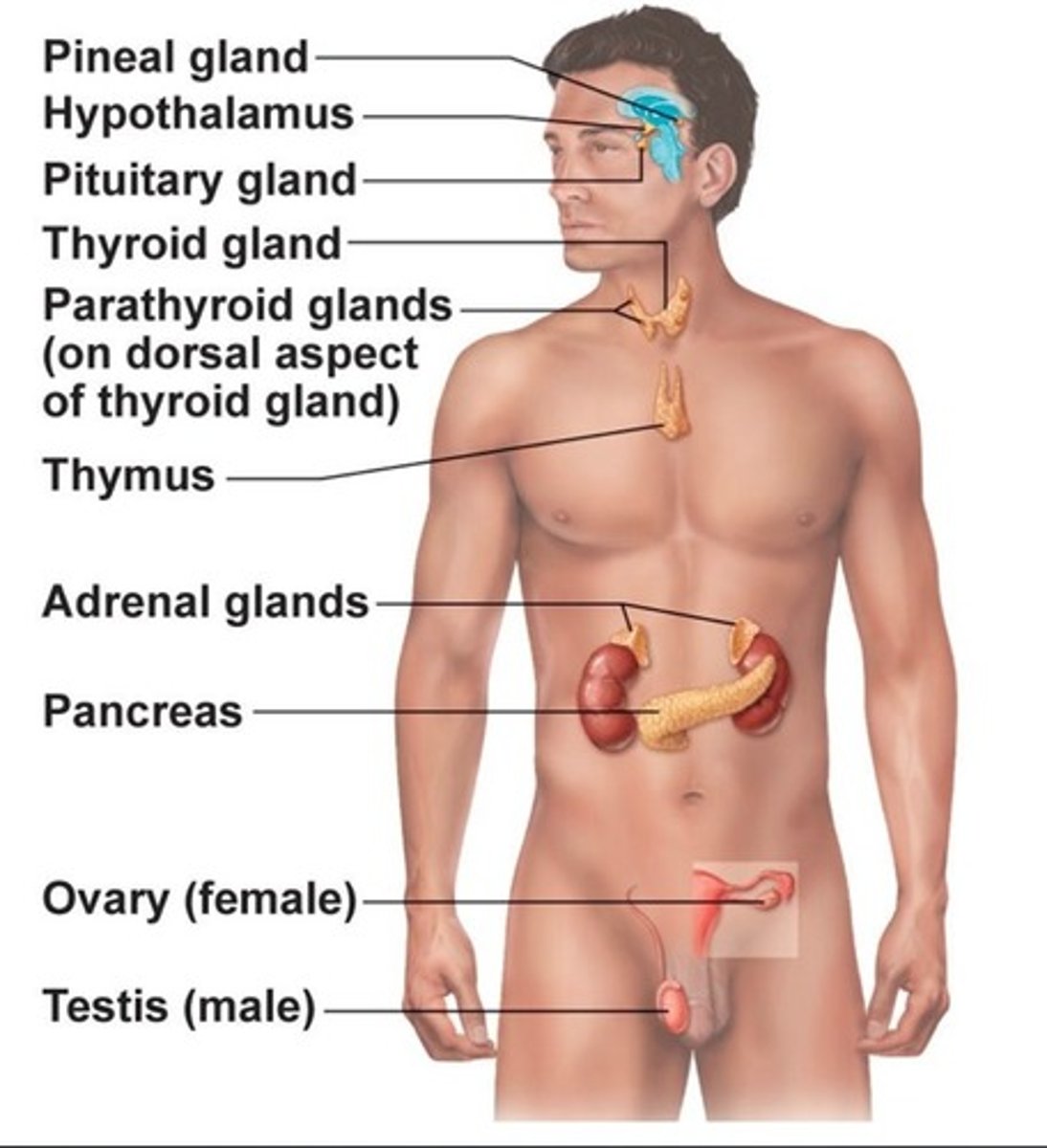
Major examples of endocrine glands?
pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands
How is the endocrine system different from the action of the nervous system?
initiates responses slowly
long-duration responses
acts via hormones released into the blood
acts at diffuse locations-targets can be anywhere blood reaches
hormones act over long distances
Location and identification of endocrine glands in the body
Distinguish between hormones, autocrines and paracrines
• Hormones: long-distance chemical signals; travel in blood or lymph
• Autocrines: chemicals that exert effects on same cells that secrete them
• Paracrines: locally acting chemicals that affect cells other than those that secrete them
Chemical structure of amino acid-based
Amino acid derivatives: peptides (short chains of amino acids) and proteins (long chains of amino acids)
Chemical structure of steroids
Synthesized from cholesterol
Of the hormones produced by major endocrine organs, only Gonadal and adrenocortical hormones are steroids.
What are target cells?
tissues with receptors for a specific hormone
Two major mechanisms by which hormones bring about their effects on target tissues
(1) Water-soluble hormones (all amino acid-based hormones except thyroid hormone), cannot enter the target cells, act on plasma membrane receptors
(2) Lipid-soluble hormones (steroid and thyroid hormones), act on intracellular receptors that activate genes

How does a hormone communicate with its target cell?
Depends on the chemical nature of the hormone and the cellular location of the receptor
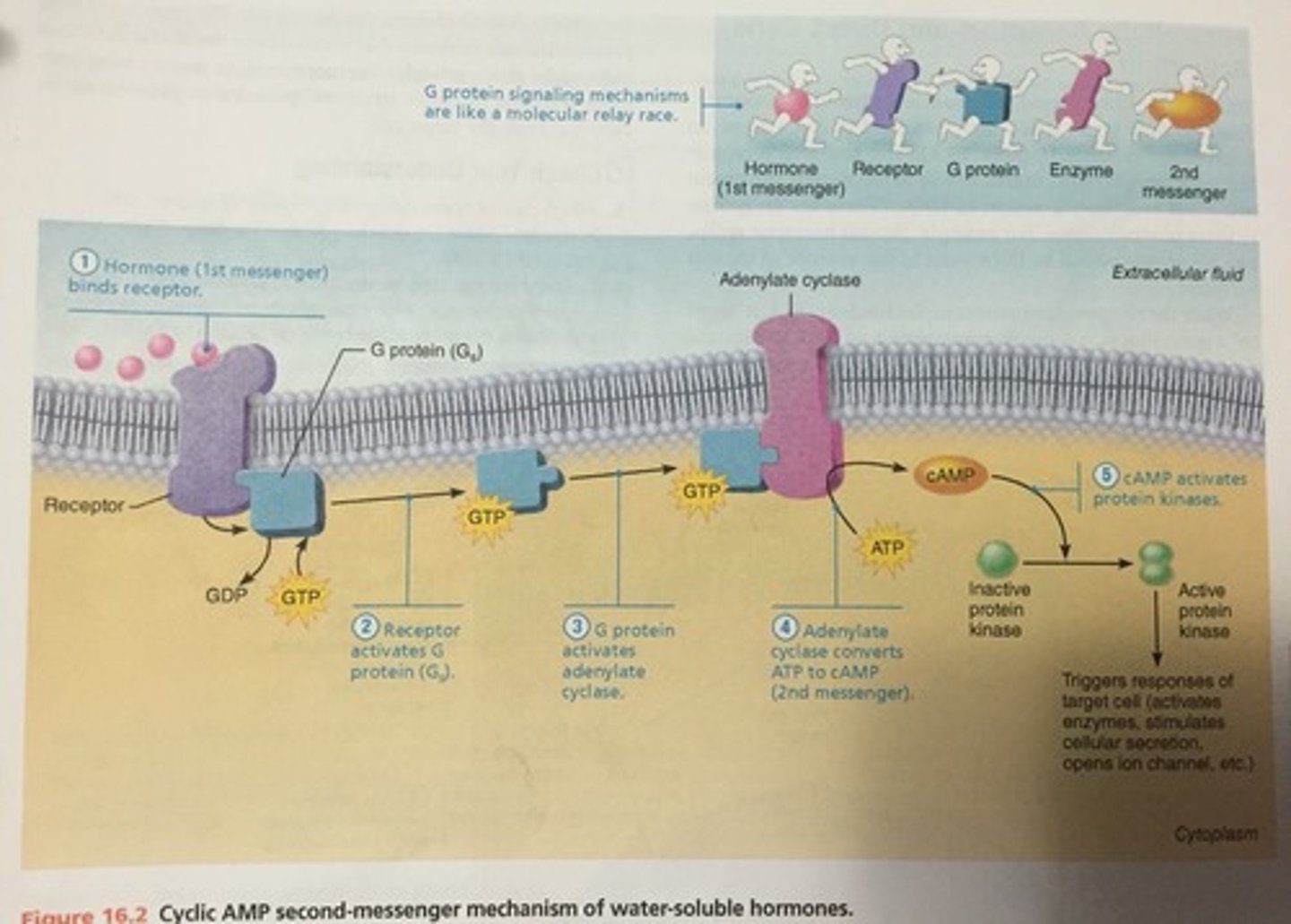
1. Water soluble hormones(all amino acid based hormones except thyroid)Act on receptors in the plasma membrane. These receptors are usually coupled via regulatory molecules called G proteins to one or more intracellular second messengers which mediate the target cell's response.
- cannot enter the cell
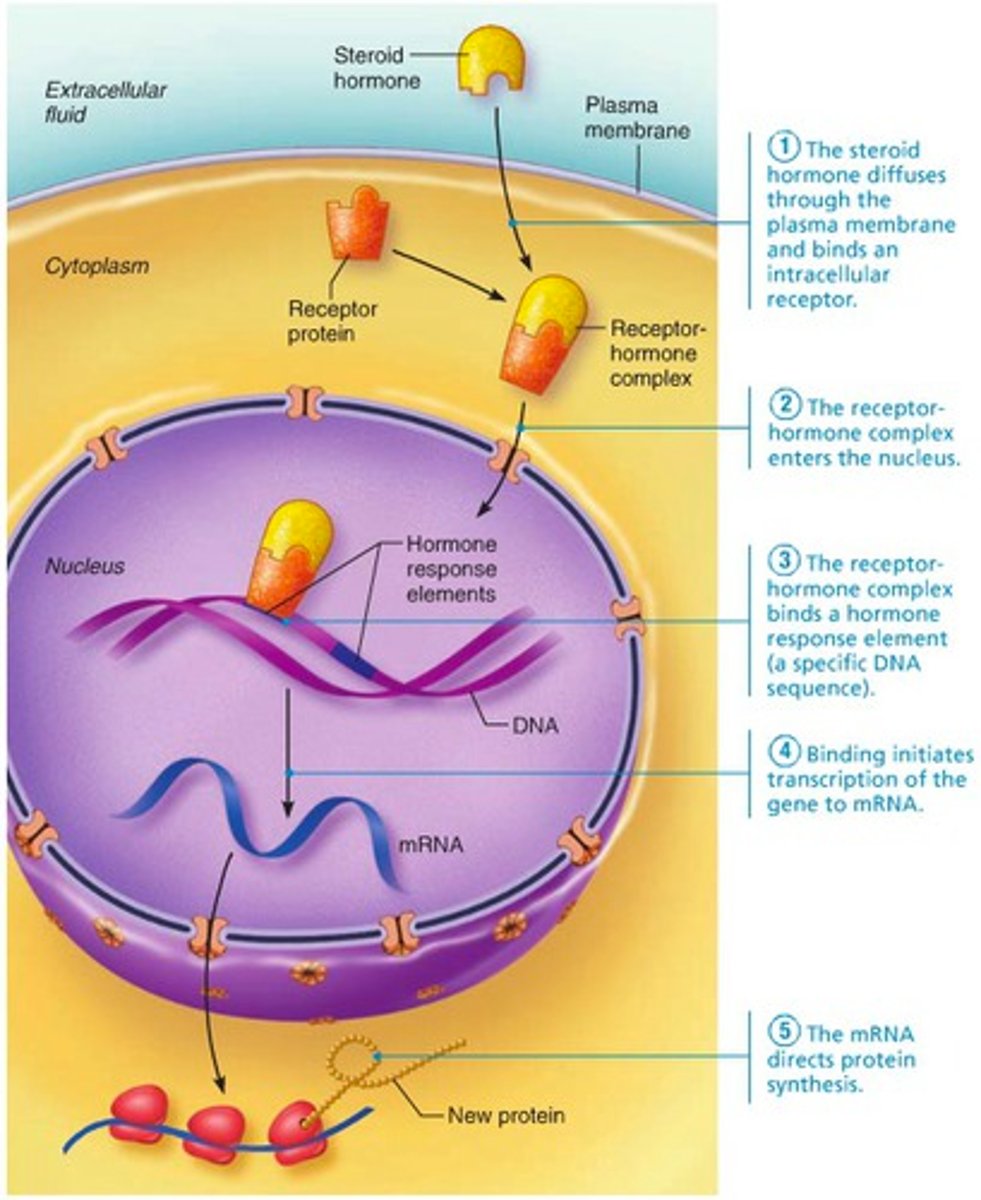
2. Lipid soluble hormones(steroid and thyroid hormones)
- Act on receptors inside the cell, which directly activate genes.- can enter the cell
Where are the receptors? Outside or inside the cell?
Water soluble hormones receptors are outside the cell
Lipid soluble hormones receptors are inside the cell
water soluble hormones
(all amino acid-based hormones except thyroid hormone)
Act on plasma membrane receptors
Act via G protein second messengers
Cannot enter cell
lipid soluble hormones
(steroid and thyroid hormones)
Act on intracellular receptors that directly activate genes
Can enter cell
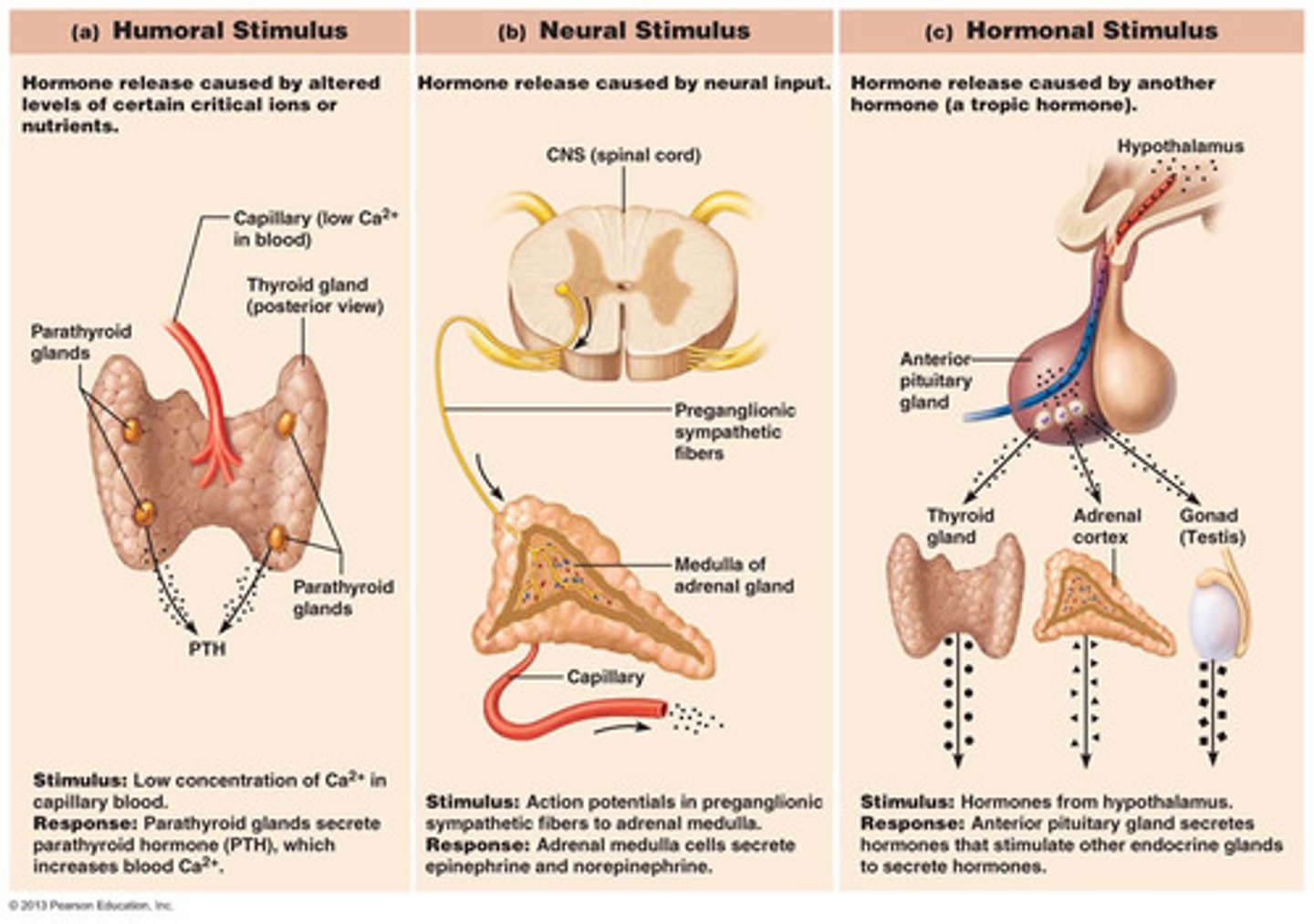
Three types of endocrine gland stimuli with examples
1. Humoral Stimulus-Cells of the parathyroid glands monitor the body's blood CA2+, glucose, and low Na+ or high K+ levels and release parathyroid hormones as need.
2. Neural Stimulus-the response to stress. The sympathetic nervous system stimulates the adrenal medulla to release norepinephrine and epinephrine.
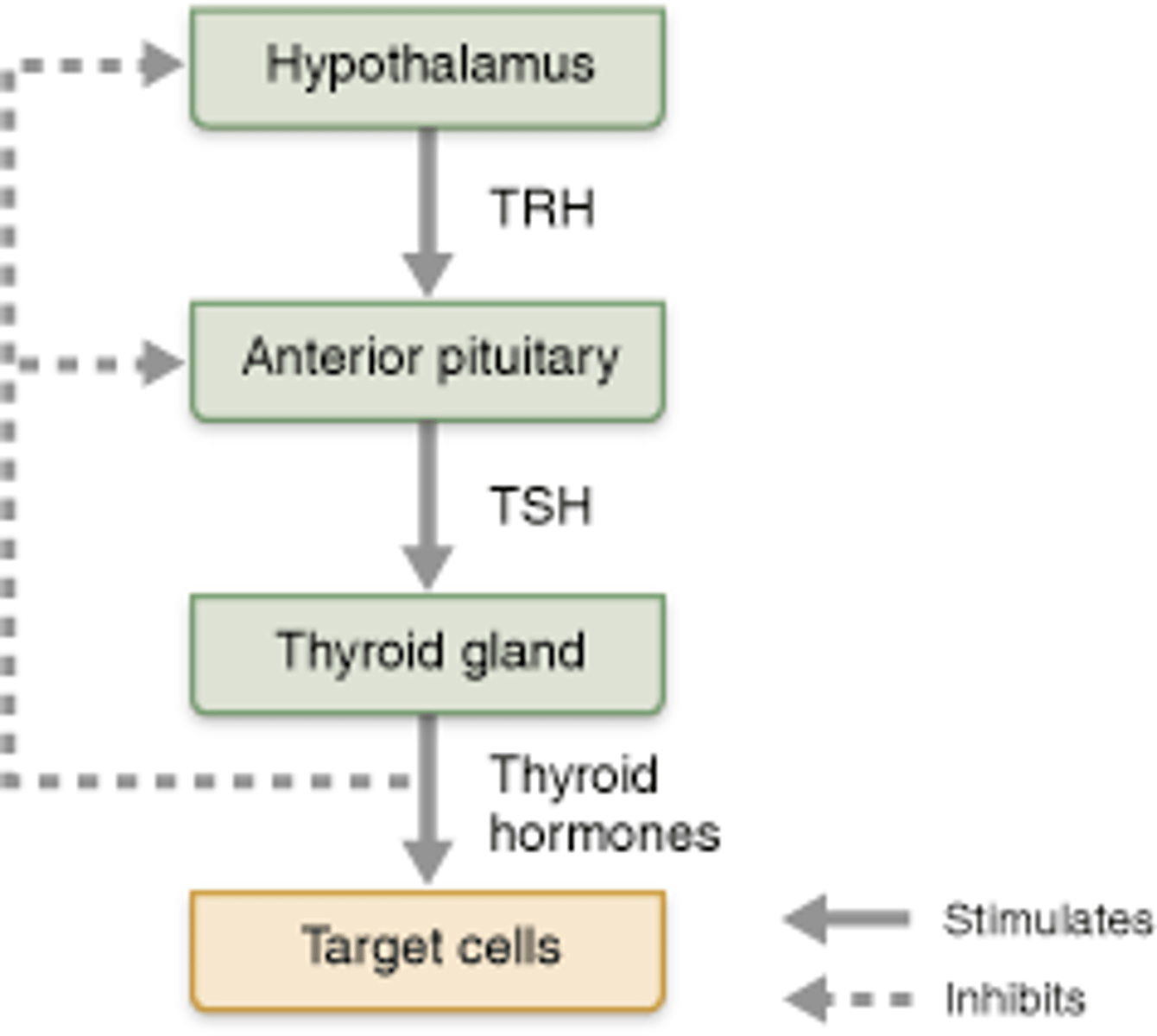
3. Hormonal Stimulus-releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus regulate the secretion of most anterior pituitary hormones, in turn, stimulate other endocrine organs to release their hormones.
What are the three factors that influence activation of a target cell by a hormone?
1. Blood levels of hormone
2. Relative number of receptors on/in target cell
3. Affinity (strength) of binding between receptor and hormone
Up-regulation
target cells form more receptors in response to low hormone levels
Down-regulation
target cells lose receptors in response to high hormone levels
Desensitizes the target cells to prevent them from overreacting to persistently high levels of hormone
Half-life
time required for level of hormone in blood level to decrease by half - varies anywhere from fraction of a minute to a week, depending on hormone
Onset (Hormones have different response times:)
Some responses are immediate
Some, especially steroid, can take hours to days
Some are inactive until they enter target cells
duration of hormone activity
(The duration of response is usually limited)
Ranges from 10 seconds to several hours
Effects may disappear rapidly as blood levels drop, but some may persist for hours at low blood levels
Synergism:
more than one hormone produces same effects on target cell, causing amplification
Example: glucagon and epinephrine both cause liver to release glucose
Antagonism:
one or more hormones oppose(s) action of another hormone
Example: insulin and glucagon
Permissiveness:
one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present
Example: reproductive hormones need thyroid hormone to have effect
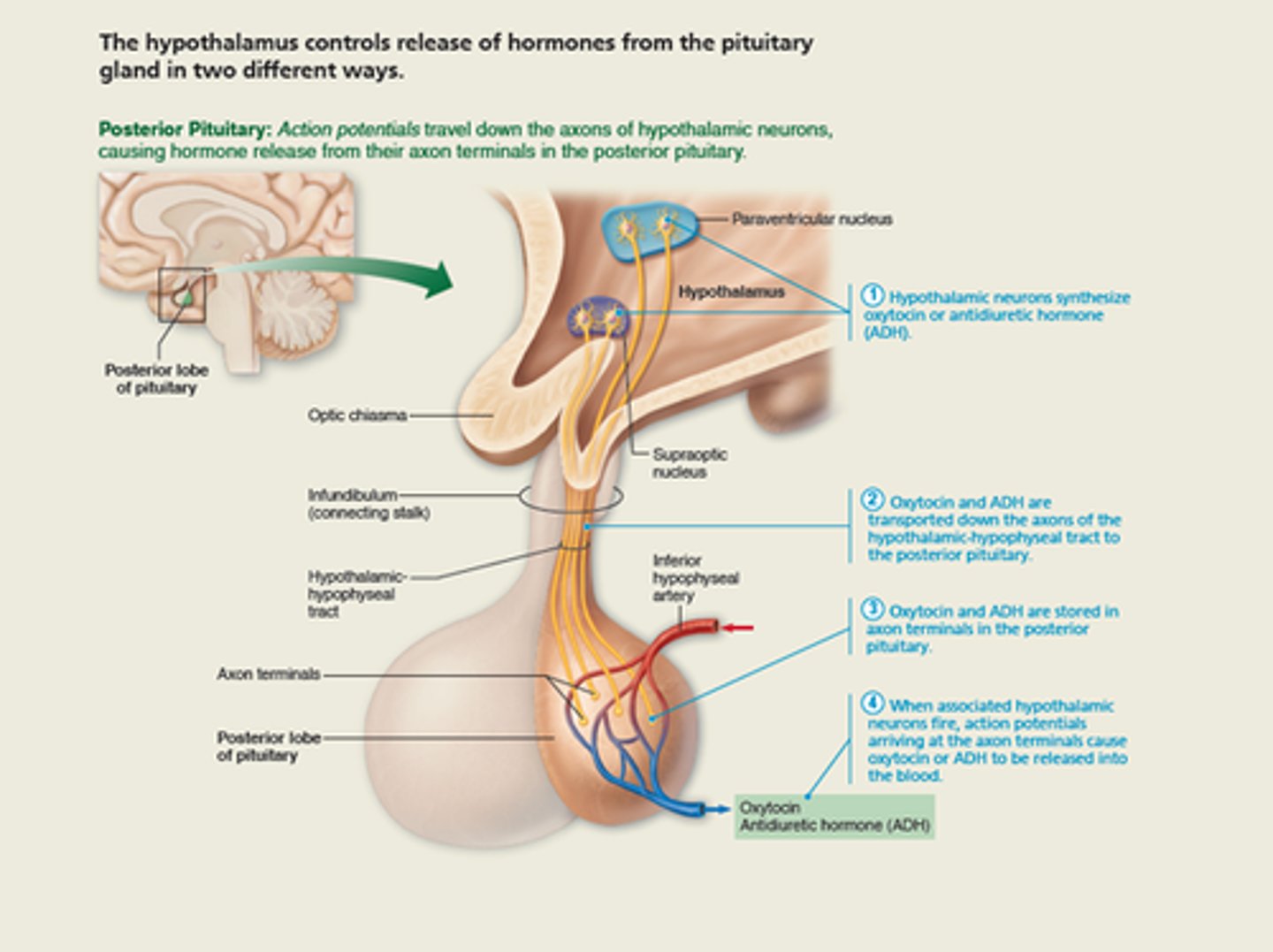
Hypothalamus and pituitary interactions (posterior pituitary)
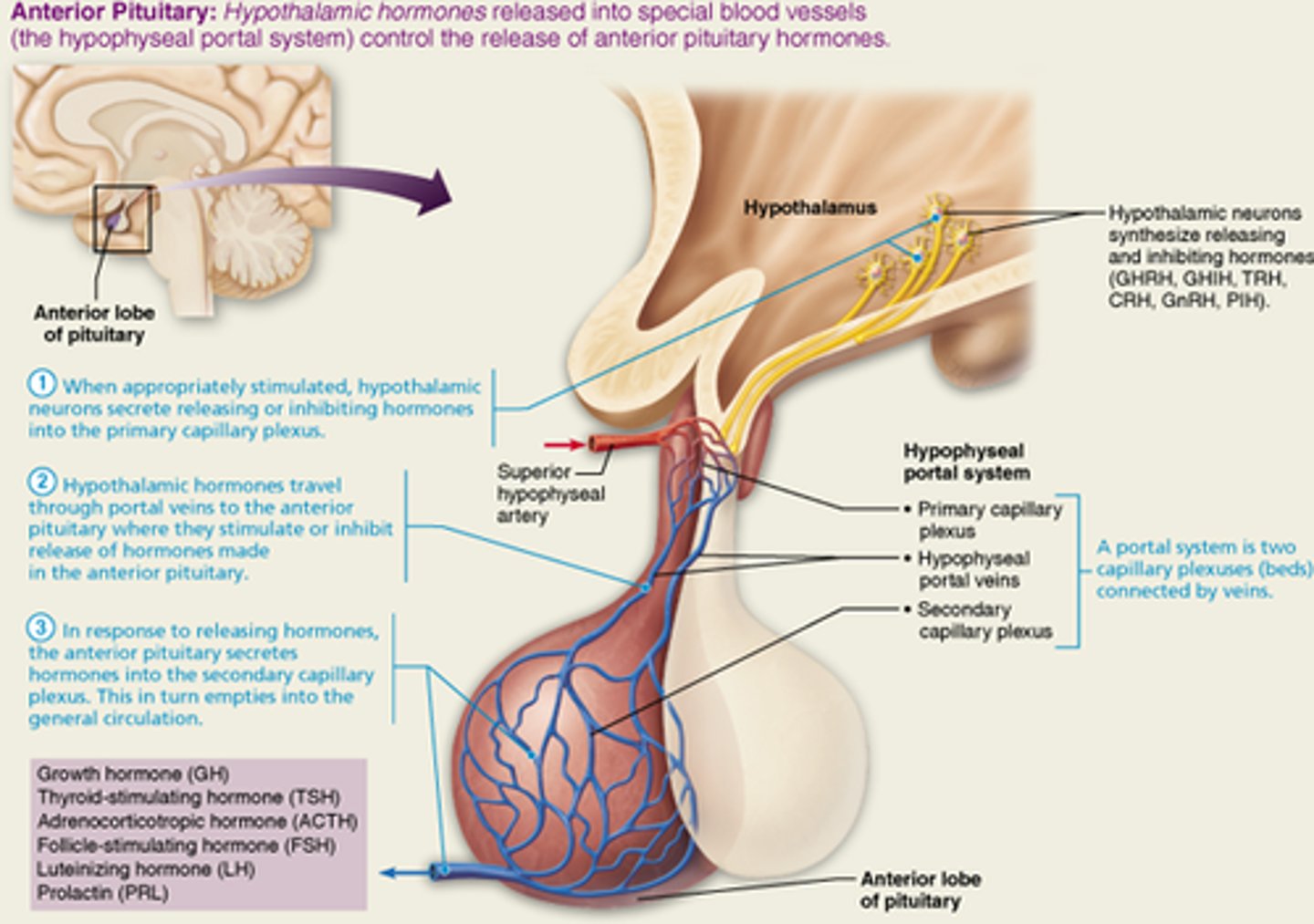
Hypothalamus and pituitary interactions (anterior pituitary)
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis)
consists of glandular tissue
Posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis):
composed of neural tissue that secretes neurohormones
Summary of posterior pituitary hormones
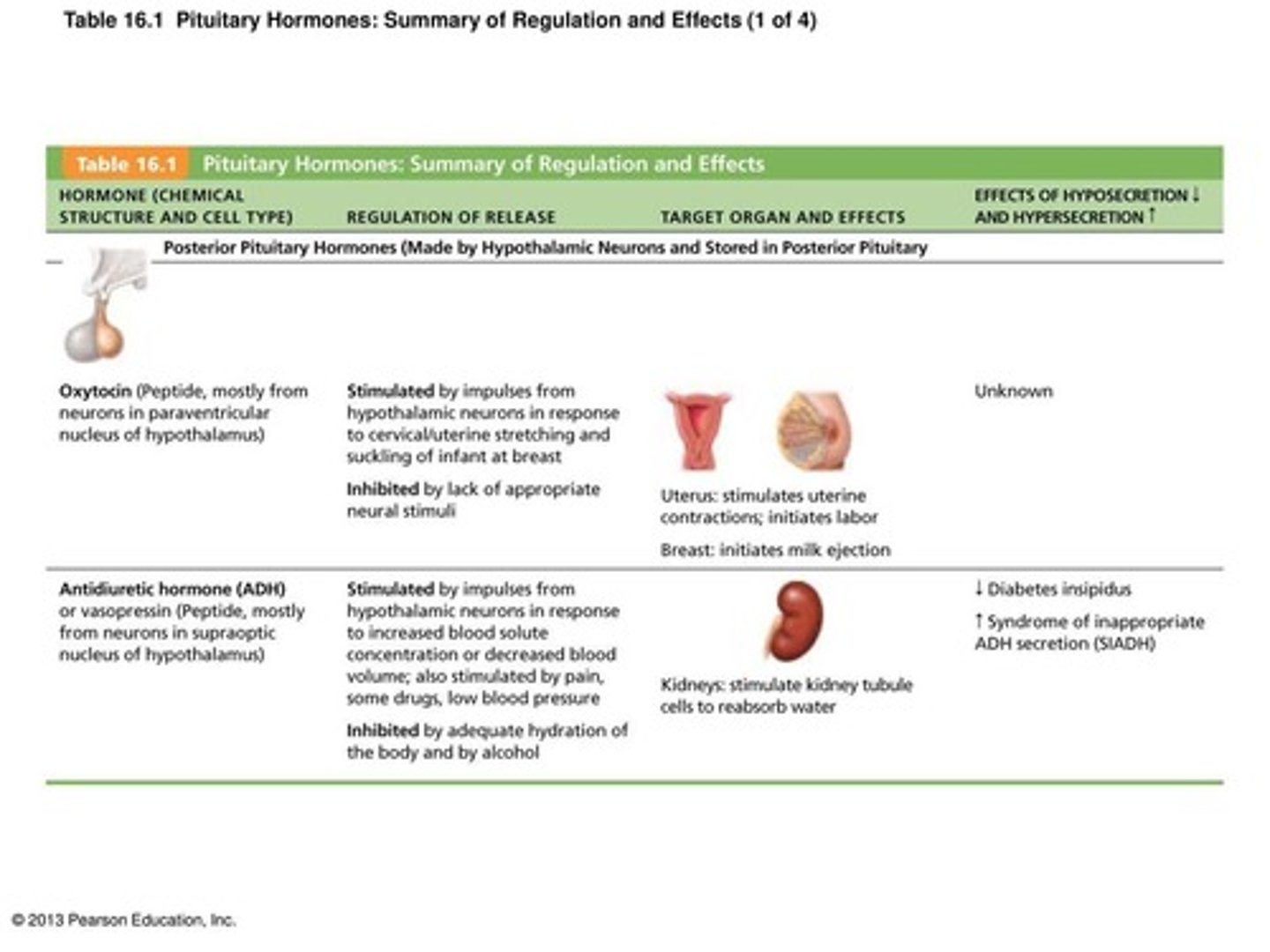
Summary of anterior pituitary hormones
1. Growth hormone (GH)
2. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
3. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
4. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
5. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
6. Prolactin (PRL)
(look in page 612-613 of the textbook for more information)
Oxytocin (OXT) (major effects on their target cell)
Strong stimulant of uterine contractions released during childbirth
Also acts as hormonal trigger for milk ejection - letdown reflex
Both are positive feedback mechanisms
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) (major effects on their target cell)
Hypothalamus contains osmoreceptors that monitor solute concentrations
If solute concentration too high, posterior pituitary triggered to release stored ADH
Targets kidney tubules to reabsorb more water to inhibit or prevent urine formation
Release also triggered by low blood pressure Inhibited by alcohol and diuretics
Growth hormone (GH) (major effects on their target cell)
Has direct actions on metabolism and indirect growth-promoting actions
It makes tissues like muscles, bones, liver, and cartilage grow
Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH) (major effects on their target cell)
Stimulates normal development and secretory activity of thyroid
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (major effects on their target cell)
stimulates adrenal cortex to release corticosteroids
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (major effects on their target cell)
stimulates production of gametes (egg or sperm)
luteinizing hormone (LH) (major effects on their target cell)
promotes the production of gonadal hormones
1. In females, LH helps mature follicles of egg, triggers ovulation and release of estrogen and progesterone
2. In males, LH stimulates the production of testosterone
Prolactin (PRL) (major effects on their target cell)
Stimulates milk production in females
Know which releasing and inhibiting hormones secreted by the hypothalamus leads to the secretion of their corresponding hormones by the anterior pituitary
growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH)
thyroid releasing hormone (TRH)
corticotropic hormone (CRH)
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH)
Growth-promoting and metabolic actions of GH
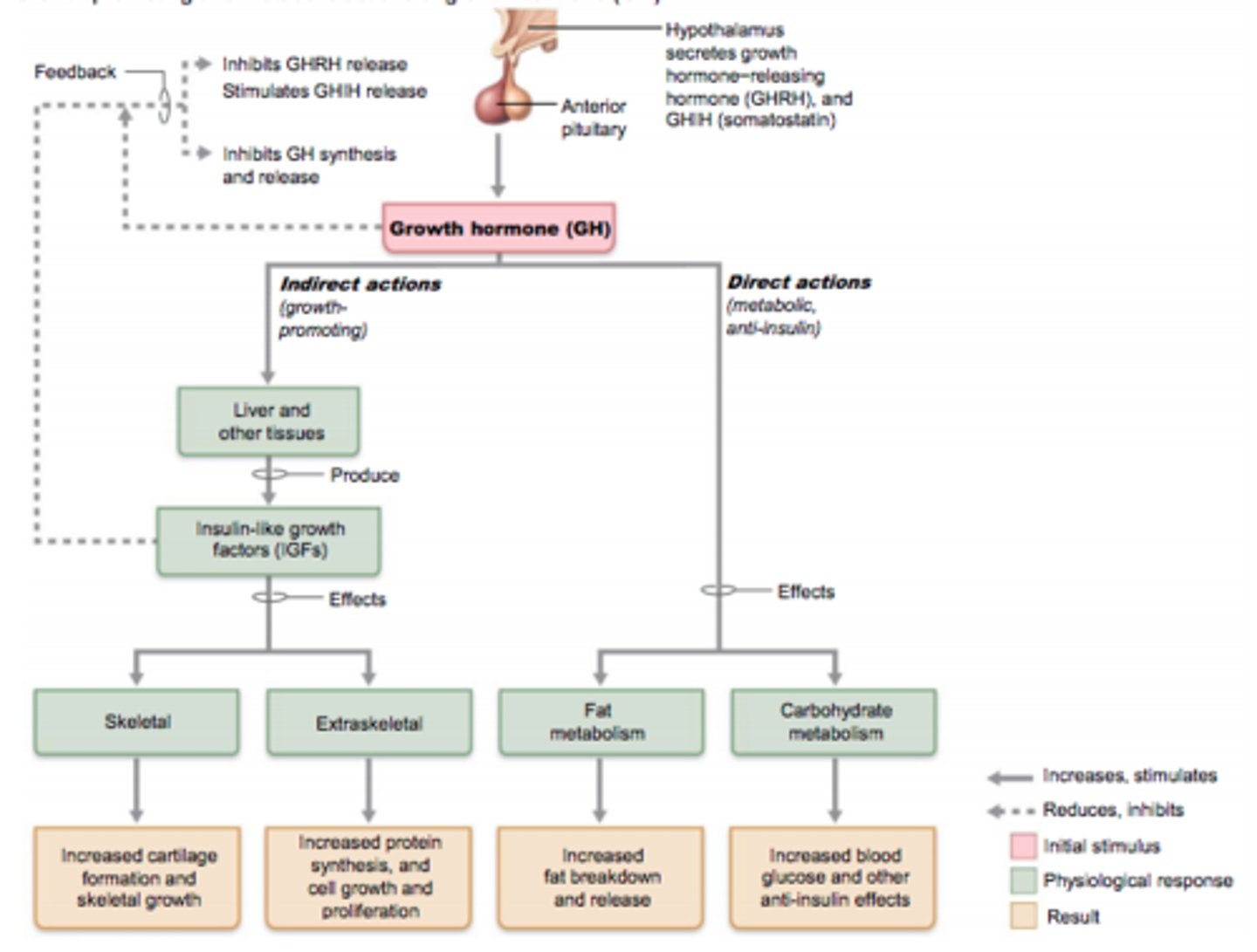
Regulation of thyroid hormone secretion
location and structure of thyroid gland
just below larynx, sits on the anterior surface of the trachea.has right and left lateral lobes. has a very rich blood supply.
Follicular cells - hormones produced?
the glycoprotein thyroglobulin and the thyroid hormone
parafollicular cells - hormones produced?
calcitonin
Thyroid hormones
Body's major metabolic and Iodine-containing amino hormone
Thyroid Hormone (TH) found in two forms
T4 (thyroxine) and T3 (triiodothyronine)
T4 (thyroxine)
major form with four bound iodine atoms
T3 (triiodothyronine)
form with three bound iodine atoms
Major effects of thyroid hormones
1. Increases basal metabolic rate (BMR) and heat production
2. Regulates tissue growth and development
Critical for normal skeletal and nervous system development and reproductive capabilities
3. Maintains blood pressure
Increases adrenergic receptors in blood vessels
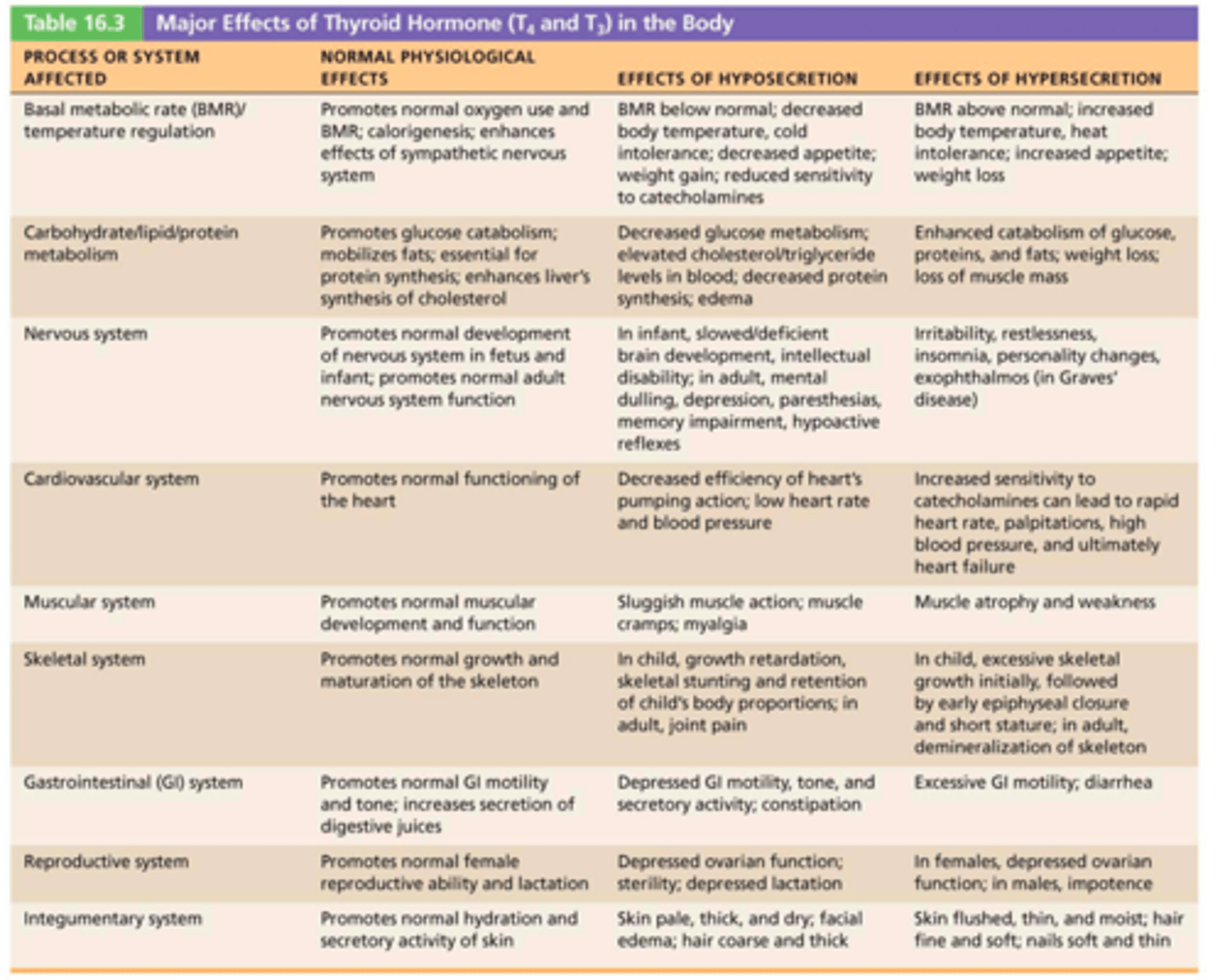
Thyroid Disorders
myxedema, goiters & Grave's disease
Myxedema
Symptoms include low metabolic rate, thick and/or dry skin, puffy eyes, feeling cold, constipation, edema, mental sluggishness, extreme tiredness or lethargy
Goiters
Thyroid gland enlarges due to lack of iodine
Grave's disease
An autoimmune disease that happens when the body makes abnormal antibodies directed against thyroid follicular cells
Symptoms: elevated metabolic rate, sweating, rapid and irregular heartbeats, nervousness, and weight loss despite adequate food
Role of calcitonin in calcium regulation
1. Decreases blood Ca2+ levels
2. Inhibits osteoclast activity and prevents release of Ca2+ from bone matrix
3. Stimulates Ca2+ uptake and incorporation into bone matrix
Role of parathyroid hormone (PTH) hormones in calcium regulation
most important hormone in Ca2+ homeostasis Response: Increases blood Ca2+ levels
Secreted in response to low blood levels of Ca2+
• Target organs: skeleton, kidneys, and intestine
Structure of adrenal glands
Capsule
Zona glomerulosa produce Mineralocorticoids
Zona fasciculata produce Glucocorticoids
Zona reticularis produce Gonadocorticoids
Adrenal medula produce catecholamines
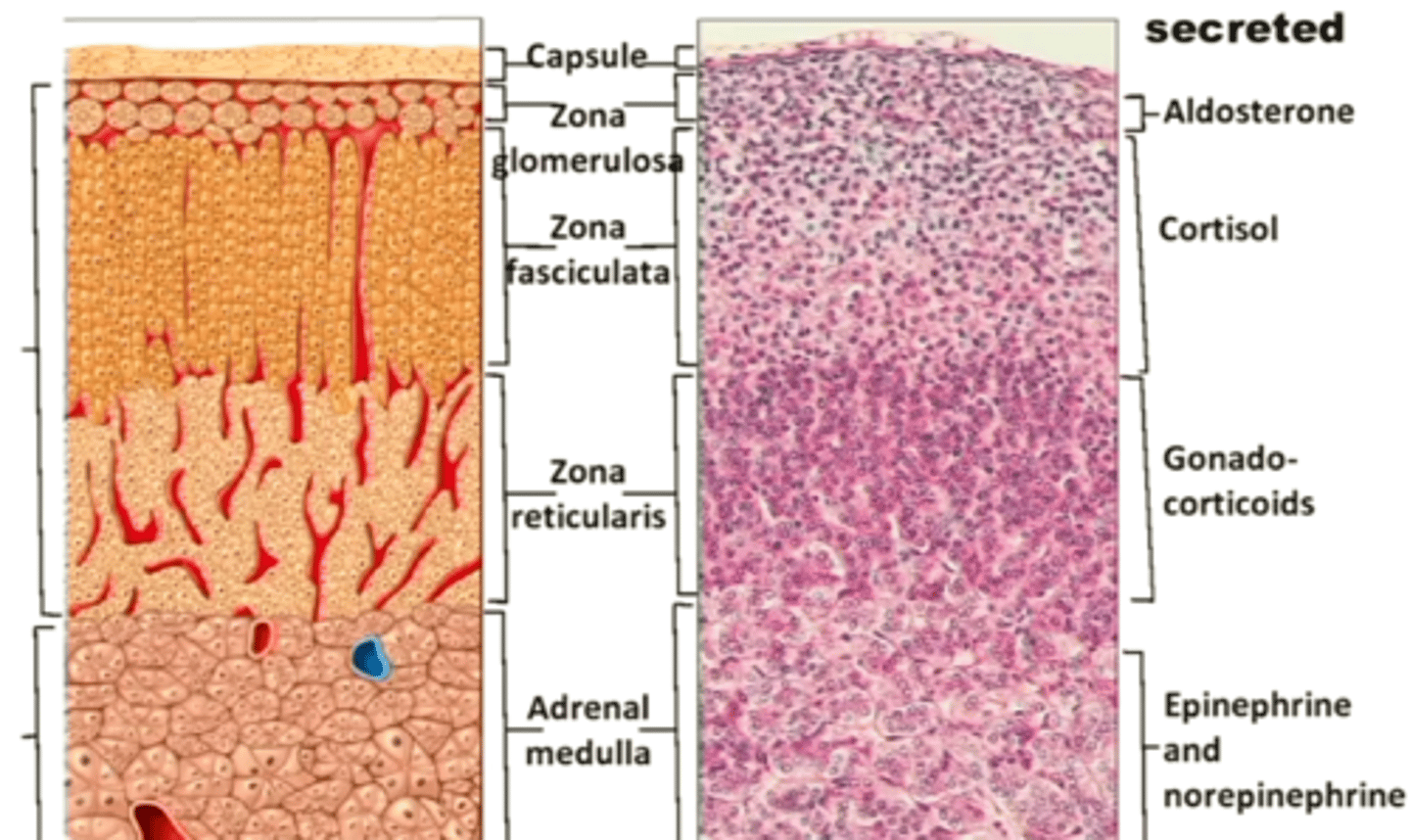
Hormones produced from the adrenal cortex and medulla
mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, gonadocorticoids, and catecholamines
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)
Regulate electrolyte concentrations (primarily Na+ and K+) in ECF
Stimulates Na+ reabsorption by kidneys - results in increased blood volume and blood pressure
Stimulates K+ elimination by kidneys
decrease urine output
Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
Influence metabolism of most cells and helps resist stressors
Keep blood glucose levels relatively constant
Maintain blood pressure by increasing action of vasoconstrictors
Gonadocorticoids (Adrenal Sex Hormones)
weak androgens convert to testosterone
1. Onset of puberty and appearance of secondary sex characteristics
2. Sex drive in women
3. Source of estrogens in postmenopausal women
catecholamines (epinephrine (80%) and norepinephrine (20%))
major effects from the adrenal medulla:
1. Vasoconstriction
2. Increased heart rate
3. Increased blood glucose levels
4. Blood diverted to brain, heart, and skeletal muscle
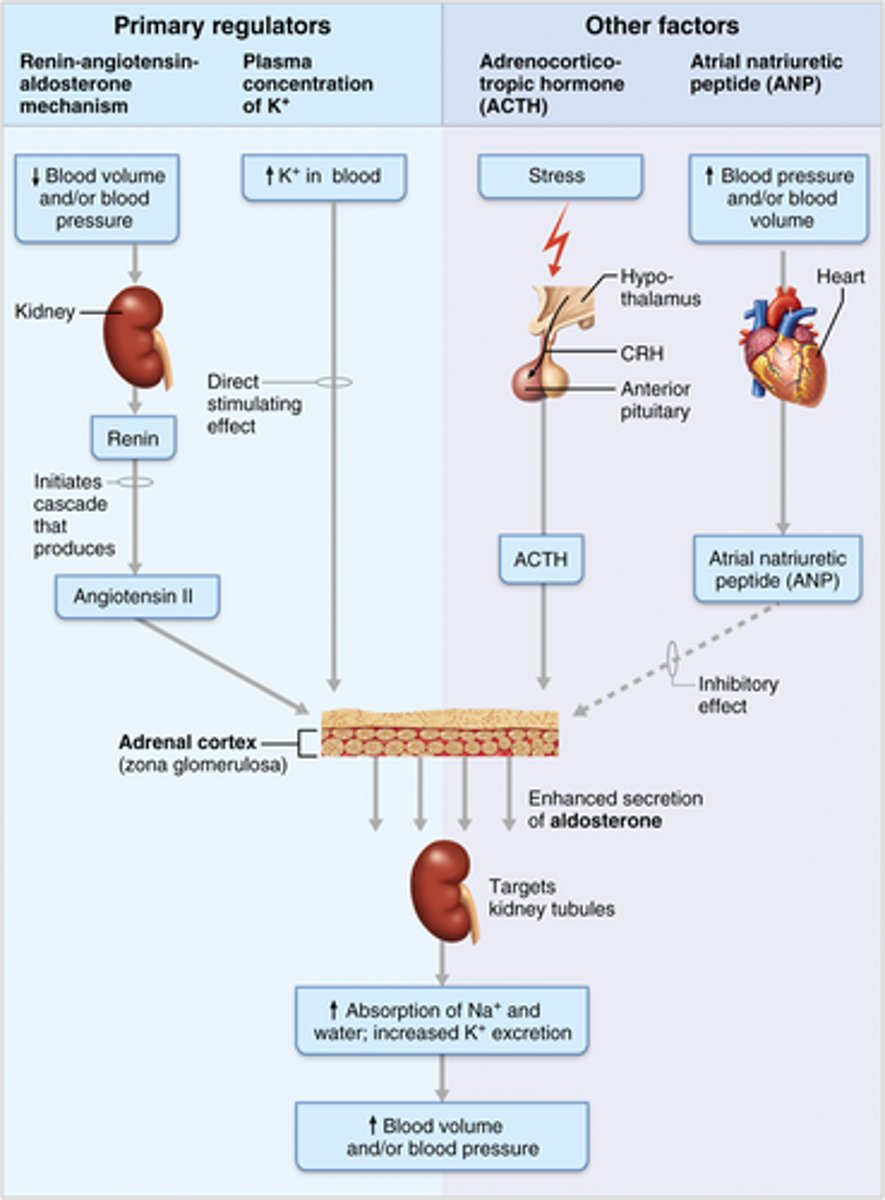
Aldosterone regulation (especially the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone mechanism)
1. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism (Decreased blood pressure stimulates special cells in kidneys. These cells release renin into blood. Renin cleaves angiotensinogen, that triggers an enzyme cascade, resulting in conversion to angiotensin I to angiotensin II (Ang-II). Ang-II is a potent stimulator of aldosterone release)
2. Plasma concentration of K+ (Increased K+ directly influences zona glomerulosa cells to release aldosterone)
3. ACTH (Can cause small increases of aldosterone during periods of increased stress)
4. Atrial natriuretic peptide (Secreted by heart in response to high blood pressure. Blocks renin and aldosterone secretion to decrease blood pressure)
Cushing's syndrome
increases too much glucose
Causes: tumor on pituitary, lungs, pancreas, kidney, or adrenal cortex
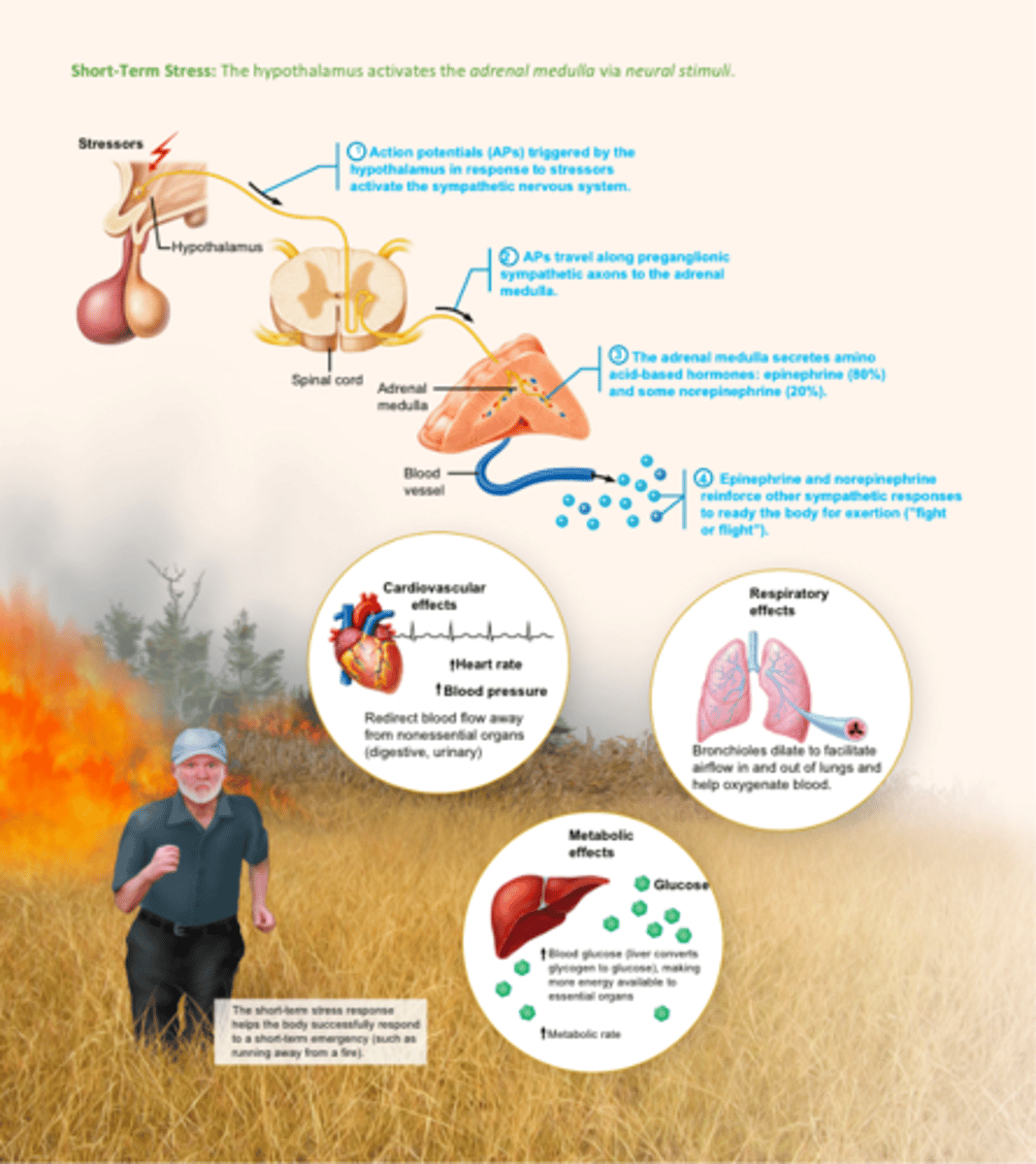
Stress and the adrenal gland (short term stress)
The hypothalamus activates the adrenal medulla via neural stimuli
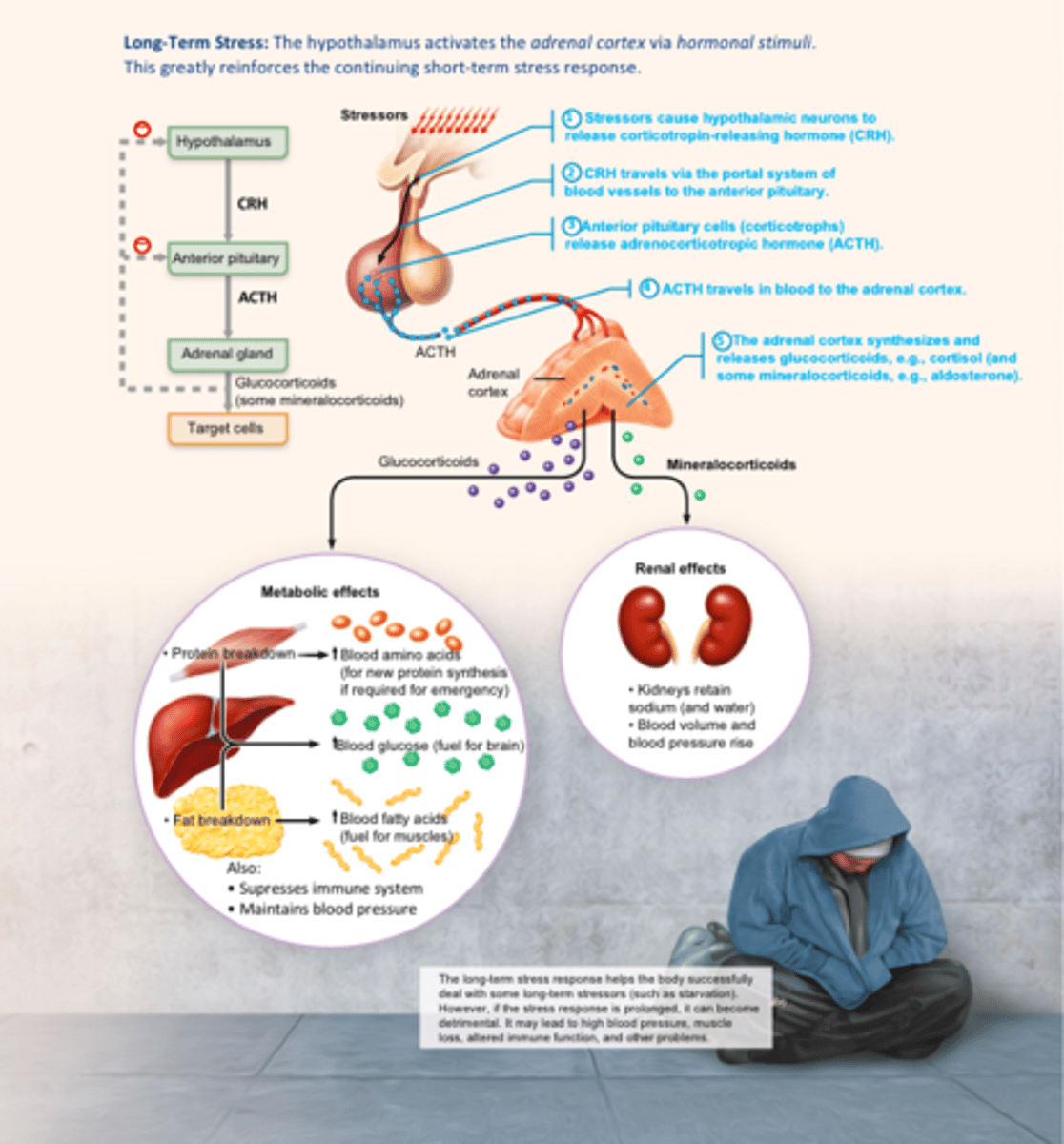
Stress and the adrenal gland (long term stress)
The hypothalamus activates the adrenal cortex via hormonal stimuli. This greatly reinforces the continuing short-term stress response.
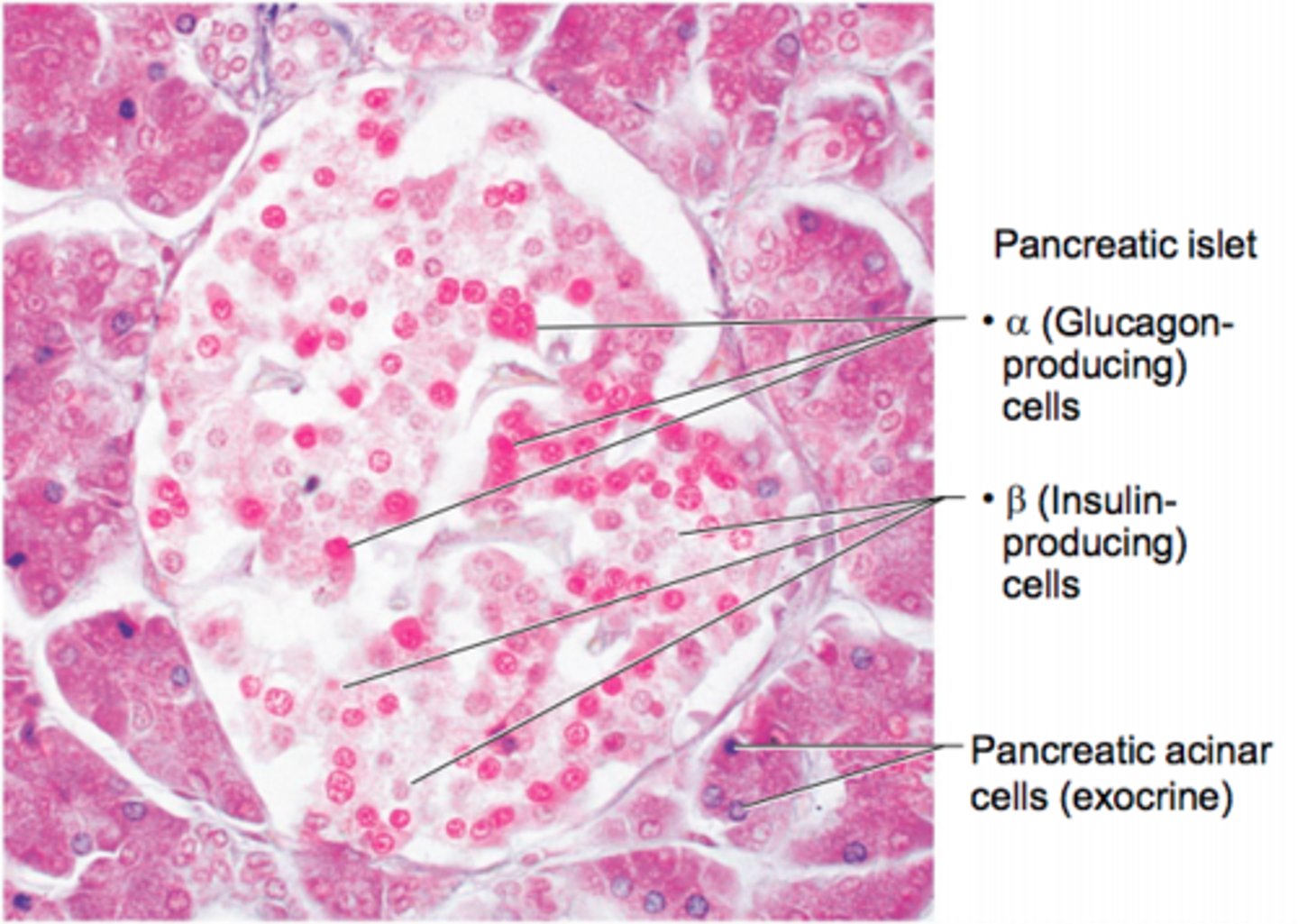
Pancreas structure and different cell populations
Triangular gland located partially behind stomach and between the kidneys
It has Acinar cells (exocrine) produce enzyme-rich juice for digestion
It has Pancreatic islets that produce:
Alpha cells which produce glucogen
Beta cells which produce insulin
Insulin and glucagon regulation of blood glucose
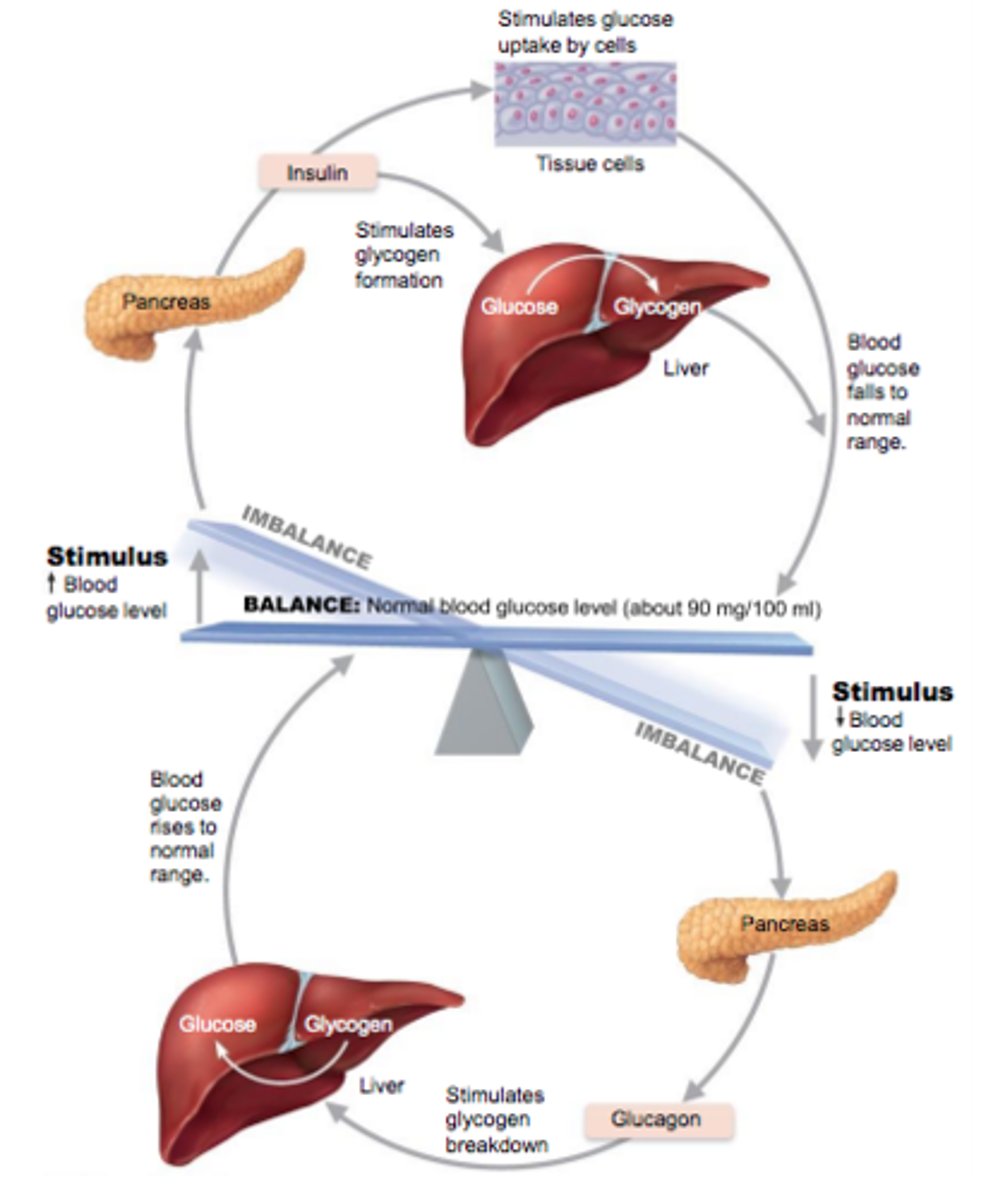
How does insulin work to reduce blood glucose levels?
1. Enhances membrane transport of glucose into all cells; catalyze oxidation of glucose for ATP production - first priority!!
2. Liver: Convert glucose to stored form glycogen = Glycogenesis
3. Adipose tissue: Convert glucose to fat
Factors that influence insulin release?
1. Elevated blood glucose levels: primary stimulus
2. Rising blood levels of amino acids and fatty acids
3. "Fed state" - Release of acetylcholine by parasympathetic nerve fibers
4. "Anti-insulin" hormones - glucagon, epinephrine, growth hormone, thyroxine, glucocorticoids
5. Sympathetic nervous system inhibit insulin release
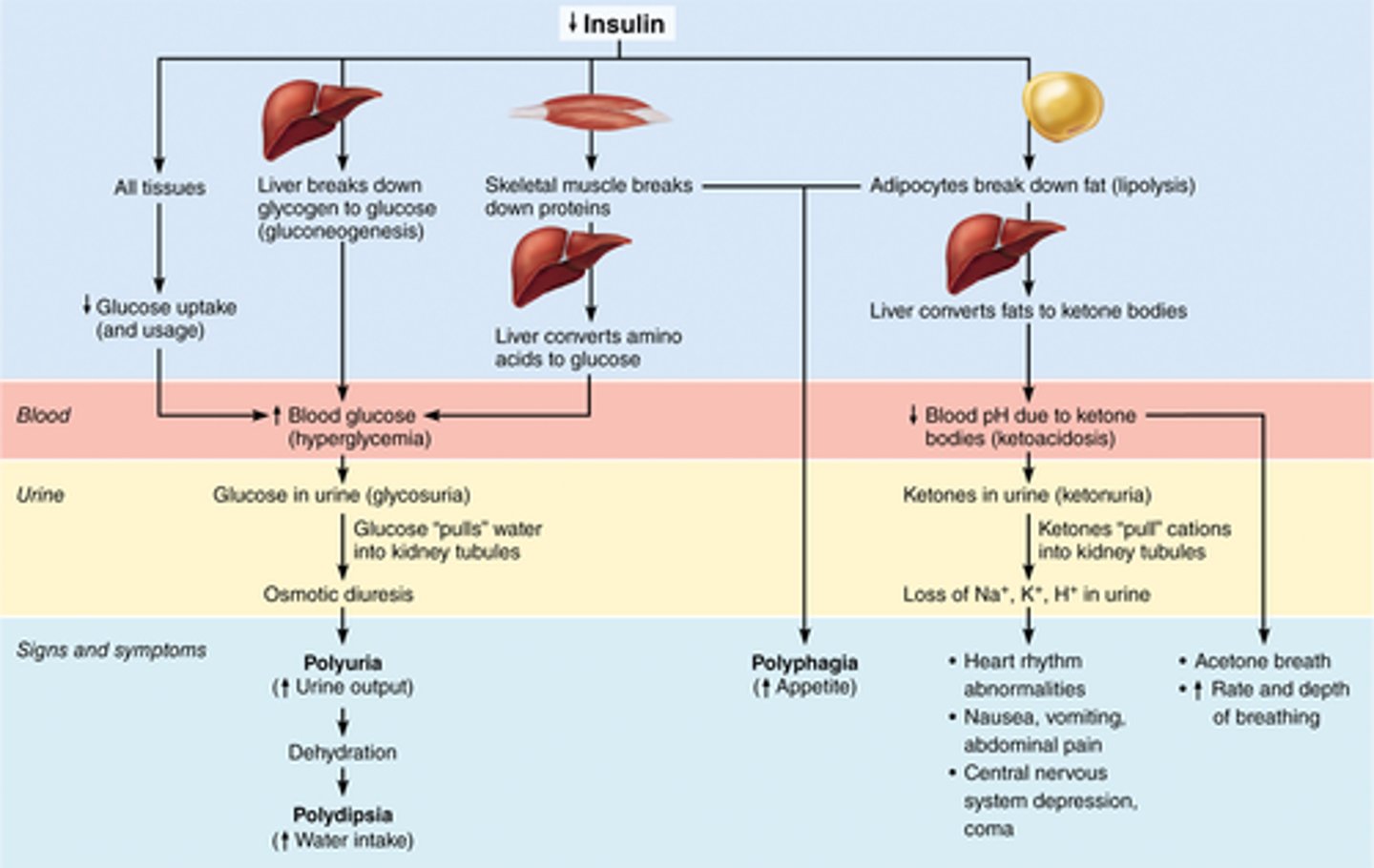
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
when hyposecretion or the absence of insulin causes high sugar levels - Type 1
when high blood sugars are not affected by insulin - Type 2
What are the three cardinal signs of DM?
1. Polyuria: huge urine output
2. Polydipsia: excessive thirst
3. Polyphagia: excessive hunger and food consumption
Consequences of insulin deficit
transport (functions of blood)
1. Delivering O2 and nutrients to body cells
2. Transporting metabolic wastes to lungs and kidneys for elimination
3. Transporting hormones from endocrine organs to target organs
regulation (functions of blood)
1. Maintaining body temperature by absorbing and distributing heat
2. Maintaining normal pH using buffers; alkaline reserve of bicarbonate ions
3. Maintaining adequate fluid volume in circulatory system
protection (functions of blood)
1. Preventing blood loss - Plasma proteins and platelets in blood initiate clot formation
2. Preventing infection - Antibodies, Complement proteins, White blood cells
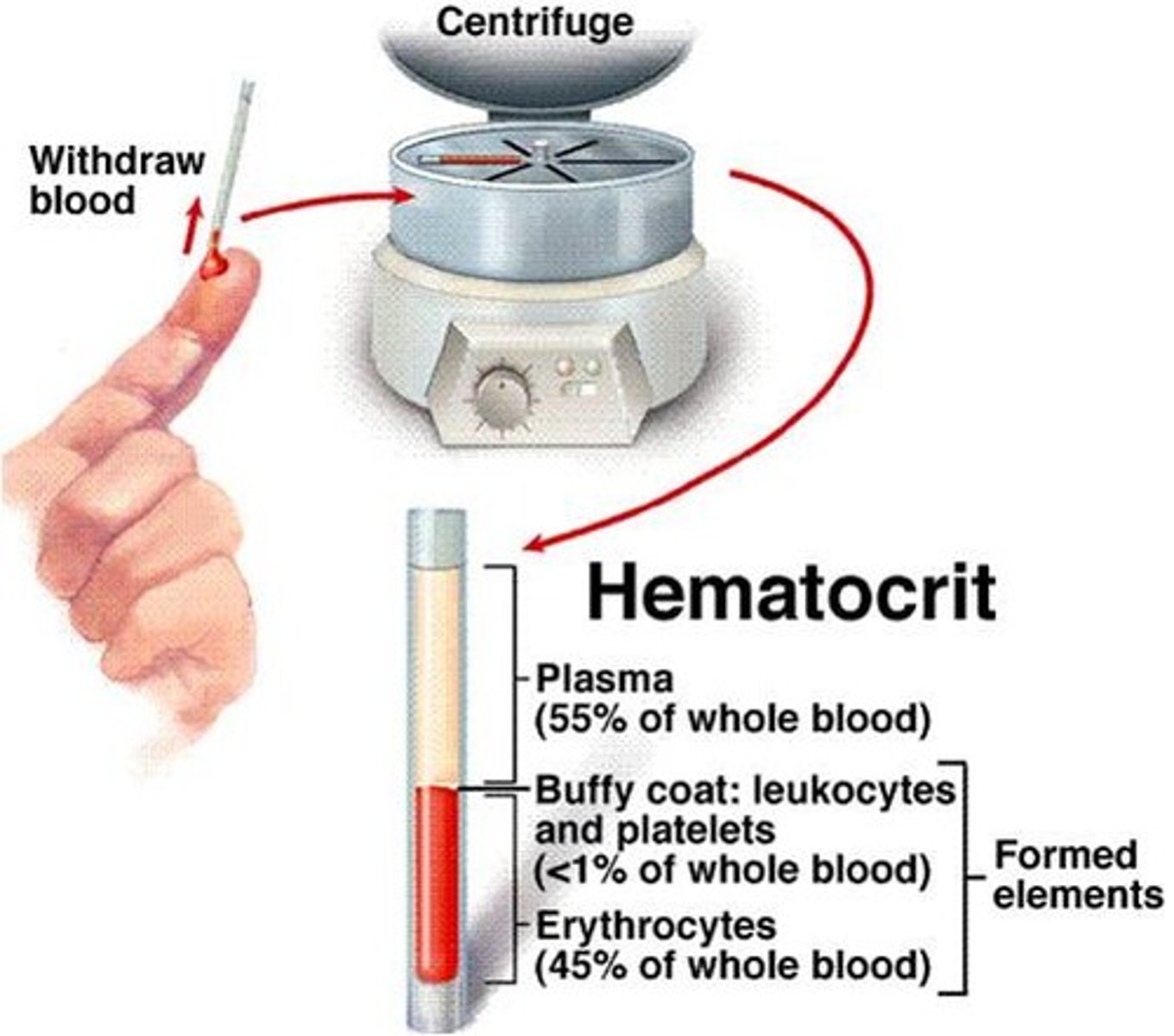
plasma
nonliving liquid portion of blood
55% of whole blood
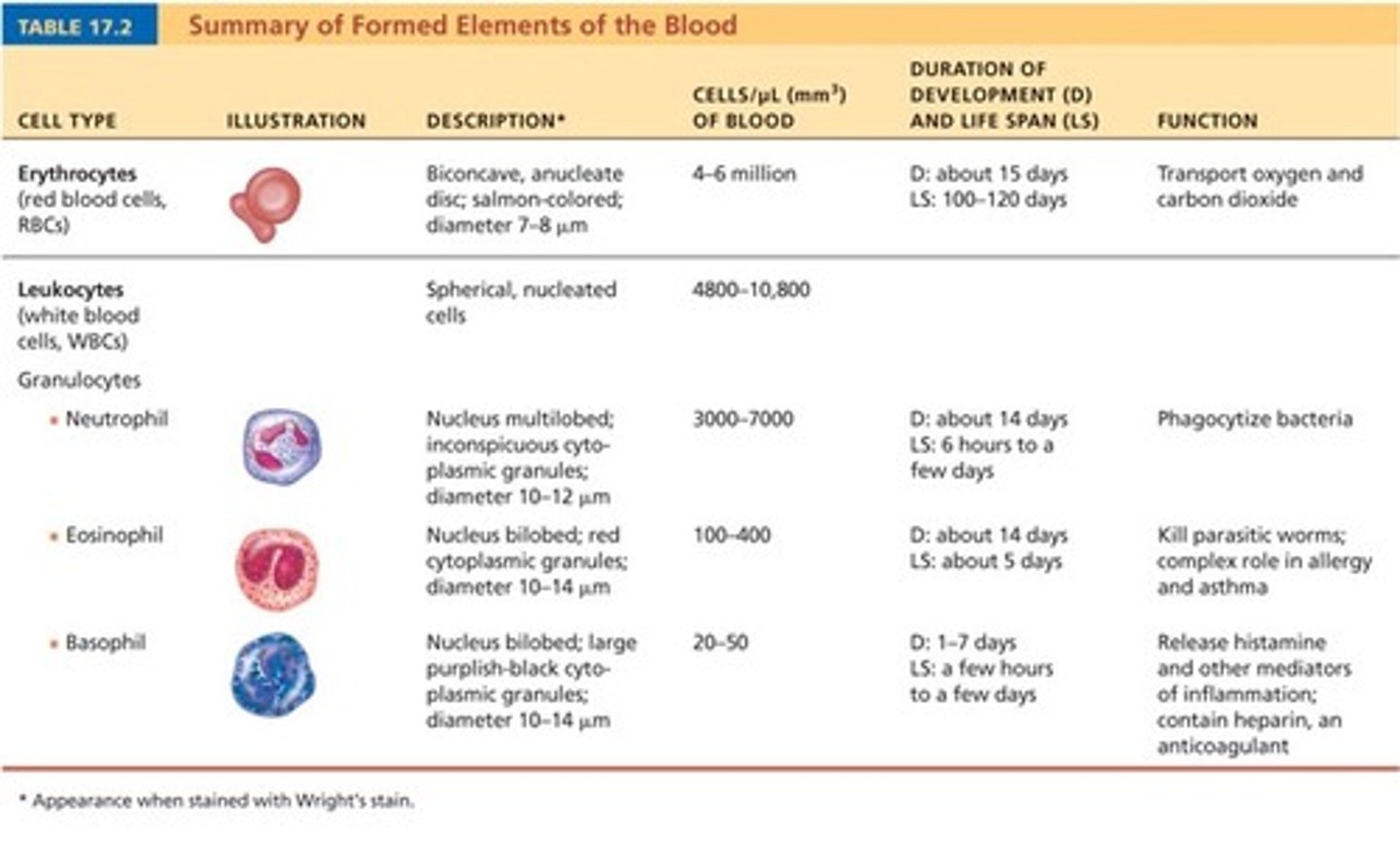
erythrocytes (formed element)
red blood cells, or RBCs
45% of whole blood
leukocytes (formed element)
white blood cells, or WBCs
greater than 1% of whole blood
Platelets (thrombocytes) (formed element)
Thin, whitish layer between RBCs and plasma layers
greater than 1% of whole blood
What comprises the buffy coat?
leukocytes and platelets
Composition of plasma
90% water
8% plasma proteins
1% other solutes
composition of plasma proteins
60% albumin
36% globulin
4% fibrinogen
What is hematocrit?
percent of blood volume that is RBCs
Structure and function of RBCs
• RBCs are dedicated to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body
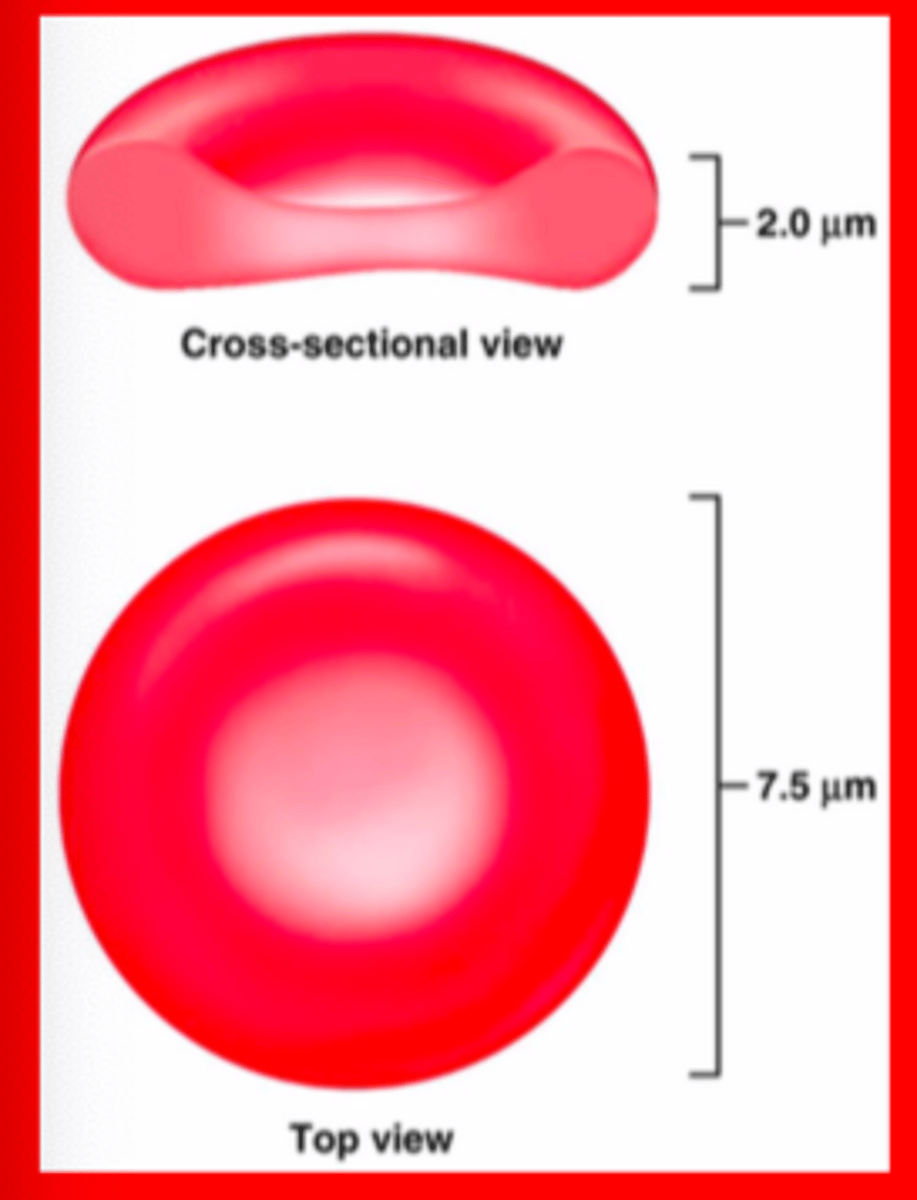
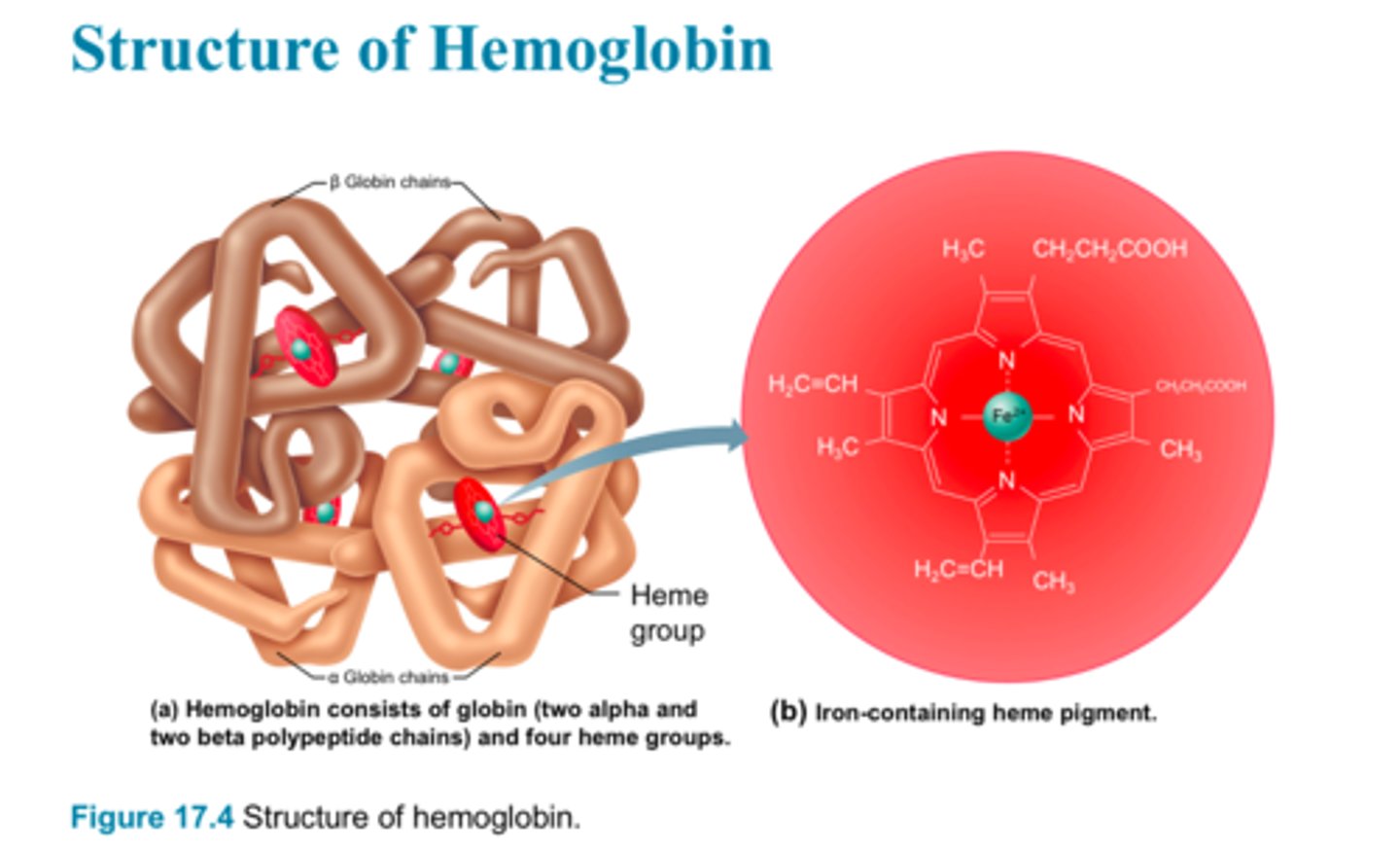
Structure of hemoglobin, role in oxygen binding/transport
Hemoglobin binds reversibly with oxygen
Every hemoglobin molecule can bind a maximum of four O2 molecules
oxyhemoglobin (ruby red)
a protein that is produced by O2 loading in lungs
deoxyhemoglobin or reduced hemoglobin (dark red)
a protein that is produced by O2 unloading in tissues
carbaminohemoglobin
a protein that is produced by CO2 loading in tissues and then being filter through the lungs
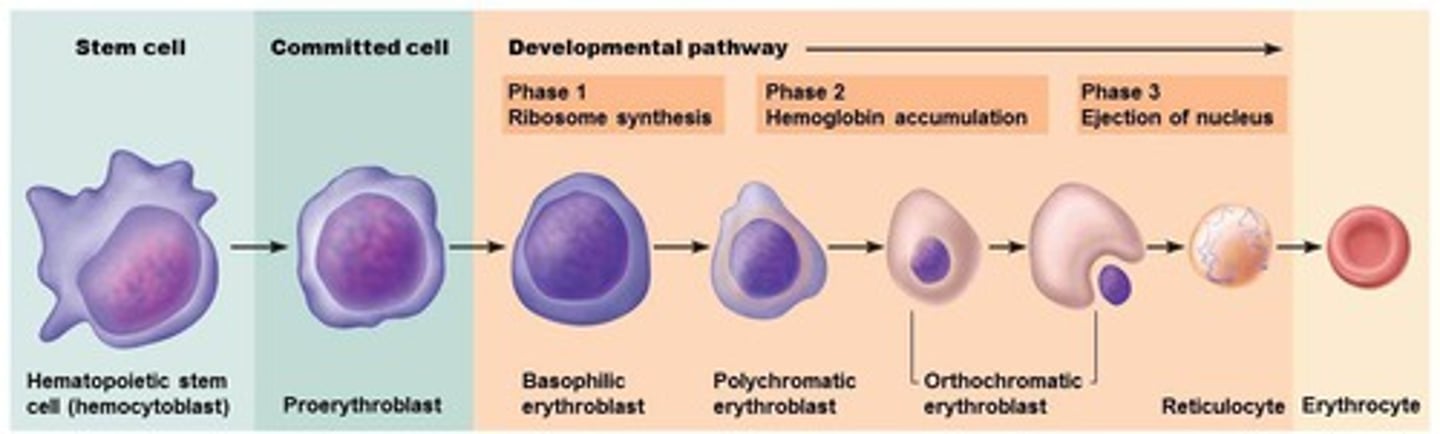
Stages of Erythropoiesis
Hematopoietic stem cell
proerythroblast
basophilic erythroblast
polychromatic erythroblast
orthochromatic erythroblast
reticulocyte
erythrocyte. (7 sequences).
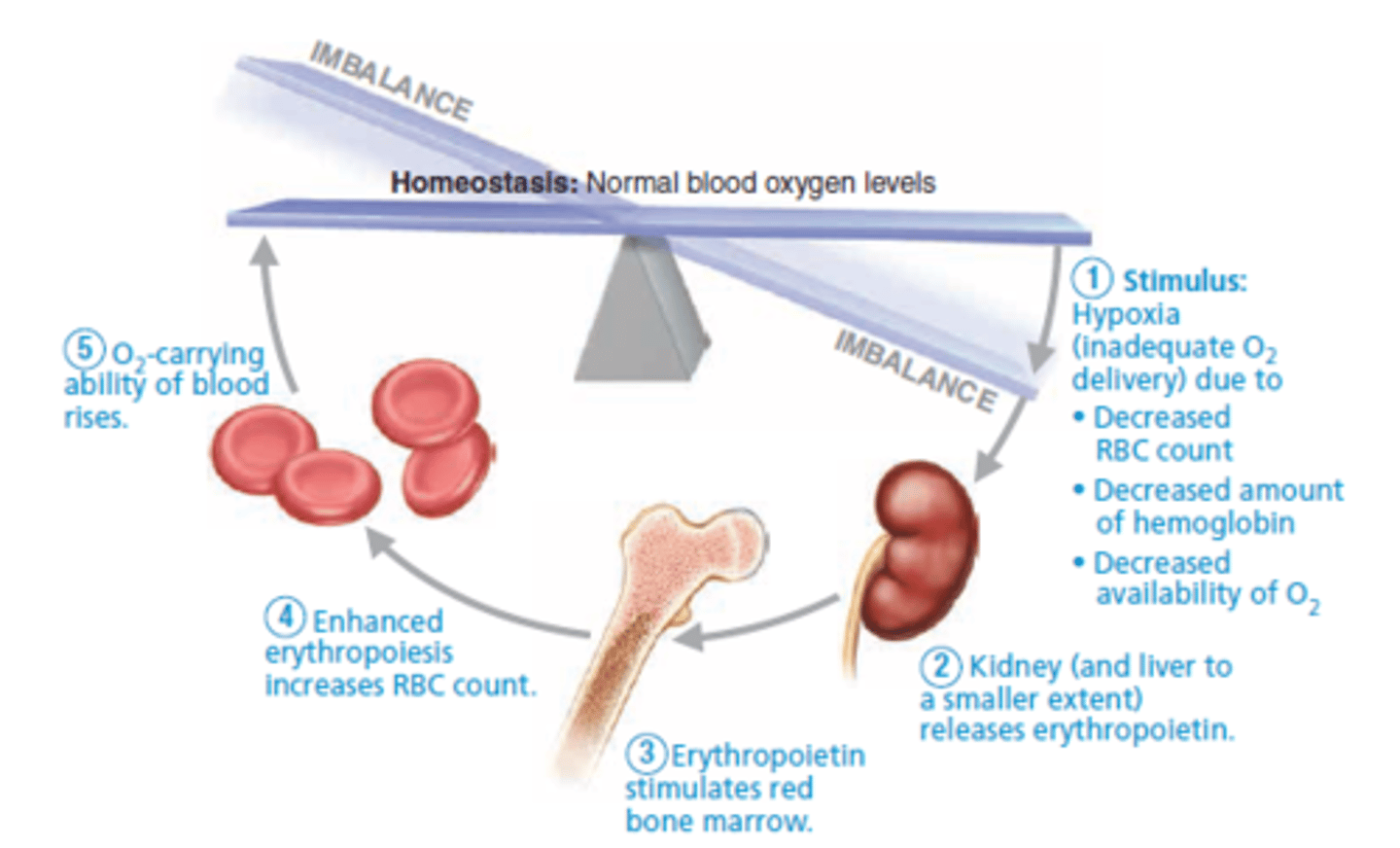
Role of erythropoietin (EPO) in erythropoiesis
stimulates formation of RBCs
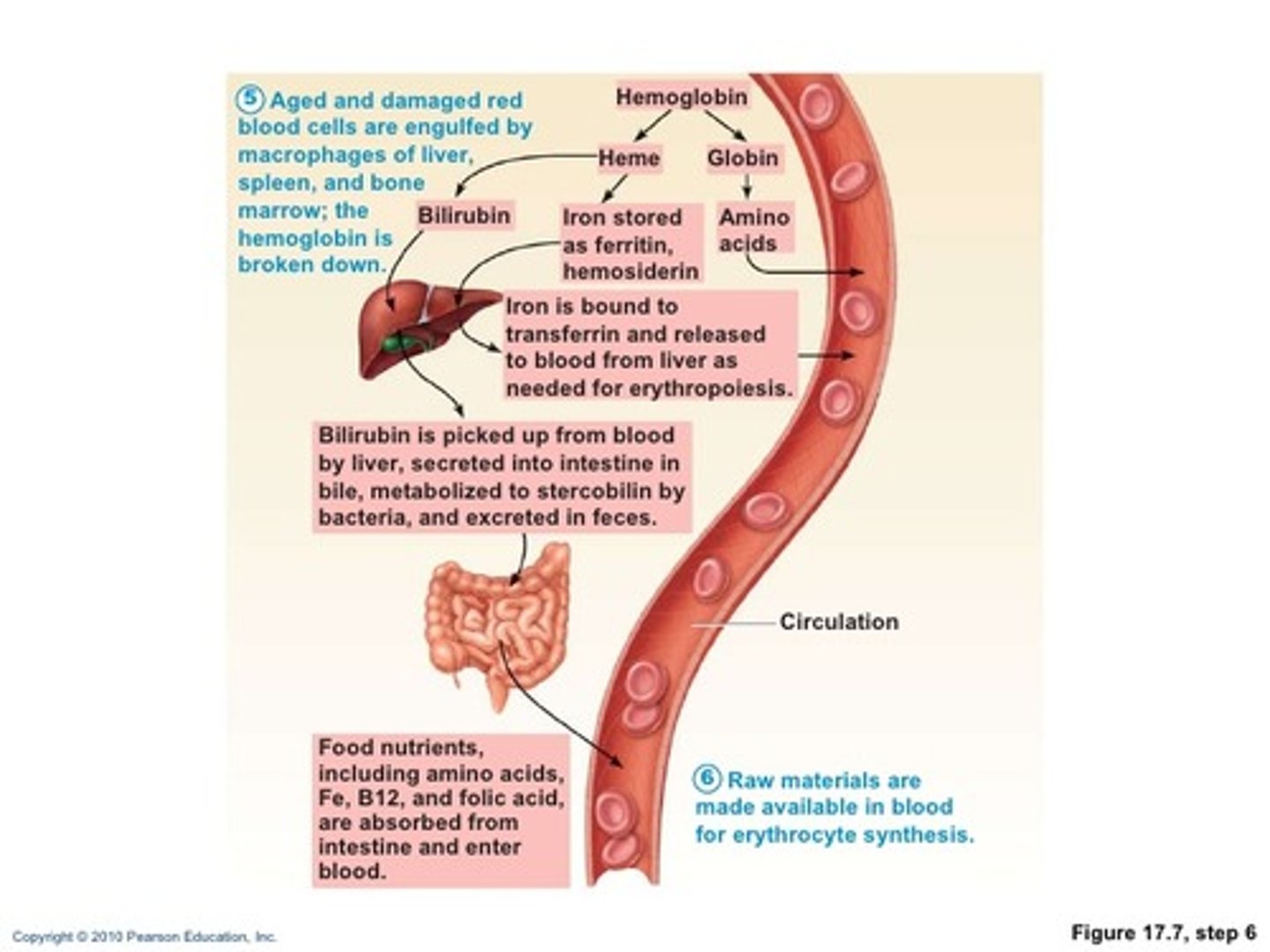
Life cycle of RBCs, fate and destruction
RBCs live from 100 to 120 days
As they get older they git rigid and stiff
Hemoglobin begins to degenerate
Macrophages in spleen and liver engulf and breakdown dying RBCs
Anemia
A disorder where blood has abnormally low O2-carrying capacity that is too low to support normal metabolism
Three groups based on cause:
I. Blood loss
II. Not enough RBCs being produced
III. Too many RBCs being destroyed too quickly
Anemia (Blood loss)
1. Hemorrhagic anemia
Major causes: Rapid blood loss (ex.: severe wound)
Treatment: blood replacement
2. Chronic hemorrhagic anemia
Major causes: Slight but persistent blood loss (ex.: hemorrhoids)
Treatment: problem must be treated to stop blood loss
Anemia (Not enough RBCs being produced)
1. Iron-deficiency anemia
Major causes: hemorrhagic anemia, low iron intake or impaired absorption
Treatment: iron supplements
2. Pernicious anemia
Major causes: low B12 RBCs intake that results in large macrocytes
Treatment: B12 injections
3. Renal anemia
Major causes: lack of EPO
Treatment: synthetic EPO
4. Aplastic anemia
Major causes: drugs, chemicals, radiation, or viruses
Treatment: short-term with transfusions, long-term with transplanted stem cells
Anemia (Too many RBCs being destroyed too quickly)
1. Premature lysis or RBC's (hemolytic anemias)
Major causes: incompatible transfusions, infections, or hemoglobin abnormalities
Treatment:
2. Thalassemias
Major cause: One globin chain is absent or faulty
Treatment: Very severe cases may require monthly blood transfusions
3. Sickle-cell anemia
Major cause: a hereditary disease
Treatments: inject Hydroxyurea drug
Polycythemia
Abnormal amount of RBCs
Increases blood viscosity causing sluggish blood flow
Treatment: therapeutic phlebotomy
Percentages of leukocytes in normal blood
Granulocytes
Neutrophils (50-70%)
Eosinophils (2-4%)
Basophils (0.5-1%)
Agranulocytes
Lymphocytes (25-45%)
Monocytes (3-8%)
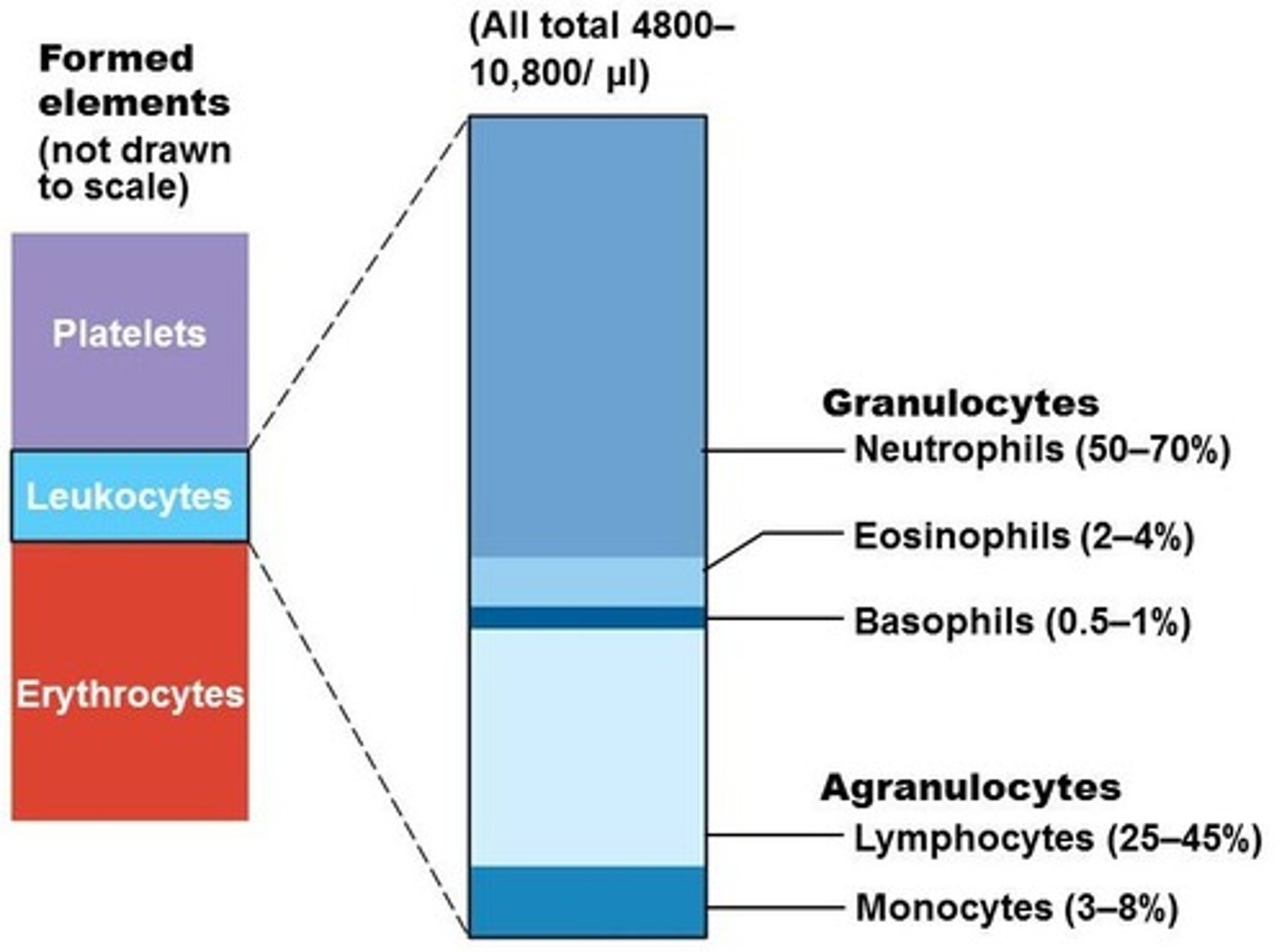
Summary of formed elements